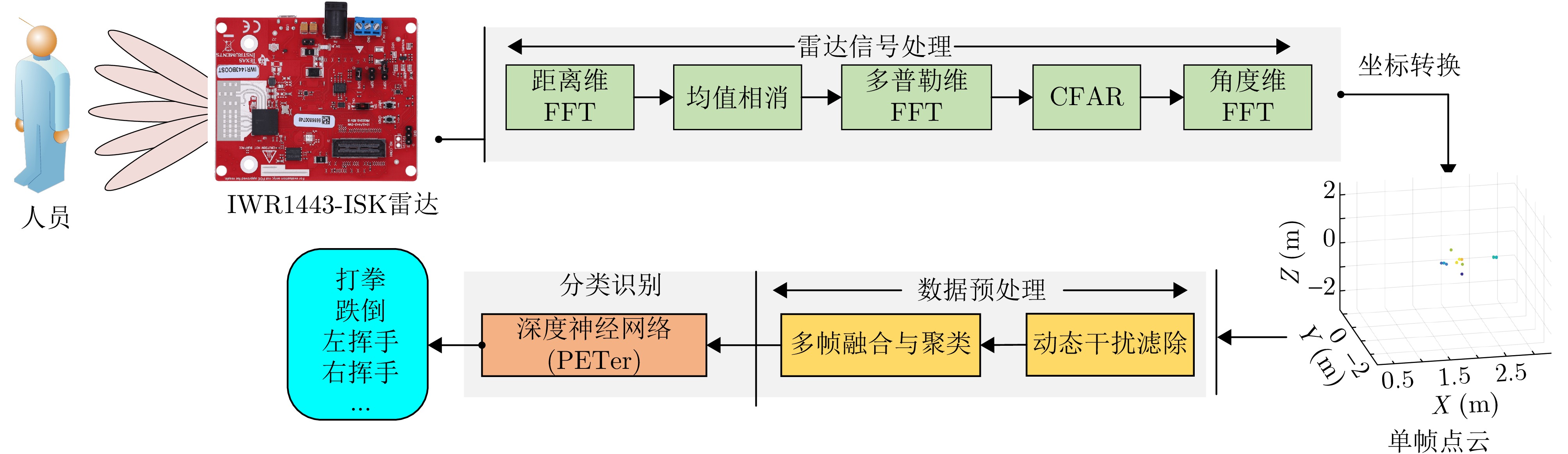
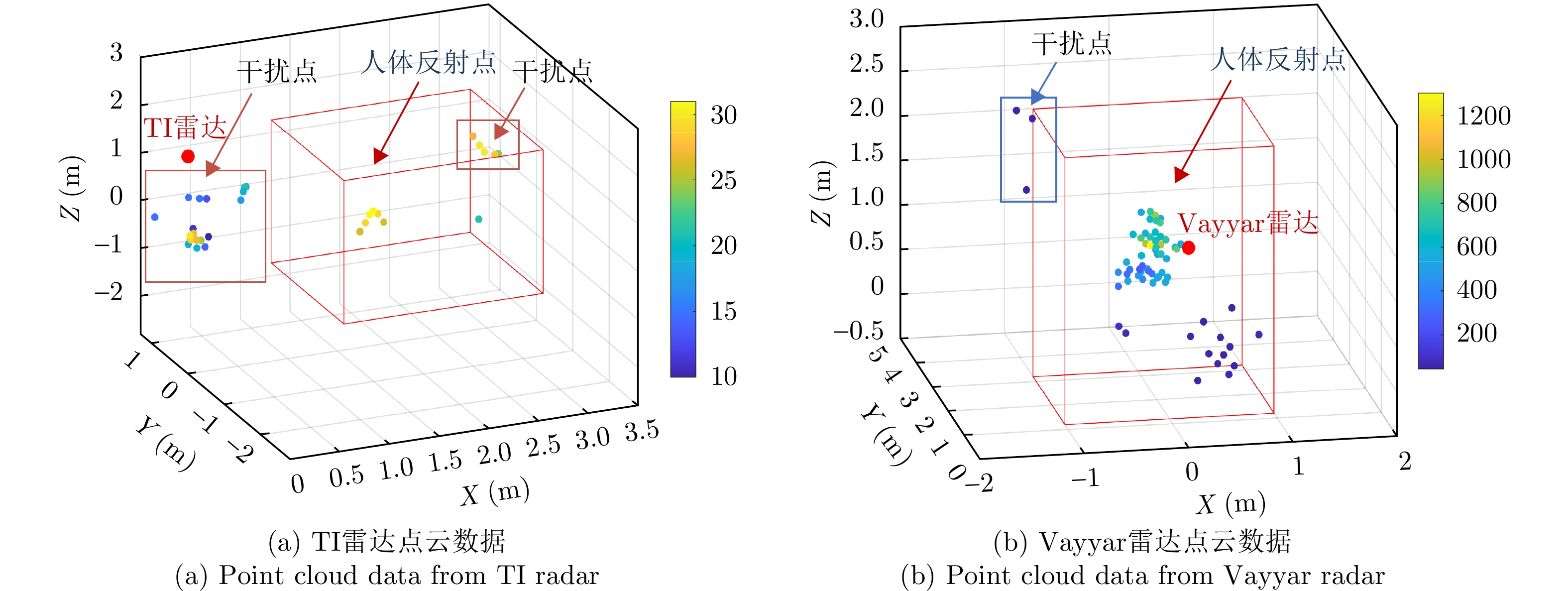
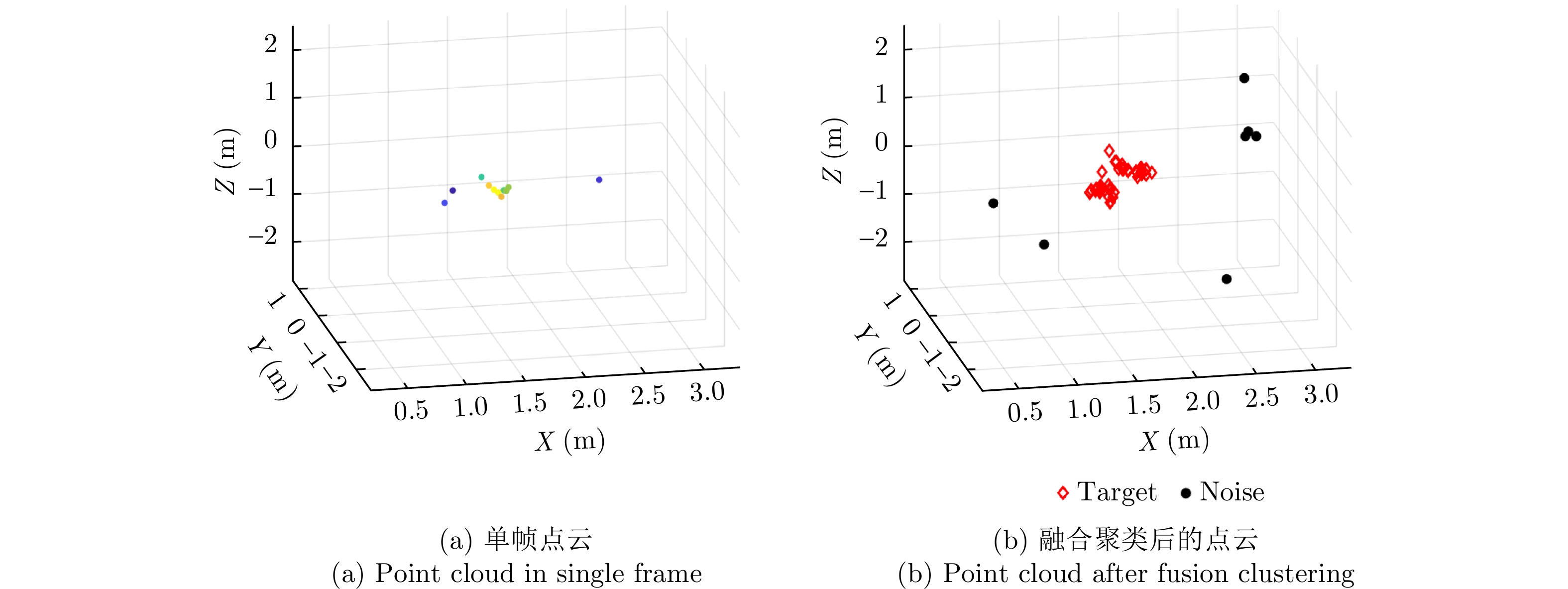
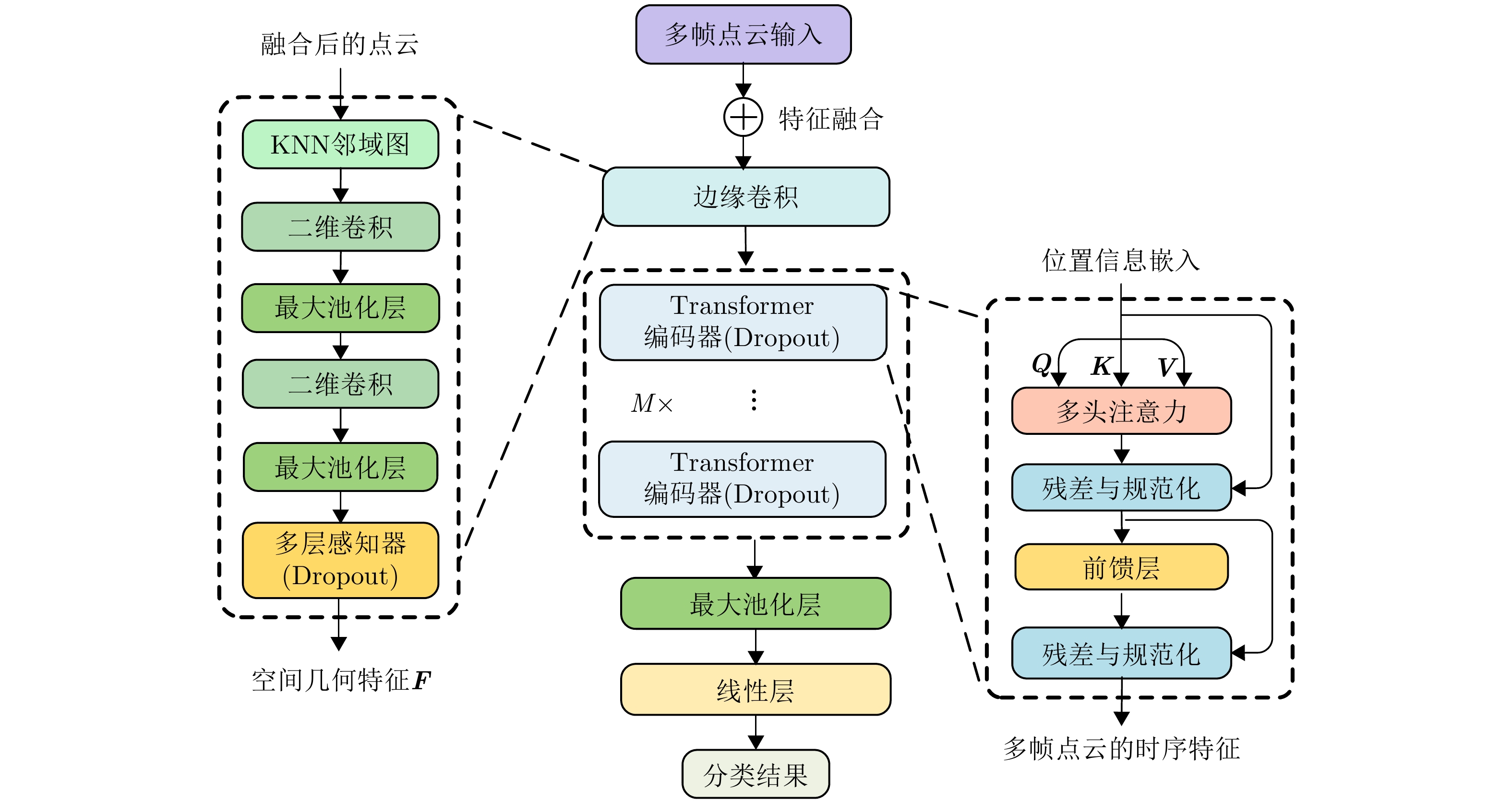
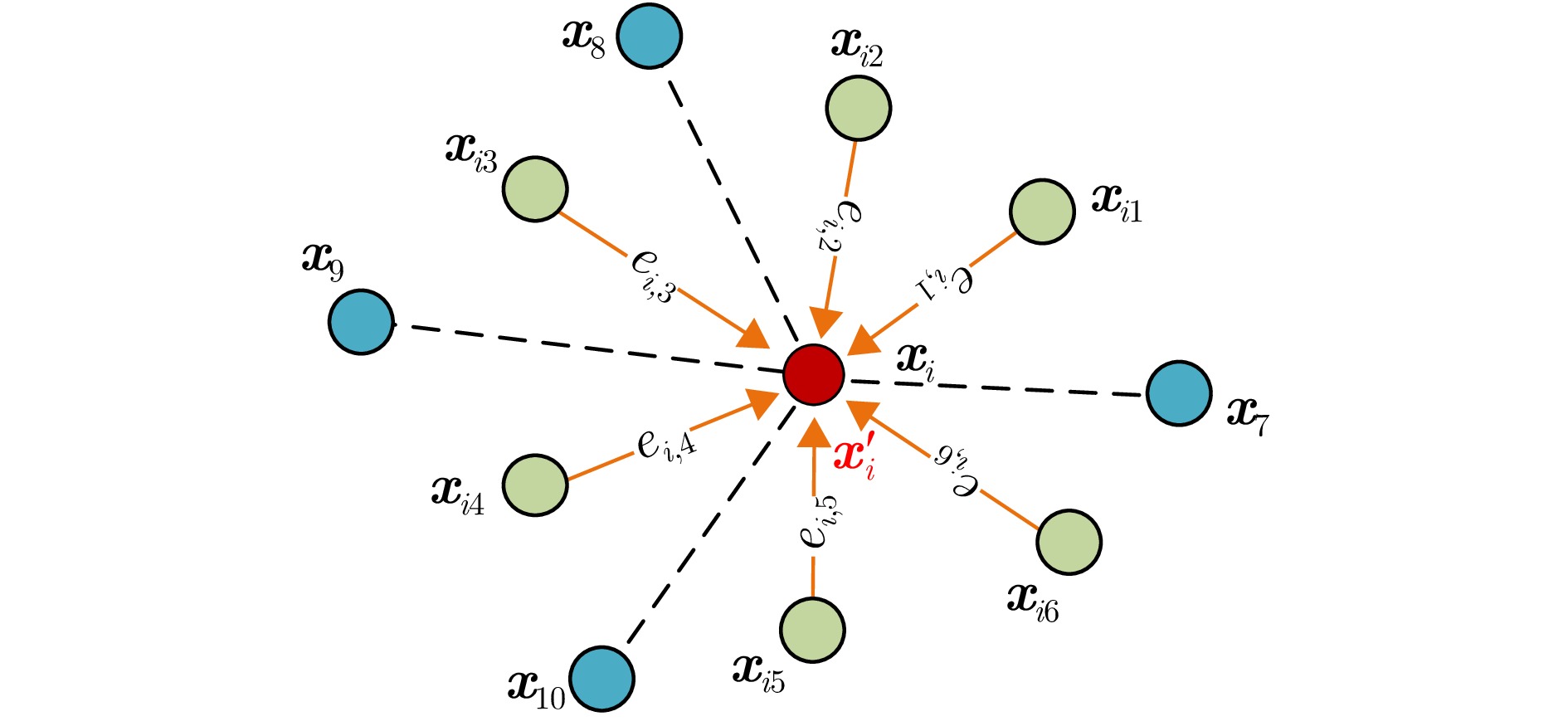
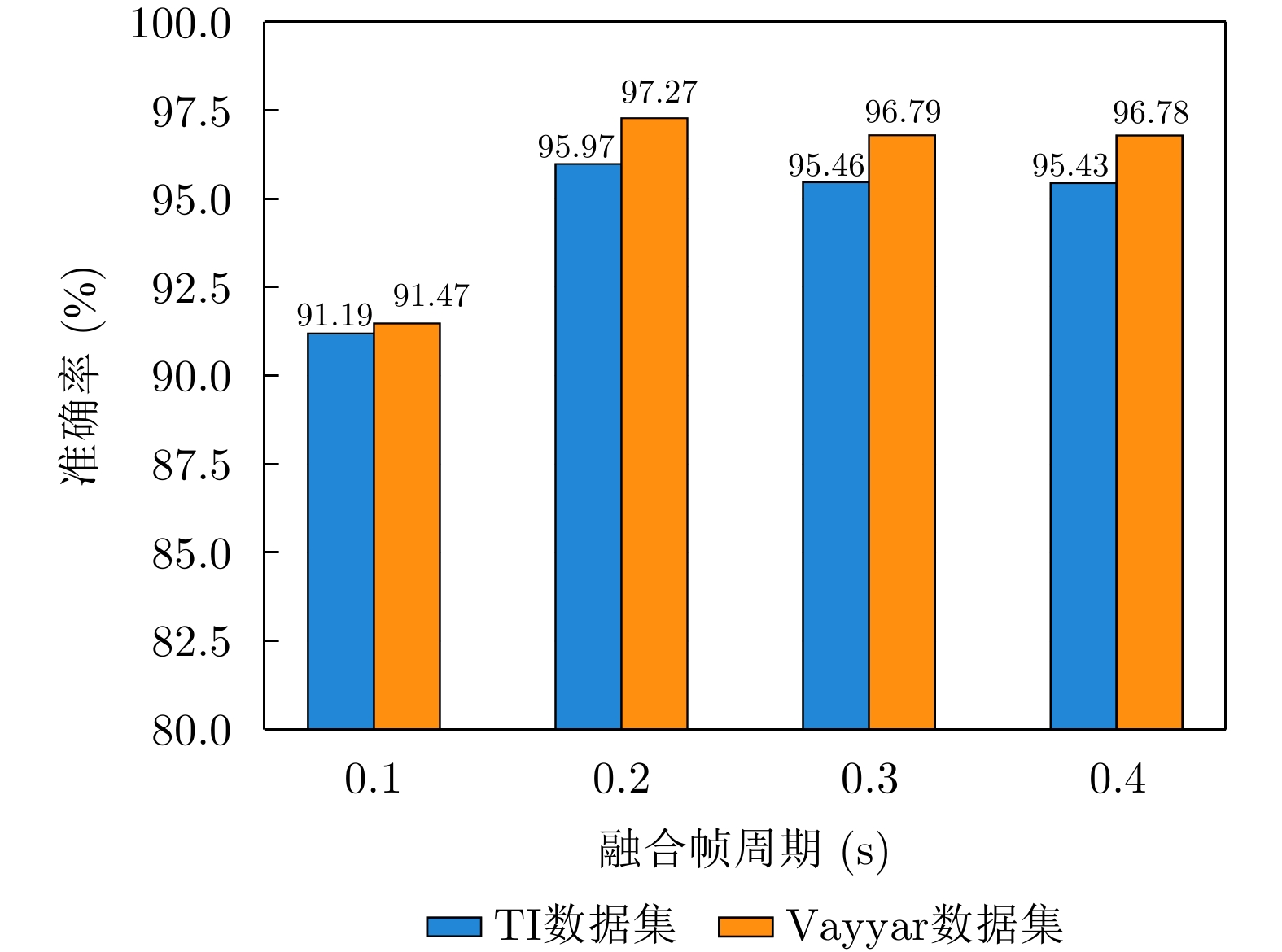
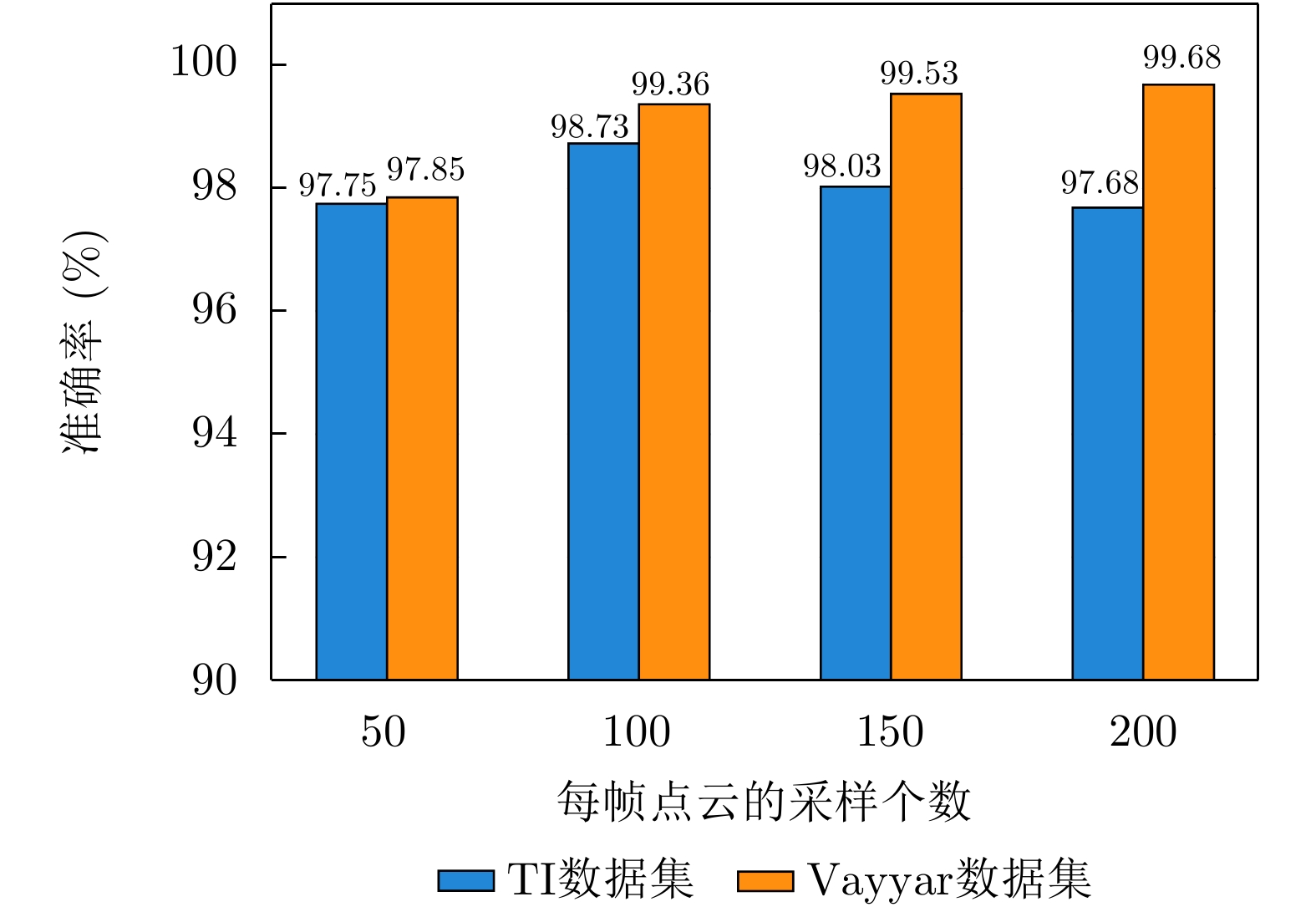
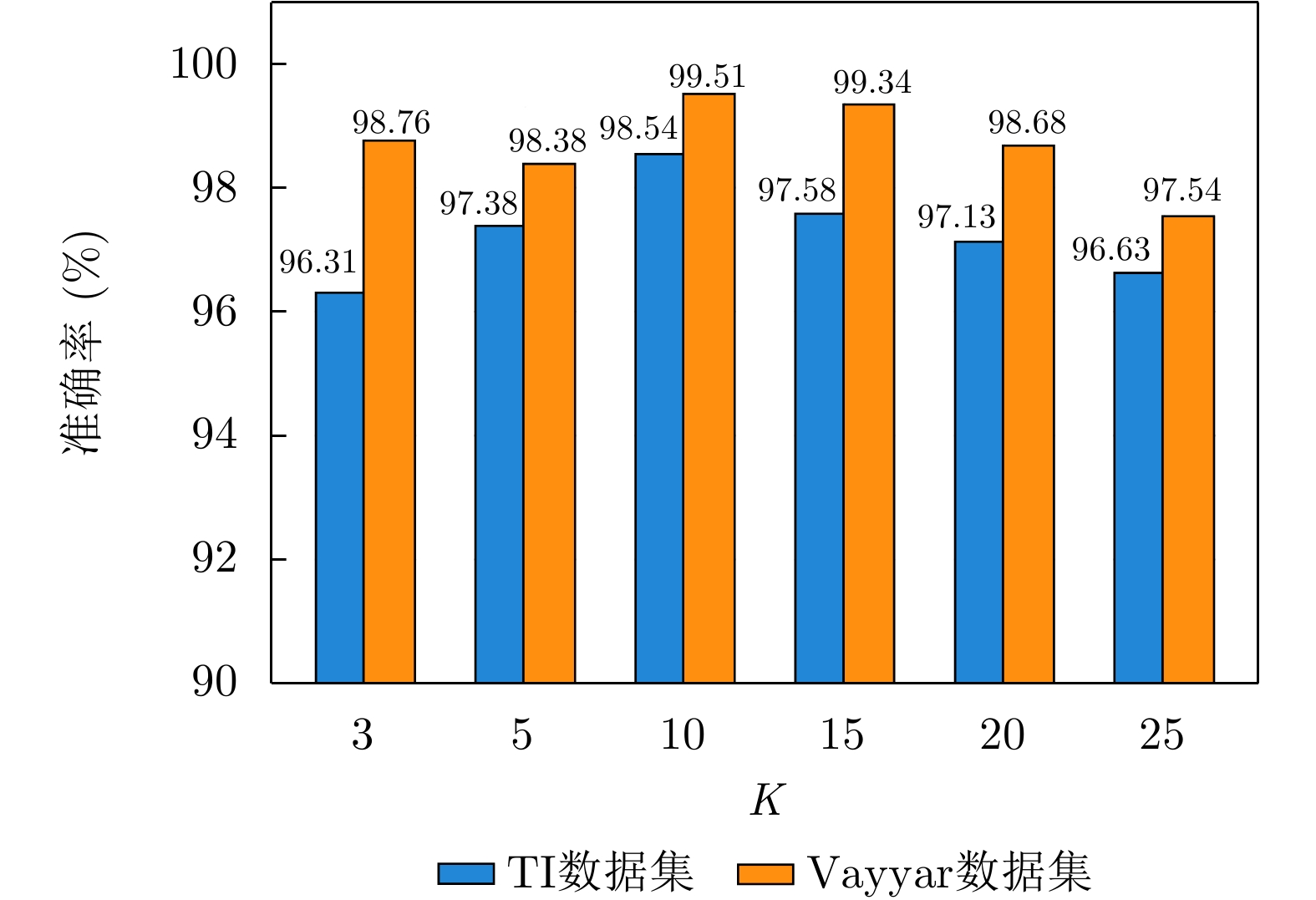
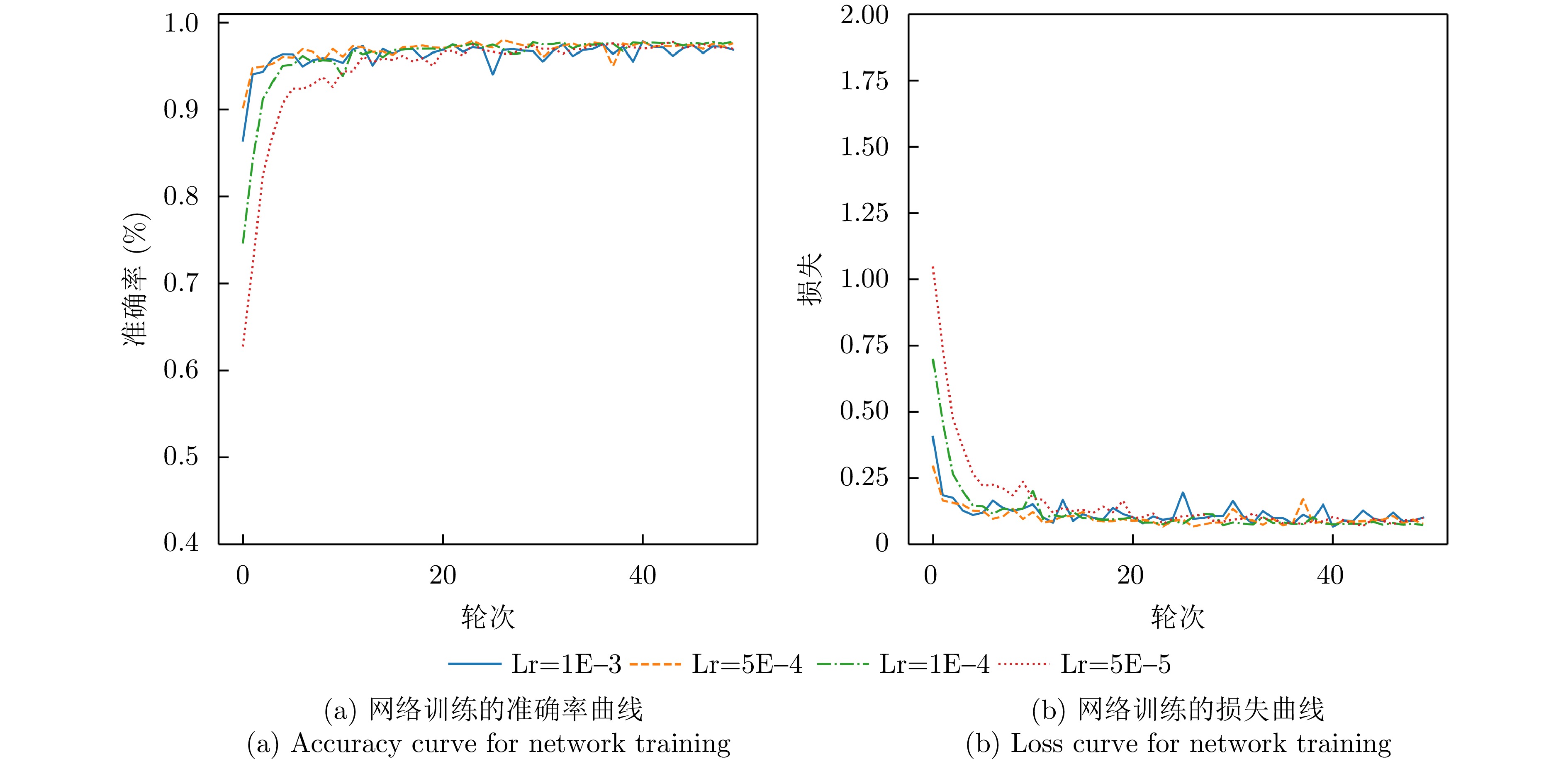
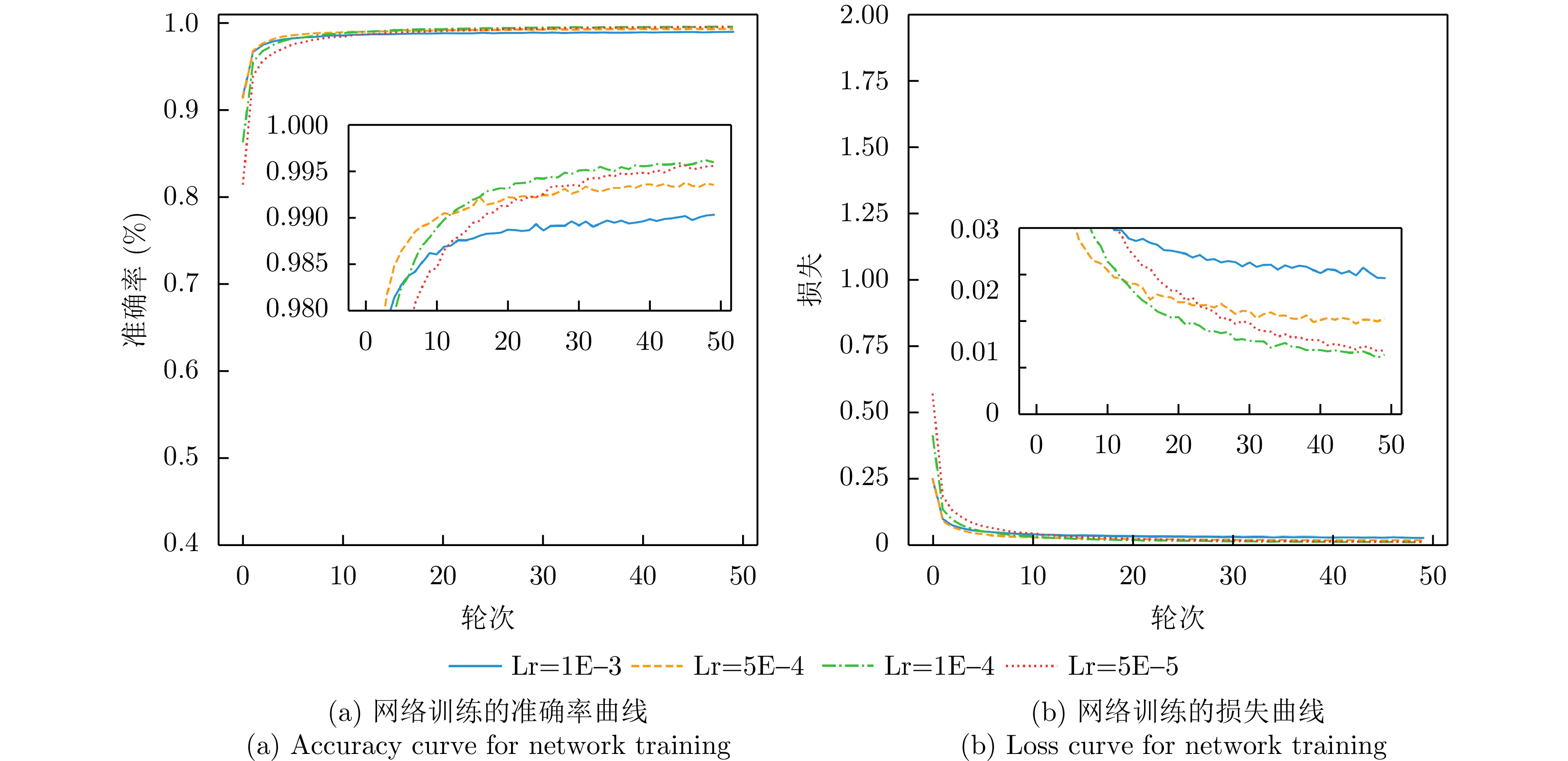
| [1] |
AHMAD T, JIN Lianwen, ZHANG Xin, et al. Graph convolutional neural network for human action recognition: A comprehensive survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 2(2): 128–145. doi: 10.1109/TAI.2021.3076974. |
| [2] |
金添, 宋永坤, 戴永鹏, 等. UWB-HA4D-1.0: 超宽带雷达人体动作四维成像数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 27–39. doi: 10.12000/JR22008. JIN Tian, SONG Yongkun, DAI Yongpeng, et al. UWB-HA4D-1.0: An ultra-wideband radar human activity 4D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 27–39. doi: 10.12000/JR22008. |
| [3] |
ANGUITA D, GHIO A, ONETO L, et al. A public domain dataset for human activity recognition using smartphones[C]. European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, Bruges, Belgium, 2013: 437–442.
|
| [4] |
SOOMRO K, ZAMIR A R, and SHAH M. UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild[R]. CRCV-TR-12-01, 2012.
|
| [5] |
AMIRI S M, POURAZAD M T, NASIOPOULOS P, et al. Non-intrusive human activity monitoring in a smart home environment[C]. 2013 IEEE 15th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom 2013), Lisbon, Portugal, 2013: 606–610. doi: 10.1109/HealthCom.2013.6720748. |
| [6] |
BLOOM V, MAKRIS D, and ARGYRIOU V. G3D: A gaming action dataset and real time action recognition evaluation framework[C]. 2012 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Providence, USA, 2012: 7–12. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2012.6239175. |
| [7] |
LIU Jun, SHAHROUDY A, PEREZ M, et al. NTU RGB+D 120: A large-scale benchmark for 3D human activity understanding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(10): 2684–2701. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2916873. |
| [8] |
RAEIS H, KAZEMI M, and SHIRMOHAMMADI S. Human activity recognition with device-free sensors for well-being assessment in smart homes[J]. IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Magazine, 2021, 24(6): 46–57. doi: 10.1109/MIM.2021.9513637. |
| [9] |
丁传威, 刘芷麟, 张力, 等. 基于MIMO雷达成像图序列的切向人体姿态识别方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(1): 151–167. doi: 10.12000/JR24116. DING Chuanwei, LIU Zhilin, ZHANG Li, et al. Tangential human posture recognition with sequential images based on MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Radar, 2025, 14(1): 151–167. doi: 10.12000/JR24116. |
| [10] |
JIN Tian, HE Yuan, LI Xinyu, et al. Advances in human activity sensing using ultra-wide band radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1147–1155. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211044. |
| [11] |
JIN Biao, MA Xiao, HU Bojun, et al. Gesture-mmWAVE: Compact and accurate millimeter-wave radar-based dynamic gesture recognition for embedded devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems, 2024, 54(3): 337–347. doi: 10.1109/THMS.2024.3385124. |
| [12] |
ZHANG Yushu, JI Junhao, WEN Wenying, et al. Understanding visual privacy protection: A generalized framework with an instance on facial privacy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2024, 19: 5046–5059. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2024.3389572. |
| [13] |
HASCH J, TOPAK E, SCHNABEL R, et al. Millimeter-wave technology for automotive radar sensors in the 77 GHz frequency band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2012, 60(3): 845–860. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2011.2178427. |
| [14] |
JIN Biao, MA Xiao, ZHANG Zhenkai, et al. Interference-robust millimeter-wave radar-based dynamic hand gesture recognition using 2-D CNN-transformer networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11(2): 2741–2752. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3293092. |
| [15] |
JIN Biao, PENG Yu, KUANG Xiaofei, et al. Robust dynamic hand gesture recognition based on millimeter wave radar using atten-TsNN[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(11): 10861–10869. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3170311. |
| [16] |
SENGUPTA A, JIN Feng, ZHANG Renyuan, et al. mm-Pose: Real-time human skeletal posture estimation using mmWave radars and CNNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(17): 10032–10044. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2991741. |
| [17] |
YU Zheqi, TAHA A, TAYLOR W, et al. A radar-based human activity recognition using a novel 3-D point cloud classifier[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(19): 18218–18227. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3198395. |
| [18] |
QI C R, SU Hao, MO Kaichun, et al. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, USA, 2017: 77–85. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.16. |
| [19] |
QI C R, YI L, SU Hao, et al. PointNet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]. 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 5105–5114.
|
| [20] |
FAN Hehe, YANG Yi, and KANKANHALLI M. Point 4D transformer networks for Spatio-temporal modeling in point cloud videos[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, USA, 2021: 14199–14208. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01398. |
| [21] |
PÜTZ S, WIEMANN T, and HERTZBERG J. Tools for visualizing, annotating and storing triangle meshes in ROS and RViz[C]. 2019 European Conference on Mobile Robots (ECMR), Prague, Czech Republic, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ECMR.2019.8870953. |
| [22] |
DENG Dingsheng. DBSCAN clustering algorithm based on density[C]. 2020 7th International Forum on Electrical Engineering and Automation (IFEEA), Hefei, China, 2020: 949–953. doi: 10.1109/IFEEA51475.2020.00199. |
| [23] |
LIN Y P, YEH Y M, CHOU Yuchen, et al. Attention EdgeConv for 3D point cloud classification[C]. 2021 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Tokyo, Japan, 2021: 2018–2022.
|
| [24] |
DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C]. 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2020: 1–11.
|
| [25] |
HENDRYCKS D and GIMPEL K. Gaussian error linear units (GELUs)[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1606.08415, 2016.
|
| [26] |
LI Xing, HUANG Qian, WANG Zhijian, et al. Real-time 3-D human action recognition based on hyperpoint sequence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(8): 8933–8942. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3223225. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

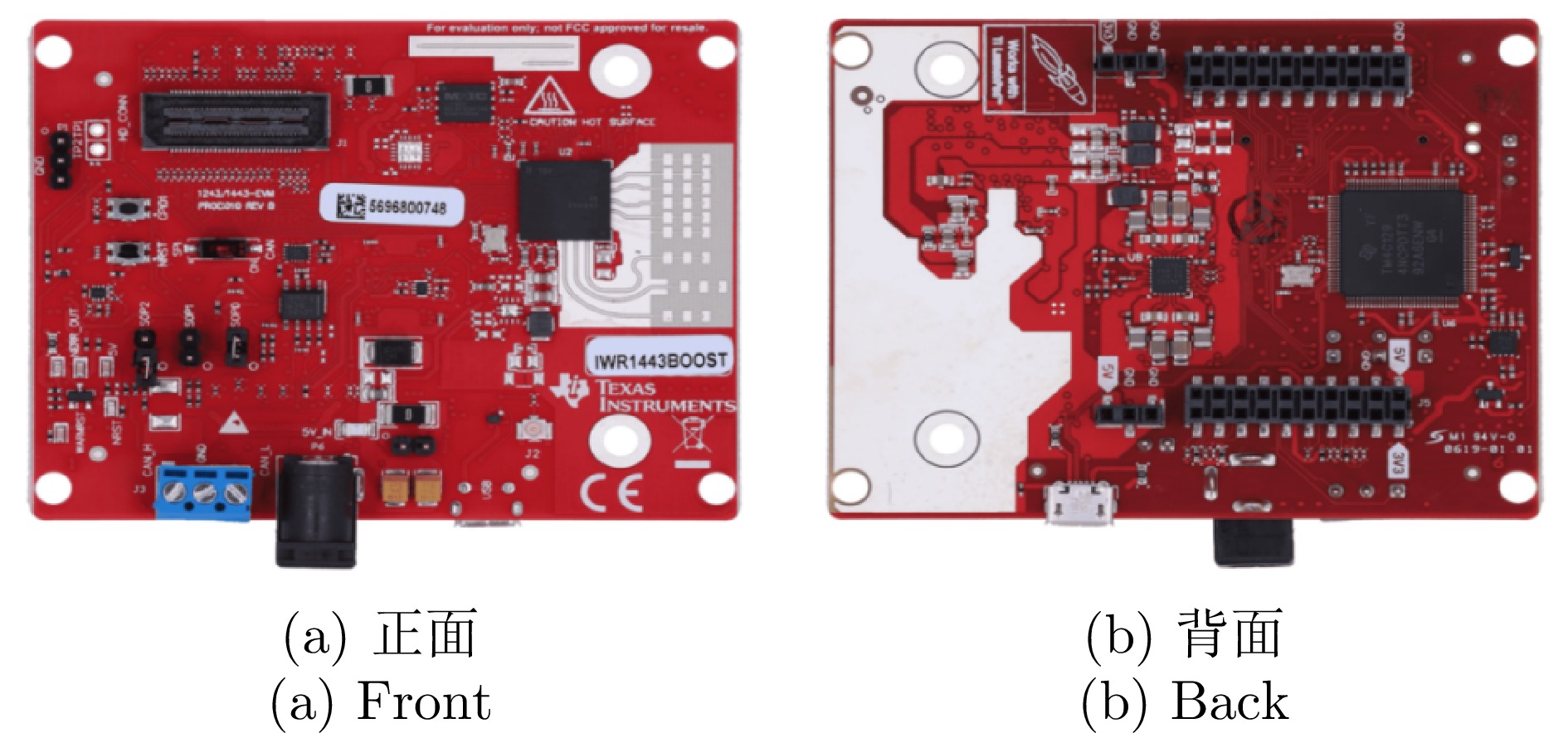



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: