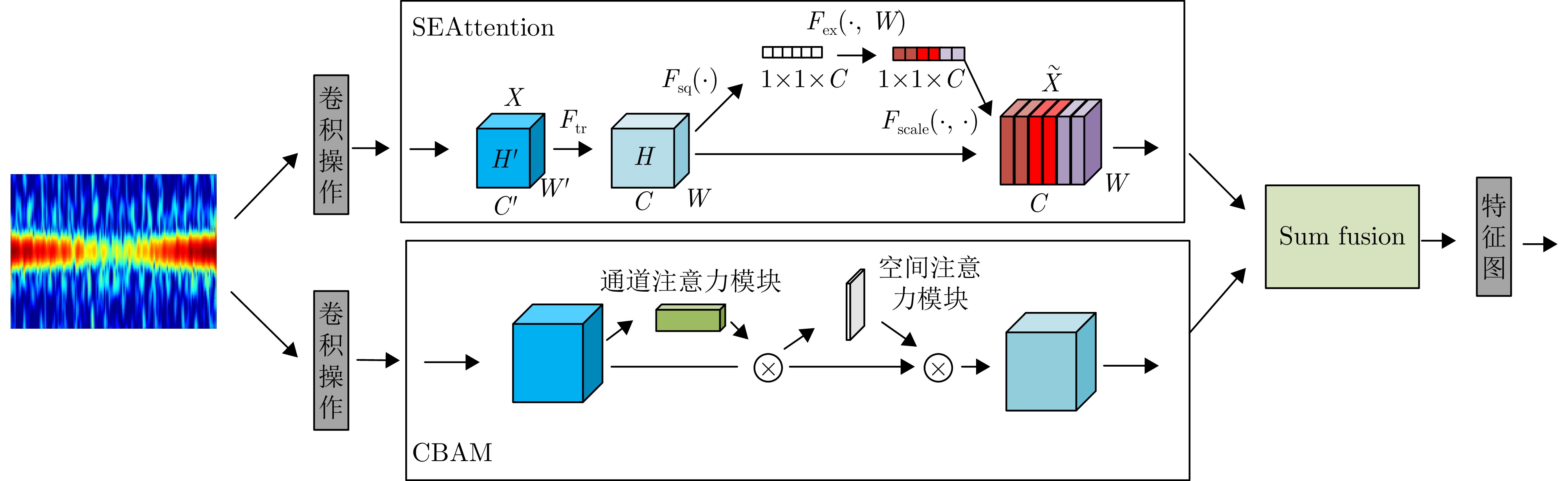
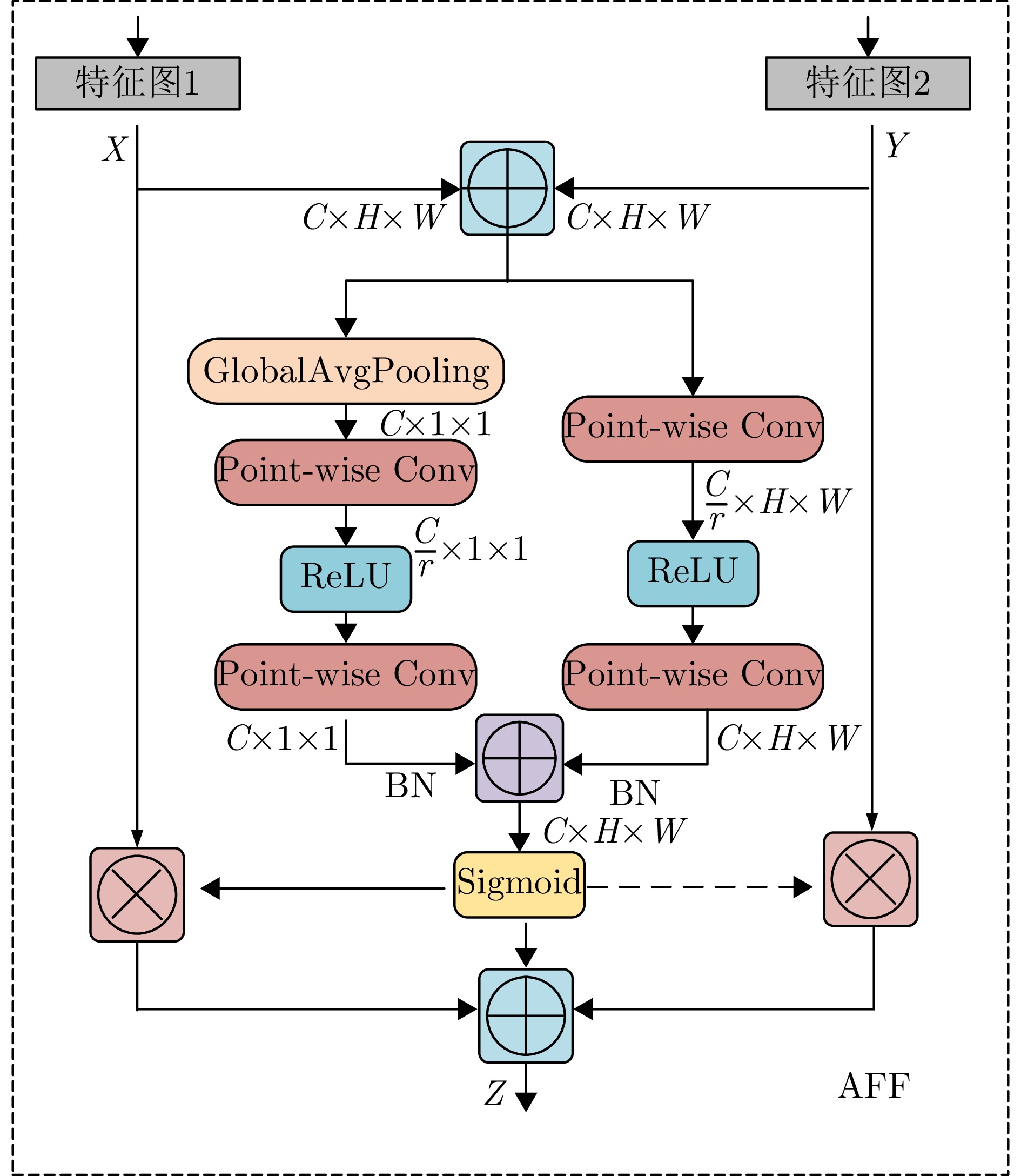
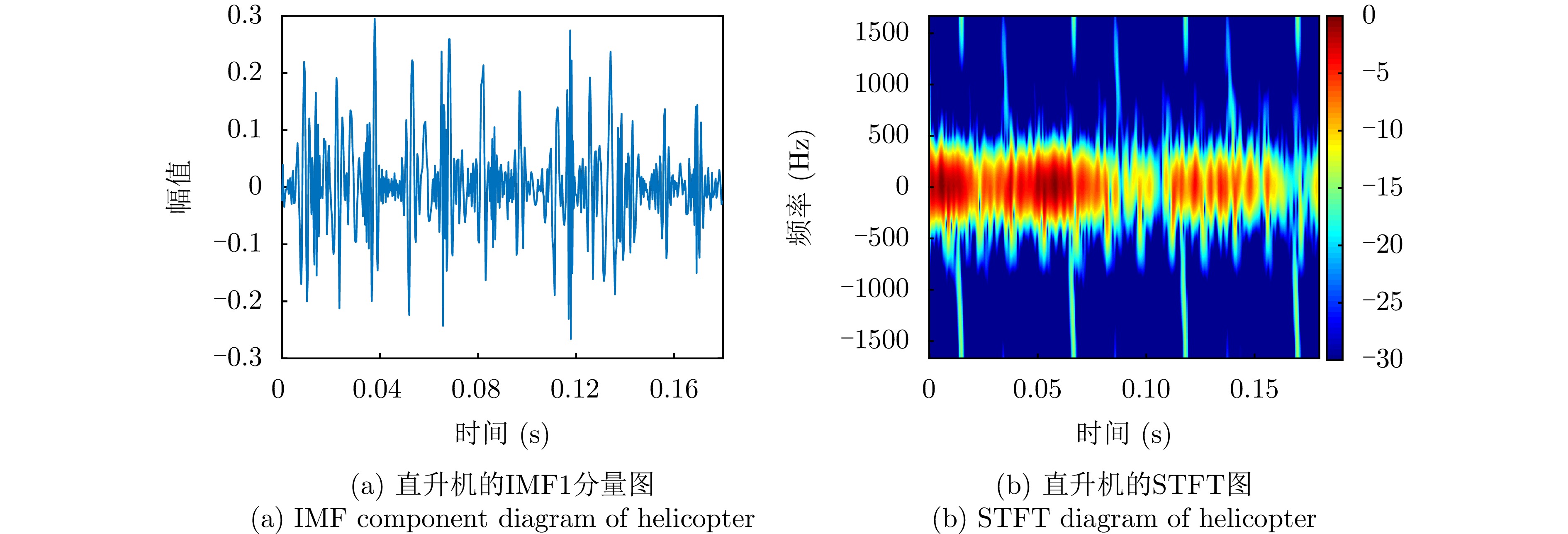
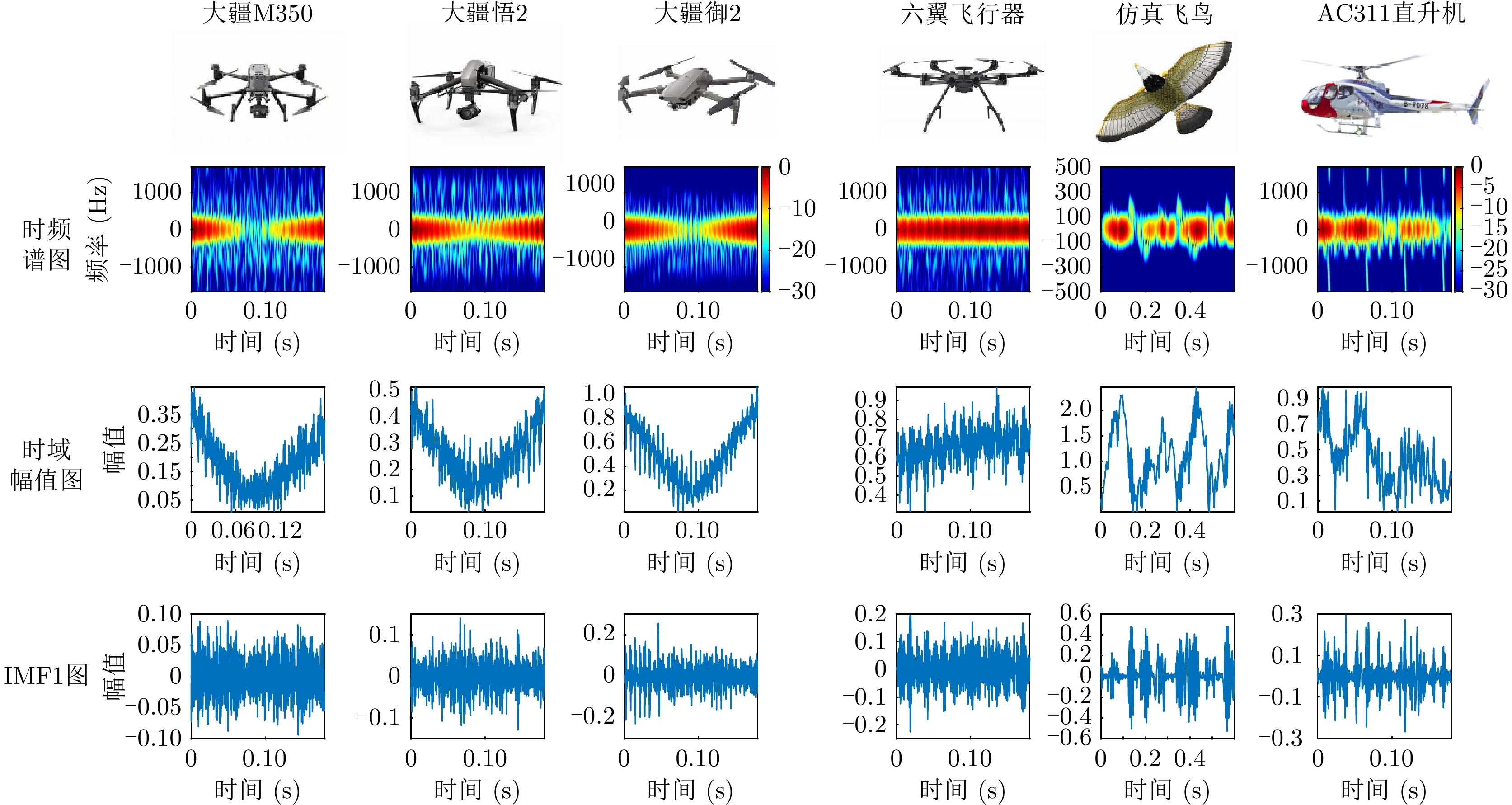
| [1] |
AJAKWE S O, IHEKORONYE V U, KIM D S, et al. DRONET: Multi-tasking framework for real-time industrial facility aerial surveillance and safety[J]. Drones, 2022, 6(2): 46. doi: 10.3390/drones6020046. |
| [2] |
CHEN Xiaolong, NAN Zhao, ZHANG Hai, et al. Experimental research on radar micro-Doppler of flying bird and rotor UAV[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2021, 36(5): 704–714. doi: 10.12265/j.cjors.2020192. |
| [3] |
陈小龙, 陈唯实, 饶云华, 等. 飞鸟与无人机目标雷达探测与识别技术进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 803–827. doi: 10.12000/JR20068. CHEN Xiaolong, CHEN Weishi, RAO Yunhua, et al. Progress and prospects of radar target detection and recognition technology for flying birds and unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 803–827. doi: 10.12000/JR20068. |
| [4] |
YAN Jun, HU Huiping, GONG Jiangkun, et al. Exploring radar micro-Doppler signatures for recognition of drone types[J]. Drones, 2023, 7(4): 280. doi: 10.3390/drones7040280. |
| [5] |
WU Jing, AI Xiaofeng, ZHENG Yuqing, et al. Micro-Doppler curve extraction based on reassociation Viterbi algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 4295–4309. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3373719. |
| [6] |
MA Xinyue, OH B S, SUN Lei, et al. EMD-based entropy features for micro-Doppler mini-UAV classification[C]. 2018 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Beijing, China, 2018: 1295–1300. doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2018.8546180. |
| [7] |
ZHAO Yichao and SU Yi. The extraction of micro-Doppler signal with EMD algorithm for radar-based small UAVs’ detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(3): 929–940. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2019.2905751. |
| [8] |
LI Ruoyu and HE D. Rotational machine health monitoring and fault detection using EMD-based acoustic emission feature quantification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2012, 61(4): 990–1001. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2011.2179819. |
| [9] |
OH B S, GUO Xin, WAN Fangyuan, et al. An EMD-based micro-Doppler signature analysis for mini-UAV blade flash reconstruction[C]. 2017 22nd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), London, UK, 2017. 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICDSP.2017.8096105. |
| [10] |
PATEL J S, FIORANELLI F, and ANDERSON D. Review of radar classification and RCS characterisation techniques for small UAVs or drones[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(9): 911–919. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.0020. |
| [11] |
LEONARDI M, LIGRESTI G, and PIRACCI E. Drones classification by the use of a multifunctional radar and micro-Doppler analysis[J]. Drones, 2022, 6(5): 124. doi: 10.3390/drones6050124. |
| [12] |
CHEN Xu, MA Chunguang, ZHAO Chaofan, et al. UAV classification based on deep learning fusion of multidimensional UAV micro-Doppler image features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3503205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3371171. |
| [13] |
KUMAWAT H C, CHAKRABORTY M, BAZIL RAJ A A, et al. DIAT-μSAT: Small aerial targets’ micro-Doppler signatures and their classification using CNN[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 6004005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3102039. |
| [14] |
WANG Chenxing, TIAN Jiangmin, CAO Jinwen, et al. Deep learning-based UAV detection in pulse-Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5105612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3104907. |
| [15] |
CHEN Tao, GAO Shuncheng, ZHENG Shilian, et al. EMD and VMD empowered deep learning for radio modulation recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2023, 9(1): 43–57. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2022.3218694. |
| [16] |
ZHU Jianping, CHEN Haiquan, and YE Wenbin. A hybrid CNN-LSTM network for the classification of human activities based on micro-Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 24713–24720. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2971064. |
| [17] |
SUN Yingxiang, ABEYWICKRAMA S, JAYASINGHE L, et al. Micro-Doppler signature-based detection, classification, and localization of small UAV with long short-term memory neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6285–6300. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3028654. |
| [18] |
CHEN Xiaolong, ZHANG Hai, SONG Jie, et al. Micro-motion classification of flying bird and rotor drones via data augmentation and modified multi-scale CNN[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(5): 1107. doi: 10.3309/rs14051107. |
| [19] |
FU Rui, AL-ABSI M A, KIM K H, et al. Deep learning-based drone classification using radar cross section signatures at mmWave frequencies[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 161431–161444. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3115805. |
| [20] |
MO Yongguang, HUANG Jianjun, and QIAN Gongbin. Deep learning approach to UAV detection and classification by using compressively sensed RF signal[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(8): 3072. doi: 10.3390/s22083072. |
| [21] |
CHEN Xiaolong, SU Ningyuan, HUANG Yong, et al. False-alarm-controllable radar detection for marine target based on multi features fusion via CNNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(7): 9099–9111. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3054744. |
| [22] |
陈小龙, 袁旺, 杜晓林, 等. 多波段FMCW雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-FMCWR-1.0)及高分辨微动特征提取方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR23142. CHEN Xiaolong, YUAN Wang, DU Xiaolin, et al. Multiband FMCW radar LSS-target detection dataset (LSS-FMCWR-1.0) and high-resolution micromotion feature extraction method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(3): 539–553. doi: 10.12000/JR23142. |
| [23] |
陈小龙, 饶桂林, 关键, 等. 被动雷达低慢小探测数据集(LSS-PR-1.0)及多域特征提取和分析方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(2): 249–268. doi: 10.12000/JR24145. CHEN Xiaolong, RAO Guilin, GUAN Jian, et al. Passive radar low slow small detection dataset (LSS-PR-1.0) and multi-domain feature extraction and analysis methods[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(2): 249–268. doi: 10.12000/JR24145. |
| [24] |
章鹏飞, 李刚, 霍超颖, 等. 基于双雷达微动特征融合的无人机分类识别[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 557–564. doi: 10.12000/JR18061. ZHANG Pengfei, LI Gang, HUO Chaoying, et al. Classification of drones based on micro-Doppler radar signatures using dual radar sensors[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 557–564. doi: 10.12000/JR18061. doi: 10.12000/JR18061. |
| [25] |
OH B S, GUO Xin, WAN Fangyuan, et al. Micro-Doppler mini-UAV classification using empirical-mode decomposition features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(2): 227–231. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2781711. |
| [26] |
WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1. |
| [27] |
HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745. |
| [28] |
DAI Yimian, GIESEKE F, OEHMCKE S, et al. Attentional feature fusion[C]. 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2021: 3559–3568. doi: 10.1109/WACV48630.2021.00360. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: