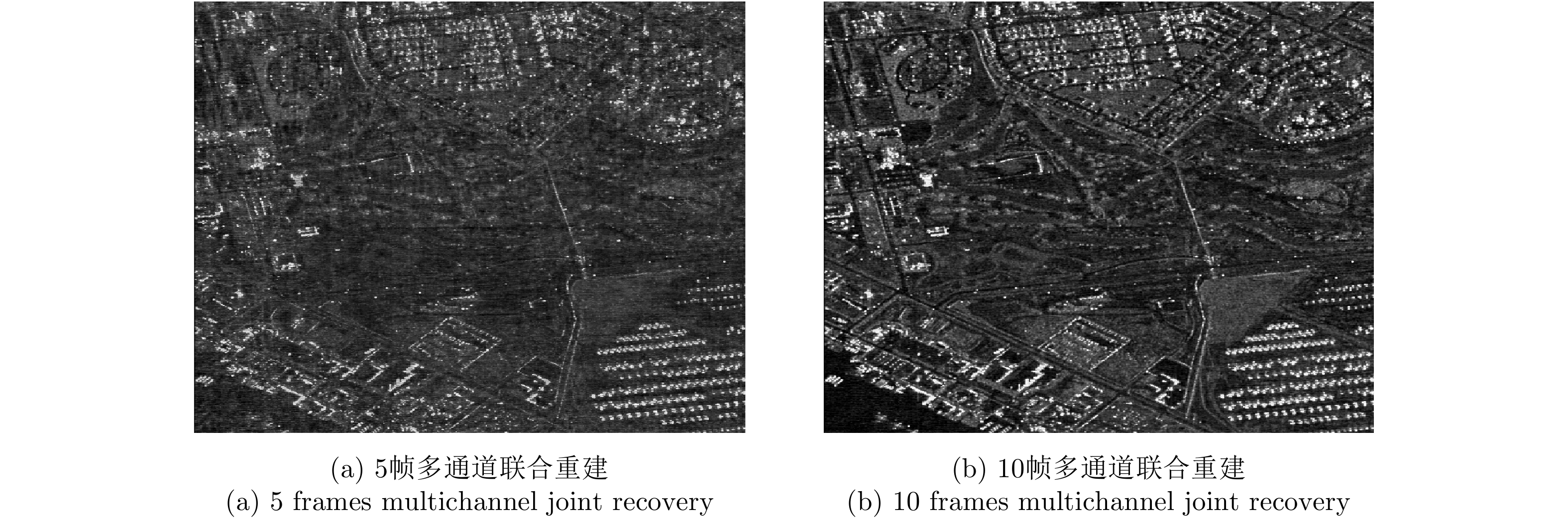
| [1] |
TOMIYASU K and PACELLI J L. Synthetic aperture radar imaging from an inclined geosynchronous orbit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1983, GE-21(3): 324–329. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.1983.350561 |
| [2] |
MADSEN S N, EDELSTEIN W, DIDOMENICO L D, et al. A geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar; for tectonic mapping, disaster management and measurements of vegetation and soil moisture[C]. IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium on Scanning the Present and Resolving the Future, Sydney, Australia, 2001: 447–449.
|
| [3] |
YANG Jianyu. Multi-directional evolution trend and law analysis of radar ground imaging technology[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 669–692. doi: 10.12000/JR19099 |
| [4] |
邢孟道, 林浩, 陈溅来, 等. 多平台合成孔径雷达成像算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102XING Mengdao, LIN Hao, CHEN Jianlai, et al. A review of imaging algorithms in multi-platform-borne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102 |
| [5] |
孙稚超. 基于GEO辐射源的星机SAR成像理论与方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2017.
SUN Zhichao. Research on the imaging theory and algorithms of geosynchronous Spaceborne-Airborne Bistatic SAR[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2017.
|
| [6] |
安洪阳. 基于高轨照射源的双基SAR成像与动目标检测技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020.
AN Hongyang. Research on imaging and moving target detection technology of bistatic SAR with geosynchronous illuminator[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020.
|
| [7] |
GUTTRICH G L, SIEVERS W E, and TOMLJANOVICH N M. Wide area surveillance concepts based on geosynchronous illumination and bistatic unmanned airborne vehicles or satellite reception[C]. 1997 IEEE National Radar Conference, Syracuse, USA, 1997: 126–131 .
|
| [8] |
LU Zheng, WANG Yuekun, XU Mingming, et al. Spacecraft formation design for bistatic SAR with GEO illuminator and LEO receiver[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 4451–4454.
|
| [9] |
WANG Jingen, WANG Yanfei, GE Jialong, et al. Ambiguous scattering point detection of bistatic downward-looking SAR with geostationary illuminator and LEO receiver[C]. The 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuremberg, Germany, 2012: 571–574.
|
| [10] |
SUN Guangcai, XING Mengdao, WANG Yong, et al. A 2-D space-variant chirp scaling algorithm based on the RCM equalization and subband synthesis to process geosynchronous SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4868–4880. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2285721 |
| [11] |
DING Zegang, SHU Bozheng, YIN Wei, et al. A modified frequency domain algorithm based on optimal azimuth quadratic factor compensation for geosynchronous SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1119–1131. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2497000 |
| [12] |
ZHANG Shuangxi, LI Shaojie, LIU Yanyang, et al. A novel azimuth Doppler signal reconstruction approach for the GEO-LEO bi-static multi-channel HRWS SAR system[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 39539–39546. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2904653 |
| [13] |
WANG Yuekun, LIU Yanyang, LI Zhenfang, et al. High-resolution wide-swath imaging of spaceborne multichannel bistatic SAR with inclined geosynchronous illuminator[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(12): 2380–2384. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2765675 |
| [14] |
AN Hongyang, WU Junjie, TEH K C, et al. Nonambiguous image formation for low-earth-orbit SAR with geosynchronous illumination based on multireceiving and CAMP[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(1): 348–362. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2992744 |
| [15] |
DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 |
| [16] |
RECHT B, FAZEL M, and PARRILO P A. Guaranteed minimum-rank solutions of linear matrix equations via nuclear norm minimization[J]. SIAM Review, 2010, 52(3): 471–501. doi: 10.1137/070697835 |
| [17] |
PU Wei and WU Junjie. OSRanP: A novel way for radar imaging utilizing joint sparsity and low-rankness[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020, 6: 868–882. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2020.2993170 |
| [18] |
WU Junjie, SUN Zhichao, LI Zhongyu, et al. Focusing translational variant bistatic forward-looking SAR using keystone transform and extended nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(10): 840. doi: 10.3390/rs8100840 |
| [19] |
BI Hui, BI Guoan, ZHANG Bingchen, et al. From theory to application: Real-time sparse SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(4): 2928–2936. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2958067 |
| [20] |
AN Hongyang, WU Junjie, TEH K C, et al. Geosynchronous spaceborne-airborne bistatic SAR imaging based on fast low-rank and sparse matrices recovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3081099. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: