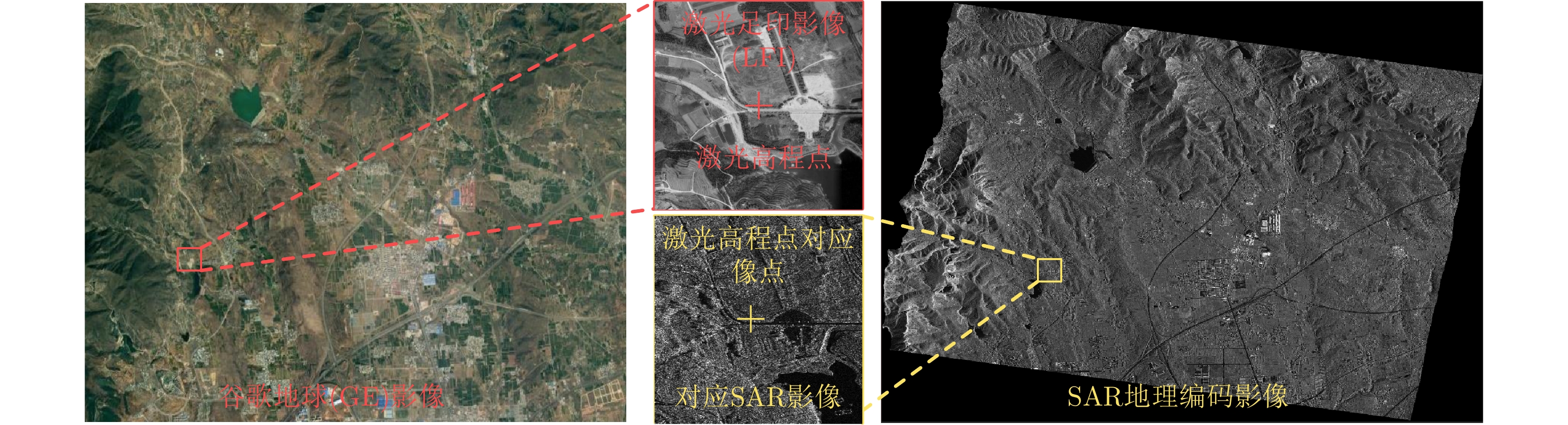
| [1] |
WANG Taoyang, LI Xin, ZHANG Guo, et al. Large-scale orthorectification of GF-3 SAR images without ground control points for China’s land area[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1–17. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3142372 |
| [2] |
润一. 高分三号卫星在轨几何定标及与高分二号光学卫星影像联合定位[D]. [硕士论文], 武汉大学, 2017.
RUN Yi. On-orbit geometric calibration of GF-3 satellite and joint-positioning of GF-3 and GF-2 satellite images[D]. [Master dissertation], Wuhan University, 2017.
|
| [3] |
ZHANG Hongmin, JIN Guowang, XU Qing, et al. Accurate positioning with stereo SAR images and one ground control point[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 85–91. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13138 |
| [4] |
WEI Jujie, ZHANG Jixian, ZHAO Zheng, et al. High-precisely direct geo-location method for TerraSAR-X image with sparse GCPs[J]. Science of Surveying and mapping, 2011, 36(1): 58–60, 50. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2011.01.006 |
| [5] |
ZHANG Zuxun and TAO Pengjie. An overview on “cloud control” photogrammetry in big data era[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(10): 1238–1248. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170337 |
| [6] |
FANG Yong, GONG Hui, ZHANG Li, et al. From global laser point cloud acquisition to 3D digital geospatial framework: The advanced road of global accurate mapping[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(12): 1200002. doi: 10.3788/LOP202259.1200002 |
| [7] |
NEUMANN T A, MARTINO A J, MARKUS T, et al. The ice, cloud, and land elevation satellite-2 mission: A global geolocated photon product derived from the advanced topographic laser altimeter system[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2019, 233: 111325. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2019.111325 |
| [8] |
XIE Huan, XU Qi, YE Dan, et al. A comparison and review of surface detection methods using MBL, MABEL, and ICESat-2 photon-counting laser altimetry data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 7604–7623. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3094195 |
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
LIN Xiaojuan, XU Min, CAO Chunxiang, et al. Estimates of forest canopy height using a combination of ICESat-2/ATLAS data and stereo-photogrammetry[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(21): 3649. doi: 10.3390/rs12213649 |
| [11] |
ZHANG Shuaitai, LI Guoyuan, ZHOU Xiaoqing, et al. Single photon point cloud denoising algorithm based on multi-features adaptive[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2022, 51(6): 20210949. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210949 |
| [12] |
ZHU Xiaoxiao, NIE Sheng, WANG Cheng, et al. A ground elevation and vegetation height retrieval algorithm using micro-pulse photon-counting Lidar data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(12): 1962. doi: 10.3390/rs10121962 |
| [13] |
MARKUS T, NEUMANN T, MARTINO A, et al. The ice, cloud, and land elevation satellite-2 (ICESat-2): Science requirements, concept, and implementation[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2017, 190: 260–273. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.12.029 |
| [14] |
ROSIEK M R, KIRK R L, ARCHINAL B A, et al. Utility of Viking orbiter images and products for Mars mapping[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 2005, 71(10): 1187–1195. doi: 10.14358/PERS.71.10.1187 |
| [15] |
HE Yu, WU Shaomin, and XING Shuai. Block adjustment of Chang’e-1 CCD images based on RFM[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2013, 38(6): 5–6, 15. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2013.06.034 |
| [16] |
耿迅. 火星形貌摄影测量技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 解放军信息工程大学, 2014.
GENG Xun. Research on photogrammetric processing for Mars topographic mapping[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Information Engineering University, 2014.
|
| [17] |
WANG Jin, ZHANG Yong, ZHNAG Zuxun, et al. ICESat laser points assisted block adjustment for mapping Satellite-1 stereo imagery[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2018, 47(3): 359–369. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2018.20170425 |
| [18] |
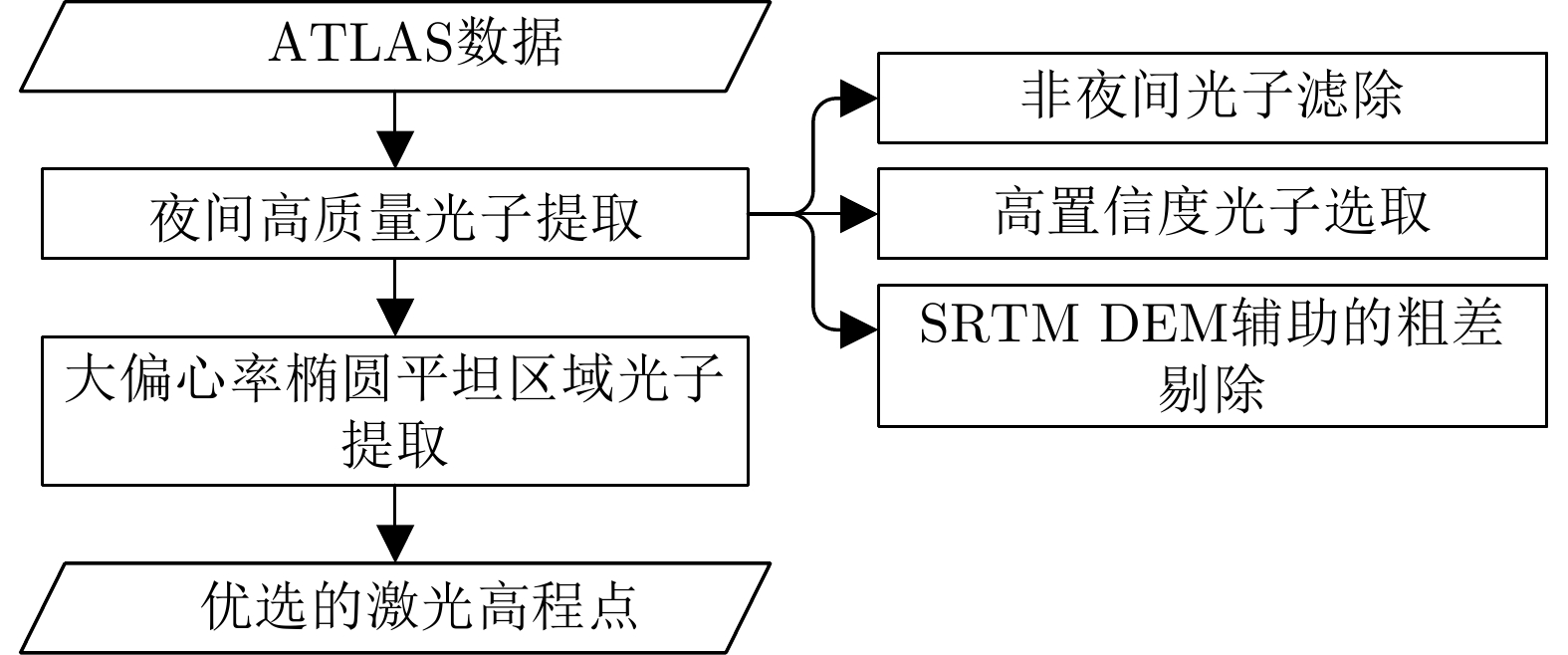
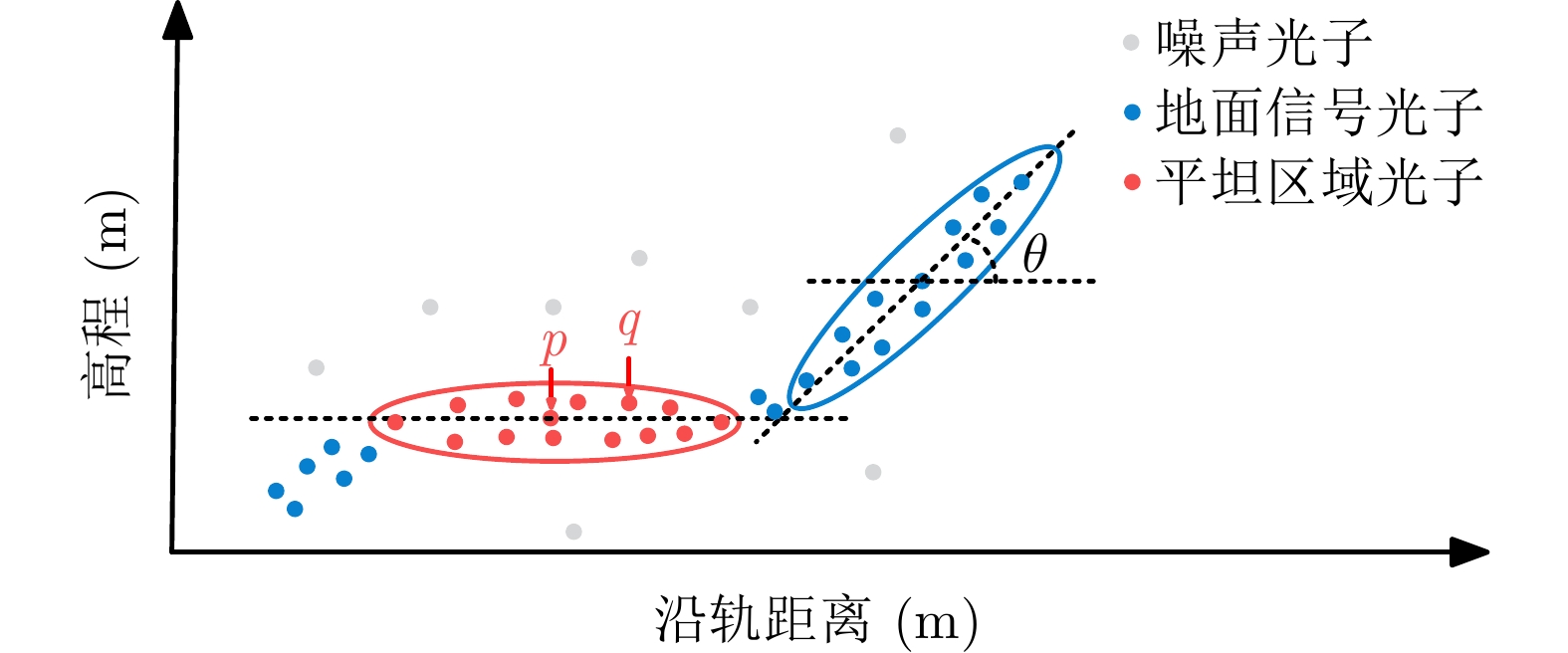
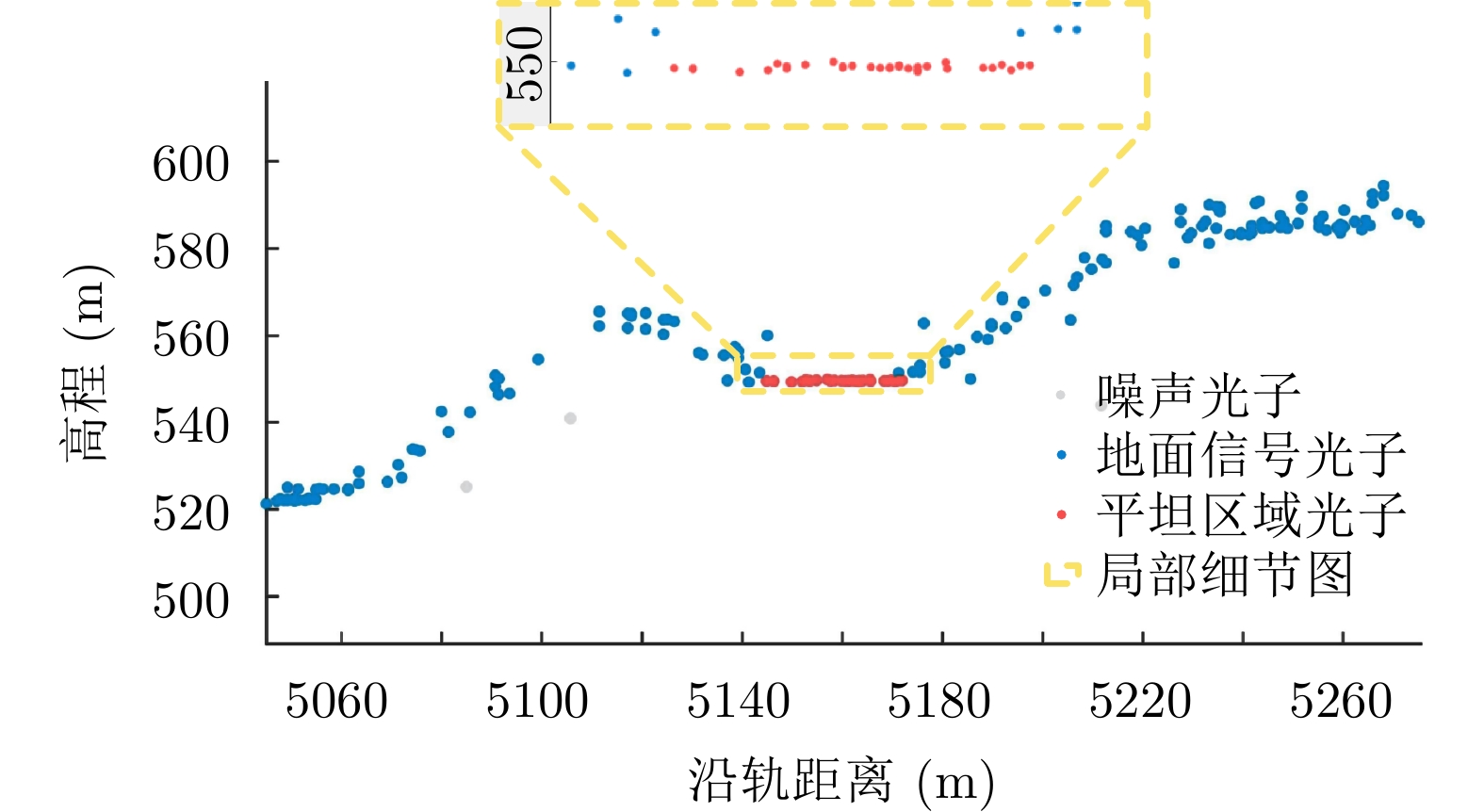
张鑫磊, 邢帅, 徐青, 等. ATLAS数据与资源三号02星影像联合区域网平差[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49(S2): 20200194. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200194ZHANG Xinlei, XING Shuai, XU Qing, et al. Joint block adjustment for ATLAS data and ZY3-02 stereo imagery[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(S2): 20200194. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20200194 |
| [19] |
ZHANG Guo, JIANG Boyang, WANG Taoyang, et al. Combined block adjustment for optical satellite stereo imagery assisted by spaceborne SAR and laser altimetry data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(16): 3062. doi: 10.3390/rs13163062 |
| [20] |
TAN Jianwei and CHENG Chunquan. Extracting building image elevation control points by decomposing full waveform of laser altimetry[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(8): 1–7, 13. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2021.08.001 |
| [21] |
WANG Mi, WEI Yu, YANG Bo, et al. Extraction and analysis of global elevation control points from ICESat-2/ATLAS data[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(2): 184–192. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20200531 |
| [22] |
ZHENG Yinghui, ZHANG Yan, WANG Tao, et al. Elevation control points extraction and accuracy validation based on ICESat-2 data[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2022, 24(7): 1234–1244. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2022.210667 |
| [23] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 12341-2008 1: 25000 1: 50000 1: 100000 地形图航空摄影测量外业规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China and Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 12341-2008 Specifications for aerophotogrammetric field work of 1∶25000 1∶50000 1∶100000 topographic maps[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008.
|
| [24] |
CAO Ning, ZHOU Ping, WANG Xia, et al. Refined processing of laser altimeter data-aided satellite geometry model[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018, 22(4): 599–610. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20187252 |
| [25] |
TANG Xinming, LIU Changru, ZHANG Heng, et al. GF-7 satellite stereo images block adjustment assisted with laser altimetry data[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(10): 1423–1430. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20210417 |
| [26] |
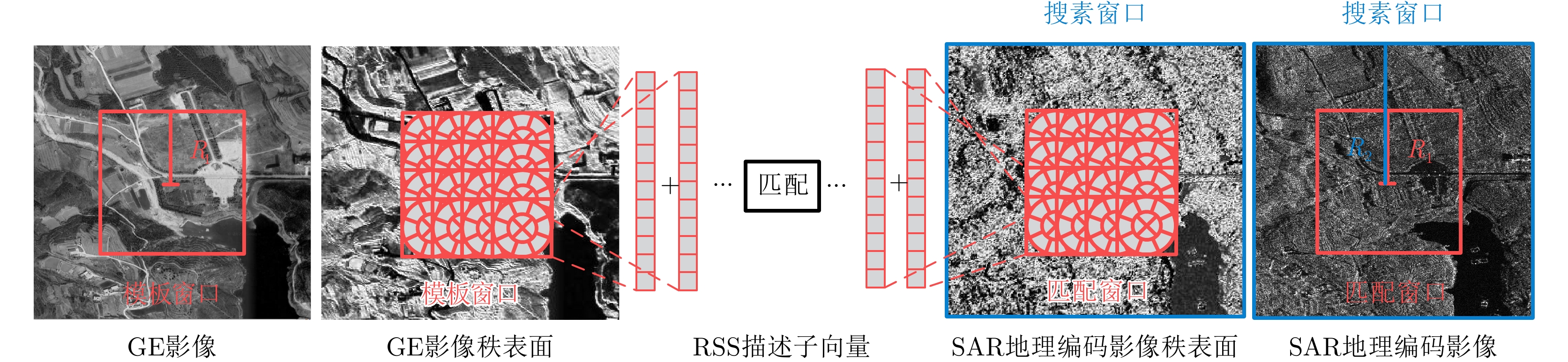
XIONG Xin, XU Qing, JIN Guowang, et al. Rank-based local self-similarity descriptor for optical-to-SAR image matching[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(10): 1742–1746. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2955153 |
| [27] |
WANG Guoan, MI Hongtao, DENG Tianhong, et al. Calculation of the change range of the sun high angle and the azimuth of sunrise and sunset in one year[J]. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences, 2007, 30(S1): 161–164. doi: 10.16765/j.cnki.1673-7148.2007.s1.031 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: