- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2025
> Online First
| Citation: | SU Xinyuan, QUAN Sinong, CAI Zhihao, et al. Optimal adversarial sample generation method in SAR ATR based on joint misleading and fidelity optimization[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25179 |
Optimal Adversarial Sample Generation Method in SAR ATR Based on Joint Misleading and Fidelity Optimization
DOI: 10.12000/JR25179 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25179
More Information-
Abstract
Adversarial sample generation is a key research direction for uncovering the vulnerabilities of deep neural networks and improving the robustness of Synthetic Aperture Radar Automatic Target Recognition (SAR ATR) systems. This study proposes an optimal adversarial sample generation method for SAR ATR that jointly optimizes misleading effectiveness and fidelity, aiming to resolve the core contradiction between adversarial effectiveness and visual concealment. The generation process is modeled as a joint optimization problem with the goals of balancing “misleading” and “fidelity”. First, an integrated composite transform attack strategy is designed to enhance attack effectiveness, and a joint measurement model is developed that combines the classification accuracy of the target model with the Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS) to quantify the two optimization goals. Next, an improved uniformity-guided multiobjective RIME algorithm is proposed. By integrating the Tent chaotic map, hybrid dynamic weighting, and golden sine guidance, the model is efficiently solved, yielding a set of Pareto-optimal solutions that represent various tradeoff degrees. Finally, the YOLOv10 object detection network is employed to identify perturbations in the samples within the solution set, thereby locating the critical points where disturbances occur and enabling the quantification of optimal parameters. Experiments on MSTAR and MiniSAR datasets show that the proposed ensemble compound transform attack method achieves an average target model recognition accuracy of 8.96% across different ensemble models and classification networks, improving the overall misleading effect by an average of 2.25% compared to other methods. Among them, the complex model increases by an average of 5.56%, while the proposed uniformity-guided multiobjective RIME algorithm improves the solution set diversity and convergence speed by over 25% compared with the comparison method. Using this method, the learned perceptual image patch similarity is maintained at 0.407 and the perturbation factor at 0.031, while classification accuracy decreases to 28.81%, demonstrating a tradeoff between misleading effectiveness and visual fidelity. This parameter maintains effective misleading performance under six different defense strategies, demonstrating strong robustness and providing a new approach and quantitative benchmark for adversarial attack research in SAR ATR. -

-
References
[1] 阮航, 崔家豪, 毛秀华, 等. SAR目标识别对抗攻击综述: 从数字域迈向物理域[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(6): 1298–1326. doi: 10.12000/JR24142.RUAN Hang, CUI Jiahao, MAO Xiuhua, et al. A survey of adversarial attacks on SAR target recognition: From digital domain to physical domain[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(6): 1298–1326. doi: 10.12000/JR24142.[2] 高勋章, 张志伟, 刘梅, 等. 雷达像智能识别对抗研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 696–712. doi: 10.12000/JR23098.GAO Xunzhang, ZHANG Zhiwei, LIU Mei, et al. Intelligent radar image recognition countermeasures: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 696–712. doi: 10.12000/JR23098.[3] 万烜申, 刘伟, 牛朝阳, 等. 基于动量迭代快速梯度符号的SAR-ATR深度神经网络黑盒攻击算法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 714–729. doi: 10.12000/JR23220.WAN Xuanshen, LIU Wei, NIU Chaoyang, et al. Black-box attack algorithm for SAR-ATR deep neural networks based on MI-FGSM[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 714–729. doi: 10.12000/JR23220.[4] 孙浩, 陈进, 雷琳, 等. 深度卷积神经网络图像识别模型对抗鲁棒性技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 571–594. doi: 10.12000/JR21048.SUN Hao, CHEN Jin, LEI Lin, et al. Adversarial robustness of deep convolutional neural network-based image recognition models: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 571–594. doi: 10.12000/JR21048.[5] 李东阳, 王林元, 彭进先, 等. 基于稀疏子空间采样的信号检测网络黑盒查询对抗攻击方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(8): 2808–2818. doi: 10.11999/JEIT241019.LI Dongyang, WANG Linyuan, PENG Jinxian, et al. A black-box query adversarial attack method for signal detection networks based on sparse subspace sampling[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(8): 2808–2818. doi: 10.11999/JEIT241019.[6] 要旭东, 郭雅萍, 刘梦阳, 等. 遥感图像中不确定性驱动的像素级对抗噪声检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2025, 47(6): 1633–1644. doi: 10.11999/JEIT241157.YAO Xudong, GUO Yaping, LIU Mengyang, et al. An uncertainty-driven pixel-level adversarial noise detection method for remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2025, 47(6): 1633–1644. doi: 10.11999/JEIT241157.[7] 董庆宽, 何浚霖. 基于信息瓶颈的深度学习模型鲁棒性增强方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(6): 2197–2204. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220603.DONG Qingkuan and HE Junlin. Robustness enhancement method of deep learning model based on information bottleneck[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(6): 2197–2204. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220603.[8] 胡军, 石艺杰. 基于动量增强特征图的对抗防御算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(12): 4548–4555. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221414.HU Jun and SHI Yijie. Adversarial defense algorithm based on momentum enhanced future map[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(12): 4548–4555. doi: 10.11999/JEIT221414.[9] 段晔鑫, 贺正芸, 张颂, 等. 针对图像分类的鲁棒物理域对抗伪装[J]. 电子学报, 2024, 52(3): 863–871. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221301.DUAN Yexin, HE Zhengyun, ZHANG Song, et al. Robust physical adversarial camouflages for image classifiers[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2024, 52(3): 863–871. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20221301.[10] 姚睿, 朱享彬, 周勇, 等. 基于重要特征的视觉目标跟踪可迁移黑盒攻击方法[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(4): 826–834. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220057.YAO Rui, ZHU Xiangbin, ZHOU Yong, et al. Transferable black box attack on visual object tracking based on important features[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2023, 51(4): 826–834. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220057.[11] 吴骥, 邵文泽, 葛琦, 等. 一种基于迭代累积梯度的多层特征重要性攻击方法[J]. 电子学报, 2024, 52(11): 3798–3808. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20230843.WU Ji, SHAO Wenze, GE Qi, et al. A multi-layer feature importance attack method based on iterative accumulated gradients[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2024, 52(11): 3798–3808. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20230843.[12] 鲍蕾, 陶蔚, 陶卿. 结合自适应步长策略和数据增强机制提升对抗攻击迁移性[J]. 电子学报, 2024, 52(1): 157–169. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220737.BAO Lei, TAO Wei, and TAO Qing. Boosting adversarial transferability through adaptive-learning-rate with data augmentation mechanism[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2024, 52(1): 157–169. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20220737.[13] 蔡伟, 狄星雨, 蒋昕昊, 等. 基于数据增强的车辆鲁棒对抗纹理生成[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2025, 47(6): 1757–1767. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.06.04.CAI Wei, DI Xingyu, JIANG Xinhao, et al. Vehicle robust adversarial texture generation based on data augmentation[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(6): 1757–1767. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.06.04.[14] 王梓聪, 张剑. 基于雅可比显著图的电磁信号无目标平滑对抗攻击方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2025, 47(7): 2127–2135. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.07.06.WANG Zicong and ZHANG Jian. Electromagnetic signal no-targeted smooth adversarial attack method based on Jacobian saliency map[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(7): 2127–2135. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.07.06.[15] PENG Bowen, PENG Bo, XIA Jingyuan, et al. Towards assessing the synthetic-to-measured adversarial vulnerability of SAR ATR[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2024, 214: 119–134. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2024.06.004.[16] PENG Guobei, LIU Ming, CHEN Shichao, et al. A directional generation algorithm for SAR image based on azimuth-guided statistical generative adversarial network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2024, 72: 5406–5421. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2024.3502454.[17] WANG Junpeng, QUAN Sinong, XING Shiqi, et al. PSO-based fine polarimetric decomposition for ship scattering characterization[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2025, 220: 18–31. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2024.11.015.[18] CAI Zhihao, XING Shiqi, QUAN Sinong, et al. A power-distribution joint optimization arrangement for multi-point source jamming system[J]. Results in Engineering, 2025, 27: 106856. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2025.106856.[19] WAN Xuanshen, LIU Wei, NIU Chaoyang, et al. Black-box universal adversarial attack for DNN-based models of SAR automatic target recognition[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 8673–8696. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3384188.[20] HUANG Jiankai, YIN Jiapeng, AN Mengyun, et al. Azimuth pointing calibration for rotating phased array radar based on ground clutter correlation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 1000315. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3514310.[21] CAI Zhihao, XING Shiqi, SU Xinyuan, et al. A joint optimization method for power and array of multi-point sources system[J]. Remote Sensing, 2025, 17(14): 2445. doi: 10.3390/rs17142445.[22] PENG Bowen, PENG Bo, YONG Shaowei, et al. An empirical study of fully black-box and universal adversarial attack for SAR target recognition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(16): 4017. doi: 10.3390/rs14164017.[23] LIU Jiyuan, ZHANG Tao, and XIONG Huilin. PolSAR ship targets generation via the polarimetric feature guided denoising diffusion probabilistic model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4011505. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3407147.[24] SUI Ran, WANG Junjie, SUN Guang, et al. A dual-polarimetric high range resolution profile modulation method based on time-modulated APCM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2025, 73(2): 1007–1017. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2025.3526901.[25] GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, and SZEGEDY C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2012: 1–12.[26] WANG Jiakai, LIU Xianglong, HU Jin, et al. Adversarial examples in the physical world: A survey[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.01473, 2023.[27] MADRY A, MAKELOV A, SCHMIDT L, et al. Towards deep learning models resistant to adversarial attacks[C]. The 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018: 1–23.[28] DONG Yinpeng, LIAO Fangzhou, PANG Tianyu, et al. Boosting adversarial attacks with momentum[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2012: 9185–9193. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00957.[29] LIN Jiadong, SONG Chuanbiao, He Kun, et al. Nesterov accelerated gradient and scale invariance for adversarial attacks[C]. The 8th International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020: 1–12.[30] WANG Xiaosen and HE Kun. Enhancing the transferability of adversarial attacks through variance tuning[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 1924–1933. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00196.[31] XIE Cihang, ZHANG Zhishuai, ZHOU Yuyin, et al. Improving transferability of adversarial examples with input diversity[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 2725–2734. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00284.[32] 徐延杰, 孙浩, 雷琳, 等. 基于对抗攻击的SAR舰船识别卷积神经网络鲁棒性研究[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(12): 1965–1978. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.002.XU Yanjie, SUN Hao, LEI Lin, et al. The research for the robustness of SAR ship identification based on adversarial example[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(12): 1965–1978. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.002.[33] PAPERNOT N, MCDANIEL P, JHA S, et al. The limitations of deep learning in adversarial settings[C]. 2016 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy, Saarbruecken, Germany, 2016: 372–387. doi: 10.1109/EuroSP.2016.36.[34] CARLINI N and WAGNER D. Towards evaluating the robustness of neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Jose, USA, 2017: 39–57. doi: 10.1109/SP.2017.49.[35] CHEN Pinyu, SHARMA Y, ZHANG Huan, et al. EAD: Elastic-net attacks to deep neural networks via adversarial examples[C]. The 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 10–17. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v32i1.11302.[36] DU Chuan, HUO Chaoying, ZHANG Lei, et al. Fast C&W: A fast adversarial attack algorithm to fool SAR target recognition with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4010005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3058011.[37] SU Jiawei, VARGAS D V, and SAKURAI K. One pixel attack for fooling deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 23(5): 828–841. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2019.2890858.[38] MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, and FROSSARD P. DeepFool: A simple and accurate method to fool deep neural networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2574–2582. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.282.[39] CHEN Jianbo, JORDAN M I, and WAINWRIGHT M J. HopSkipJumpAttack: A query-efficient decision-based attack[C]. 2020 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, USA, 2020: 1277–1294. doi: 10.1109/SP40000.2020.00045.[40] XIE Chulin, HUANG Keli, CHEN Pinyu, et al. DBA: Distributed backdoor attacks against federated learning[C]. The 8th International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020: 1–19.[41] QIN Weibo and WANG Feng. A universal adversarial attack on CNN-SAR image classification by feature dictionary modeling[C]. IGARSS 2022–2022 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2022: 1027–1030. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS46834.2022.9883668.[42] GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2672–2680.[43] XIAO Chaowei, LI Bo, ZHU Junyan, et al. Generating adversarial examples with adversarial networks[C]. The 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 3905–3911. doi: 10.24963/ijcai.2018/543.[44] MANGLA P, JANDIAL S, VARSHNEY S, et al. AdvGAN++ : Harnessing latent layers for adversary generation[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.00706, 2019.[45] NASEER M, KHAN S, HAYAT M, et al. On generating transferable targeted perturbations[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2018: 7688–7697. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00761.[46] POURSAEED O, KATSMAN I, GAO Bicheng, et al. Generative adversarial perturbations[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4422–4431. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00465.[47] DU Meng, SUN Yuxin, SUN Bing, et al. TAN: A transferable adversarial network for DNN-based UAV SAR automatic target recognition models[J]. Drones, 2023, 7(3): 205. doi: 10.3390/drones7030205.[48] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28.[49] LIN Gengyou, PAN Zhisong, ZHOU Xingyu, et al. Boosting adversarial transferability with shallow-feature attack on SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(10): 2699. doi: 10.3390/rs15102699.[50] CHEN Yuzhou, DU Jiawei, YANG Yang, et al. Positive weighted feature attack: Toward transferable adversarial attack to SAR target recognition[C]. 2023 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronic Technology, Communication and Information (ICETCI), Changchun, China, 2023: 93–98. doi: 10.1109/ICETCI57876.2023.10176719.[51] PENG Bo, PENG Bowen, ZHOU Jie, et al. Low-frequency features optimization for transferability enhancement in radar target adversarial attack[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning, Heraklion, Greece, 2023: 115–129. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-44192-9_10.[52] WANG Jiafeng, CHEN Zhaoyu, JIANG Kaixun, et al. Boosting the transferability of adversarial attacks with global momentum initialization[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 255: 124757. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.124757.[53] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]. The 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 2017: 4278–4284. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v31i1.11231.[54] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–14.[55] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90.[56] PANDYA S B, KALITA K, JANGIR P, et al. Multi-objective RIME algorithm-based techno economic analysis for security constraints load dispatch and power flow including uncertainties model of hybrid power systems[J]. Energy Reports, 2024, 11: 4423–4451. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2024.04.016.[57] ROSS T D, WORRELL S W, VELTEN V J, et al. Standard SAR ATR evaluation experiments using the MSTAR public release data set[C]. The SPIE 3370, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery V, Orlando, USA, 1998: 566–573. doi: 10.1117/12.321859.[58] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, PLEISS G, et al. Convolutional networks with dense connectivity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(12): 8704–8716. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2918284.[59] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84–90. doi: 10.1145/3065386.[60] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2818–2826. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.308.[61] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. The 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021: 1–21.[62] KALITA K, RAMESH J V N, CEPOVA L, et al. Multi-objective exponential distribution optimizer (MOEDO): A novel math-inspired multi-objective algorithm for global optimization and real-world engineering design problems[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 1816. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-52083-7.[63] LV Pin, WANG Ning, SU Xunwen, et al. Research on no-load air-gap magnetic field and multi-objective optimization of a three-segment Halbach PMSLM with partially magnetized poles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2025, 61(9): 8102914. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2025.3593828.[64] WANG Chao, LI Jian, RAO Haidi, et al. Multi-objective grasshopper optimization algorithm based on multi-group and co-evolution[J]. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering, 2021, 18(3): 2527–2561. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2021129.[65] BAHRAMI B, KHAYYAMBASHI M R, and MIRJALILI S. Multiobjective placement of edge servers in MEC environment using a hybrid algorithm based on NSGA-II and MOPSO[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(18): 29819–29837. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3409569.[66] KHWAJA A S and MA Jianwei. Applications of compressed sensing for SAR moving-target velocity estimation and image compression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2011, 60(8): 2848–2860. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2011.2122190.[67] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031.[68] CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 213–229. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_13. -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. Optimal adversarial sample generation method flow chart
- Figure 2. The contradictory relationship between misleading and fidelity of adversarial samples
- Figure 3. Comparison diagram before and after composite transformation
- Figure 4. Comparison of attack effectiveness of EGCT method under different surrogate models
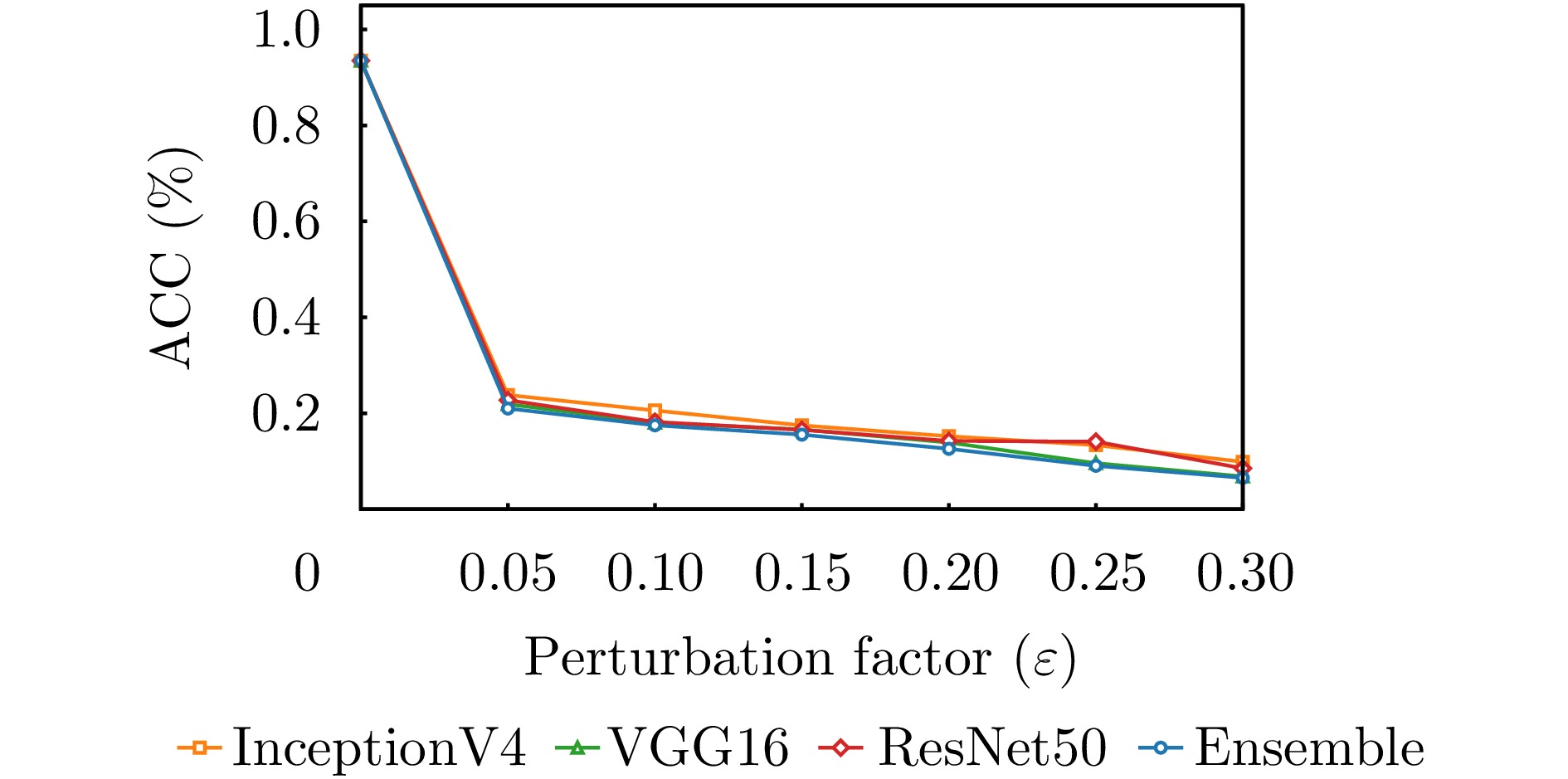
- Figure 5. Comparison of the effectiveness of the ensemble strategy and the experimental results
- Figure 6. Visual comparison diagram of effectiveness of EGCT
- Figure 7. Perturbation and adversarial samples generated by EGCT under different perturbation factors
- Figure 8. Migration comparison of different sample generation methods under various integration strategies
- Figure 9. The Pareto solution set obtained by UMORIME solution
- Figure 10. YOLOv10 network training set and its heat map
- Figure 11. Optimal balanced adversarial samples and scene detection graph
- Figure 12. Different detection networks correspond to the optimal balanced adversarial sample detection graph


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: