- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
| Citation: | CHEN Hui, TIAN Xiang, LI Zihao, et al. Reduced-dimension target parameter estimation for conformal FDA-MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 811–821. DOI: 10.12000/JR21197 |
Reduced-dimension Target Parameter Estimation For Conformal FDA-MIMO Radar
DOI: 10.12000/JR21197 CSTR: 32380.14.JR21197
More Information-
Abstract
Frequency Diverse Array (FDA) Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) radar equipped with a FDA can possess beam patterns that are dependent on range, angle, and time, and it can increase the degree of freedom. This paper introduces a conformal array attached to the surface of the carrier, the array can reduce the aerodynamic impact on the carrier and reduce the cross section of the FDA-MIMO radar. First, the conformal FDA-MIMO measurement model is formulated, and a Cramér-Rao Lower Bound (CRLB) is derived to evaluate the parameter estimation performance. To avoid the three-dimensional search of the traditional three-dimensional MUltiple SIgnal Classification (3D-MUSIC) algorithm, a Reduced-Dimension MUltiple SIgnal Classification (RD-MUSIC) algorithm is proposed for parameter estimation. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm has a slightly lower estimation accuracy than the 3D-MUSIC algorithm but a much lower computational complexity. In addition, the proposed algorithm has better range estimation performance for multiple targets than the 3D-MUSIC algorithm.
-
Keywords:
- Conformal array,
- FDA-MIMO,
- Parameter estimation,
- 3D-MUSIC,
- RD-MUSIC
-

-
References
[1] ANTONIK P, WICKS M C, GRIFFITHS H D, et al. Frequency diverse array radars[C]. 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006: 215–216. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2006.1631800.[2] WANG Wenqin, SHAO Huaizong, and CAI Jingye. Range-angle-dependent beamforming by frequency diverse array antenna[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2012, 2012: 760489. doi: 10.1155/2012/760489[3] SAMMARTINO P F, BAKER C J, and GRIFFITHS H D. Frequency diverse MIMO techniques for radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(1): 201–222. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6404099[4] LI Shengyuan, ZHANG Linrang, LIU Nan, et al. Range-angle dependent detection for FDA-MIMO radar[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 2016: 6629–6632. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7730731.[5] CHENG Jie, CHEN Hui, GUI Ronghua, et al. Persymmetric adaptive detector for FDA-MIMO radar[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2043947.2020.9266641.[6] ZHU Yu, LIU Lei, LU Zheng, et al. Target detection performance analysis of FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 164276–164285. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2943082[7] LAN Lan, MARINO A, AUBRY A, et al. GLRT-based adaptive target detection in FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(1): 597–613. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3028485[8] LAN Lan, XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, et al. Suppression of mainbeam deceptive jammer with FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 11584–11598. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3014689[9] LAN Lan, ROSAMILIA M, AUBRY A, et al. Single-snapshot angle and incremental range estimation for FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 3705–3718. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3083591[10] CHEN Hui and SHAO Huaizong. Sparse reconstruction based target localization with frequency diverse array MIMO radar[C]. 2015 IEEE China Summit and International Conference on Signal and Information Processing (ChinaSIP), Chengdu, China, 2015: 94–98. doi: 10.1109/ChinaSIP.2015.7230369.[11] XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Joint range and angle estimation using MIMO radar with frequency diverse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(13): 3396–3410. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2422680[12] XIONG Jie, WANG Wenqin, and GAO Kuandong. FDA-MIMO radar range-angle estimation: CRLB, MSE, and resolution analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(1): 284–294. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2756498[13] CUI Can, YAN Yisheng, WANG Wenqin, et al. Resolution threshold of music algorithm for FDA-MIMO radar[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf18), Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 230–234. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8378562.[14] CHEN Xiaolong, CHEN Baoxin, XUE Yonghua, et al. Space-range-Doppler focus processing: A novel solution for moving target integration and estimation using FDA-MIMO radar[C]. 2018 International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8557297.[15] CUI Can, XU Jian, GUI Ronghua, et al. Search-free DOD, DOA and range estimation for bistatic FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 15431–15445. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2816780[16] LIU Yi, YANG Hu, JIN Zusheng, et al. A multibeam cylindrically conformal slot array antenna based on a modified rotman lens[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(7): 3441–3452. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2829816[17] DOHMEN C, ODENDAAL J W, and JOUBERT J. Synthesis of conformal arrays with optimized polarization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2007, 55(10): 2922–2925. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2007.905501[18] XIAO Shiwei, YANG Shiwen, ZHANG Hangyu, et al. Practical implementation of wideband and wide-scanning cylindrically conformal phased array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 67(8): 5729–5733. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2922760[19] COSTA M, RICHTER A, and KOIVUNEN V. DoA and polarization estimation for arbitrary array configurations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(5): 2330–2343. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2187519[20] MOHAMMADI S, GHANI A, and SEDIGHY S H. Direction-of-arrival estimation in conformal microstrip patch array antenna[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(1): 511–515. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2017.2772085[21] NECHAEV Y B, ALGAZINOV E K, and PESHKOV I W. Estimation of the Cramer-Rao bound for radio direction-finding on the azimuth and elevation of the cylindical antenna arrays[C]. 2018 41st International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Athens, Greece, 2018: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.8441419.[22] LI Wentao, CUI Can, YE Xiutiao, et al. Quasi-time-invariant 3-D focusing beampattern synthesis for conformal frequency diverse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2020, 68(4): 2684–2697. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2955199[23] FENG Maoyuan, CUI Zhongma, YANG Yunxiu, et al. A reduced-dimension MUSIC algorithm for monostatic FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(4): 1279–1282. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3045440[24] ZHANG Xiaofei, CHEN Weiyang, ZHENG Wang, et al. Localization of near-field sources: A reduced-dimension MUSIC algorithm[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(7): 1422–1425. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2837049[25] BURGER H A. Use of Euler-rotation angles for generating antenna patterns[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 1995, 37(2): 56–63. doi: 10.1109/74.382344[26] MILLIGAN T. More applications of Euler rotation angles[J]. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 1999, 41(4): 78–83. doi: 10.1109/74.789738[27] STOICA P and NEHORAI A. MUSIC, maximum likelihood and Cramer-Rao bound[C]. International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, New York, USA, 1988: 2296–2299. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.1988.197097.[28] STOICA P and NEHORAI A. MUSIC, maximum likelihood and Cramer-Rao bound: Further results and comparisons[C]. International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Glasgow, UK, 1989: 2605–2608. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.1989.267001. -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. Conformal FDA-MIMO radar
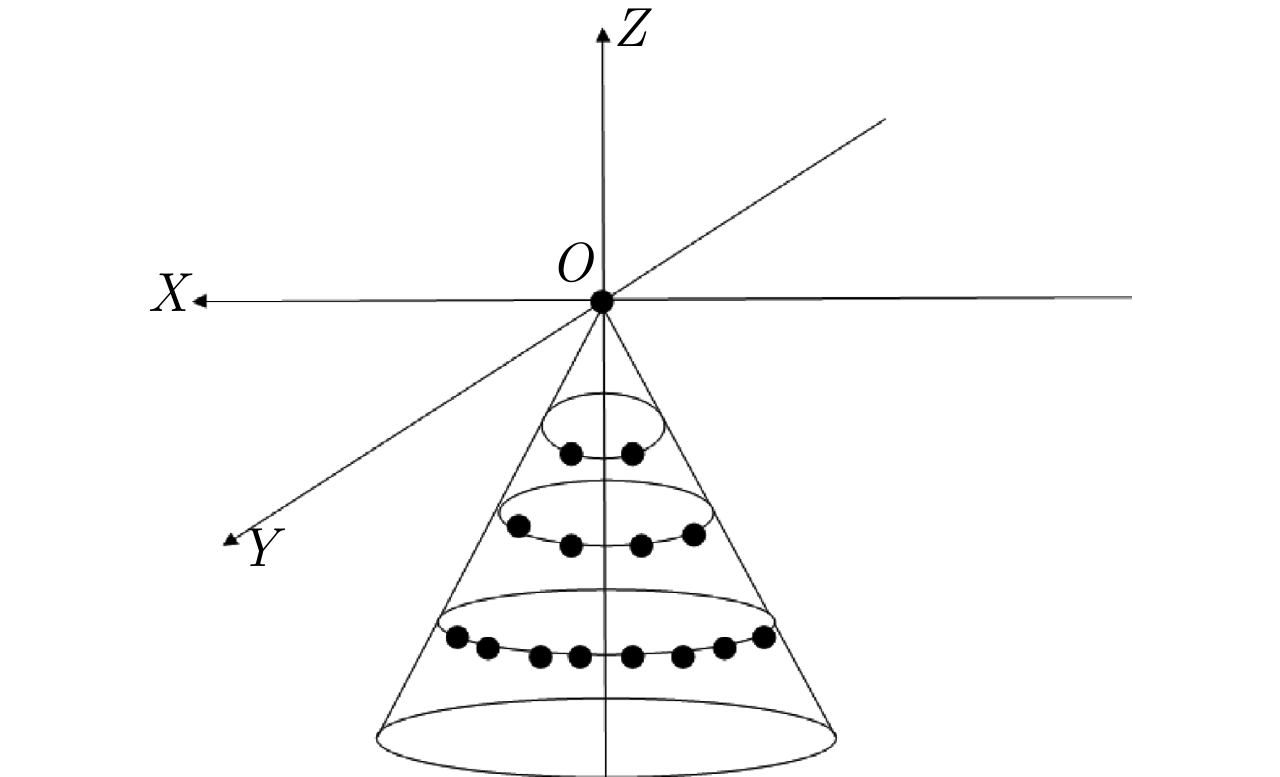
- Figure 2. Conformal FDA-MIMO semi conical receiving array
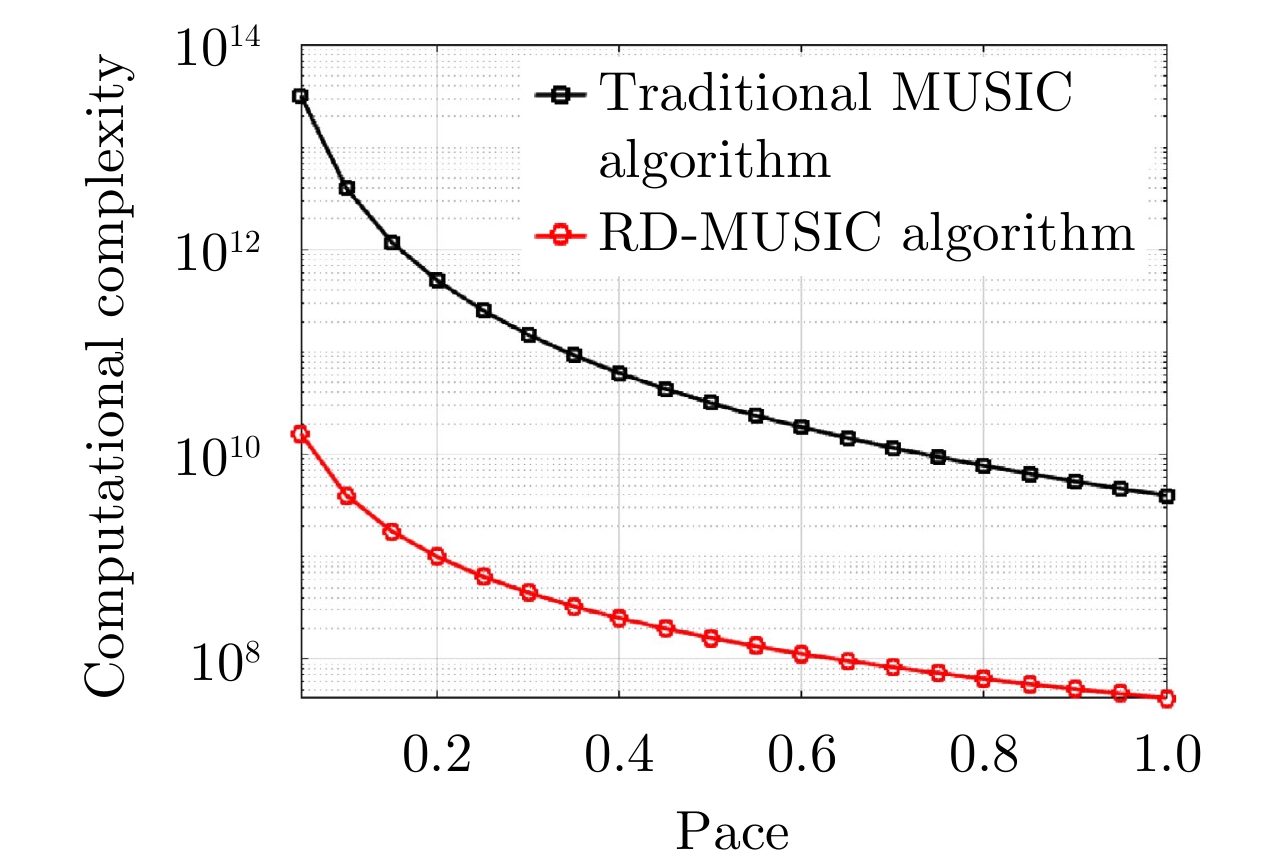
- Figure 3. Comparison of computational complexity under different scan spacing
- Figure 4. The parameter estimation probability of RD-MUSIC algorithm with different thresholds
- Figure 5. The RMSE versus snapshot for single target case
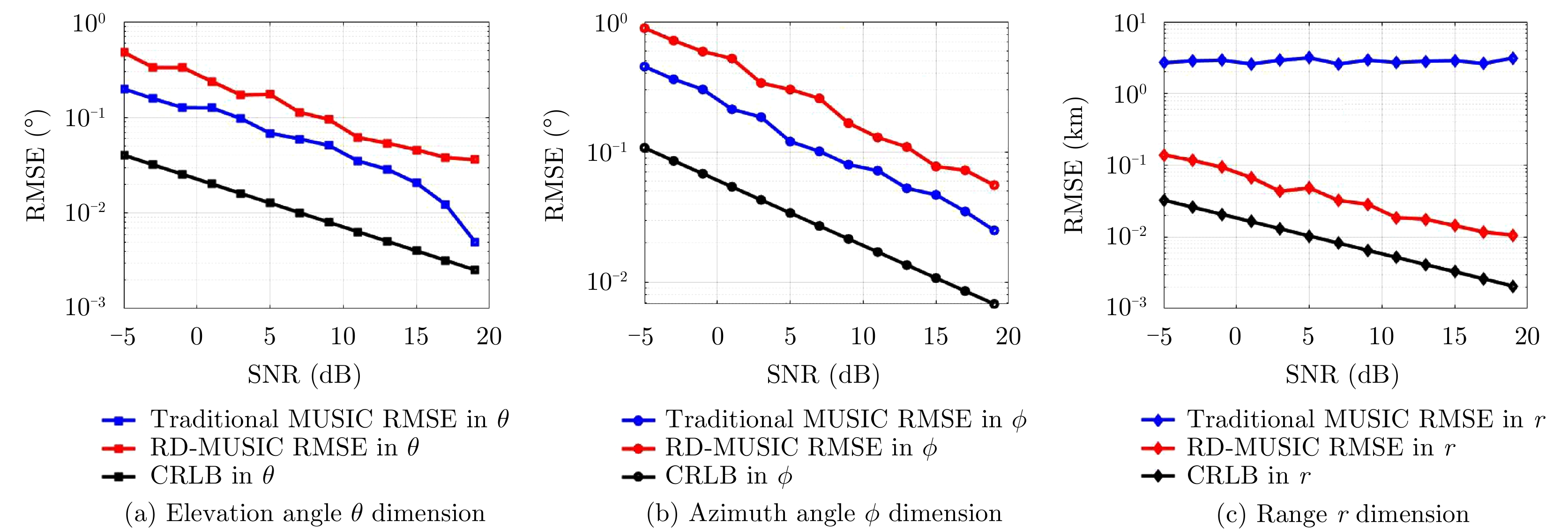
- Figure 6. The RMSE versus SNR for two targets case
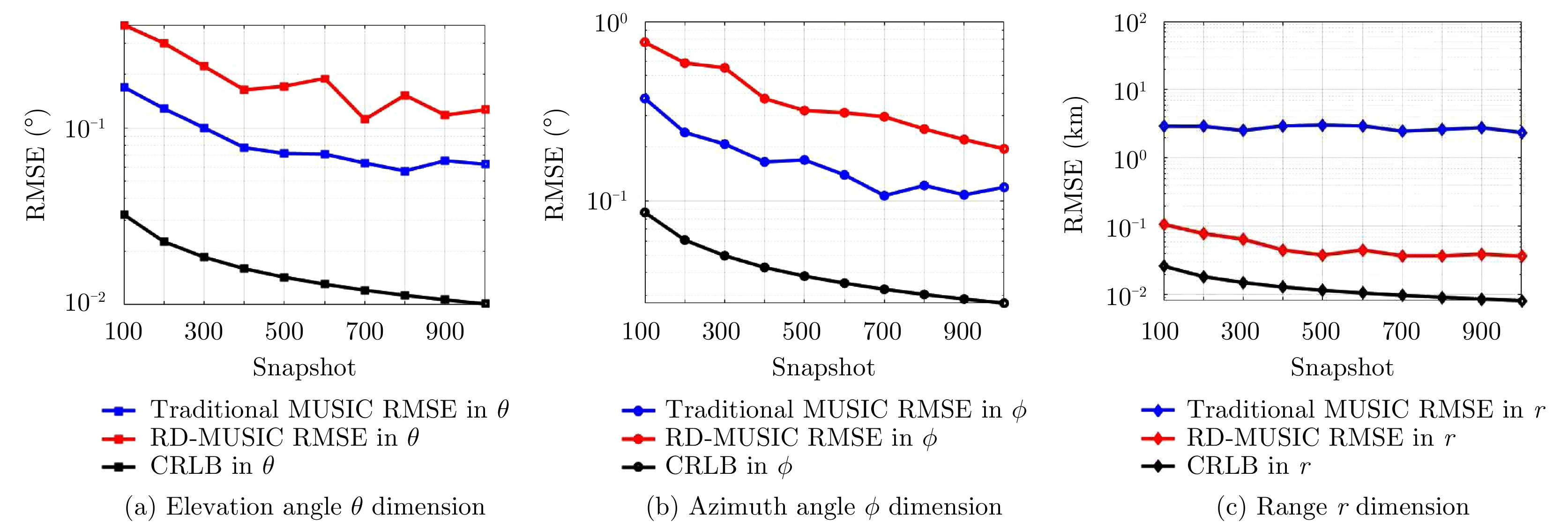
- Figure 7. The RMSE versus snapshot for two targets case
- Figure 8. The RMSE versus snapshot for two targets case


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: