- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2025
> Online First
| Citation: | ZHANG Fan, MENG Fanle, MA Fei, et al. Multi-temporal polarimetric synthetic aperture radar salt field regional classification based on dominant scattering temporal entropy[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25087 |
Multi-temporal Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar Salt Field Regional Classification Based on Dominant Scattering Temporal Entropy
DOI: 10.12000/JR25087 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25087
More Information-
Abstract
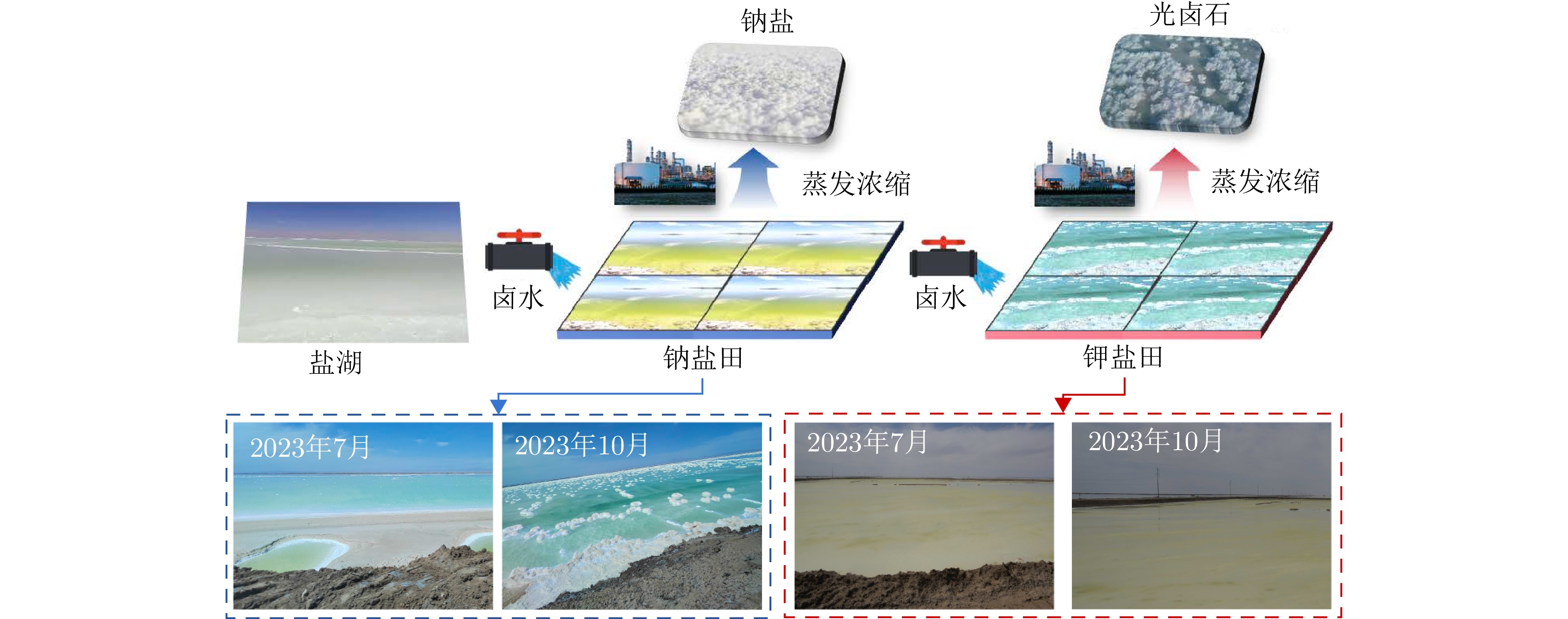
Salt lakes, rich in potassium and lithium mineral resources, are typically mined using the salt field crystallization method. Specifically, brine is first moved to sodium salt fields where sodium salts crystallize, and then it is moved to potassium salt fields for the precipitation of potassium salts. Determining the type of salt field is essential for accurately estimating salt production and ensuring efficient mining operations. Because different types of salt fields exhibit different salt precipitation rates, they also produce distinct variations in scattering intensity that can be observed in multi-temporal Polarimetric Synthetic Aperture Radar (PolSAR) data. To explore this property, this study proposes a salt field classification method based on multi-temporal PolSAR. First, to accurately characterize the long-term scattering variations in salt fields, a new multi-temporal polarization feature, i.e., dominant scattering temporal entropy, is introduced. The main scattering mechanism of the target area is extracted from the polarimetric covariance matrix, from which the temporal correlation between any two PolSAR images is calculated to construct a temporal correlation matrix. The principal change direction and magnitude of scattering variation in land cover across the time series are then obtained from the temporal correlation matrix through diagonalization, and entropy is used to quantify change intensity and provide an accurate measure of cumulative change. Second, this study demonstrates that the dominant scattering temporal entropy follows the Gaussian distribution, enabling the design of a classifier based on Chernoff distance. Classification is performed by comparing the Chernoff distance of entropy probability distributions within superpixels. The proposed method achieves overall classification accuracies of 84.13% and 86.13% on the Qarhan Salt Lake and Dead Sea Sentinel-1 datasets, respectively, representing an improvement of about 10% over existing time-series PolSAR methods. The classification results exhibit superior spatial consistency and noise robustness compared with other methods. -

-
References
[1] 张苏江, 张琳, 姜爱玲, 等. 中国盐湖资源开发利用现状与发展建议[J]. 无机盐工业, 2022, 54(10): 13–21. doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2022-0425.ZHANG Sujiang, ZHANG Lin, JIANG Ailing, et al. Current situation and development suggestions of development and utilization of Salt Lake resources in China[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(10): 13–21. doi: 10.19964/j.issn.1006-4990.2022-0425.[2] 韩积斌, 许建新, 安朝, 等. 盐湖地下卤水的开采技术及其展望[J]. 盐湖研究, 2015, 23(1): 67–72. doi: 10.12119/j.yhyj.201501010.HAN Jibin, XU Jianxin, AN Zhao, et al. Research advance of the Salt Lake underground brine extraction technology[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2015, 23(1): 67–72. doi: 10.12119/j.yhyj.201501010.[3] 陈奥. 基于遥感技术的盐湖资源开发行为对柴达木盆地盐湖区景观变化的影响评估[D]. [硕士论文], 中国科学院大学(中国科学院青海盐湖研究所), 2018.CHEN Ao. Evaluation of resources exploitation to landscape variation of Salt Lake area in Qaidam Basin by remote sensing[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2018.[4] HAN Wentao, FU Haiqiang, ZHU Jianjun, et al. A polarimetric projection-based scattering characteristics extraction tool and its application to PolSAR image classification[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2023, 202: 314–333. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.05.031.[5] GAO Li, LIN Zhiyuan, YIN Qiang, et al. Classification performance comparison of time-variant scattering features of multi-temporal polarimetric SAR data[C]. IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2023: 8050–8053. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS52108.2023.10282315.[6] YU Xiaoping and YUE Xijuan. Similarity matrix entropy for multitemporal polarimetric SAR change detection[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4003805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3030674.[7] WEI Jujie, ZHANG Yonghong, YU Xiaoping, et al. A temporal difference matrix for historical cumulative change detection in time series PolSAR data[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2024, 131: 103978. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2024.103978.[8] WANG Guanya, LI Zhiwei, HU Jun, et al. A modified EVD-based phase linking method in decorrelated scenario with time series polarimetric scattering consistency[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 7694–7706. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2025.3547947.[9] BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5–32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324.[10] GEURTS P, ERNST D, and WEHENKEL L. Extremely randomized trees[J]. Machine Learning, 2006, 63(1): 3–42. doi: 10.1007/s10994-006-6226-1.[11] REIGBER A, JÄGER M, NEUMANN M, et al. Classifying polarimetric SAR data by combining expectation methods with spatial context[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2010, 31(3): 727–744. doi: 10.1080/01431160902897809.[12] BHATTACHARYA A and TOUZI R. Polarimetric SAR urban classification using the Touzi target scattering decomposition[J]. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 2011, 37(4): 323–332. doi: 10.5589/m11-042.[13] IOANNIDOU M, KOUKOS A, SITOKONSTANTINOU V, et al. Assessing the added value of sentinel-1 PolSAR data for crop classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(22): 5739. doi: 10.3390/rs14225739.[14] MAUS V, CÂMARA G, CARTAXO R, et al. A time-weighted dynamic time warping method for land-use and land-cover mapping[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(8): 3729–3739. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2517118.[15] GAO Han, WANG Changcheng, WANG Guanya, et al. A novel crop classification method based on ppfSVM classifier with time-series alignment kernel from dual-polarization SAR datasets[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2021, 264: 112628. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112628.[16] BARGIEL D. A new method for crop classification combining time series of radar images and crop phenology information[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2017, 198: 369–383. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.06.022.[17] KENDUIYWO B K, BARGIEL D, and SOERGEL U. Higher order dynamic conditional random fields ensemble for crop type classification in radar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(8): 4638–4654. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2695326.[18] LEITE P B C, FEITOSA R Q, FORMAGGIO A R, et al. Hidden Markov models for crop recognition in remote sensing image sequences[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2011, 32(1): 19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2010.02.008.[19] LI Mengmeng and BIJKER W. Potential of multi-temporal sentinel-1A dual polarization SAR images for vegetable classification in Indonesia[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 3820–3823. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2018.8517325.[20] NI Jun, LÓPEZ-MARTÍNEZ C, HU Zhongbo, et al. Multitemporal SAR and polarimetric SAR optimization and classification: Reinterpreting temporal coherence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5236617. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3214097.[21] HAN Zhu, ZHANG Ce, GAO Lianru, et al. Spatio-temporal multi-level attention crop mapping method using time-series SAR imagery[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2023, 206: 293–310. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.11.016.[22] LEVY Y and GVIRTZMAN H. Industry-driven versus natural groundwater flow regime at the dead sea coastal aquifer[J]. Water, 2021, 13(4): 498. doi: 10.3390/w13040498.[23] YIN Qiang, HONG Wen, ZHANG Fan, et al. Optimal combination of polarimetric features for vegetation classification in PolSAR image[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(10): 3919–3931. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2940973.[24] KERSTEN P R, LEE J S, and AINSWORTH T L. Unsupervised classification of polarimetric synthetic aperture radar images using fuzzy clustering and EM clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(3): 519–527. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.842108.[25] ZHANG Fan, MENG Fanle, MA Fei, et al. Time correlation entropy: A novel multitemporal PolSAR feature and its application in Salt Lake classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 4506814. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3404598.[26] DABBOOR M and SHOKR M. A new likelihood ratio for supervised classification of fully polarimetric SAR data: An application for sea ice type mapping[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2013, 84: 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2013.06.010.[27] DUDA R O, HART P E, and STORK D G. Pattern Classification[M]. 2nd ed. Hoboken: Wiley-Interscience, 2000.[28] HE Yuting, WANG Shigang, and GAO Xueshan. Analysis and research of spinal CT image segmentation based on improved watershed algorithm[C]. IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronic Communications, Internet of Things and Big Data, Taichung, China, 2023: 119–123. doi: 10.1109/ICEIB57887.2023.10170668.[29] TANG Yincai and WEI Xiaoling. Existence of maximum likelihood estimation for three-parameter log-normal distribution[C]. The 8th International Conference on Reliability, Maintainability and Safety, Chengdu, China, 2009: 305–307. doi: 10.1109/ICRMS.2009.5270184.[30] AHN S, LEE J, YOON D, et al. Enhanced modulation classification algorithm based on Kolmogorov-Smirnov test[C]. 2017 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence, Jeju, Korea (South), 2017: 232–234. doi: 10.1109/ICTC.2017.8190976.[31] MARINO A and ALONSO-GONZÁLEZ A. An optimization of the difference of covariance matrices for PolSAR change detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017: 5315–5318. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2017.8128204.[32] ALONSO-GONZÁLEZ A, LÓPEZ-MARTÍNEZ C, PAPATHANASSIOU K P, et al. Polarimetric SAR time series change analysis over agricultural areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(10): 7317–7330. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2981929.[33] PREETHI S, PRAKASH A A, RAMYEA R, et al. CNN based automated land use classification from remotely sensed image[C]. 2021 Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2021: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/i-PACT52855.2021.9696772.[34] WANG Yuxing and JIANG Yulian. A weighted minimum distance classifier based on relative offset[C]. IEEE 4th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Big Data Analysis, Chengdu, China, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICCCBDA.2019.8725734.[35] PAL S, ALAM S, and MITRA M. Binary coding of Arrhythmic beats for generation of simplified classification rule[C]. 2011 International Conference on Communication and Industrial Application, Kolkata, India, 2011: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICCIndA.2011.6146674.[36] JITKONGCHUEN D and SUKPONGTHAI W. Handling imbalanced data classification problem using artificial immune system with mahalanobis distance[C]. The 20th IEEE/ACIS International Conference on Software Engineering, Artificial Intelligence, Networking and Parallel/Distributed Computing, Toyama, Japan, 2019: 67–71. doi: 10.1109/SNPD.2019.8935760.[37] WITTENBERG L J. Salt-gradient Solar Ponds: Design, Construction and Power Production[M]. JANZEN A F and SWARTMAN R K. Solar Energy Conversion II. Toronto: Pergamon, 1981: 411–429. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-08-025388-6.50057-X. -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. Salt mining process and types of salt fields
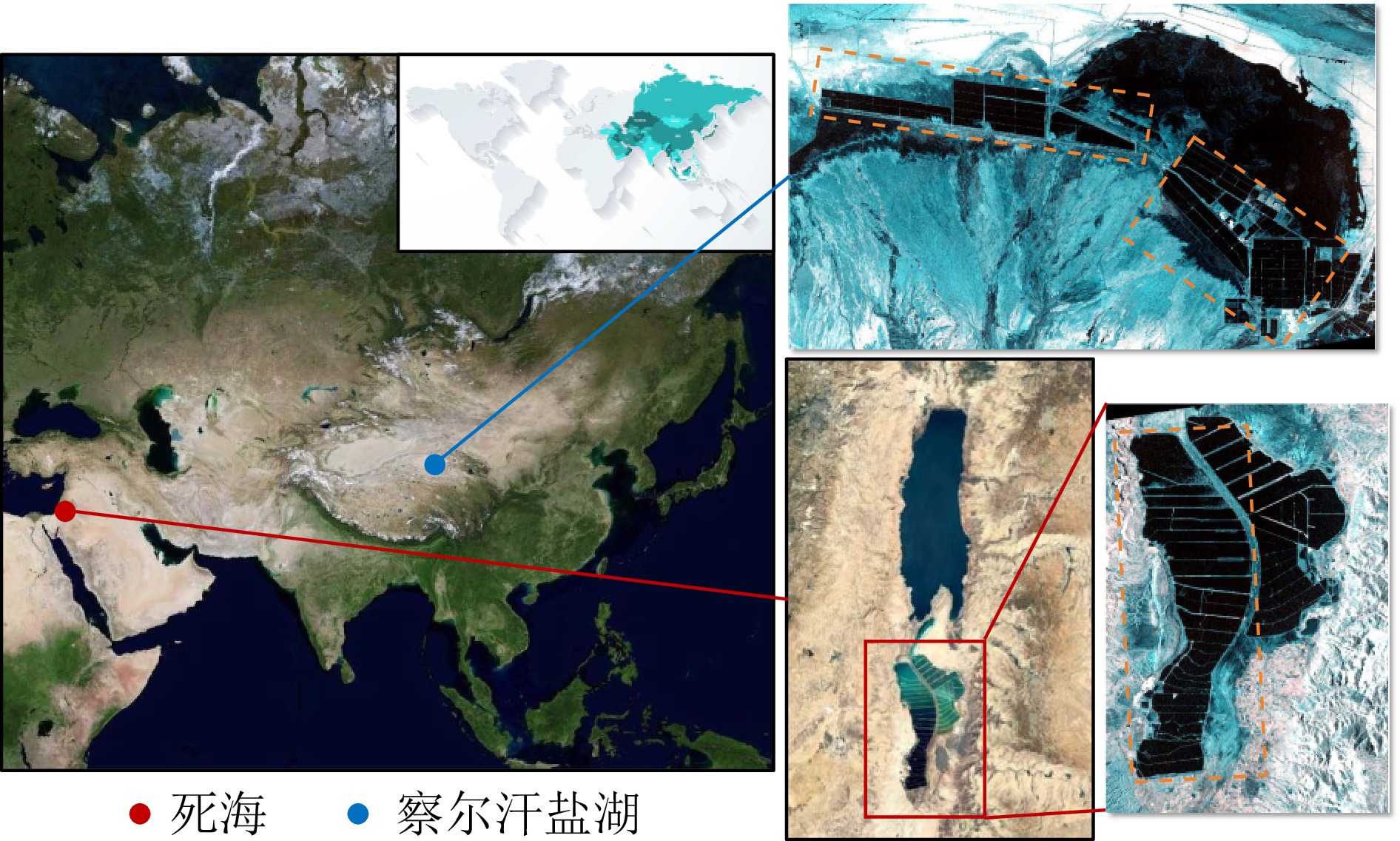
- Figure 2. Geographic location of the study datasets
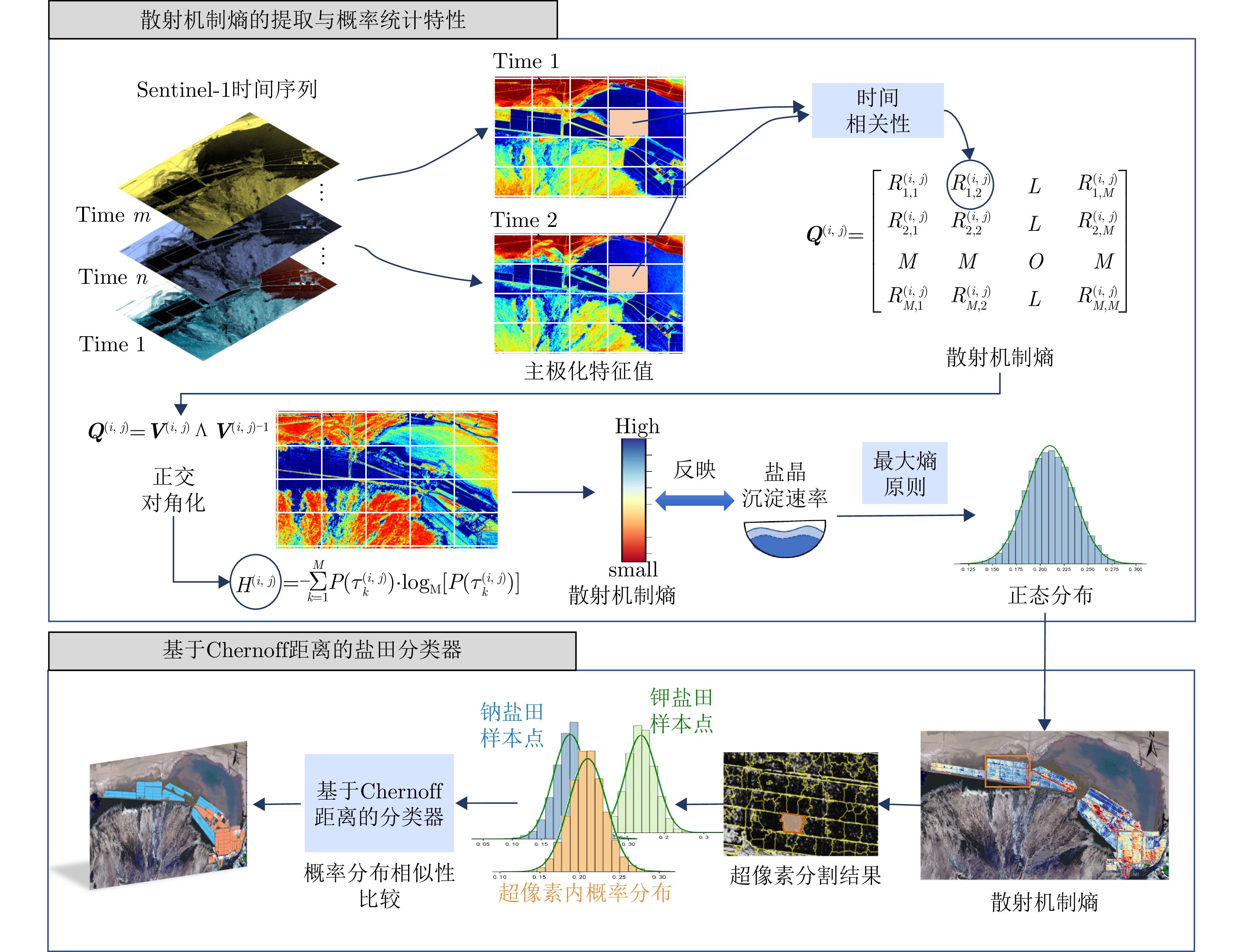
- Figure 3. Algorithmic flow of the proposed method
- Figure 4. Superpixel segmentation and normal distribution fitting results
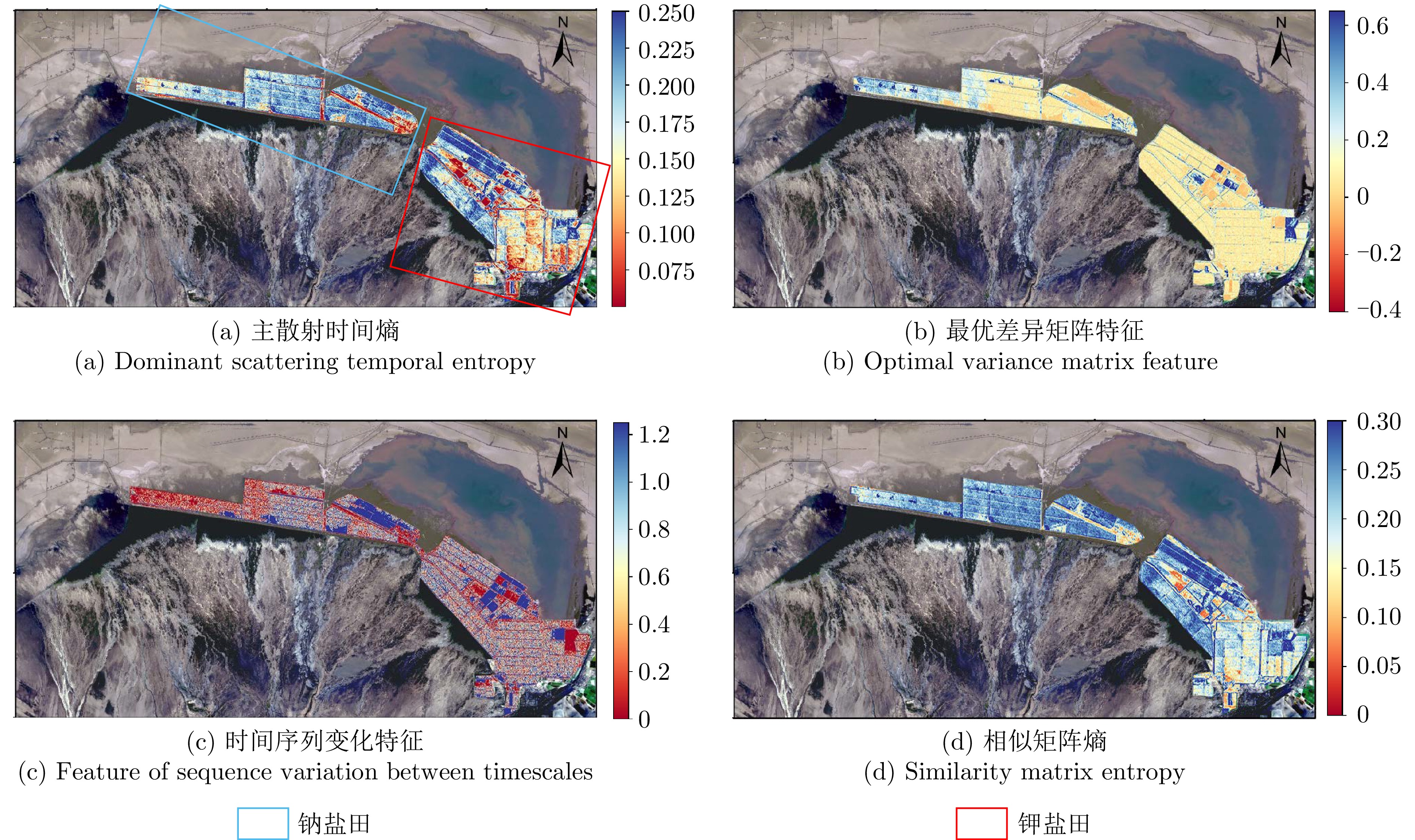
- Figure 5. A visual comparison of different multi-temporal polarization features on the Qarhan Salt Lake dataset
- Figure 6. Classification results of methods on the Qarhan Salt Lake dataset
- Figure 7. Classification results of methods on the Dead Sea dataset
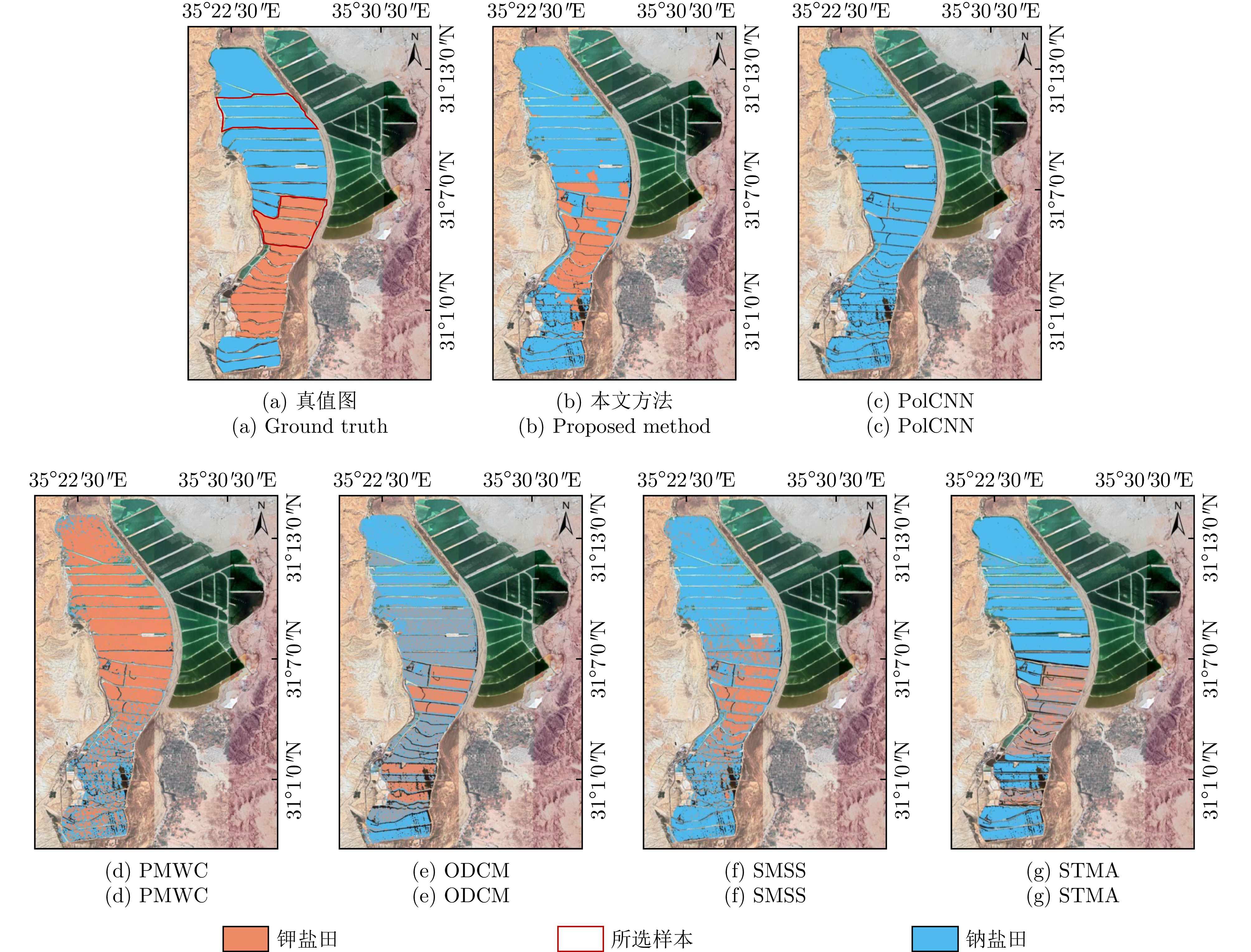
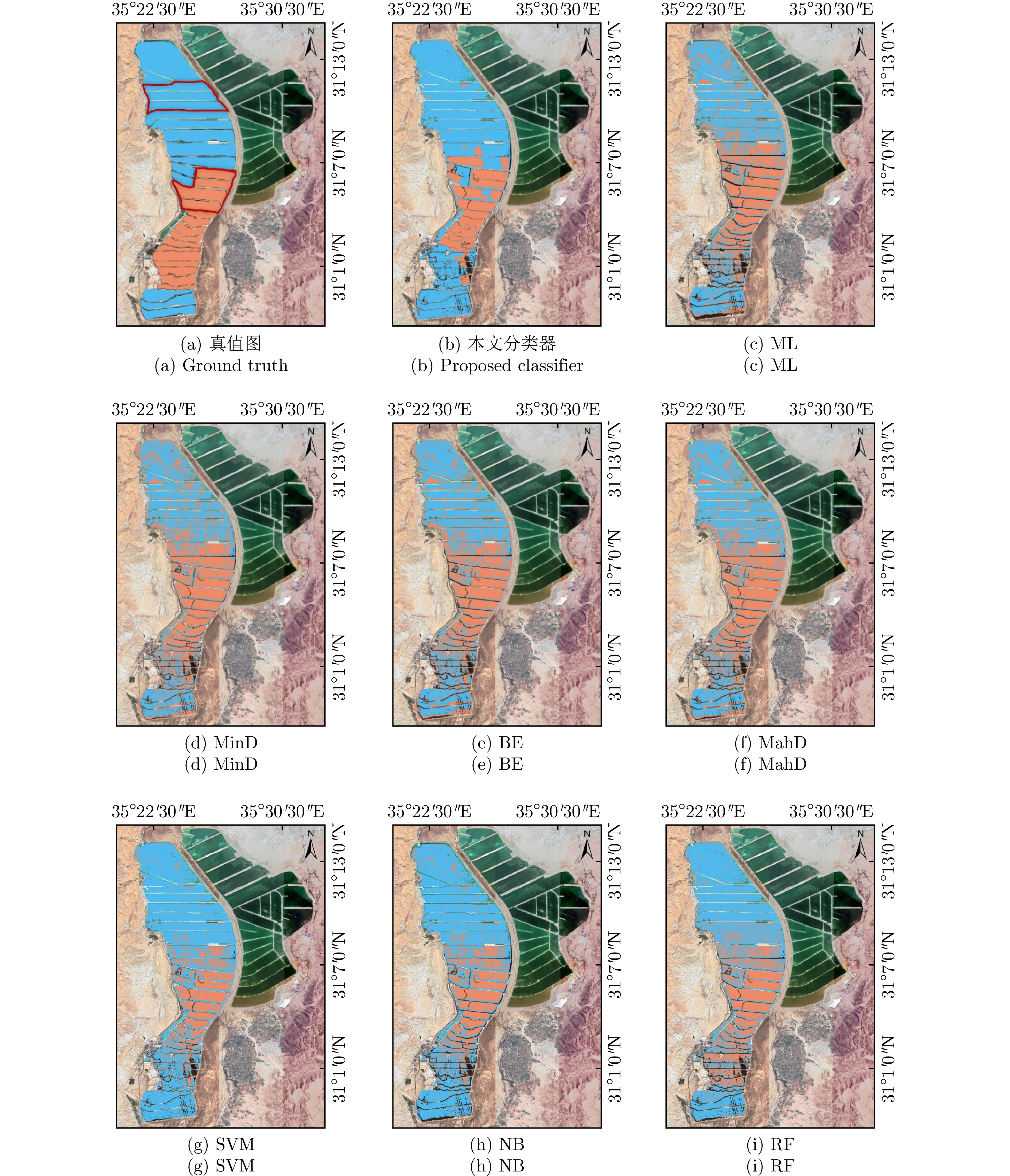
- Figure 8. Classification results for subregion of Dead Sea dataset
- Figure 9. Comparison of classification results from different classifiers on the Qarhan Salt Lake dataset
- Figure 10. Classification results of various methods for an enlarged subregion of the Qarhan Salt Lake dataset
- Figure 11. Classification results of Dead Sea dataset
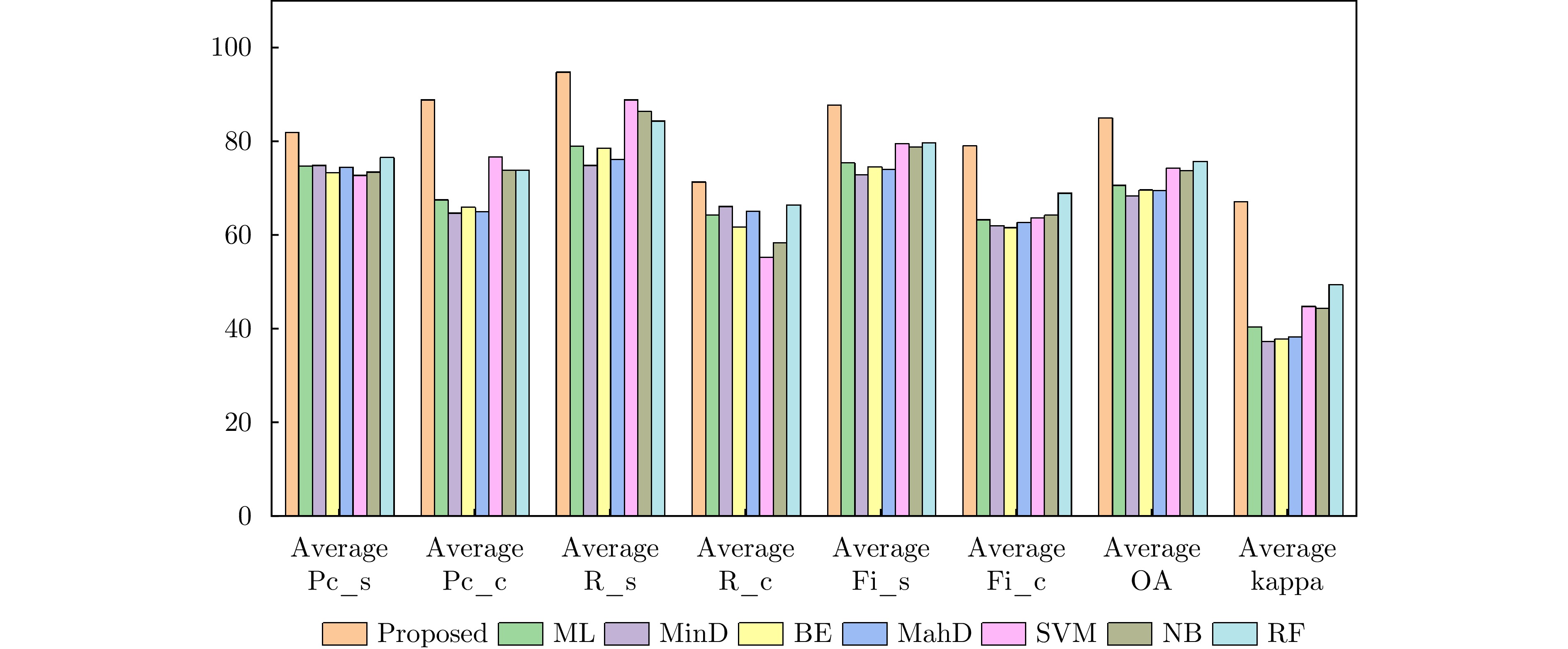
- Figure 12. The mean of five indicators obtained by different methods for all datasets
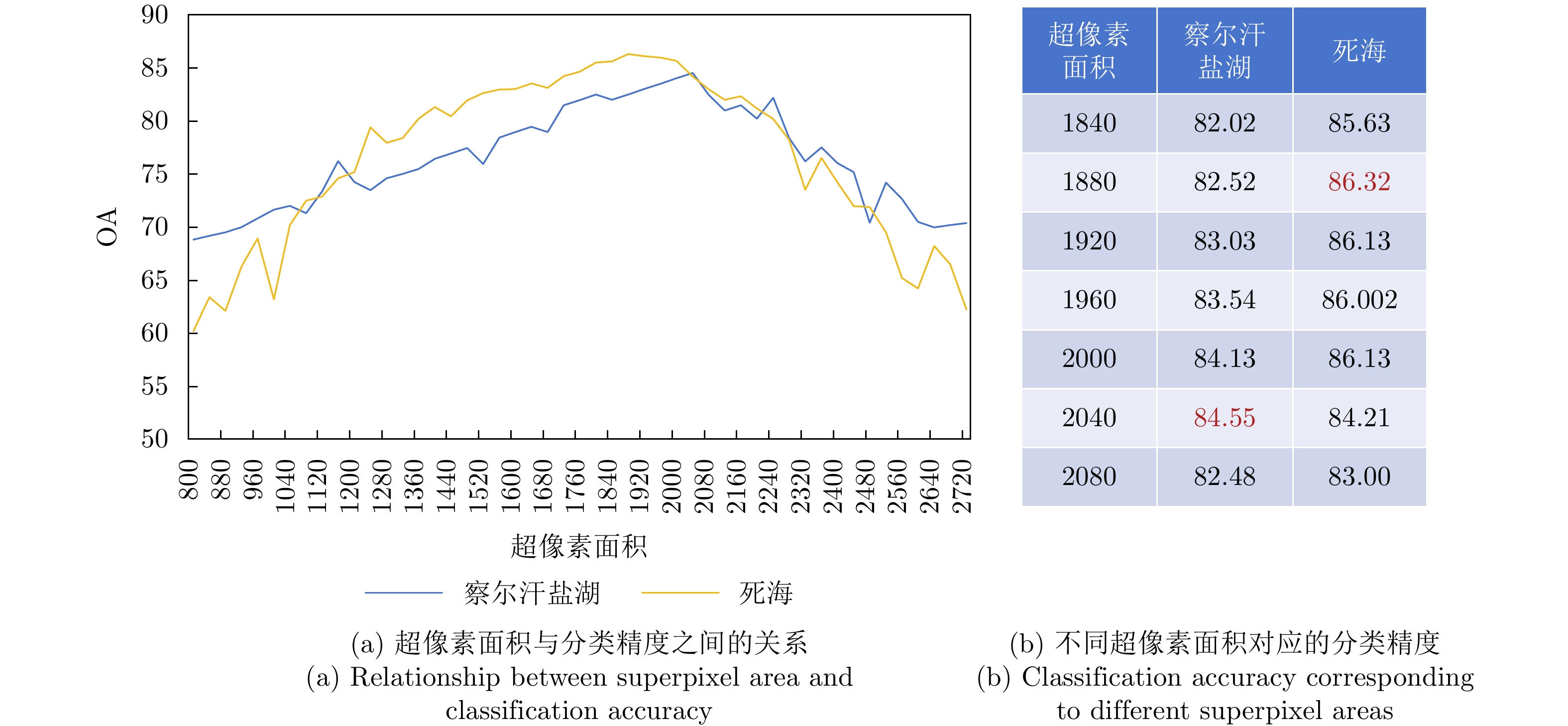
- Figure 13. Relationship between superpixel area and classification accuracy


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: