- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2025
> Online First
| Citation: | WANG Bohong, SHEN Biao, MU Wenxing, et al. An improved bat-inspired super-resolution algorithm for mechanical rotation polarimetric radar[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25113 |
An Improved Bat-inspired Super-resolution Algorithm for Mechanical Rotation Polarimetric Radar
DOI: 10.12000/JR25113 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25113
More Information-
Abstract
In recent years, bionic super-resolution technology, inspired by biological perception mechanisms, has emerged as a substantial research direction aimed at overcoming the limitations of radar resolution. The Baseband Spectrogram Correlation and Transformation (BSCT) model, which is based on bat hearing, offers a novel approach to enhancing traditional radar resolution. However, the model exhibits inherent limitations, including insufficient multi-target adaptability and the inability to utilize polarization information. To address these problems, this paper proposes a polarization-enhanced bionic super-resolution model: Polarimetric Baseband Spectrogram Correlation and Transformation (P-BSCT) for Mechanical Rotation Polarimetric Radar (MRPR). The primary contributions of this study are as follows: first, the integration of the bat BSCT model with MRPR, thereby enabling the utilization of polarization information and the execution of polarization measurements; second, the proposal of an advanced signal processing method, which overcomes the limitations of the original BSCT in two-target and static scenes, effectively applying to multi-target and moving-target scenarios, and exhibiting no impact on the resolution effect due to signal modulation. P-BSCT has been demonstrated to enhance resolving power by approximately 15 dB under optimal conditions when compared with the original BSCT model. In scenarios involving moving targets, targets exhibiting equivalent polarization scattering properties, and nonlinear FM signals, the resolving performance of P-BSCT remains essentially unchanged, demonstrating notable robustness. -

-
References
[1] HEISENBERG W. Über den anschaulichen Inhalt der quantentheoretischen Kinematik und Mechanik[J]. Zeitschrift für Physik, 1927, 43(3): 172–198. doi: 10.1007/BF01397280.[2] GABOR D. Theory of communication. Part 1: The analysis of information[J]. Journal of the Institution of Electrical Engineers-Part III: Radio and Communication Engineering, 1946, 93(26): 429–441. doi: 10.1049/ji-3-2.1946.0074.[3] FOLLAND G B and SITARAM A. The uncertainty principle: A mathematical survey[J]. Journal of Fourier Analysis and Applications, 1997, 3(3): 207–238. doi: 10.1007/BF02649110.[4] NAMIAS V. The fractional order Fourier transform and its application to quantum mechanics[J]. IMA Journal of Applied Mathematics, 1980, 25(3): 241–265. doi: 10.1093/imamat/25.3.241.[5] ALMEIDA L B. The fractional Fourier transform and time-frequency representations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(11): 3084–3091. doi: 10.1109/78.330368.[6] MOSHINSKY M and QUESNE C. Linear canonical transformations and their unitary representations[J]. Journal of Mathematical Physics, 1971, 12(8): 1772–1780. doi: 10.1063/1.1665805.[7] DAUBECHIES I. The wavelet transform, time-frequency localization and signal analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1990, 36(5): 961–1005. doi: 10.1109/18.57199.[8] ELAD M and BRUCKSTEIN A M. A generalized uncertainty principle and sparse representation in pairs of bases[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2002, 48(9): 2558–2567. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2002.801410.[9] DONOHO D L and STARK P B. Uncertainty principles and signal recovery[J]. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 1989, 49(3): 906–931. doi: 10.1137/0149053.[10] KUMARESAN R and TUFTS D. Estimating the parameters of exponentially damped sinusoids and pole-zero modeling in noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1982, 30(6): 833–840. doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1982.1163974.[11] STOICA P and SELEN Y. Model-order selection: A review of information criterion rules[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2004, 21(4): 36–47. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2004.1311138.[12] 倪晋麟, 储晓彬, 林幼权. 基于去卷积距离超分辨方法的机理及限制条件[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2000, 22(3): 62–64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2000.03.019.NI Jinlin, CHU Xiaobin, and LIN Youquan. The principle and limitation of the range super-resolution algorithms based on deconvolution[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2000, 22(3): 62–64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2000.03.019.[13] 王永良. 空间谱估计理论与算法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2004: 18–52, 306–336.WANG Yongliang. Space Spectral Estimation Theory and Algorithms[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004: 18–52, 306–336.[14] 郑昱. 复杂相关信号的DOA估计方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 哈尔滨工程大学, 2021. doi: 10.27060/d.cnki.ghbcu.2021.002074.ZHENG Yu. Research on DOA estimation methods for complicated correlated signals[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Harbin Engineering University, 2021. doi: 10.27060/d.cnki.ghbcu.2021.002074.[15] KIM K T, SEO D K, and KIM H T. Efficient radar target recognition using the MUSIC algorithm and invariant features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2002, 50(3): 325–337. doi: 10.1109/8.999623.[16] 代大海, 王雪松, 肖顺平, 等. 全极化散射中心提取与参数估计: P-MUSIC方法[J]. 信号处理, 2007, 23(6): 818–822. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2007.06.005.DAI Dahai, WANG Xuesong, XIAO Shunping, et al. Fully polarized scattering center extraction and parameter estimation: P-MUSIC algorithm[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2007, 23(6): 818–822. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2007.06.005.[17] LI Liang, ZHANG Xiaoling, SHI Jun, et al. Range direction focusing method based on single-snap MUSIC for SAR imaging[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference, Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 1195–1200. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8378732.[18] KONG Lingyu, HE Xiaoyu, and XU Xiaojian. A fully-polarized unitary MUSIC for polarimetric SAR tomography[C]. 2019 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications, Granada, Spain, 2019: 0964–0967. doi: 10.1109/ICEAA.2019.8879343.[19] SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830.[20] ROY R and KAILATH T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(7): 984–995. doi: 10.1109/29.32276.[21] DAI Dahai, WANG Xuesong, CHANG Yuliang, et al. Fully-polarized scattering center extraction and parameter estimation: P-ESPRIT algorithm[C]. 2006 CIE International Conference on Radar, Shanghai, China, 2006: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICR.2006.343293.[22] DING Shanshan, TONG Ningning, ZHANG Yongshun, et al. Super-resolution 3D imaging in MIMO radar using spectrum estimation theory[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(2): 304–312. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2016.0233.[23] 陈希信. 基于LFM信号频域去斜和压缩感知的雷达距离超分辨[J]. 现代雷达, 2022, 44(12): 70–73. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.12.010.CHEN Xixin. Radar range super-resolution based on LFM frequency dechirp and compressive sensing[J]. Modern Radar, 2022, 44(12): 70–73. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2022.12.010.[24] WEI Shunjun, ZHOU Zichen, WANG Mou, et al. 3DRIED: A high-resolution 3-D millimeter-wave radar dataset dedicated to imaging and evaluation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(17): 3366. doi: 10.3390/rs13173366.[25] 康乐, 张群, 李涛泳, 等. 基于贝叶斯学习的下视三维合成孔径雷达成像方法[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37(6): 0611003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0611003.KANG Le, ZHANG Qun, LI Taoyong, et al. Imaging method of downward-looking three-dimensional synthetic aperture radar based on Bayesian learning[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(6): 0611003. doi: 10.3788/AOS201737.0611003.[26] SIMMONS J A, FERRAGAMO M, MOSS C F, et al. Discrimination of jittered sonar echoes by the echolocating bat, Eptesicus fuscus: The shape of target images in echolocation[J]. Journal of Comparative Physiology A, 1990, 167(5): 589–616. doi: 10.1007/BF00192654.[27] SIMMONS J A, SAILLANT P A, WOTTON J M, et al. Composition of biosonar images for target recognition by echolocating bats[J]. Neural Networks, 1995, 8(7/8): 1239–1261. doi: 10.1016/0893-6080(95)00059-3.[28] SCHMIDT S. Perception of structured phantom targets in the echolocating bat, Megaderma lyra[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1992, 91(4): 2203–2223. doi: 10.1121/1.403654.[29] 成彬彬. 自适应雷达波形的仿生处理研究[D]. [博士论文], 清华大学, 2009.CHENG Binbin. Research on bionic processing for auto-adaptive radar waveform[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Tsinghua University, 2009.[30] 杨琳. 镫骨、耳蜗及其Corti器的建模与生物力学研究[D]. [博士论文], 复旦大学, 2009: 17–34. doi: 10.7666/d.y1970550.YANG Lin. Modeling and biomechanical analysis of the stapes, cochlea and organ of Corti[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Fudan University, 2009: 17–34. doi: 10.7666/d.y1970550.[31] 秦晓瑜. 基于听觉仿生的听觉谱生成方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 东北师范大学, 2013: 1–18.QIN Xiaoyu. Study on the generation method of auditory spectrum based on auditory bionics[D]. [Master dissertation], Northeast Normal University, 2013: 1–18.[32] BALLERI A, GRIFFITHS H, and BAKER C. Biologically-Inspired Radar and Sonar: Lessons from Nature[M]. Edison: SciTech Publishing, 2017: 1–81.[33] CHI T, RU Powen, and SHAMMA S A. Multiresolution spectrotemporal analysis of complex sounds[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2005, 118(2): 887–906. doi: 10.1121/1.1945807.[34] VANDERELST D, STECKEL J, BOEN A, et al. Place recognition using batlike sonar[J]. eLife, 2016, 5: e14188. doi: 10.7554/eLife.14188.[35] CIGANOVIĆ N, WARREN R L, KEÇELI B, et al. Static length changes of cochlear outer hair cells can tune low-frequency hearing[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2018, 14(1): e1005936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005936.[36] HOLDERIED M W, BAKER C J, VESPE M, et al. Understanding signal design during the pursuit of aerial insects by echolocating bats: Tools and applications[J]. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 2008, 48(1): 74–84. doi: 10.1093/icb/icn035.[37] SAILLANT P A, SIMMONS J A, DEAR S P, et al. A computational model of echo processing and acoustic imaging in frequency-modulated echolocating bats: The spectrogram correlation and transformation receiver[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1993, 94(5): 2691–2712. doi: 10.1121/1.407353.[38] SIMMONS J A, SAILLANT P A, FERRAGAMO M J, et al. Auditory Computations for Biosonar Target Imaging in Bats[M]. HAWKINS H L, MCMULLEN T A, POPPER A N, et al. Auditory Computation. New York: Springer, 1996: 401–468. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-4070-9_9.[39] PEREMANS H and HALLAM J. The spectrogram correlation and transformation receiver, revisited[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1998, 104(2): 1101–1110. doi: 10.1121/1.423326.[40] MATSUO I, KUNUGIYAMA K, and YANO M. An echolocation model for range discrimination of multiple closely spaced objects: Transformation of spectrogram into the reflected intensity distribution[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2004, 115(2): 920–928. doi: 10.1121/1.1642626.[41] MATSUO I and YANO M. An echolocation model for the restoration of an acoustic image from a single-emission echo[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2004, 116(6): 3782–3788. doi: 10.1121/1.1811411.[42] WIEGREBE L. An autocorrelation model of bat sonar[J]. Biological Cyber-Netics, 2008, 98(6): 587–595. doi: 10.1007/s00422-008-0216-2.[43] PARK M and ALLEN R. Pattern-matching analysis of fine echo delays by the spectrogram correlation and transformation receiver[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2010, 128(3): 1490–1500. doi: 10.1121/1.3466844.[44] SIMON R, KNÖRNSCHILD M, TSCHAPKA M, et al. Biosonar resolving power: Echo-acoustic perception of surface structures in the submillimeter range[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2014, 5: 64. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00064.[45] 苏梦娜, 梁红, 杨长生. 基于SCAT模型的水下多目标高分辨仿生成像方法[J]. 水下无人系统学报, 2019, 27(2): 189–193. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-1509.2019.02.010.SU Mengna, LIANG Hong, and YANG Changsheng. Bionic imaging of underwater multiple targets with high resolution based on SCAT model[J]. Journal of Unmanned Undersea Systems, 2019, 27(2): 189–193. doi: 10.11993/j.issn.2096-1509.2019.02.010.[46] CHEN Ming, BATES M E, and SIMMONS J A. How frequency hopping suppresses pulse-echo ambiguity in bat biosonar[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(29): 17288–17295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2001105117.[47] CHEN Ming, HARO S, SIMMONS A M, et al. A comprehensive computational model of animal biosonar signal processing[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2021, 17(2): e1008677. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008677.[48] GEORGIEV K, BALLERI A, STOVE A, et al. Baseband version of the bat-inspired spectrogram correlation and transformation receiver[C]. 2016 IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2016: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.7485152.[49] GEORGIEV K, BALLERI A, STOVE A, et al. Bio-inspired two target resolution at radio frequencies[C]. 2017 IEEE Radar Conference, Seattle, USA, 2017: 0436–0440. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2017.7944242.[50] GEORGIEV K, BALLERI A, STOVE A, et al. Bio-inspired processing of radar target echoes[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(12): 1402–1409. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5241.[51] GEORGIEV K. Exploiting the phase of a bio-inspired receiver[C]. 2021 IEEE Radar Conference, Atlanta, USA, 2021: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2147009.2021.9454987.[52] 王博弘, 申彪, 穆文星, 等. 基于蝙蝠谱相关及变换模型的雷达目标超分辨方法研究[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(2): 293–308. doi: 10.12000/JR24239.WANG Bohong, SHEN Biao, MU Wenxing, et al. Research on super-resolution methods for radar targets based on bat-inspired spectrogram correlation and transformation models[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(2): 293–308. doi: 10.12000/JR24239.[53] 赵春雷, 王亚梁, 阳云龙, 等. 雷达极化信息获取及极化信号处理技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(6): 620–638. doi: 10.12000/JR16092.ZHAO Chunlei, WANG Yaliang, YANG Yunlong, et al. Review of radar polarization information acquisition and polarimetric signal processing techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(6): 620–638. doi: 10.12000/JR16092.[54] 邢孟道, 谢意远, 高悦欣, 等. 电磁散射特征提取与成像识别算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 921–942. doi: 10.12000/JR22232.XING Mengdao, XIE Yiyuan, GAO Yuexin, et al. Electromagnetic scattering characteristic extraction and imaging recognition algorithm: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 921–942. doi: 10.12000/JR22232.[55] 韩静雯, 杨勇, 连静, 等. 基于极化与距离像特征融合的雷达导引头角反射器鉴别方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46(11): 3658–3670. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.11.08.HAN Jingwen, YANG Yong, LIAN Jing, et al. Identification method of corner reflector based on polarization and HRRP feature fusion for radar seeker[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(11): 3658–3670. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.11.08.[56] LIU Tao, YANG Ziyuan, GAO Gui, et al. A general framework of polarimetric detectors based on quadratic optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5237418. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3217336.[57] LIU Tao, ZHANG Jiafeng, GAO Gui, et al. CFAR ship detection in polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images based on whitening filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(1): 58–81. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2931353.[58] WANG Luoshengbin, XU Zhenhai, DONG Wei, et al. A scheme of polarimetric superresolution for multitarget detection and localization[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 439–443. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3058007.[59] 王罗胜斌, 王雪松, 徐振海. 雷达极化域调控超分辨的原理与方法[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2023, 53(5): 993–1007. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2022-0141.WANG Luoshengbin, WANG Xuesong, and XU Zhenhai. Principle and approach to polarization modulation for radar super-resolution[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2023, 53(5): 993–1007. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2022-0141.[60] HUYNEN J R. Measurement of the target scattering matrix[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1965, 53(8): 936–946. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1965.4072.[61] GIULI D, FOSSI M, and FACHERIS L. Radar target scattering matrix measurement through orthogonal signals[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Radar and Signal Processing), 1993, 140(4): 233–242. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1993.0033.[62] GIULI D, FACHERIS L, FOSSI M, et al. Simultaneous scattering matrix measurement through signal coding[C]. IEEE International Conference on Radar, Arlington, USA, 1990: 258–262. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.1990.201173.[63] WANG Xuesong, LI Yongzhen, DAI Huanyao, et al. Research on instantaneous polarization radar system and external experiment[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15): 1560–1567. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3102-y.[64] SANTALLA V and ANTAR Y M M. A comparison between different polarimetric measurement schemes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(5): 1007–1017. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.1010888.[65] WANG Fulai, LI Chao, PANG Chen, et al. A method for estimating the polarimetric scattering matrix of moving target for simultaneous fully polarimetric radar[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(5): 1418. doi: 10.3390/s18051418.[66] SOUYRIS J C, IMBO P, FJØRTOFT R, et al. Compact polarimetry based on symmetry properties of geophysical media: The π/4 mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(3): 634–646. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.842486.[67] SIMMONS A J. Phase shift by periodic loading of waveguide and its application to broad-band circular polarization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1955, 3(6): 18–21. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.1955.1124986.[68] BERTIN G, PIOVANO B, ACCATINO L, et al. Full-wave design and optimization of circular waveguide polarizers with elliptical irises[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2002, 50(4): 1077–1083. doi: 10.1109/22.993409.[69] WU Tekao. Meander-line polarizer for arbitrary rotation of linear polarization[J]. IEEE Microwave and Guided Wave Letters, 1994, 4(6): 199–201. doi: 10.1109/75.294292.[70] ANG T W and CHAN K K. A broadband wide angle variable linear polarization rotator[C]. 2013 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium (APSURSI), Orlando, USA, 2013: 2229–2230. doi: 10.1109/APS.2013.6711773.[71] GUO Lu, TAN P K, and CHIO T H. A simple method to realize polarization diversity in broadband reflectarrays using single-layered rectangular patch elements[C]. 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, Canada, 2015: 2161–2162. doi: 10.1109/APS.2015.7305469.[72] LI Yongjiu and LI Long. Polarization diversity converter based on multilayer frequency selective surfaces[C]. 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, Vancouver, Canada, 2015: 2401–2402. doi: 10.1109/APS.2015.7305589.[73] QIN Nan and GUO Lu. On the use of metallic polarization conversion element with continuous 360° phase for high- efficiency all-metal planar folded reflectarrays[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2024, 23(6): 1859–1863. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2024.3371591.[74] SHEN Biao, LIU Tao, GAO Gui, et al. A low-cost polarimetric radar system based on mechanical rotation and its signal processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2025, 61(2): 4744–4765. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3507776.[75] SHEN Biao, LIU Tao, LIU Weijian, et al. Polarimetric measurement methods for mechanical rotation polarimetric radar system in multiple-target scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, in press. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2025.3580390.[76] WILLIAMS R T, PRASAD S, MAHALANABIS A K, et al. An improved spatial smoothing technique for bearing estimation in a multipath environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1988, 36(4): 425–432. doi: 10.1109/29.1546. -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. Block diagram and physical diagram of the MRPR system structure[74]
- Figure 2. Flowchart of P-BSCT signal processing
- Figure 3. Resolution effects of different algorithms at various relative distances under two-target condition
- Figure 4. Comparison of resolution among several algorithms
- Figure 5. Comparison of multi-target resolution effects of 6 algorithms under no-noise condition
- Figure 6. Comparison of resolution effects of P-BSCT and Single-snap MUSIC in multi-target scenarios under no-noise condition
- Figure 7. Influence of noise on resolution effects of 4 bionic super-resolution algorithms under two-target condition
- Figure 8. Influence of noise on resolution effects of P-BSCT and Single-snap MUSIC in multi-target scenarios
- Figure 9. Influence of coherent pulse number on resolution effect
- Figure 10. Curve of polarization measurement error variation with coherent pulse number
- Figure 11. Investigation on the role of rotating variable polarization in improving resolution effect
- Figure 12. Influence of signal forms on resolution effects of P-BSCT and Single-snap MUSIC
- Figure 13. Velocity estimation and super-resolution effect of P-BSCT for moving extended targets
- Figure 14. Influence of whether target PSMs are identical or not on resolution effect of P-BSCT
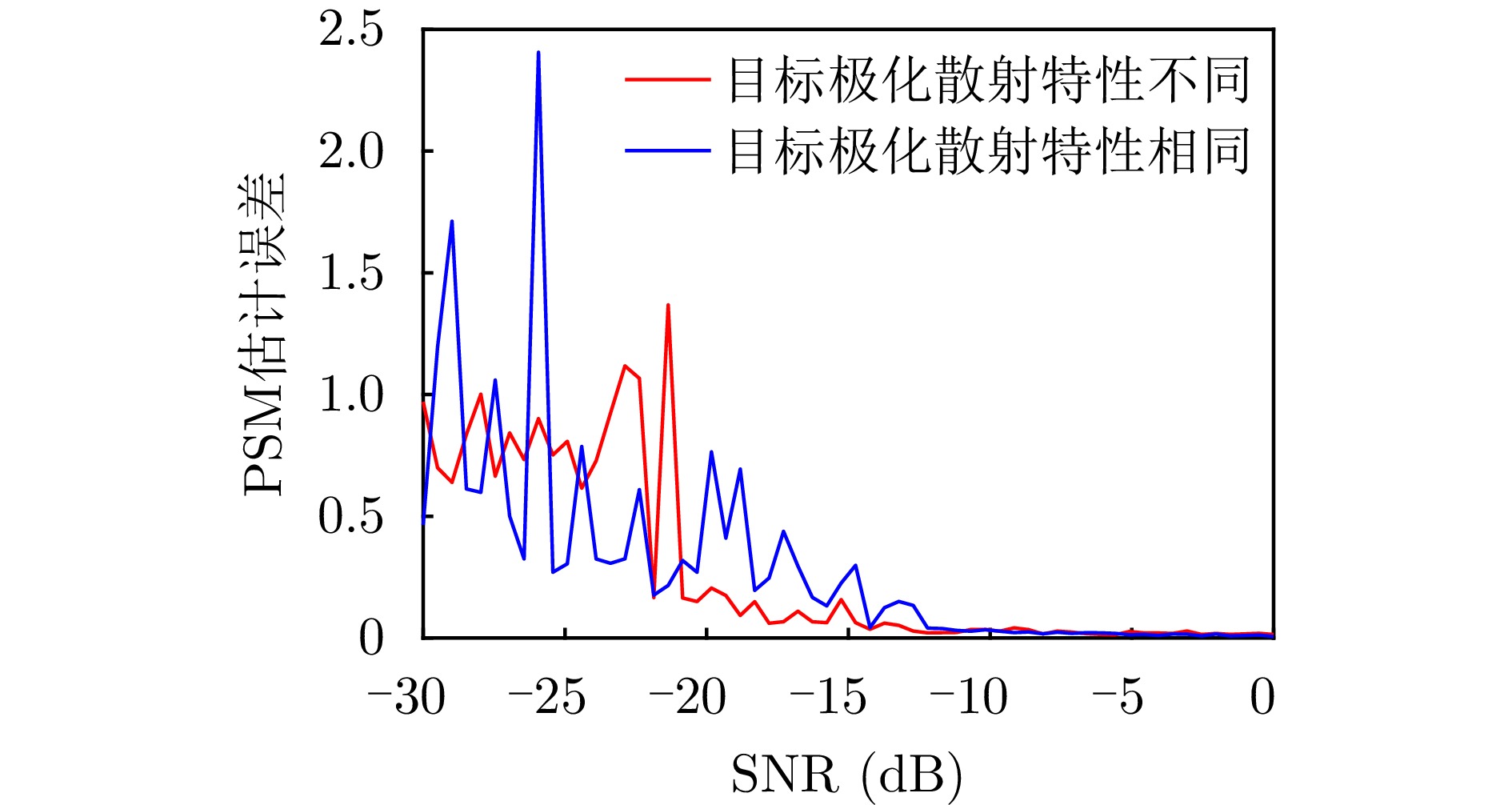
- Figure 15. Curves of polarization measurement error of P-BSCT varied with SNR when target PSMs are different or identical
- Figure 16. Influence of SNR on polarization measurement error
- Figure 17. Relationship between resolution effect of P-BSCT in resolution cell and number of targets, target spacing, and SNR
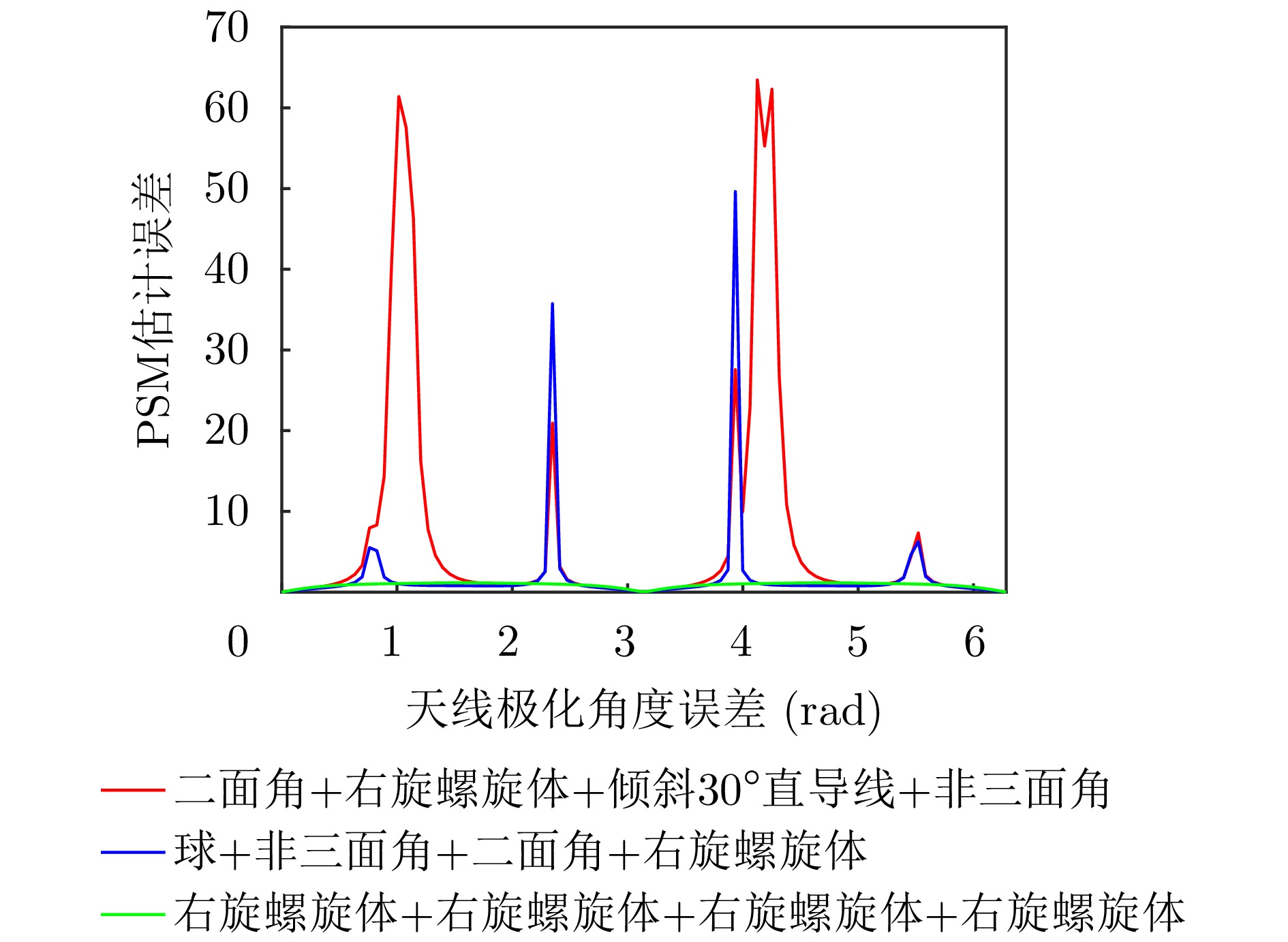
- Figure 18. Curve of polarization measurement error variation with polarization angle error
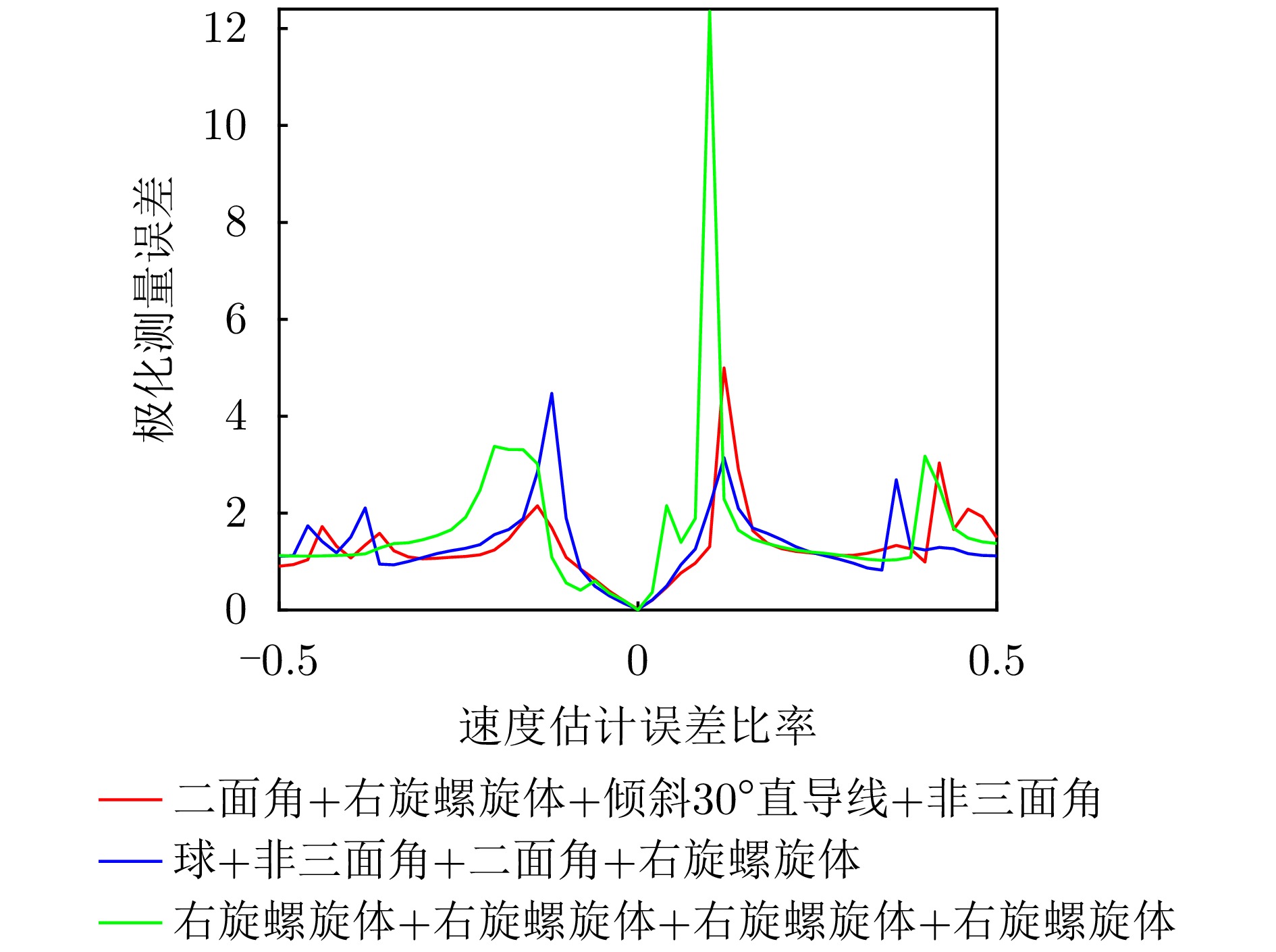
- Figure 19. Curve of polarization measurement error variation with velocity estimation error


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: