- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2025
> Online First
| Citation: | ZHANG Shunsheng, CAI Zihan, and LIU Yongxu. Synthetic aperture passive localization of a single-satellite multi-radar emitter via time-frequency parameter estimation[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25165 |
Synthetic Aperture Passive Localization of a Single-satellite Multi-radar Emitter via Time-frequency Parameter Estimation
DOI: 10.12000/JR25165 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25165
More Information-
Abstract
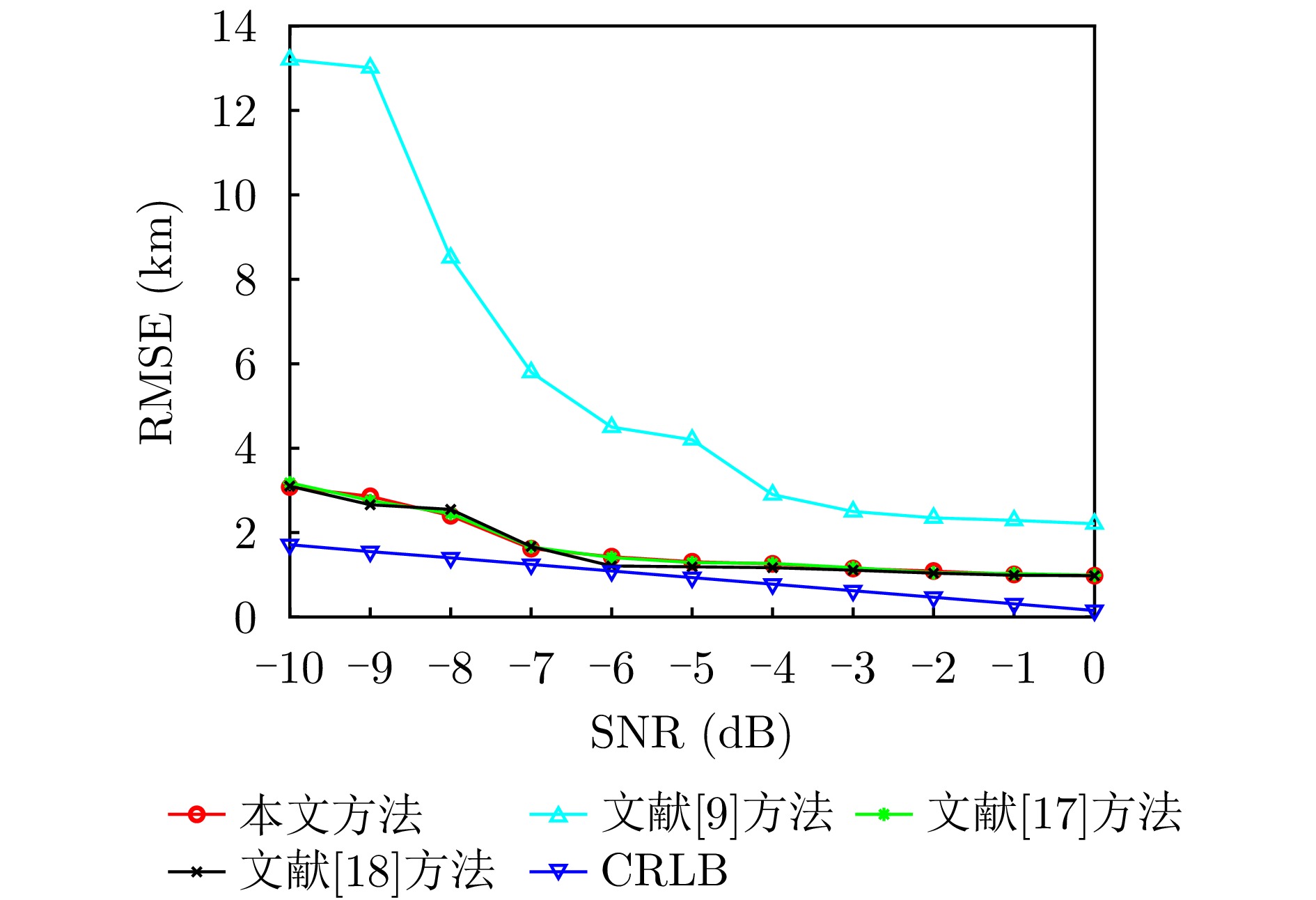
Passive localization methods based on synthetic aperture imaging offer high positioning accuracy. However, in scenarios involving multiple radar emitters transmitting Linear Frequency-Modulated (LFM) signals, distinguishing signals that are overlapped in the time and frequency domains can be challenging. This phenomenon, known as phase overlap, results in a significant degradation of localization performance. To address this issue, the present paper proposes a single-satellite multi-radar-emitter passive localization method based on synthetic aperture imaging using time-frequency parameter estimation. First, a signal model for multiple radar emitters transmitting LFM signals is constructed. The time-frequency parameters of the multiple radar emitter signals are estimated concurrently via a combination of Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) and DBSCAN. A rapid approximation of the azimuth chirp rate is attained through a coarse-to-fine search strategy founded upon the use of the STFT. The accurate localization of multiple radar emitters is ultimately realized through the implementation of two-dimensional focusing in the range and azimuth dimensions. The Cramer-Rao lower bound of the proposed method is derived on this basis. The experimental findings demonstrate that the proposed method enhances the localization accuracy by approximately 10 km at a signal-to-noise ratio of −10 dB, in comparison with the enhanced real-valued space-time subspace data fusion-based direct positioning method. Moreover, it reduces the computational time by half relative to the CLEAN-based synthetic aperture multi-source localization approach. -

-
References
[1] 马振洋, 周中华, 张帆, 等. 北斗三号仅用作追踪的机载设备适航要求分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(4): 1162–1175. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0452.MA Zhenyang, ZHOU Zhonghua, ZHANG Fan, et al. Analysis of airworthiness requirements of Beidou-3 airborne equipment only used for tracking[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(4): 1162–1175. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0452.[2] 刘清, 谢坚, 王伶, 等. 卫星导航欺骗式干扰源高精度直接定位方法[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(5): 1117–1122. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210527.LIU Qing, XIE Jian, WANG Ling, et al. High precision direct position determination method for satellite navigation spoofing[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(5): 1117–1122. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210527.[3] ZHU Yifan and ZHANG Shunsheng.Passive location based on an accurate Doppler measurement by single satellite[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Seattle, USA, 2017: 1424–1427. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944430.[4] ELLIS P, VAN RHEEDEN D, and DOWLA F. Use of Doppler and Doppler rate for RF geolocation using a single LEO satellite[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 12907–12920. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2965931.[5] 严航, 姚山峰. 低轨单星测频定位技术及其精度分析[J]. 计算机工程, 2012, 38(18): 6–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2012.18.002.YAN Hang and YAO Shanfeng. Localization technology of frequency measurement for single low earth orbit satellite and its precision analysis[J]. Computer Engineering, 2012, 38(18): 6–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2012.18.002.[6] 吴顺华, 辛勤, 万建伟. 一种单星对星仅测角无源定轨跟踪方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2009, 21(12): 3701–3704.WU Shunhua, XIN Qin, and WAN Jianwei. Novel satellite-to-satellite passive orbit determination and tracking method with bearing-only measurements[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2009, 21(12): 3701–3704.[7] 李腾, 郭福成, 姜文利. 星载干涉仪无源定位新方法及其误差分析[J]. 国防科技大学学报, 2012, 34(3): 164–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2012.03.032.LI Teng, GUO Fucheng, and JIANG Wenli. A novel method for satellite-borne passive localization using interferometer and its error analysis[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2012, 34(3): 164–170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2012.03.032.[8] AMAR A and WEISS A J. Direct position determination of multiple radio signals[C]. 2004 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Montreal, Canada, 2004: ii–81. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2004.1326199.[9] 招乾民, 张顺生. 改进实值空时子空间数据融合的单星直接定位方法[J]. 信号处理, 2024, 40(6): 1111–1121. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.06.011.ZHAO Qianmin and ZHANG Shunsheng. Improved single-satellite direct position determination method via real-valued space-time subspace data fusion[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2024, 40(6): 1111–1121. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2024.06.011.[10] 黄凯, 尤明懿, 陆安南, 等. 星载测向系统的测向误差及其定位误差计算方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2024, 45(9): 1488–1497. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2024.09.014.HUANG Kai, YOU Mingyi, LU Annan, et al. A calculation method of direction-finding errors and localization errors by a single satellite[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2024, 45(9): 1488–1497. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2024.09.014.[11] WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, XIANG Jixiang, et al. A imaging passive localization method for wideband signal based on SAR[C]. 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Xiamen, China, 2019: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/APSAR46974.2019.9048398.[12] 张莉婷, 郇浩, 陶然. 基于被动合成孔径的单星无源高精度定位方法[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2020, 36(6): 43–48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2020.06.010.ZHANG Liting, HUAN Hao, and TAO Ran. Highprecision emitter localization based on spaceborne passive synthetic aperture[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2020, 36(6): 43–48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2020.06.010.[13] WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, et al. Long synthetic aperture passive localization using azimuth chirp-rate contour map[C]. IGARSS 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, USA, 2020: 928–931. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS39084.2020.9323154.[14] 王裕旗, 孙光才, 杨军, 等. 基于长合成孔径的辐射源成像定位算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 185–194. doi: 10.12000/JR19080.WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, YANG Jun, et al. Passive localization algorithm for radiation source based on long synthetic aperture[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 185–194. doi: 10.12000/JR19080.[15] CHEN Bowei, WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, et al. A long synthetic aperture passive localization method using two planes[C]. 2021 CIE International Conference on Radar (Radar), Haikou, China, 2021: 767–769. doi: 10.1109/Radar53847.2021.10028522.[16] WANG Yuqi, SUN Guangcai, WANG Yong, et al. A high-resolution and high-precision passive positioning system based on synthetic aperture technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5230613. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3186767.[17] WANG Yuqi, DONG Wenlong, SUN Guangcai, et al. A CLEAN-based synthetic aperture passive localization algorithm for multiple signal sources[J]. IEEE Journal on Miniaturization for Air and Space Systems, 2022, 3(4): 294–301. doi: 10.1109/JMASS.2022.3215982.[18] ZHANG Liting, HUAN Hao, RAN Tao, et al. A spaceborne passive localization algorithm based on MSD-HOUGH for multiple signal sources[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(22): 4303. doi: 10.3390/rs16224303.[19] ZHONG Qi, HE Zhiyi, and WEI Shaoren. Interrupted sampling repeater jamming recognition and suppression method based on DBSCAN algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12: 62597–62608. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3395537.[20] 李杨寰, 初翠强, 徐晖, 等. 一种新的脉冲重复频率估计方法[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2007, 22(2): 18–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2007.02.005.LI Yanghuan, CHU Cuiqiang, XU Hui, et al. A novel algorithm for estimating pulse repetition frequency[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2007, 22(2): 18–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2007.02.005. -
Proportional views

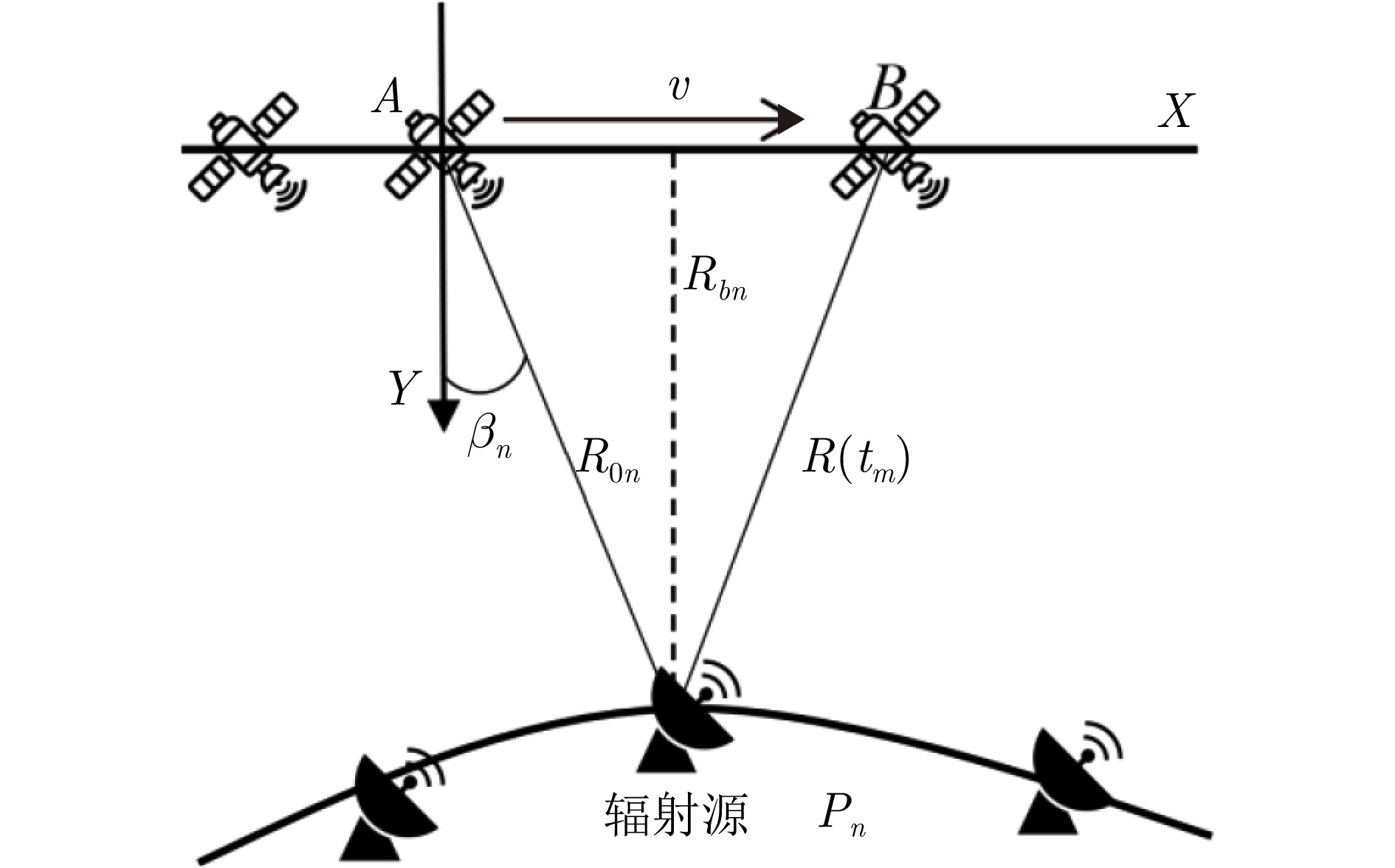
- Figure 1. Single-satellite passive localization scenario based on synthetic aperture
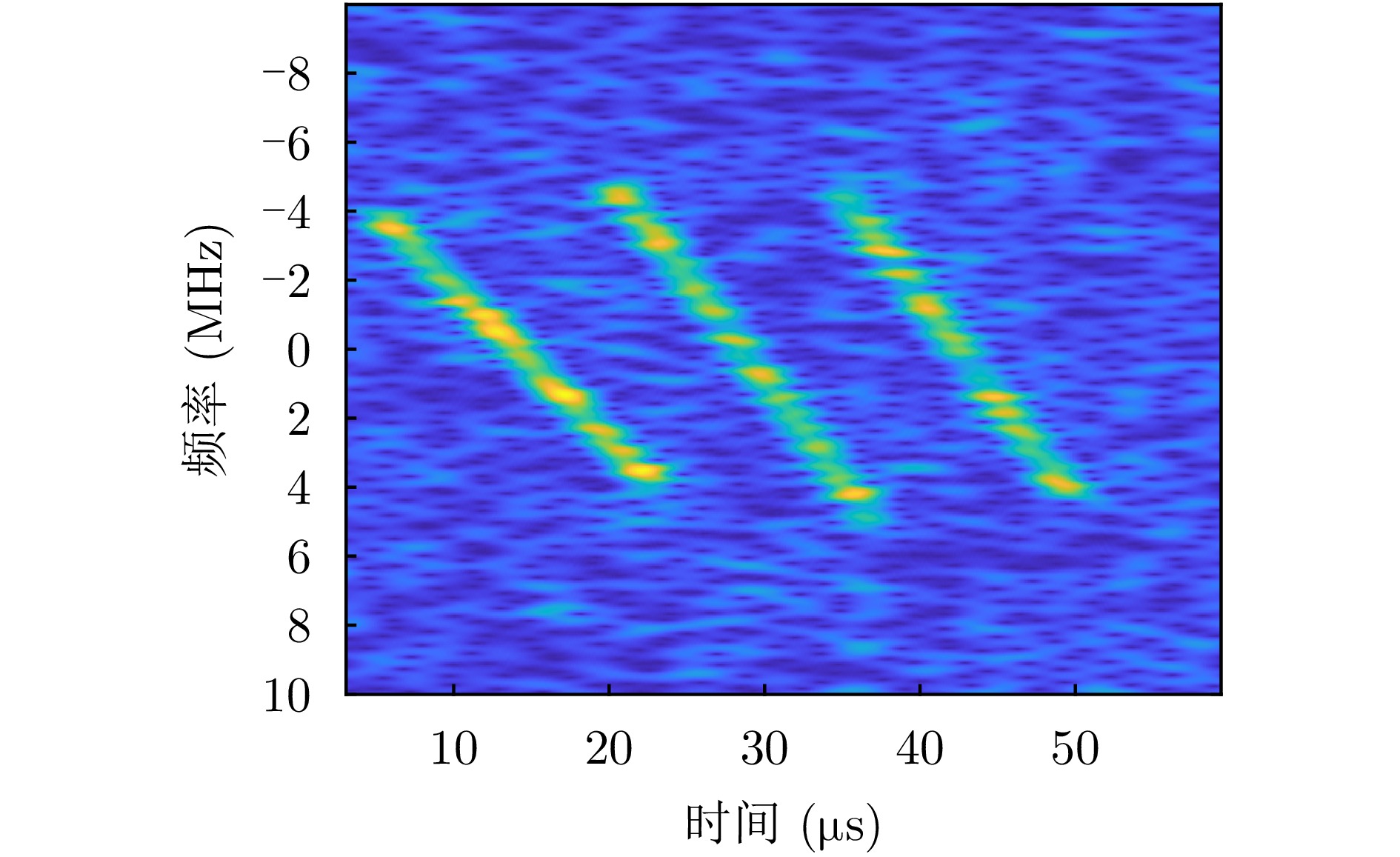
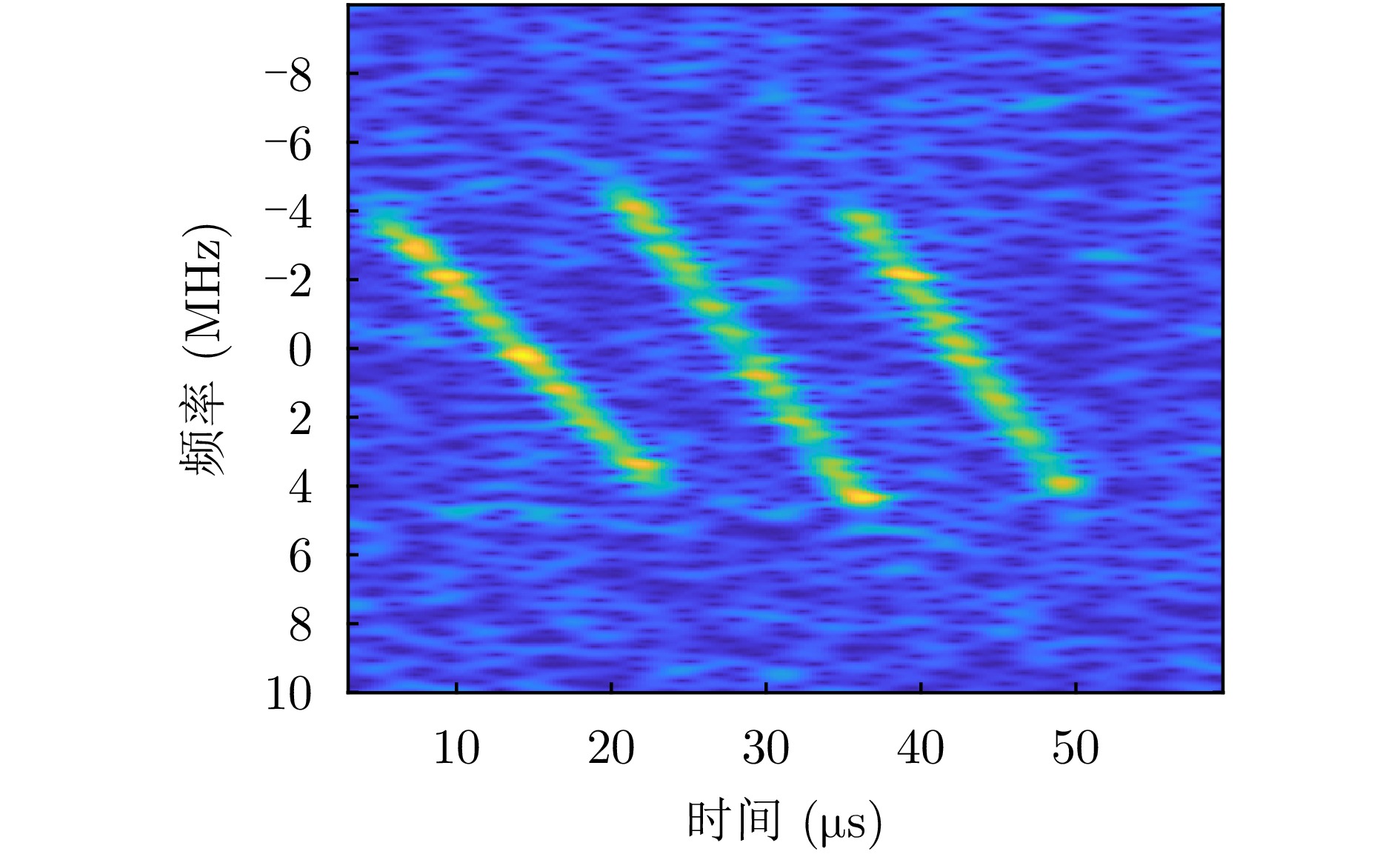
- Figure 2. Time-frequency distribution of multiple LFM signals
- Figure 3. Edge extraction
- Figure 4. The proposed synthetic aperture-based passive localization workflow for multi-radar emitters
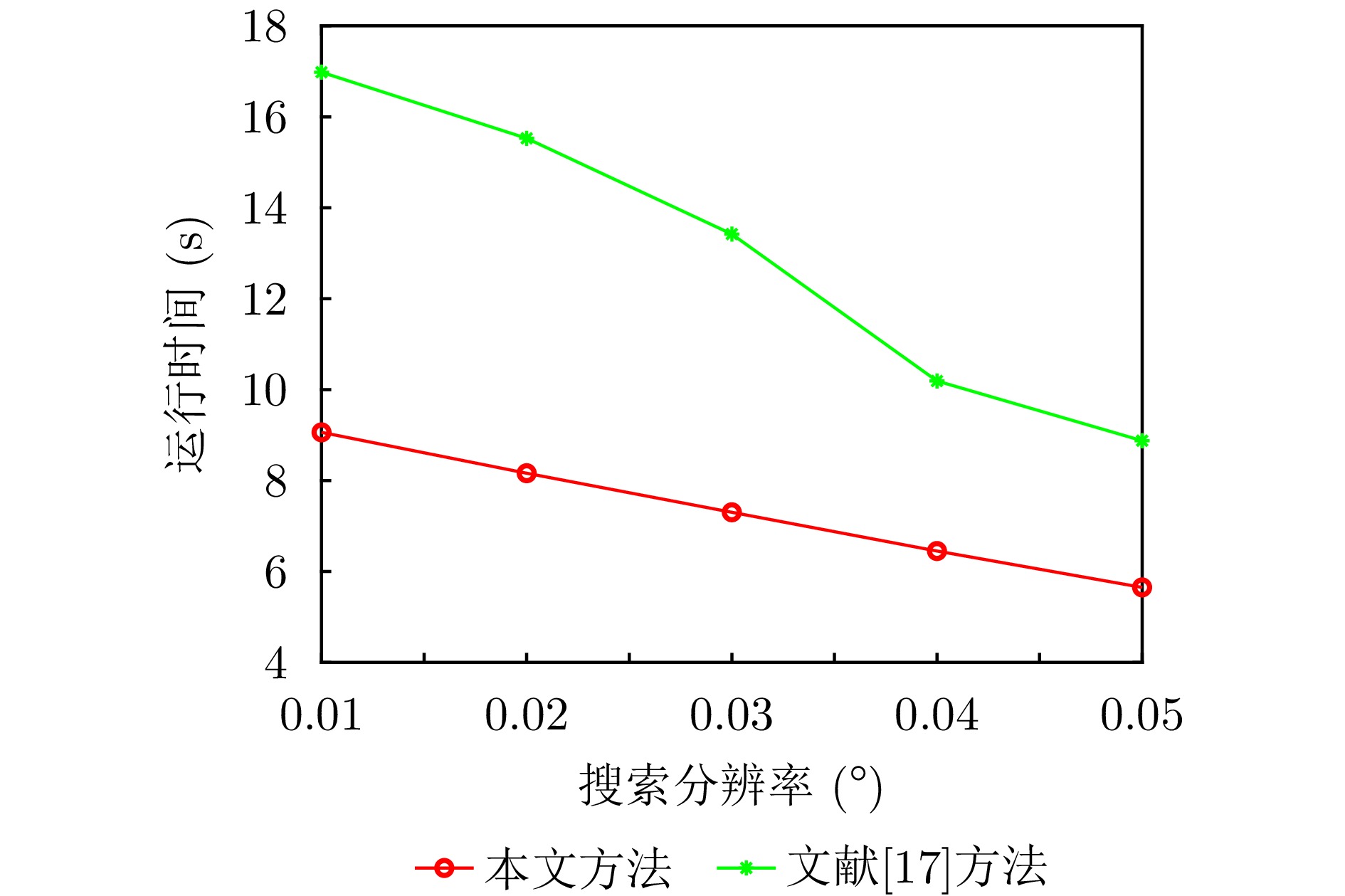
- Figure 5. The relationship between the running time and search resolution of different positioning methods
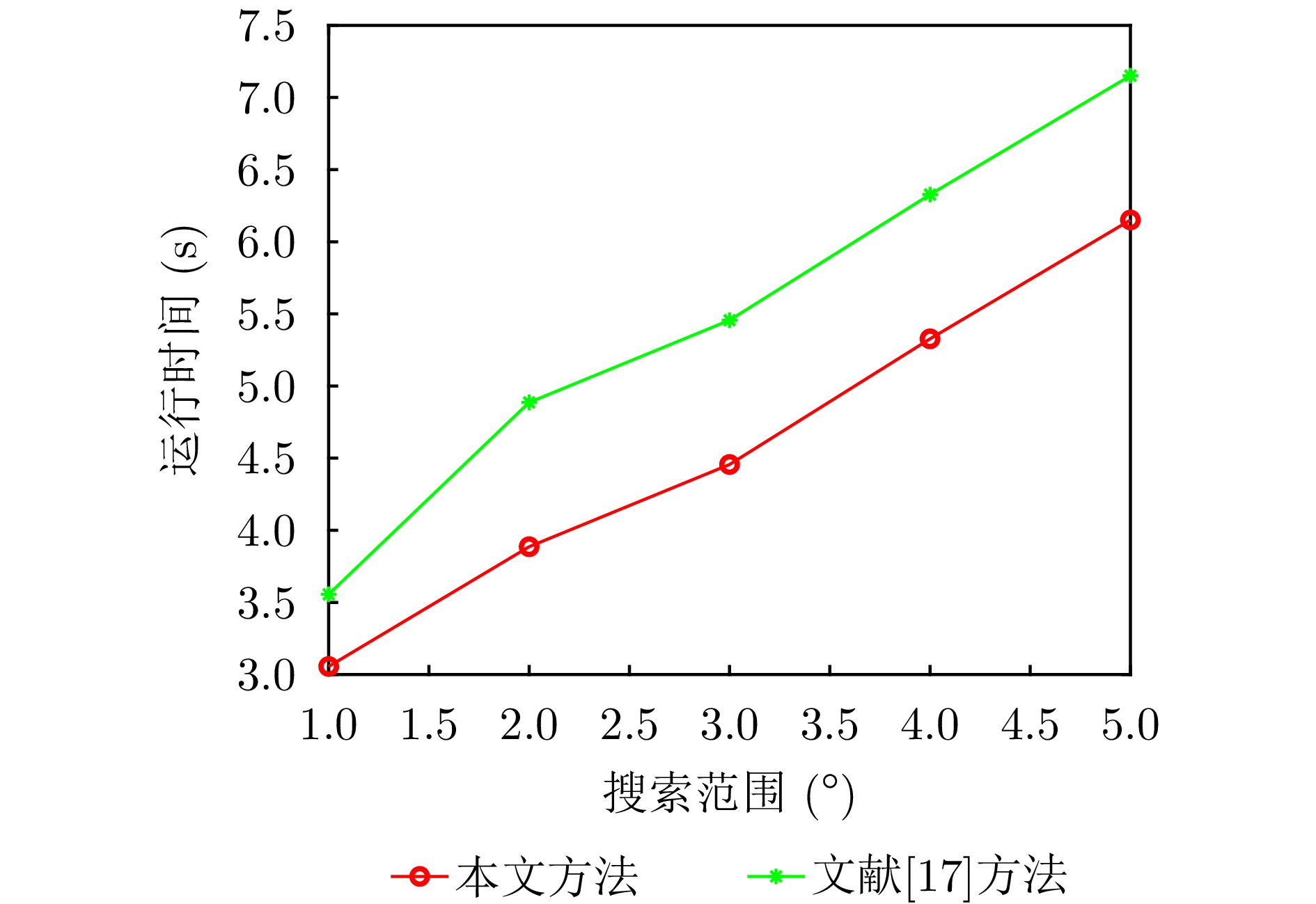
- Figure 6. The relationship between the running time and search range of different positioning methods
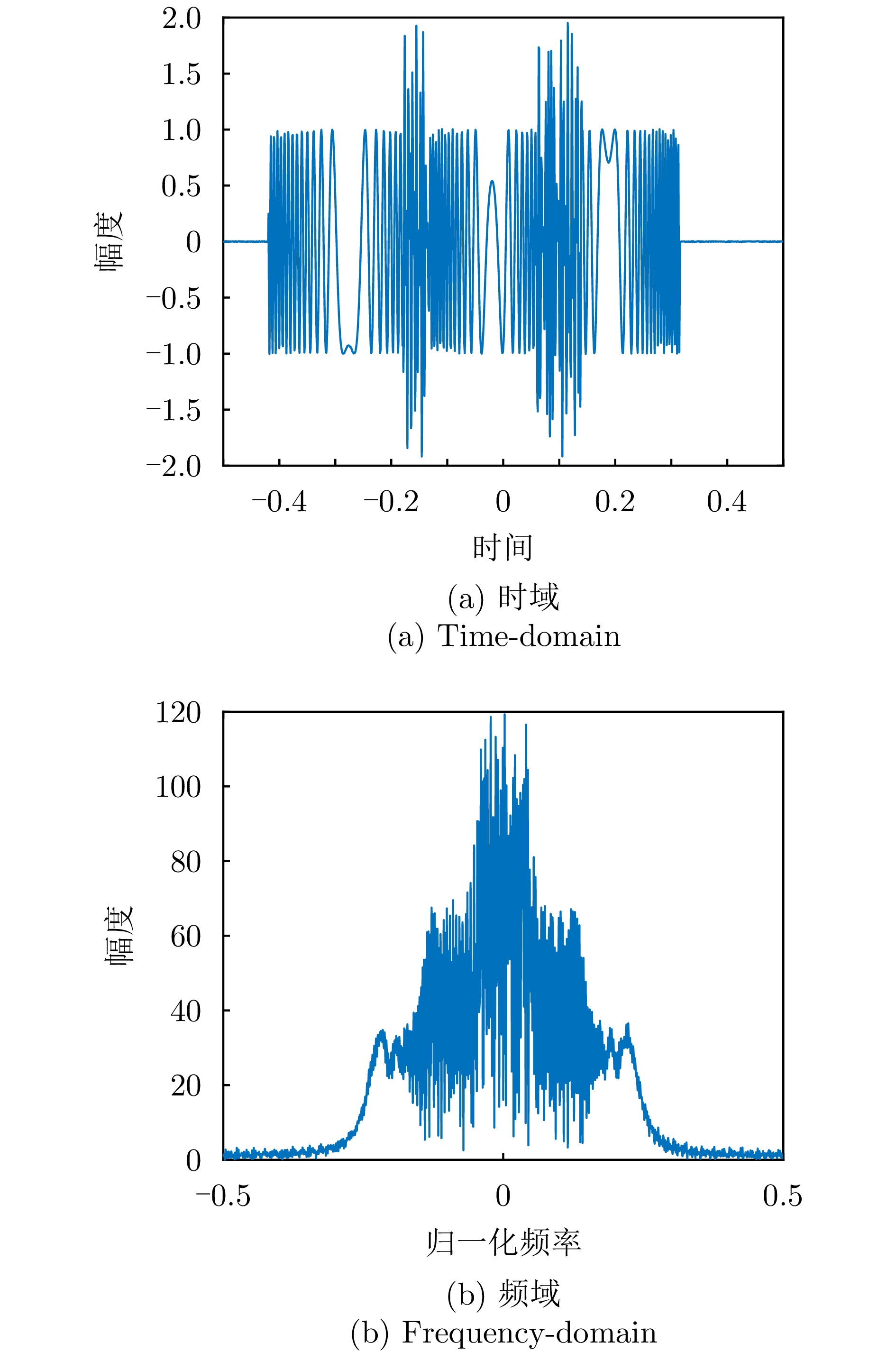
- Figure 7. Time-domain and frequency-domain overlap of multi-radar radiation source signals
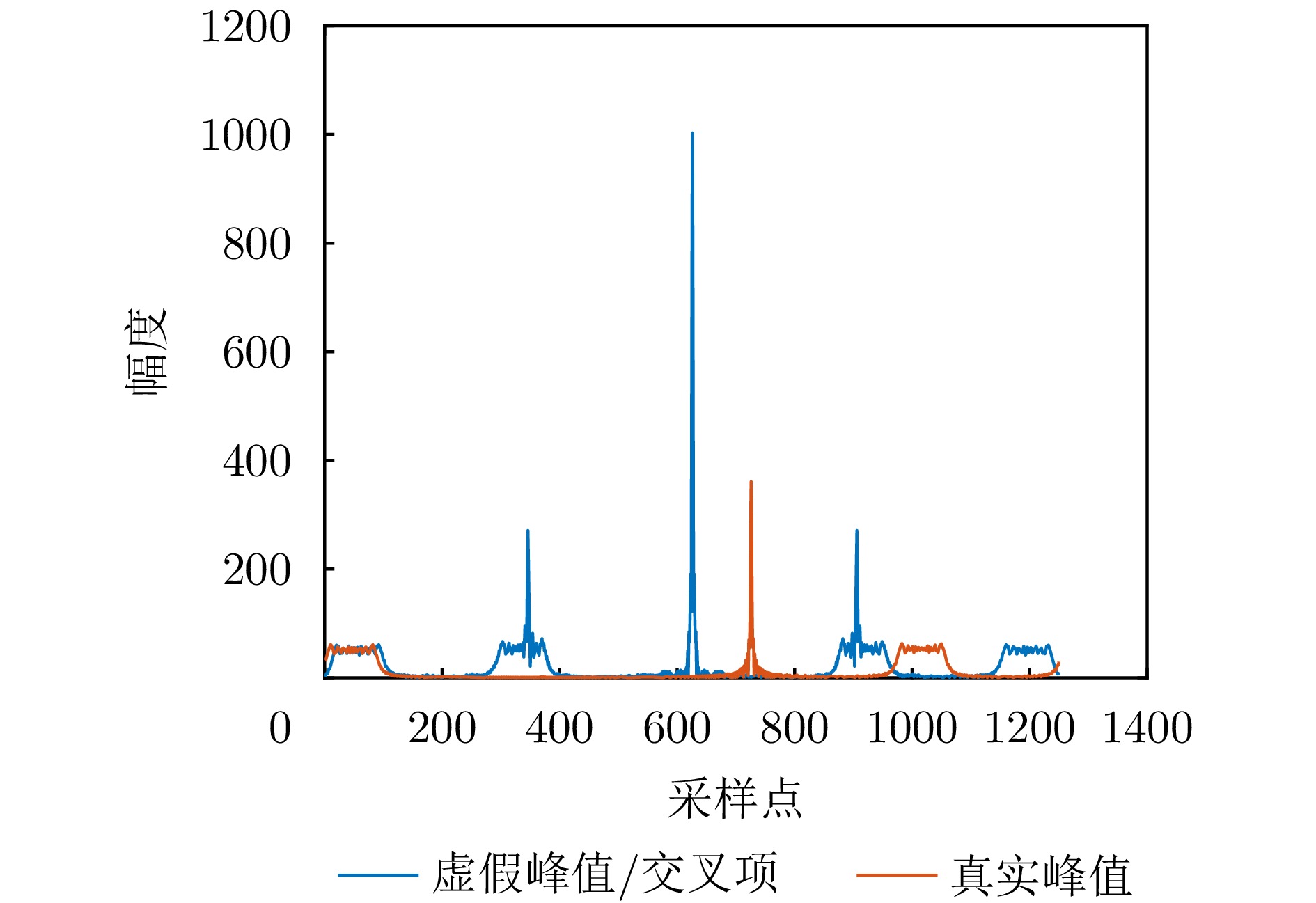
- Figure 8. Processing results from Ref. [11]
- Figure 9. Time-frequency distribution of target signal
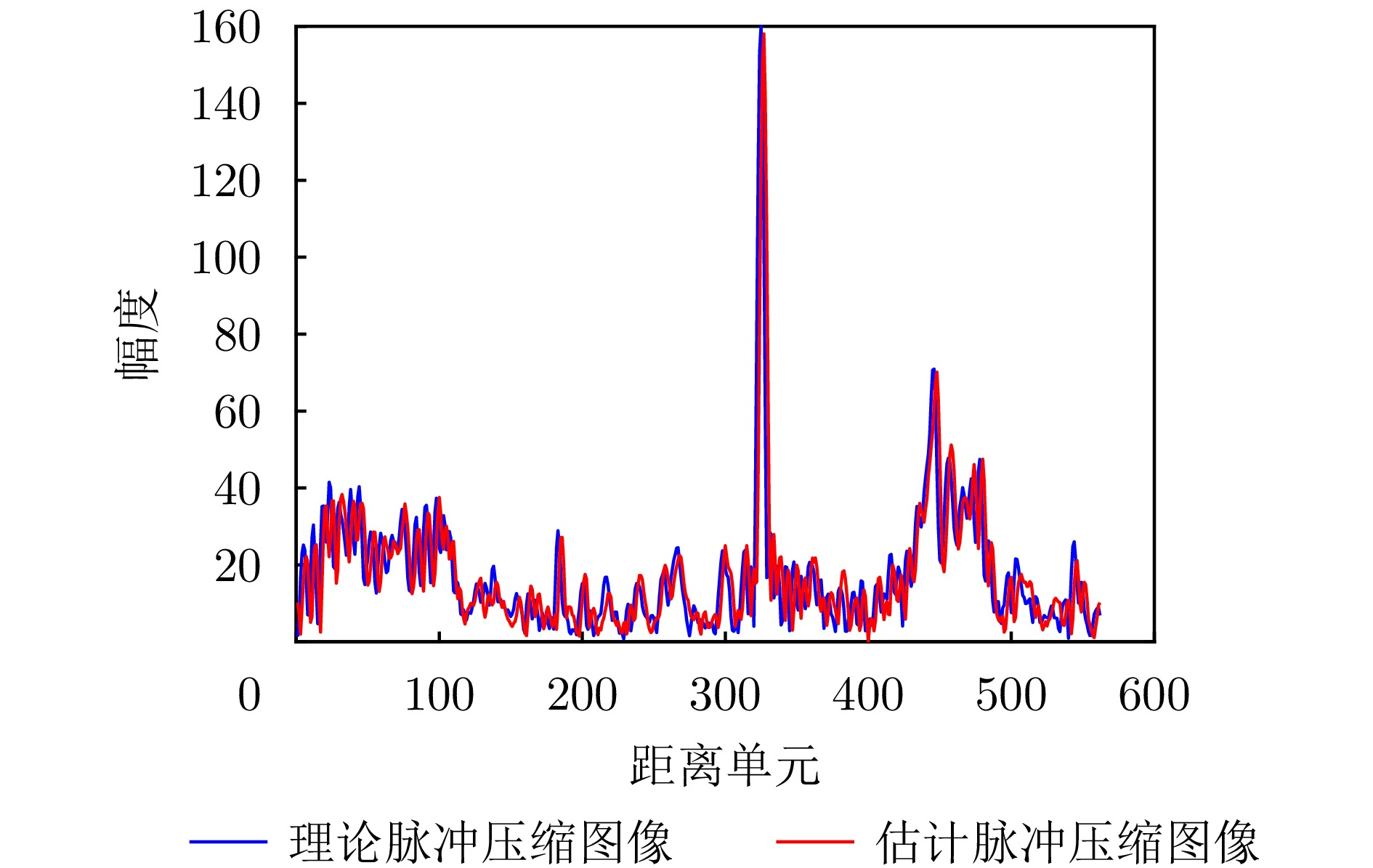
- Figure 10. Comparison between theoretical pulse compression and practical application
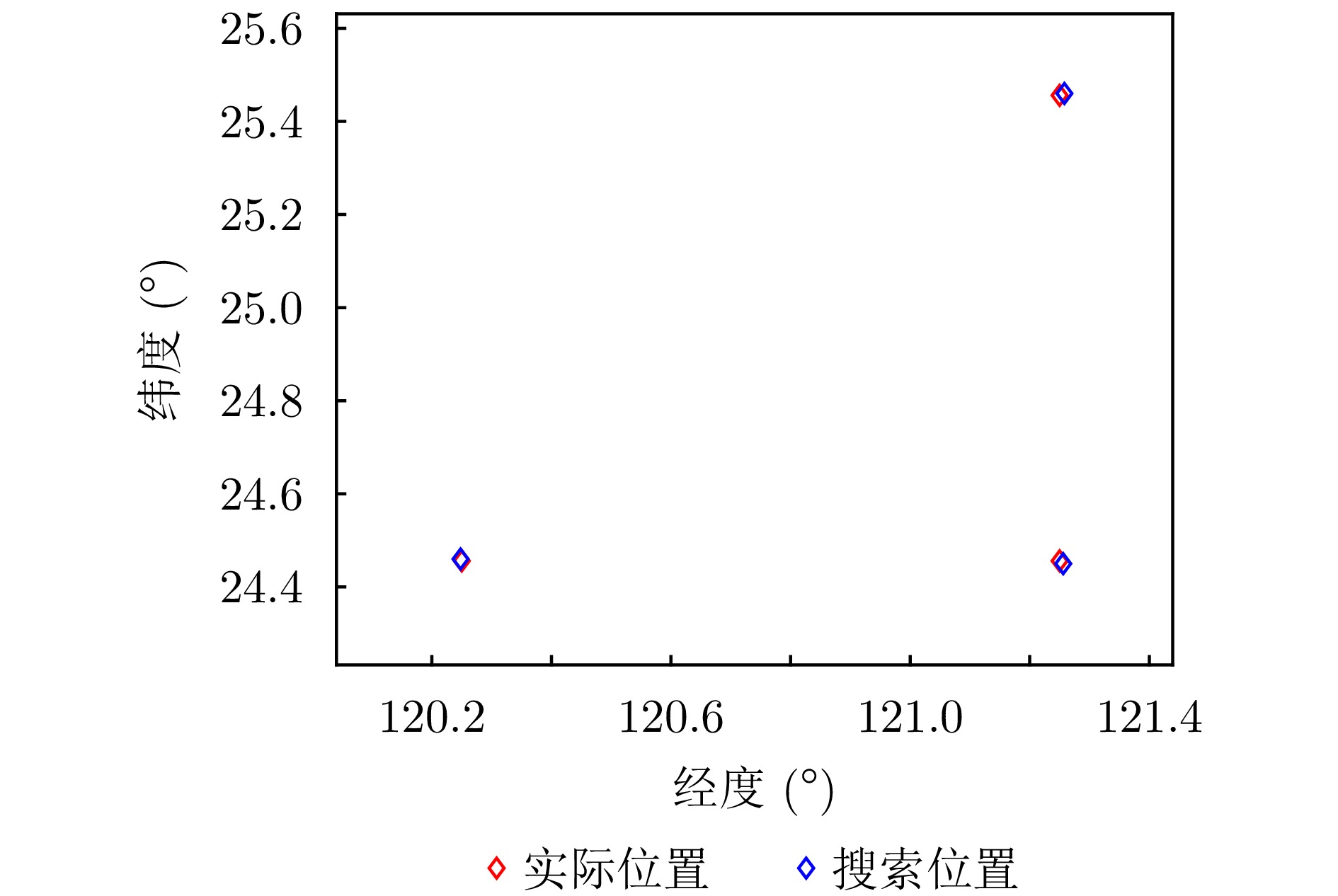
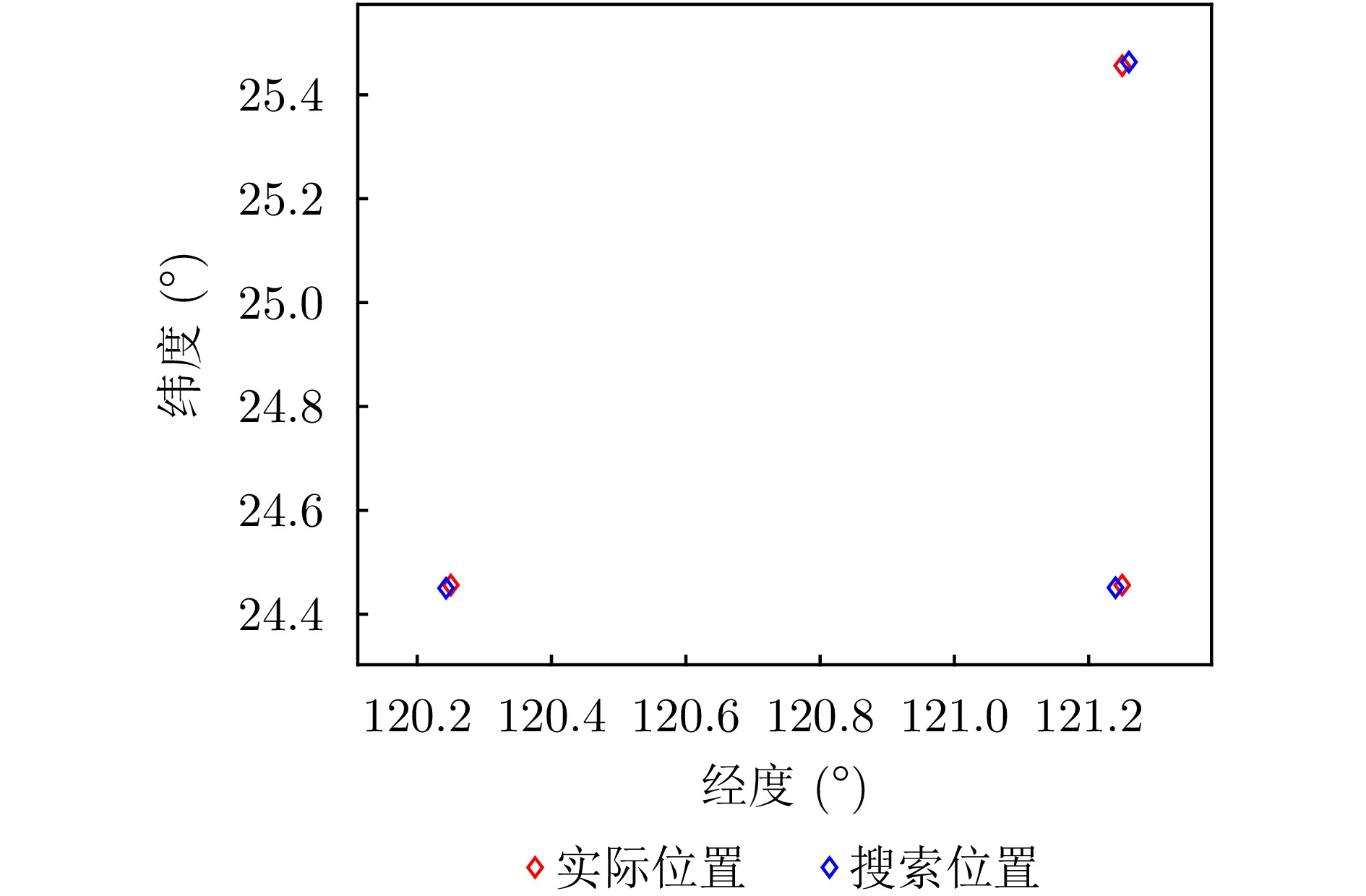
- Figure 11. Localization results using the proposed method
- Figure 12. Time-frequency distribution of different modulated emitter signals
- Figure 13. Localization results of different modulated emitter signals
- Figure 14. Localization RMSE versus SNR using different methods


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: