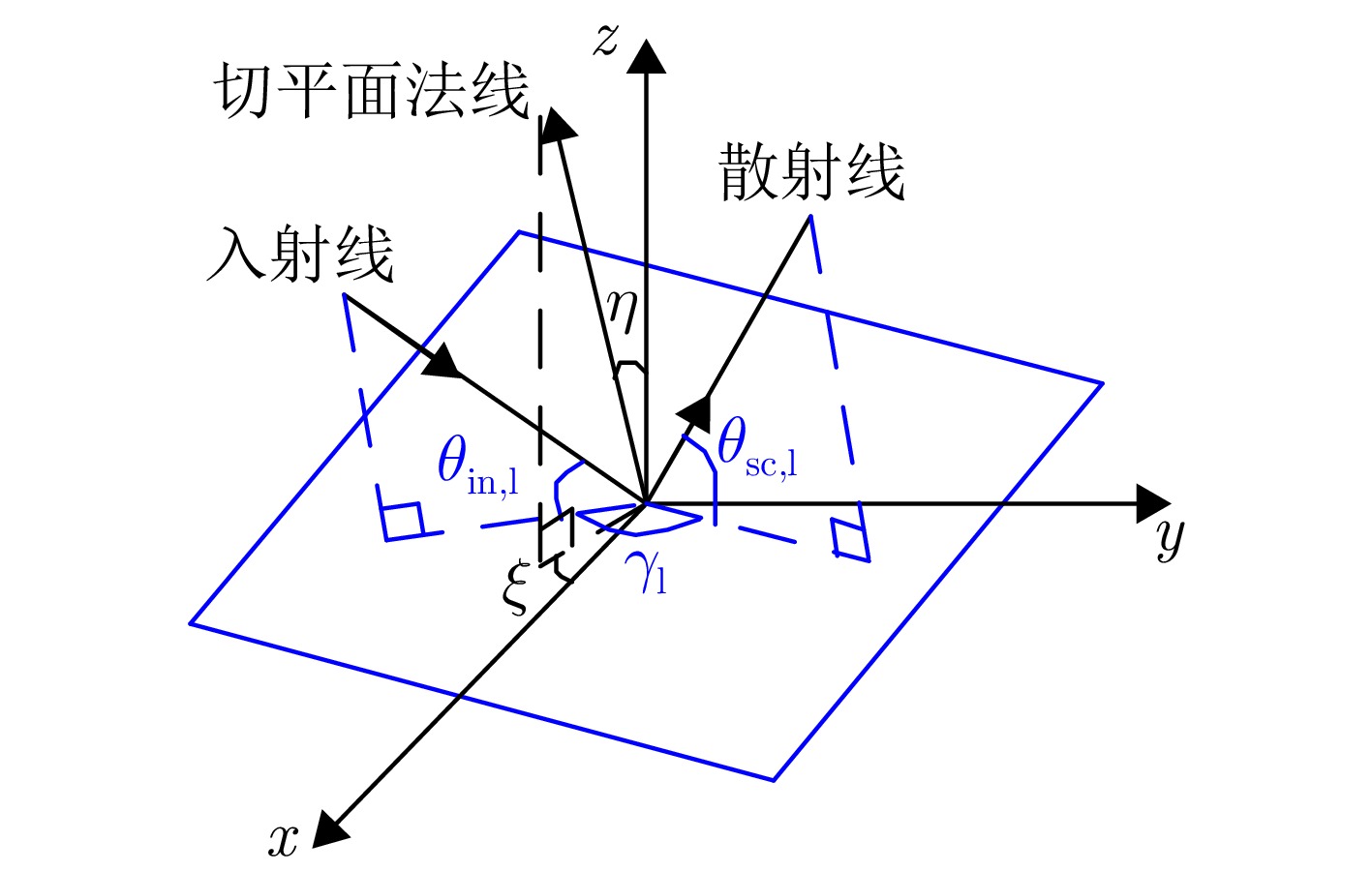
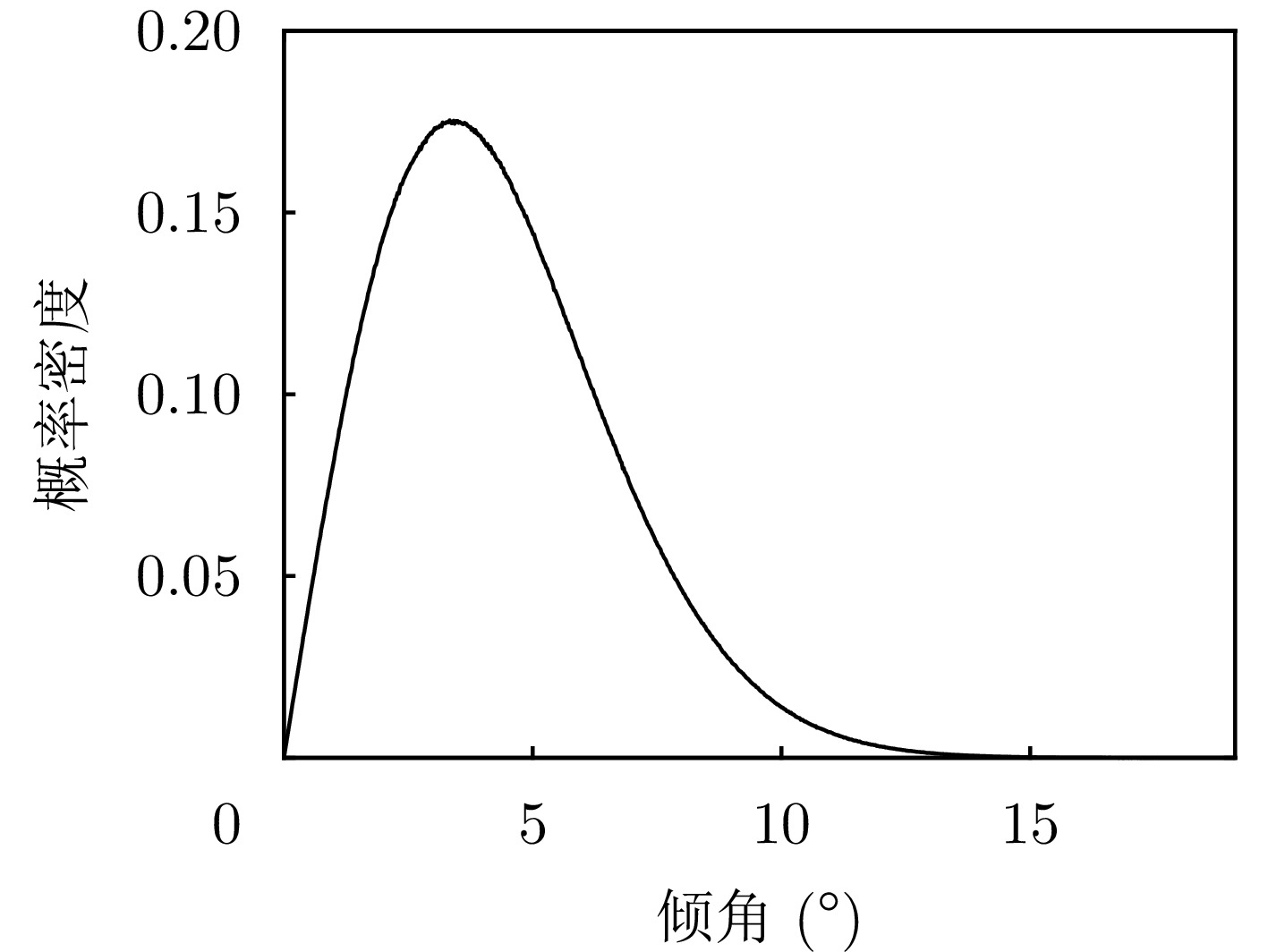
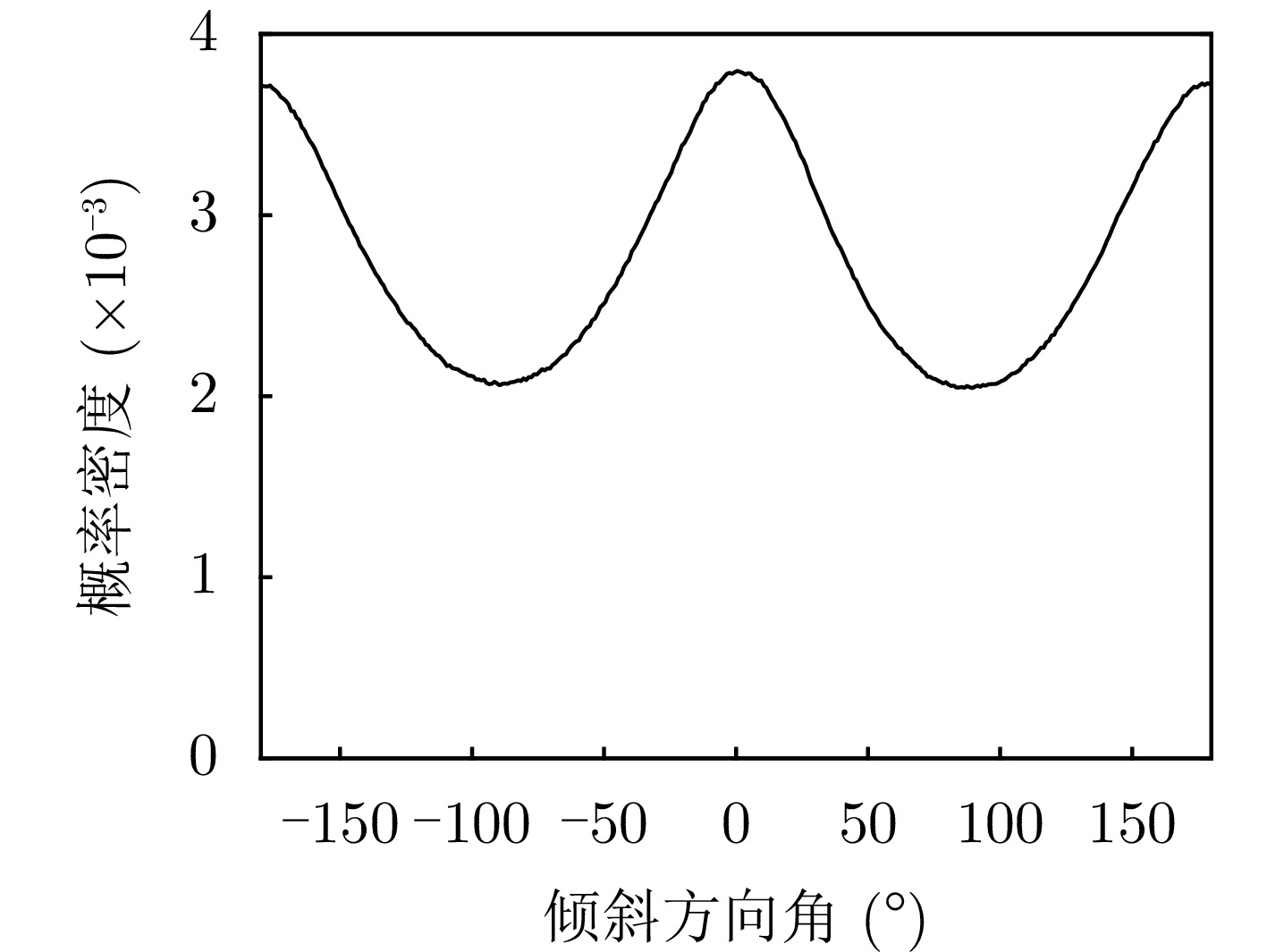
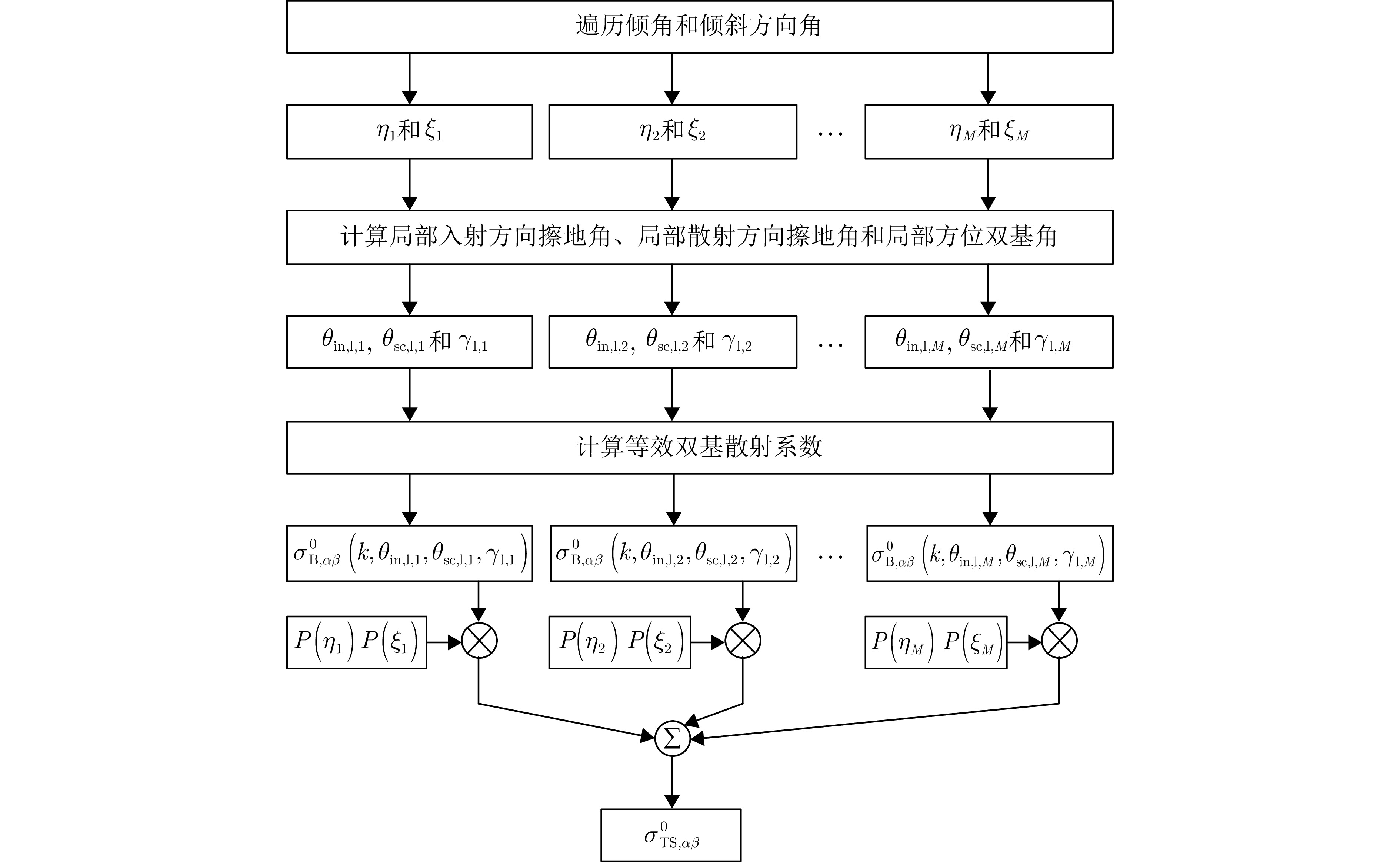
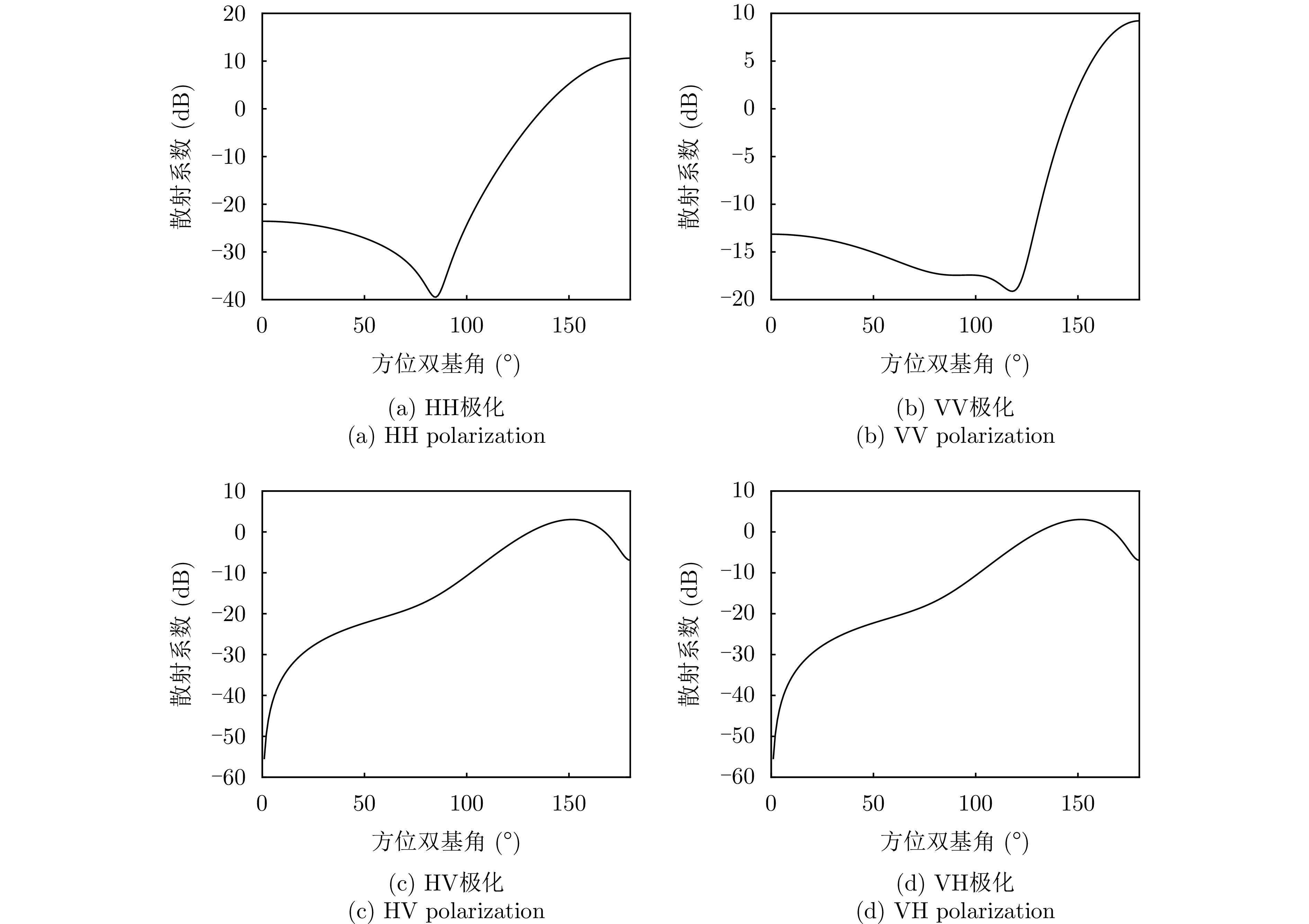
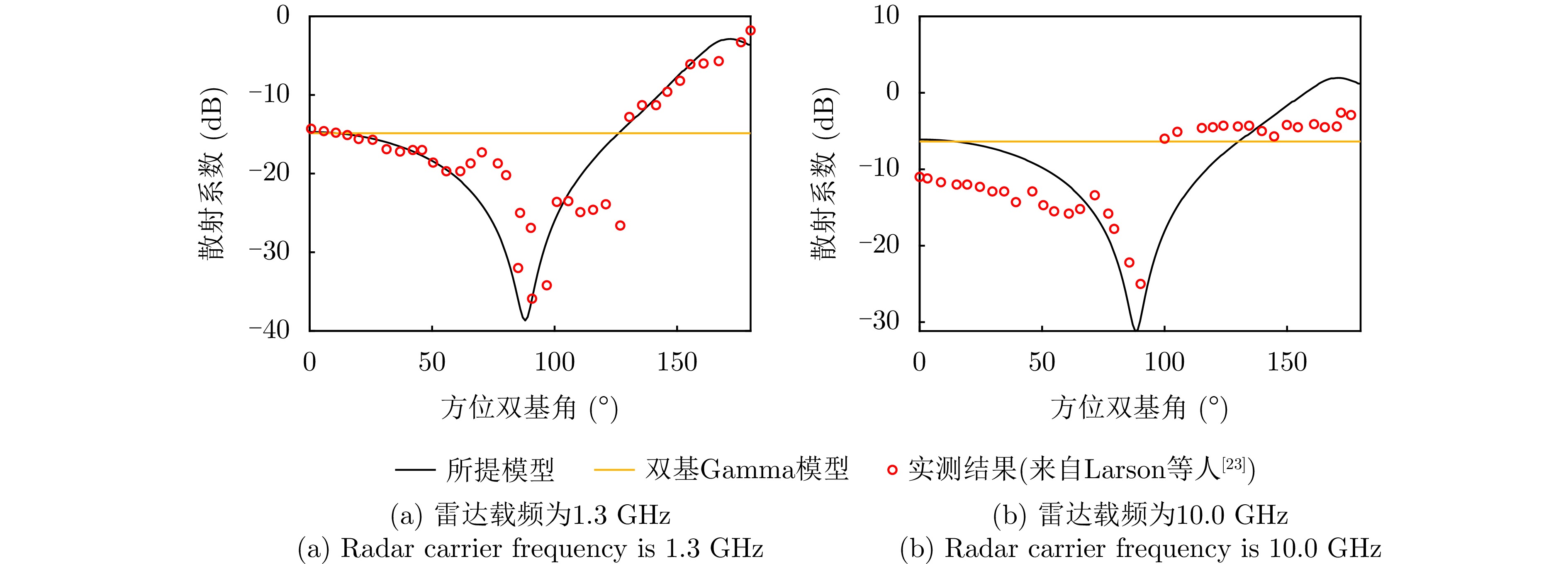
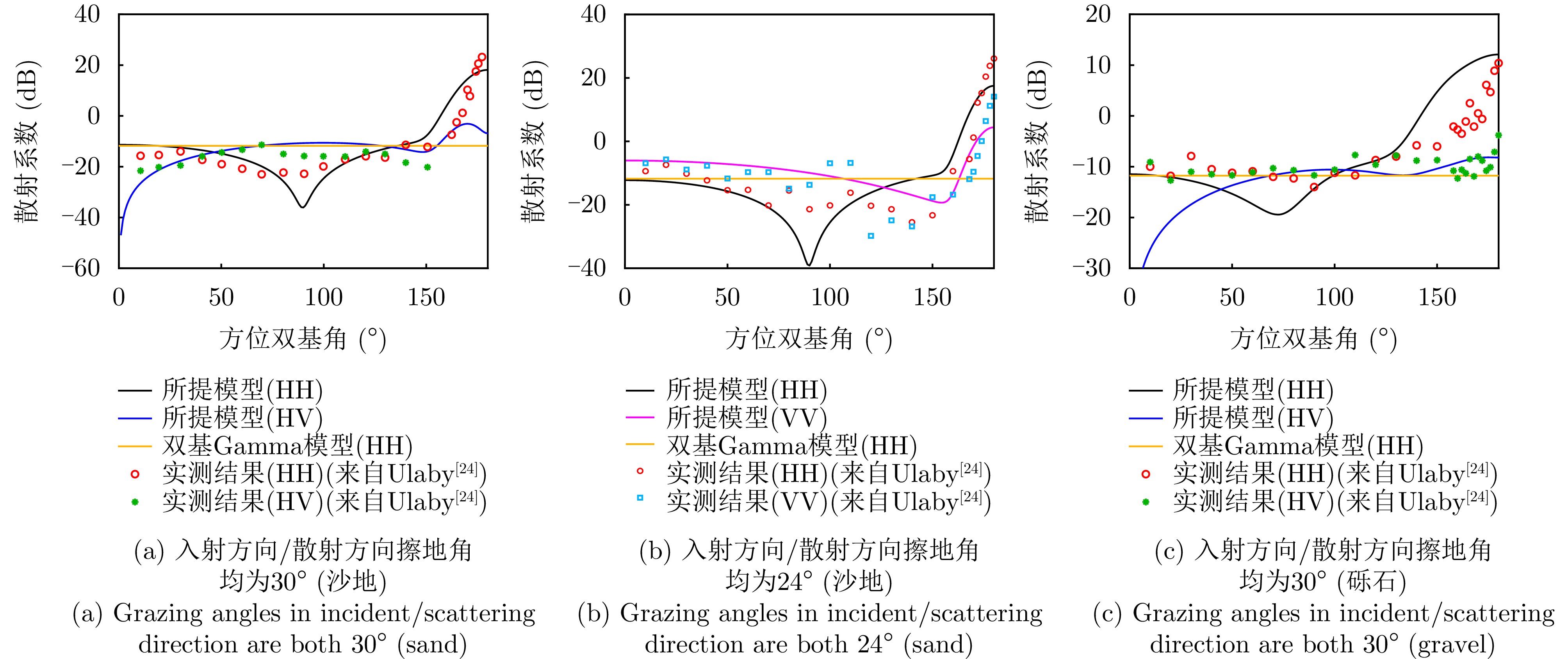
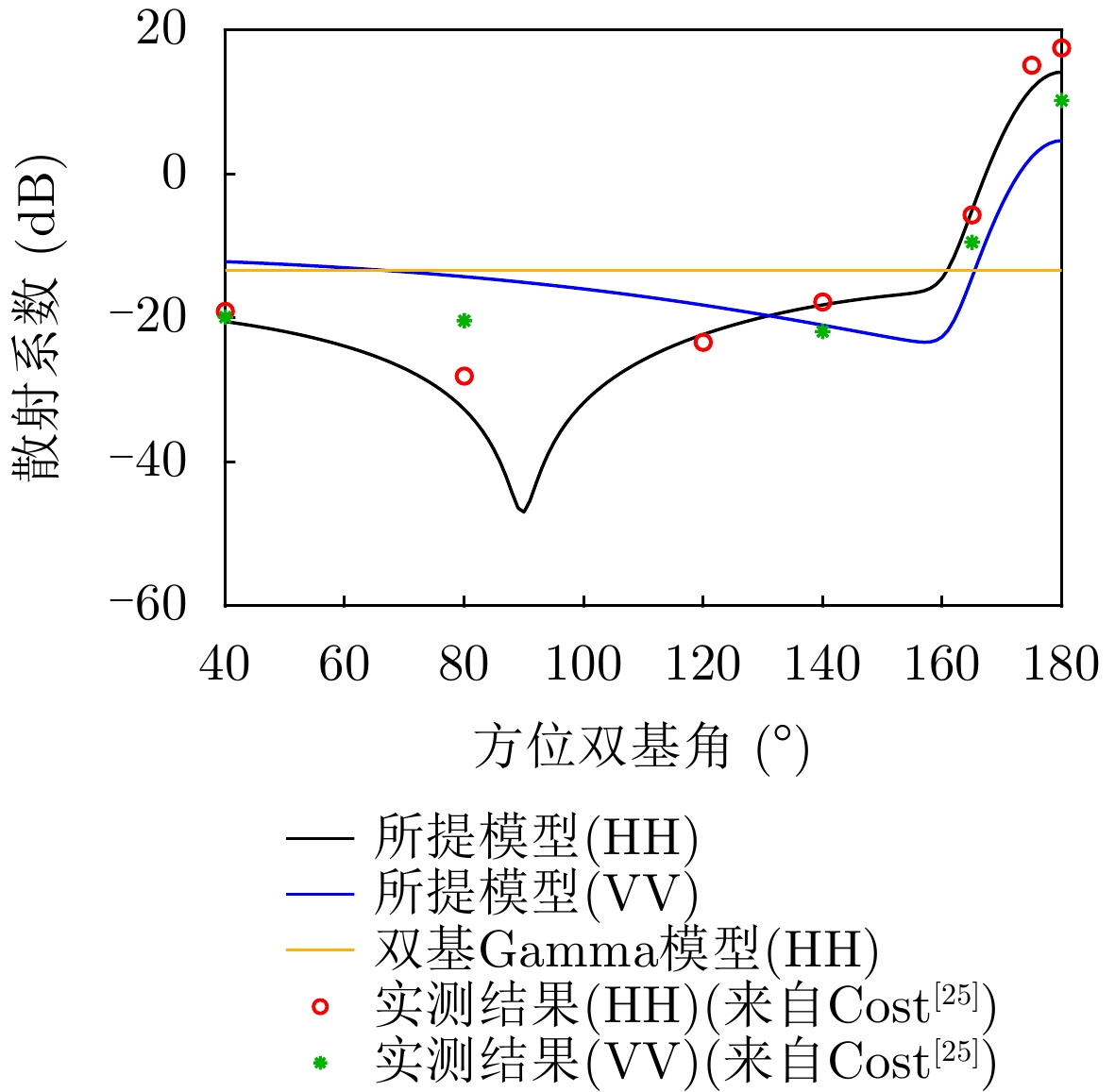
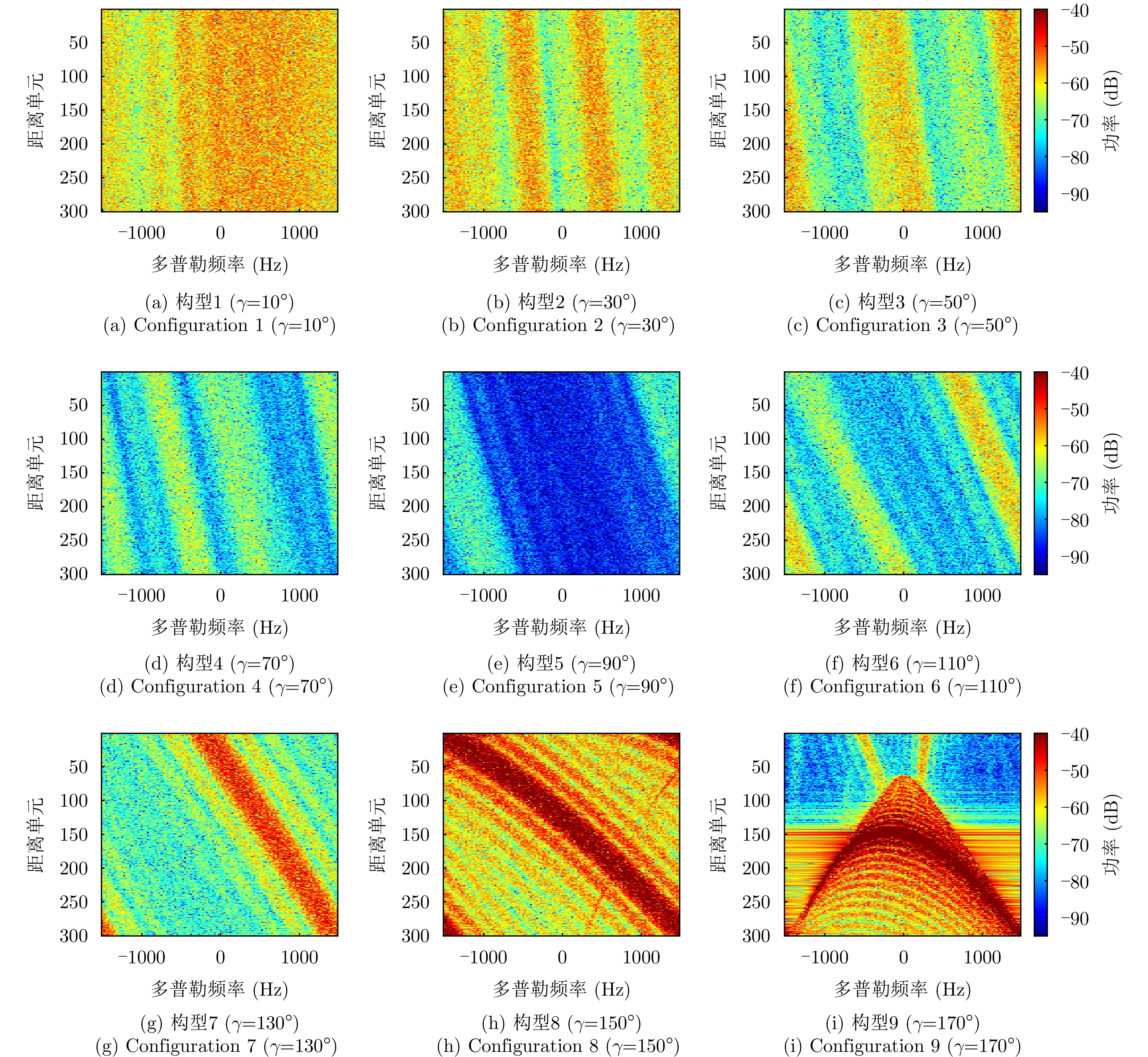
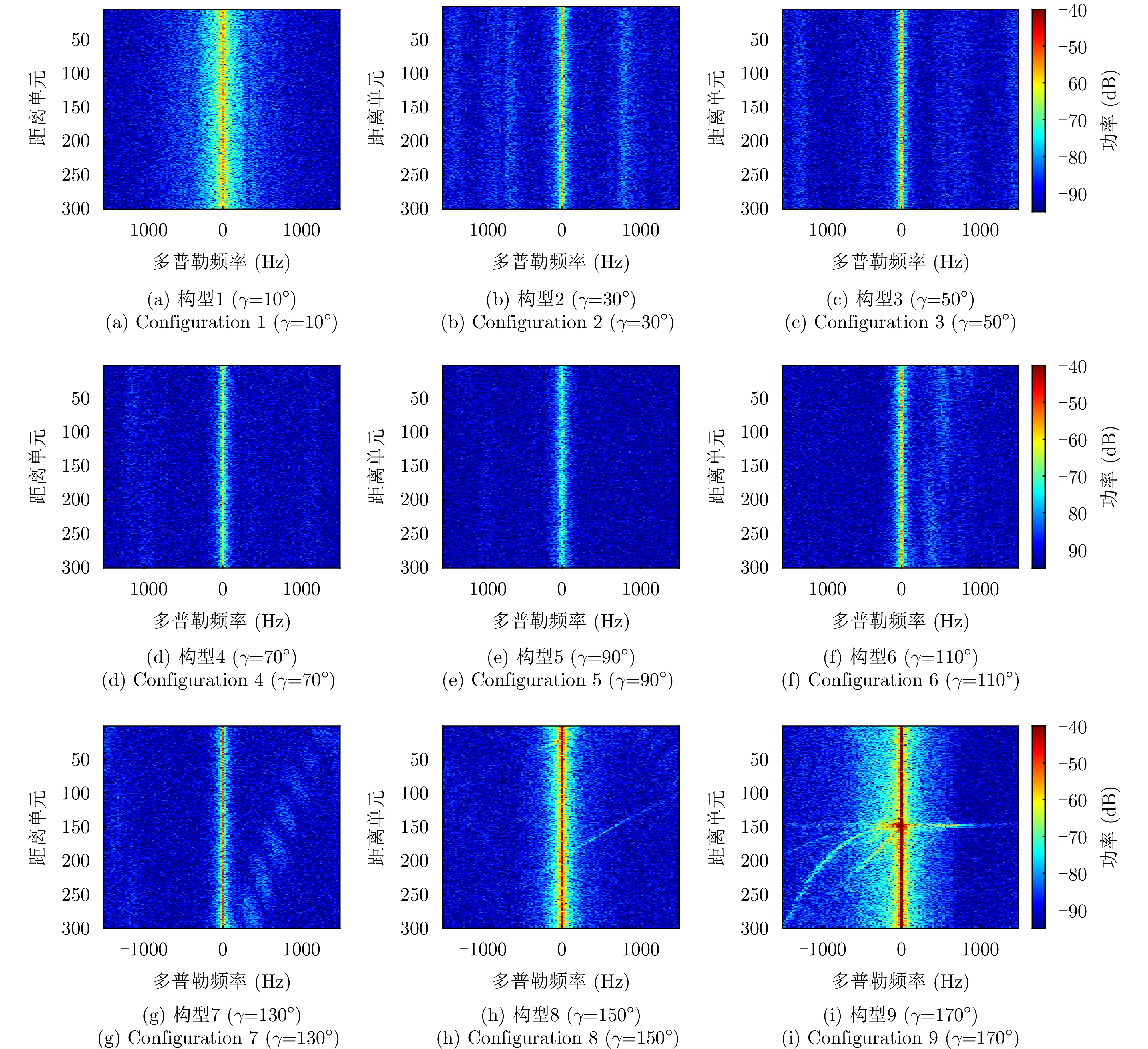
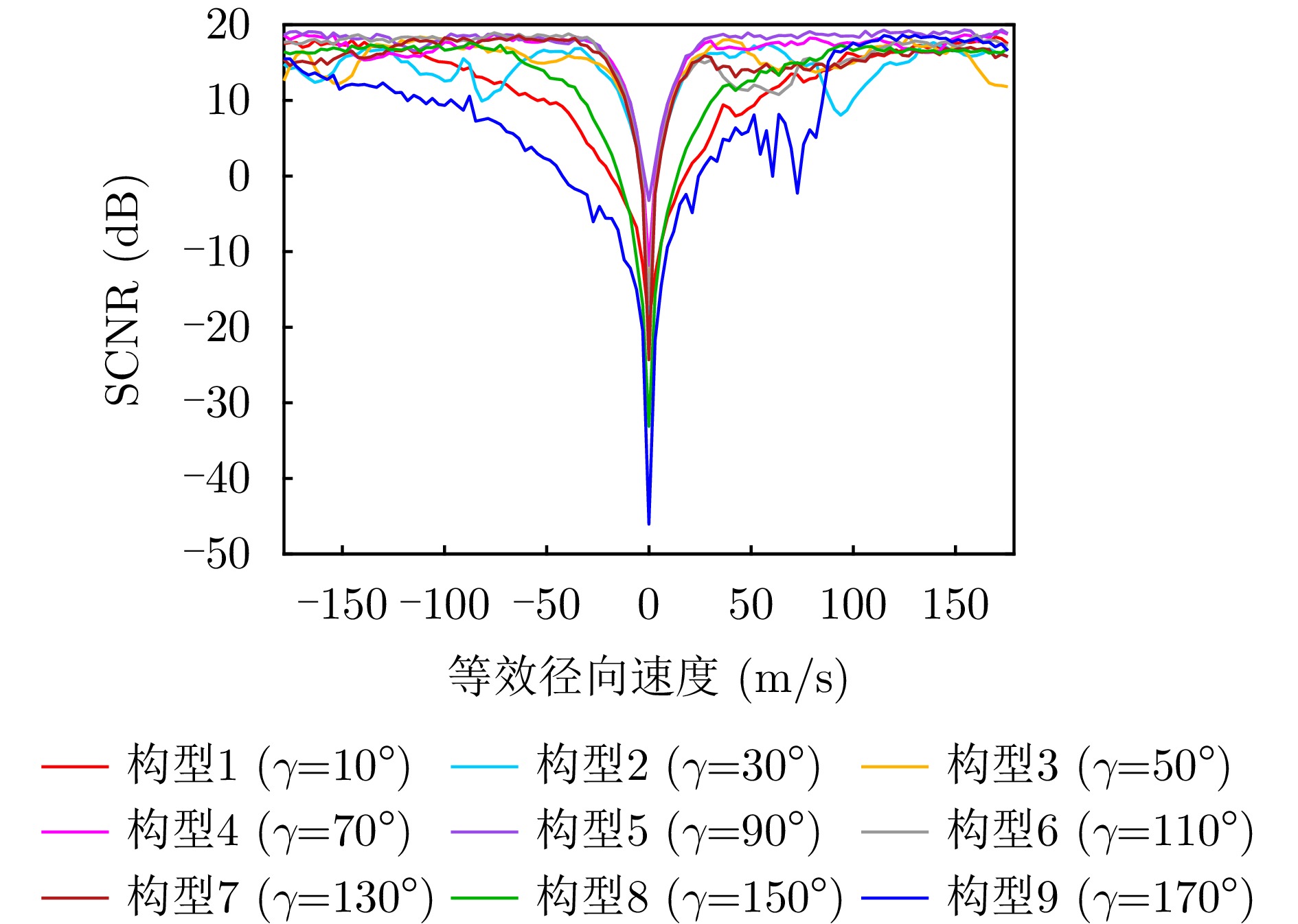
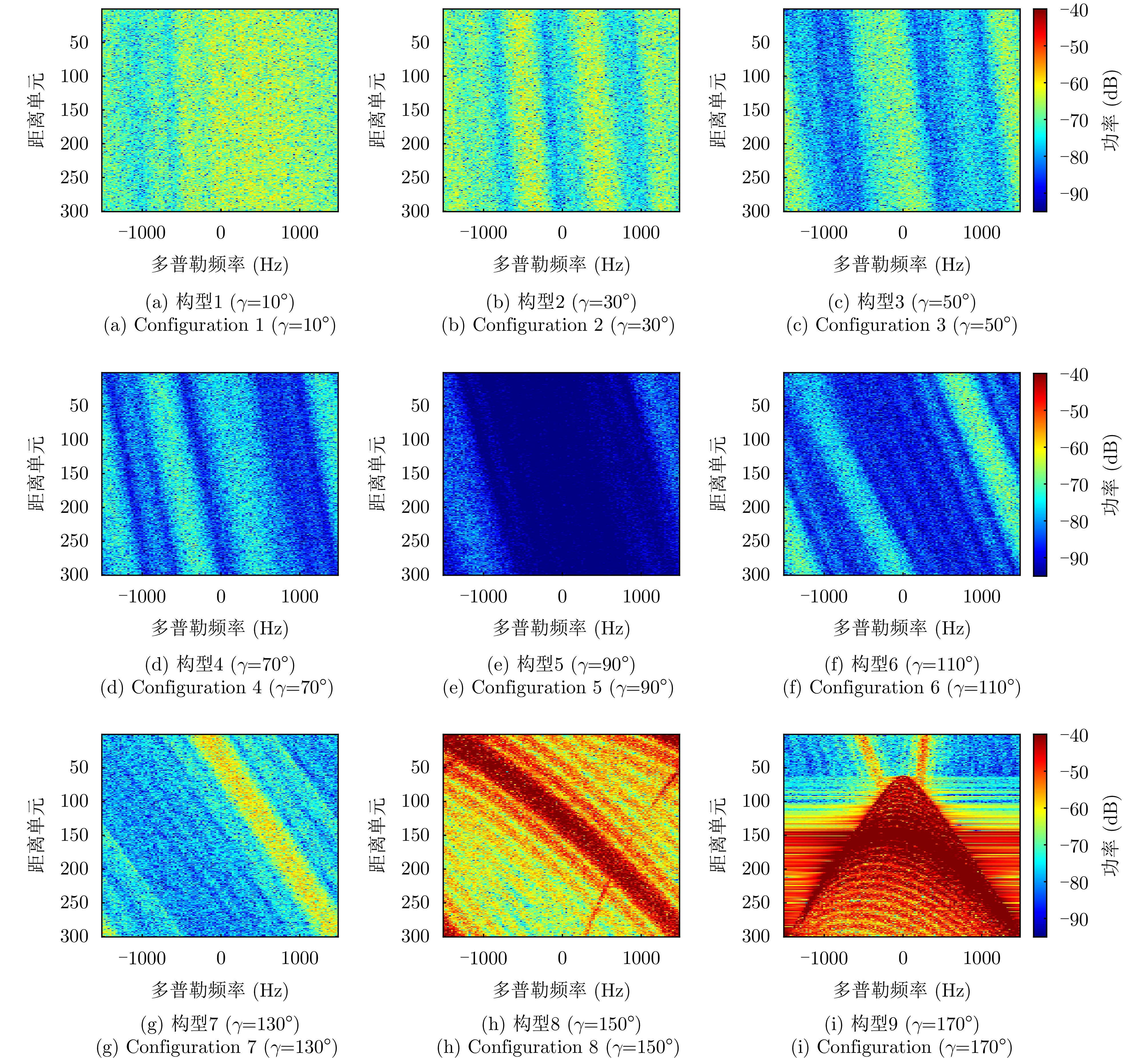
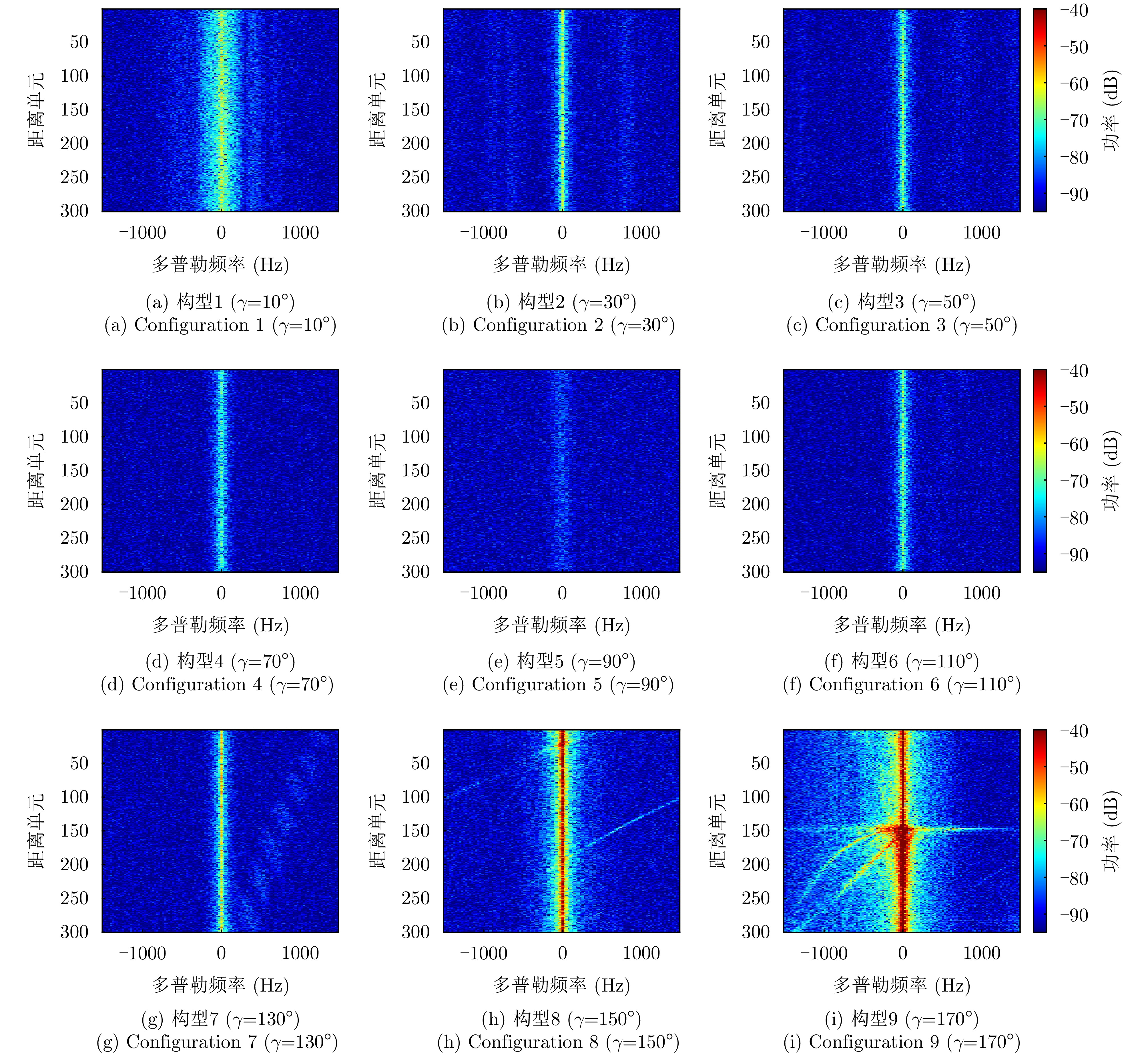
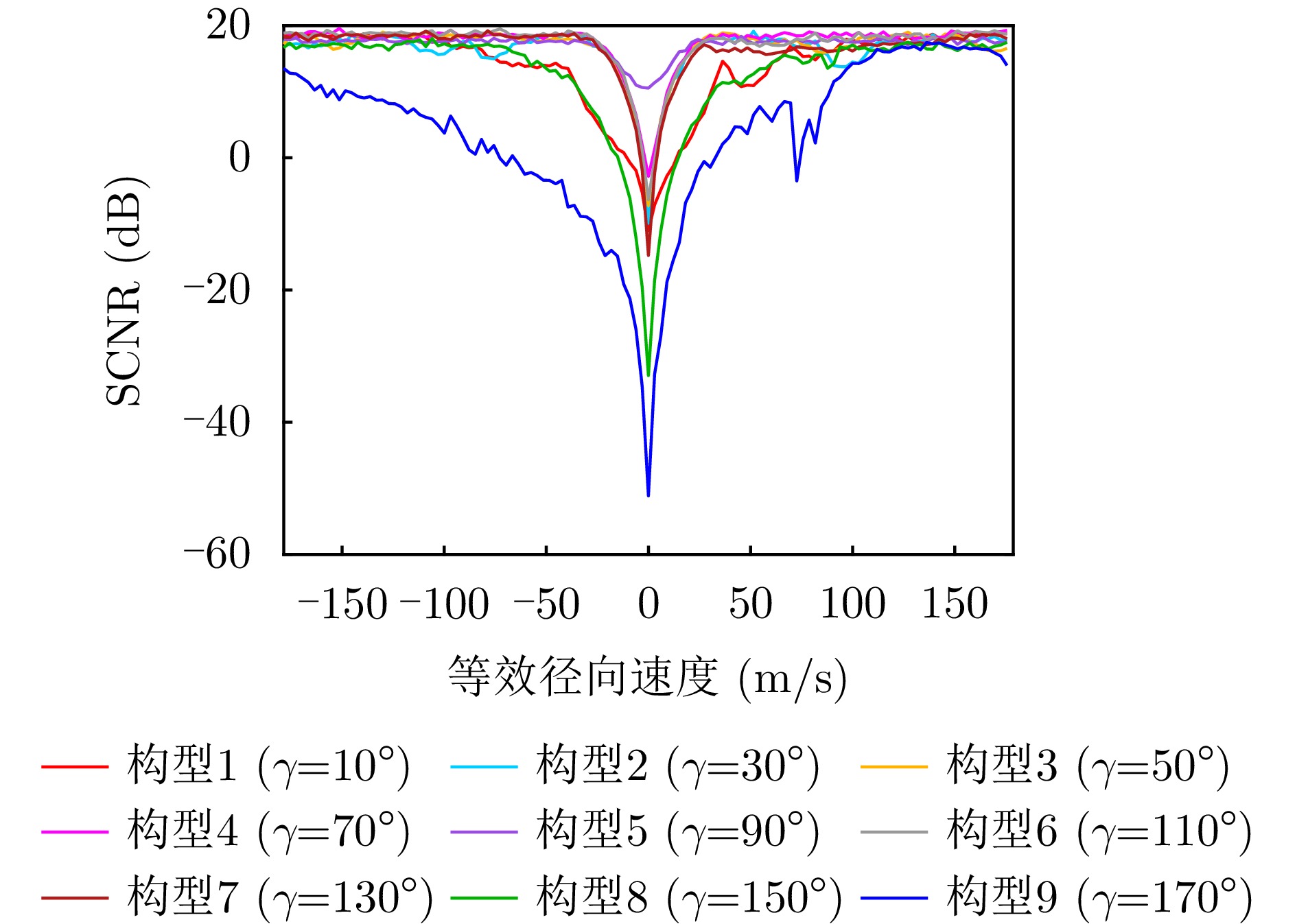
| [1] |
ROSEN P A and DAVIS M E. A joint space-borne radar technology demonstration mission for NASA and the air force[C]. 2020 IEEE Aerospace Conference Proceedings (Cat. No.03TH8652), Big Sky, USA, 2003: 437–444. doi: 10.1109/AERO.2003.1235073. |
| [2] |
FIEDLER S and PREISS B. Geosynchronous space based radar concept development for theater surveillance[C]. 1996 IEEE Aerospace Applications Conference. Proceedings, Aspen, USA, 1996: 77–90. doi: 10.1109/AERO.1996.499404. |
| [3] |
王增福, 杨广宇, 金术玲. 考虑综合性能最优的非短视快速天基雷达多目标跟踪资源调度算法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(1): 253–269. doi: 10.12000/JR23162. WANG Zengfu, YANG Guangyu, and JIN Shuling. A non-myopic and fast resource scheduling algorithm for multi-target tracking of space-based radar considering optimal integrated performance[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 253–269. doi: 10.12000/JR23162. |
| [4] |
ZOU Zihao, MA Jingtao, HUANG Penghui, et al. Multichannel sea clutter modeling and clutter suppression performance analysis for spaceborne bistatic surveillance radar systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5108424. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3424562. |
| [5] |
WANG Jianbo, YE Jianyu, WU Xiaoliang, et al. RCS statistical modeling of stealth targets based on fractional-order Legendre polynomials[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(6): 9807–9820. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3309613. |
| [6] |
ZHU Lei, LIANG Xiaolong, LI Jiong, et al. Simulation analysis on static scattering characteristics of stealth aircraft[C]. 2016 IEEE Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Xi’an, China, 2016: 1774–1778. doi: 10.1109/IMCEC.2016.7867524. |
| [7] |
GUTTRICH G L, SIEVERS W E, and TOMLJANOVICH N M. Wide area surveillance concepts based on geosynchronous illumination and bistatic unmanned airborne vehicles or satellite reception[C]. 1997 IEEE National Radar Conference, Syracuse, USA, 1997: 126–131. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1997.588225. |
| [8] |
BARTON D K. Land clutter models for radar design and analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1985, 73(2): 198–204. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1985.13133. |
| [9] |
MORCHIN W C. Airborne Early Warning Radar[M]. Norwood, USA: Artech House, 1990: 147–153.
|
| [10] |
HORST M M, DYER F B, and TULEY M T. Radar sea clutter model[C]. International IEEE AP/S URSI Symposium, Washington, USA, 1978: 6–10.
|
| [11] |
ANTIPOV I. Simulation of sea clutter returns[R]. DSTO-TR-0679, 1998.
|
| [12] |
REILLY J P and DOCKERY G D. Influence of evaporation ducts on radar sea return[J]. IEE Proceedings F—Radar and Signal Processing, 1990, 137(2): 80–88. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1990.0012. |
| [13] |
GREGERS-HANSEN V and MITAL R. An improved empirical model for radar sea clutter reflectivity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2012, 48(4): 3512–3524. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2012.6324732. |
| [14] |
WILLIS N J. Bistatic Radar[M]. 2nd ed. Raleigh, USA: SciTech, 2005: 157–171.
|
| [15] |
AL-ASHWAL W A, GRIFFITHS H D, and WOODBRIDGE K. An empirical model for bistatic sea clutter normalised radar cross section[C]. IET International Conference on Radar Systems, Glasgow, UK, 2012: 1–5. doi: 10.1049/cp.2012.1672. |
| [16] |
GRIFFITHS H D, AL-ASHWAL W A, WARD K D, et al. Measurement and modelling of bistatic radar sea clutter[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2010, 4(2): 280–292. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2009.0124. |
| [17] |
谢文冲, 段克清, 王永良. 机载雷达空时自适应处理技术研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 575–586. doi: 10.12000/JR17073. XIE Wenchong, DUAN Keqing, and WANG Yongliang. Space time adaptive processing technique for airborne radar: An overview of its development and prospects[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 575–586. doi: 10.12000/JR17073. |
| [18] |
JOHNSON J T, BAKER C J, SMITH G E, et al. The monostatic-bistatic equivalence theorem and bistatic radar clutter[C]. 2014 11th European Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2014: 105–108. doi: 10.1109/EuRAD.2014.6991218. |
| [19] |
JOHNSON J T and OUELLETTE J D. Polarization features in bistatic scattering from rough surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(3): 1616–1626. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2252909. |
| [20] |
SKOLNIK M I. Radar Handbook[M]. 3rd ed. New York, USA: McGraw-Hill, 2008: 15.30–15.32.
|
| [21] |
PIERSON W J and MOSKOWITZ L. A proposed spectral form for fully developed wind seas based on the similarity theory of S. A. Kitaigorodskii[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1964, 69(24): 5181–5190. doi: 10.1029/JZ069i024p05181. |
| [22] |
CHASE J, COTE L J, MARKS W, et al. The directional spectrum of a wind generated sea as determined from data obtained by the Stereo Wave Observation Project[R]. 1957.
|
| [23] |
LARSON R W, MAFFETT A L, HEIMILLER R C, et al. Bistatic clutter measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1978, 26(6): 801–804. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1978.1141947. |
| [24] |
ULABY F T, VAN DEVENTER T E, EAST J R, et al. Millimeter-wave bistatic scattering from ground and vegetation targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1988, 26(3): 229–243. doi: 10.1109/36.3026. |
| [25] |
COST S T. Measurements of the bistatic echo area of terrain at X-band[R]. 1965.
|
| [26] |
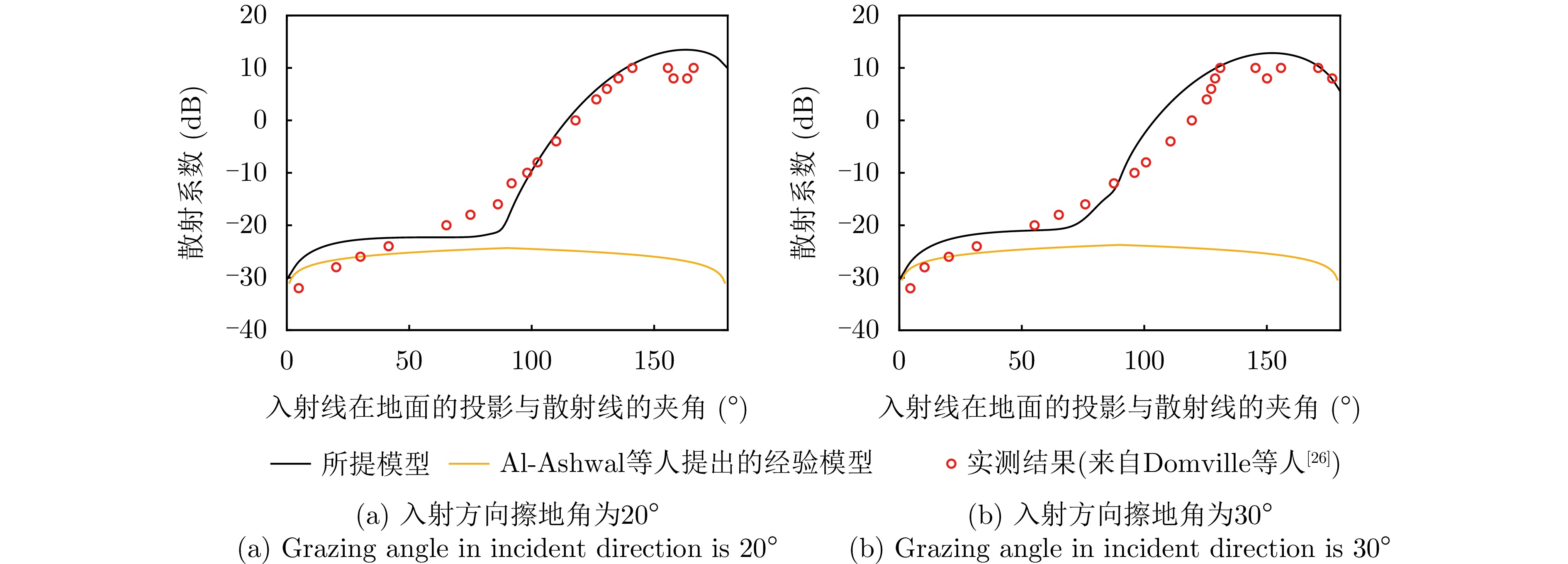
DOMVILLE A R. The bistatic reflection from land and sea of X-band radio waves[R]. 1967.
|
| [27] |
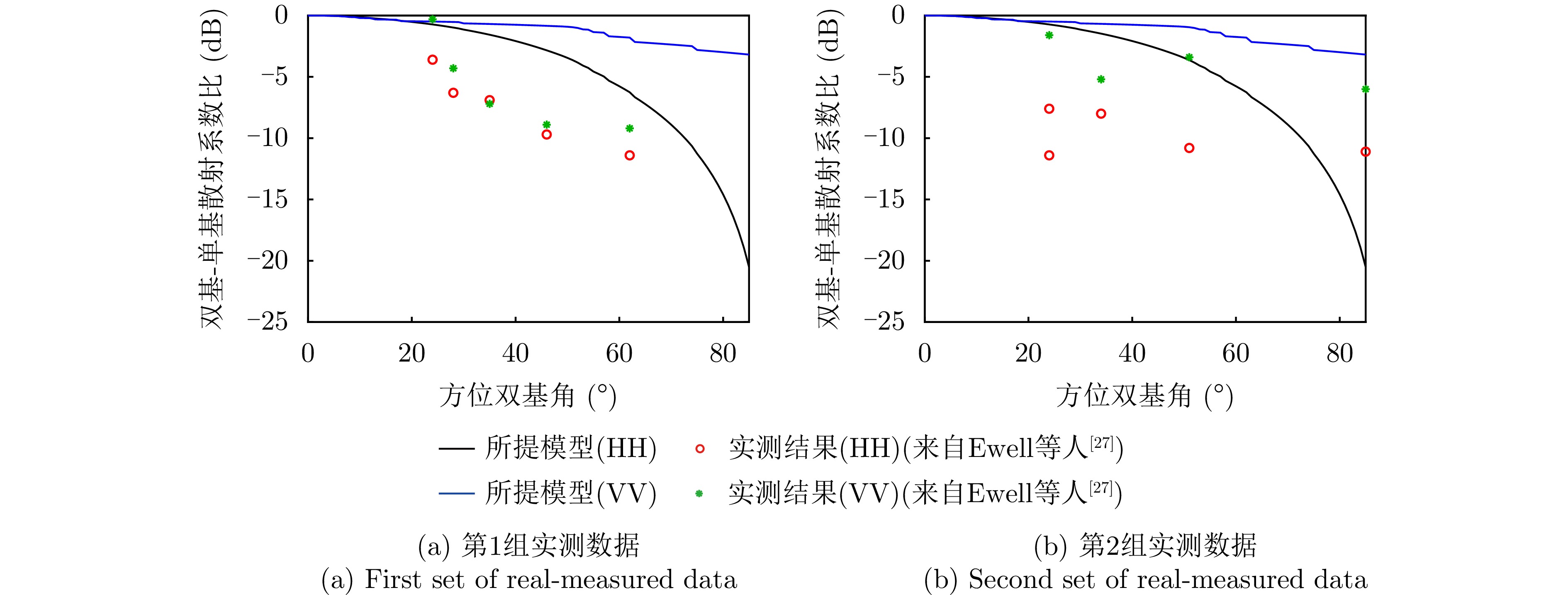
EWELL G W. Bistatic Radar Cross Section Measurements[M]. CURRIE N C. Techniques of Radar Reflectivity Measurement. Dedham, USA: Artech House, 1984: Chapter 7.
|
| [28] |
HALE T B, TEMPLE M A, RAQUET J F, et al. Localized three-dimensional adaptive spatial-temporal processing for airborne radar[C]. RADAR 2002, Edinburgh, UK, 2002: 191–195. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2002.1174680. |
| [29] |
段克清, 李雨凡, 杨兴家, 等. 天基预警雷达低自由度STAP方法研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 871–883. doi: 10.12000/JR22075. DUAN Keqing, LI Yufan, YANG Xingjia, et al. Reduced degrees of freedom in space-time adaptive processing for space-based early warning radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 871–883. doi: 10.12000/JR22075. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: