- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2025
> Online First
| Citation: | XIANG Yuming, CHEN Jinyang, HONG Zhonghua, et al. OSDataset2.0: SAR-optical image matching dataset and evaluation benchmark[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25176 |
OSDataset2.0: SAR-optical Image Matching Dataset and Evaluation Benchmark
DOI: 10.12000/JR25176 CSTR: 32380.14.J25176
More Information-
Abstract
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and optical imagery are two key remote-sensing modalities in Earth observation, and cross-modal image matching between them is widely applied in tasks such as image fusion, joint interpretation, and high-precision geolocation. In recent years, with the rapid growth of Earth-observation data, the importance of cross-modal image matching between SAR and optical data has become increasingly prominent, and related studies have achieved notable progress. In particular, Deep Learning (DL)-based methods, owing to their strengths in cross-modal feature representation and high-level semantic extraction, have demonstrated excellent matching accuracy and adaptability across varying imaging conditions. However, most publicly available datasets are limited to small image patches and lack complete full-scene image pairs that cover realistic large-scale scenarios, making it difficult to comprehensively evaluate the performance of matching algorithms in practical remote-sensing settings and constraining advances in the training and generalization of DL models. To address these issues, this study develops and releases OSDataset2.0, a large-scale benchmark dataset for SAR-optical image matching. The dataset comprises two parts: A patch-level subset and a scene-level subset. The patch-level subset is composed of 6,476 registered 512 × 512 image pairs covering 14 countries (Argentina, Australia, Poland, Germany, Russia, France, Qatar, Malaysia, the United States, Japan, Türkiye, Singapore, India, and China); the scene-level subset consists of one pair of full-scene optical and SAR images. For full-scene images, high-precision, uniformly distributed ground-truth correspondences are provided, extracted under the principle of imaging-mechanism consistency, together with a general evaluation codebase that supports quantitative analysis of registration accuracy for arbitrary matching algorithms. To further assess the dataset’s effectiveness and challenge level, a systematic evaluation of 11 representative optical-SAR matching methods on OSDataset2.0 is conducted, covering traditional feature-based approaches and mainstream DL models. Experimental results show that the dataset not only supports effective algorithmic comparisons but also provides reliable training resources and a unified evaluation benchmark for subsequent research. -

-
References
[1] 向俞明, 滕飞, 王林徽, 等. 基于快速异源配准的高分辨率SAR影像海岛区域正射校正[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(4): 866–884. doi: 10.12000/JR24022.XIANG Yuming, TENG Fei, WANG Linhui, et al. Orthorectification of high-resolution SAR images in island regions based on fast multimodal registration[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(4): 866–884. doi: 10.12000/JR24022.[2] YE Yuanxin, ZHANG Jiacheng, ZHOU Liang, et al. Optical and SAR image fusion based on complementary feature decomposition and visual saliency features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5205315. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3366519.[3] HONG Zhonghua, ZHANG Zihao, HU Shangcheng, et al. A robust seamline extraction method for large-scale orthoimages using an adaptive cost A* algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 13322–13347. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2025.3570614.[4] HONG Zhonghua, ZHANG Hongyang, TONG Xiaohua, et al. Rapid fine-grained damage assessment of buildings on a large scale: A case study of the February 2023 earthquake in turkey[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 5204–5220. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3362809.[5] WAN Ling, XIANG Yuming, KANG Wenchao, et al. A self-supervised learning pretraining framework for remote sensing image change detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5630116. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3579416.[6] YOO J C and HAN T H. Fast normalized cross-correlation[J]. Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing, 2009, 28(6): 819–843. doi: 10.1007/s00034-009-9130-7.[7] YE Yuanxin, SHAN Jie, BRUZZONE L, et al. Robust registration of multimodal remote sensing images based on structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(5): 2941–2958. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2656380.[8] DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2005.177.[9] FAN Jianwei, WU Yan, LI Ming, et al. SAR and optical image registration using nonlinear diffusion and phase congruency structural descriptor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(9): 5368–5379. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2815523.[10] XIANG Yuming, TAO Rongshu, WANG Feng, et al. Automatic registration of optical and SAR images via improved phase congruency model[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 5847–5861. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3026162.[11] YE Yuanxin, BRUZZONE L, SHAN Jie, et al. Fast and robust matching for multimodal remote sensing image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(11): 9059–9070. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2924684.[12] YE Yuanxin, ZHU Bai, TANG Tengfeng, et al. A robust multimodal remote sensing image registration method and system using steerable filters with first-and second-order gradients[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2022, 188: 331–350. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2022.04.011.[13] LOWE D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91–110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94.[14] XIANG Yuming, WANG Feng, and YOU Hongjian. OS-SIFT: A robust SIFT-like algorithm for high-resolution optical-to-SAR image registration in suburban areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(6): 3078–3090. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2790483.[15] HOU Zhuolu, LIU Yuxuan, and ZHANG Li. POS-GIFT: A geometric and intensity-invariant feature transformation for multimodal images[J]. Information Fusion, 2024, 102: 102027. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.102027.[16] TOLA E, LEPETIT V, and FUA P. A fast local descriptor for dense matching[C]. 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, USA, 2008: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2008.4587673.[17] LI Jiayuan, HU Qingwu, and ZHANG Yongjun. Multimodal image matching: A scale-invariant algorithm and an open dataset[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2023, 204: 77–88. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.08.010.[18] XIONG Xin, JIN Guowang, WANG Jiajun, et al. Robust multimodal remote sensing image matching based on enhanced oriented self-similarity descriptor[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4010705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3398725.[19] HONG Zhonghua, CHEN Jinyang, TONG Xiaohua, et al. Robust multimodal remote sensing image matching using edge consistency scale-space and significant relative response[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5627022. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3577755.[20] ZHANG Han, LEI Lin, NI Weiping, et al. Explore better network framework for high-resolution optical and SAR image matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4704418. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3126939.[21] DENG Yuxin and MA Jiayi. ReDFeat: Recoupling detection and description for multimodal feature learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2023, 32: 591–602. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3231135.[22] REN Jiangwei, JIANG Xingyu, LI Zizhuo, et al. MINIMA: Modality invariant image matching[C]. 2025 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2025: 23059–23068. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52734.2025.02147.[23] XIANG Yuming, WANG Xuanqi, WANG Feng, et al. A global-to-local algorithm for high-resolution optical and SAR image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5215320. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3309855.[24] HUANG Meiyu, XU Yao, QIAN Lixin, et al. The QXS-SAROPT dataset for deep learning in SAR-optical data fusion[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.08259, 2021. doi: 10.48550/ARXIV.2103.08259.[25] CHEN Hongruixuan, SONG Jian, DIETRICH O, et al. BRIGHT: A globally distributed multimodal building damage assessment dataset with very-high-resolution for all-weather disaster response[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.06019, 2025. doi: 10.48550/ARXIV.2501.06019.[26] ZHANG Wenfei, ZHAO Ruipeng, YAO Yongxiang, et al. Multi-resolution SAR and optical remote sensing image registration methods: A review, datasets, and future perspectives[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.01002, 2025. doi: 10.48550/ARXIV.2502.01002.[27] WU Yue, MA Wenping, GONG Maoguo, et al. A novel point-matching algorithm based on fast sample consensus for image registration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(1): 43–47. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2325970.[28] POTJE G, CADAR F, ARAUJO A, et al. XFeat: Accelerated features for lightweight image matching[C]. 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2024: 2682–2691. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.00259.[29] FISCHLER M A and BOLLES R C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1981, 24(6): 381–395. doi: 10.1145/358669.358692. -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. SAR-optical image pairs of the same object
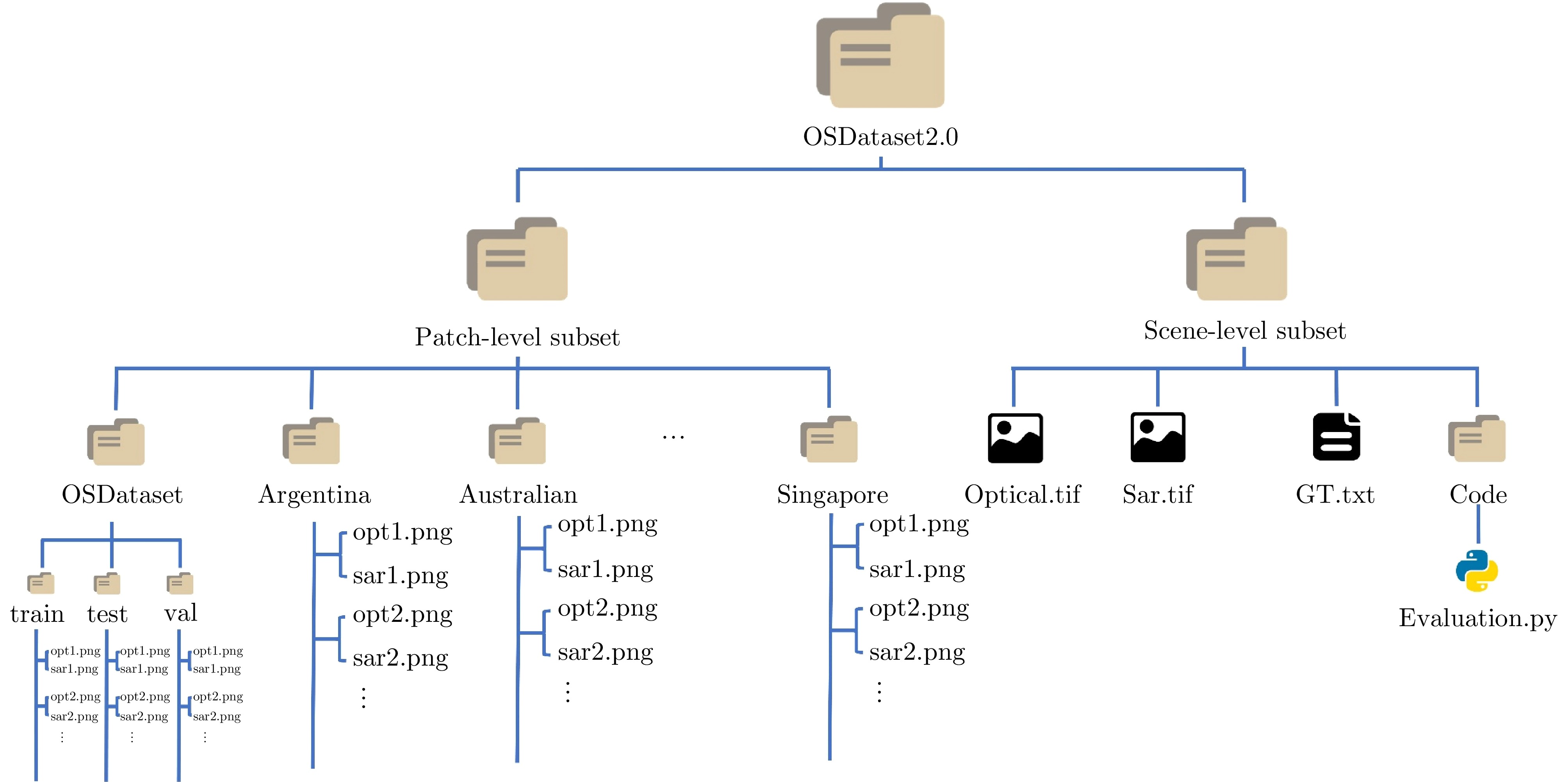
- Figure 2. Structure of OSDataset2.0
- Figure 3. Partial data display from OSDataset2.0
- Figure 4. Patch-level subset construction flowchart
- Figure 5. Streetlight poles exhibiting cross-shaped strong scatter responses in SAR images
- Figure 6. SR of different methods at different th on the patch-level subset
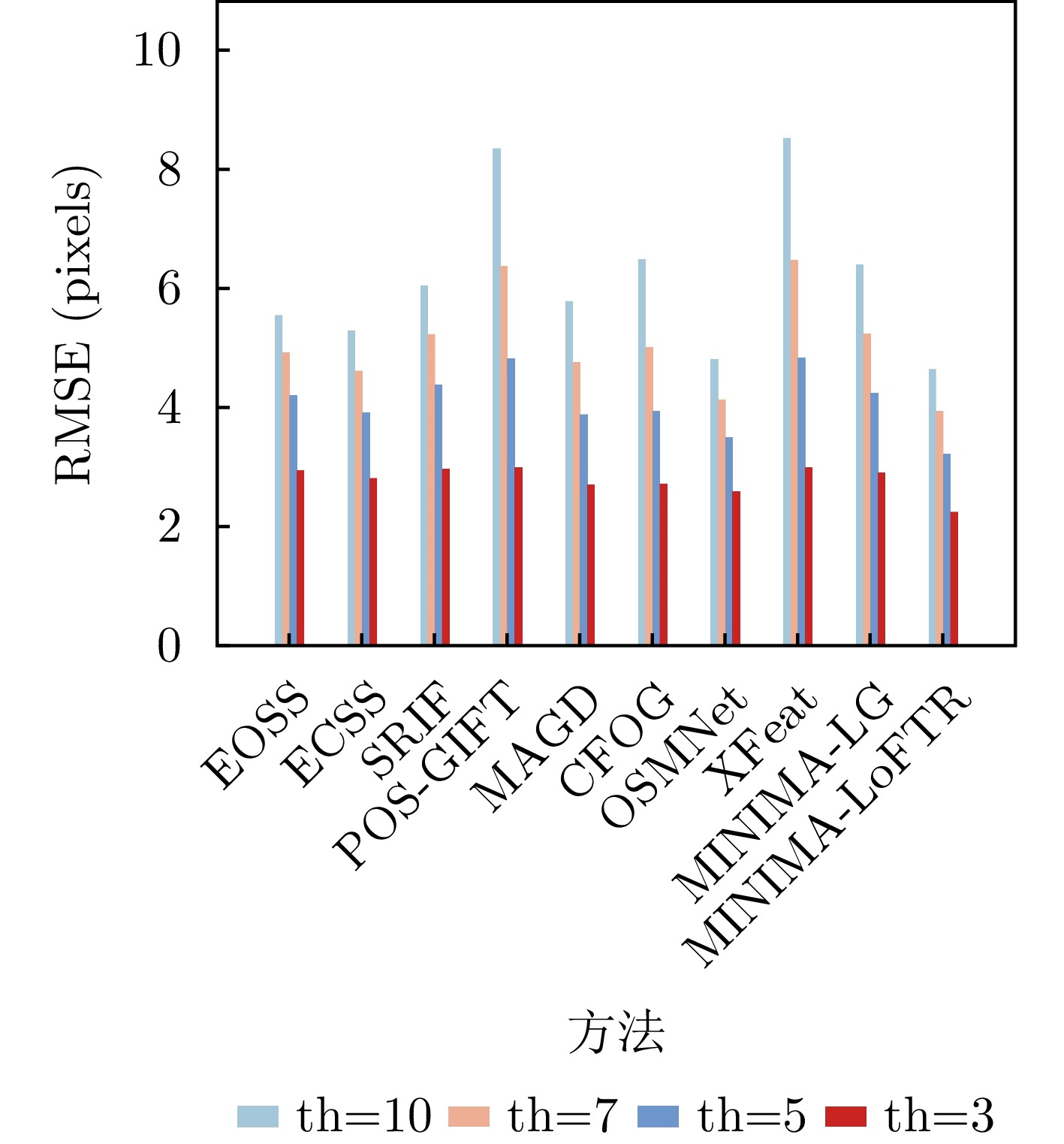
- Figure 7. RMSE of different methods at different th on the patch-level subset
- Figure 8. NCM of different methods at different th on the patch-level subset
- Figure 9. Boxplots evaluating 11 methods using ground truth points
- Figure 10. Release webpage of OSDataset2.0


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: