- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2025
> Online First
| Citation: | WANG Jiaxiang, MENG Jin, LI Wei, et al. YOLO-S3: a lightweight network for radar composite jamming signal recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR25080 |
YOLO-S3: A Lightweight Network for Radar Composite Jamming Signal Recognition
DOI: 10.12000/JR25080 CSTR: 32380.14.JR25080
More Information-
Abstract
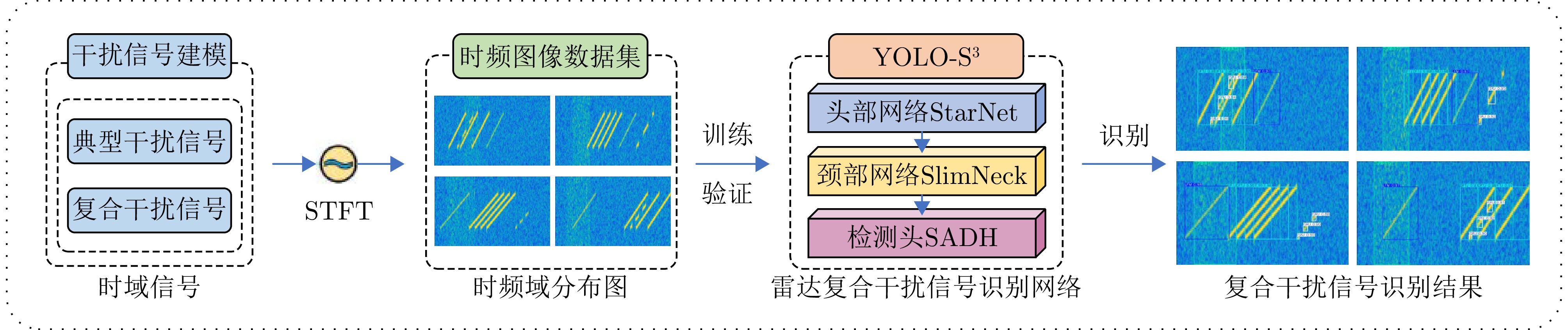
To enhance the jamming recognition capabilities of radars in complex electromagnetic environments, this study proposes YOLO-S3, a lightweight network for recognizing composite jamming signals. YOLO-S3 is characterized by three core attributes: Smartness, slimness, and high speed. Initially, a technical approach based on visual detection algorithms is introduced to identify 2D time-frequency representations of jamming signals. An image dataset of composite jamming signals is constructed using signal modeling, simulation technology, and the short-time Fourier transform. Next, the backbone and neck networks of YOLOv8n are restructured by integrating StarNet and SlimNeck, and a Self-Attention Detect Head (SADH) is designed to enhance feature extraction. These modifications result in a lightweight network without compromising recognition accuracy. Finally, the network’s performance is validated through ablation and comparative experiments. Results show that YOLO-S3 features a highly lightweight network design. When the signal-to-jamming ratio varies from −10 to 0 dB and the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) is ≥0 dB, the network achieves an impressive average recognition accuracy of 99.5%. Even when the SNR decreases to −10 dB, it maintains a robust average recognition accuracy of 95.5%, exhibiting strong performance under low SNR conditions. These findings provide a promising solution for the real-time recognition of composite jamming signals on resource-constrained platforms such as airborne radar signal processors and portable electronic devices. -

-
References
[1] 崔国龙, 余显祥, 魏文强, 等. 认知智能雷达抗干扰技术综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191.CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, WEI Wenqiang, et al. An overview of antijamming methods and future works on cognitive intelligent radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191.[2] 张顺生, 陈爽, 陈晓莹, 等. 面向小样本的多模态雷达有源欺骗干扰识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 882–891. doi: 10.12000/JR23104.ZHANG Shunsheng, CHEN Shuang, CHEN Xiaoying, et al. Active deception jamming recognition method in multimodal radar based on small samples[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 882–891. doi: 10.12000/JR23104.[3] 郭文杰, 吴振华, 曹宜策, 等. 多域浅层特征引导下雷达有源干扰多模态对比识别方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(5): 1004–1018. doi: 10.12000/JR24129.GUO Wenjie, WU Zhenhua, CAO Yice, et al. Multidomain characteristic-guided multimodal contrastive recognition method for active radar jamming[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(5): 1004–1018. doi: 10.12000/JR24129.[4] WANG Zan, GUO Zhengwei, SHU Gaofeng, et al. Radar jamming recognition: Models, methods, and prospects[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2025, 18: 3315–3343. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3522951.[5] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, and HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539.[6] ZHANG Haoyu, YU Lei, CHEN Yushi, et al. Fast complex-valued CNN for radar jamming signal recognition[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(15): 2867. doi: 10.3390/rs13152867.[7] LIU Qiang and ZHANG Wei. Deep learning and recognition of radar jamming based on CNN[C]. The 12th International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Design, Hangzhou, China, 2019: 208–212. doi: 10.1109/ISCID.2019.00054.[8] CAI Yuan, SHI Kai, SONG Fei, et al. Jamming pattern recognition using spectrum waterfall: A deep learning method[C]. The 5th International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 2019: 2113–2117. doi: 10.1109/ICCC47050.2019.9064207.[9] WANG Jingyi, DONG Wenhao, SONG Zhiyong, et al. Identification of radar active interference types based on three-dimensional residual network[C]. The 3rd International Academic Exchange Conference on Science and Technology Innovation, Guangzhou, China, 2021: 167–172. doi: 10.1109/IAECST54258.2021.9695564.[10] 陈思伟, 崔兴超, 李铭典, 等. 基于深度CNN模型的SAR图像有源干扰类型识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 897–908. doi: 10.12000/JR22143.CHEN Siwei, CUI Xingchao, LI Mingdian, et al. SAR image active jamming type recognition based on deep CNN model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 897–908. doi: 10.12000/JR22143.[11] QU Qizhe, WEI Shunjun, LIU Shan, et al. JRNet: Jamming recognition networks for radar compound suppression jamming signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(12): 15035–15045. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3032197.[12] LV Qinzhe, QUAN Yinghui, FENG Wei, et al. Radar deception jamming recognition based on weighted ensemble CNN with transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5107511. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3129645.[13] LV Qinzhe, QUAN Yinghui, SHA Minghui, et al. Deep neural network-based interrupted sampling deceptive jamming countermeasure method[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 9073–9085. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3214969.[14] ZHANG Jiaxiang, LIANG Zhennan, ZHOU Chao, et al. Radar compound jamming cognition based on a deep object detection network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(3): 3251–3263. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3224695.[15] ZHU Xuan, WU Hao, HE Fangmin, et al. YOLO-CJ: A lightweight network for compound jamming signal detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(5): 6807–6821. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3406491.[16] MA Xu, DAI Xiyang, BAI Yue, et al. Rewrite the stars[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 5694–5703. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.00544.[17] LI Hulin, LI Jun, WEI Hanbing, et al. Slim-neck by GSConv: A lightweight-design for real-time detector architectures[J]. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 2024, 21(3): 62. doi: 10.1007/s11554-024-01436-6.[18] YU Hongyuan, WAN Cheng, DAI Xiyang, et al. Real-time image segmentation via hybrid convolutional-transformer architecture search[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.10413, 2025.[19] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010.[20] ZHANG Haoyang, WANG Ying, DAYOUB F, et al. VarifocalNet: An IOU-aware dense object detector[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 8510–8519. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00841.[21] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031.[22] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2.[23] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2999–3007. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.324.[24] ZHAO Yi’an, LV Wenyu, XU Shangliang, et al. DETRS beat YOLOs on real-time object detection[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2024: 16965–16974. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.01605.[25] 翟永杰, 田济铭, 陈鹏晖, 等. 基于YOLOv8n-Aerolite的轻量化蝴蝶兰种苗目标检测算法[J]. 农业工程学报, 2025, 41(4): 220–229. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202408192.ZHAI Yongjie, TIAN Jiming, CHEN Penghui, et al. Algorithm for the target detection of phalaenopsis seedlings using lightweight YOLOv8n-Aerolite[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2025, 41(4): 220–229. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202408192.[26] WANG C Y, YEH I H, and LIAO H Y M. YOLOv9: Learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information[C]. The 18th European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 2025: 1–21. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-72751-1_1.[27] WANG Ao, CHEN Hui, LIU Lihao, et al. YOLOv10: Real-time end-to-end object detection[C]. The 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2024: 3429.[28] ZHUO Shulong, BAI Hao, JIANG Lifeng, et al. SCL-YOLOv11: A lightweight object detection network for low-illumination environments[J]. IEEE Access, 2025, 13: 47653–47662. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3550947.[29] TIAN Yunjie, YE Qixiang, and DOERMANN D. YOLOv12: Attention-centric real-time object detectors[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.12524, 2025. -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. Technical roadmap for composite jamming signal recognition
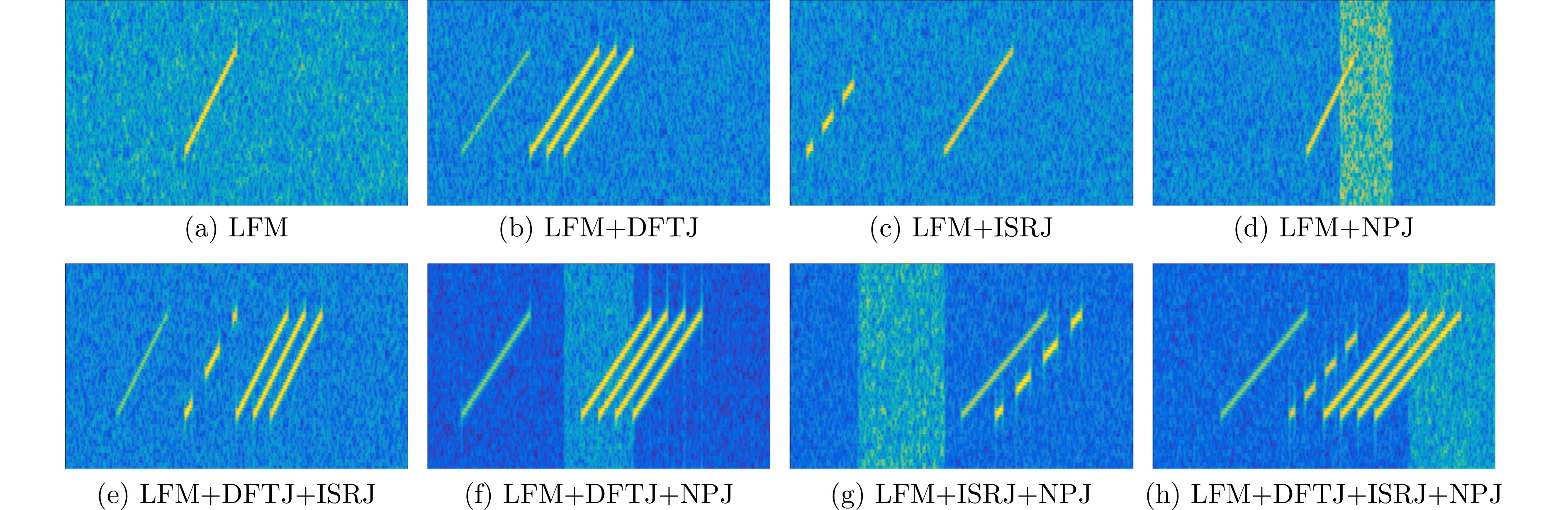
- Figure 2. Time-frequency representation of signals
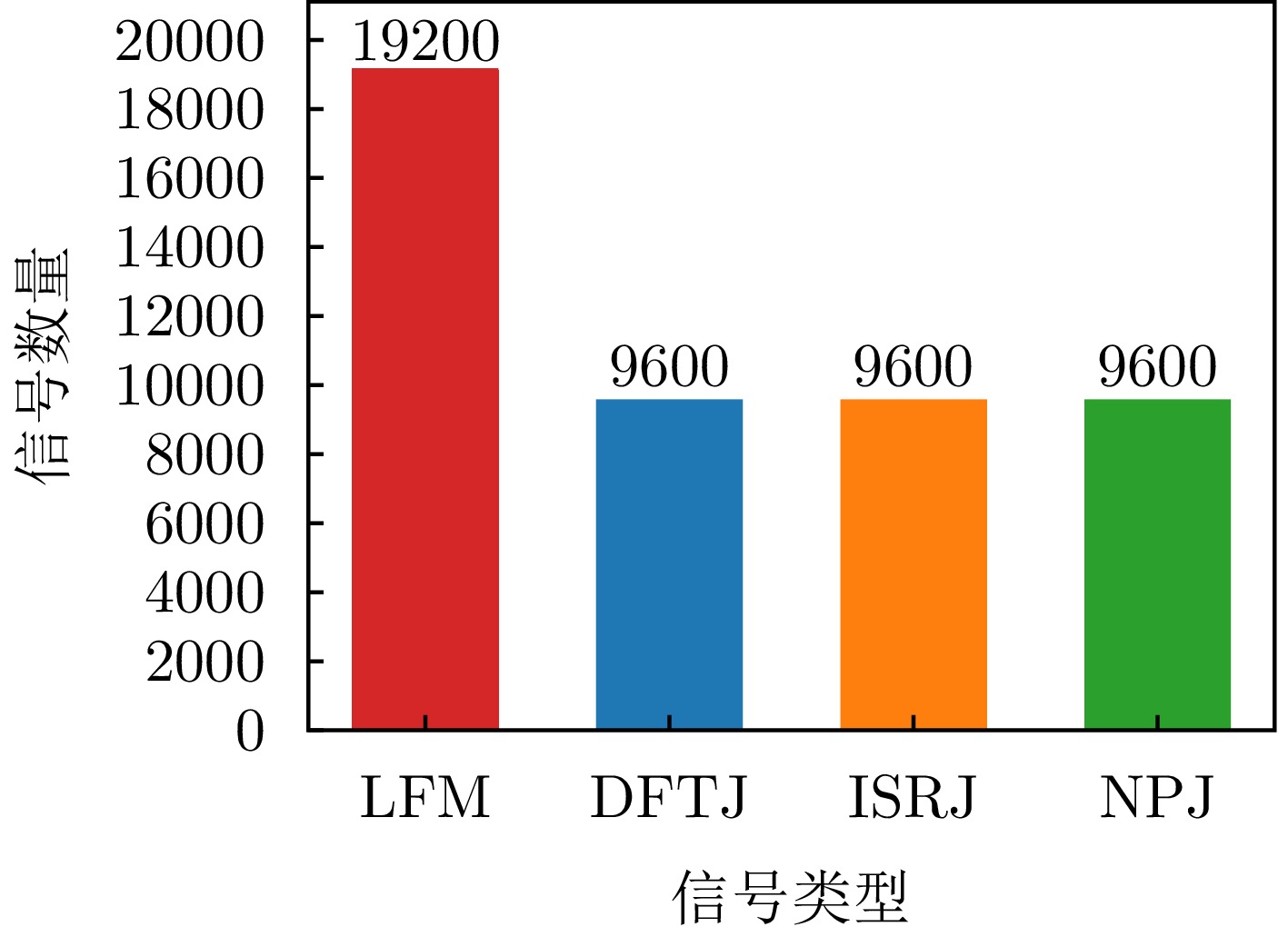
- Figure 3. Composition of jamming signal types in the JSID19200 dataset
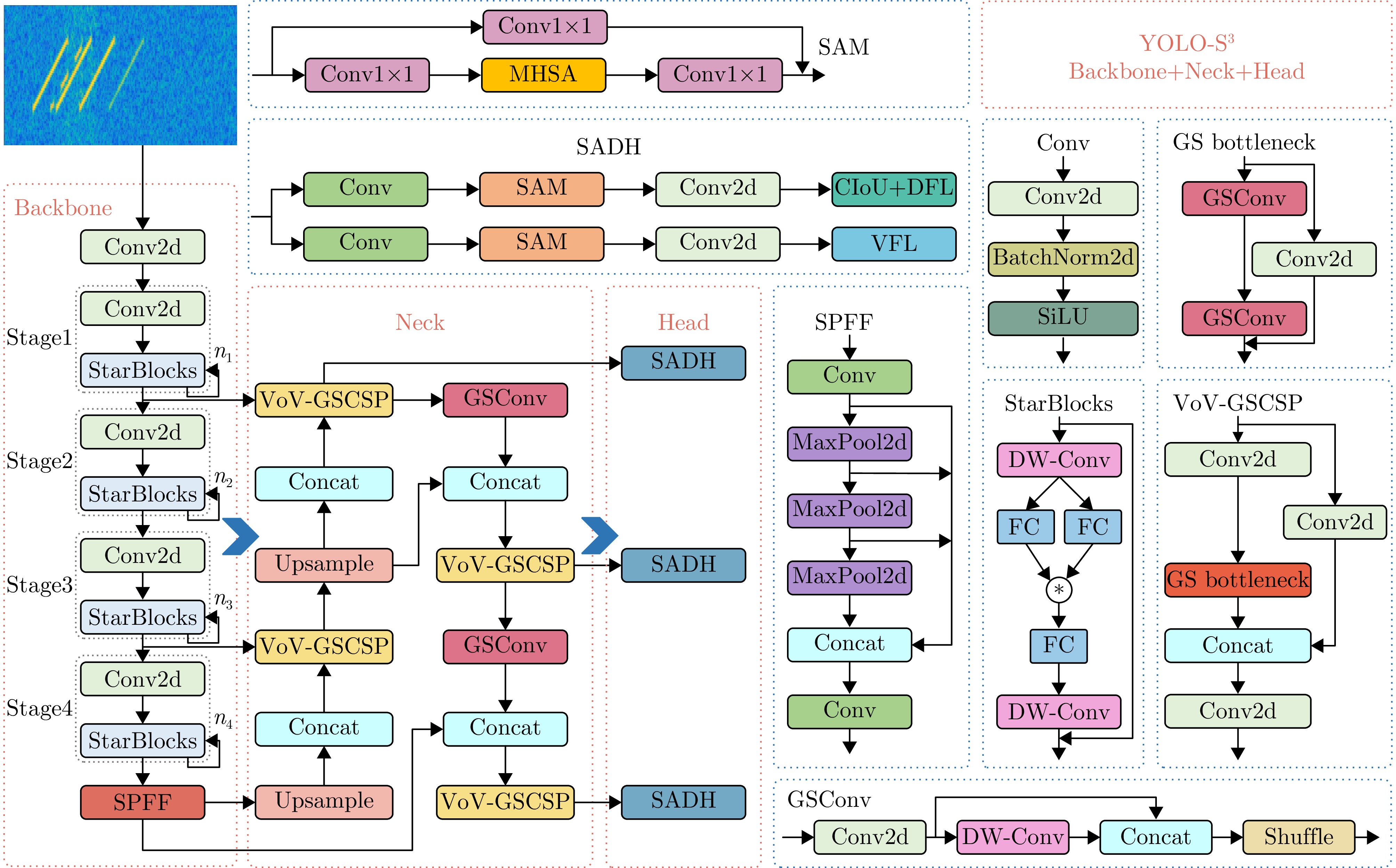
- Figure 4. YOLO-S3 network architecture
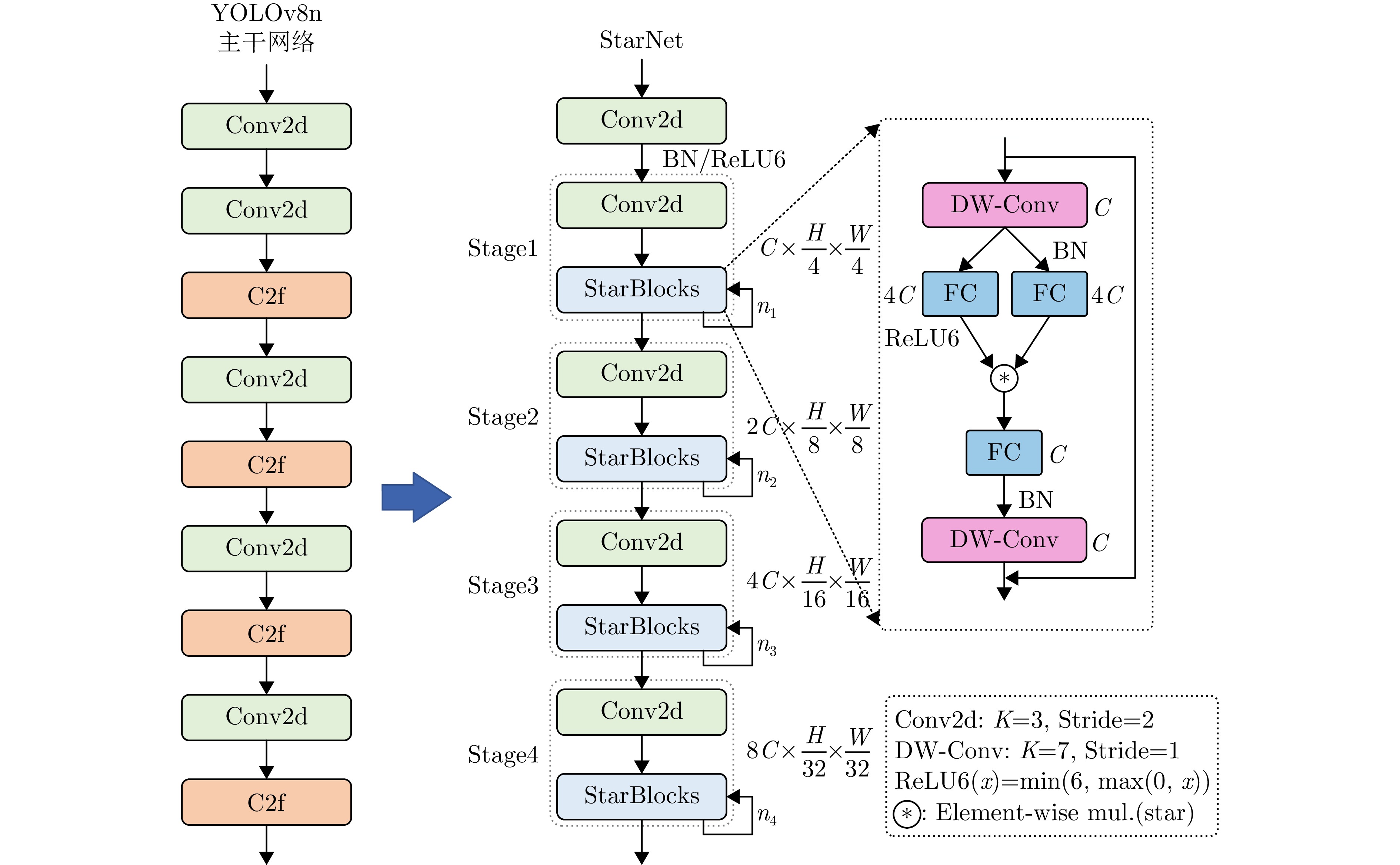
- Figure 5. StarNet network architecture
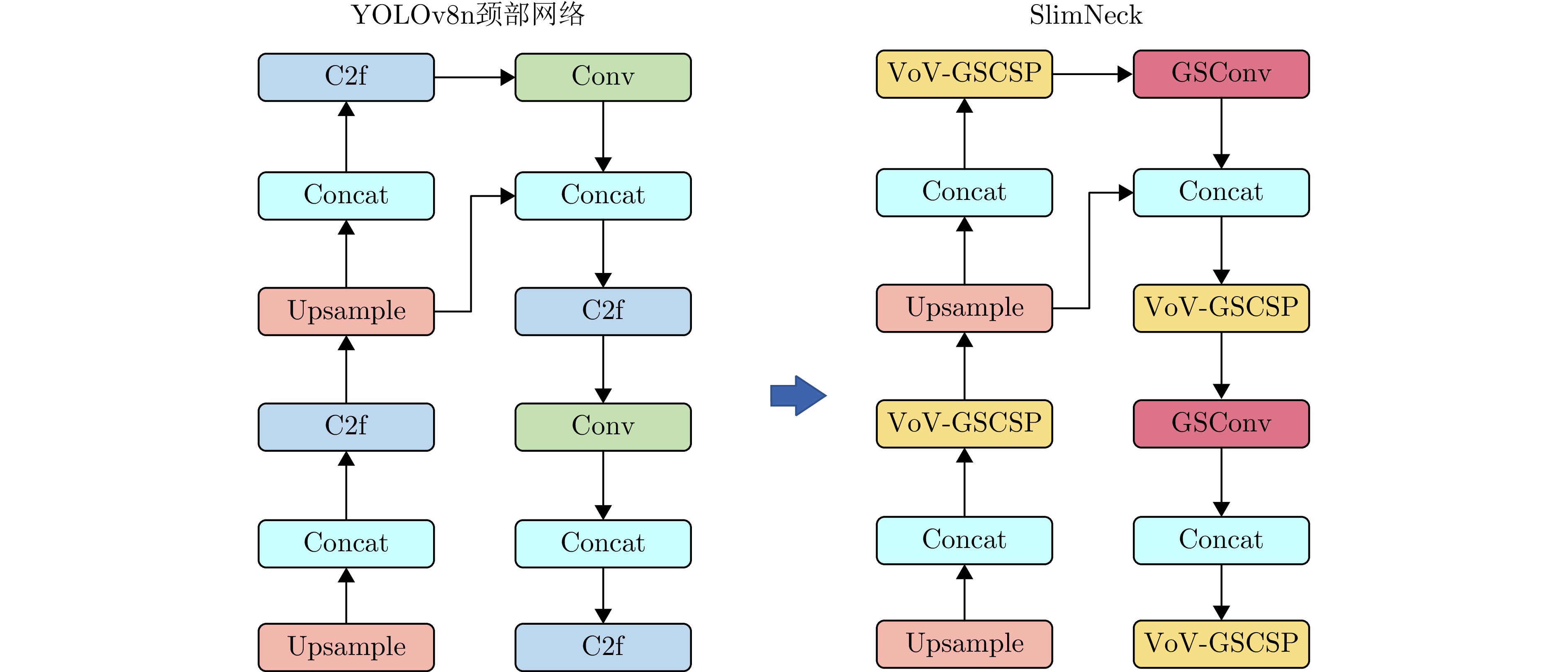
- Figure 6. SlimNeck network architecture
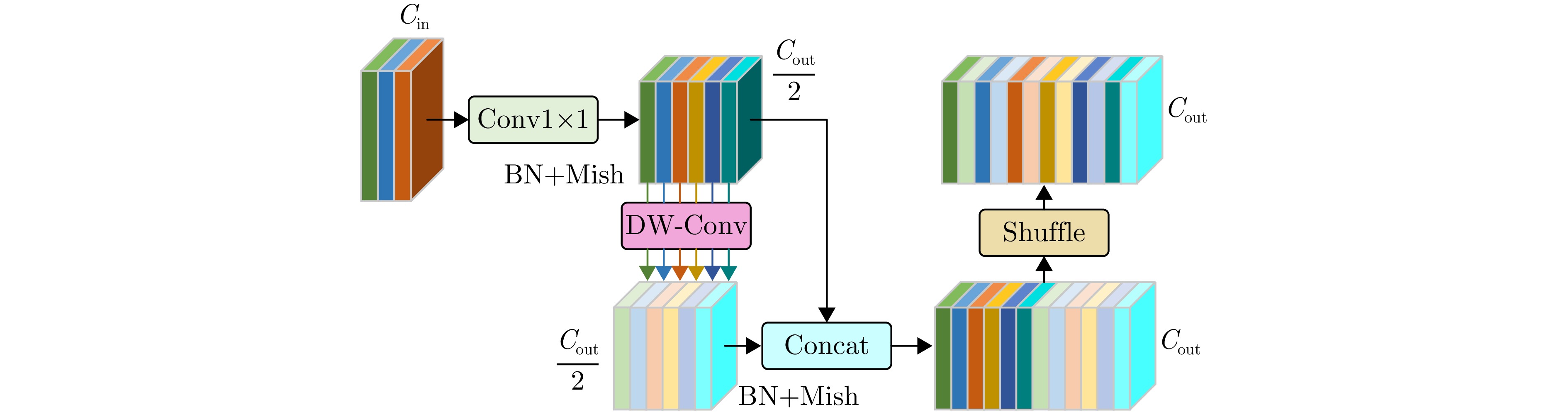
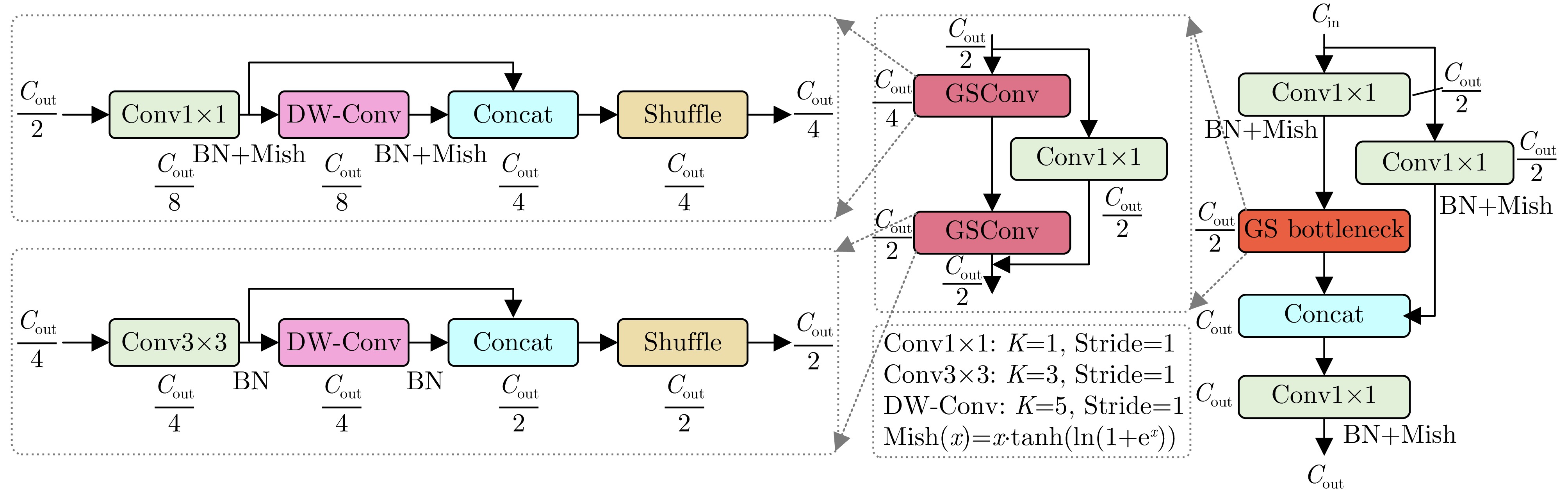
- Figure 7. GSConv network architecture
- Figure 8. VoV-GSCSP network architecture
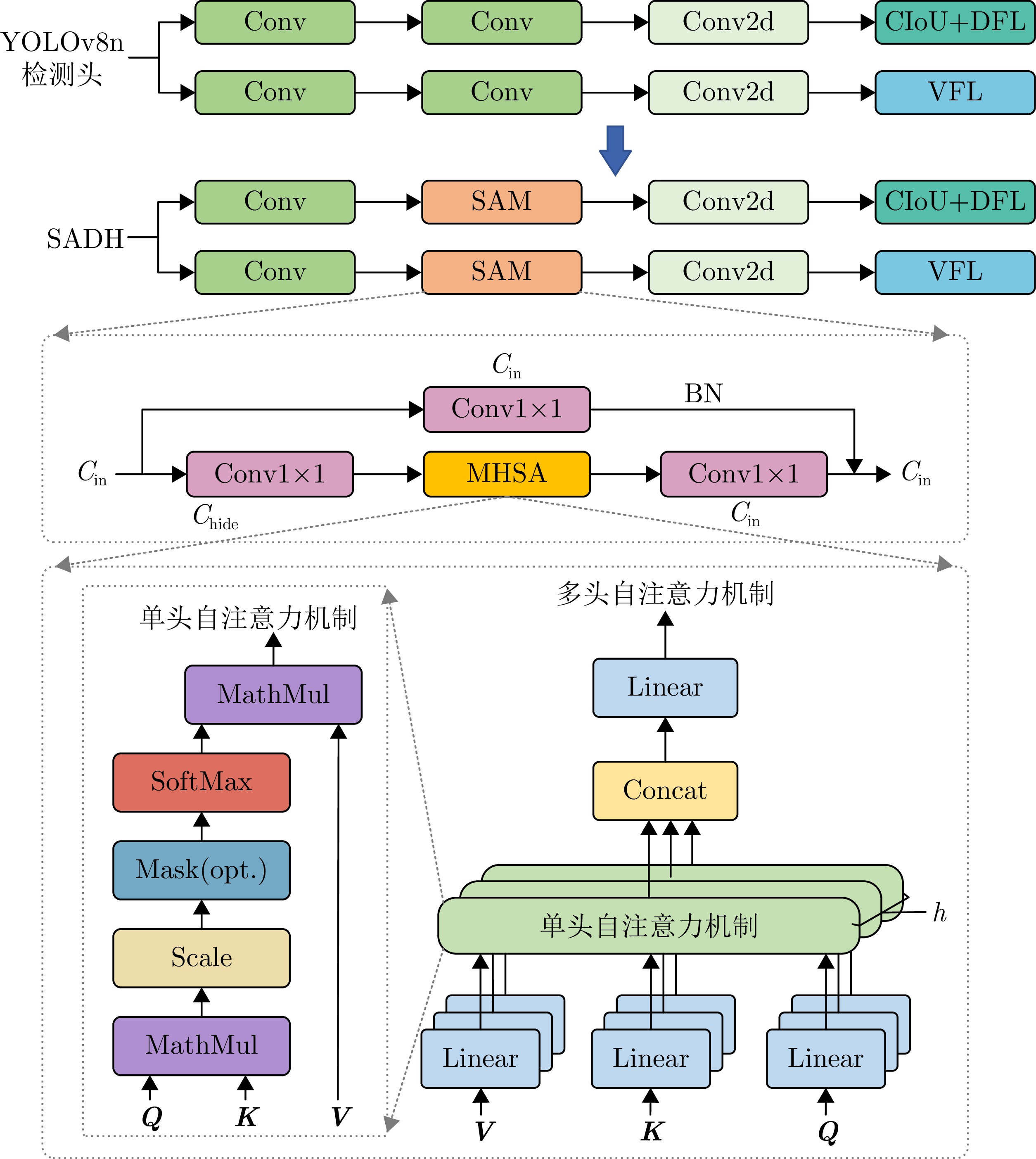
- Figure 9. SADH network architecture
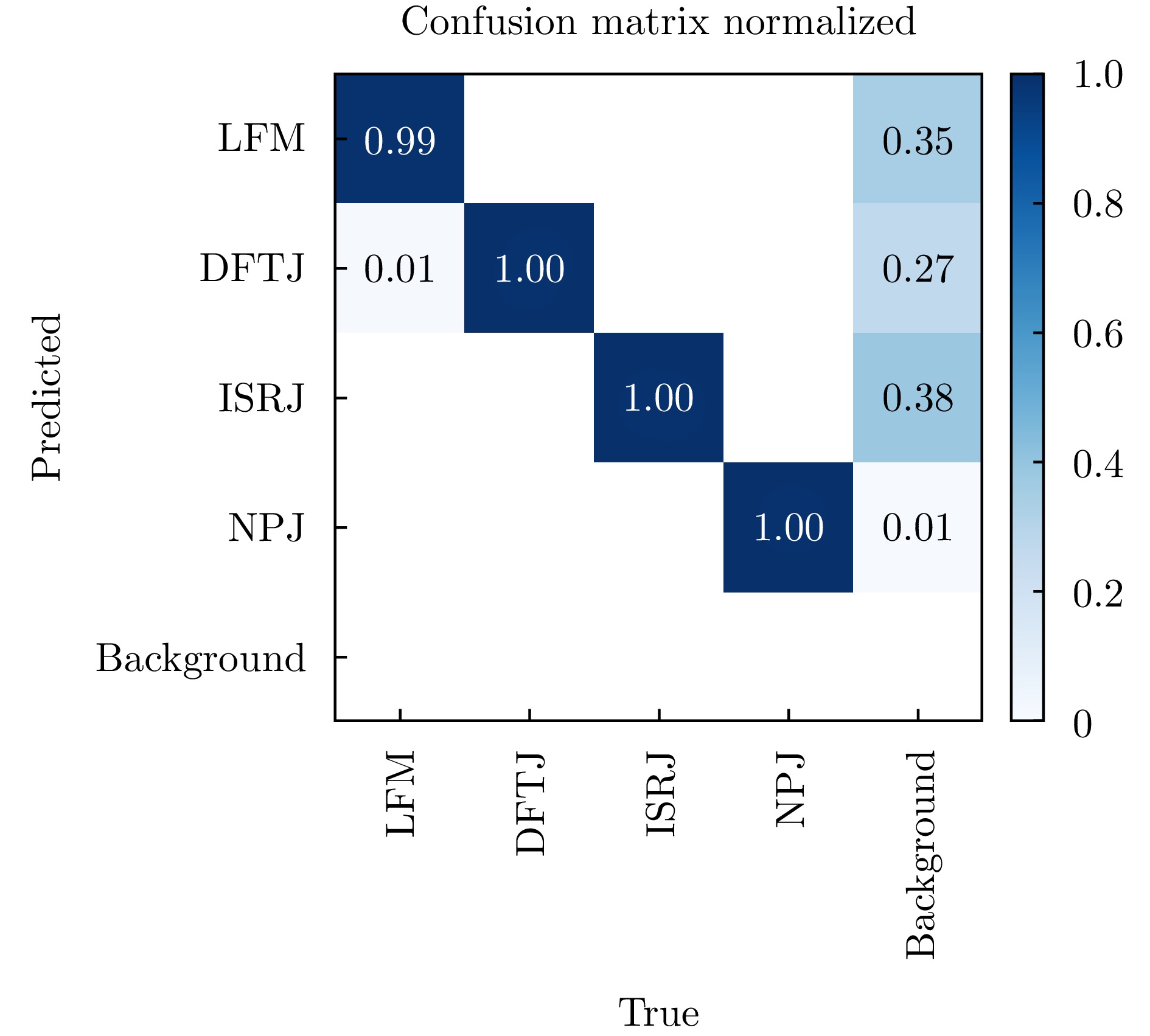
- Figure 10. Confusion matrix for multi-class signal recognition
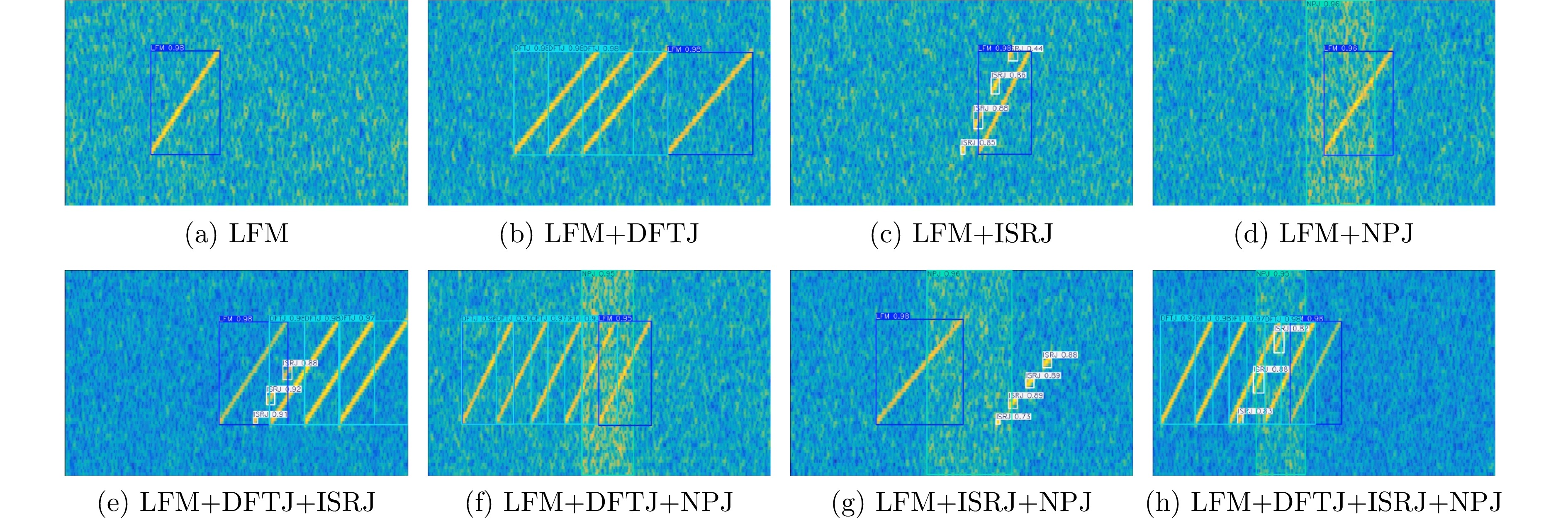
- Figure 11. Composite jamming signal recognition results
- Figure 12. Confusion matrix of signal recognition under varying SNR conditions
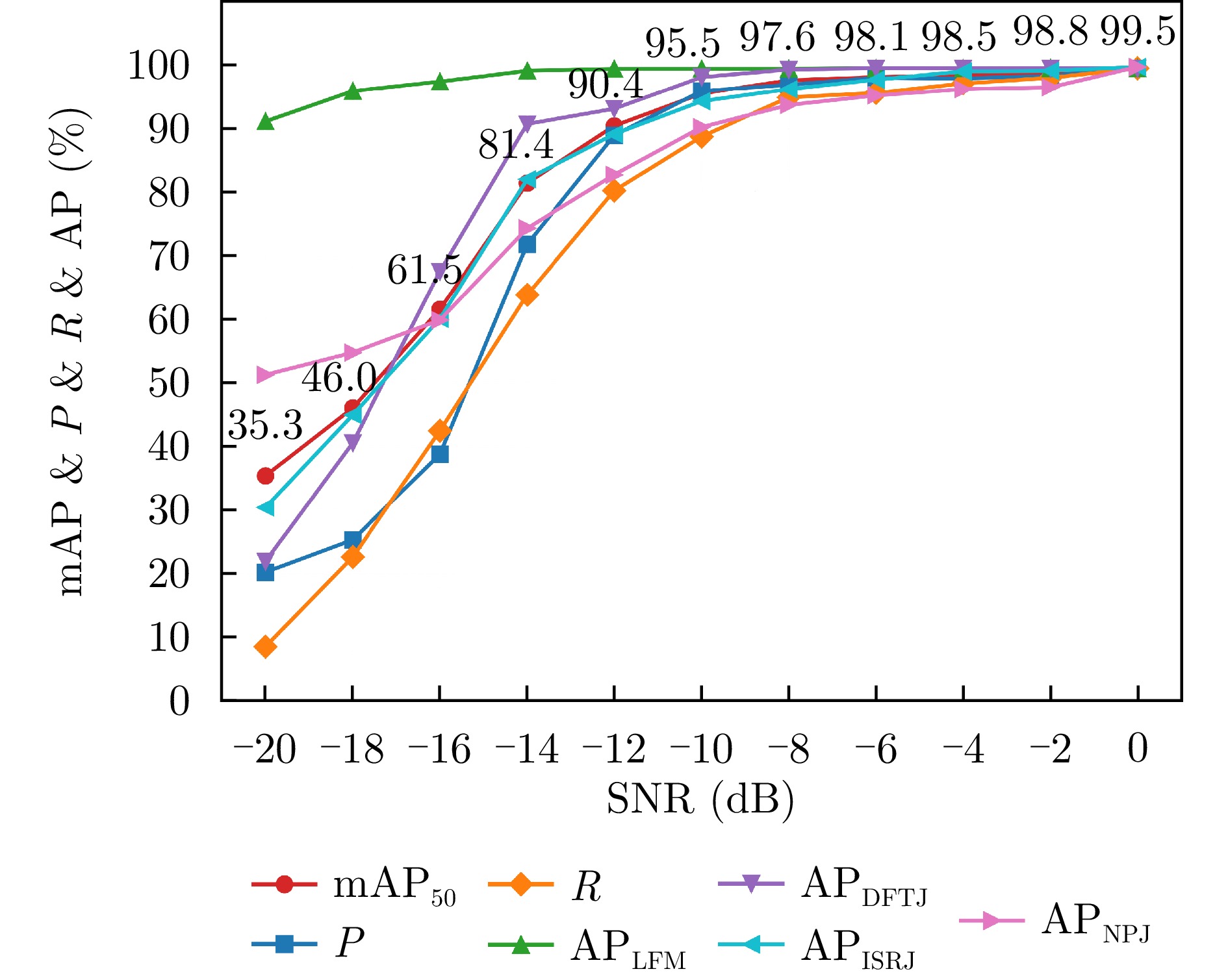
- Figure 13. Recognition accuracy vs. SNR curves
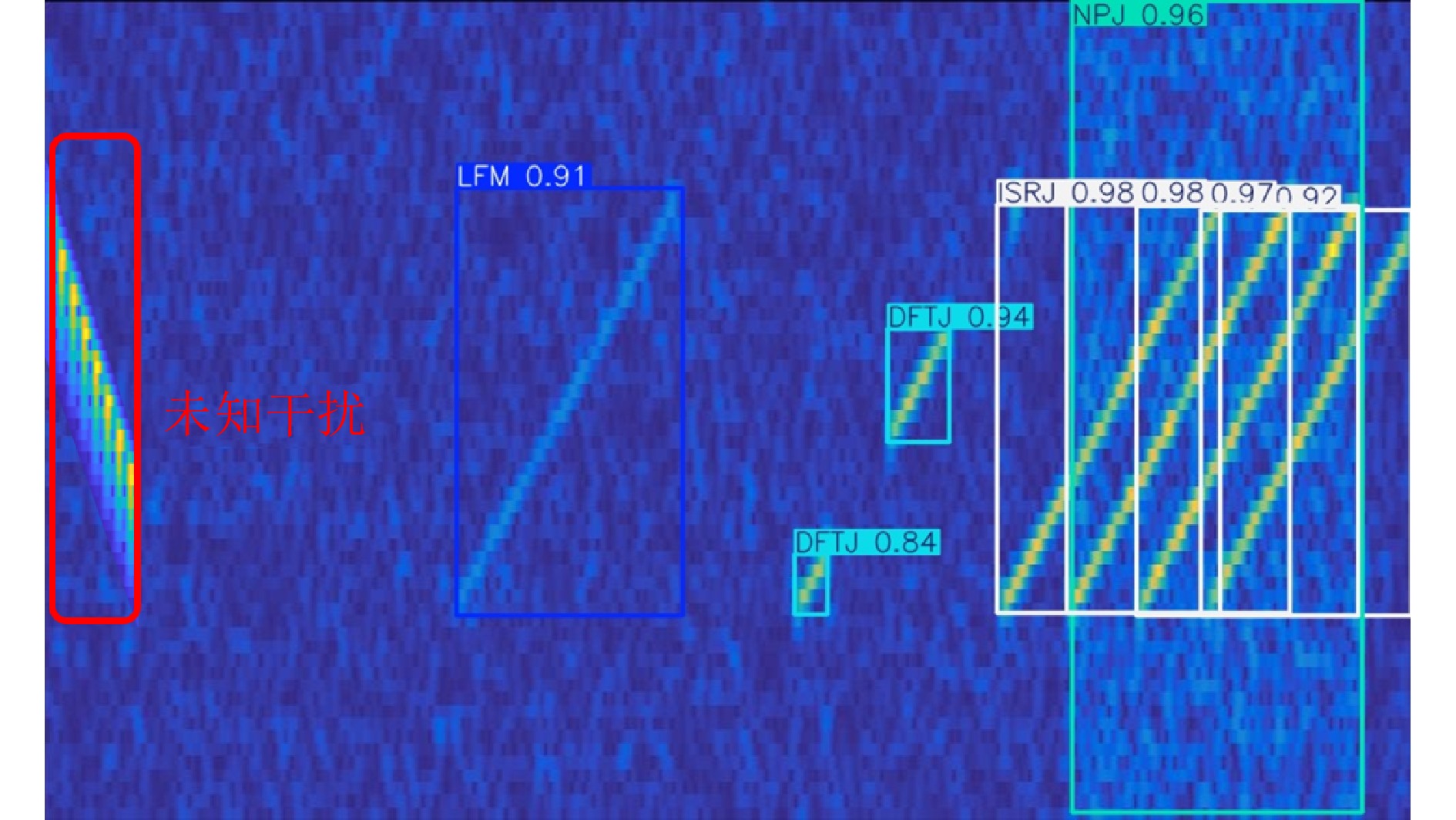
- Figure 14. Recognition results for unseen jamming signals


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: