- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2025
> Online First
| Citation: | ZHOU Yating, ZHOU Yongsheng, XUE Qinghua, et al. An active jammer-based adversarial attack method against SAR automatic target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25110 |
An Active Jammer-based Adversarial Attack Method Against SAR Automatic Target Recognition
DOI: 10.12000/JR25110 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25110
More Information-
Abstract
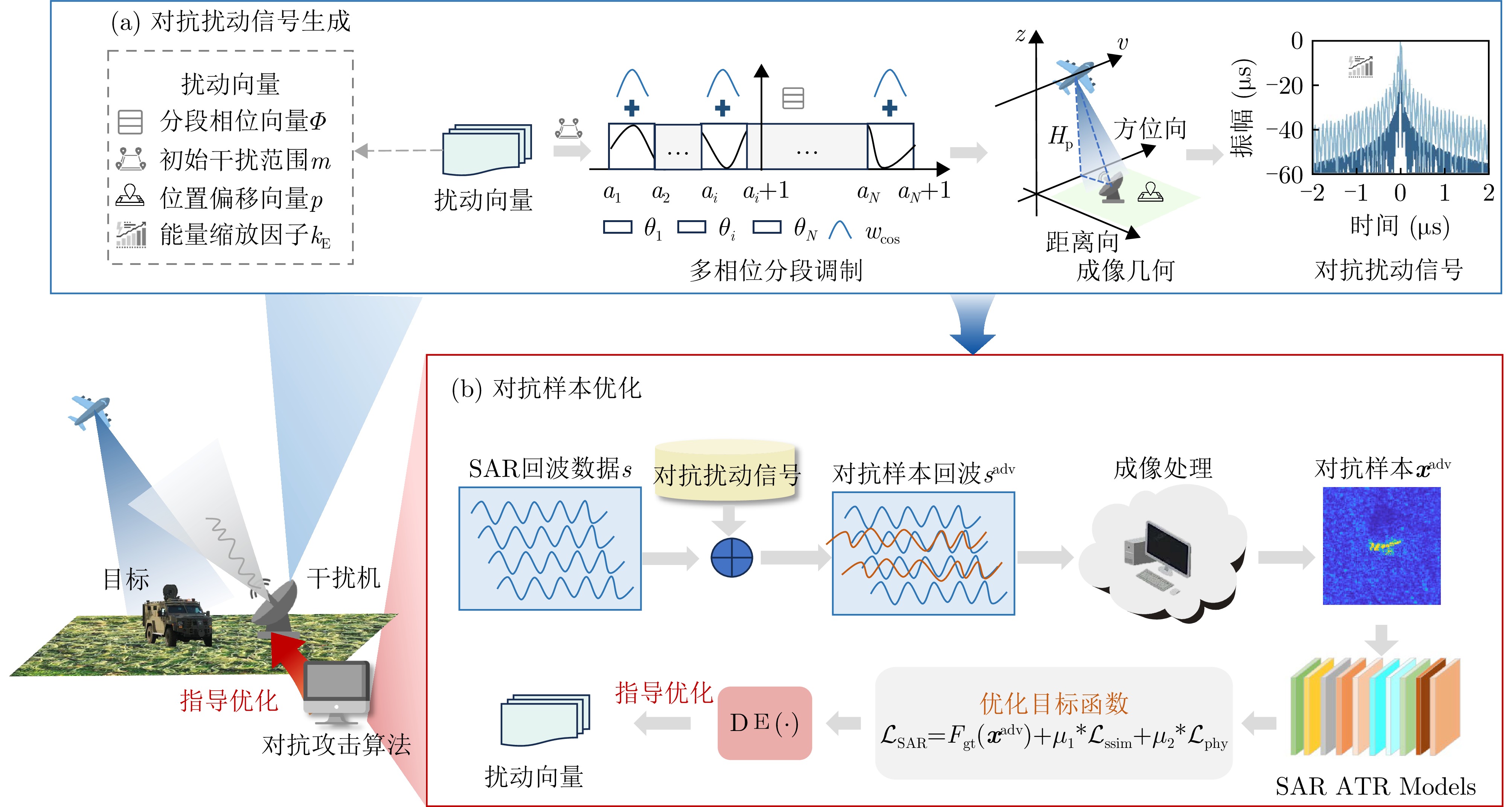
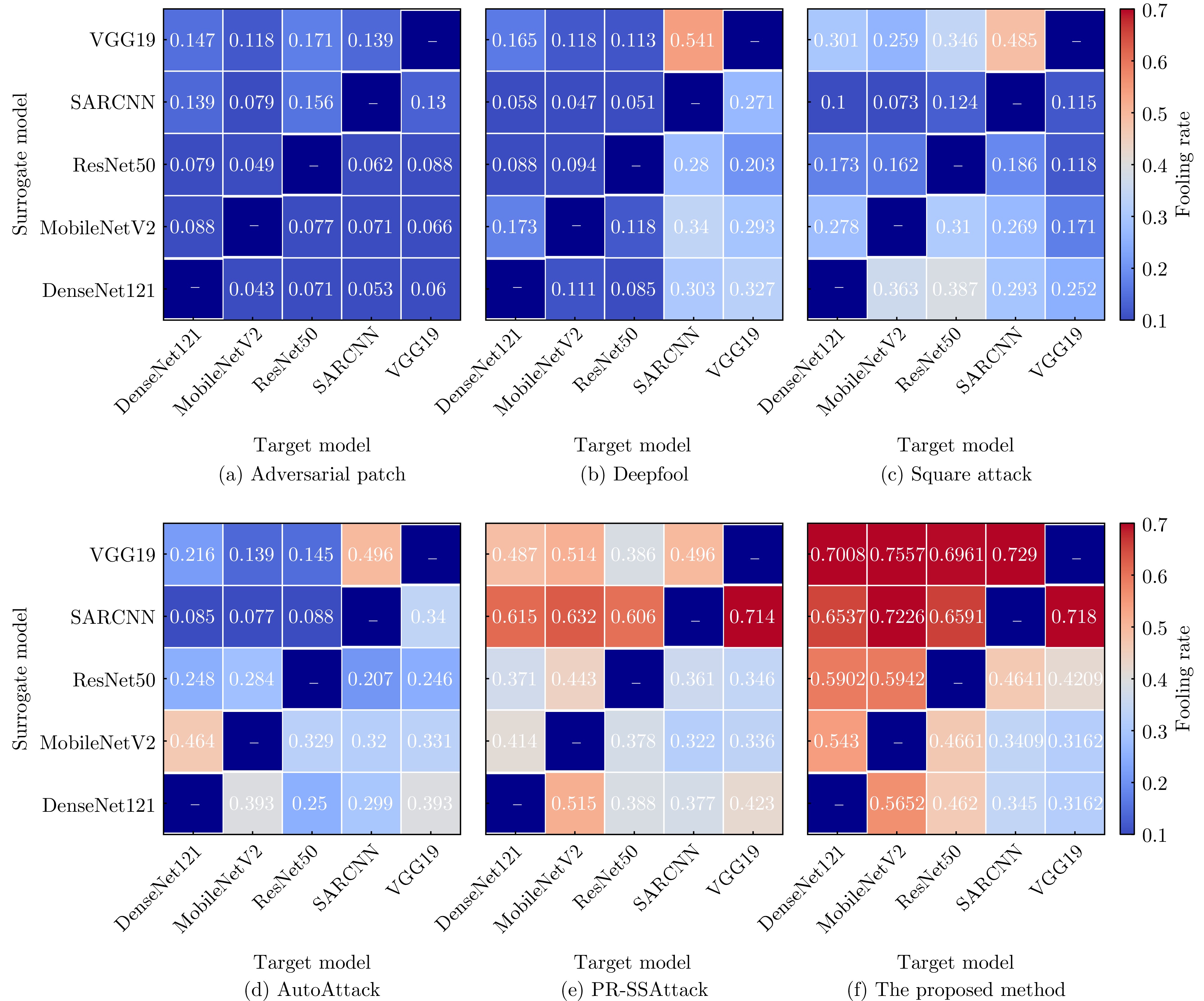
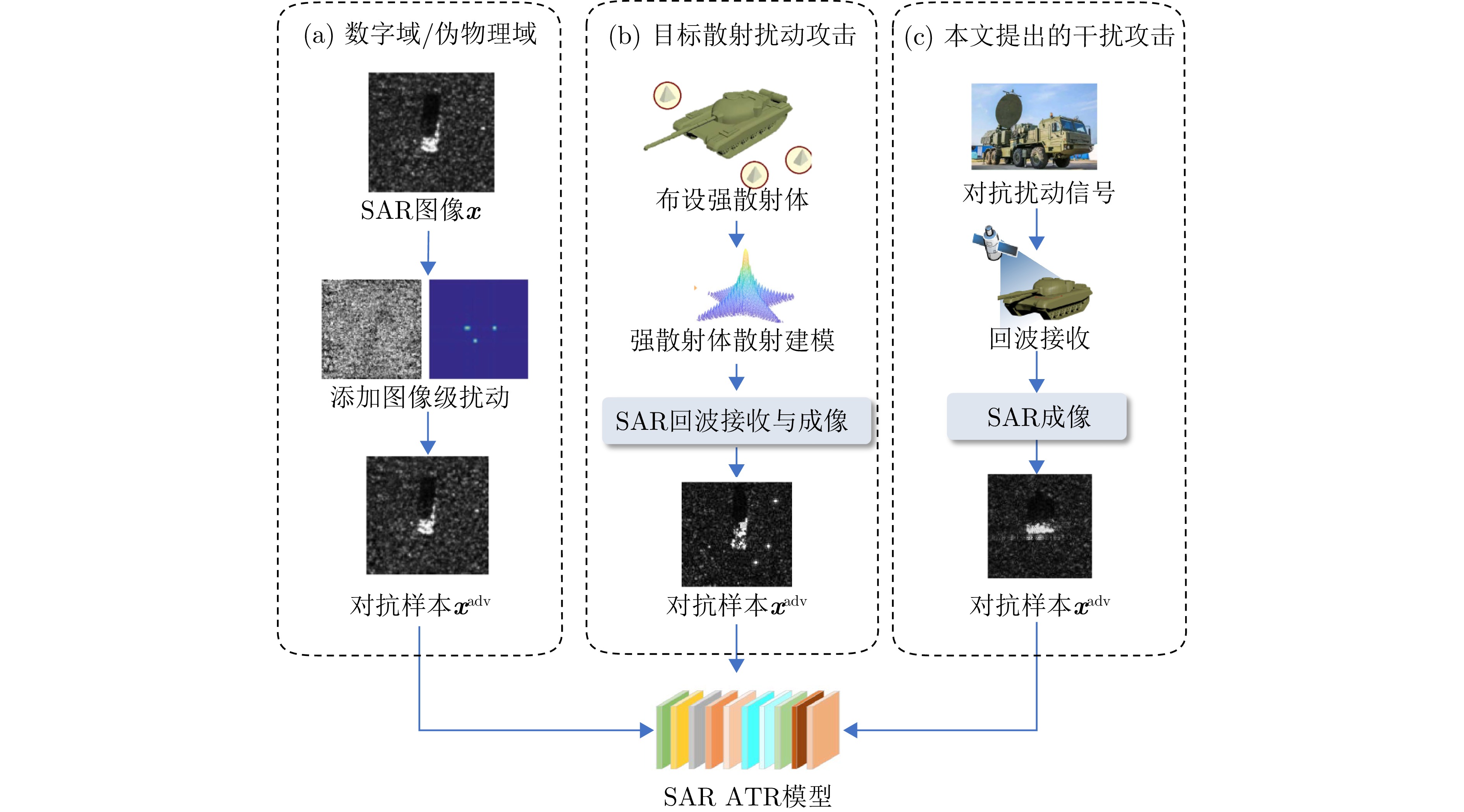
The effective utilization of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) adversarial examples enables specific targets to achieve remote sensing stealth against intelligent detection systems, thereby evading detection and recognition by adversaries. Digital domain SAR adversarial methods, which operate exclusively in the image domain, produce adversarial images that are not physically realizable and therefore cannot generated by real SAR imaging systems. Existing physical domain approaches typically involve deploying corner reflectors or electromagnetic metasurfaces around targets and simulating adversarial examples using via computational electromagnetics. However, the limited accuracy of scattering estimation often constrains the practical protective efficacy of these methods. To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes an active jammer-based adversarial attack method that integrates SAR active jamming technology with adversarial attack methods to generate adversarial examples by perturbing the target’s echo signals in the signal domain. First, a multiple-phase sectionalized modulation jamming method based on cosine amplitude weighting is selected, enabling parameterized control of the adversarial jamming signal through the design of perturbation components. Next, the adversarial jamming signal generated by the active jammer is fused with the target’s echo signal according to the principles and actual processes of SAR imaging and is then subjected to imaging processing to produce physically realizable SAR adversarial examples. Finally, the differential evolution algorithm is employed to dynamically adjust parameters, such as the energy distribution and jamming range of the adversarial jamming signal, thereby optimizing the SAR adversarial examples to achieve optimal attack success rates even with minimal interference intensity. Experimental results on the MSTAR dataset, a widely used benchmark in the field of SAR Automatic Target Recognition (ATR), show that the proposed method achieves an average fooling rate of 90.88% and demonstrates superior transferability across five different SAR ATR models, with the highest transfer fooling rate reaching 75.57%. Overall, the proposed method generates more physically realizable adversarial examples compared with existing digital domain methods, effectively protecting specific targets in remote sensing detection and providing guidance for the practical application of active jamming signals in real-world scenarios. -

-
References
[1] SZEGEDY C, ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, et al. Intriguing properties of neural networks[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, Canada, 2014. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1312.6199.[2] 陈岳峰, 毛潇锋, 李裕宏, 等. AI安全—对抗样本技术综述与应用[J]. 信息安全研究, 2019, 5(11): 1000–1007. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1057.2019.11.009.CHEN Yuefeng, MAO Xiaofeng, LI Yuhong, et al. AI security—research and application on adversarial example[J]. Journal of Information Security Research, 2019, 5(11): 1000–1007. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1057.2019.11.009.[3] GOODFELLOW I J, SHLENS J, and SZEGEDY C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1412.6572.[4] CHEN Pinyu, ZHANG Huan, SHARMA Y, et al. ZOO: Zeroth order optimization based black-box attacks to deep neural networks without training substitute models[C]. The 10th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security, Dallas, USA, 2017: 15–26. doi: 10.1145/3128572.3140448.[5] BROWN T B, MANÉ D, ROY A, et al. Adversarial patch[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.09665, 2018.[6] DUAN Ranjie, MA Xingjun, WANG Yisen, et al. Adversarial camouflage: Hiding physical-world attacks with natural styles[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 997–1005. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00108.[7] 阮航, 崔家豪, 毛秀华, 等. SAR目标识别对抗攻击综述: 从数字域迈向物理域[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(6): 1298–1326. doi: 10.12000/JR24142.RUAN Hang, CUI Jiahao, MAO Xiuhua, et al. A survey of adversarial attacks on SAR target recognition: From digital domain to physical domain[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(6): 1298–1326. doi: 10.12000/JR24142.[8] 万烜申, 刘伟, 牛朝阳, 等. 基于动量迭代快速梯度符号的SAR ATR深度神经网络黑盒攻击算法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 714–729. doi: 10.12000/JR23220.WAN Xuanshen, LIU Wei, NIU Chaoyang, et al. Black-box attack algorithm for SAR ATR deep neural networks based on MI-FGSM[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 714–729. doi: 10.12000/JR23220.[9] ZHOU Jie, PENG Bo, XIE Jianyue, et al. Conditional random field-based adversarial attack against SAR target detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4004505. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3365788.[10] DUAN Jiale, QIU Linyao, HE Guangjun, et al. A region-adaptive local perturbation-based method for generating adversarial examples in synthetic aperture radar object detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(6): 997. doi: 10.3390/rs16060997.[11] DANG Xunwang, YAN Hua, HU Liping, et al. SAR image adversarial samples generation based on parametric model[C]. 2021 International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology (ICMMT), Nanjing, China, 2021: 1–3. doi: 10.1109/ICMMT52847.2021.9618140.[12] PENG Bowen, PENG Bo, ZHOU Jie, et al. Scattering model guided adversarial examples for SAR target recognition: Attack and defense[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5236217. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3213305.[13] YE Tian, KANNAN R, PRASANNA V, et al. Realistic scatterer based adversarial attacks on SAR image classifiers[C]. 2023 IEEE International Radar Conference (RADAR), Sydney, Australia, 2023: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR54928.2023.10371090.[14] ZHOU Junfan, FENG Sijia, SUN Hao, et al. Attributed scattering center guided adversarial attack for DCNN SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 4001805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3235051.[15] ZHANG Fan, YU Yameng, MA Fei, et al. A physically realizable adversarial attack method against SAR target recognition model[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 11943–11957. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3420690.[16] LIU Zhe, XIA Weijie, and LEI Yongzhen. SAR-GPA: SAR generation perturbation algorithm[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Advanced Information Science and System, Sanya, China, 2021: 83. doi: 10.1145/3503047.3503136.[17] XIA Weijie, LIU Zhe, and LI Yi. SAR-PeGA: A generation method of adversarial examples for SAR image target recognition network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(2): 1910–1920. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3206261.[18] XIE Jianyue, PENG Bo, LU Zhengzhi, et al. MIGAA: A physical adversarial attack method against SAR recognition models[C]. 2024 9th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), Xi’an, China, 2024: 309–314. doi: 10.1109/ICCCS61882.2024.10602913.[19] CUI Jiahao, GUO Wang, SHAO Run, et al. Physics-oriented adversarial attacks on SAR image target recognition[C]. The Second Workshop on New Frontiers in Adversarial Machine Learning, Honolulu, USA, 2023. https://advml-frontier.github.io/past/icml2023/#award.[20] LUO Binyan, CAO Hang, CUI Jiahao, et al. SAR-PATT: A physical adversarial attack for SAR image automatic target recognition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 17(1): 21. doi: 10.3390/rs17010021.[21] LIU Wei, WAN Xuanshen, NIU Chaoyang, et al. Template-based universal adversarial attack for synthetic aperture radar automatic target recognition network[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2025, 19(1): e12691. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12691.[22] 徐沙, 黄和国, 张夫龙. 反导雷达新进展及有源干扰技术需求分析[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2016, 32(2): 54–57. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2016.02.015.XU Sha, HUANG Heguo, and ZHANG Fulong. New progress in anti-missile radar and active jamming techniques requirement[J]. Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2016, 32(2): 54–57. doi: 10.16328/j.htdz8511.2016.02.015.[23] FRANCESCHETTI G, MIGLIACCIO M, RICCIO D, et al. SARAS: A synthetic aperture radar (SAR) raw signal simulator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 30(1): 110–123. doi: 10.1109/36.124221.[24] 张皓宇, 邢世其. SAR有源干扰对抗仿真软件设计与实现[J]. 舰船电子对抗, 2023, 46(6): 102–110, 120. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2023.06.019.ZHANG Haoyu and XING Shiqi. Design and implementation of active jamming countermeasure simulation software to SAR[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeasure, 2023, 46(6): 102–110, 120. doi: 10.16426/j.cnki.jcdzdk.2023.06.019.[25] 王雪松, 刘建成, 张文明, 等. 间歇采样转发干扰的数学原理[J]. 中国科学E辑: 信息科学, 2006, 36(8): 891–901. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7259.2006.08.007.WANG Xuesong, LIU Jiancheng, ZHANG Wenming, et al. Mathematical principles of intermittent sampling repeater jamming[J]. Science in China Ser. E Information Sciences, 2006, 36(8): 891–901. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7259.2006.08.007.[26] 吴晓芳, 代大海, 王雪松, 等. 基于微动调制的SAR新型有源干扰方法[J]. 电子学报, 2010, 38(4): 954–959.WU Xiaofang, DAI Dahai, WANG Xuesong, et al. A novel method of active jamming for SAR based on micro motion modulation[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 38(4): 954–959.[27] 胡东辉, 吴一戎. 合成孔径雷达散射波干扰研究[J]. 电子学报, 2002, 30(12): 1882–1884. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2002.12.040.HU Donghui and WU Yirong. The scatter-wave jamming to SAR[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2002, 30(12): 1882–1884. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2002.12.040.[28] 王宏艳, 降佳伟, 蒲娟, 等. 基于余弦幅度加权的低旁瓣多相位分段调制干扰方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43(11): 3185–3193. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.18.WANG Hongyan, JIANG Jiawei, PU Juan, et al. Multiple phases sectionalized modulation jamming method with low sidelobe based on cosine amplitude weighting[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(11): 3185–3193. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.11.18.[29] 伊志勇, 王鸿. 复杂电磁环境下雷达有源干扰机的设计与实现[J]. 应用科技, 2017, 44(2): 84–88. doi: 10.11991/yykj.201608013.YI Zhiyong and WANG Hong. Design and implementation of radar active jammer in complex electromagnetic environment[J]. Computing Magazine of the CCF, 2017, 44(2): 84–88. doi: 10.11991/yykj.201608013.[30] 汪丙南, 张帆, 向茂生. 基于混合域的SAR回波快速算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(3): 690–695. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00555.WANG Bingnan, ZHANG Fan, and XIANG Maosheng. SAR raw signal fast algorithm in mixed domain[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2011, 33(3): 690–695. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00555.[31] 金啸宇, 尹嫱, 倪军, 等. 一种基于场景合成和锚点约束的SAR目标检测网络[J]. 南京信息工程大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 12(2): 210–215. doi: 10.13878/j.cnki.jnuist.2020.02.008.JIN Xiaoyu, YIN Qiang, NI Jun, et al. SAR target detection network based on scenario synthesis and anchor constraint[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 12(2): 210–215. doi: 10.13878/j.cnki.jnuist.2020.02.008.[32] STORN R and PRICE K. Differential evolution—a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces[J]. Journal of Global Optimization, 1997, 11(4): 341–359. doi: 10.1023/A:1008202821328.[33] ZHANG Fan, MENG Tianying, XIANG Deliang, et al. Adversarial deception against SAR target recognition network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 4507–4520. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3179171.[34] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1409.1556.[35] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90.[36] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.06993, 2018.[37] MEHTA S and RASTEGARI M. MobileViT: Light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer[C]. The 10th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2022. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2110.02178.[38] LIU Ze, LIN Yutong, CAO Yue, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9992–10002. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00986.[39] MOOSAVI-DEZFOOLI S M, FAWZI A, and FROSSARD P. DeepFool: A simple and accurate method to fool deep neural networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2574–2582. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.282.[40] CROCE F and HEIN M. Reliable evaluation of adversarial robustness with an ensemble of diverse parameter-free attacks[C]. The 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2020: 2206–2216. https://icml.cc/Conferences/2020.[41] LI Haifeng, HUANG Haikuo, CHEN Li, et al. Adversarial examples for CNN-based SAR image classification: An experience study[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 1333–1347. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3038683. -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. Attack flows of different SAR adversarial attack methods
- Figure 2. Algorithmic flow of the proposed method
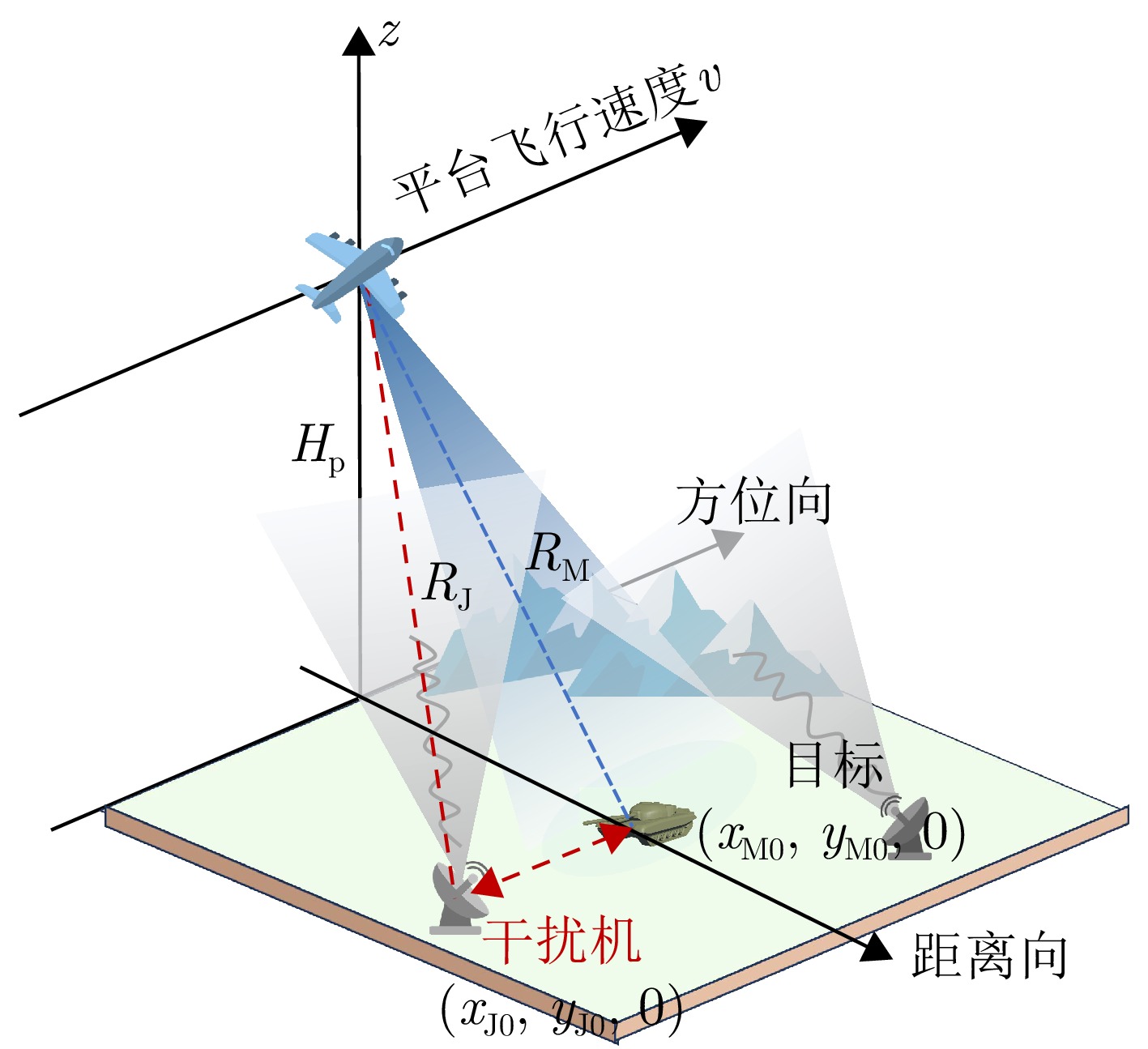
- Figure 3. Schematic of the working principle and geometric relationship for SAR system and active jammer
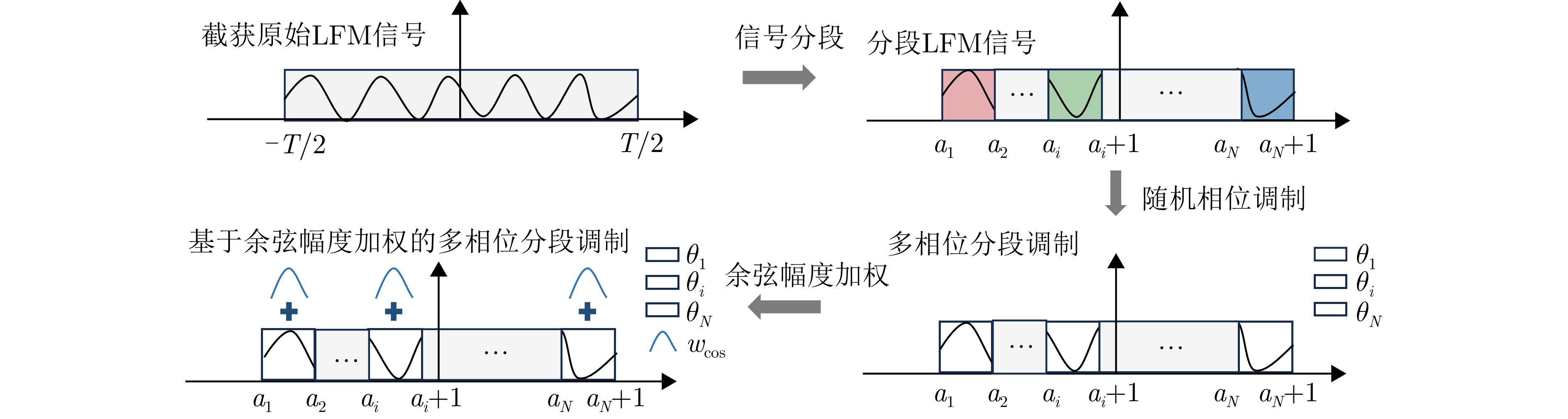
- Figure 4. Schematic of the generation of a multiple phase sectionalized modulation jamming signal based on cosine amplitude weighting
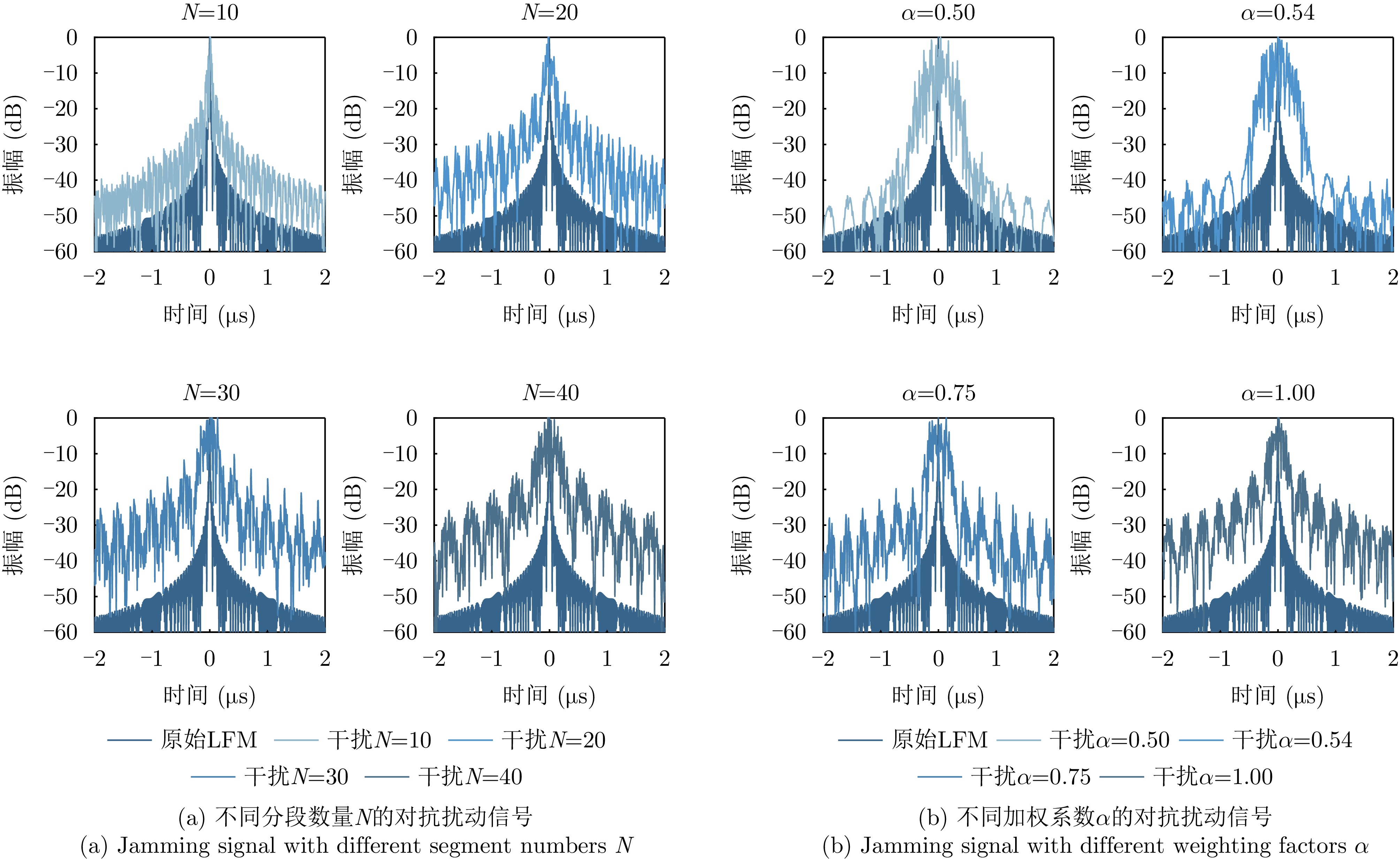
- Figure 5. Simulation results of the jamming signal under different parameters
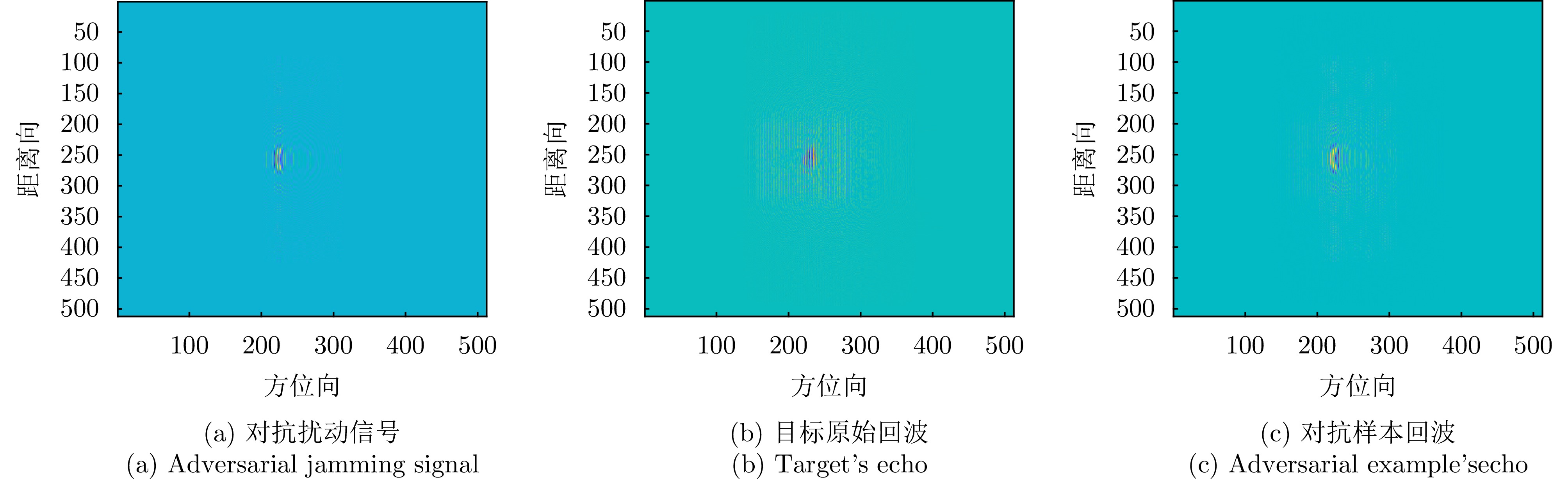
- Figure 6. Simulation results of the echo data
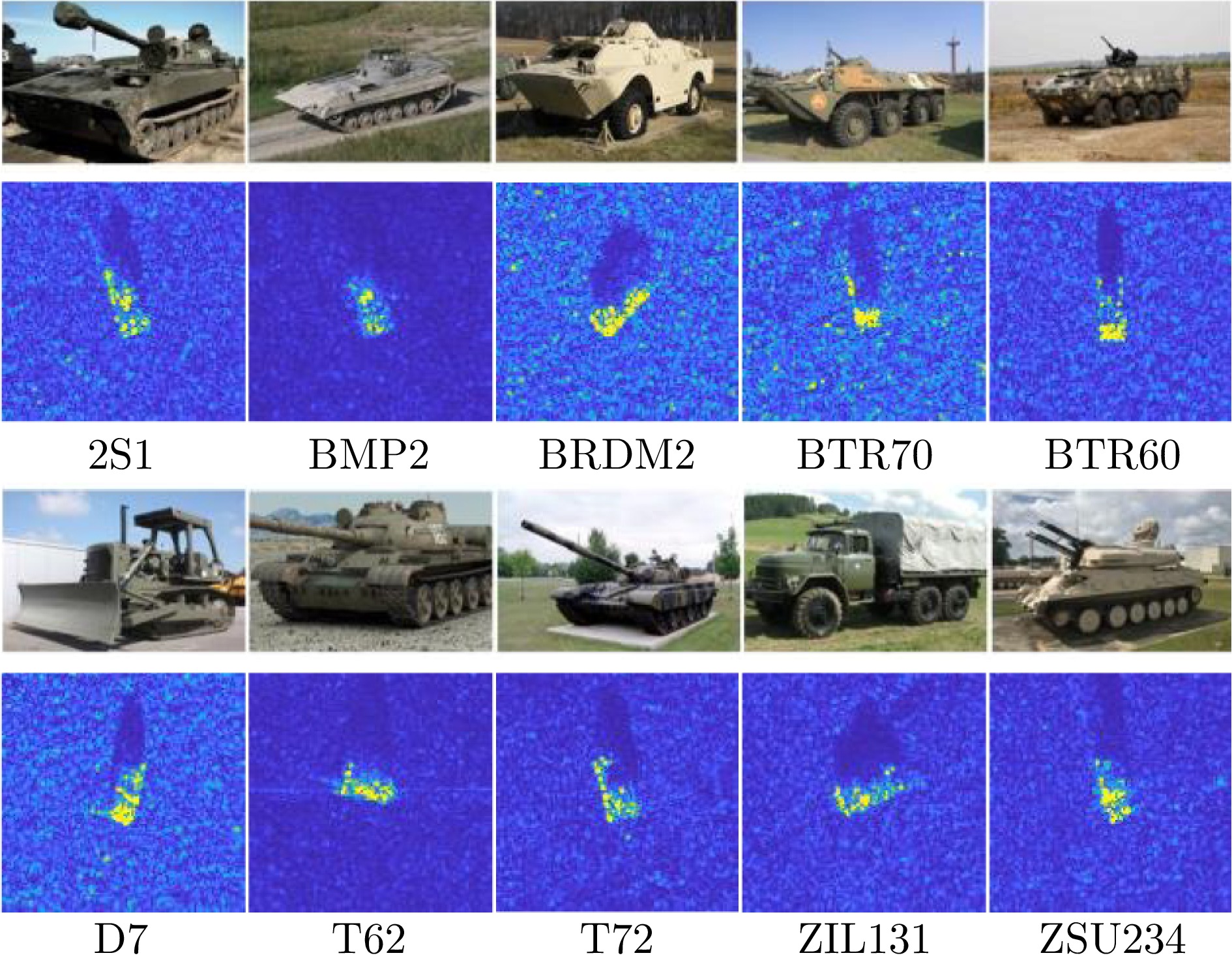
- Figure 7. Optical vs. SAR comparison of ten ground vehicle target types in the MSTAR dataset
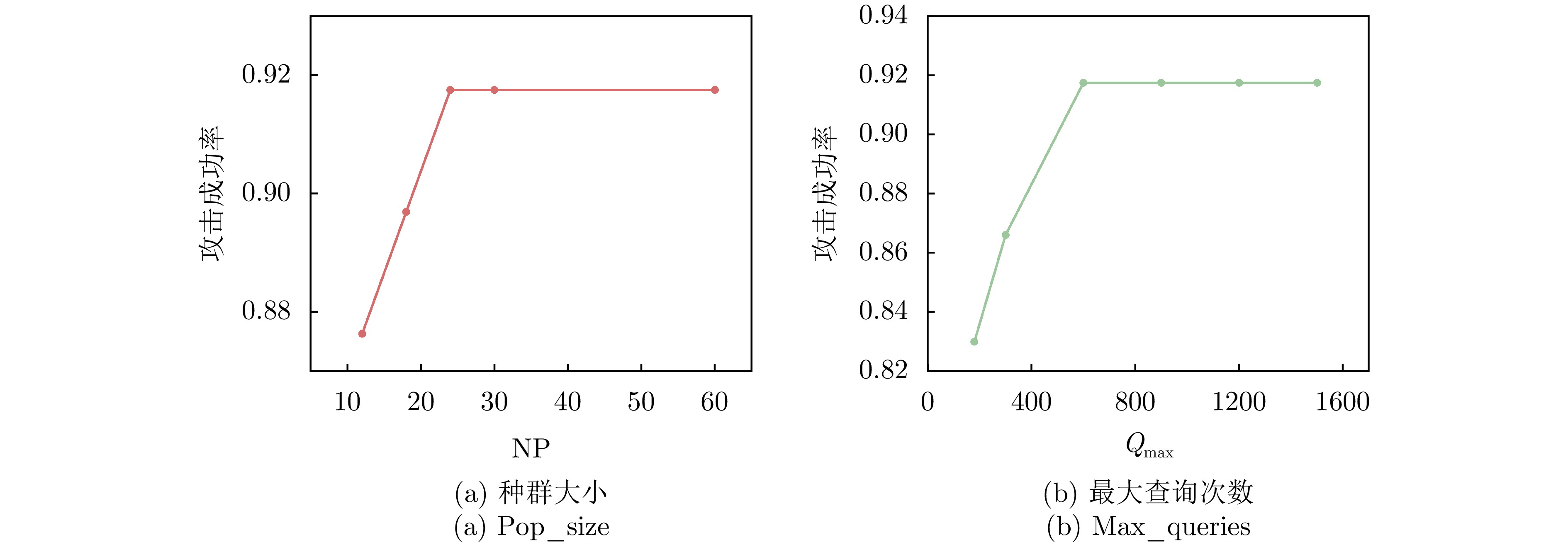
- Figure 8. Fooling rate under different hyperparameters
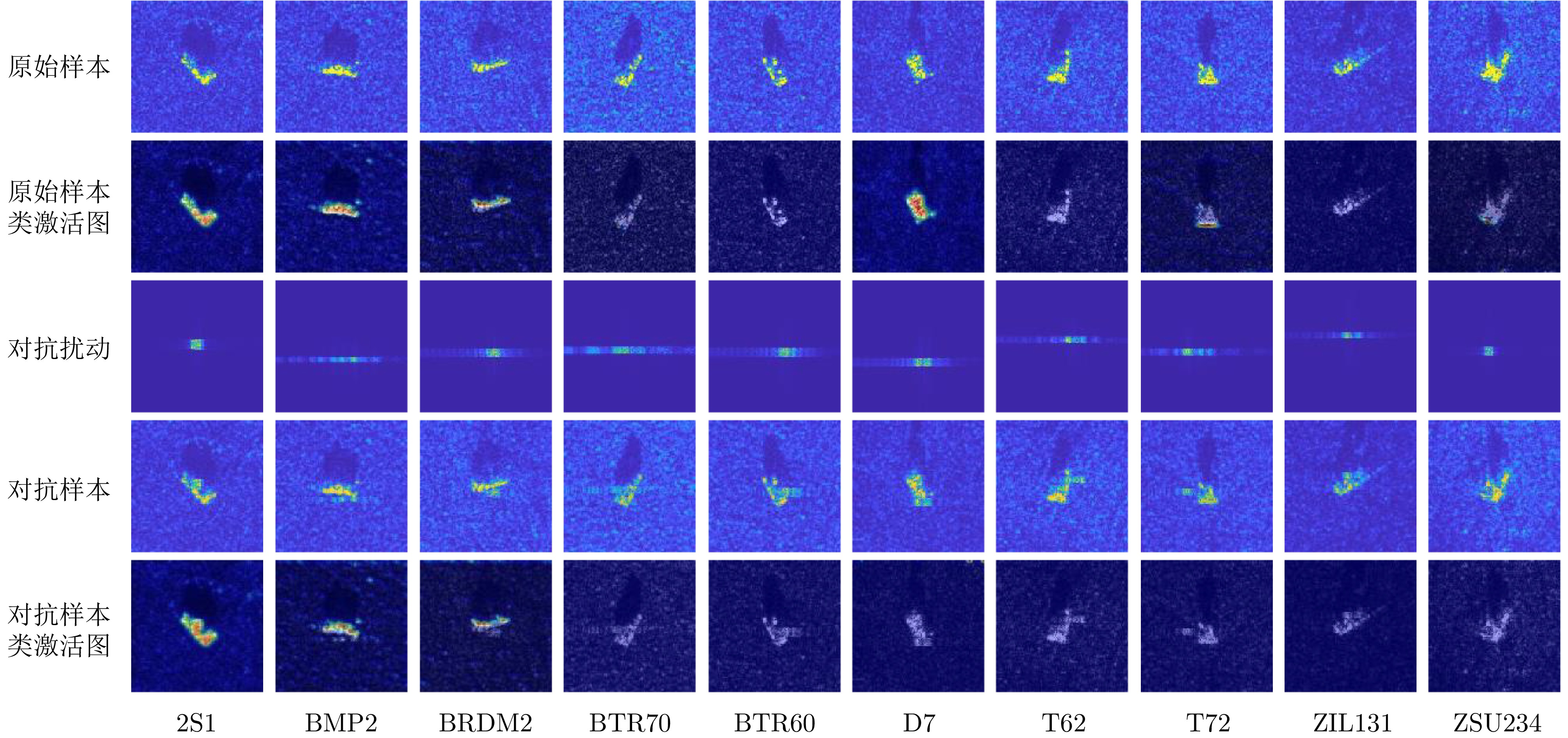
- Figure 9. Generated SAR adversarial examples and Grad-CAM visualization analysis
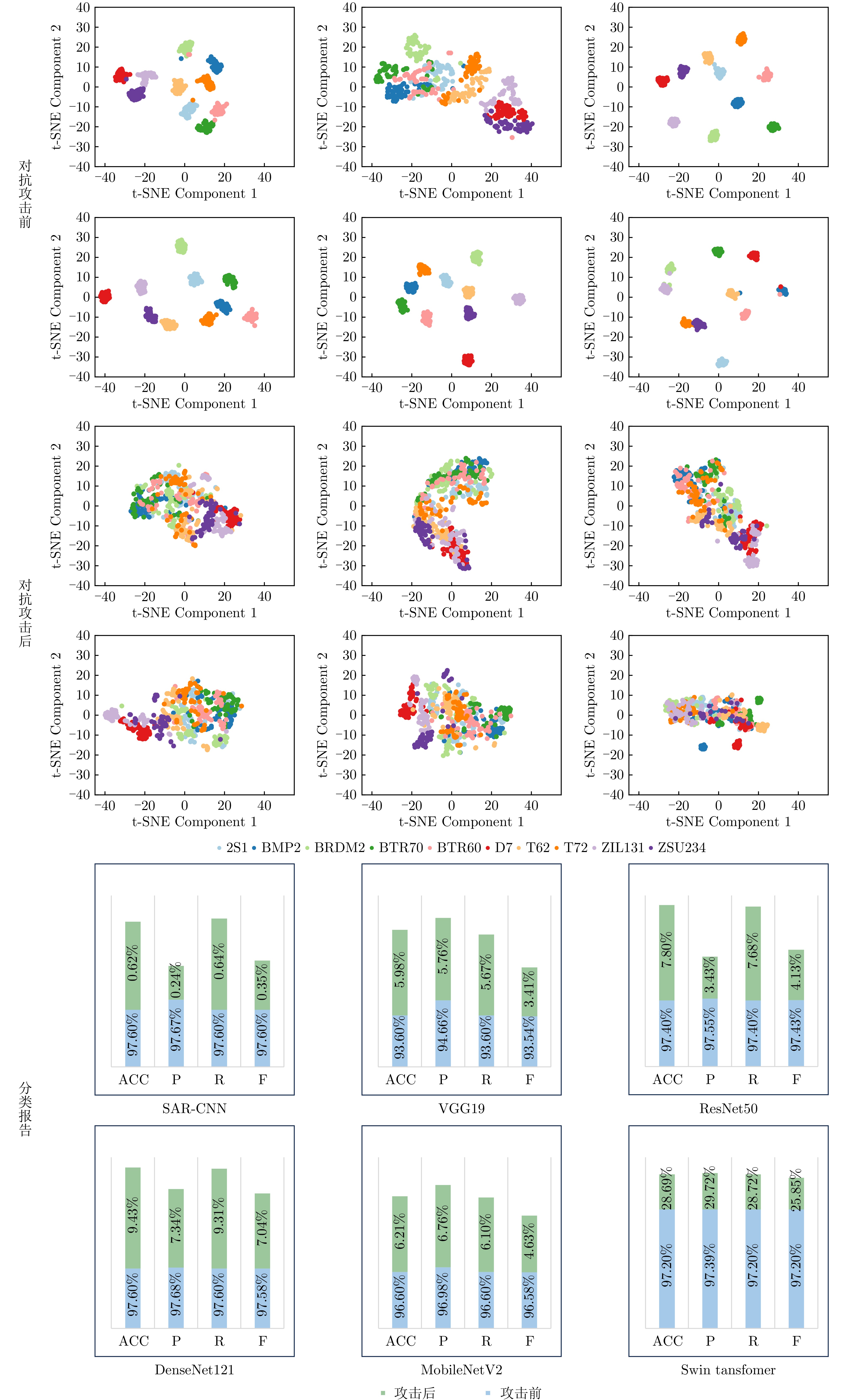
- Figure 10. Attack results of the proposed method on different SAR ATR models
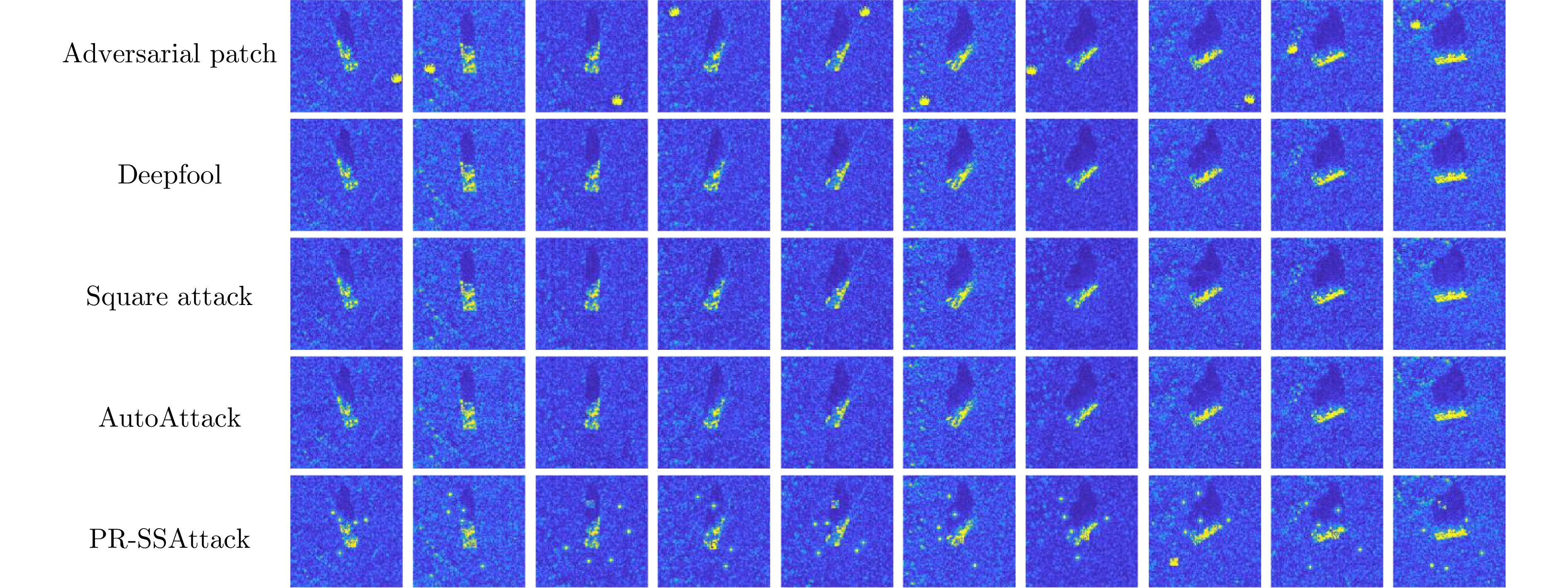
- Figure 11. Adversarial samples generated by different adversarial attack methods
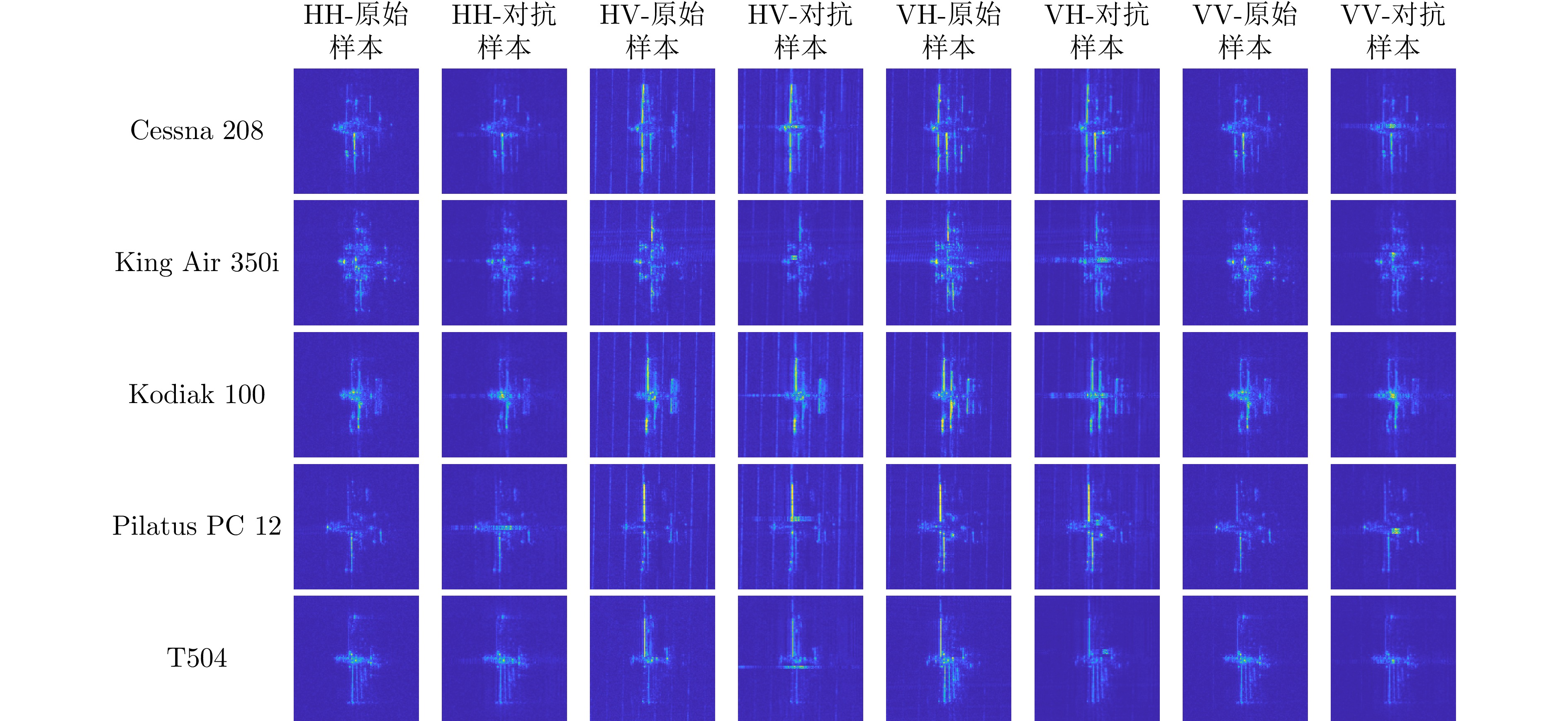
- Figure 12. Original and adversarial samples of targets under different polarizations
- Figure 13. Transferability of adversarial examples generated by different attack methods
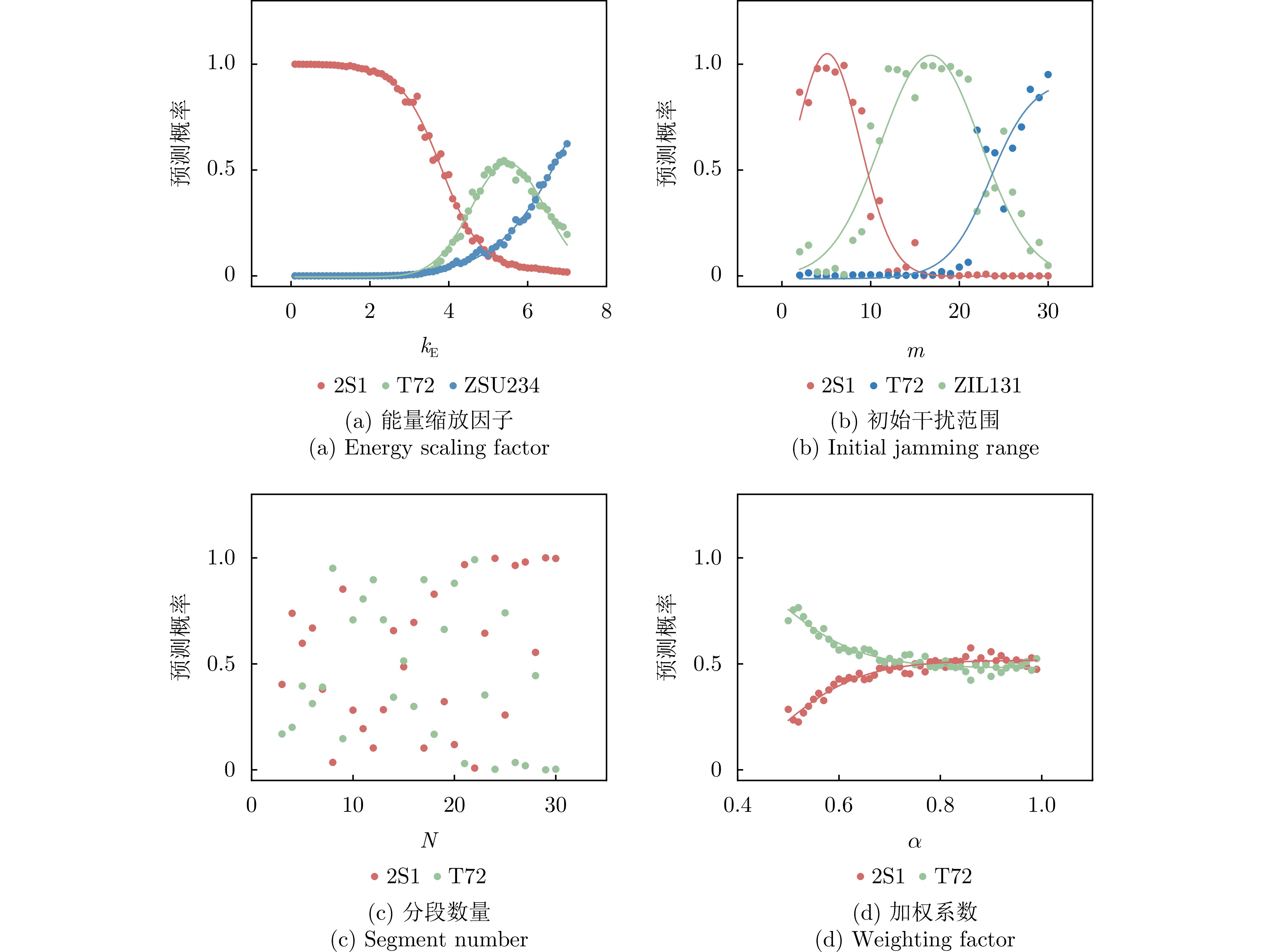
- Figure 14. Curves of prediction probability variations for individual classes under different parameters
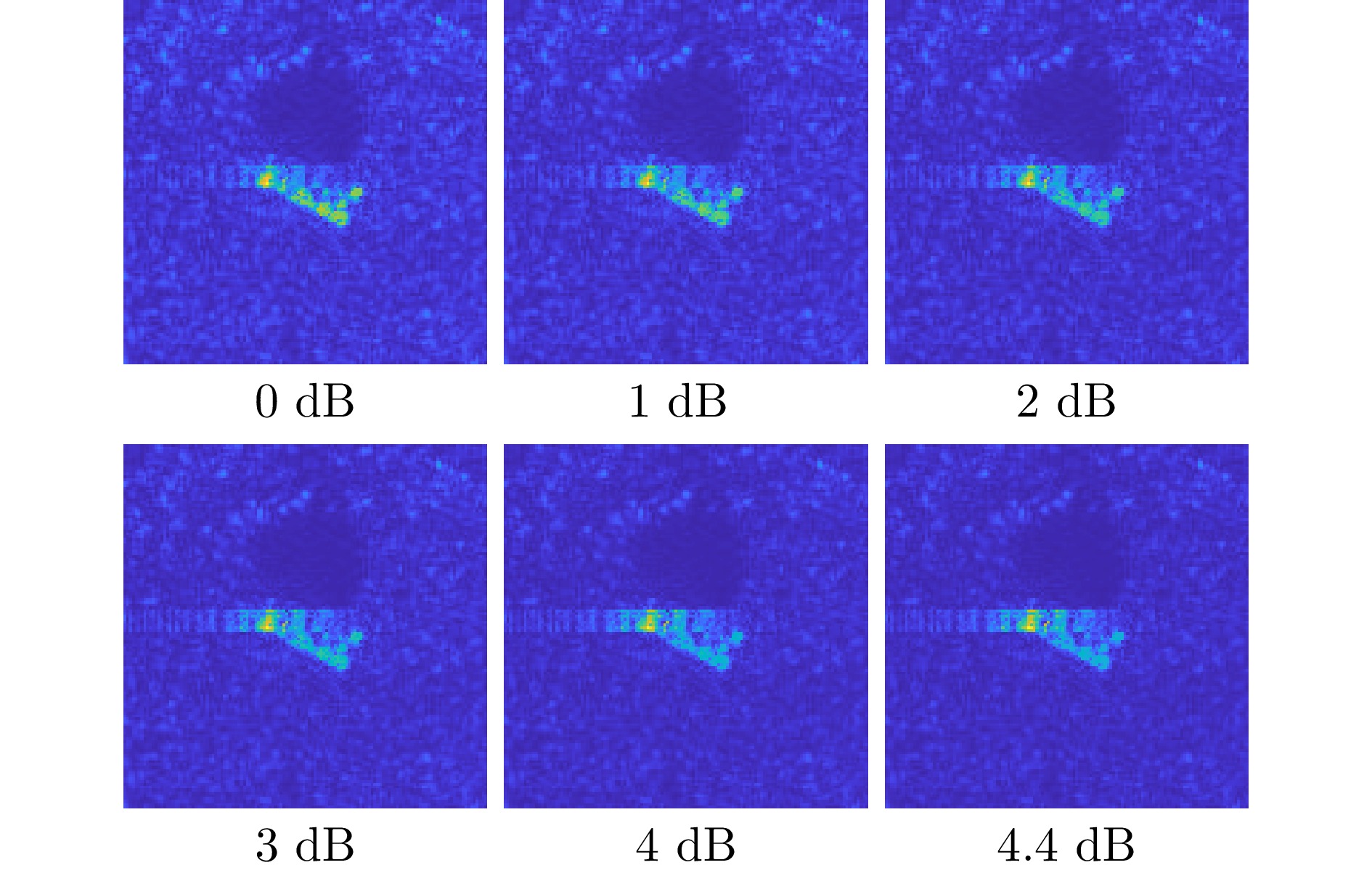
- Figure 15. 2S1 adversarial examples under different energy scaling factor
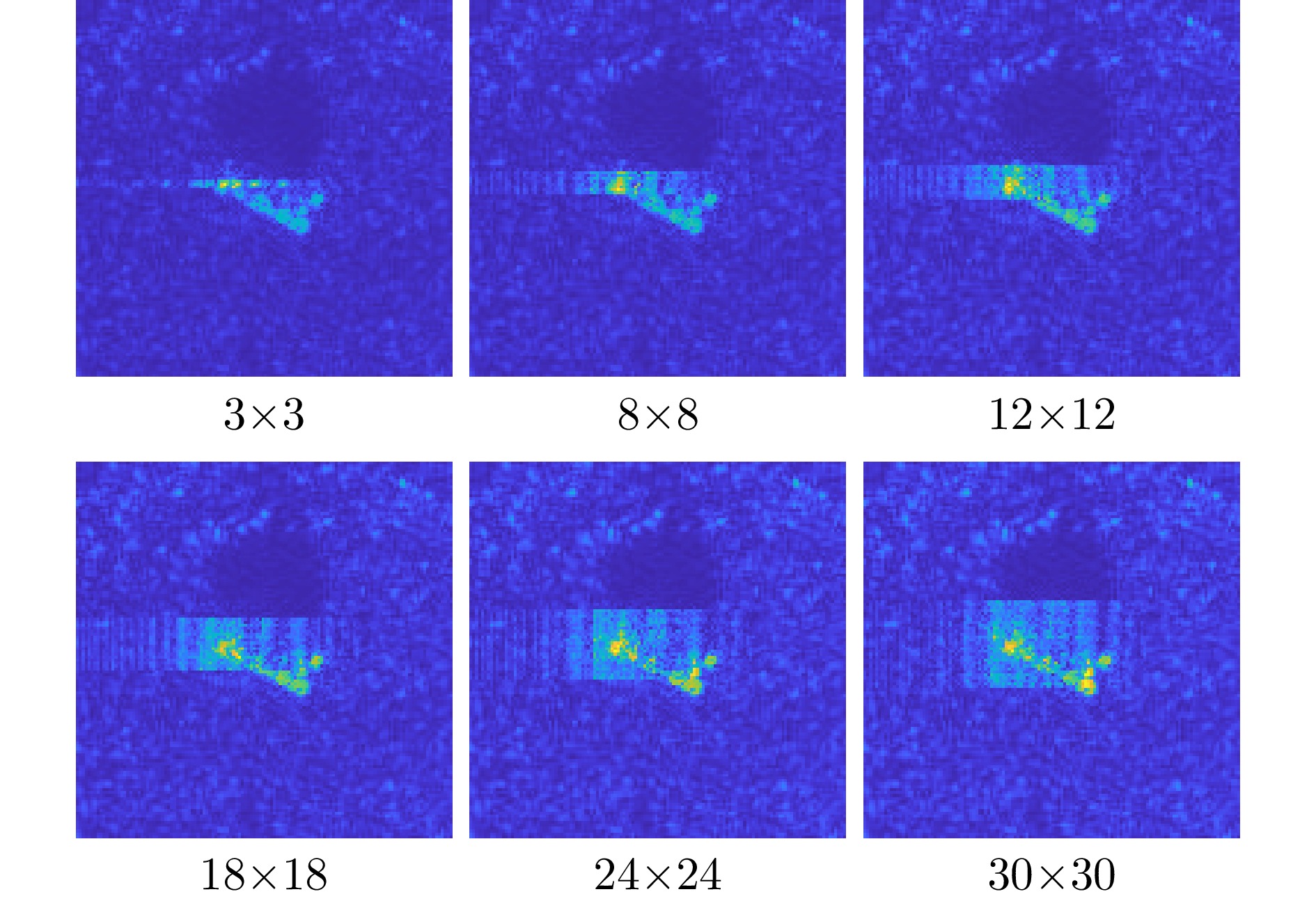
- Figure 16. 2S1 adversarial examples under different initial jamming range
- Figure 17. 2S1 adversarial examples under different multi-segment phase vectors
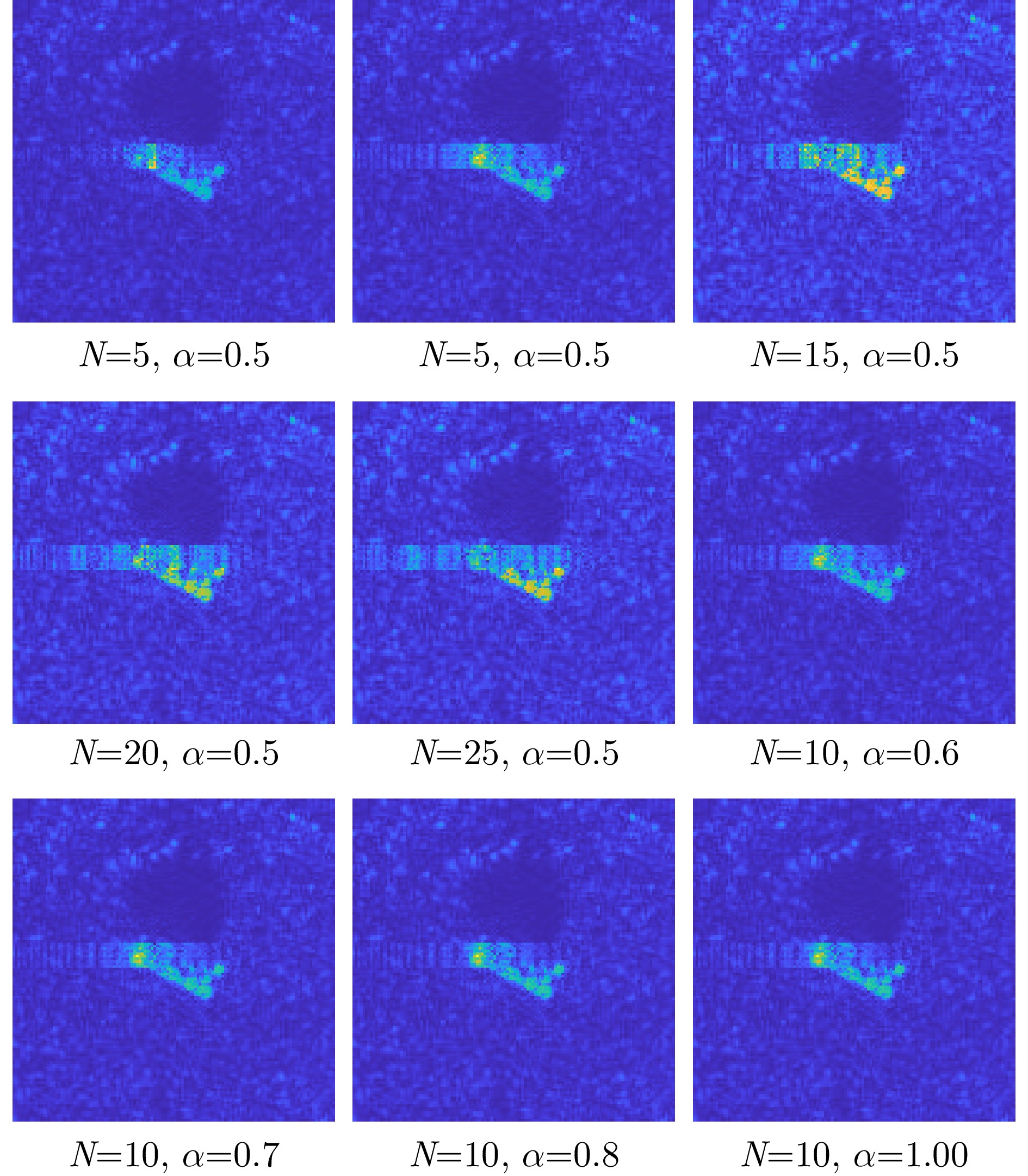
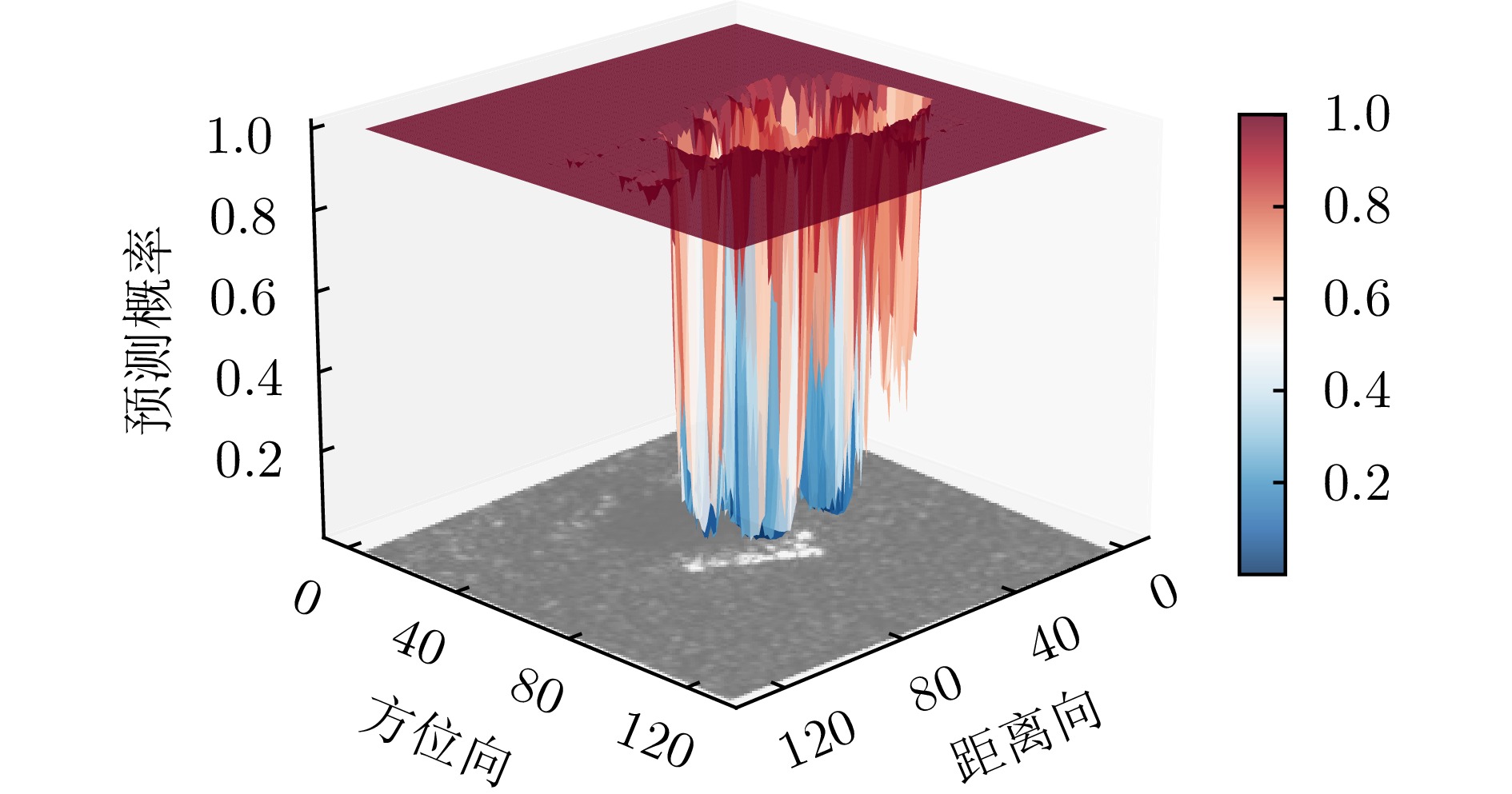
- Figure 18. Plot of prediction probability variations for the 2S1 target under different positional offsets
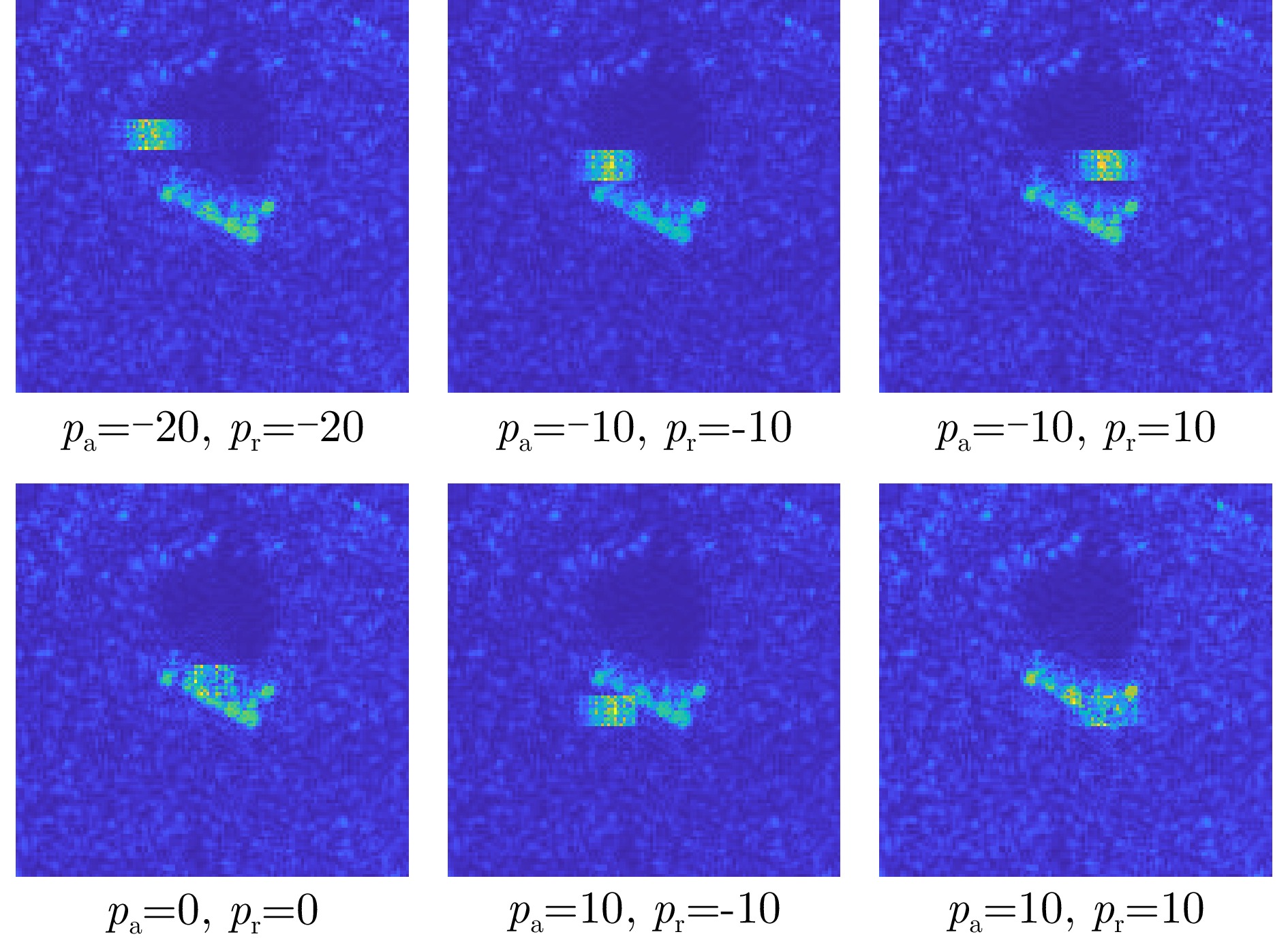
- Figure 19. 2S1 adversarial examples under different positional offsets
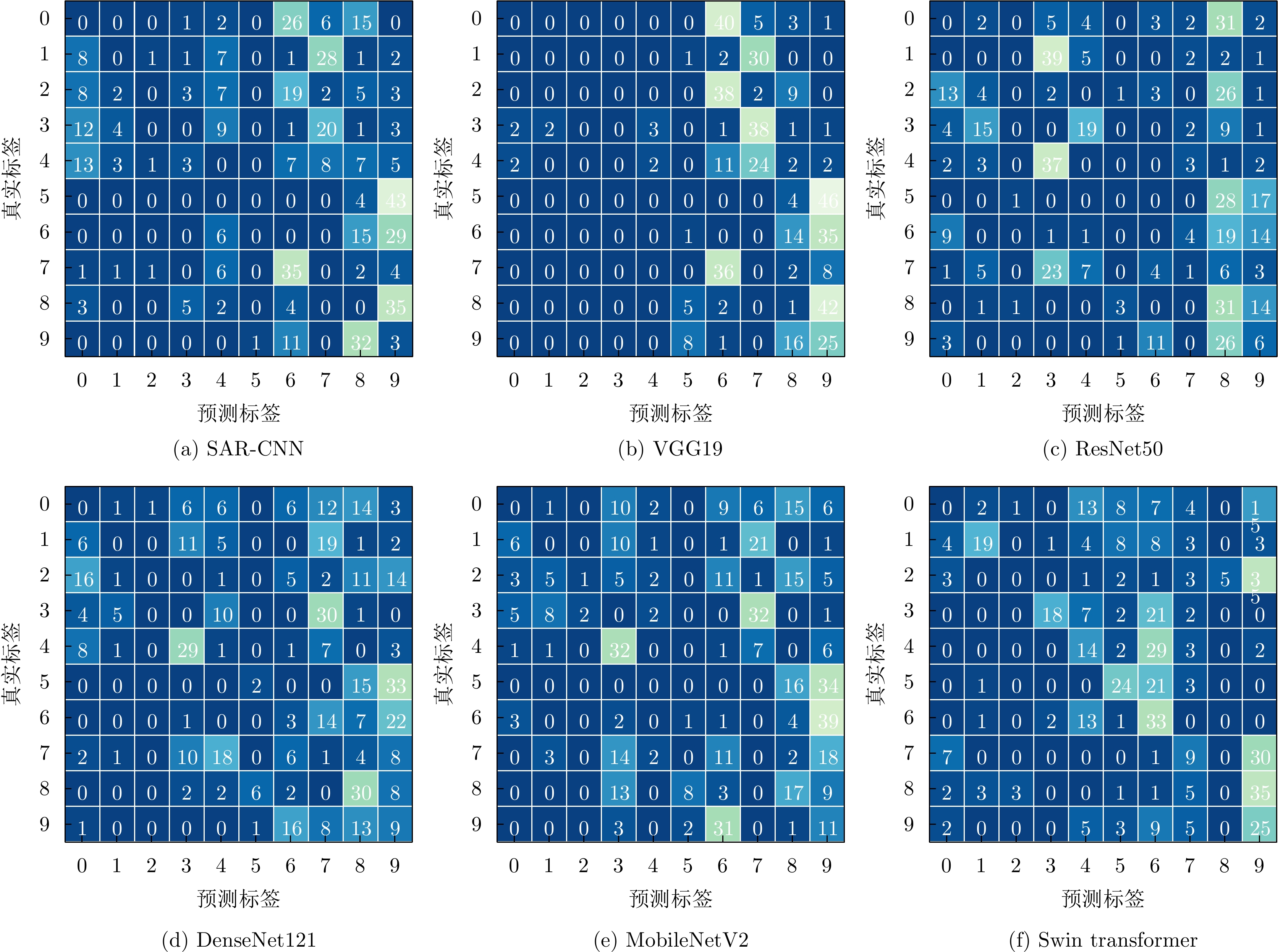
- Figure 20. Classification confusion matrices for different SAR ATR models


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: