- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2025
> Online First
| Citation: | LIU Qi, GUO Rui, WANG Jiajia, et al. A high-accuracy beamspace DOA estimation method for low-elevation angle targets[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25173 |
A High-accuracy Beamspace DOA Estimation Method for Low-elevation Angle Targets
DOI: 10.12000/JR25173 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25173
More Information-
Abstract
Direction of Arrival (DOA) estimation for low-elevation angle targets is a critical challenge in meter-wave and holographic staring radar systems, as its accuracy directly affects target height measurement performance. Traditional beamspace methods reduce computational complexity by projecting high-dimensional element-space data onto a low-dimensional beamspace using a beamformer. However, this lossy mapping leads to partial information loss, resulting in degraded elevation-angle estimation accuracy compared to that of element-space methods. To address this issue, this study proposes a high-accuracy beamspace DOA estimation method for low-elevation angle targets. First, the Cramér-Rao Bound (CRB) for both element-space and beamspace DOA estimation is derived, and the conditions under which these bounds are equal are analyzed. Since these conditions are difficult to satisfy in practical scenarios, an approximate-condition-based beamformer design strategy is developed to reduce data dimensionality while preserving effective target information. Finally, precise elevation-angle estimation is achieved using the maximum likelihood criterion. Simulation and experimental results show that the proposed method significantly reduces data dimensionality while maintaining estimation accuracy comparable to that of element-space methods at low-elevation angles, clearly outperforming existing beamspace algorithms. -

-
References
[1] 郭瑞, 张月, 田彪, 等. 全息凝视雷达系统技术与发展应用综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 389–411. doi: 10.12000/JR22153.GUO Rui, ZHANG Yue, TIAN Biao, et al. Review of the technology, development and applications of holographic staring radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 389–411. doi: 10.12000/JR22153.[2] LAN Lan, ROSAMILIA M, AUBRY A, et al. Adaptive target detection and DOA estimation with uniform rectangular arrays in the presence of unknown mutual coupling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Radar Systems, 2023, 1: 325–338. doi: 10.1109/TRS.2023.3289991.[3] WEN Fangqing, WANG Han, GUI Guan, et al. Polarized intelligent reflecting surface aided 2D-DOA estimation for NLoS sources[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(7): 8085–8098. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2023.3348520.[4] YU Canping, LI Yingsong, LI Liping, et al. Dual Lawson norm-based robust DOA estimation for RIS-Aided wireless communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(1): 582–592. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3446752.[5] WAN Liangtian, SUN Yuchen, SUN Lu, et al. Deep learning based autonomous vehicle super resolution DOA estimation for safety driving[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(7): 4301–4315. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.3009223.[6] XU He, LIU Wei, JIN Ming, et al. Positioning and contour extraction of autonomous vehicles based on enhanced DOA estimation by large-scale arrays[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(13): 11792–11803. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3244861.[7] 马健钧, 魏少鹏, 马晖, 等. 基于ADMM的低仰角目标二维DOA估计算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(8): 2859–2866. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210582.MA Jianjun, WEI Shaopeng, MA Hui, et al. Two-dimensional DOA estimation for low-angle target based on ADMM[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(8): 2859–2866. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210582.[8] LIU Qi, GUO Rui, WANG Jiajia, et al. Signal-level fusion-based height estimation of low-elevation target for distributed radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2025, 74: 6508114. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2025.3593573.[9] CHEN Sheng, ZHAO Yongbo, HU Yili, et al. A beamspace maximum likelihood algorithm for target height estimation for a bistatic MIMO radar[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2022, 122: 103330. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2021.103330.[10] ZHENG Guimei, CHEN Chen, and SONG Yuwei. Height measurement for meter wave MIMO radar based on matrix pencil under complex terrain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(9): 11844–11854. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3268791.[11] TANG Derui, ZHAO Yongbo, NIU Ben, et al. Bistatic MIMO radar height estimation method based on adaptive beam-space RML data fusion[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2024, 145: 104346. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2023.104346.[12] LIU Qi, GUO Rui, WANG Bo, et al. Direct altitude estimation of low-elevation target for bistatic holographic staring radar based on coprime array[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(11): 17926–17940. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3387534.[13] 刘源. 米波阵列雷达低仰角目标测高方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2018: 1–146.LIU Yuan. Research on some issues of low-angle target height measurement for VHF array radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2018: 1–146.[14] 谭俊. 米波雷达低仰角测角中多径效应影响抑制及关键技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2019: 1–130.TAN Jun. Research on multipath effect suppression and key technologies in low-angle measurement of meter wave radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019: 1–130.[15] 王鸿帧, 郑桂妹, 陈晨, 等. 米波雷达低仰角估计技术分析与展望[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2023, 48(11): 6–16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2023.11.002.WANG Hongzhen, ZHENG Guimei, CHEN Chen, et al. Analysis and prospect of low elevation estimation technology for meter wave radar[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2023, 48(11): 6–16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2023.11.002.[16] GUO Rui, ZHANG Yue, TIAN Biao, et al. Height measurement of Micro-UAVs with L-Band staring radar[C]. 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 7967–7970. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS47720.2021.9553143.[17] MA Jianjun, LIU Hongwei, and MA Hui. Low-elevation target DOA estimation based on multi-scattering center equivalent model[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(15): 3533. doi: 10.3390/rs14153533.[18] CHEN Sheng, ZHAO Yongbo, and HU Yili. Beamspace phase solving algorithm for elevation angle estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022, 29: 742–746. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2022.3154686.[19] XIANG Houhong, CHEN Baixiao, YANG Ting, et al. Improved de-multipath neural network models with self-paced feature-to-feature learning for DOA estimation in multipath environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(5): 5068–5078. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2977894.[20] LIU Wei, HAARDT M, GRECO M S, et al. Twenty-five years of sensor array and multichannel signal processing: A review of progress to date and potential research directions[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2023, 40(4): 80–91. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2023.3258060.[21] SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830.[22] PILLAI S U and KWON B H. Forward/backward spatial smoothing techniques for coherent signal identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(1): 8–15. doi: 10.1109/29.17496.[23] ZOLTOWSKI M and HABER F. A vector space approach to direction finding in a coherent multipath environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(9): 1069–1079. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143956.[24] LIU Yuan, LIU Hongwei, XIA Xianggen, et al. Projection techniques for altitude estimation over complex multipath condition-based VHF radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(7): 2362–2375. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2835448.[25] ZISKIND I and WAX M. Maximum likelihood localization of multiple sources by alternating projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1988, 36(10): 1553–1560. doi: 10.1109/29.7543.[26] LO T and LITVA J. Use of a highly deterministic multipath signal model in low-angle tracking[J]. IEE Proceedings F-Radar and Signal Processing, 1991, 138(2): 163–171. doi: 10.1049/Ip-f-2.1991.0022.[27] LIU Yuan, JIU Bo, XIA Xianggen, et al. Height measurement of low-angle target using MIMO radar under multipath interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(2): 808–818. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2767919.[28] MA Jianjun, MA Hui, LIU Hongwei, et al. A novel DOA estimation for low-elevation target method based on multiscattering center equivalent model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 3501605. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3242977.[29] WU Jianqi, ZHU Wei, and CHEN Baixiao. Compressed sensing techniques for altitude estimation in multipath conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(3): 1891–1900. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.130841.[30] GUO Rui, PENG Xiangyu, and TIAN Biao. Low elevation target altitude measurement for ubiquitous radar based on known transmitted waveform and sparse representation[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2022, 16(2): 346–355. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12187.[31] LIU Yuan, LIU Hongwei, WANG Lu, et al. Target localization in high-coherence multipath environment based on low-rank decomposition and sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(9): 6197–6209. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2975218.[32] LIU Yuan, LIU Hongwei, JIU Bo, et al. Altitude measurement of low-angle target under complex terrain environment for meter-wave radar[C]. The 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, Canada, 2018: 3464–3468. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2018.8462623.[33] ZOLTOWSKI M D and LEE T S. Maximum likelihood based sensor array signal processing in the beamspace domain for low angle radar tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1991, 39(3): 656–671. doi: 10.1109/78.80885.[34] CHEN Sheng, ZHAO Yongbo, HU Yili, et al. Beamspace maximum likelihood algorithm based on sum and difference beams for elevation estimation[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 35(3): 589–598. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2024.000057.[35] WEISS A J and FRIEDLANDER B. On the Cramer-Rao bound for direction finding of correlated signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1993, 41(1): 495. doi: 10.1109/TSP.1993.193187. -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. Geometric model of low-elevation target multipath propagation
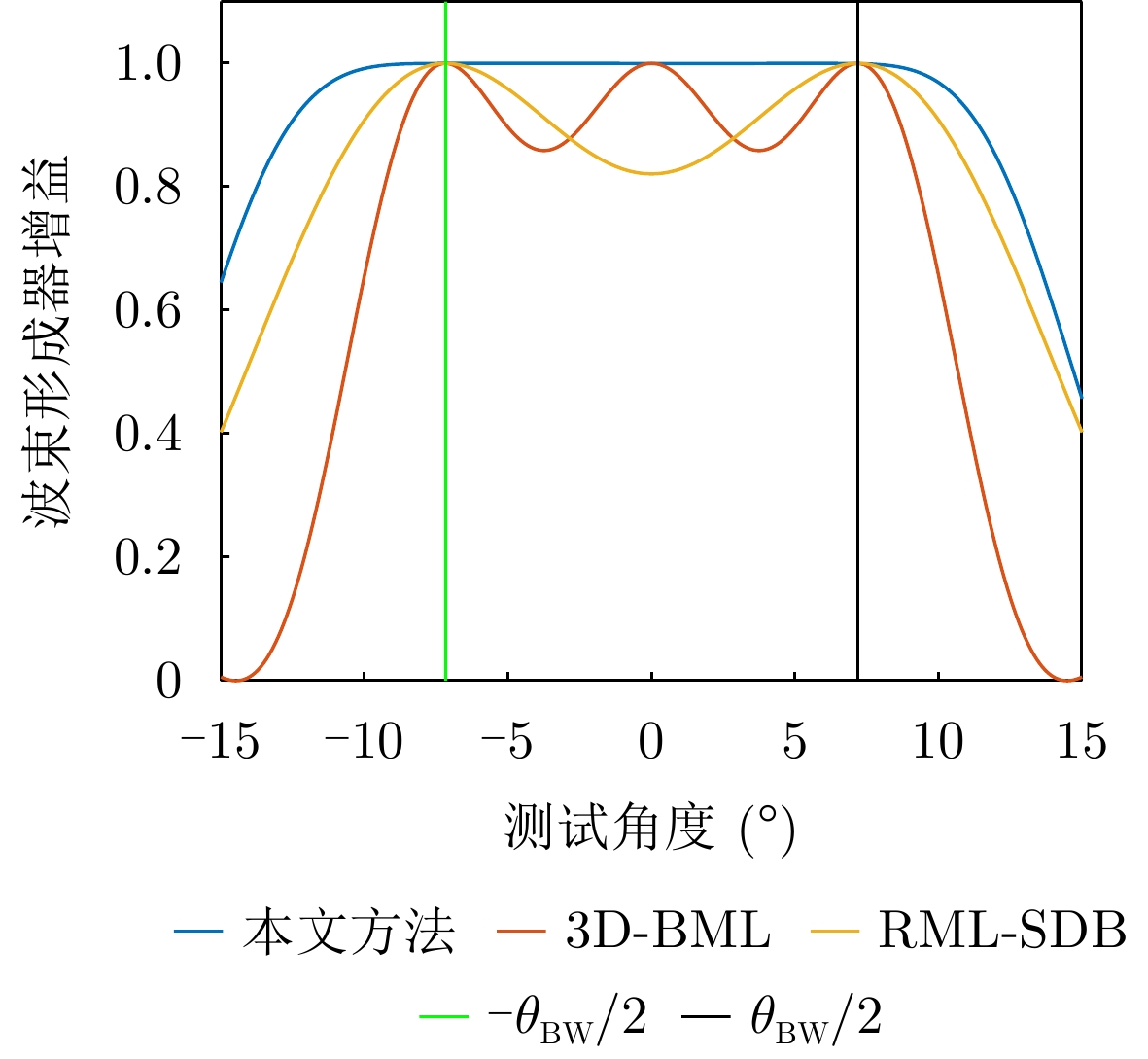
- Figure 2. Beamformer gain versus test angle for different algorithms
- Figure 3. RMSE of target elevation angle estimation versus target elevation angle
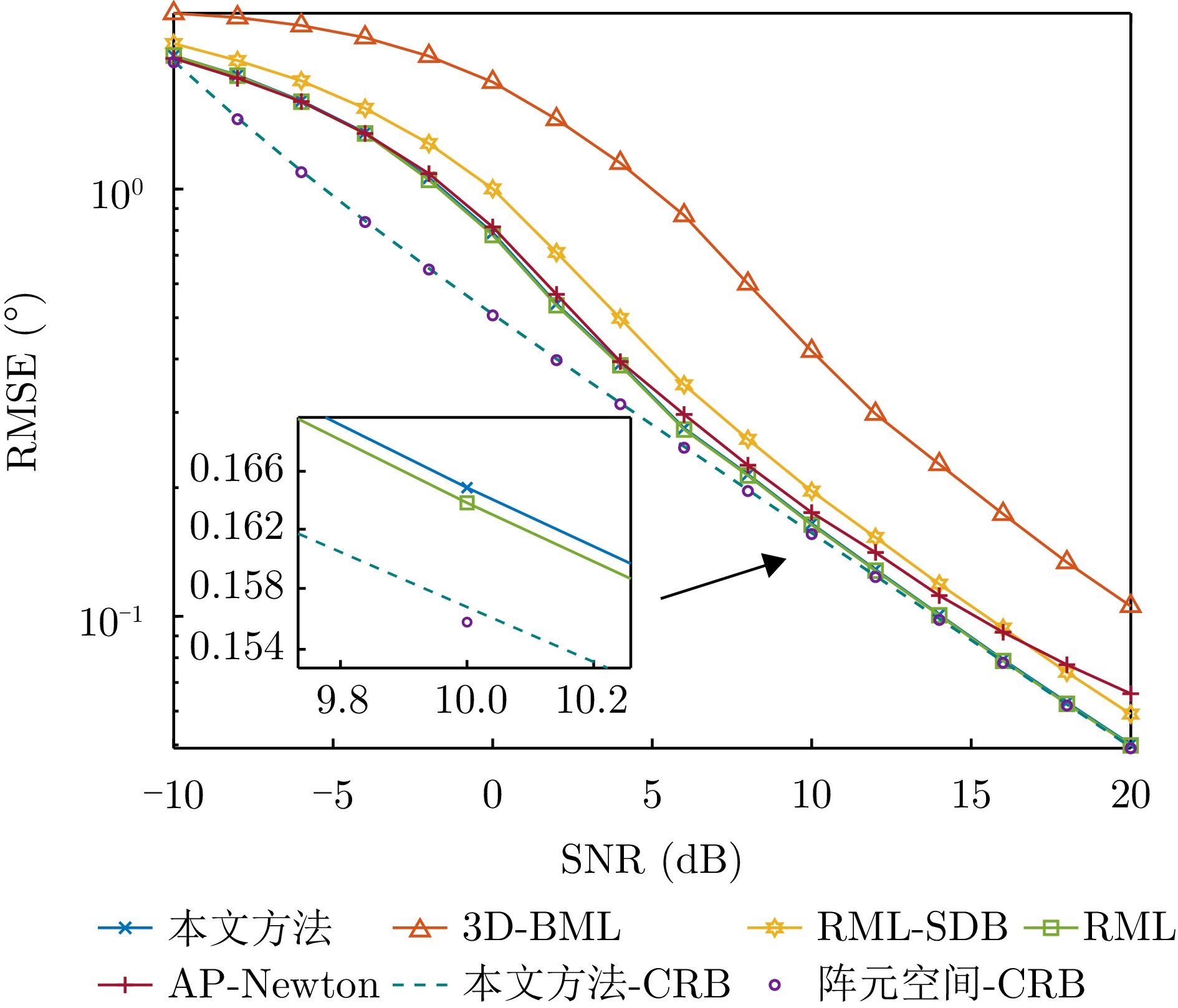
- Figure 4. RMSE of target elevation angle estimation versus SNR
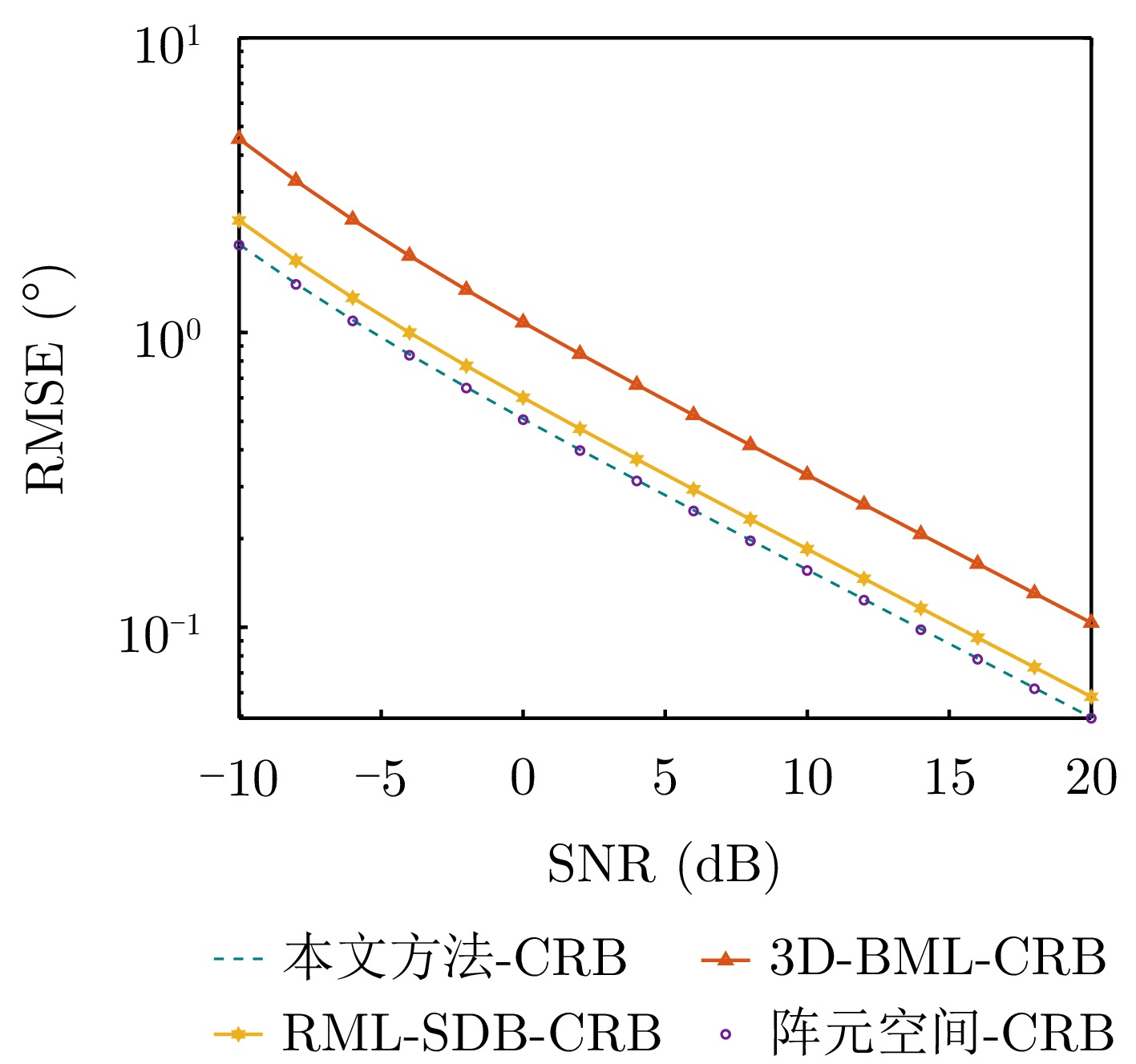
- Figure 5. CRB of target elevation angle estimation versus SNR for different algorithms
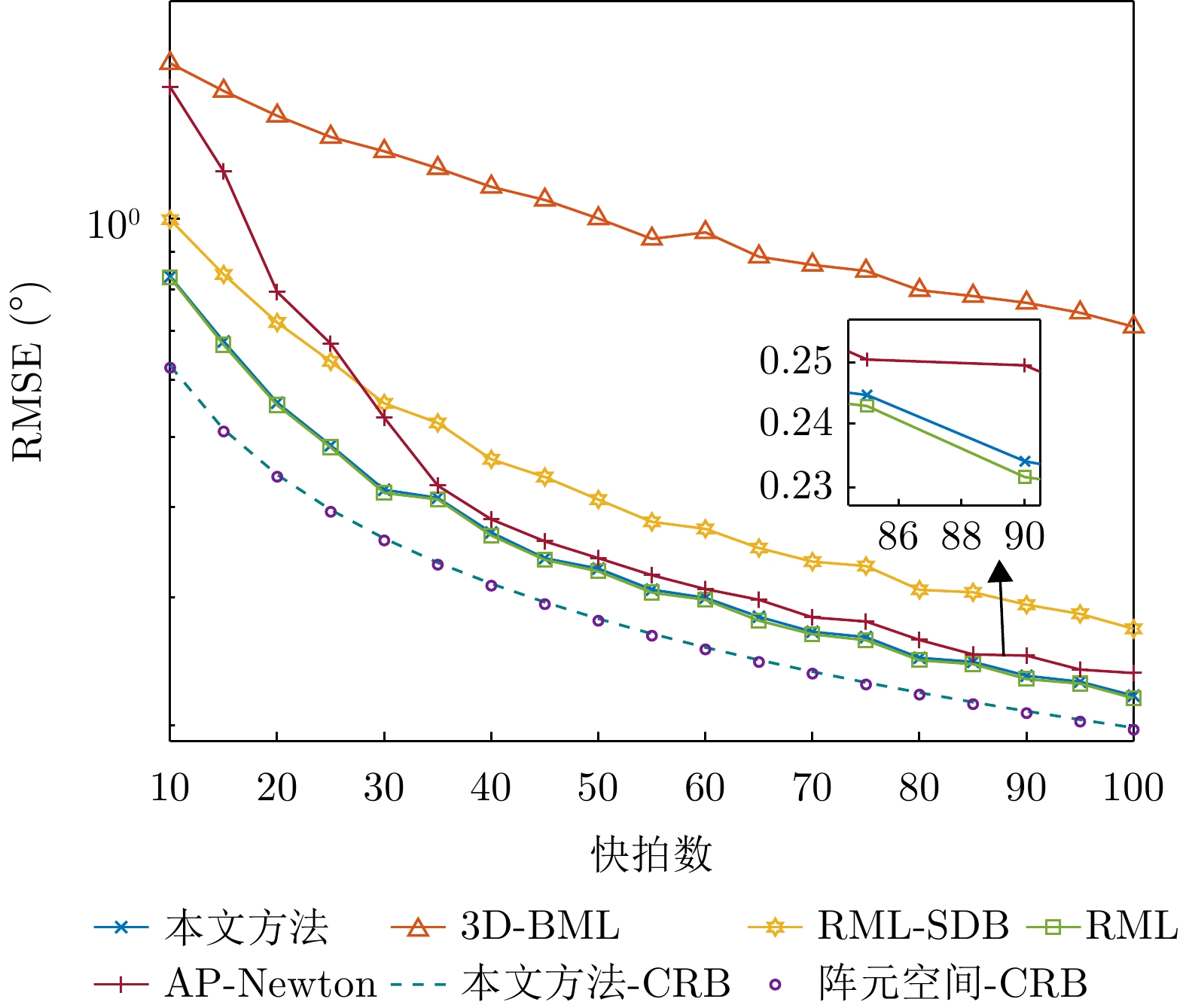
- Figure 6. RMSE of target elevation angle estimation versus number of snapshots
-
Figure 7. RMSE of target elevation angle estimation versus target elevation angle for different
$ \gamma $ -
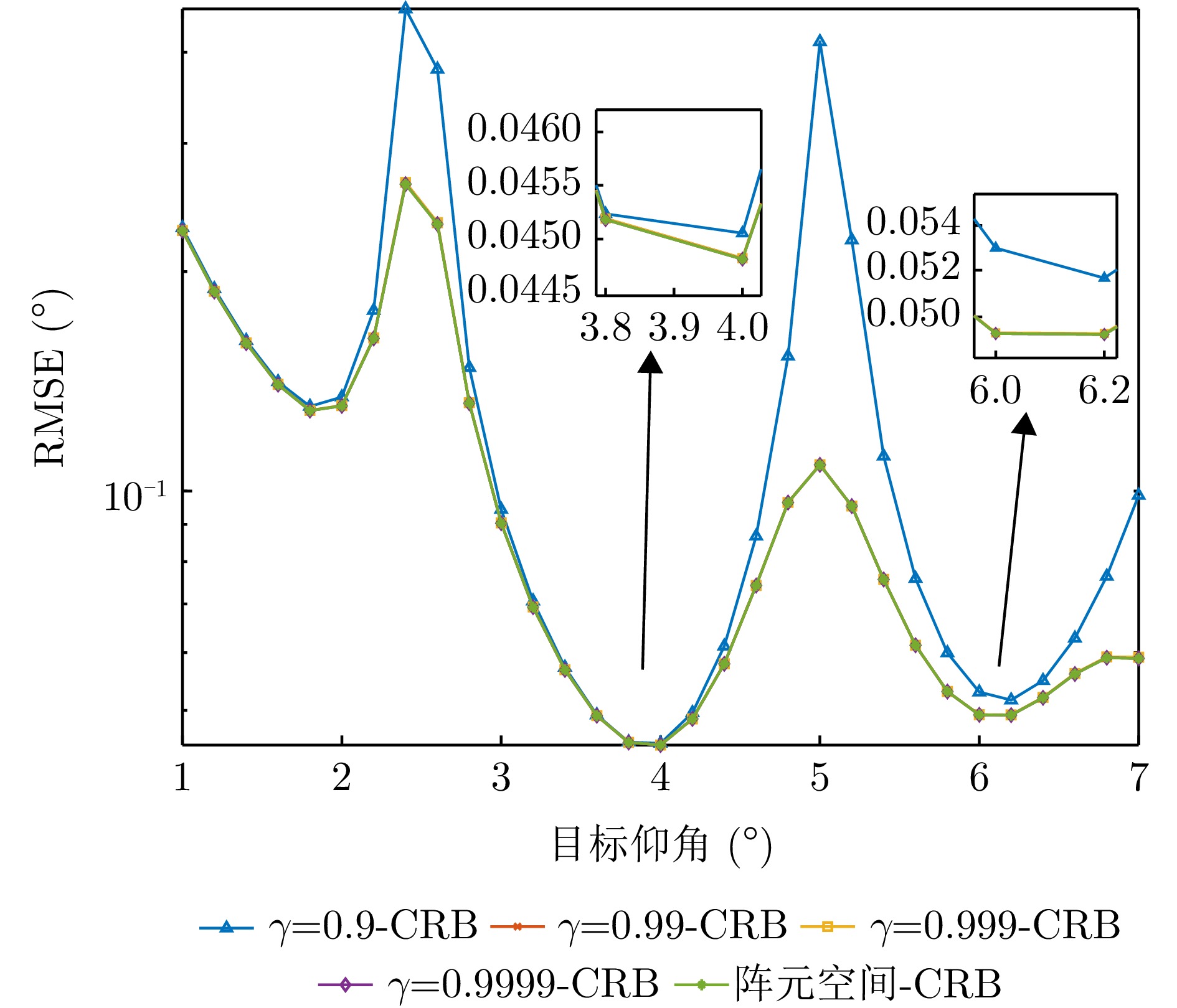
Figure 8. CRB of target elevation angle estimation versus target elevation angle for different
$ \gamma $ -
Figure 9. RMSE of target elevation angle estimation versus
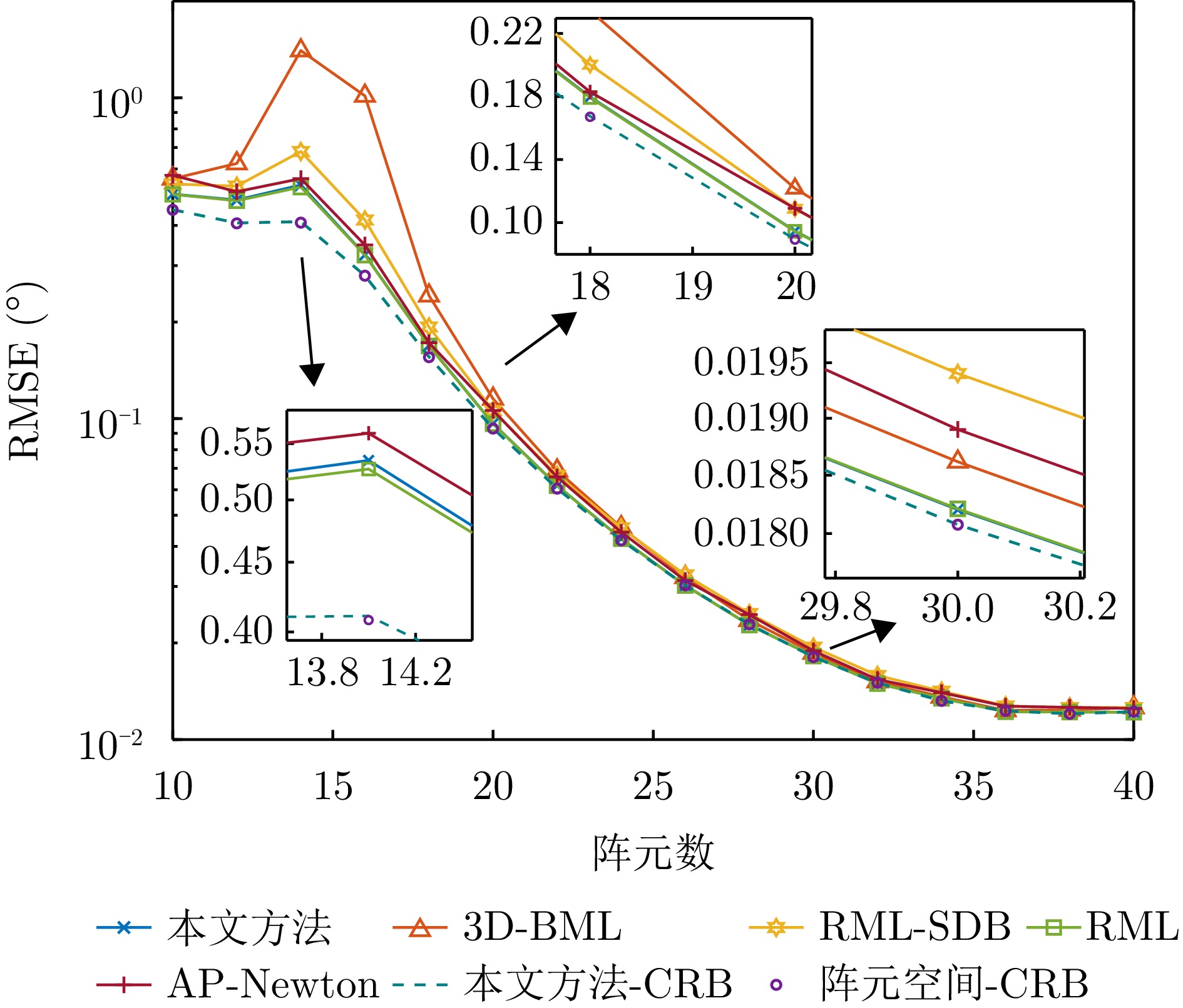
$ \left| \rho \right| $ - Figure 10. RMSE of target elevation angle estimation versus number of array elements
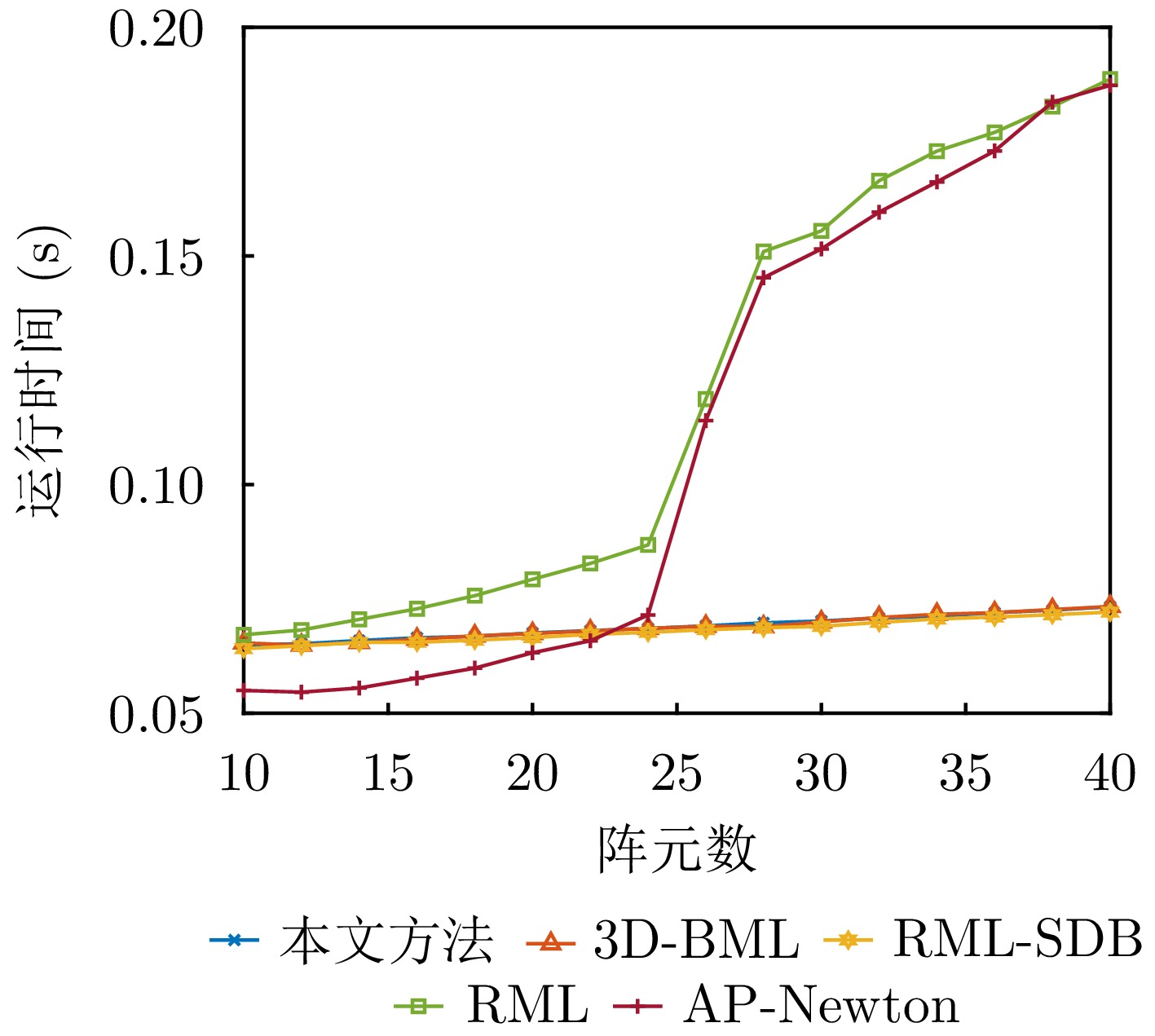
- Figure 11. Average runtime versus number of array elements for different algorithms
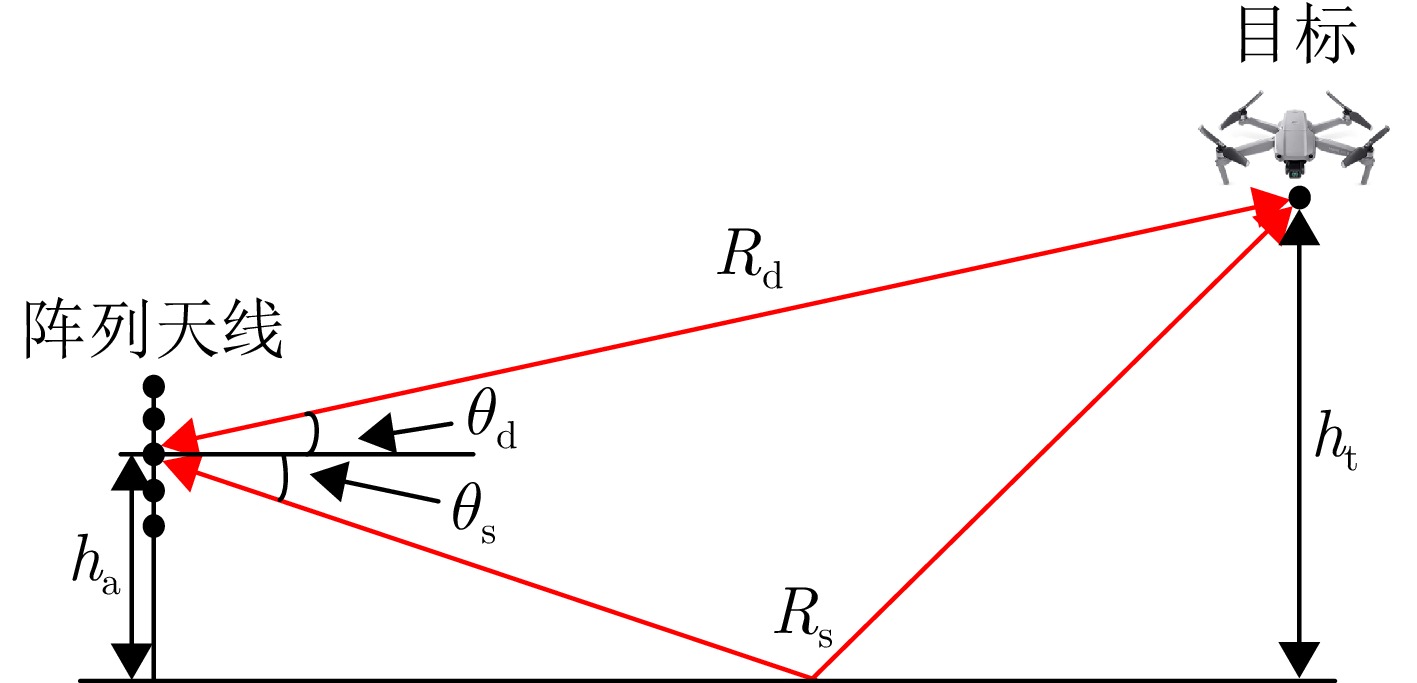
- Figure 12. Experimental scene
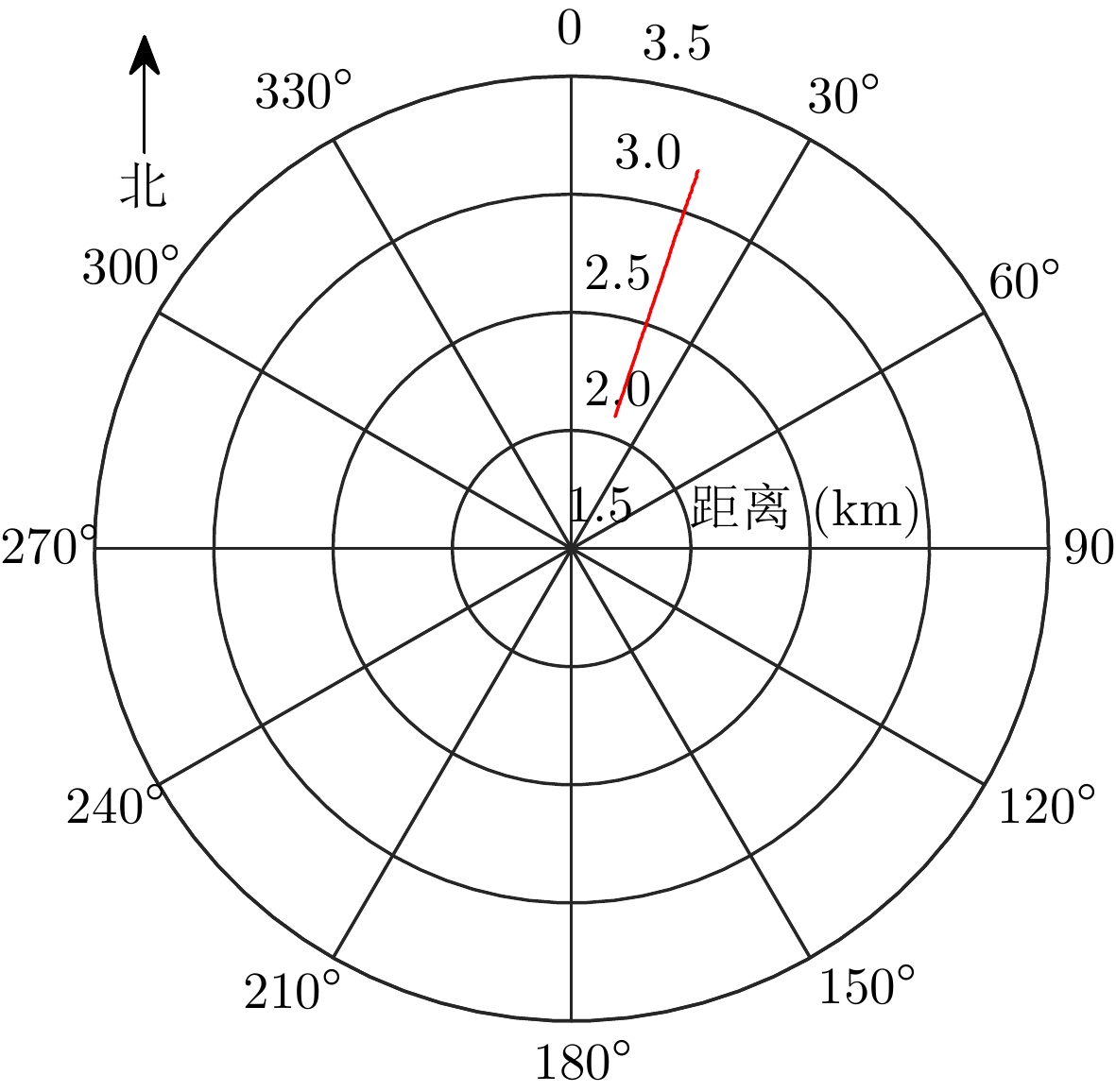
- Figure 13. Schematic diagram of the UAV flight trajectory
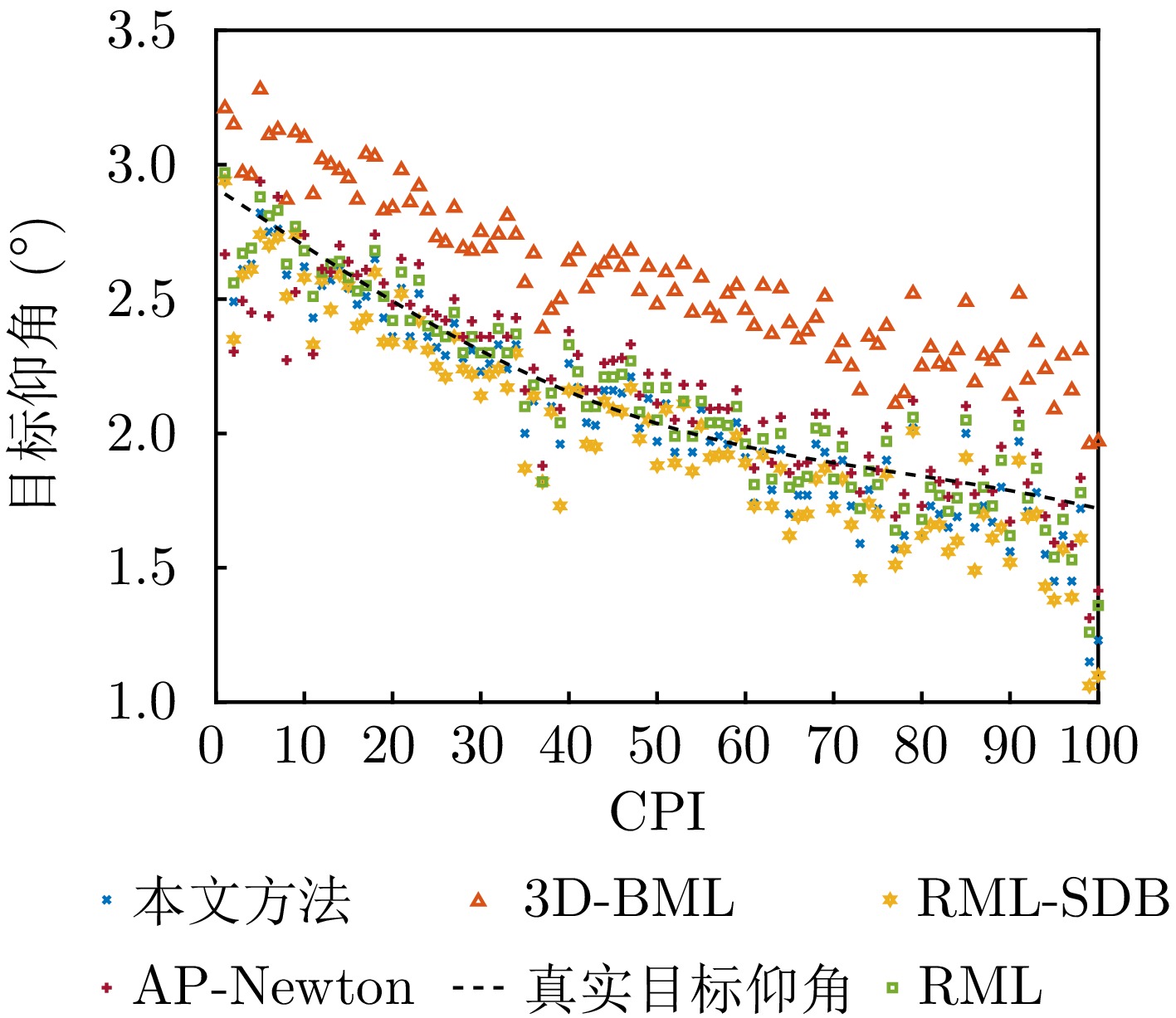
- Figure 14. Estimation results of target elevation angle using different algorithms
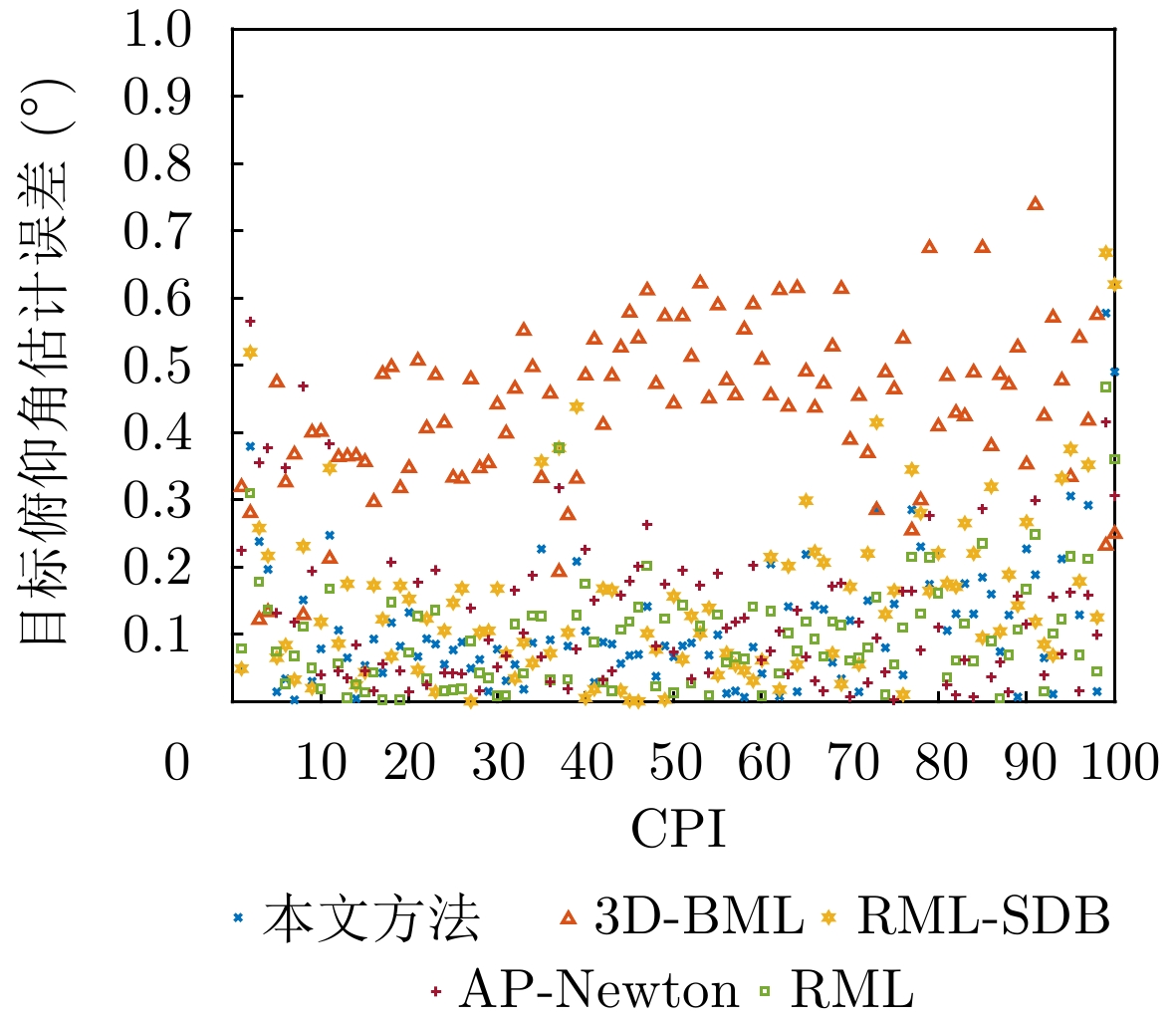
- Figure 15. Estimation errors of target elevation angle using different algorithms


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: