- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2025
> Online First
| Citation: | XIONG Junlong, WANG Zhen, HUANG Yuchen, et al. Adaptive multifocus correlation filter with Bayesian fusion for maritime radar target tracking[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25106 |
Adaptive Multifocus Correlation Filter with Bayesian Fusion for Maritime Radar Target Tracking
DOI: 10.12000/JR25106 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25106
More Information-
Abstract
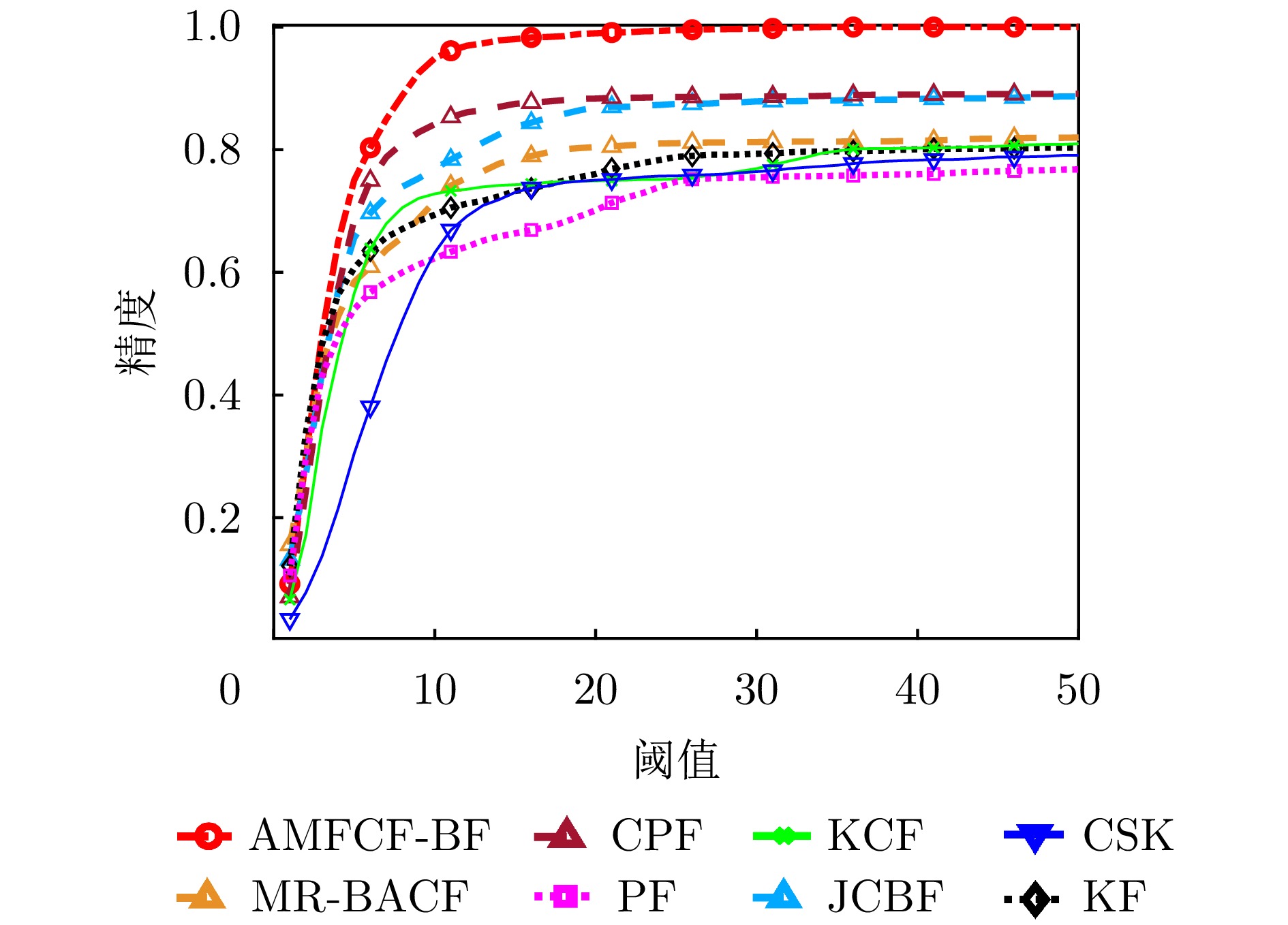
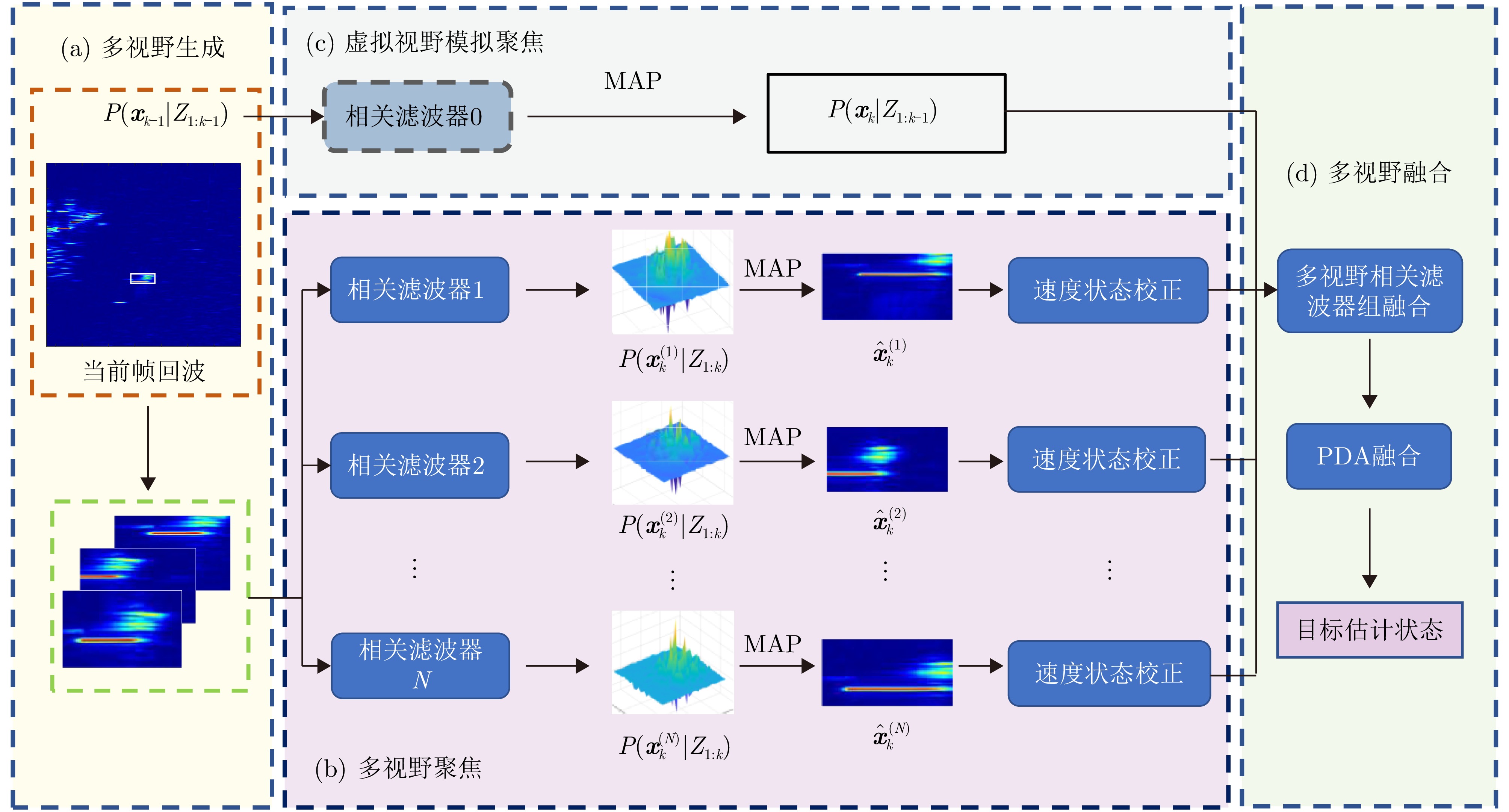
This study addresses the critical challenge of radar target tracking in complex maritime environments. Although conventional feature-aided Bayesian tracking methods have advanced in maritime radar applications, their robustness considerably deteriorates in scenarios with severe sea clutter and interacting targets. To overcome these limitations, an Adaptive Multifocus Correlation Filter with Bayesian Fusion (AMFCF-BF) is proposed herein. The method constructs multiple subviews within the probabilistic distribution of the target state, with each subview assigned an independent correlation filter to generate a local response map, enabling multihypothesis state modeling. During iterative tracking, these response maps are used to estimate states and dynamically guide the focusing of subviews toward high-confidence regions, enhancing adaptability to complex target maneuvers. To further mitigate false alarms and missed detections caused by strong sea clutter, a virtual-view simulation based focusing model is developed, which effectively suppresses filter drift under adverse conditions. Finally, all subview responses are fused within a Bayesian multimeasurement framework to produce a globally consistent target-state estimate. Experimental results using simulated and real maritime radar data demonstrate that the proposed AMFCF-BF achieves an average center location error of 3.47 pixels, reducing tracking error by ~70% compared with typical feature-assisted correlation filtering methods. In terms of location precision, the proposed filter achieves an overall improvement of ~21%, showing significantly enhanced tracking accuracy and anti-interference performance, validating the effectiveness of the multifocus correlation filtering mechanism and Bayesian fusion strategy. -

-
References
[1] KIM D Y, RISTIC B, GUAN R, et al. A Bernoulli track-before-detect filter for interacting targets in maritime radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(3): 1981–1991. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3054715.[2] 关键. 雷达海上目标特性综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 674–683. doi: 10.12000/JR20114.GUAN Jian. Summary of marine radar target characteristics[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 674–683. doi: 10.12000/JR20114.[3] 柳超, 王月基. 对海探测雷达多目标跟踪技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 10(1): 100–115. doi: 10.12000/JR20081.LIU Chao and WANG Yueji. Review of multi-target tracking technology for marine radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 100–115. doi: 10.12000/JR20081.[4] LI Yangfan, WANG Nan, LI Wei, et al. Object tracking in satellite videos with distractor–occlusion-aware correlation particle filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5605412. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3353298.[5] WARD K, TOUGH R, and WATTS S. Sea Clutter: Scattering, the K Distribution and Radar Performance[M]. 2nd ed. London: The Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2013. doi: 10.1049/PBRA025E.[6] 许述文, 白晓惠, 郭子薰, 等. 海杂波背景下雷达目标特征检测方法的现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084.XU Shuwen, BAI Xiaohui, GUO Zixun, et al. Status and prospects of feature-based detection methods for floating targets on the sea surface[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084.[7] VIVONE G, BRACA P, and ERRASTI-ALCALA B. Extended target tracking applied to X-band marine radar data[C]. OCEANS 2015 – Genova, Genova, Italy, 2015: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/OCEANS-Genova.2015.7271630.[8] GRANSTRÖM K and BAUM M. A tutorial on multiple extended object tracking[J]. TechRxiv, 2022, in press. doi: 10.36227/techrxiv.19115858.v1.[9] MANNARI P, THARMARASA R, and KIRUBARAJAN T. Extended target tracking under multitarget tracking framework for convex polytope shapes[J]. Signal Processing, 2024, 217: 109321. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2023.109321.[10] 陈辉, 边斌超, 连峰, 等. 基于Transformer复杂运动辨识的机动星凸形扩展目标跟踪方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 629–645. doi: 10.12000/JR24031.CHEN Hui, BIAN Binchao, LIAN Feng, et al. A novel method for tracking complex maneuvering star convex extended targets using Transformer network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 629–645. doi: 10.12000/JR24031.[11] BAR-SHALOM B Y, WILLETT P K, and TIAN Xin. Tracking and Data Fusion: A Handbook of Algorithms[M]. Storrs: Yaakov Bar-Shalom, 2011.[12] KOCH J W. Bayesian approach to extended object and cluster tracking using random matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(3): 1042–1059. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4655362.[13] FELDMANN M, FRÄNKEN D, and KOCH W. Tracking of extended objects and group targets using random matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(4): 1409–1420. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2101064.[14] ERRASTI-ALCALA B, FUSCALDO W, BRACA P, et al. Realistic extended target model for track before detect in maritime surveillance[C]. OCEANS 2015-Genova, Genova, Italy, 2015: 1–9. doi: 10.1109/OCEANS-Genova.2015.7271624.[15] ZEA A, FAION F, BAUM M, et al. Level-set random hypersurface models for tracking nonconvex extended objects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace & Electronic Systems, 2017, 52(6): 2990–3007. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.130704.[16] VIVONE G, BRACA P, GRANSTROM K, et al. Converted measurements Bayesian extended target tracking applied to X-band marine radar data[J]. Journal of Advances in Information Fusion (JAIF), 2016, 12(2): 189–210.[17] 柳超, 孙进平, 陈小龙, 等. 结合幅度信息的扩展目标随机有限集跟踪方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 730–738. doi: 10.12000/JR19071.LIU Chao, SUN Jinping, CHEN Xiaolong, et al. Random finite set-based extended target tracking method with amplitude information[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 730–738. doi: 10.12000/JR19071.[18] GRANSTROM K, BAUM M, and REUTER S. Extended object tracking: Introduction, overview and applications[J]. Journal of Advances in Information Fusion, 2017, 12(2): 139–174. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1604.00970.[19] LERRO D and BAR-SHALOM Y. Automated tracking with target amplitude information[C]. 1990 American Control Conference, San Diego, USA, 1990: 2875–2880. doi: 10.23919/ACC.1990.4791244.[20] KIM D and HWANG I. Dynamic model-based feature aided data association filter in target tracking[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(2): 279–289. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2019.0381.[21] ZHU Yingpei, WANG Zhen, YIN Yupei, et al. Feature-aided multi-target tracking method in sea clutter using scanning radar data[C]. 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, Nanjing, China, 2021: 615–619. doi: 10.1109/ICSIP52628.2021.9688716.[22] BOLME D S, BEVERIDGE J R, DRAPER B A, et al. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters[C]. 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, USA, 2010: 2544–2550. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2010.5539960.[23] YUAN Di, CHANG Xiaojun, LI Zhihui, et al. Learning adaptive spatial-temporal context-aware correlation filters for UAV tracking[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), 2022, 18(3): 70. doi: 10.1145/3486678.[24] DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, SHAHBAZ KHAN F, et al. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4310–4318. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.4900.[25] KUMAR A, VOHRA R, JAIN R, et al. Correlation filter based single object tracking: A review[J]. Information Fusion, 2024, 112: 102562. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102562.[26] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583–596. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345390.[27] ZHOU Yi, WANG Tian, HU Ronghua, et al. Multiple kernelized correlation filters (MKCF) for extended object tracking using X-band marine radar data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(14): 3676–3688. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2917812.[28] ZHOU Yi, SU Hang, TIAN Shuai, et al. Multiple-kernelized-correlation-filter-based track-before-detect algorithm for tracking weak and extended target in marine radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 3411–3426. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3150262.[29] LIU Jiaqi, WANG Zhen, CHENG Di, et al. Marine extended target tracking for scanning radar data using correlation filter and Bayes filter jointly[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(23): 5937. doi: 10.3390/rs14235937.[30] ZHANG Tianzhu, LIU Si, XU Changsheng, et al. Correlation particle filter for visual tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(6): 2676–2687. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2781304.[31] GORDON N J and SALMOND D J. Novel approach to nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian state estimation[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Radar and Signal Processing), 1993, 40(2): 107–113. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1993.0015.[32] ARULAMPALAM M S, MASKELL S, GORDON N, et al. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(2): 174–188. doi: 10.1109/78.978374.[33] REID D. An algorithm for tracking multiple targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1979, 24(6): 843–854. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1979.1102177.[34] BLACKMAN S S. Multiple hypothesis tracking for multiple target tracking[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2004, 19(1): 5–18. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2004.1263228.[35] BAR-SHALOM Y. Tracking methods in a multitarget environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1978, 23(4): 618–626. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1978.1101790.[36] MUSICKI D, EVANS R, and STANKOVIC S. Integrated probabilistic data association (IPDA)[C]. 31st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Tucson, USA, 1992: 3796–3798. doi: 10.1109/CDC.1992.370951.[37] CARPENTER J, CLIFFORD P, and FEARNHEAD P. Improved particle filter for nonlinear problems[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1999, 146(1): 2–7. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19990255.[38] DE VLIEGER J H and MEYLING R H J G. Maximum likelihood estimation for long-range target tracking using passive sonar measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1992, 40(5): 1216–1225. doi: 10.1109/78.134483.[39] ZHANG Xudong, LI Hongbin, and HIMED B. Maximum likelihood delay and Doppler estimation for passive sensing[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(1): 180–188. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2875664.[40] MUSICKI D, EVANS R, and STANKOVIC S. Integrated probabilistic data association[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1994, 39(6): 1237–1241. doi: 10.1109/9.293185.[41] YUAN Xinru, LIU Jiaqi, CHENG Di, et al. Motion-regularized background-aware correlation filter for marine radar target tracking[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 3504705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3276790.[42] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels[C]. 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 2012: 702–715. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33765-9_50.[43] KALMAN R E. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems[J]. Journal of Basic Engineering, 1960, 82(1): 35–45. doi: 10.1115/1.3662552.[44] DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2005.177.[45] 刘宁波, 董云龙, 王国庆, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089.LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, WANG Guoqing, et al. Sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 656–667. doi: 10.12000/JR19089.[46] 陈小龙, 何肖阳, 邓振华, 等. 雷达微弱目标智能化处理技术与应用[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 501–524. doi: 10.12000/JR23160.CHEN Xiaolong, HE Xiaoyang, DENG Zhenhua, et al. Radar intelligent processing technology and application for weak target[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 501–524. doi: 10.12000/JR23160.[47] RISTIC B, VO B N, CLARK D, et al. A metric for performance evaluation of multi-target tracking algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(7): 3452–3457. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2140111.[48] WANG Zhen, LIU Jiaqi, YUAN Xinru, et al. A dynamic model-based Doppler-adaptive correlation filter for maritime radar target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5101415. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3346998. -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. Pipeline of the proposed tracking framework
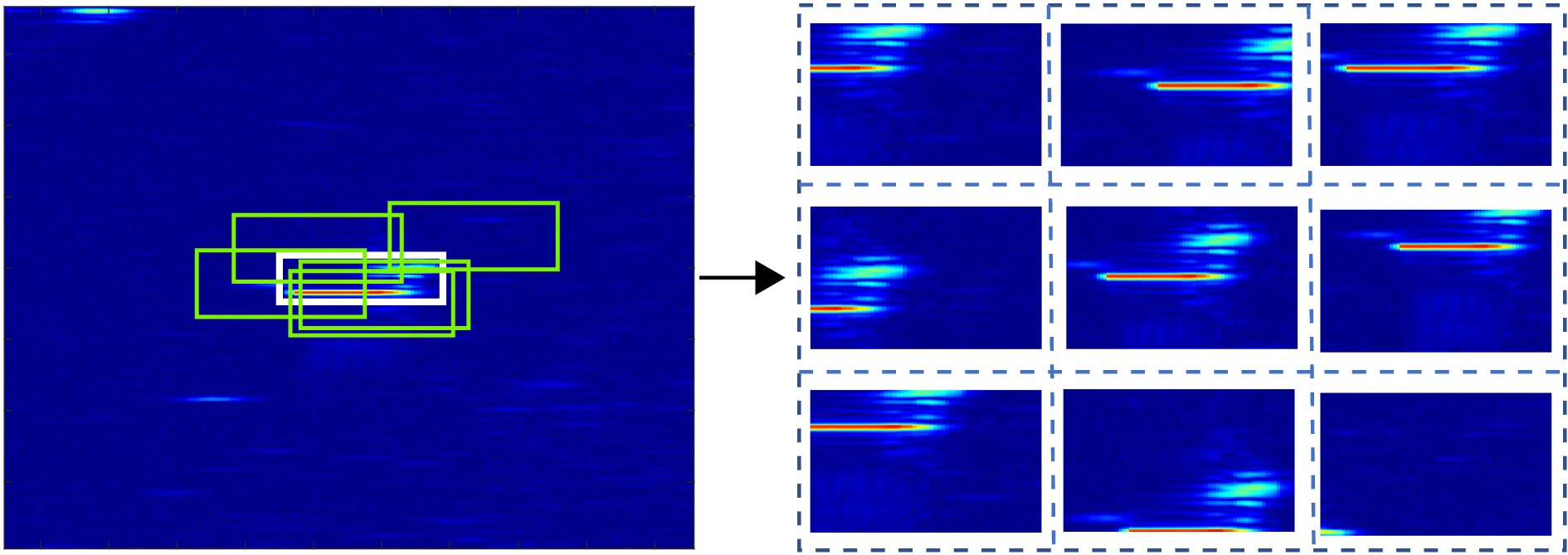
- Figure 2. Multiple view generation
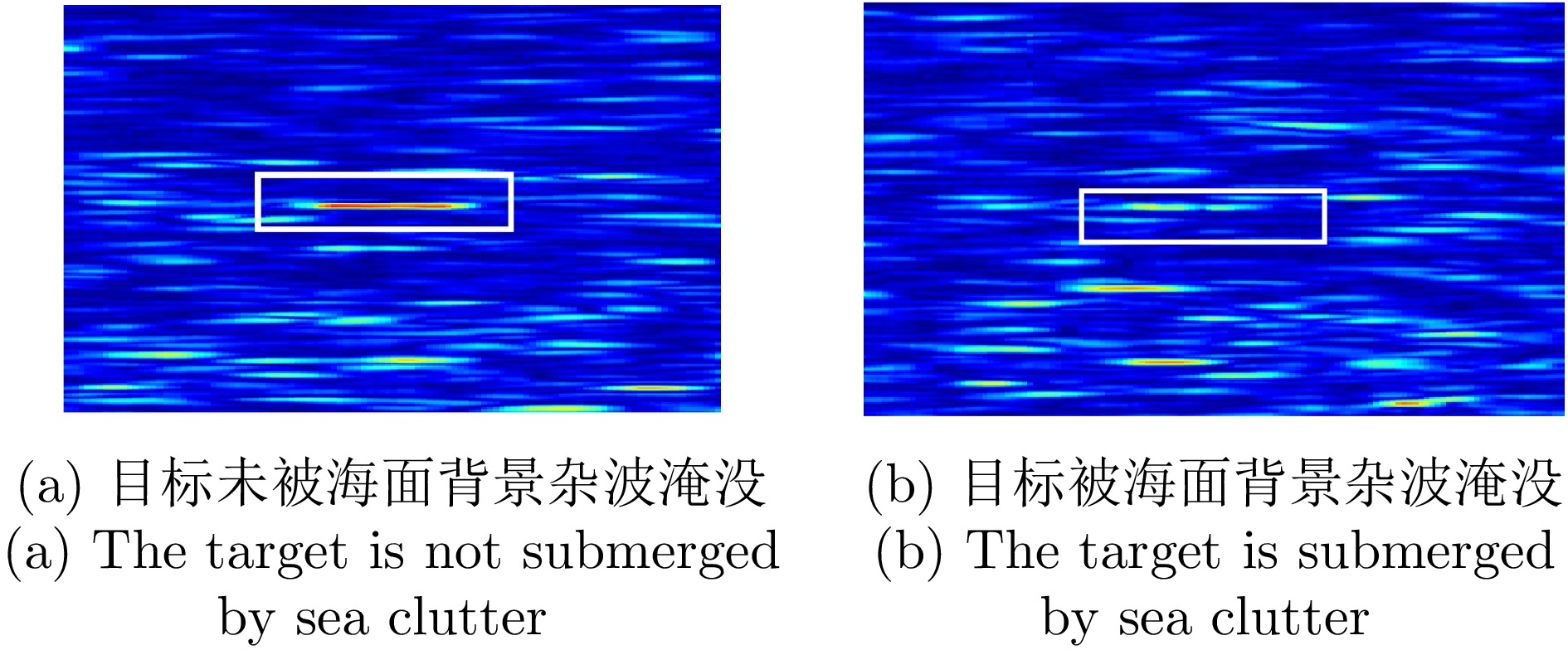
- Figure 3. Illustration of the target submerged by background clutter on the sea surface
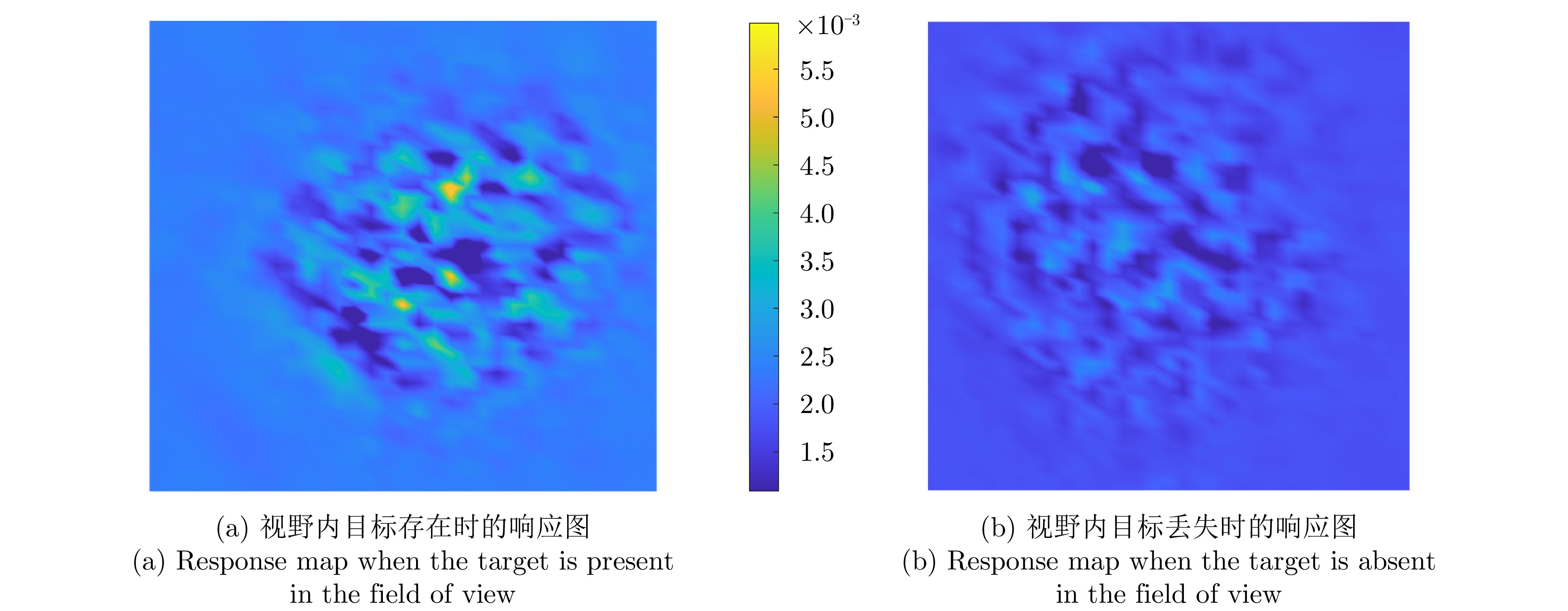
- Figure 4. Response map for target presence or absence in the field of view
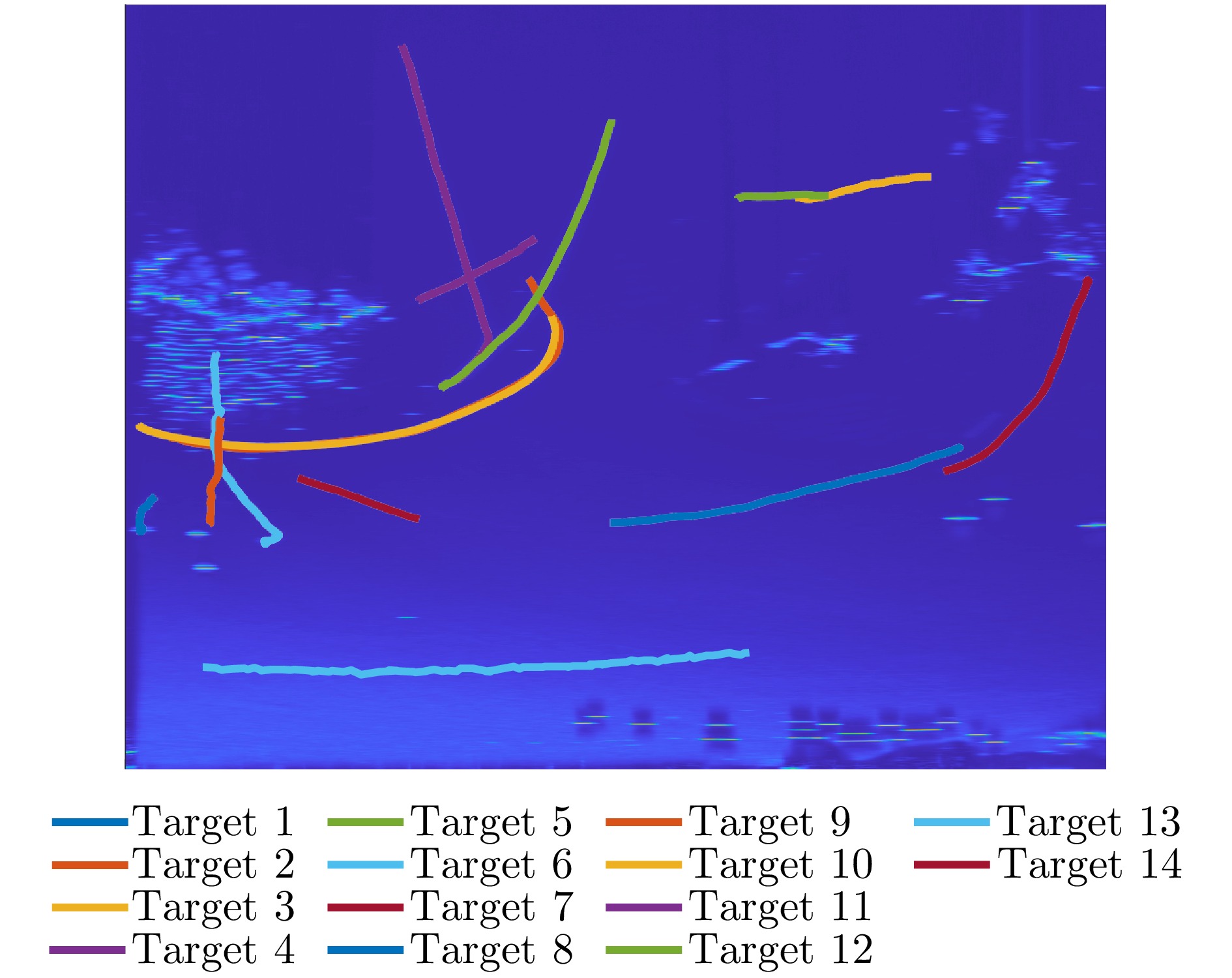
- Figure 5. The processed trajectories of the 14 targets in the dataset
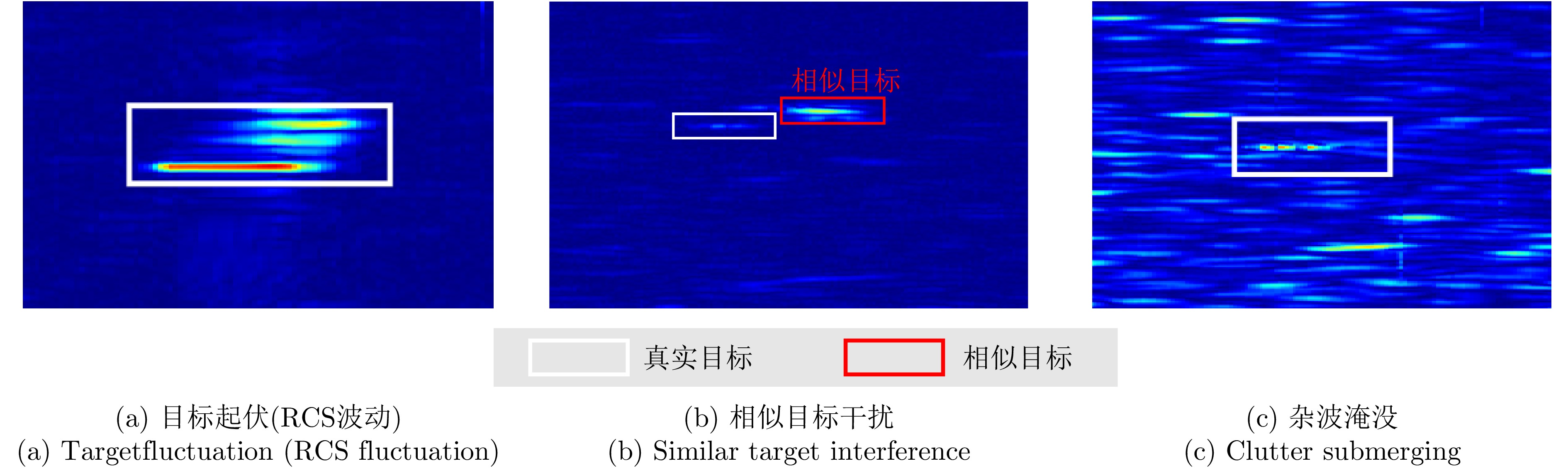
- Figure 6. The target trackers in this dataset primarily confront three typical challenging scenarios
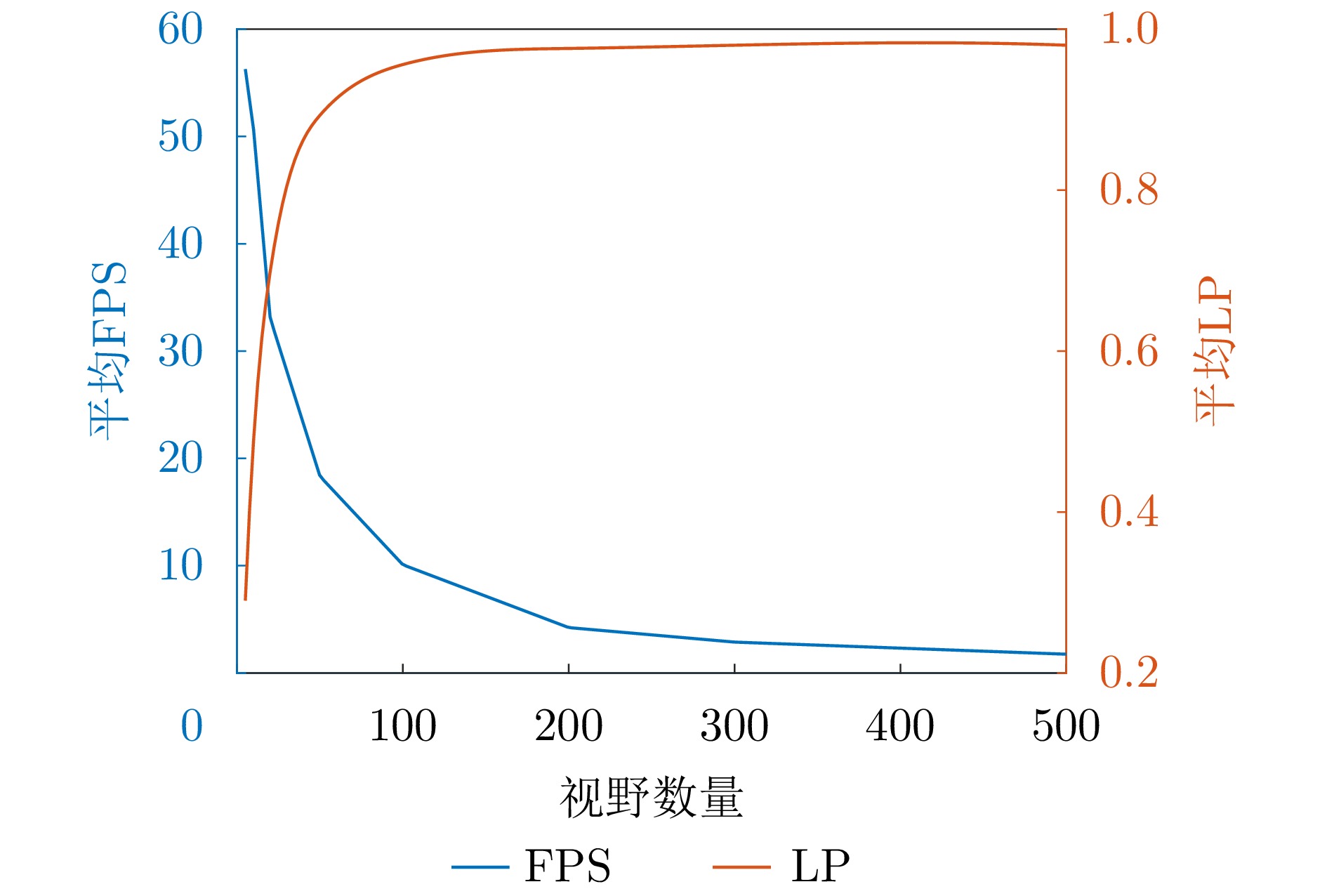
- Figure 7. LP accuracy versus FPS of the number of views
- Figure 8. Multiframe accumulation images of two simulated scenarios
-
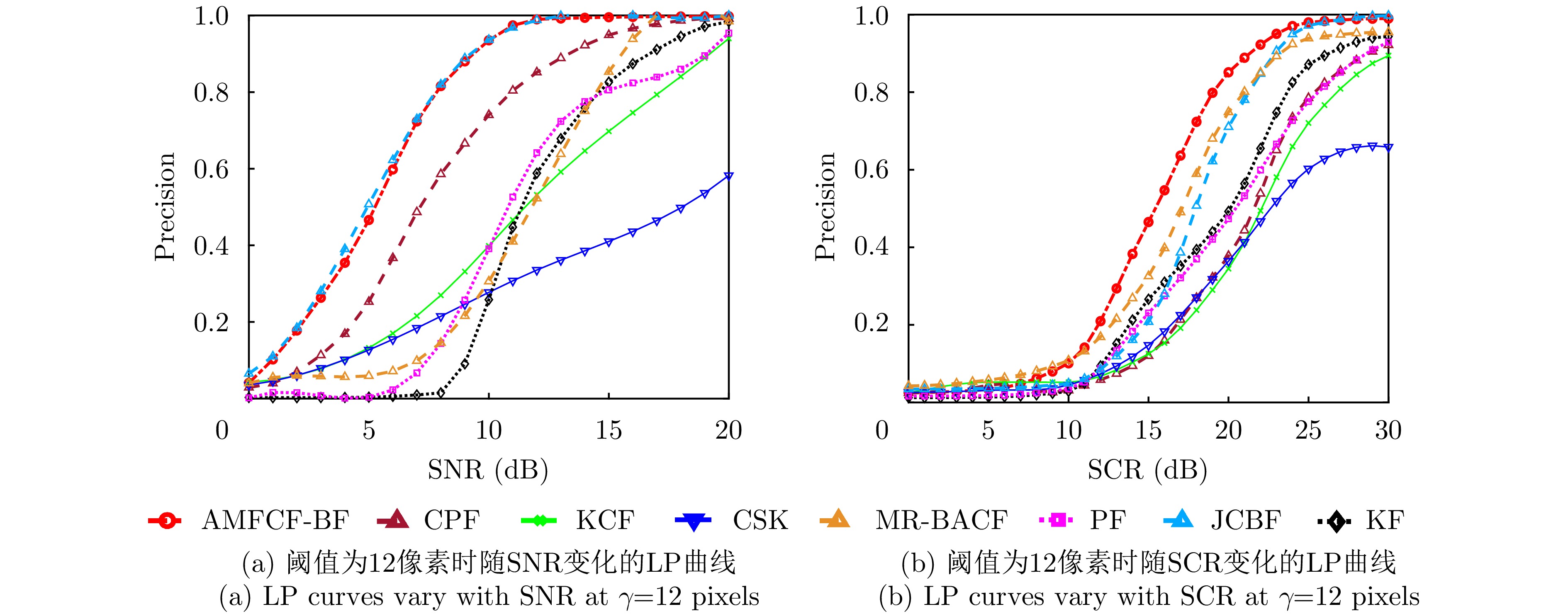
Figure 9. LP curves on the simulated dataset at
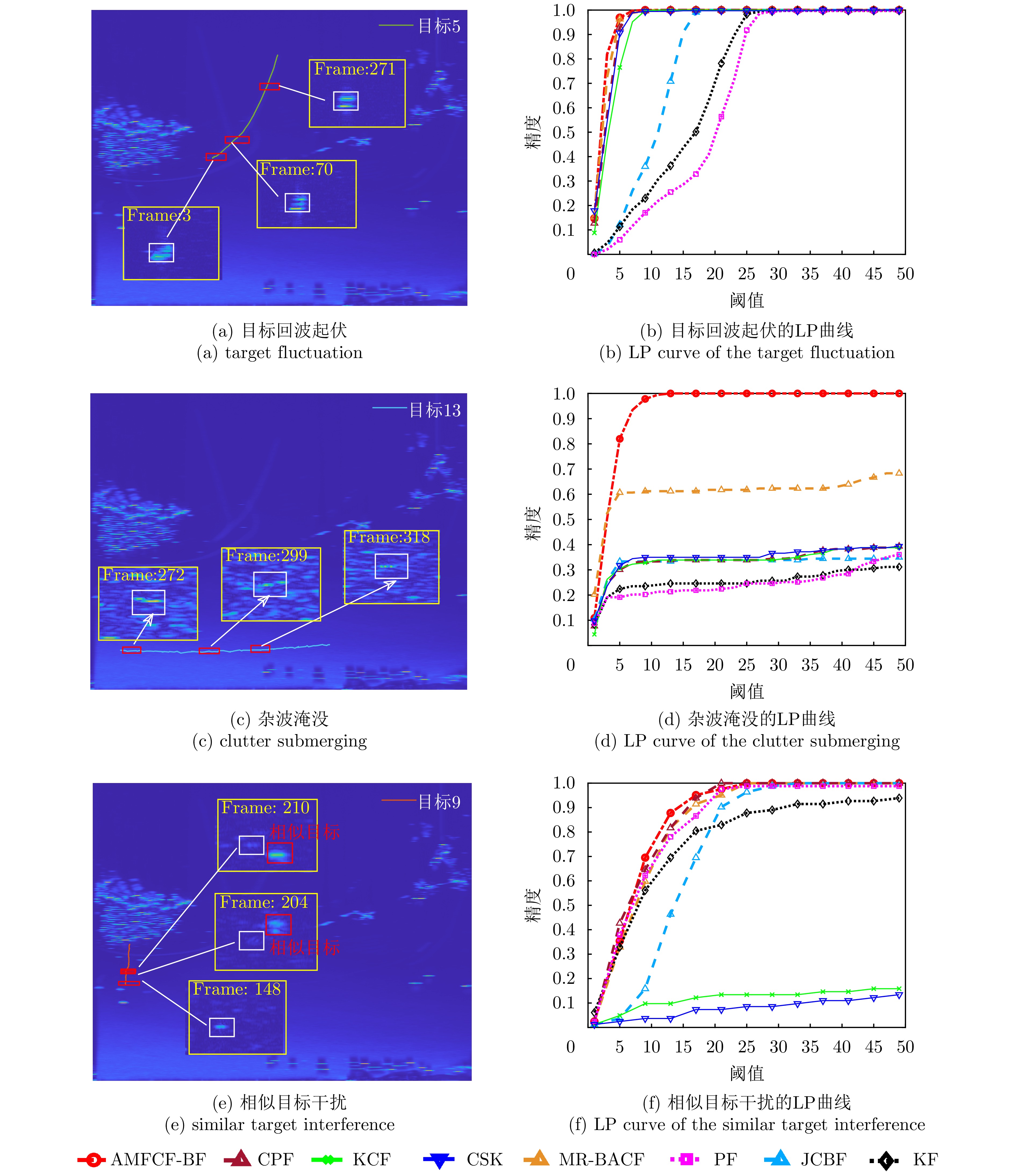
$\gamma $ - Figure 10. The tracking scenarios and LP curves of various types of targets in the measured data
- Figure 11. The average LP curve of all targets in the measured dataset


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: