- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2025
> Online First
| Citation: | DENG Kun, TIAN Xinran, YIN Chenxiao, et al. Fifth-order NCS algorithm for high-speed squint-forward-looking SAR imaging with low derivation complexity[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25187 |
Fifth-order NCS Algorithm for High-speed Squint-forward-looking SAR Imaging with Low Derivation Complexity
DOI: 10.12000/JR25187 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25187
More Information-
Abstract
High-speed squint-forward-looking Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imaging (squint angle: >70°) is challenged by severe range-Doppler coupling and Doppler space variance. Traditional Nonlinear Chirp Scaling (NCS) algorithms can effectively mitigate Doppler space variance under high-squint conditions (squint angle: >30°), but they rely on approximate treatments and exhibit rapidly increasing derivation complexity at high scaling orders. This makes high-order generalization difficult and limits their application in high-speed squint-forward-looking SAR systems. To address this issue, this study demonstrates that Fourier Transform (FT) and Inverse FT (IFT) implementations, based on the Principle of Stationary Phase (POSP) and the Method of Series Reversion (MSR) for azimuth data domain transformation, exhibit regular structural patterns. Building on this insight, a fifth-order NCS algorithm with low derivation complexity is proposed, along with a dedicated geometric correction method. For a given predefined slant range model and NCS order, the proposed algorithm requires only a single FT/IFT derivation to obtain the analytical expression of the signal after NCS processing, thereby simplifying both the construction of the Doppler parameter linear equation system and the solution of NCS parameters. This significantly reduces the complexity of the algorithm derivation. Furthermore, an instantaneous projection geometric model is established based on the high-speed squint-forward-looking SAR imaging geometry, enabling the development of a tailored geometric correction method. Compared with traditional NCS algorithms, the proposed fifth-order NCS algorithm achieves superior imaging performance while maintaining computational efficiency. Simulated and real data processing validate its effectiveness and advantages in high-speed squint-forward-looking scenarios. -

-
References
[1] CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2005: 225–362.[2] CHEN Xing, DONG Zhen, ZHANG Zehua, et al. Very high resolution synthetic aperture radar systems and imaging: A review[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 7104–7123. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3374429.[3] 李春升, 杨威, 王鹏波. 星载SAR成像处理算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2013, 2(1): 111–122. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20071.LI Chunsheng, YANG Wei, and WANG Pengbo. A review of spaceborne SAR algorithm for image formation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2013, 2(1): 111–122. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2013.20071.[4] 邢孟道, 林浩, 陈溅来, 等. 多平台合成孔径雷达成像算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102.XING Mengdao, LIN Hao, CHEN Jianlai, et al. A review of imaging algorithms in multi-platform-borne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102.[5] MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301.[6] DENG Kun, HUANG Yan, CHEN Zhanye, et al. A modified frequency nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for high-speed high-squint synthetic aperture radar with curved trajectory[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(9): 1588. doi: 10.3390/rs16091588.[7] ZHANG Lei, QIAO Zhijun, XING Mengdao, et al. A robust motion compensation approach for UAV SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(8): 3202–3218. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2180392.[8] 李亚超, 王家东, 张廷豪, 等. 弹载雷达成像技术发展现状与趋势[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 943–973. doi: 10.12000/JR22119.LI Yachao, WANG Jiadong, ZHANG Tinghao, et al. Present situation and prospect of missile-borne radar imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 943–973. doi: 10.12000/JR22119.[9] 邢孟道, 马鹏辉, 楼屹杉, 等. 合成孔径雷达快速后向投影算法综述[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(1): 1–22. doi: 10.12000/JR23183.XING Mengdao, MA Penghui, LOU Yishan, et al. Review of fast back projection algorithms in synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 1–22. doi: 10.12000/JR23183.[10] LIANG Yi, LI Guofei, WEN Jun, et al. A fast time-domain SAR imaging and corresponding autofocus method based on hybrid coordinate system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 8627–8640. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2921917.[11] LOU Yishan, LIN Hao, LI Ning, et al. A prior 2-D autofocus algorithm with ground Cartesian BP imaging for curved trajectory SAR[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 2422–2436. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3346942.[12] LOU Yishan, XING Mengdao, LIN Hao, et al. A time-domain processing framework for airborne and vehicle-borne microwave photonic SAR with a resolution of 0.02 m[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5211420. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3565299.[13] LU Jingyue, ZHANG Lei, and MENG Zhichao. A pulse-by-pulse Doppler ambiguity resolving algorithm for FLMC-SAR imaging based on fast factorized back-projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5205419. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3351766.[14] BIE Bowen, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. A frequency domain backprojection algorithm based on local Cartesian coordinate and subregion range migration correction for high-squint SAR mounted on maneuvering platforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(12): 7086–7101. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2848249.[15] CHEN Xiaoxiang, SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, et al. Ground Cartesian back-projection algorithm for high squint diving TOPS SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(7): 5812–5827. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3011589.[16] XIONG Tao, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. New applications of omega-K algorithm for SAR data processing using effective wavelength at high squint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(5): 3156–3169. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2213342.[17] XING Mengdao, WU Yufeng, ZHANG Y D, et al. Azimuth resampling processing for highly squinted synthetic aperture radar imaging with several modes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(7): 4339–4352. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2281454.[18] CHEN Jianlai, XIONG Rongqi, YU Hanwen, et al. Nonparametric full-aperture autofocus imaging for microwave photonic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5214815. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3411392.[19] MAO Xinhua. Spherical geometry algorithm for spaceborne synthetic aperture radar imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5217215. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3427014.[20] DING Zegang, ZHENG Pengnan, LI Han, et al. Spaceborne high-squint high-resolution SAR imaging based on two-dimensional spatial-variant range cell migration correction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5240114. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3222230.[21] LI Yachao, ZHANG Tinghao, MEI Haiwen, et al. Focusing translational-variant bistatic forward-looking SAR data using the modified omega-K algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5203916. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3063780.[22] DESAI M D and JENKINS W K. Convolution backprojection image reconstruction for spotlight mode synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1992, 1(4): 505–517. doi: 10.1109/83.199920.[23] ULANDER L M H, HELLSTEN H, and STENSTROM G. Synthetic-aperture radar processing using fast factorized back-projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2003, 39(3): 760–776. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1238734.[24] LI Yachao, XU Gaotian, ZHOU Song, et al. A novel CFFBP algorithm with noninterpolation image merging for bistatic forward-looking SAR focusing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5225916. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3162230.[25] LOU Yishan, LIU Wenkang, XING Mengdao, et al. A novel motion compensation method applicable to ground Cartesian back-projection algorithm for airborne circular SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5208917. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3276051.[26] AN Daoxiang, HUANG Xiaotao, JIN Tian, et al. Extended nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for high-resolution highly squint SAR data focusing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(9): 3595–3609. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2183606.[27] LI Zhenyu, LIANG Yi, XING Mengdao, et al. An improved range model and omega-K-based imaging algorithm for high-squint SAR with curved trajectory and constant acceleration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(5): 656–660. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2533631.[28] LI Zhenyu, XING Mengdao, XING Wenjie, et al. A modified equivalent range model and wavenumber-domain imaging approach for high-resolution-high-squint SAR with curved trajectory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(7): 3721–3734. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2678763.[29] ZHANG Tinghao, LI Yachao, WANG Jun, et al. A modified range model and extended omega-K algorithm for high-speed-high-squint SAR with curved trajectory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5204515. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3255518.[30] BIE Bowen, QUAN Yinghui, SUN Guangcai, et al. A modified range model and Doppler resampling based imaging algorithm for high squint SAR on maneuvering platforms[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(11): 1923–1927. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2959660.[31] XI Zirui, WANG Guanyong, ZHANG Lei, et al. An improved parametric polar format algorithm for missile-borne SAR imaging with large squint angles and dive trajectories[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2025, 22: 4002705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3522277.[32] LI Yongkang, ZHANG Yonghui, LIANG Junli, et al. An improved omega-K algorithm for squinted SAR with curved trajectory[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4000905. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3335650.[33] LI Zhenyu, XING Mengdao, LIANG Yi, et al. A frequency-domain imaging algorithm for highly squinted SAR mounted on maneuvering platforms with nonlinear trajectory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(7): 4023–4038. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2535391.[34] LIANG Yi, LI Zhenyu, ZENG Letian, et al. A high-order phase correction approach for focusing HS-SAR small-aperture data of high-speed moving platforms[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(9): 4551–4561. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2459765.[35] WANG Zhigui, LIU Mei, AI Gengting, et al. Focusing of bistatic SAR with curved trajectory based on extended azimuth nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(6): 4160–4179. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2961562.[36] QU Tan, ZHANG Yan, and WU Jiaji. A novel AFNCS algorithm for super-resolution SAR in curve trajectory[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2021, 27(4): 837–844. doi: 10.1007/s00530-020-00715-z.[37] DENG Yuhui, SUN Guangcai, HAN Liang, et al. 2-D wavenumber domain autofocusing for high-resolution highly squinted SAR imaging based on equivalent broadside model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5220515. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3328392.[38] ZHANG Tinghao, LI Yachao, YUAN Mingze, et al. Focusing highly squinted FMCW-SAR data using the modified wavenumber-domain algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 1999–2011. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3266886.[39] SUN Guangcai, JIANG Xiuwei, XING Mengdao, et al. Focus improvement of highly squinted data based on azimuth nonlinear scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(6): 2308–2322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2102040.[40] ZHANG Shuangxi, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. Focus improvement of high-squint SAR based on azimuth dependence of quadratic range cell migration correction[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(1): 150–154. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2195634.[41] CHEN Jianlai, ZHANG Junchao, YU Hanwen, et al. Blind NCS-based autofocus for airborne wide-beam SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2022, 8: 626–638. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2022.3194745.[42] LIAO Yi, LUO Zhibang, WANG Jian, et al. Processing of mosaic SAR using time frequency analysis and azimuth NCS algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 4625–4639. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3246433.[43] 刘裕洲, 蔡天倚, 李亚超, 等. 联合距离方位二维NCS的星弹双基前视SAR成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(6): 1202–1214. doi: 10.12000/JR23144.LIU Yuzhou, CAI Tianyi, LI Yachao, et al. A range and azimuth combined two-dimensional NCS algorithm for spaceborne-missile bistatic forward-looking SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(6): 1202–1214. doi: 10.12000/JR23144.[44] 陈溅来, 熊毅, 徐刚, 等. 基于子图像变标的非线性轨迹SAR成像及其自聚焦方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 1098–1109. doi: 10.12000/JR22171.CHEN Jianlai, XIONG Yi, XU Gang, et al. Nonlinear trajectory synthetic aperture radar imaging and autofocus algorithm based on sub-image nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 1098–1109. doi: 10.12000/JR22171.[45] WU Yufeng, SUN Guangcai, XIA Xianggen, et al. An azimuth frequency non-linear chirp scaling (FNCS) algorithm for TOPS SAR imaging with high squint angle[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(1): 213–221. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2013.2258893.[46] LI Zhenyu, LIANG Yi, XING Mengdao, et al. Focusing of highly squinted SAR data with frequency nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(1): 23–27. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2492681.[47] ZENG Tao, LI Yinghe, DING Zegang, et al. Subaperture approach based on azimuth-dependent range cell migration correction and azimuth focusing parameter equalization for maneuvering high-squint-mode SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(12): 6718–6734. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2447393.[48] CHEN Si, ZHAO Huichang, ZHANG Shuning, et al. An extended nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for missile borne SAR imaging[J]. Signal Processing, 2014, 99: 58–68. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.12.017.[49] SUN Zhichao, WU Junjie, LI Zhongyu, et al. Highly squint SAR data focusing based on keystone transform and azimuth extended nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(1): 145–149. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2329554.[50] NEO Y L, WONG G, and CUMMING I G. A two-dimensional spectrum for bistatic SAR processing using series reversion[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2007, 4(1): 93–96. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.885862.[51] LI Zhenyu, CHEN Jianlai, DU Wentao, et al. Focusing of maneuvering high-squint-mode SAR data based on equivalent range model and wavenumber-domain imaging algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 2419–2433. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2993466.[52] 李震宇. 机动平台SAR大斜视成像算法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2017.LI Zhenyu. Study on high squint imaging algorithms for SAR mounted on maneuvering platforms[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2017.[53] MEI Haiwen, LI Yachao, XING Mengdao, et al. A frequency-domain imaging algorithm for translational variant bistatic forward-looking SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(3): 1502–1515. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2943743.[54] ZHANG Shuanghui, LIU Yongxiang, and LI Xiang. Fast entropy minimization based autofocusing technique for ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(13): 3425–3434. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2422686.[55] DENG Kun, HUANG Yan, CHEN Zhanye, et al. A novel sub-aperture contrast-based WPGA method for automotive SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025, 26(7): 10386–10403. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2025.3552092.[56] MORRISON R L, DO M N, and MUNSON D C. SAR image autofocus by sharpness optimization: A theoretical study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(9): 2309–2321. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.903252. -
Proportional views

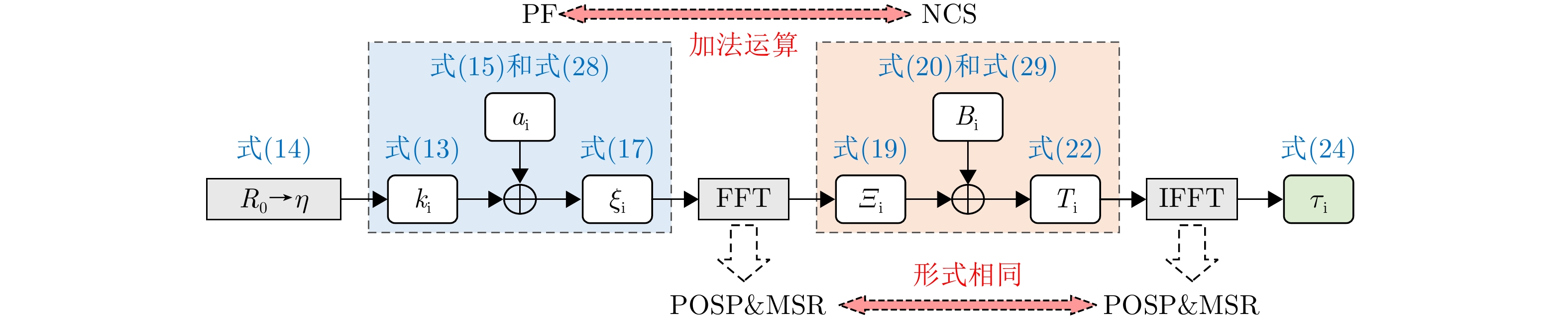
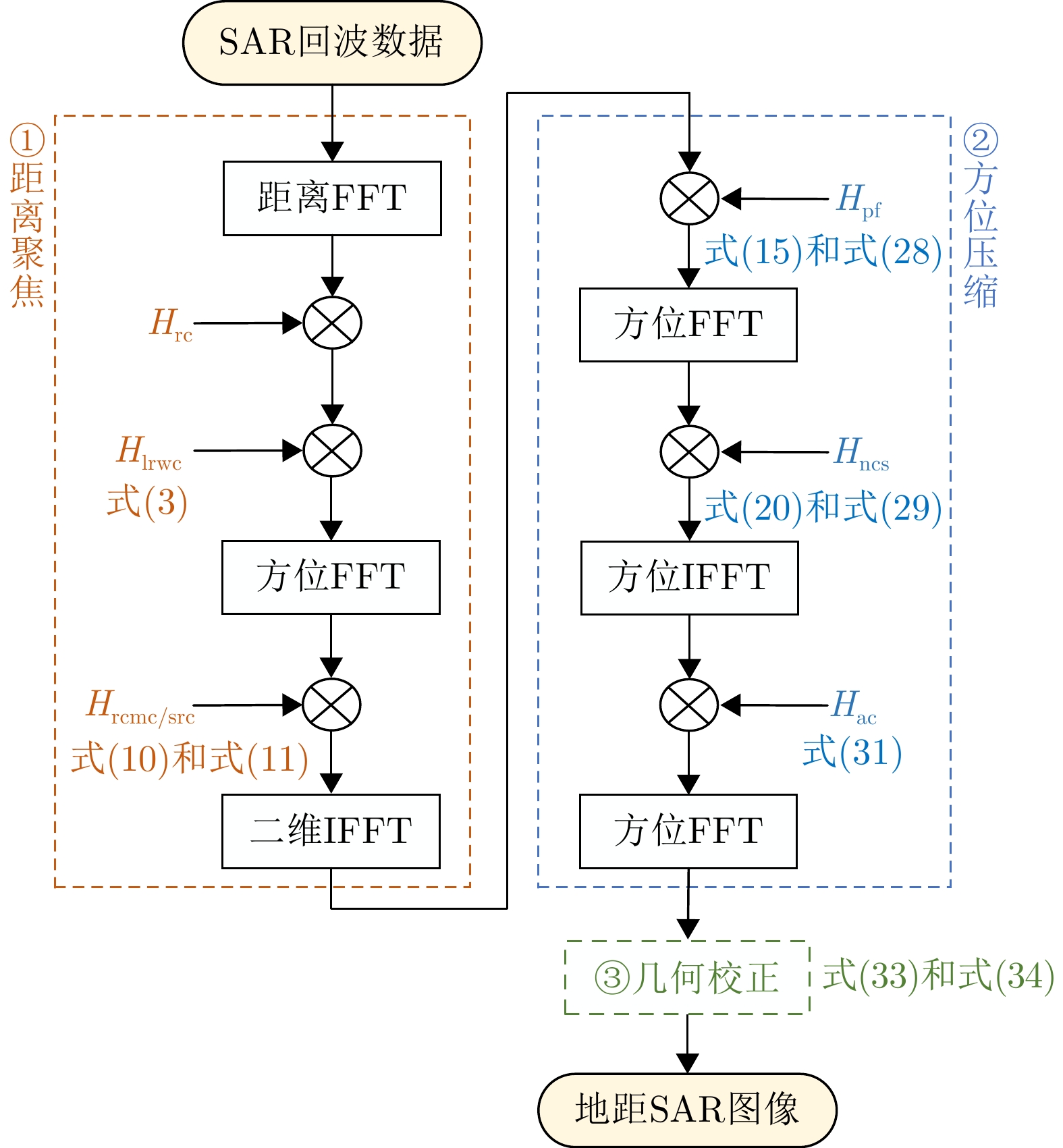
- Figure 1. Nonlinear Chirp Scaling (NCS) processing flowcharts
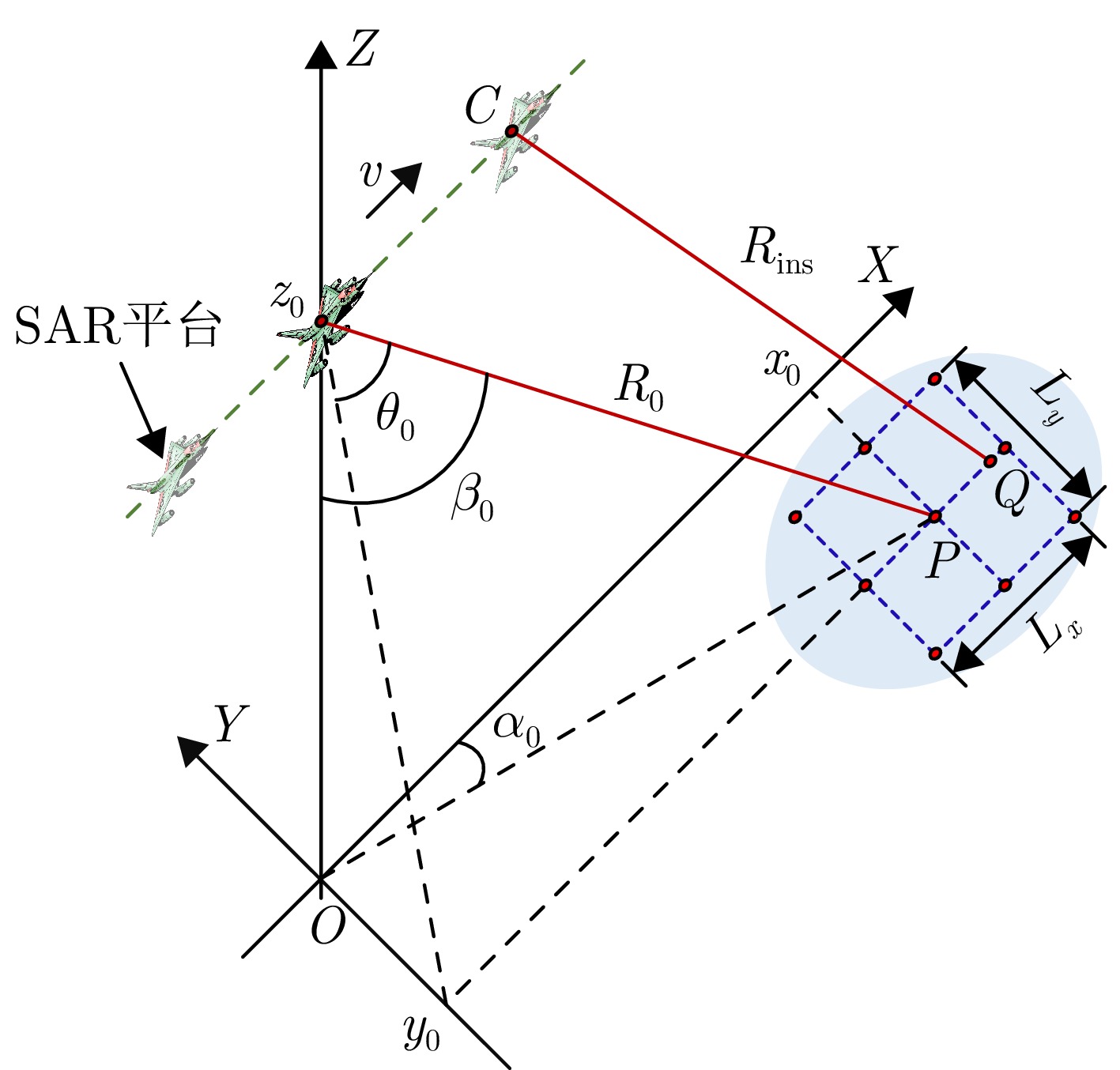
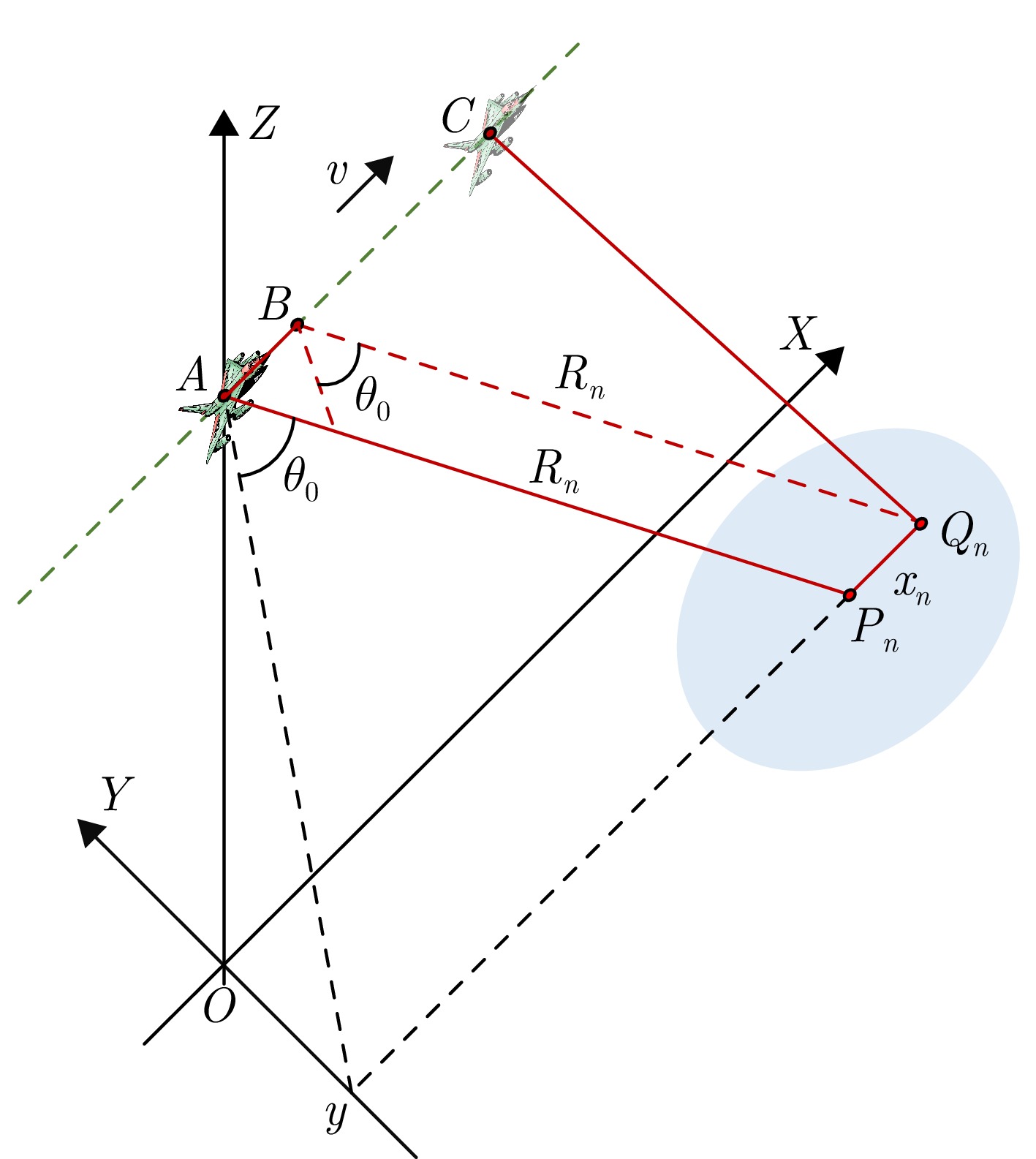
- Figure 2. Geometric model of high-speed squint-forward SAR imaging
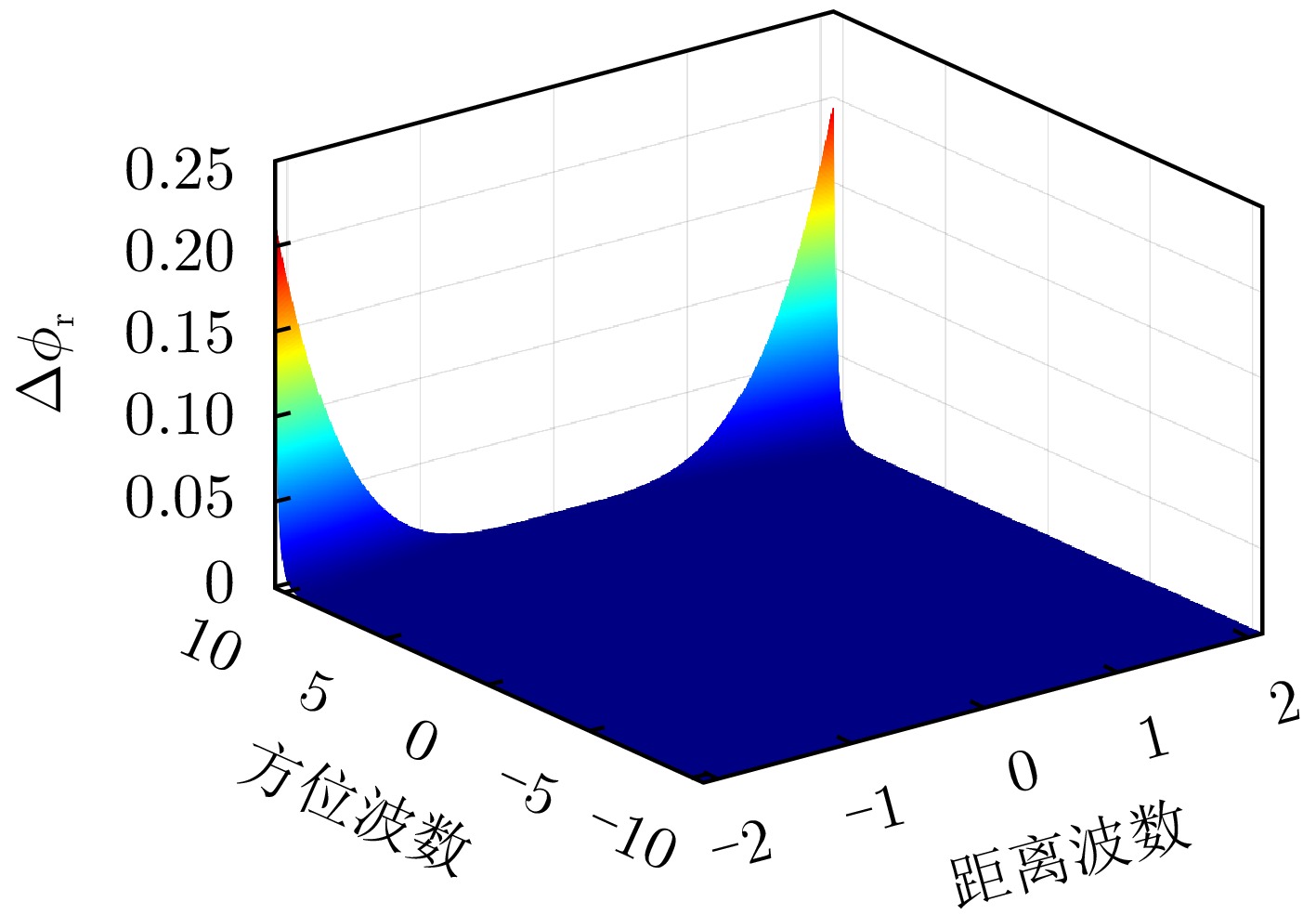
- Figure 3. Taylor series approximation error for 2D wavenumber spectrum
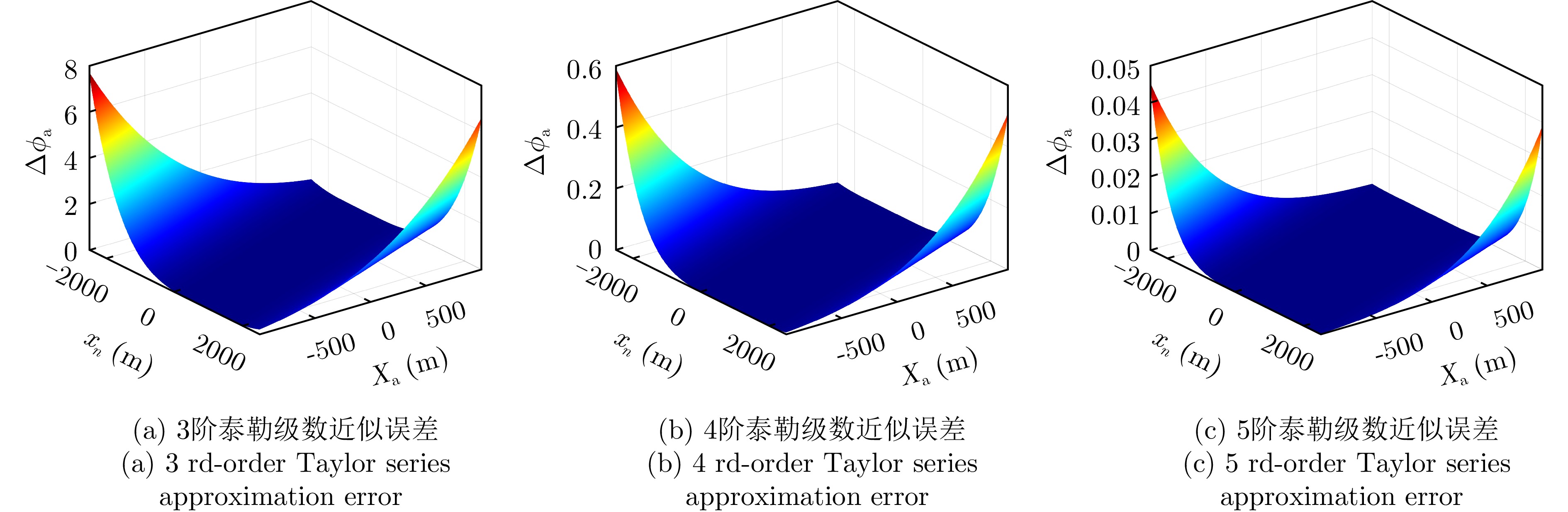
- Figure 4. Taylor series approximation error for azimuth time-domain phases
- Figure 5. NCS parameter transformation relationship diagram
- Figure 6. Instantaneous high-speed squint-forward SAR imaging geometry
- Figure 7. Flowchart of the proposed algorithm
- Figure 8. Simulation results of the proposed algorithm
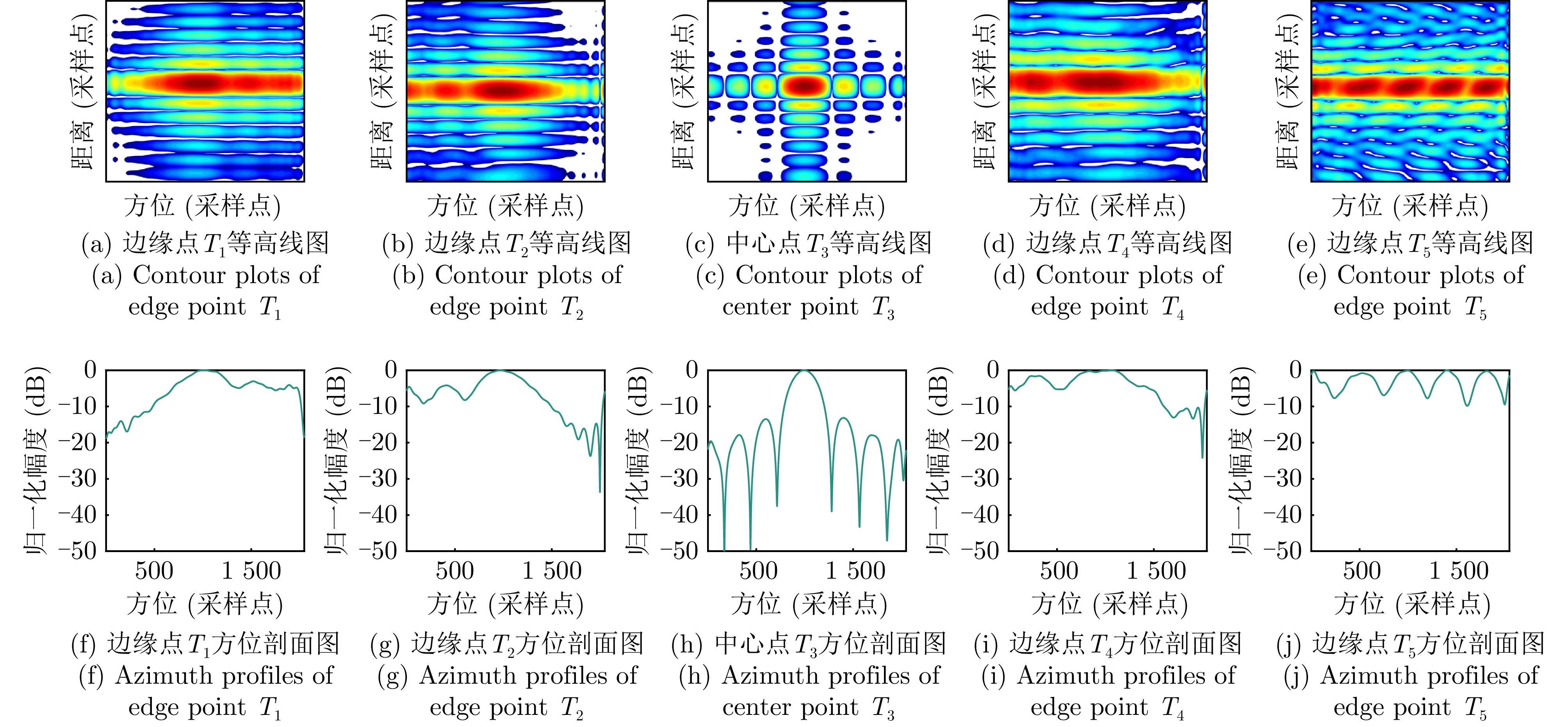
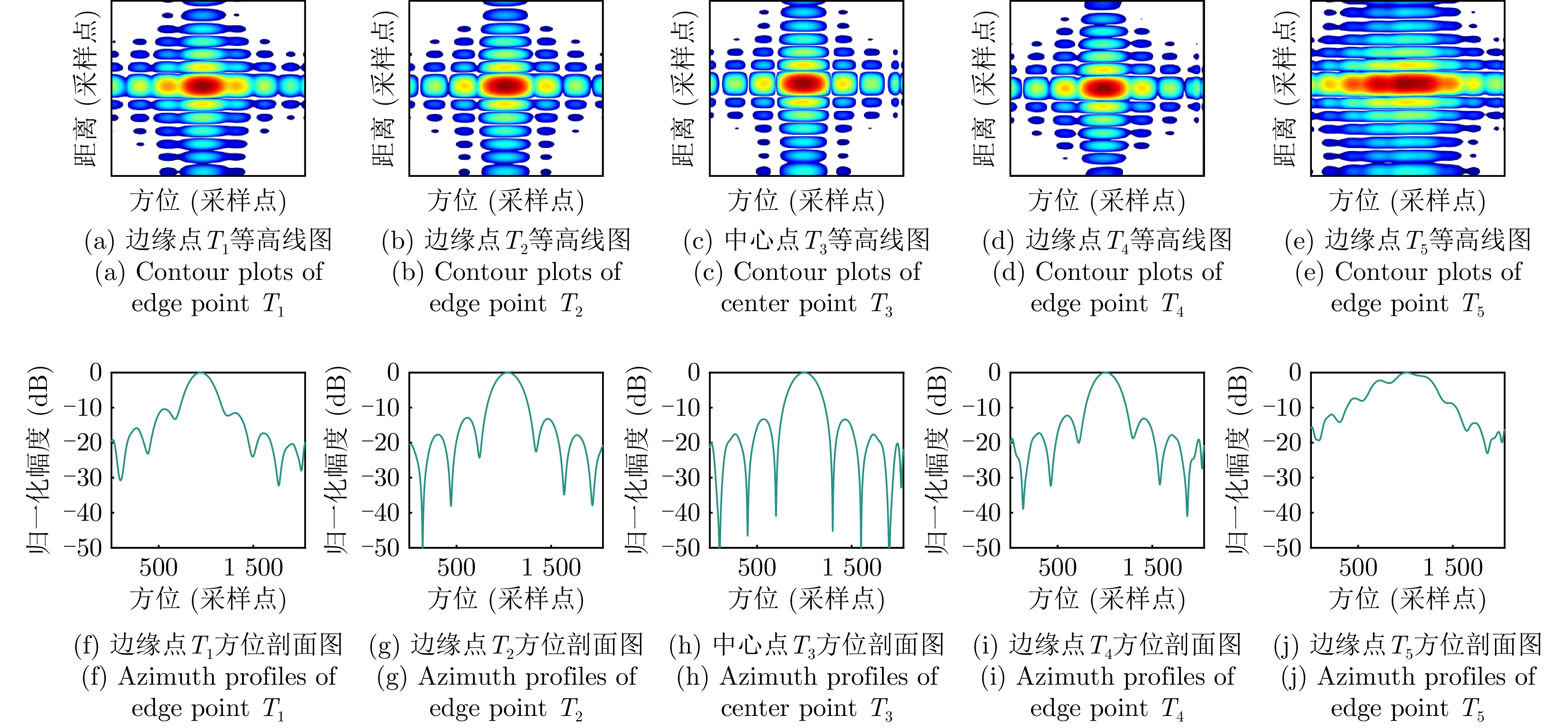
- Figure 9. Simulation data processing results of the TNCS algorithm[33]
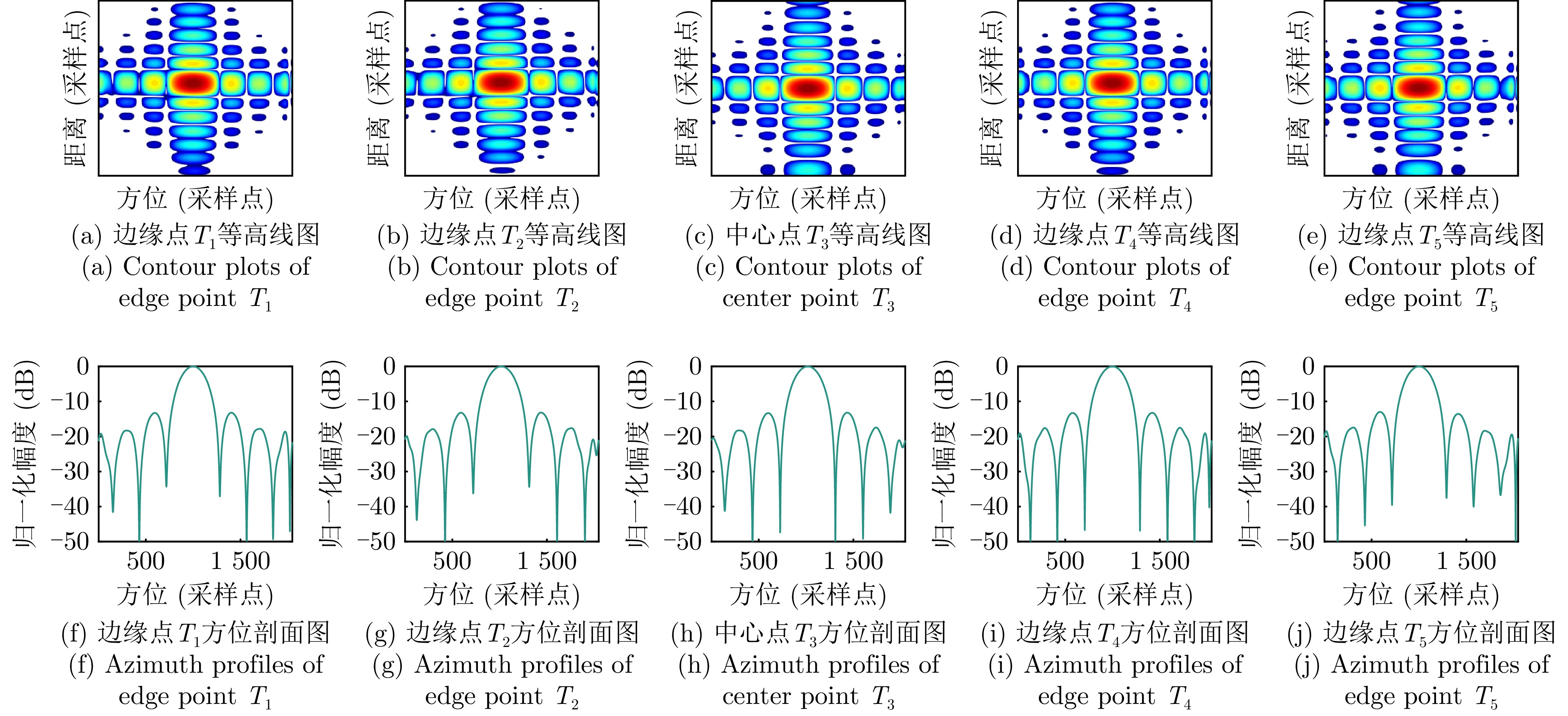
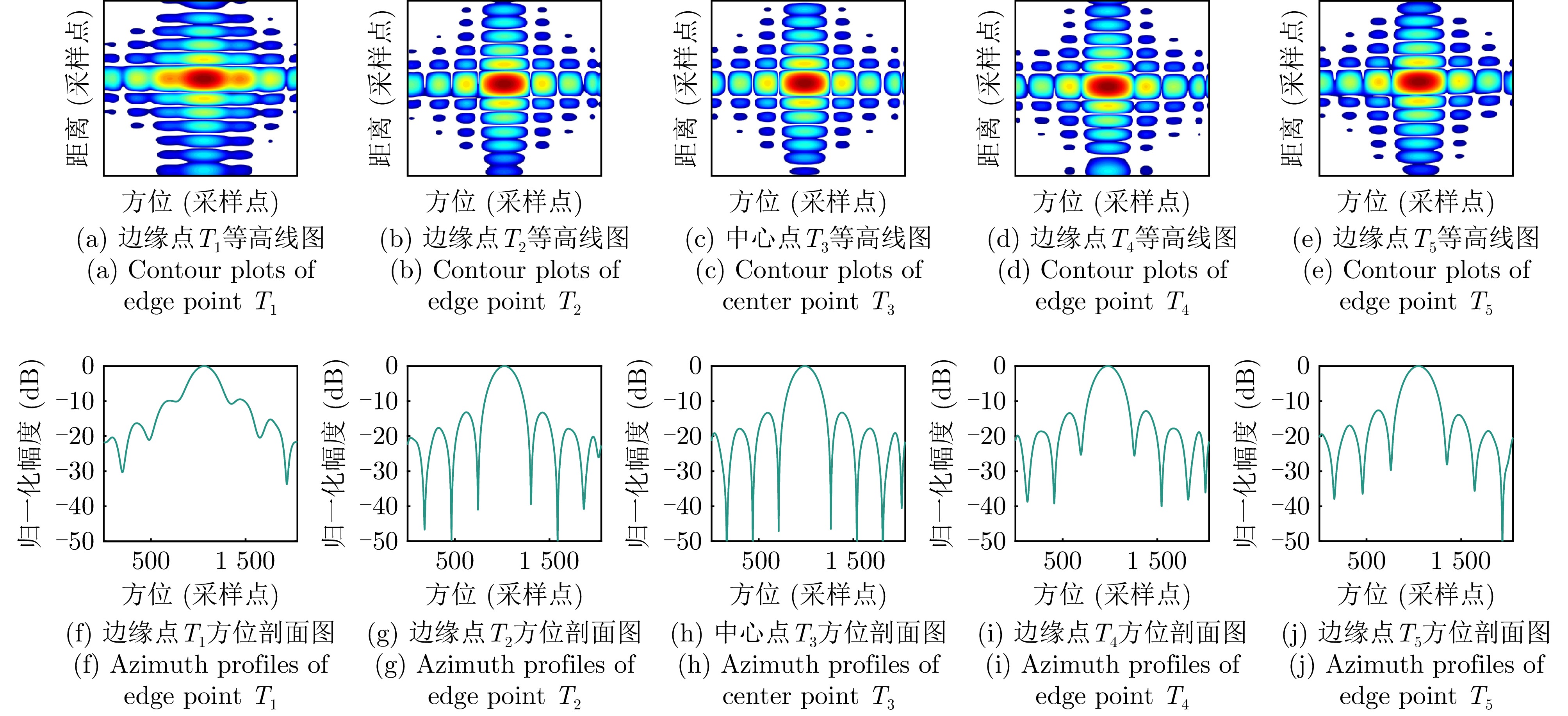
- Figure 12. Simulation data processing results of the proposed algorithm
- Figure 10. Simulation data processing results of HPCA algorithm[34]
- Figure 11. Simulation data processing results of MFNCS algorithm[6]
- Figure 13. Imaging results of the measured data
- Figure 14. Magnified results of the region A in Fig. 13
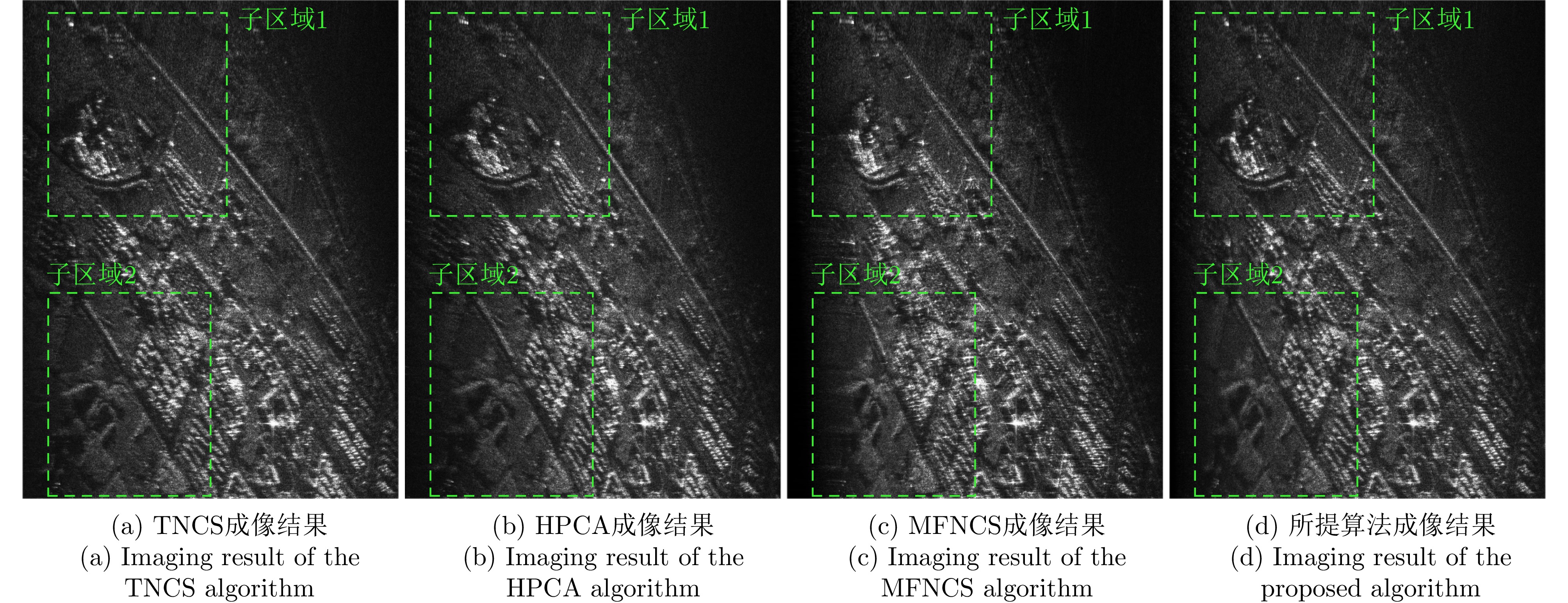
- Figure 15. Magnified results of the sub-regions in Fig. 14
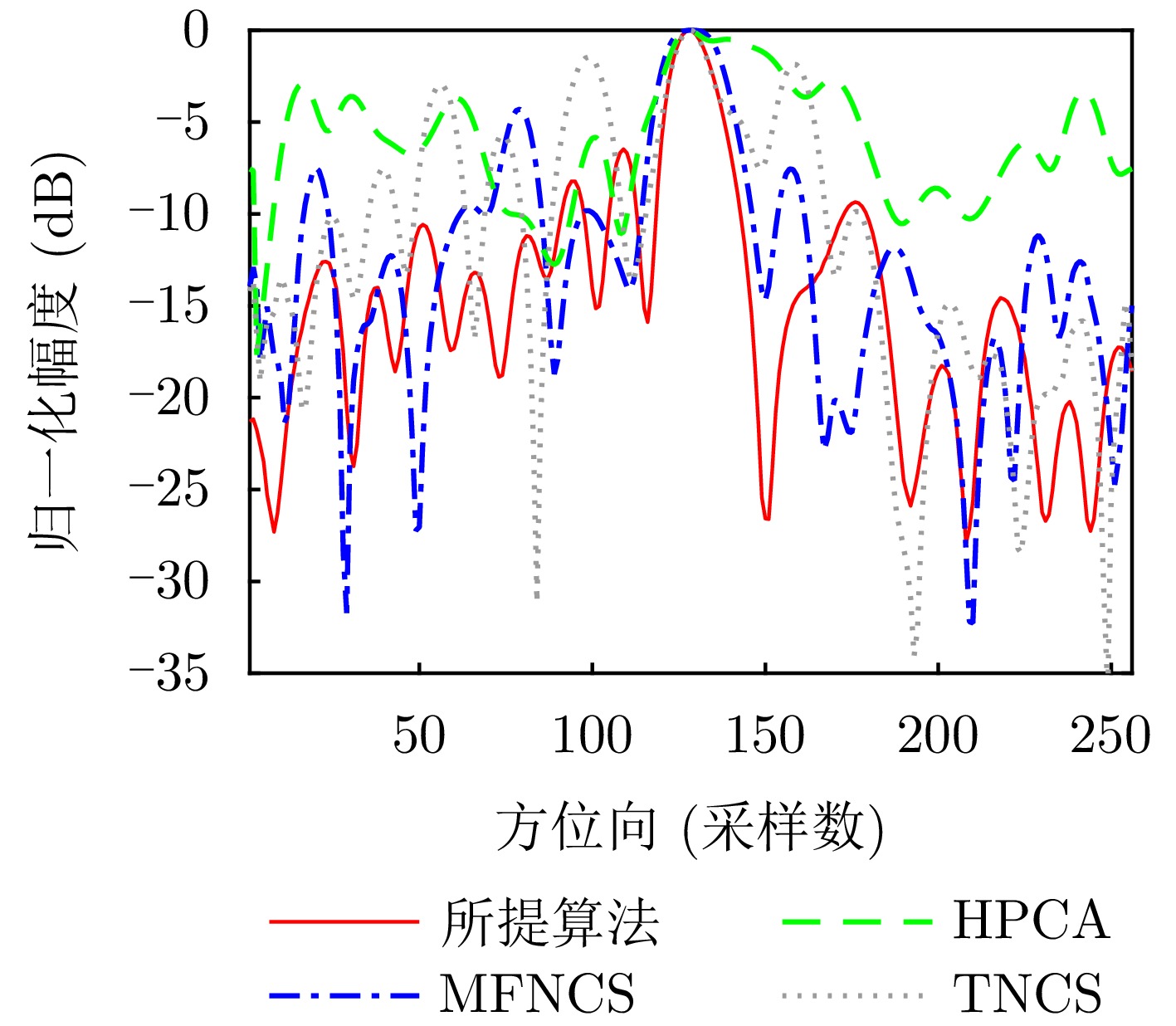
- Figure 16. Azimuth profiles of the target a in Fig. 15
- Figure 17. Geometric correction result of the measured SAR image


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: