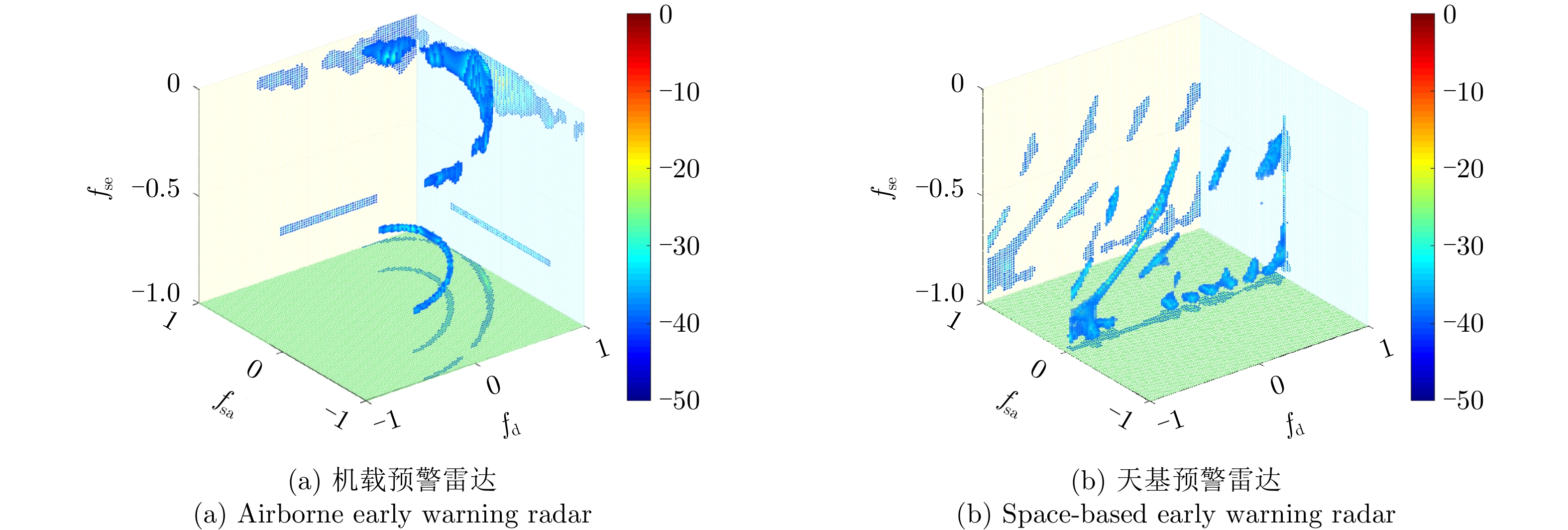
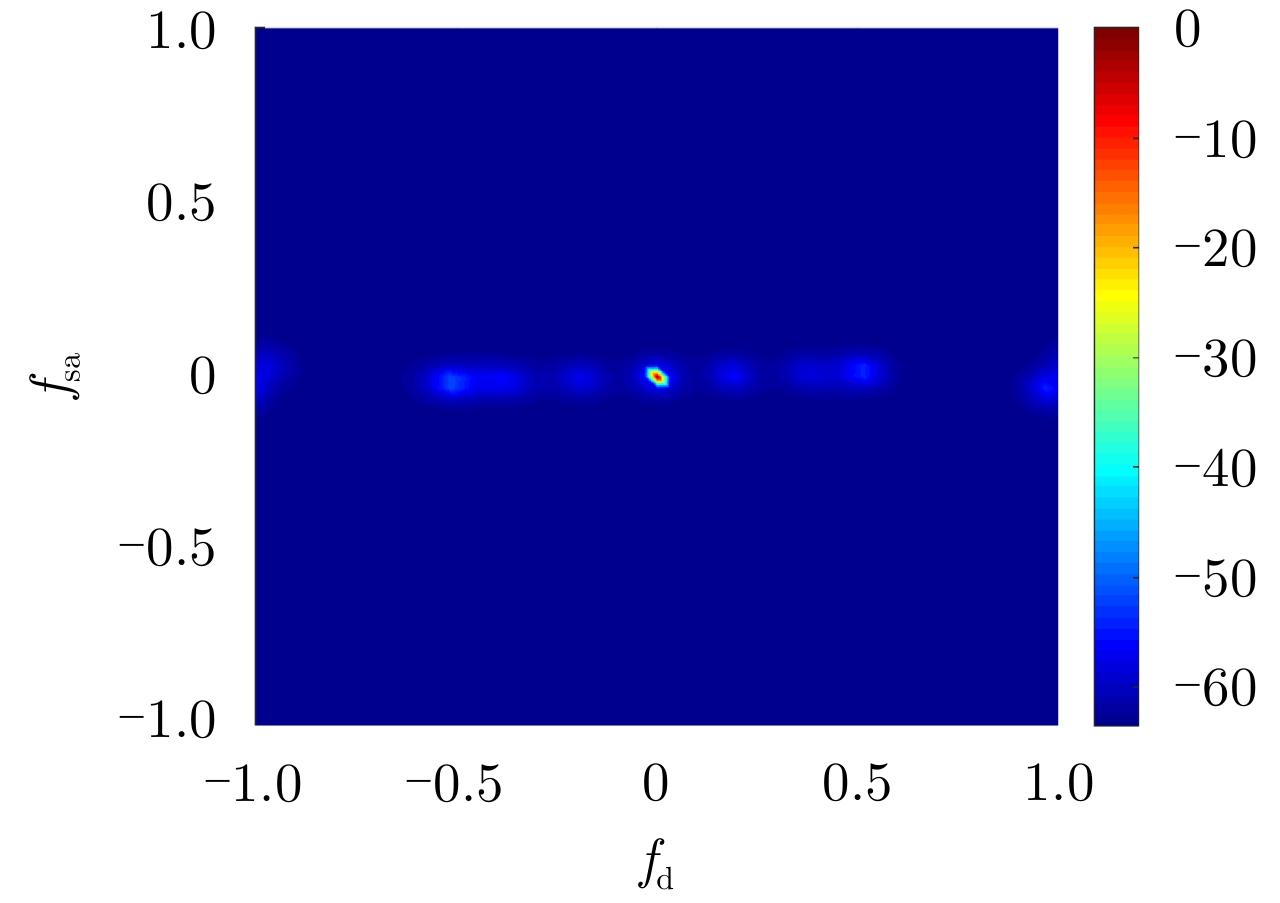
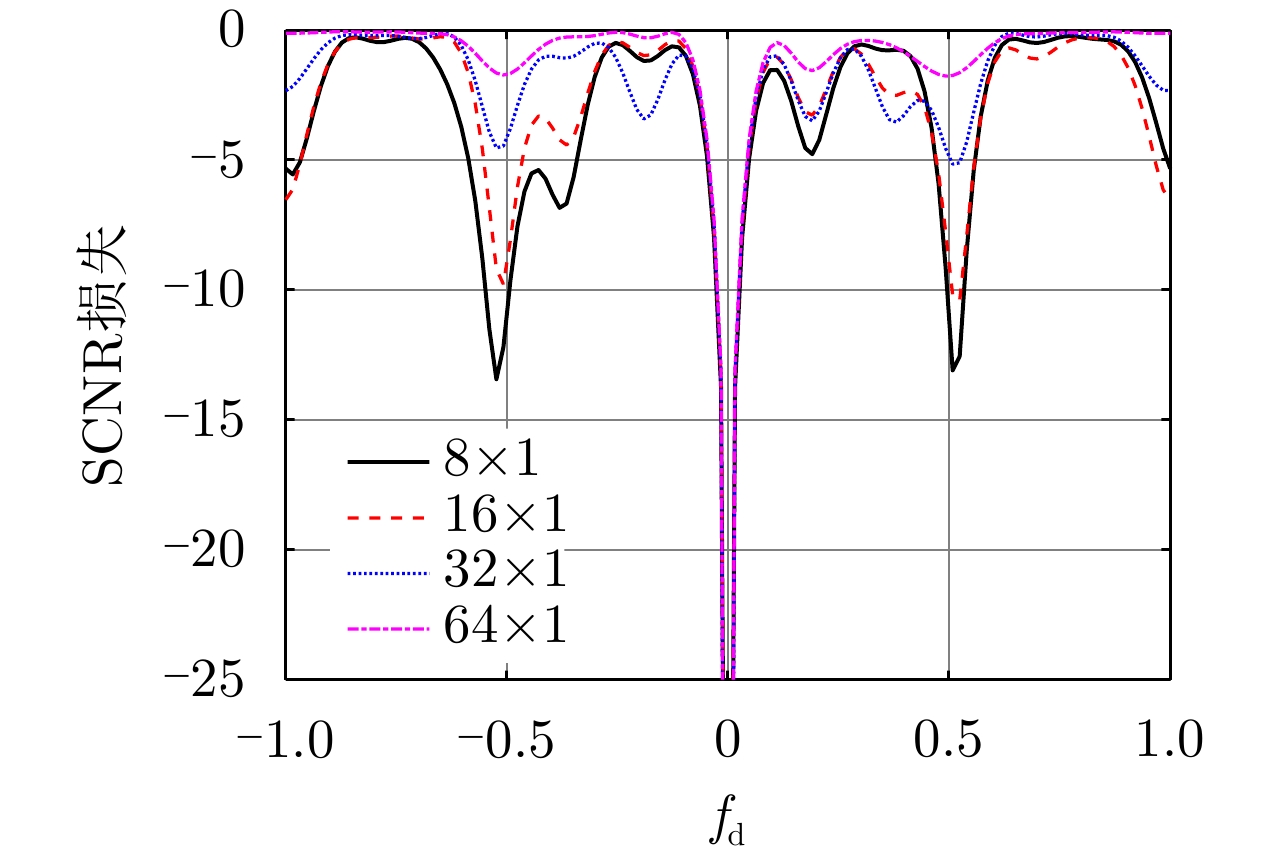
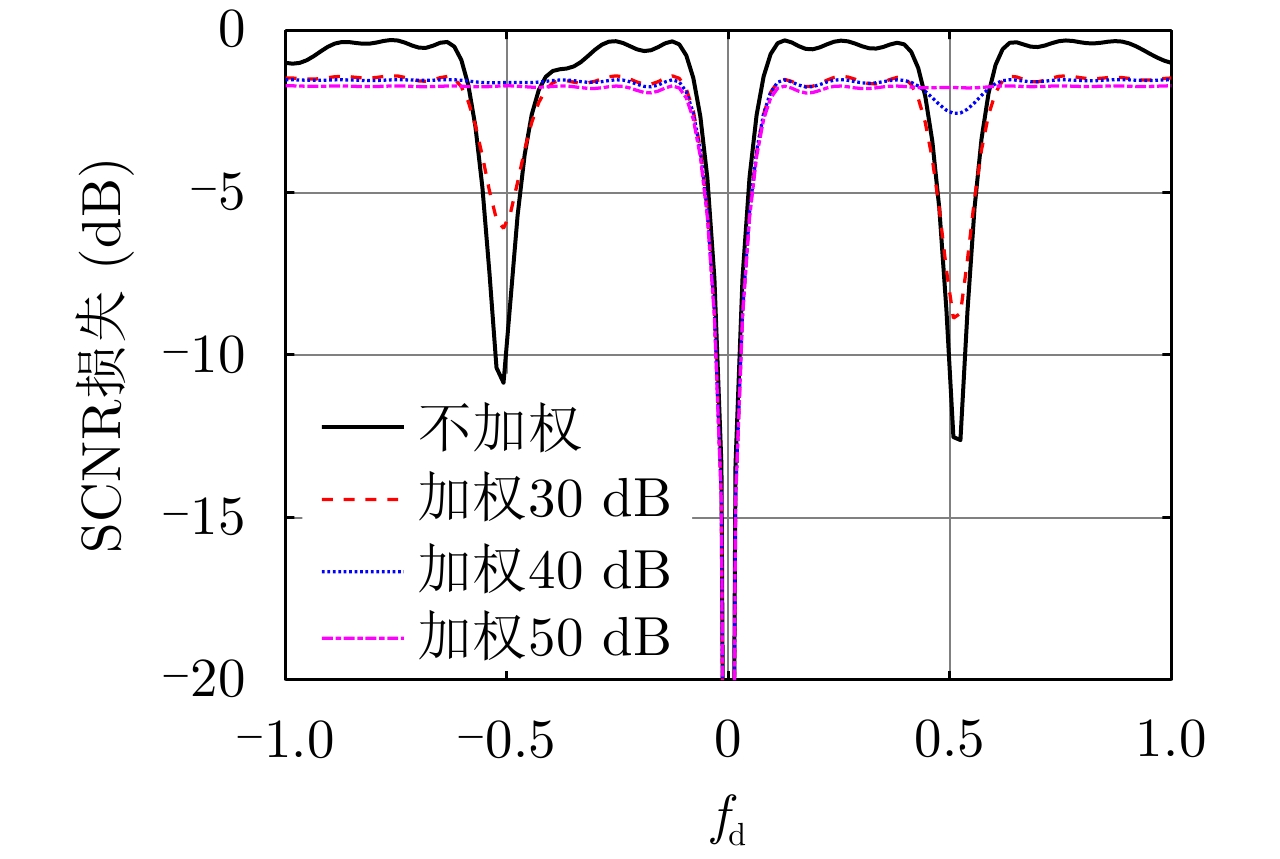
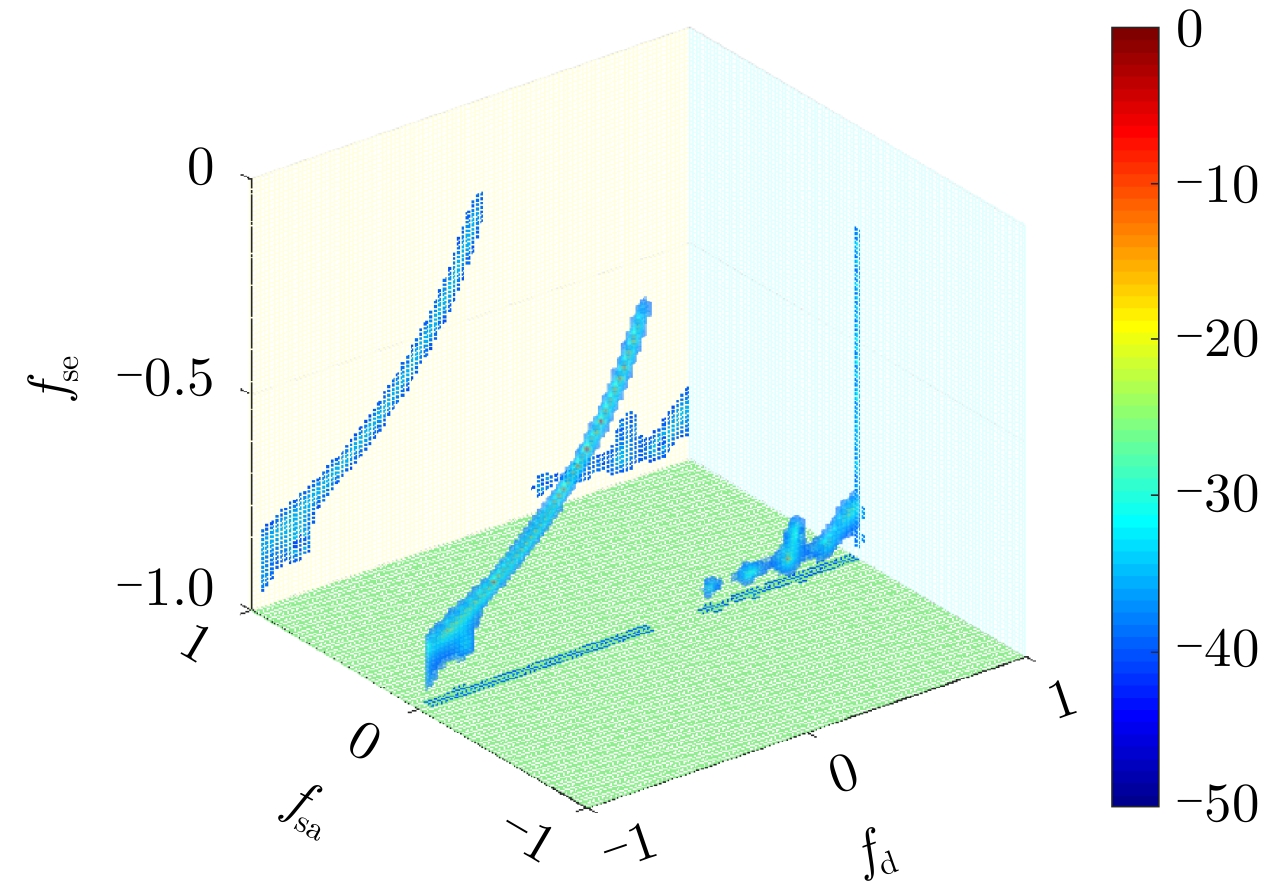
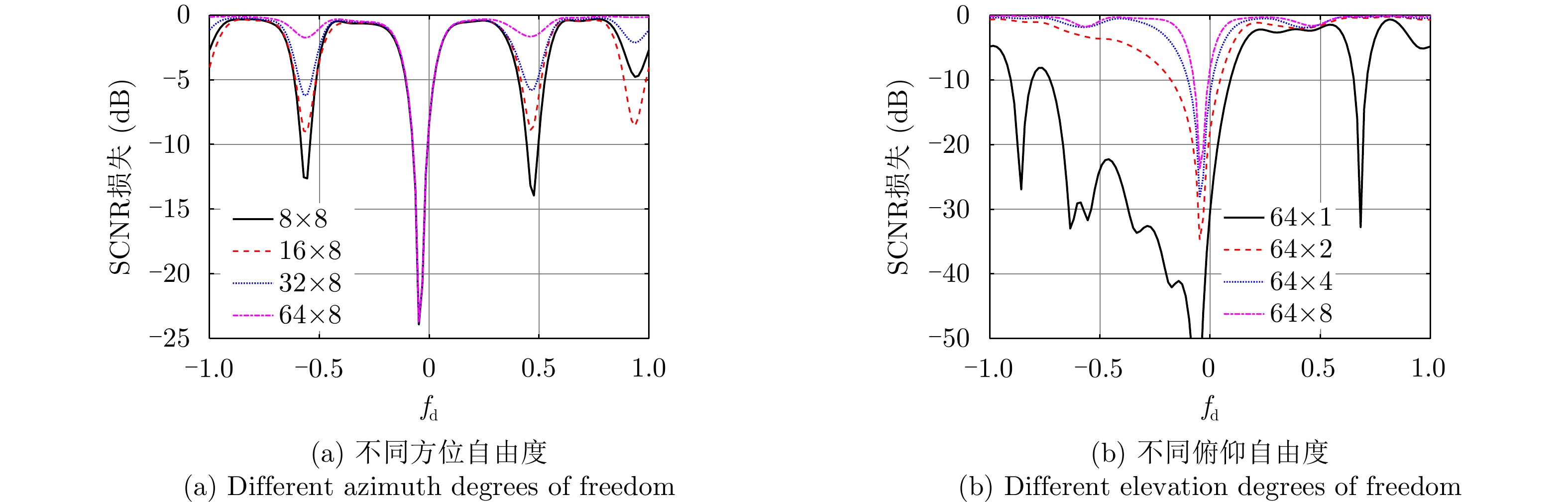
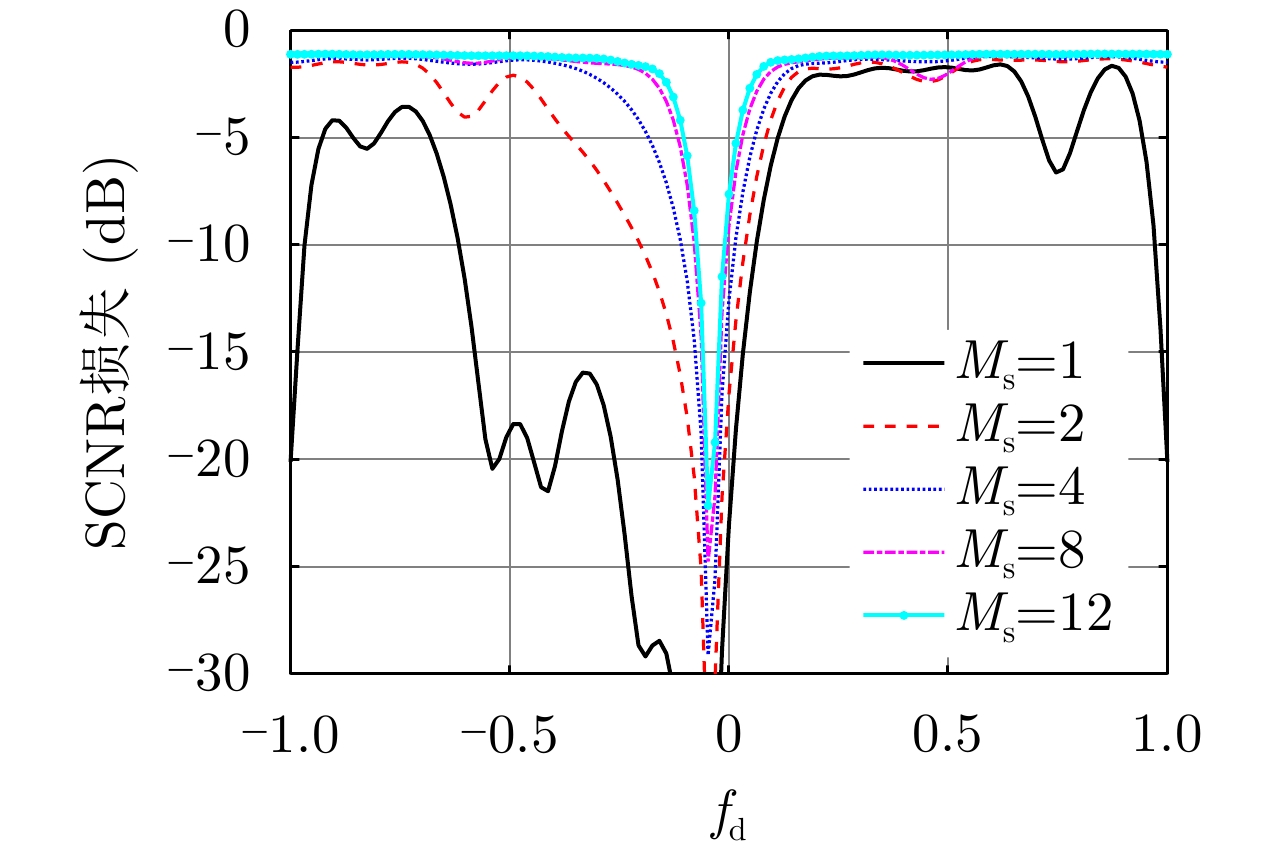
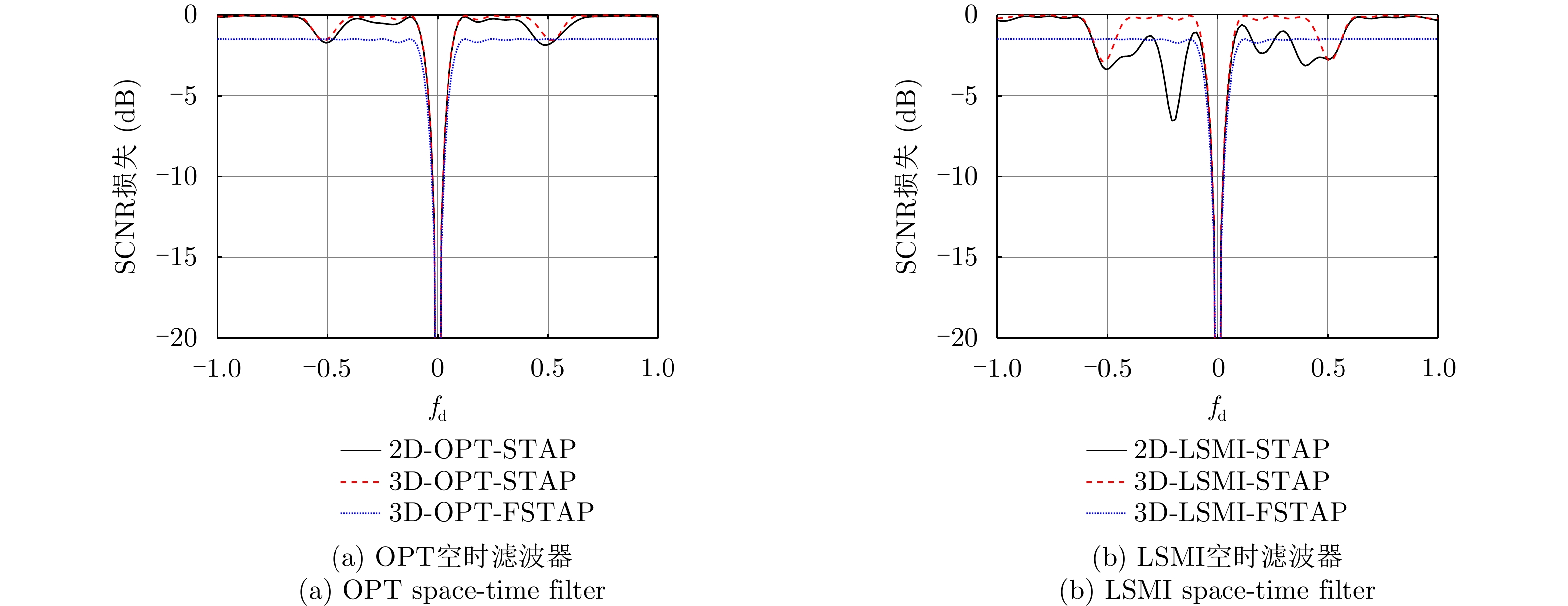
| [1] |
DAVIS M E. Technology challenges in affordable space based radar[C]. Record of the IEEE 2000 International Radar Conference, Alexandria, USA, 2000: 18–23.
|
| [2] |
PILLAI S U, LI Keyong, and HIMED B. Space Based Radar: Theory & Applications[M]. McGraw Hill, 2008.
|
| [3] |
林幼权, 武楠. 天基预警雷达[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 1–2.
LIN Youquan and WU Nan. Space Based Early Warning Radar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 1–2.
|
| [4] |
HOVANESSIAN S A, JOCIC L B, and LOPEZ J M. Spaceborne radar design equations and concepts[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Snowmass, USA, 1997: 125–136.
|
| [5] |
DAVIS M E. L-band SBR moving target detection in SAR-GMTI modes[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2004: 2211–2219.
|
| [6] |
CROCI R, DELFINO A, and MARCHETTI F. Space based radar technology evolution[C]. The 6th European Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 2009: 601–604.
|
| [7] |
LANE S A, MURPHEY T W, and ZATMAN M. Overview of the innovative space-based radar antenna technology program[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2011, 48(1): 135–145. doi: 10.2514/1.50252 |
| [8] |
LI Qing, LIN Youquan, and WU Nan. Analysis of development history and status for American space-base early warning radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2018, 40(1): 7–10. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2018.01.002 |
| [9] |
BRENNAN L E and REED I S. Theory of adaptive radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1973, AES-9(2): 237–252. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1973.309792 |
| [10] |
MELVIN W L. A STAP overview[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2004, 19(1): 19–35. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2004.1263229 |
| [11] |
SCHUMAN H K, LI P G, SZCZEPANSKI W, et al. Space-time adaptive processing for space based radar[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2004: 1904–1910.
|
| [12] |
ZULCH P, DAVIS M, ADZIMA L, et al. The earth rotation effect on a LEO L-Band GMTI SBR and mitigation strategies[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2004: 27–32.
|
| [13] |
PILLAI S U, HIMED B, and LI Keyong. Effect of earth’s rotation and range foldover on space-based radar performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(3): 917–932. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.248188 |
| [14] |
LEI Zhiyong, YU Yong, and ZHENG Zhibin. Analysis of earth rotation effect for clutter characteristic of space-based radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2017, 39(7): 21–24. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2017.07.005 |
| [15] |
KOGON S M, RABIDEAU D J, and BARNES R M. Clutter mitigation techniques for space-based radar[C]. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Phoenix, USA, 1999: 2323–2326.
|
| [16] |
LI Keyong, MANGIAT S, ZULCH P, et al. Clutter impacts on space based radar GMTI: A global perspective[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2007: 1–15.
|
| [17] |
ZULCH P A, HANCOCK R H, MORAN W, et al. Transmit waveform diversity for space based radar[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2006: 10–16.
|
| [18] |
LAPIERRE F D, VERLY J G, and VAN DROOGENBROECK M. New solutions to the problem of range dependence in bistatic STAP radars[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Huntsville, USA, 2003: 452–459.
|
| [19] |
YU Wenxian, ZHANG Zenghui, and HU Weidong. STAP method for space based radar based on spectrum registration with non-uniformed frequency samples[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2009, 31(2): 358–362. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.01244 |
| [20] |
HALE T B, TEMPLE M A, and WICKS M C. Clutter suppression using elevation interferometry fused with space-time adaptive processing[J]. Electronics Letters, 2001, 37(12): 793–794. doi: 10.1049/el:20010494 |
| [21] |
CORBELL P M and HALE T B. 3-dimensional STAP performance analysis using the cross-spectral metric[C]. IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, USA, 2004: 610–615.
|
| [22] |
DUAN Keqing, XU Hong, YUAN Huadong, et al. Reduced-DOF three-dimensional STAP via subarray synthesis for nonsidelooking planar array airborne radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(4): 3311–3325. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2958174 |
| [23] |
段克清, 李想, 行坤, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的天基预警雷达杂波抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(3): 386–398. doi: 10.12000/JR21161DUAN Keqing, LI Xiang, XING Kun, et al. Clutter mitigation in space-based early warning radar using a convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(3): 386–398. doi: 10.12000/JR21161 |
| [24] |
MELVIN W L and SHOWMAN G A. An approach to knowledge-aided covariance estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2006, 42(3): 1021–1042. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2006.248216 |
| [25] |
ROSEN P A and DAVIS M E. A joint space-borne radar technology demonstration mission for NASA and the air force[C]. IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2003: 437–444.
|
| [26] |
CAPON J. High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1969, 57(8): 1408–1418. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1969.7278 |
| [27] |
FERTIG L B. Analytical expressions for space-time adaptive processing (STAP) performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(1): 42–53. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130676 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: