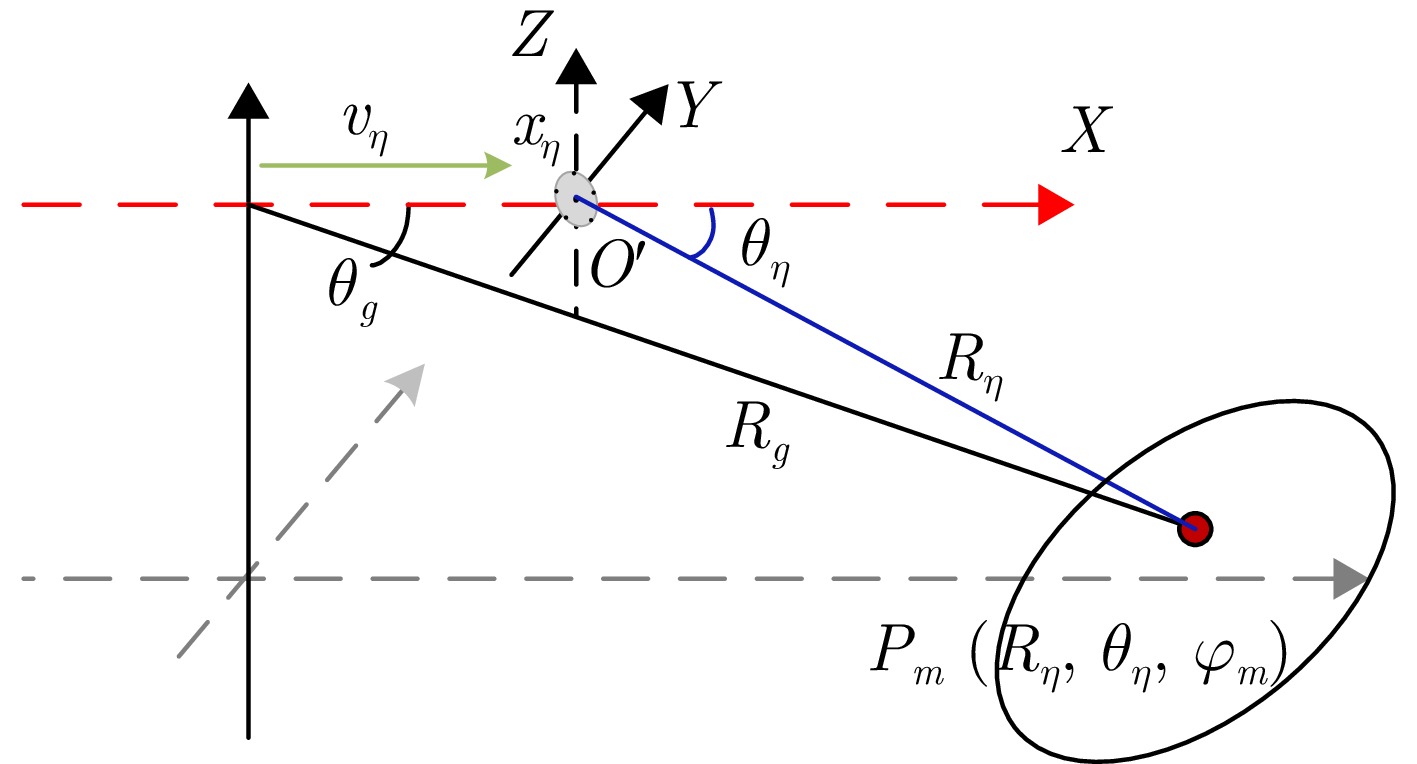
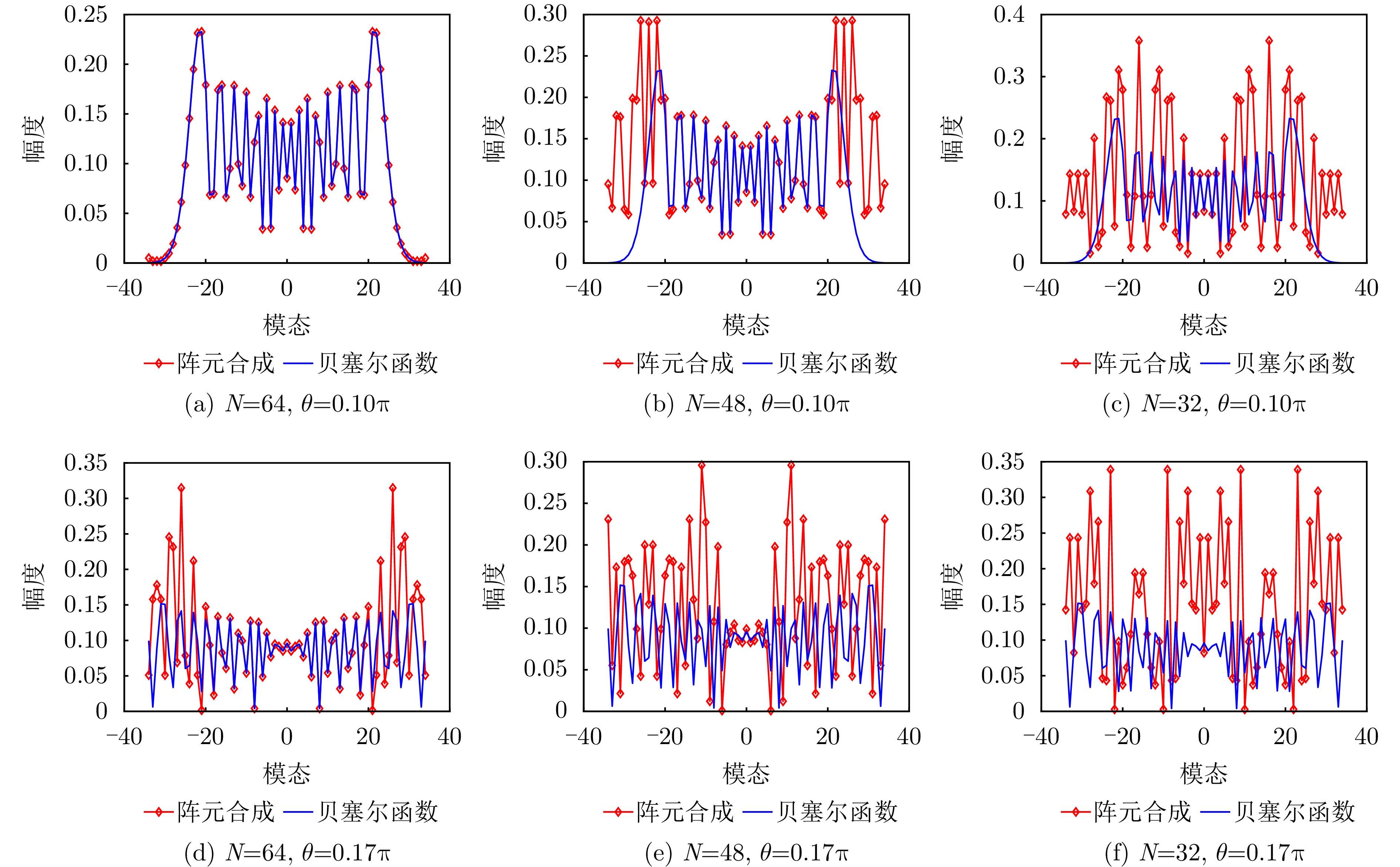
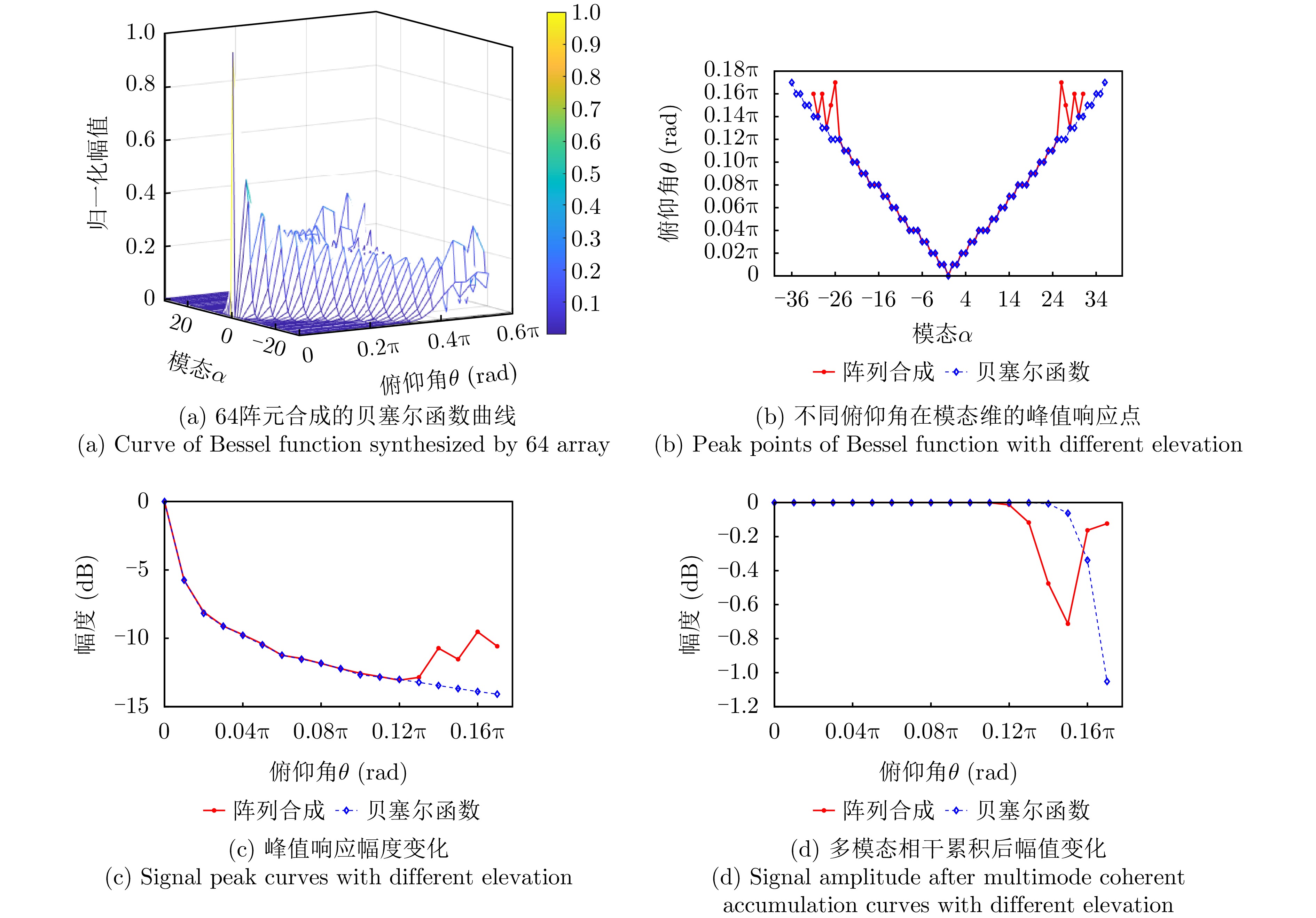
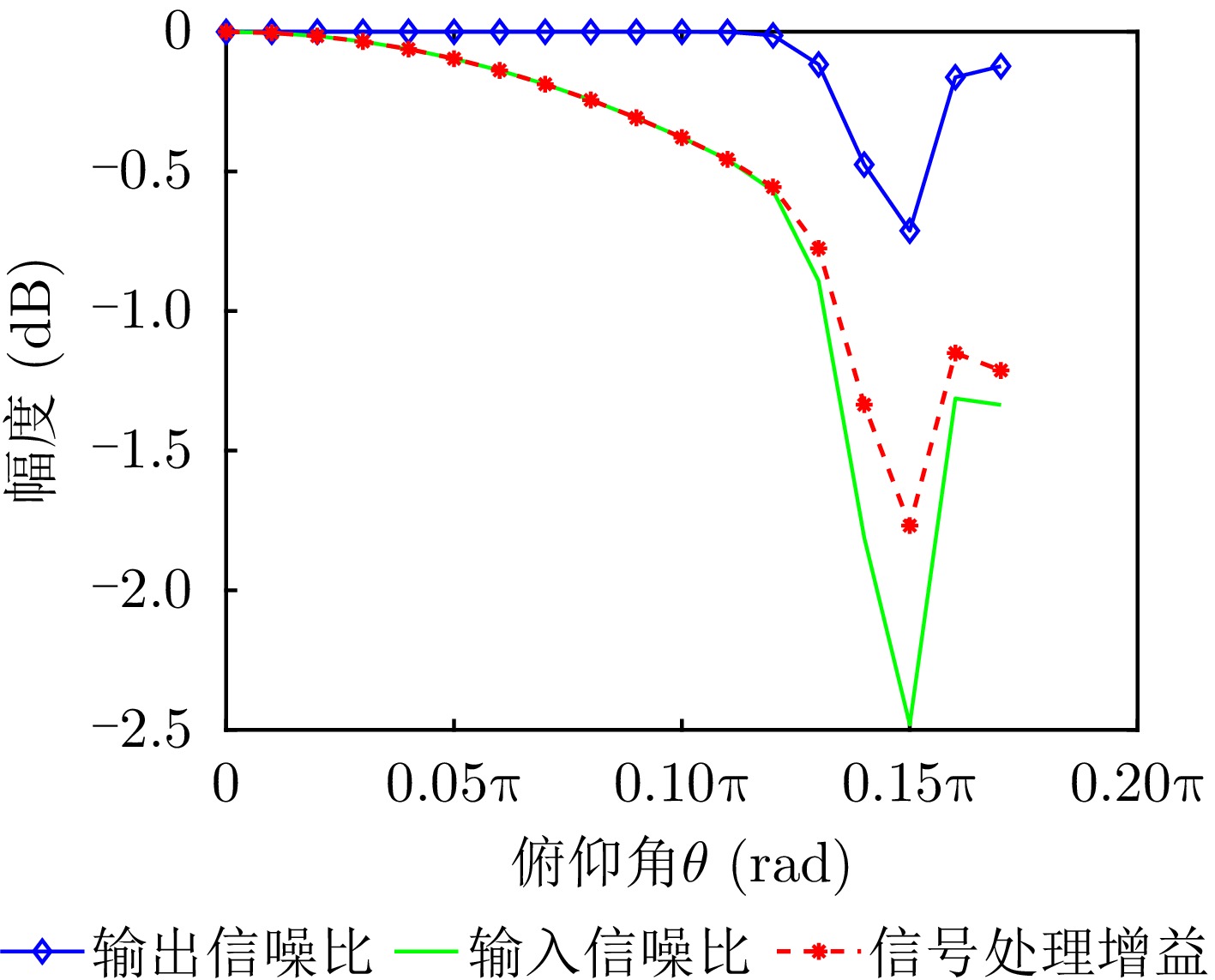
| [1] |
SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. Multichannel full-aperture azimuth processing for beam steering SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(9): 4761–4778. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2230267. |
| [2] |
宗竹林, 胡剑浩, 朱立东, 等. 编队卫星合成孔径雷达空时二维压缩感知成像[J]. 电波科学学报, 2012, 27(3): 626–636.
ZONG Zhulin, HU Jianhao, ZHU Lidong, et al. Formation-flying small satellites SAR imaging algorithm using space-time compressive sensing[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2012, 27(3): 626–636.
|
| [3] |
YANIK M E, WANG Dan, and TORLAK M. Development and demonstration of MIMO-SAR mmWave imaging testbeds[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 126019–126038. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3007877. |
| [4] |
YAO A M and PADGETT M J. Orbital angular momentum: Origins, behavior and applications[J]. Advances in Optics and Photonics, 2011, 3(2): 161–204. doi: 10.1364/AOP.3.000161. |
| [5] |
ALLEN L, BEIJERSBERGEN M W, SPREEUW R J C, et al. Orbital angular momentum of light and the transformation of Laguerre-Gaussian laser modes[J]. Physical Review Applied, 1992, 45(11): 8185–8189. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.45.8185. |
| [6] |
LIU Kang, LI Xiang, GAO Yue, et al. Microwave imaging of spinning object using orbital angular momentum[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 122(12): 124903. doi: 10.1063/1.4991655. |
| [7] |
吕坤, 马晖, 刘宏伟. 基于涡旋电磁波体制的三维SAR成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(5): 691–698. doi: 10.12000/JR21125. LYU Kun, MA Hui, and LIU Hongwei. Three-dimensional imaging using the electromagnetic vortex synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(5): 691–698. doi: 10.12000/JR21125. |
| [8] |
GONG Ting, CHENG Yongqiang, LI Xiang, et al. Micromotion detection of moving and spinning object based on rotational Doppler shift[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2018, 28(9): 843–845. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2018.2858552. |
| [9] |
王建秋, 刘康, 王煜, 等. 涡旋电磁波雷达成像分辨力研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(5): 680–690. doi: 10.12000/JR21054. WANG Jianqiu, LIU Kang, WANG Yu, et al. Resolution analysis of vortex electromagnetic radar imaging[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(5): 680–690. doi: 10.12000/JR21054. |
| [10] |
GUO Guirong, HU Weidong, and DU Xiaoyong. Electromagnetic vortex based radar target imaging[J]. Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2013, 35(6): 71–76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2013.06.013. |
| [11] |
BU Xiangxi, ZHANG Zhuo, CHEN Longyong, et al. Implementation of vortex electromagnetic waves high-resolution synthetic aperture radar imaging[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2018, 17(5): 764–767. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2018.2814980. |
| [12] |
JIANG Xuefeng, ZHAO Yufei, and ZHANG Chao. Capacity evaluation on the long-distance orbital angular momentum non-orthogonal transmission[C]. 2018 IEEE MTT-S International Wireless Symposium (IWS), Chengdu, China, 2018: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/IEEE-IWS.2018.8400839. |
| [13] |
FANG Yue, CHEN Jie, WANG Pengbo, et al. A novel image formation method for electromagnetic vortex SAR with orbital-angular-momentum[J]. Progress in Electromagnetics Research M, 2019, 82: 129–137. doi: 10.2528/PIERM19011704. |
| [14] |
BU Xiangxi, ZHANG Zhuo, CHEN Longyong, et al. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry based on vortex electromagnetic waves[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 82693–82700. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2908209. |
| [15] |
YUAN Hang, NI Jiacheng, RONG Nan, et al. Fine gait recognition of human target with single-frequency vortex electromagnetic wave radar[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 21(6): 39–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2020.06.007. |
| [16] |
WANG Zhaji, SUN Guanqun, ZHANG Fangzheng, et al. Microwave-photonics-based vortex electromagnetic wave generation for high resolution radar imaging[C]. 2022 Asia Communications and Photonics Conference (ACP), Shenzhen, China, 2022: 1687–1690. doi: 10.1109/ACP55869.2022.10088880. |
| [17] |
MA Hui and LIU Hongwei. Waveform diversity-based generation of convergent beam carrying orbital angular momentum[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(7): 5487–5495. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.2981724. |
| [18] |
袁铁柱. 涡旋电磁波在雷达成像中的应用研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2017.
YUAN Tiezhu. Research on radar imaging using electromagnetic vortex wave[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2017.
|
| [19] |
LIU Kang, CHENG Yongqiang, GAO Yue, et al. Super-resolution radar imaging based on experimental OAM beams[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 110(16): 164102. doi: 10.1063/1.4981253. |
| [20] |
WANG Jianqiu, LIU Kang, LIU Hongyan, et al. 3-D object imaging method with electromagnetic vortex[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 2000512. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3069914. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: