- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2025
> Online First
| Citation: | ZHOU Enji, WEN Gongjian, SONG Haibo, et al. Target parameter and time-frequency bias estimation method based on multitemporal measurement data for distributed MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25201 |
Target Parameter and Time-frequency Bias Estimation Method Based on Multitemporal Measurement Data for Distributed MIMO Radar
DOI: 10.12000/JR25201 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25201
More Information-
Abstract
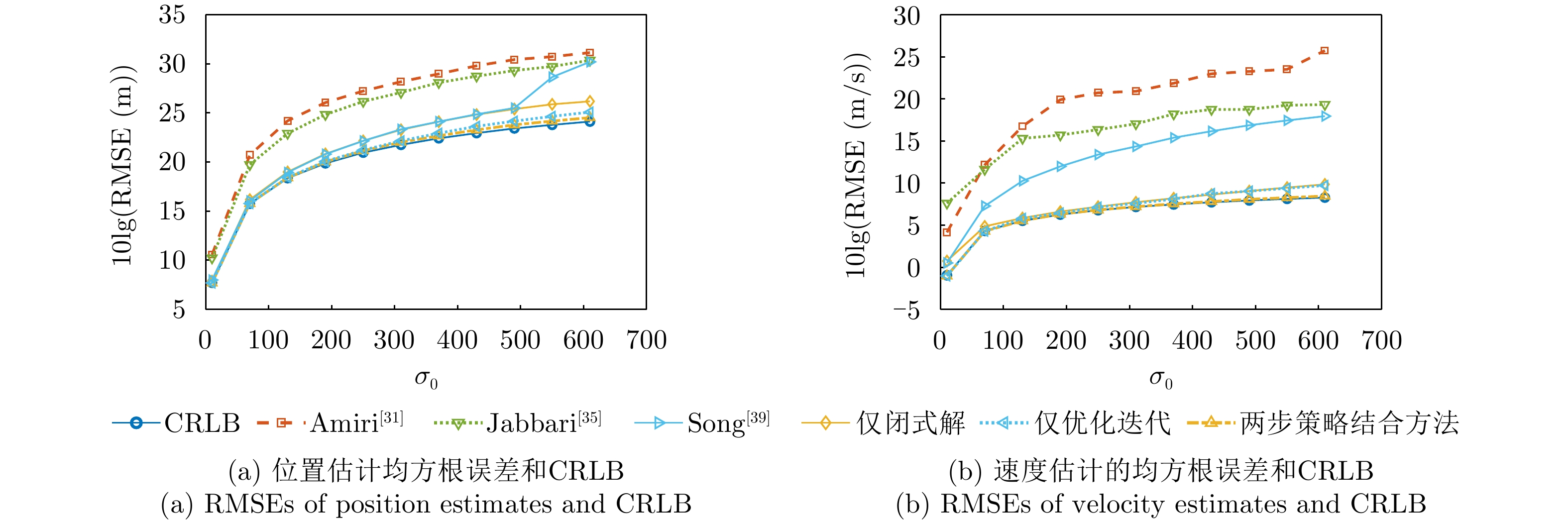
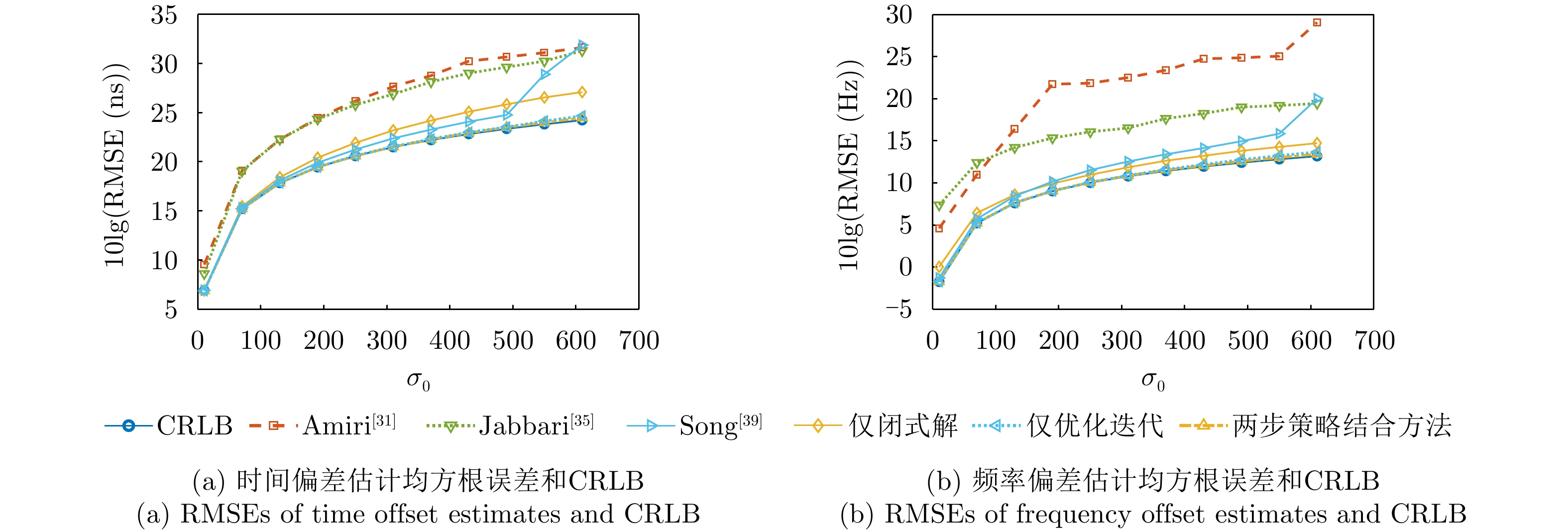
This study addresses time-frequency synchronization errors in distributed Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) radar systems and proposes a joint estimation method for target parameters and system time-frequency biases based on multitemporal measurement data. The method overcomes the limitations of traditional approaches that rely on singletemporal measurement data and direct-path signals, enabling high-accuracy joint parameter estimation through multiepoch data fusion without requiring direct-path information. The proposed method adopts a two-step strategy that combines a closed-form solution with iterative optimization. First, a closed-form solution is derived within a two-stage weighted least-squares framework using only the first- and last-epoch observations to obtain initial estimates of the target position, velocity, and auxiliary variables. This stage explicitly models second-order error terms and optimizes the construction of the weighting matrix, significantly improving accuracy and robustness under high-error conditions. Second, using the closed-form estimates as initialization, a maximum likelihood-maximum a posteriori objective function is formulated based on the full multi-epoch measurement data, and a trust-region iterative optimization method is applied to refine the estimates and recover the time-frequency bias parameters. Simulation results show that the proposed method outperforms existing approaches across various error levels and geometric configurations, significantly enhancing the accuracy and robustness of target localization, velocity estimation, and time-frequency bias estimation. These results demonstrate strong theoretical significance and promising practical application potential. -

-
References
[1] FISHLER E, HAIMOVICH A, BLUM R S, et al. Spatial diversity in radars-models and detection performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(3): 823–838. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.862813.[2] KRIEGER G. MIMO-SAR: Opportunities and pitfalls[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2628–2645. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2263934.[3] WANG Wenqin. MIMO SAR OFDM chirp waveform diversity design with random matrix modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(3): 1615–1625. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2346478.[4] LIANG Yuanyuan, WEN Gongjian, ZHU Lingxiao, et al. Target detection performance of distributed MIMO radar systems under nonideal conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(2): 1951–1969. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3344553.[5] CHEN Ruilin, GUO Shisheng, CHEN Jiahui, et al. Low-complexity multitarget detection and localization method for distributed MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radar Systems, 2025, 3: 599–614. doi: 10.1109/TRS.2025.3554198.[6] MA Cong, CAO Fengting, YANG Yue, et al. Distributed microwave photonic MIMO radar with accurate target position estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2023, 71(4): 1711–1719. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2022.3218287.[7] ZHANG Guoxin, YI Wei, VARSHNEY P K, et al. Direct target localization with quantized measurements in noncoherent distributed MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5103618. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3267499.[8] AMIRI R, KAZEMI S A R, BEHNIA F, et al. Efficient elliptic localization in the presence of antenna position uncertainties and clock parameter imperfections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(10): 9797–9805. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2933406.[9] KAZEMI S A R, AMIRI R, and BEHNIA F. Efficient joint localization and synchronization in distributed MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 1200–1204. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.3007033.[10] LUO Shuai, WANG Yuexian, WANG Ling, et al. Direction finding for bistatic MIMO radar using a sparse moving array with sensor position errors[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11(9): 1840–1844. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2022.3184114.[11] BAR-SHALOM O and WEISS A J. Direct positioning of stationary targets using MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2011, 91(10): 2345–2358. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2011.04.019.[12] HE Qian, BLUM R S, and HAIMOVICH A M. Noncoherent MIMO radar for location and velocity estimation: More antennas means better performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(7): 3661–3680. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2044613.[13] NIU Ruixin, BLUM R S, VARSHNEY P K, et al. Target localization and tracking in noncoherent multiple-input multiple-output radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(2): 1466–1489. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6178073.[14] WEISS A J. Direct geolocation of wideband emitters based on delay and Doppler[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(6): 2513–2521. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2128311.[15] ALAMDARI E, BEHNIA F, and AMIRI R. Conical localization from angle measurements: An approximate convex solution[J]. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2022, 6(5): 7001404. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2022.3163186.[16] WANG Gang, XIANG Peng, and HO K C. Bias reduced semidefinite relaxation method for 3-D moving object localization using AOA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2023, 22(11): 7377–7392. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3250420.[17] SHI Zhanglei, WANG Hao, LEUNG C S, et al. Robust MIMO radar target localization based on Lagrange programming neural network[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 174: 107574. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107574.[18] SUN Ting, DONG Chunxi, MAO Yu, et al. Moving target localization in multiple-input multiple-output radar systems without the prior knowledge of measurement noise powers[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(9): 1957–1960. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3001950.[19] SONG Haibo, WEN Gongjian, LIANG Yuanyuan, et al. Target localization and clock refinement in distributed MIMO radar systems with time synchronization errors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 3088–3103. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3081038.[20] ZHENG Zhi, ZHANG Hongwang, and WANG Wenqin. Target localization in distributed MIMO radars via improved semidefinite relaxation[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2021, 358(10): 5588–5598. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2021.04.035.[21] SUN Bin, CHEN Haowen, WEI Xizhang, et al. Semidefinite relaxation method for target localization by MIMO radar using bistatic ranges[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2014, 10(8): 1–6. doi: 10.1155/2014/984812.[22] ZHENG Ruichao, WANG Gang, and HO K C. Accurate semidefinite relaxation method for elliptic localization with unknown transmitter position[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(4): 2746–2760. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3044217.[23] AMIRI R, BEHNIA F, and SADR M A M. Exact solution for elliptic localization in distributed MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(2): 1075–1086. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2762631.[24] AMIRI R, BEHNIA F, and MALEKI SADR M A. Positioning in MIMO radars based on constrained least squares estimation[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(10): 2222–2225. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2724541.[25] QI Qinke, LI Youming, and GUO Qiang. A convex relaxation algorithm for source localization considering sensor motion in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(6): 1867–1871. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3062668.[26] JIA Tianyi, HO K C, WANG Haiyan, et al. Effect of sensor motion on time delay and Doppler shift localization: Analysis and solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(22): 5881–5895. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2946025.[27] QI Hengnian, WU Xiaoping, XIONG Naixue, et al. A source prediction system for dynamic networks based on TDOA measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021, 8(3): 2388–2401. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2021.3092175.[28] MENG Xiangpei, LI Youming, WU Zhenqian, et al. A semidefinite relaxation approach for mobile target localization based on TOA and Doppler frequency shift measurements[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(14): 16051–16057. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3272565.[29] HO K C and XU Wenwei. An accurate algebraic solution for moving source location using TDOA and FDOA measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(9): 2453–2463. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.831921.[30] YANG H and CHUN J. An improved algebraic solution for moving target localization in noncoherent MIMO radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(1): 258–270. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2477803.[31] AMIRI R, BEHNIA F, and MALEKI SADR M A. Efficient positioning in MIMO radars with widely separated antennas[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2017, 21(7): 1569–1572. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2688373.[32] NOROOZI A, AMIRI R, NAYEBI M M, et al. Efficient closed-form solution for moving target localization in MIMO radars with minimum number of antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 2545–2557. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.2986163.[33] KAZEMI S A R, AMIRI R, and BEHNIA F. Efficient closed-form solution for 3-D hybrid localization in multistatic radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 3886–3895. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3082664.[34] NOROOZI A, SEBT M A, HOSSEINI S M, et al. Closed-form solution for elliptic localization in distributed MIMO radar systems with minimum number of sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(4): 3123–3133. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.2965668.[35] JABBARI M R, TABAN M R, and GAZOR S. A robust TSWLS localization of moving target in widely separated MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(2): 897–906. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3194112.[36] WU Xiaoping, MAO Xiaoting, and QI Hengnian. Semidefinite relaxation for moving target localization in asynchronous MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2024, 72(2): 1075–1089. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2023.3326492.[37] ZHANG Yang and HO K C. Multistatic moving object localization by a moving transmitter of unknown location and offset[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2020, 68: 4438–4453. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3008752.[38] ZHENG Ruichao, WANG Gang, HO K C, et al. Semidefinite relaxation method for moving object localization using a stationary transmitter at unknown position[C]. ICASSP 2022 - 2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, Singapore, 2022: 5128–5132. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9746393.[39] SONG Haibo, YUAN Fu, WANG Jie, et al. An algebraic solution for moving target localization in distributed MIMO radar systems with clock synchronization errors[C]. Proceedings Volume 13091, Fifteenth International Conference on Signal Processing Systems (ICSPS 2023), Xi’an, China, 2023. doi: 10.1117/12.3023350. -
Proportional views

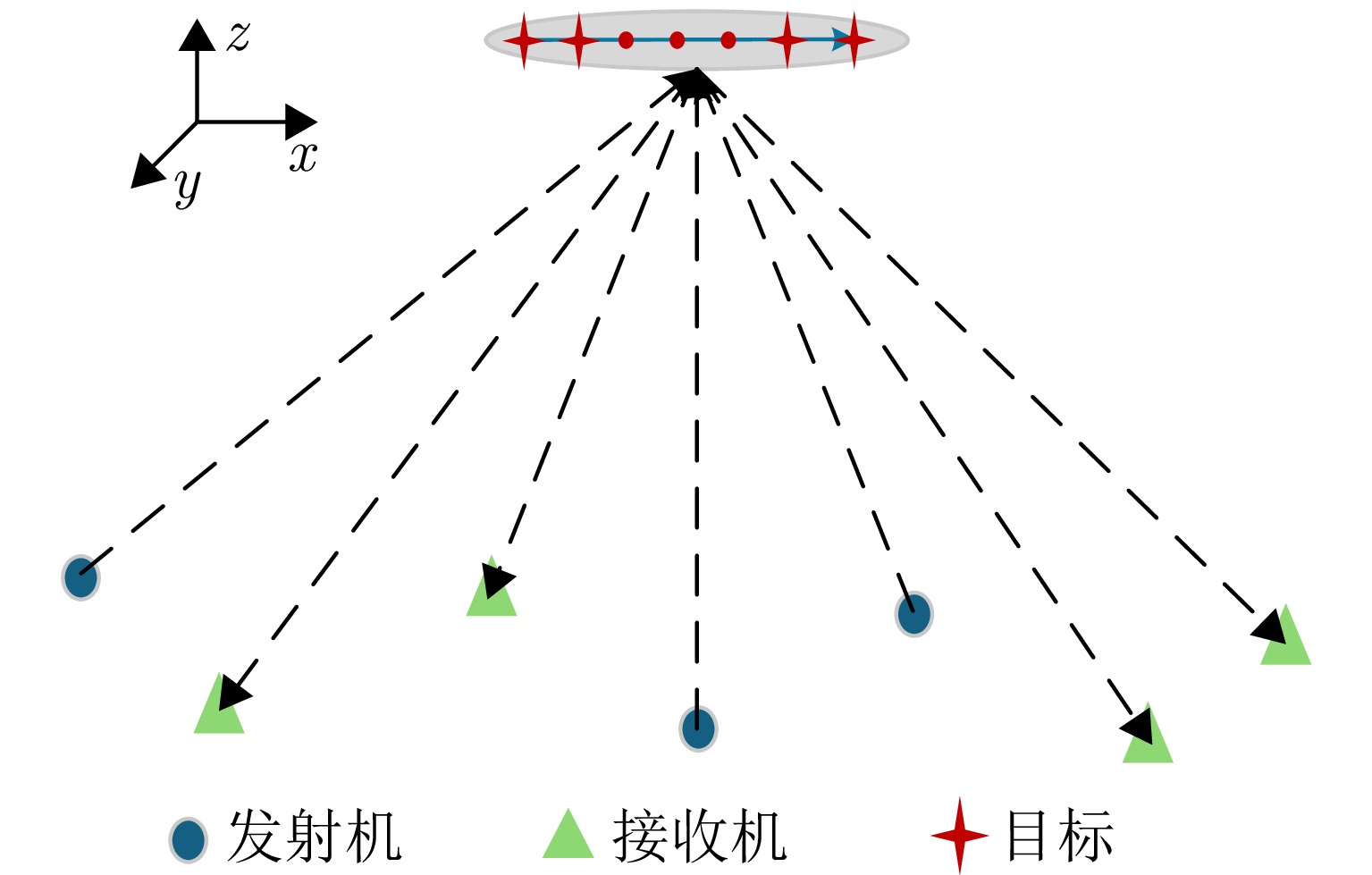
- Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a distributed MIMO radar multitemporal moving target localization scenario
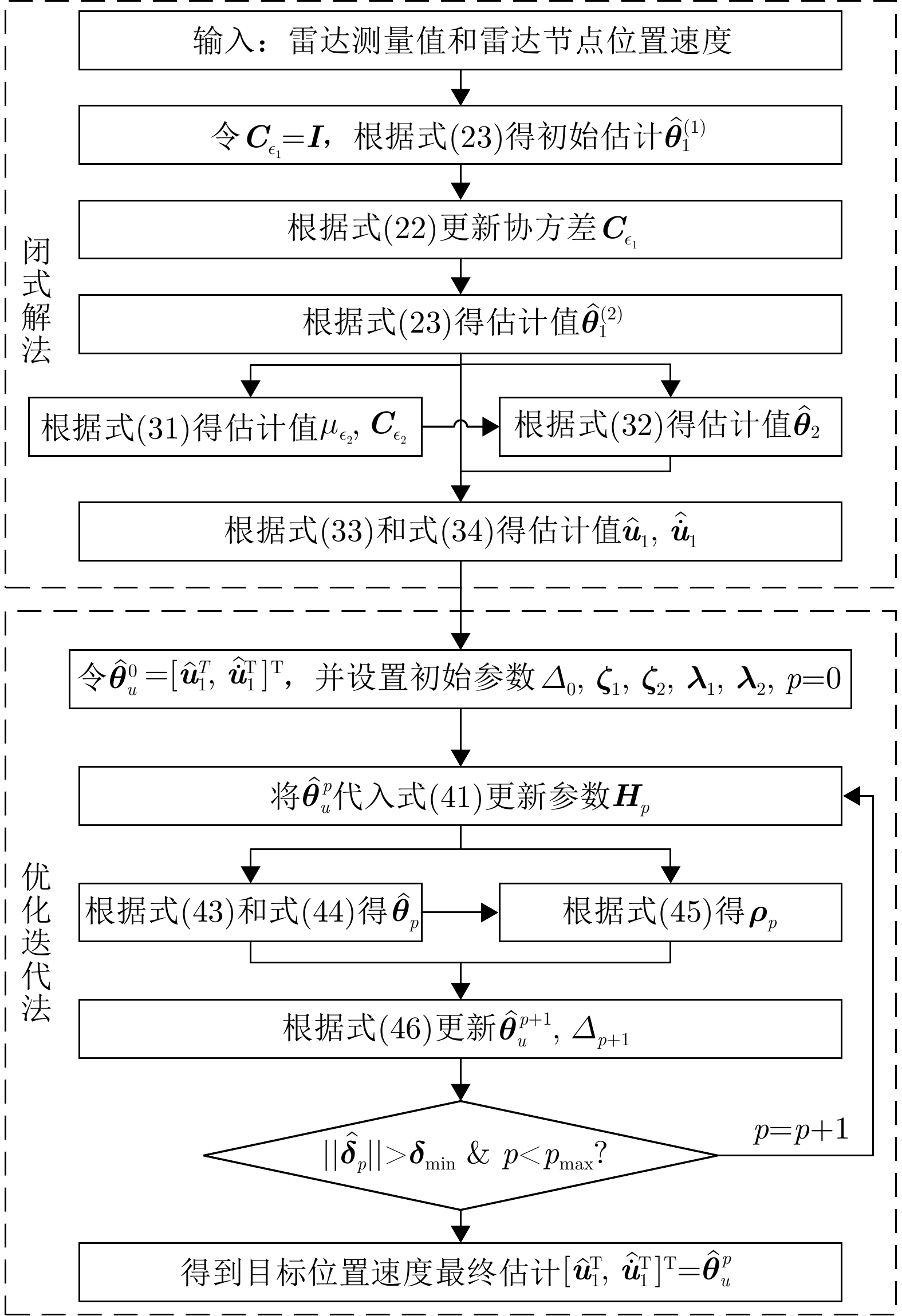
- Figure 2. Flowchart of the parameter estimation method using a two-step strategy
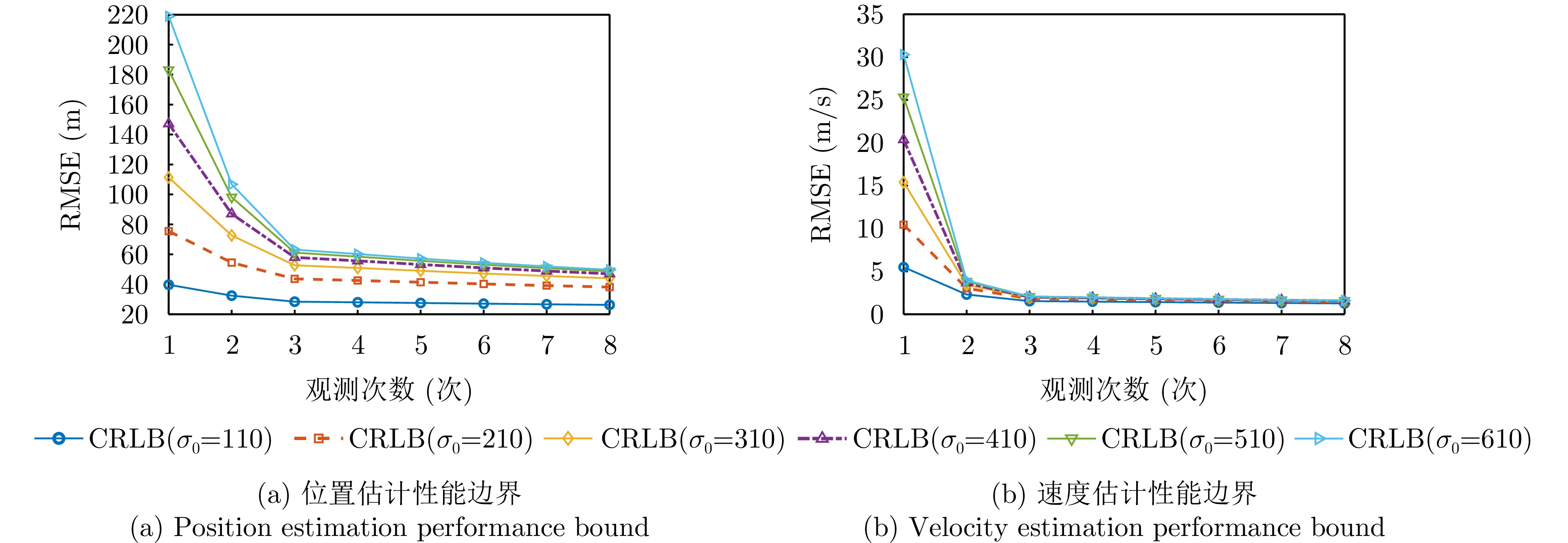
- Figure 3. Graph of target parameter estimation performance bound versus number of observations
- Figure 4. Graph of target parameter estimation performance bound versus total observation duration
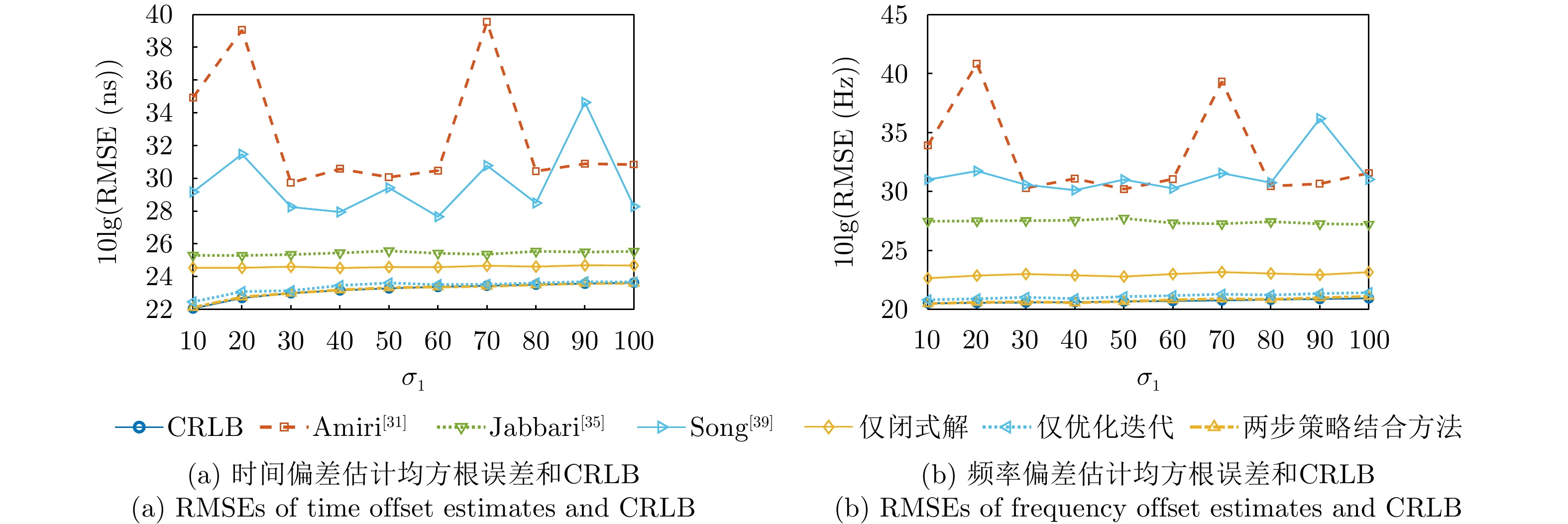
- Figure 5. Graph of target parameter estimation error versus measurement error level
- Figure 6. Graph of time-frequency parameter estimation error versus measurement error level
- Figure 7. Graph of target parameter estimation error versus time-frequency synchronization error level
- Figure 8. Graph of time-frequency parameter estimation error versus time-frequency synchronization error level
- Figure 9. Cumulative distribution graph of target parameter estimation error probability
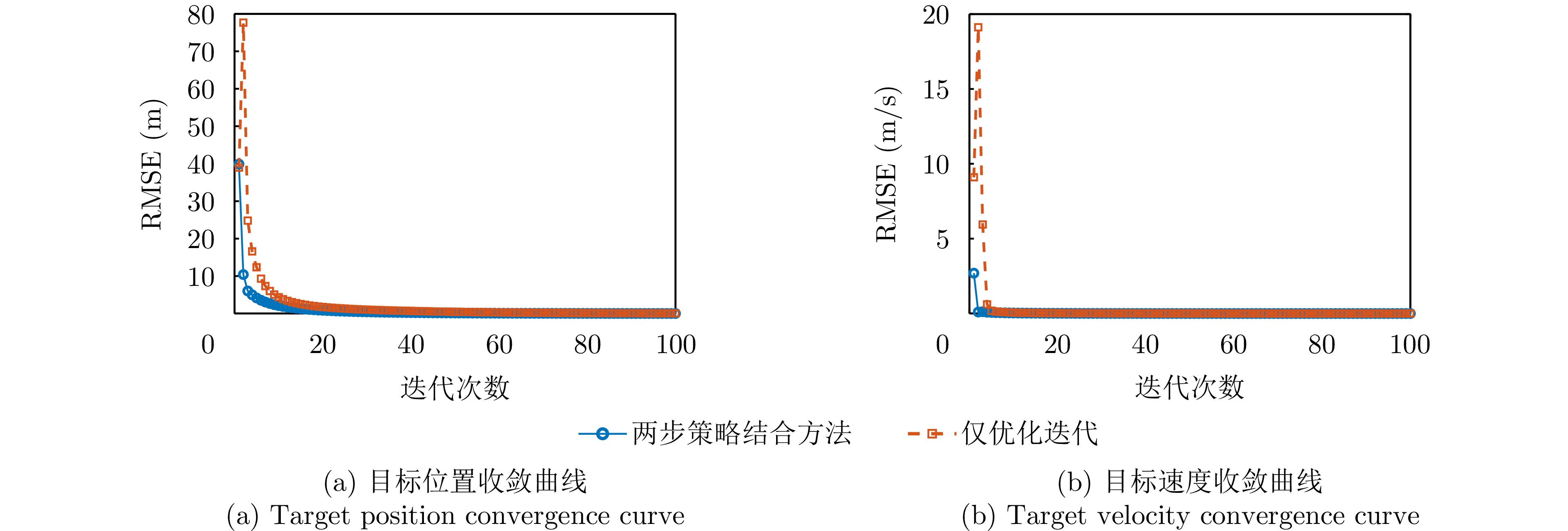
- Figure 10. Target parameter convergence curve
- Figure 11. Target parameter estimation error under geometric distribution of radar nodes
- Figure 12. Time-frequency parameter estimation error under geometric distribution of radar nodes


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: