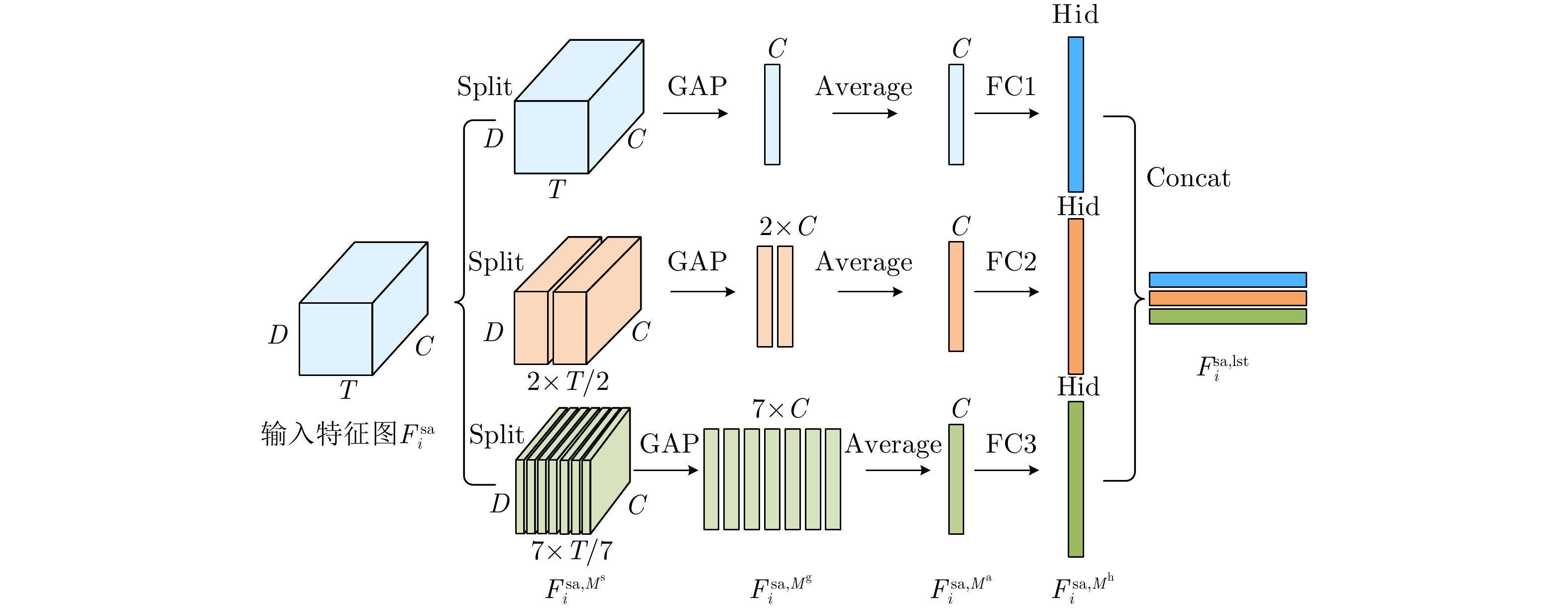
| [1] |
DELIGIANNI F, GUO Yao, and YANG Guangzhong. From emotions to mood disorders: A survey on gait analysis methodology[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2019, 23(6): 2302–2316. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2019.2938111 |
| [2] |
SEPAS-MOGHADDAM A and ETEMAD A. Deep gait recognition: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(1): 264–284. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3151865 |
| [3] |
LI Haobo, MEHUL A, LE KERNEC J, et al. Sequential human gait classification with distributed radar sensor fusion[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(6): 7590–7603. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3046991 |
| [4] |
CAO Peibei, XIA Weijie, YE Ming, et al. Radar-ID: Human identification based on radar micro-Doppler signatures using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(7): 729–734. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0511 |
| [5] |
LANG Yue, WANG Qing, YANG Yang, et al. Joint motion classification and person identification via multitask learning for smart homes[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 9596–9605. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2929833 |
| [6] |
PAPANASTASIOU V S, TROMMEL R P, HARMANNY R I A, et al. Deep learning-based identification of human gait by radar micro-Doppler measurements[C]. The 17th European Radar Conference (EuRAD), Utrecht, Netherlands, 2021: 49–52.
|
| [7] |
DONG Shiqi, XIA Weijie, LI Yi, et al. Radar-based human identification using deep neural network for long-term stability[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(10): 1521–1527. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2019.0618 |
| [8] |
NIAZI U, HAZRA S, SANTRA A, et al. Radar-based efficient gait classification using Gaussian prototypical networks[C]. 2021 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf21), Atlanta, USA, 2021: 1–5.
|
| [9] |
CHEN V C, LI F, HO S S, et al. Micro-Doppler effect in radar: Phenomenon, model, and simulation study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(1): 2–21. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.1603402 |
| [10] |
BAI Xueru, HUI Ye, WANG Li, et al. Radar-based human gait recognition using dual-channel deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 9767–9778. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2929096 |
| [11] |
ADDABBO P, BERNARDI M L, BIONDI F, et al. Gait recognition using FMCW radar and temporal convolutional deep neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE 7th International Workshop on Metrology for AeroSpace (MetroAeroSpace), Pisa, Italy, 2020: 171–175.
|
| [12] |
DOHERTY H G, BURGUEÑO R A, TROMMEL R P, et al. Attention-based deep learning networks for identification of human gait using radar micro-Doppler spectrograms[J]. International Journal of Microwave and Wireless Technologies, 2021, 13(7): 734–739. doi: 10.1017/S1759078721000830 |
| [13] |
YANG Yang, HOU Chunping, LANG Yue, et al. Person identification using micro-Doppler signatures of human motions and UWB radar[J]. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 2019, 29(5): 366–368. doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2019.2907547 |
| [14] |
XIA Zhaoyang, DING Genming, WANG Hui, et al. Person identification with millimeter-wave radar in realistic smart home scenarios[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 19: 3509405. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3117001 |
| [15] |
CHENG Yuwei and LIU Yimin. Person reidentification based on automotive radar point clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5101913. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3073664 |
| [16] |
TAHMOUSH D and SILVIOUS J. Angle, elevation, PRF, and illumination in radar microDoppler for security applications[C]. 2009 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, North Charleston, USA, 2009: 1–4.
|
| [17] |
YANG Yang, YANG Xiaoyi, SAKAMOTO T, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation for disguised-gait-based person identification on micro-Doppler signatures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(9): 6448–6460. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3161515 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
CHEN V C and LING Hao. Time-Frequency Transforms for Radar Imaging and Signal Analysis[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2002, 28–31.
|
| [20] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778.
|
| [21] |
HERMANS A, BEYER L, and LEIBE B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1703.07737, 2017.
|
| [22] |
WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19.
|
| [23] |
WANG Guanshuo, YUAN Yufeng, CHEN Xiong, et al. Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification[C]. 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Korea, 2018: 274–282.
|
| [24] |
FU Yang, WEI Yunchao, ZHOU Yuqian, et al. Horizontal pyramid matching for person re-identification[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1): 8295–8302. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33018295 |
| [25] |
SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015.
|
| [26] |
CHAO Hanqing, HE Yiwei, ZHANG Junping, et al. GaitSet: Regarding gait as a set for cross-view gait recognition[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1): 8126–8133. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33018126 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

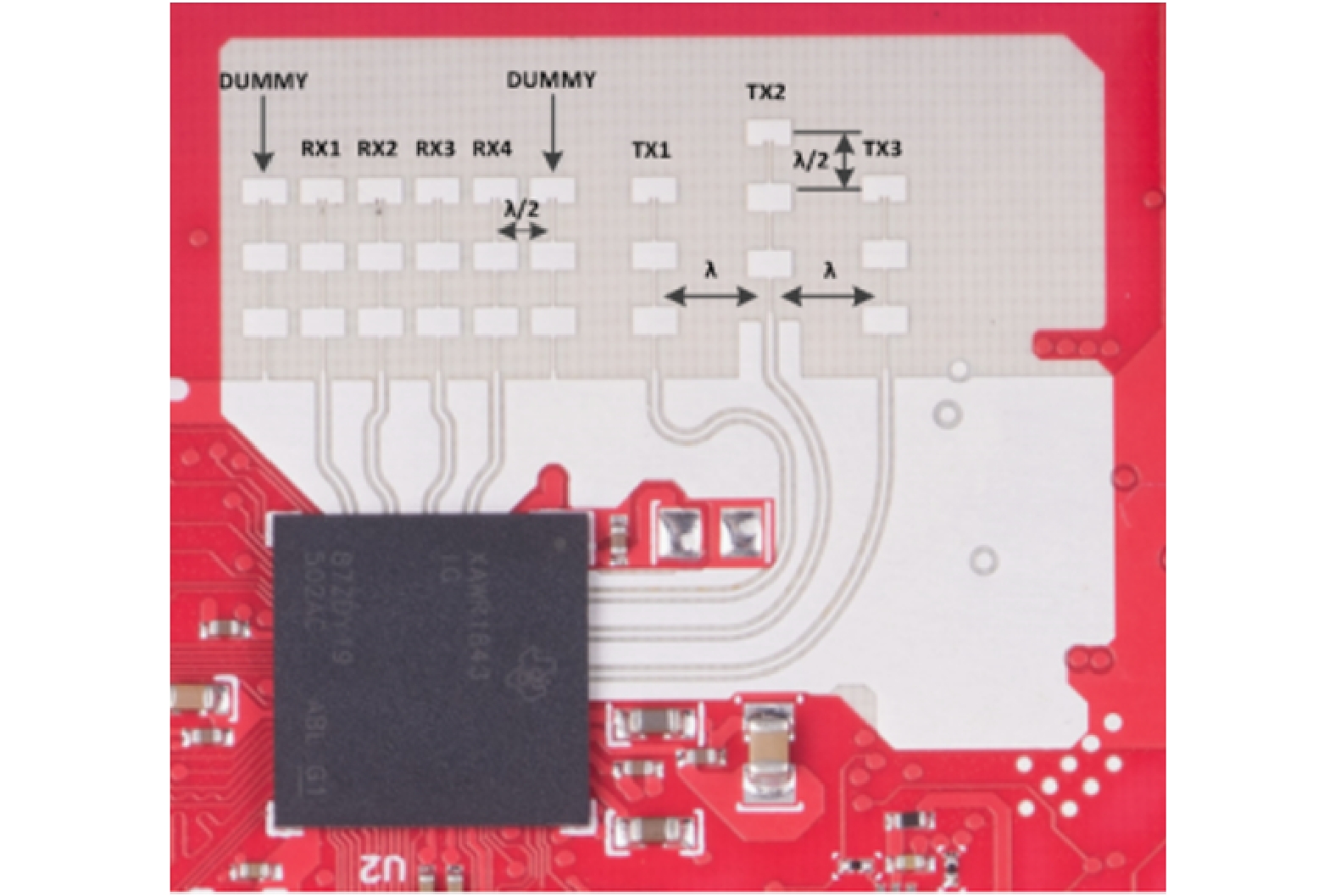



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: