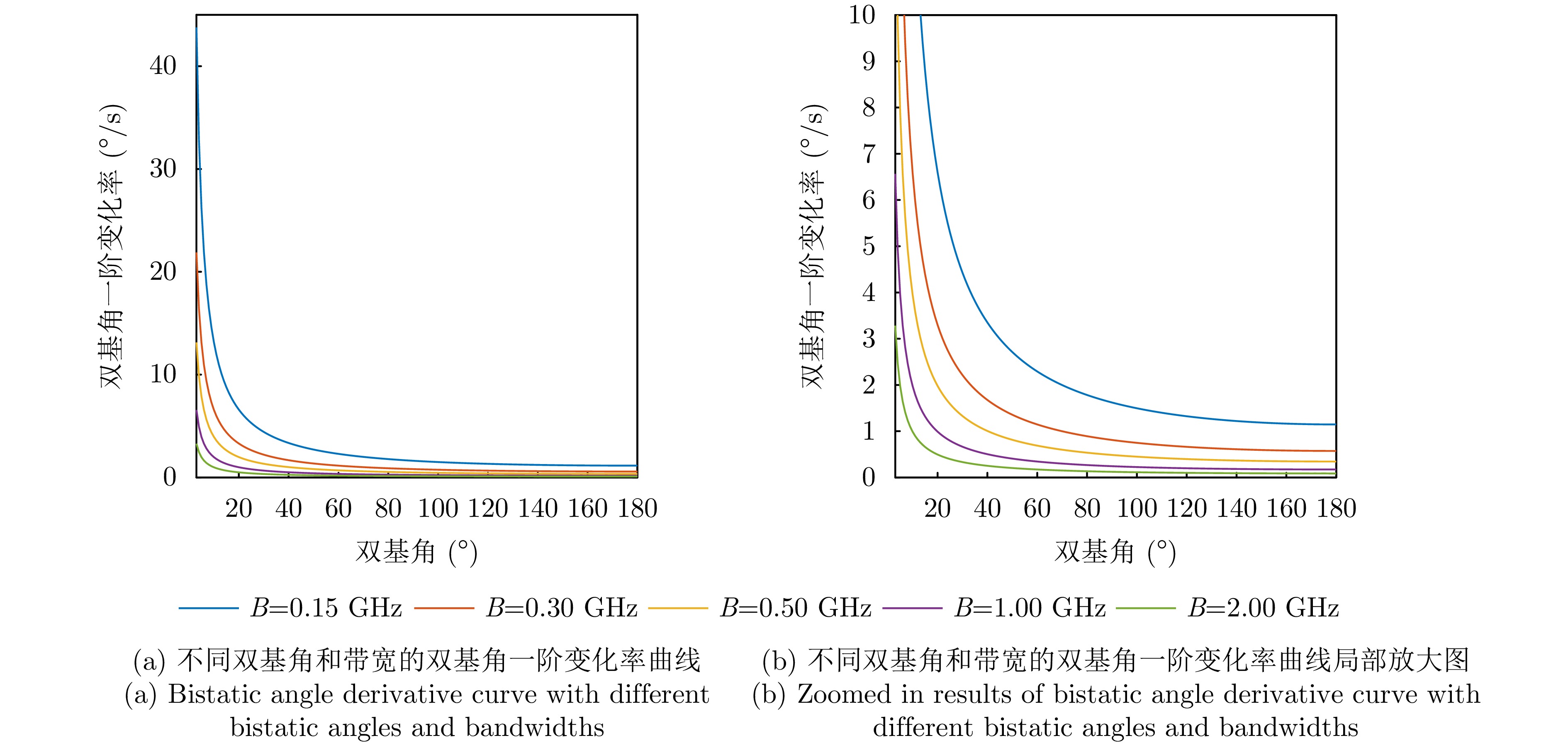
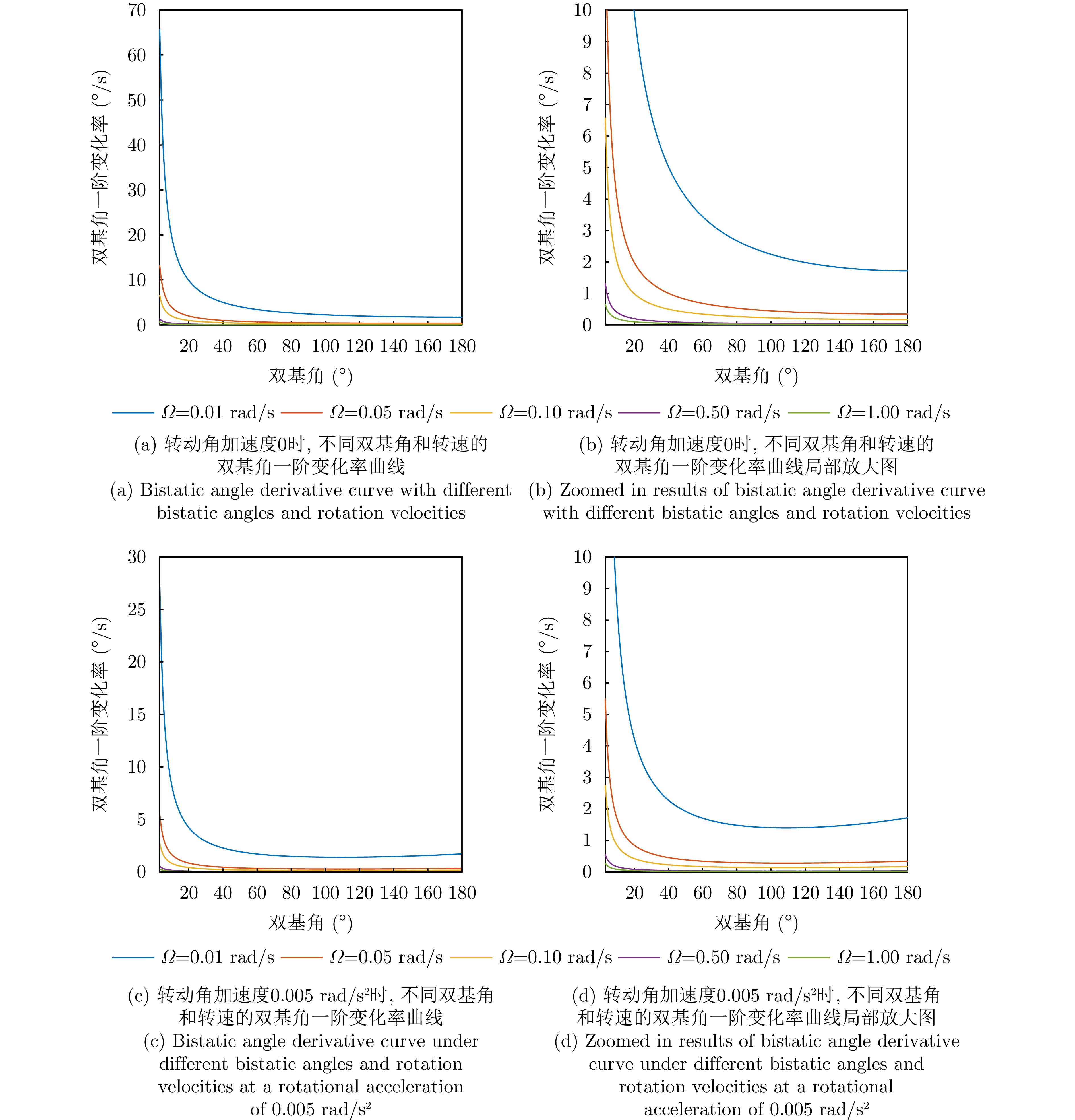
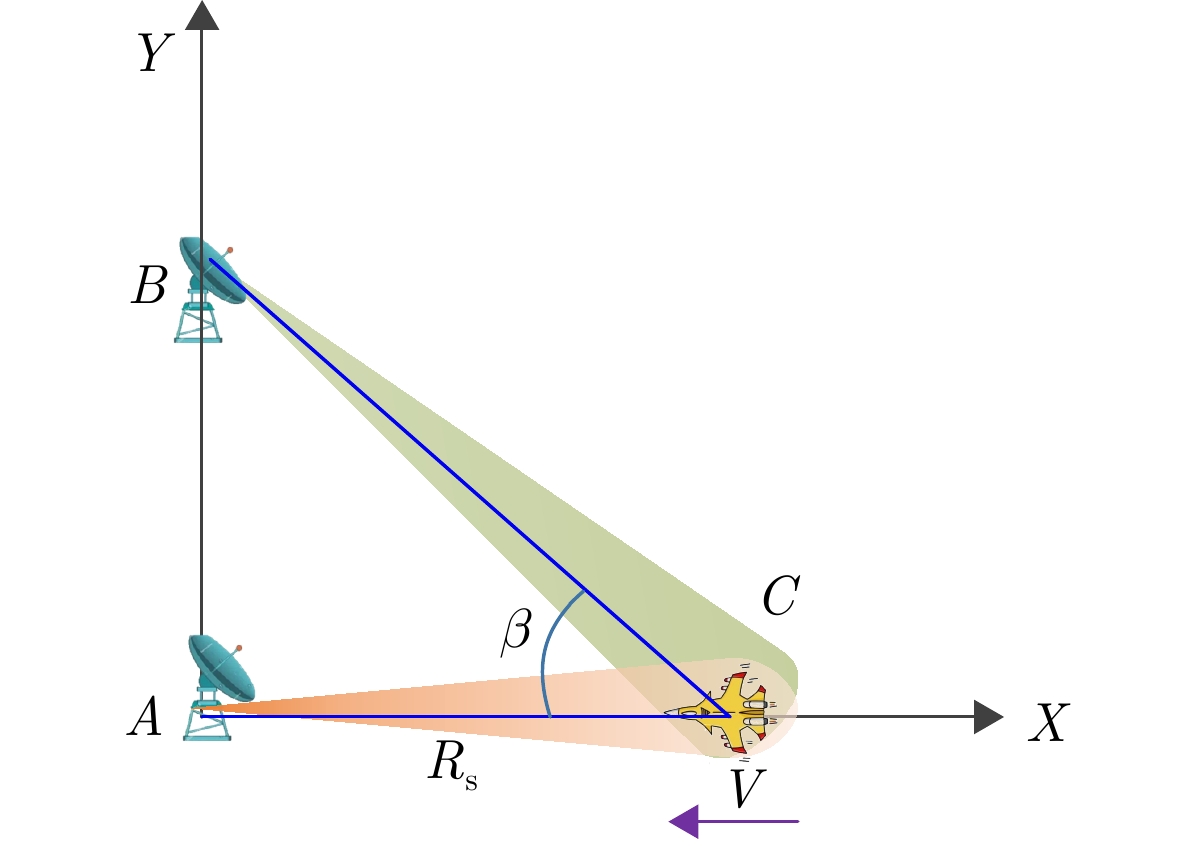
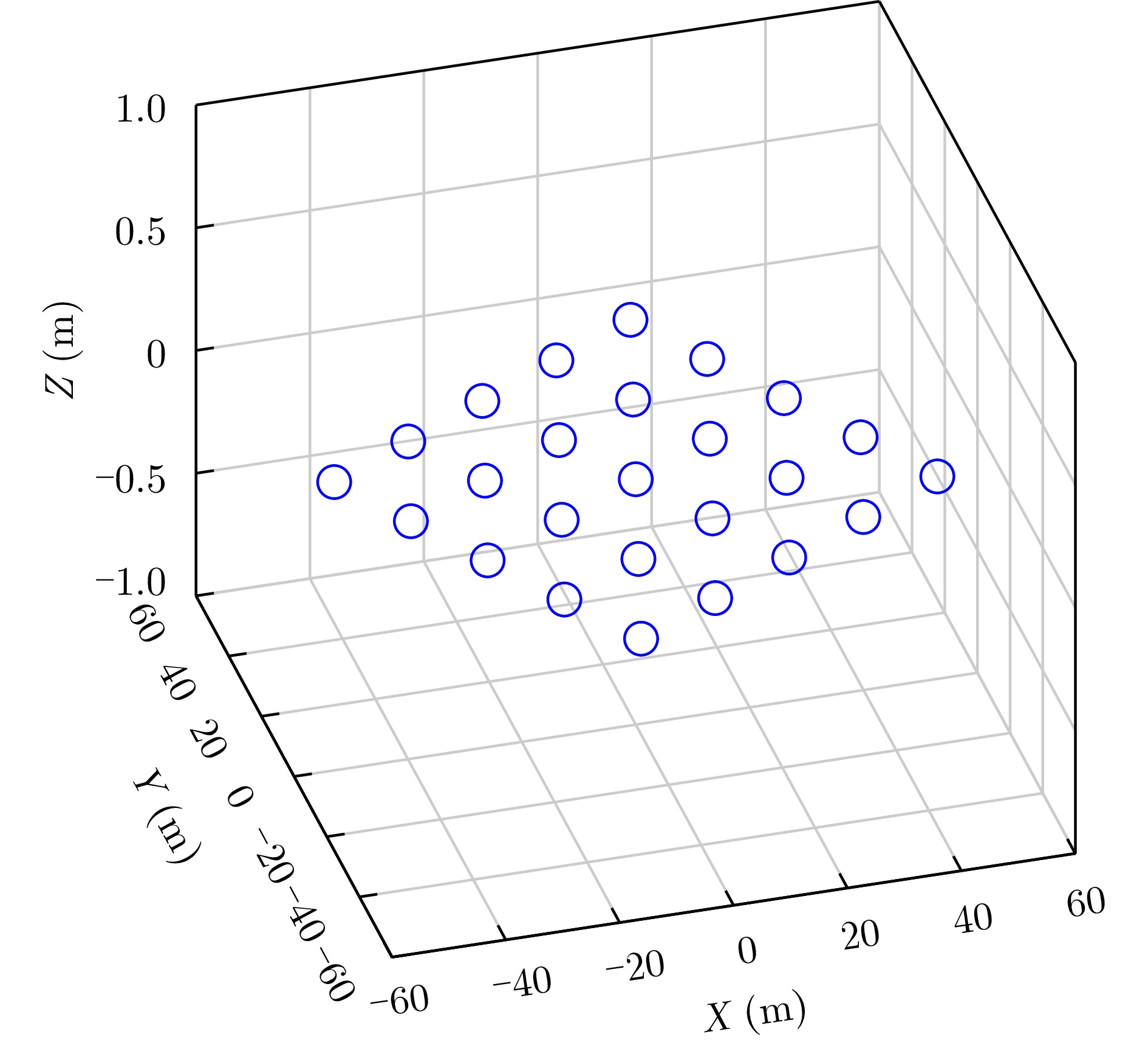
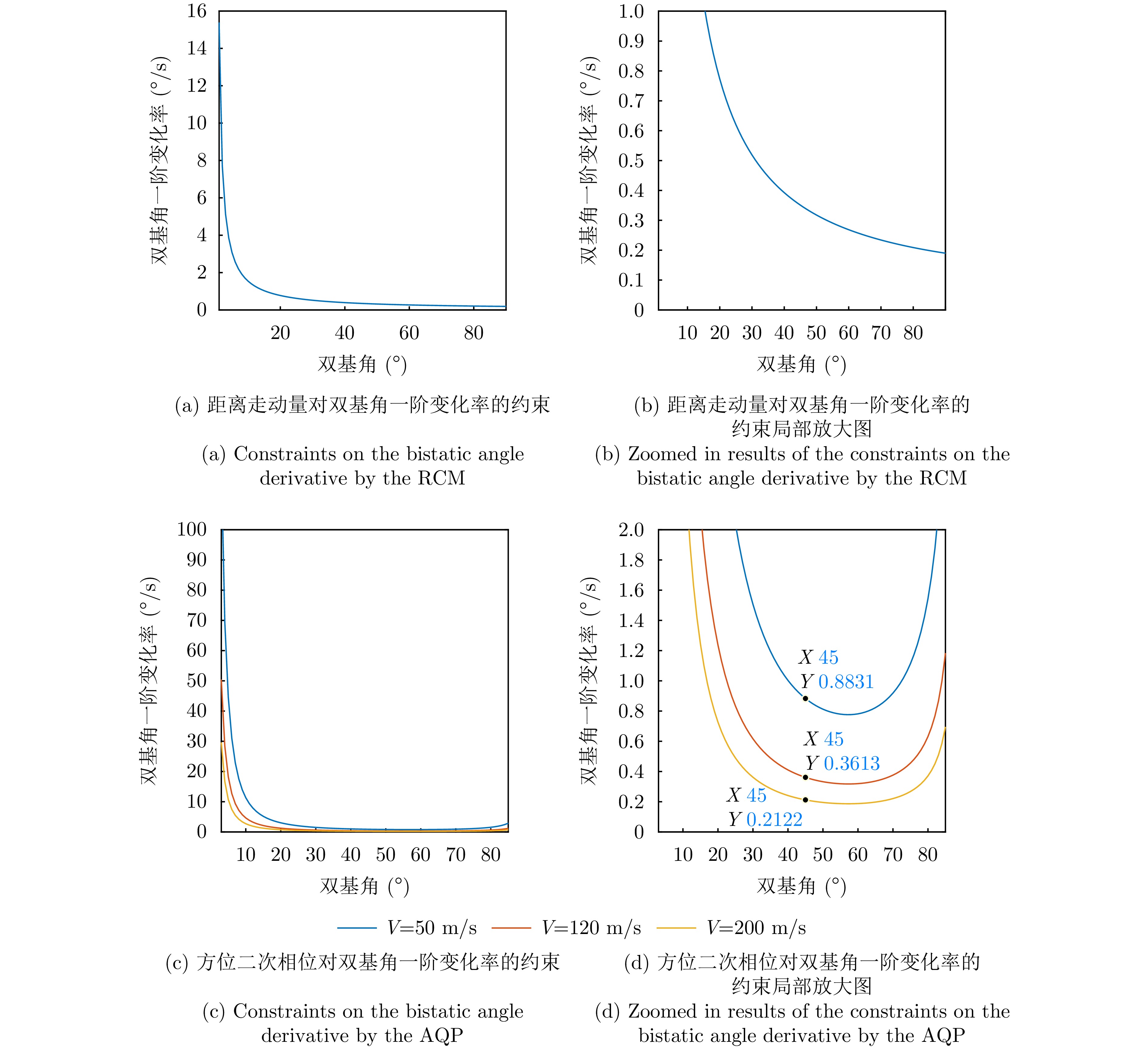
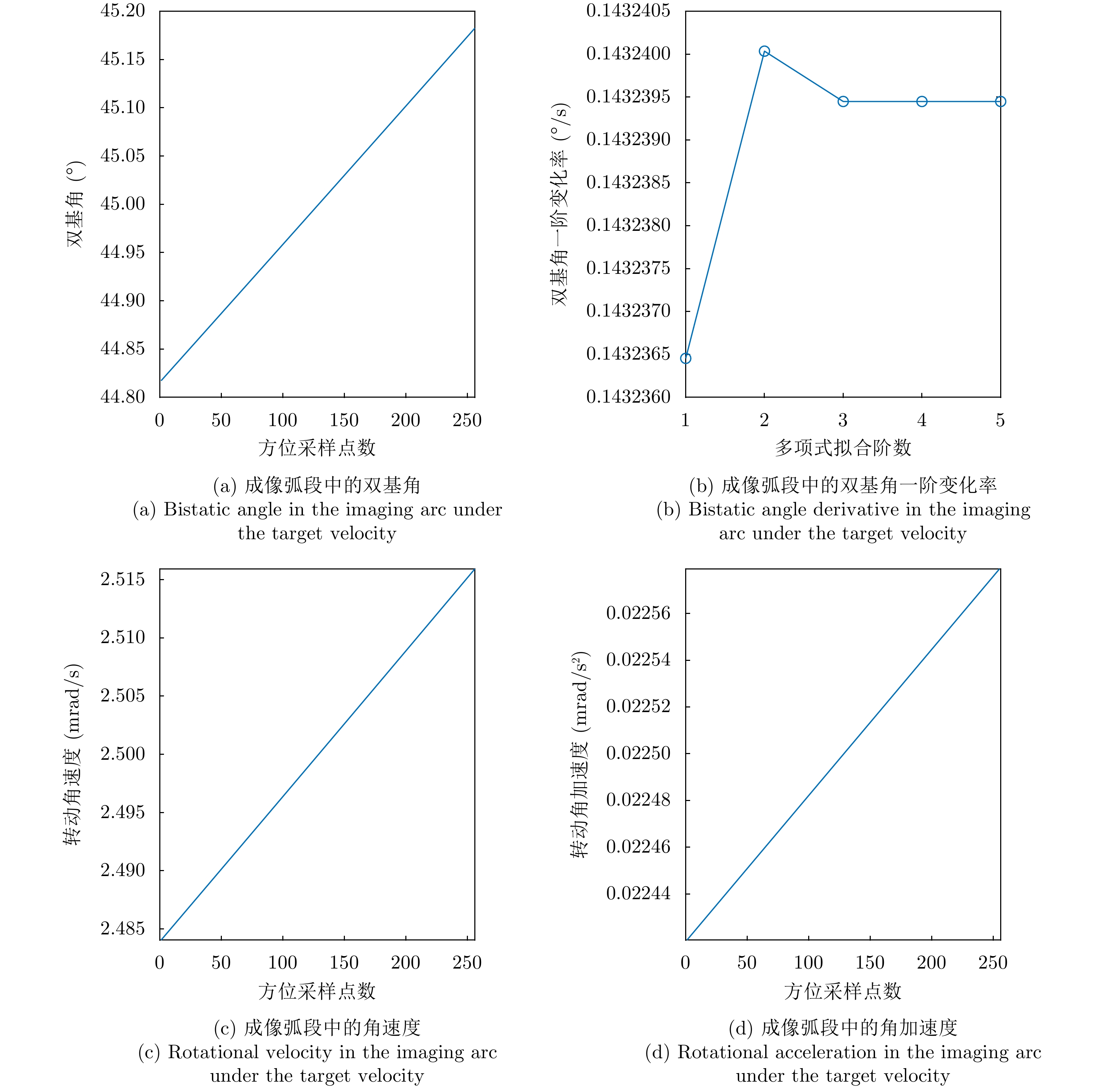
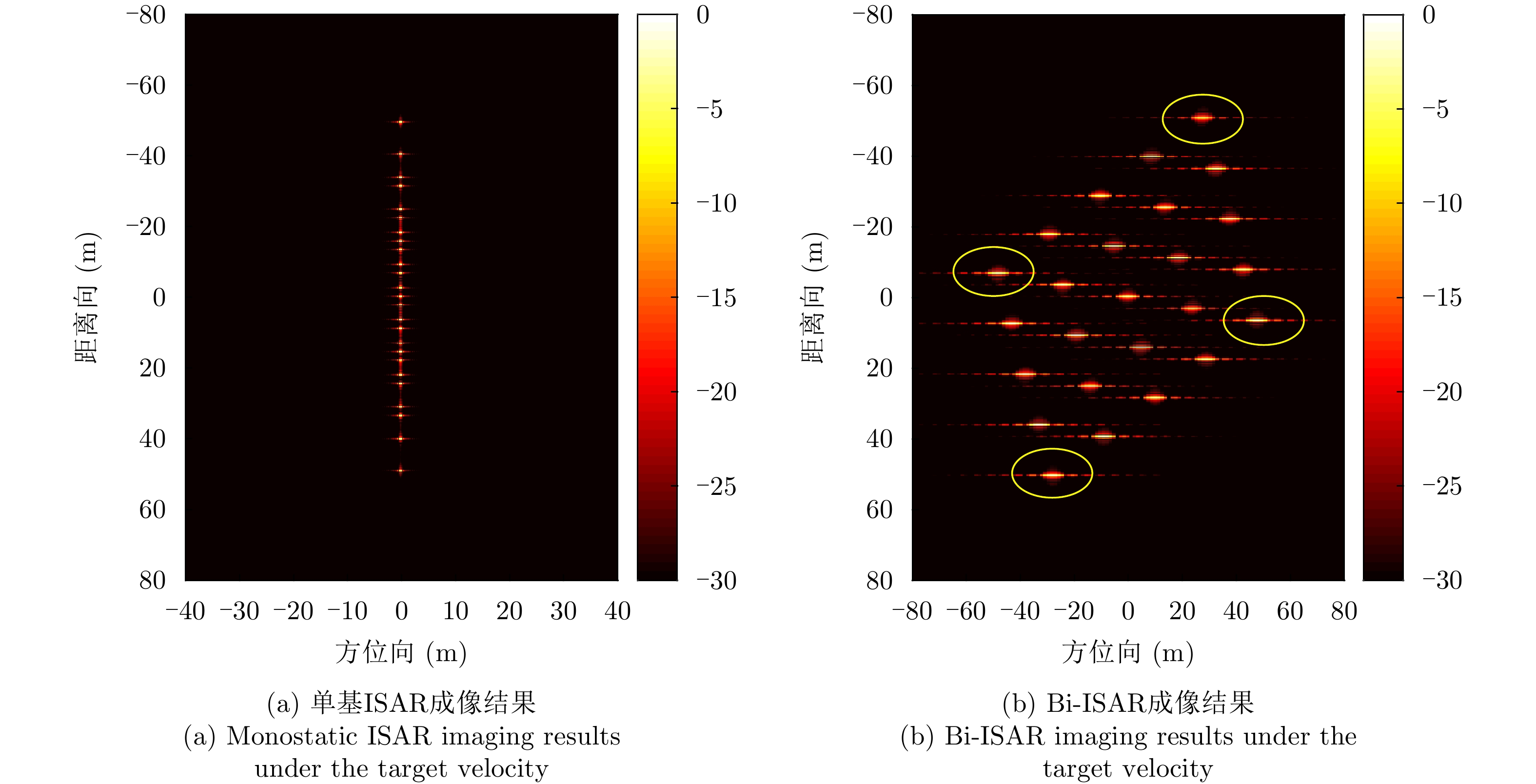
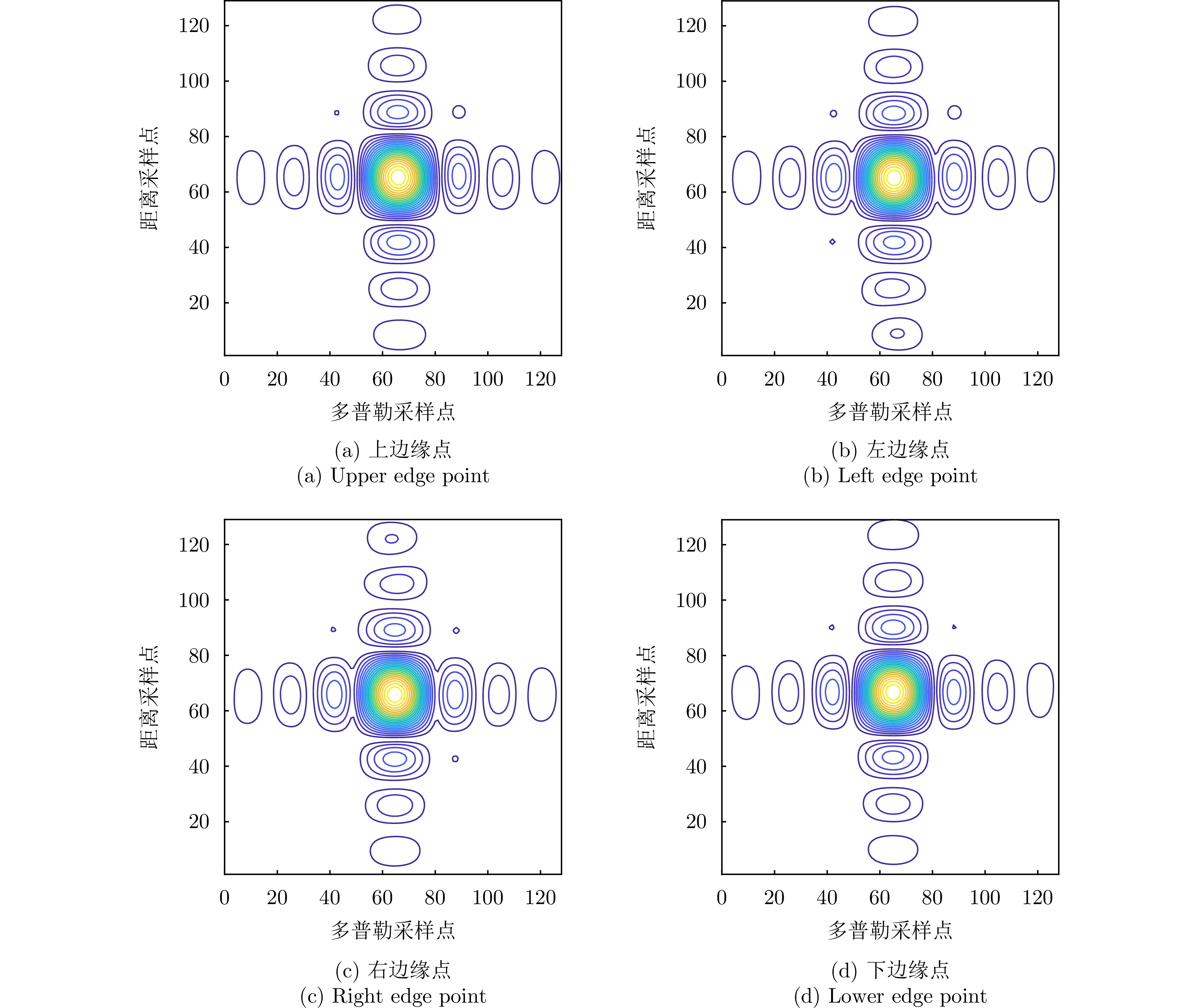
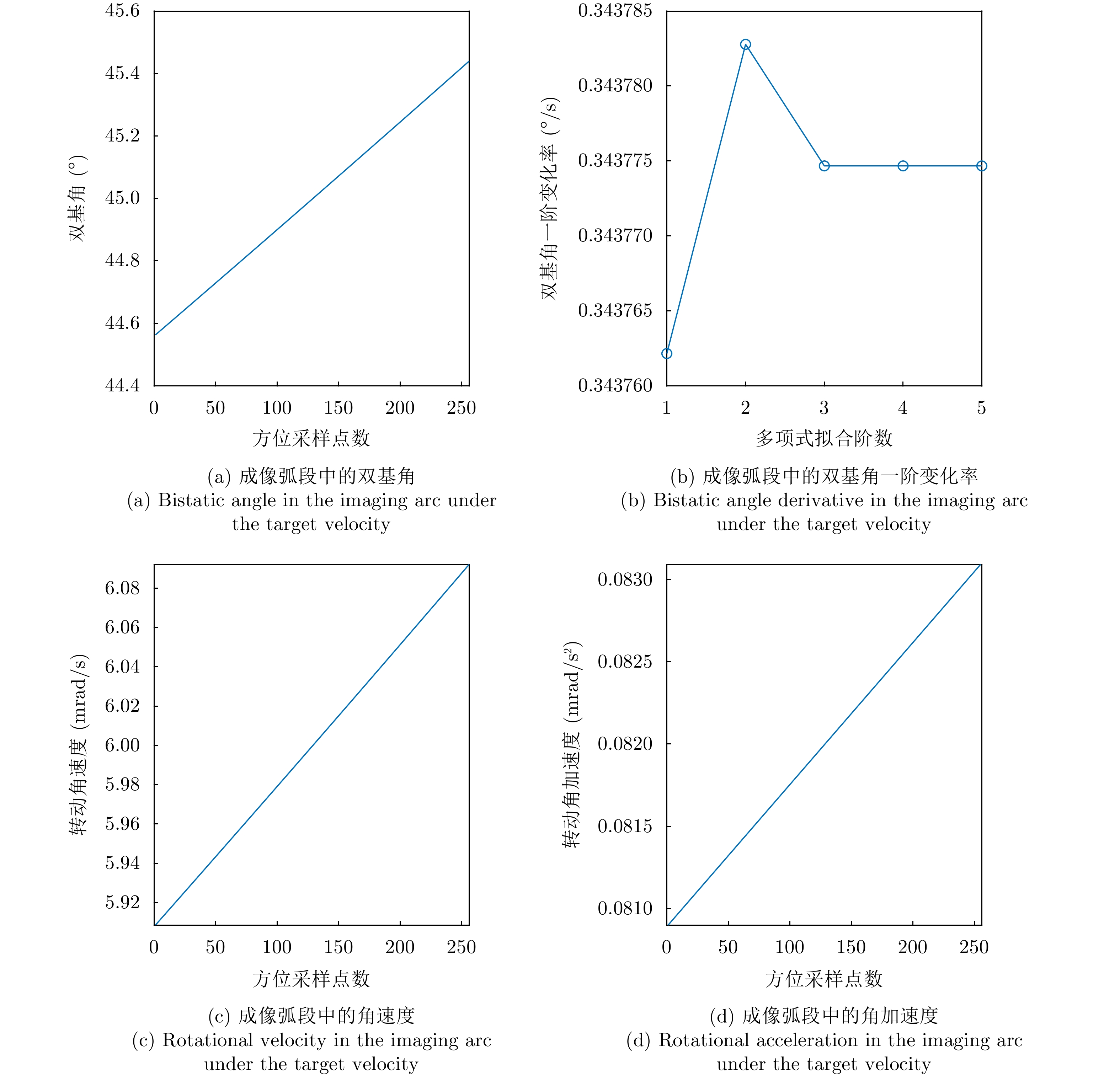
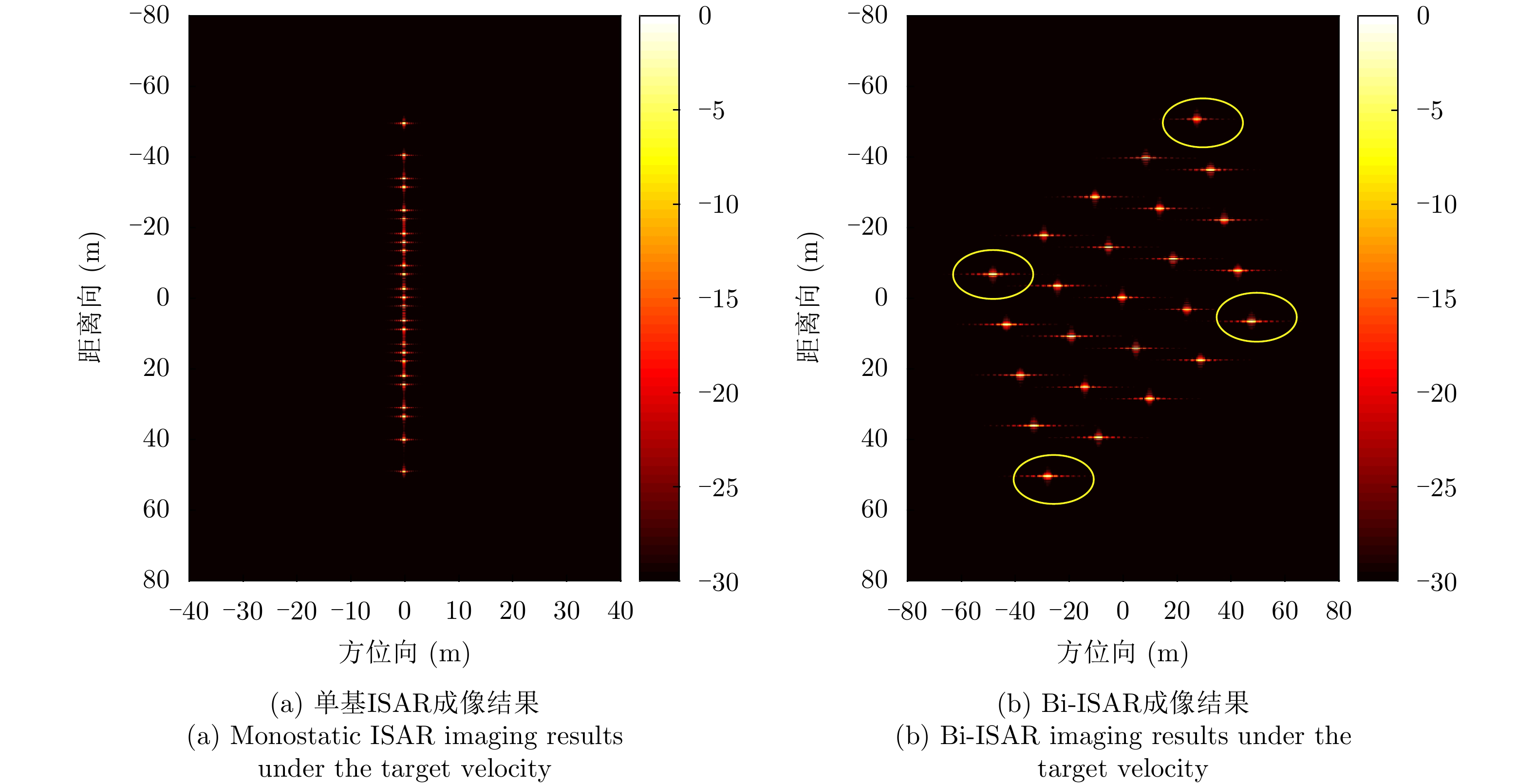
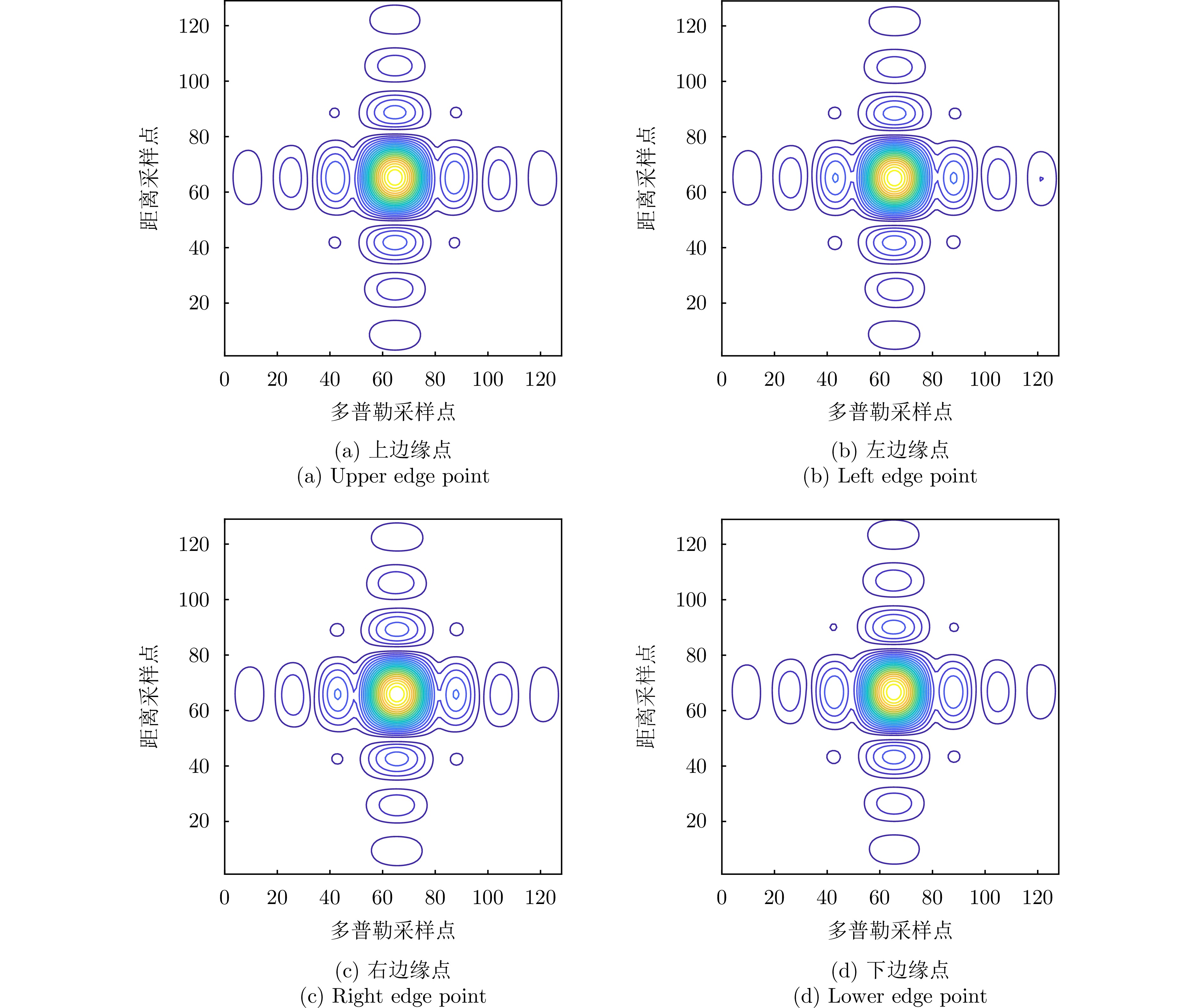
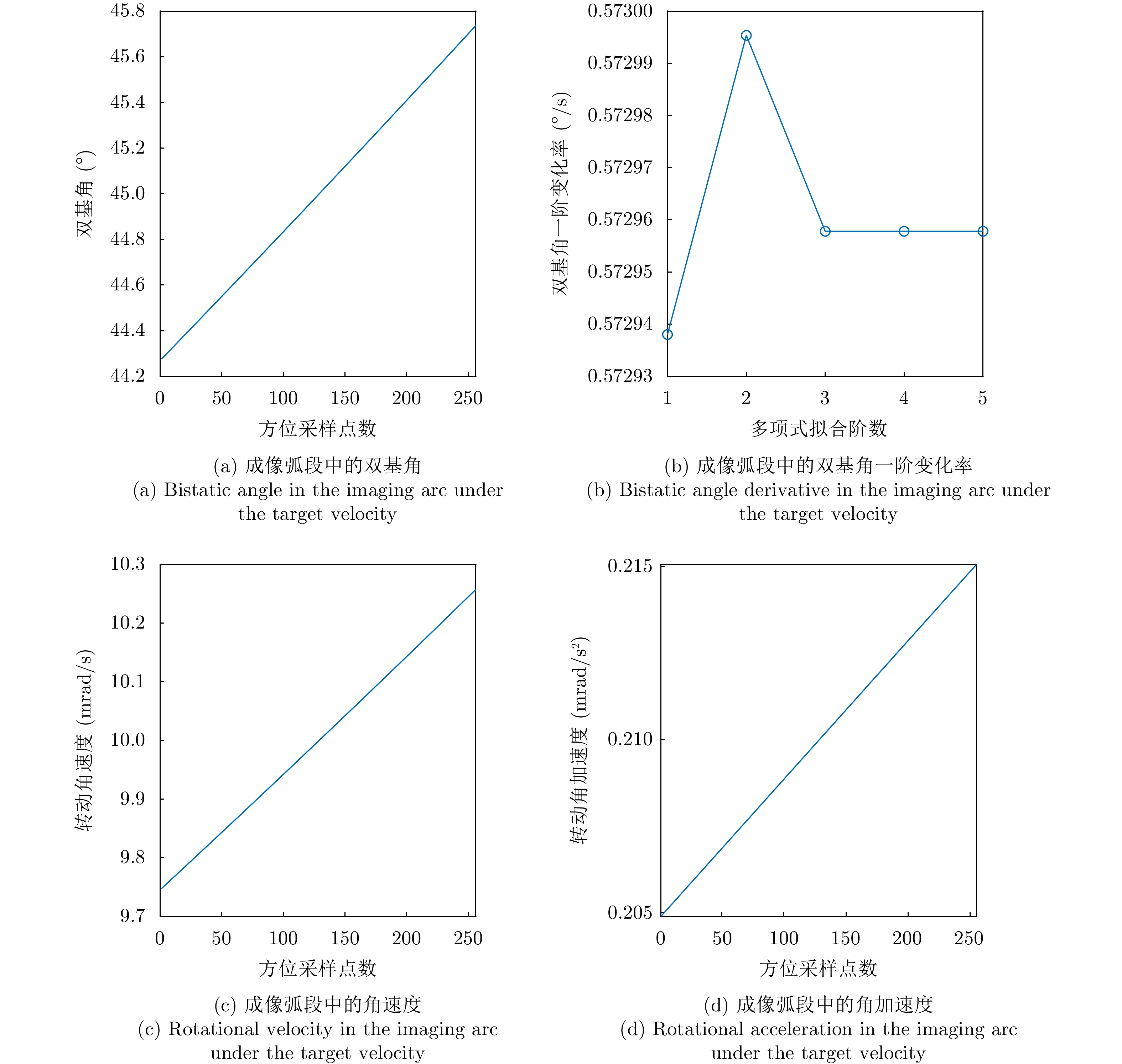
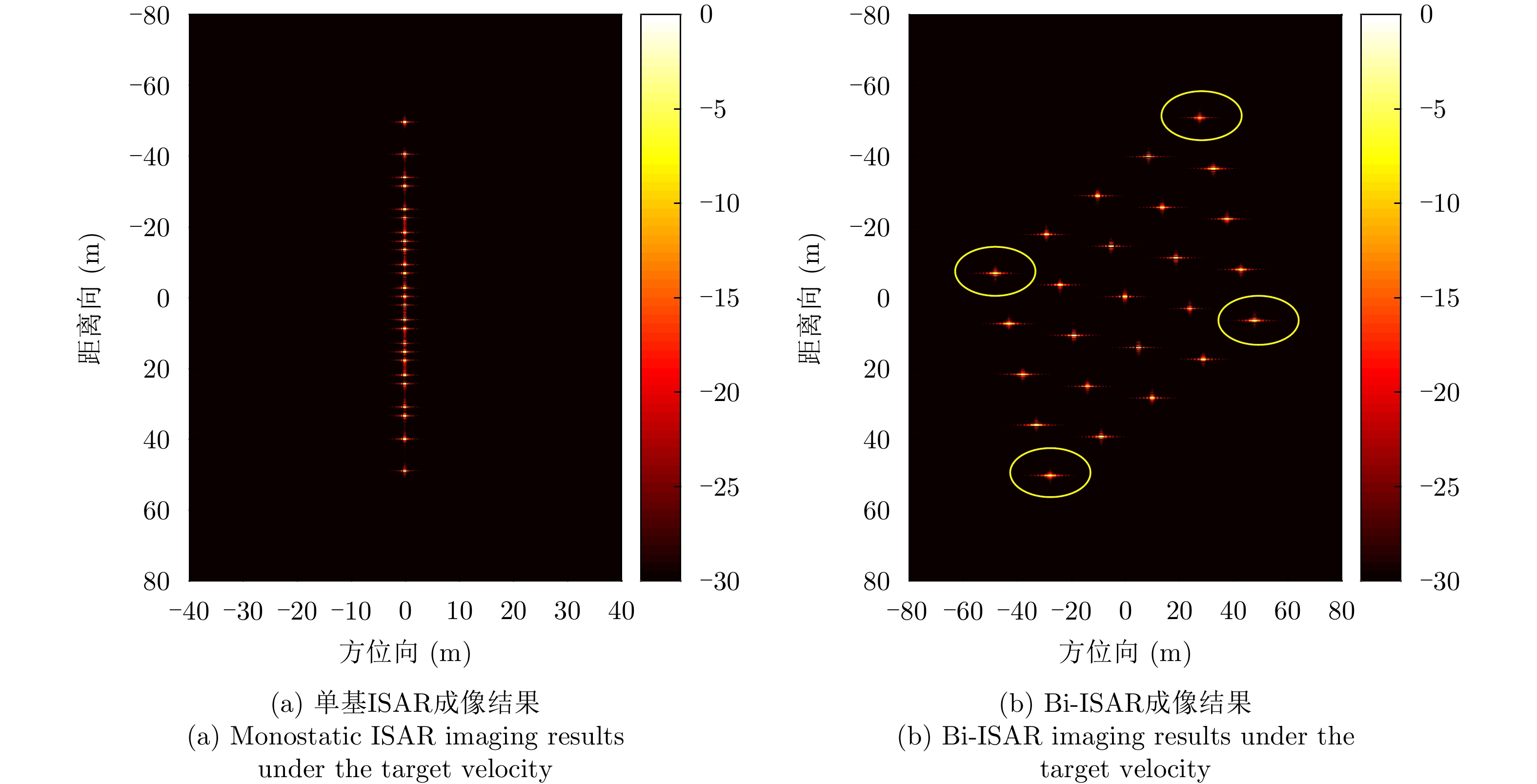
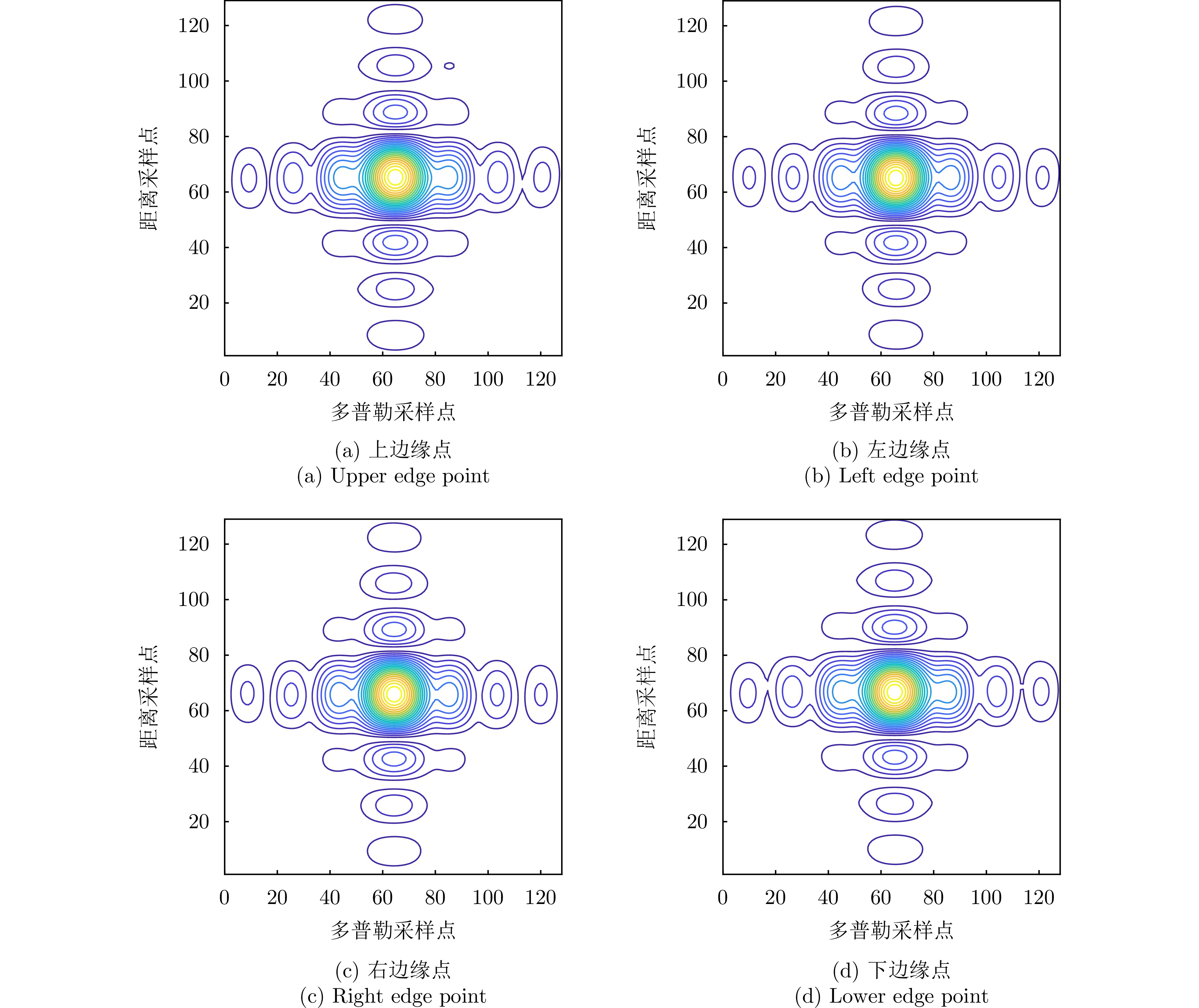
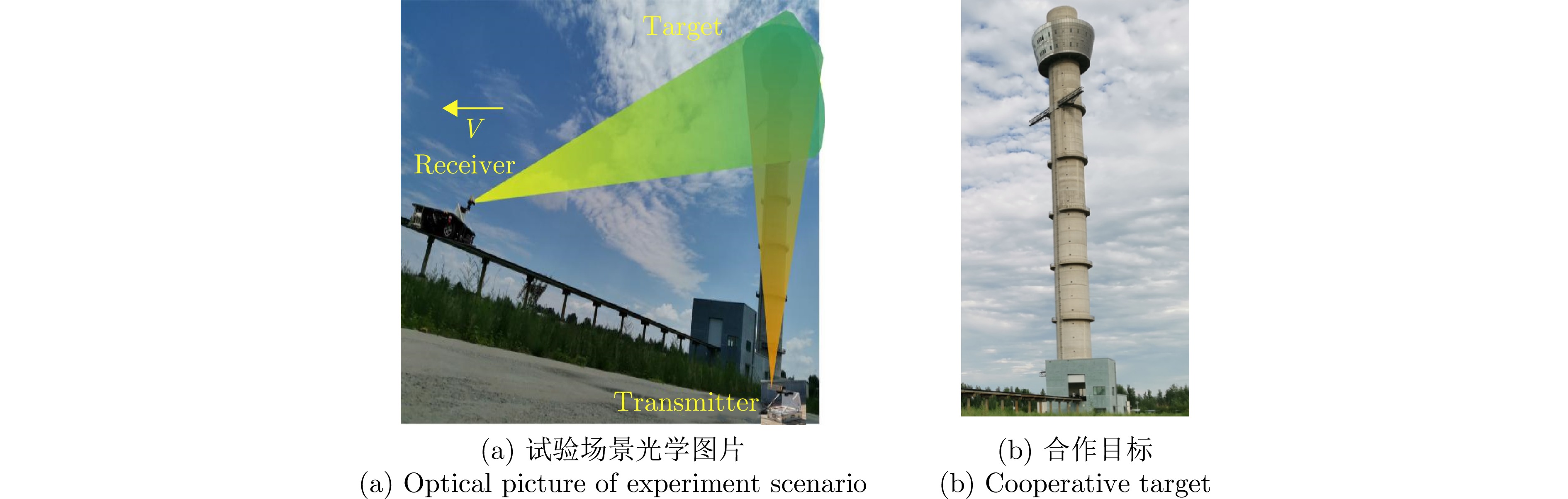
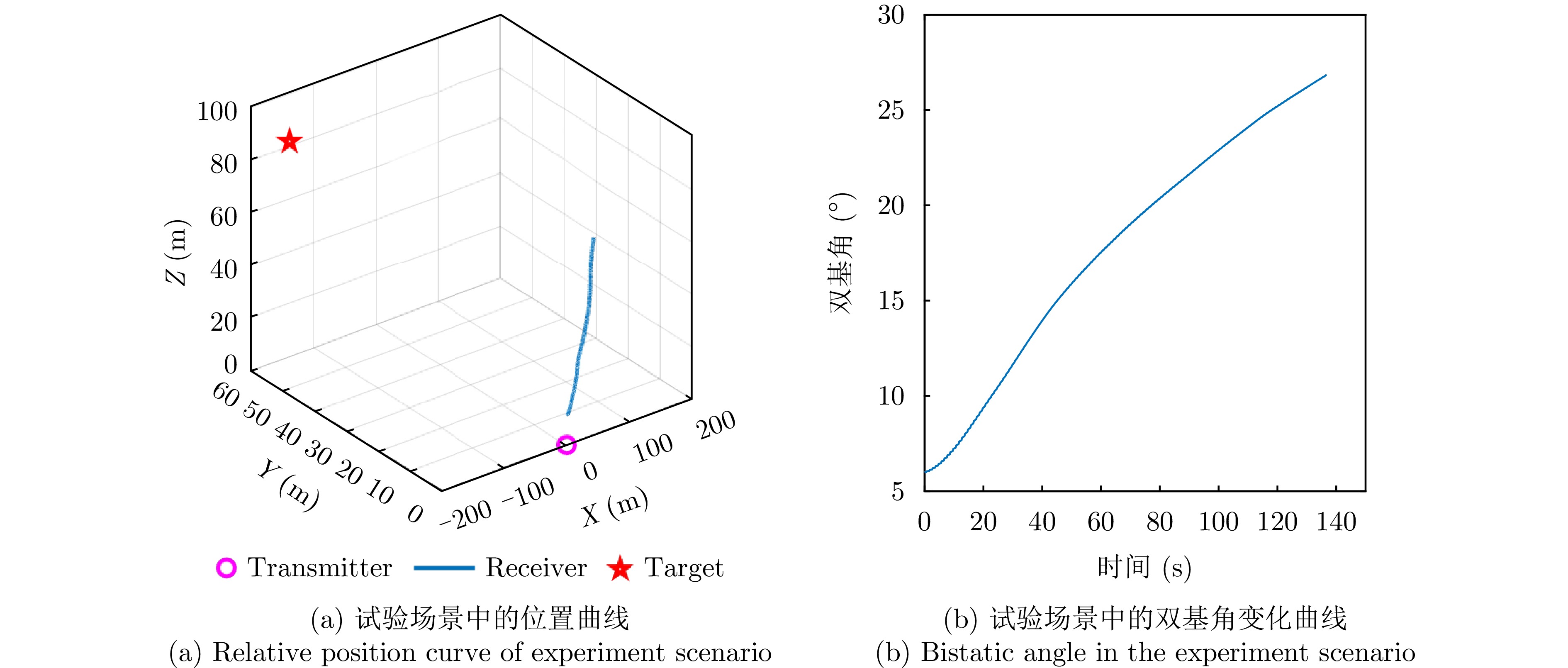
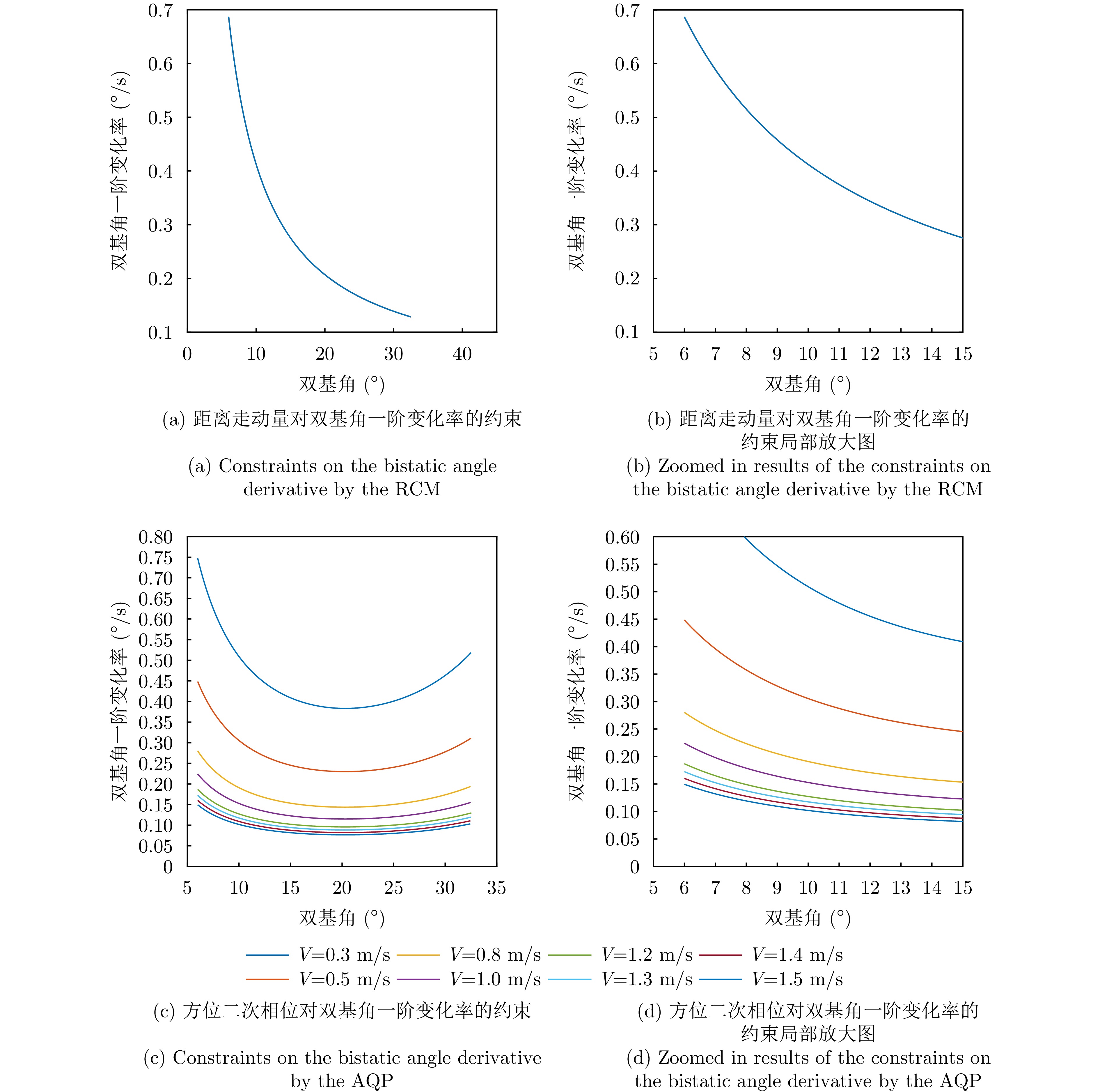
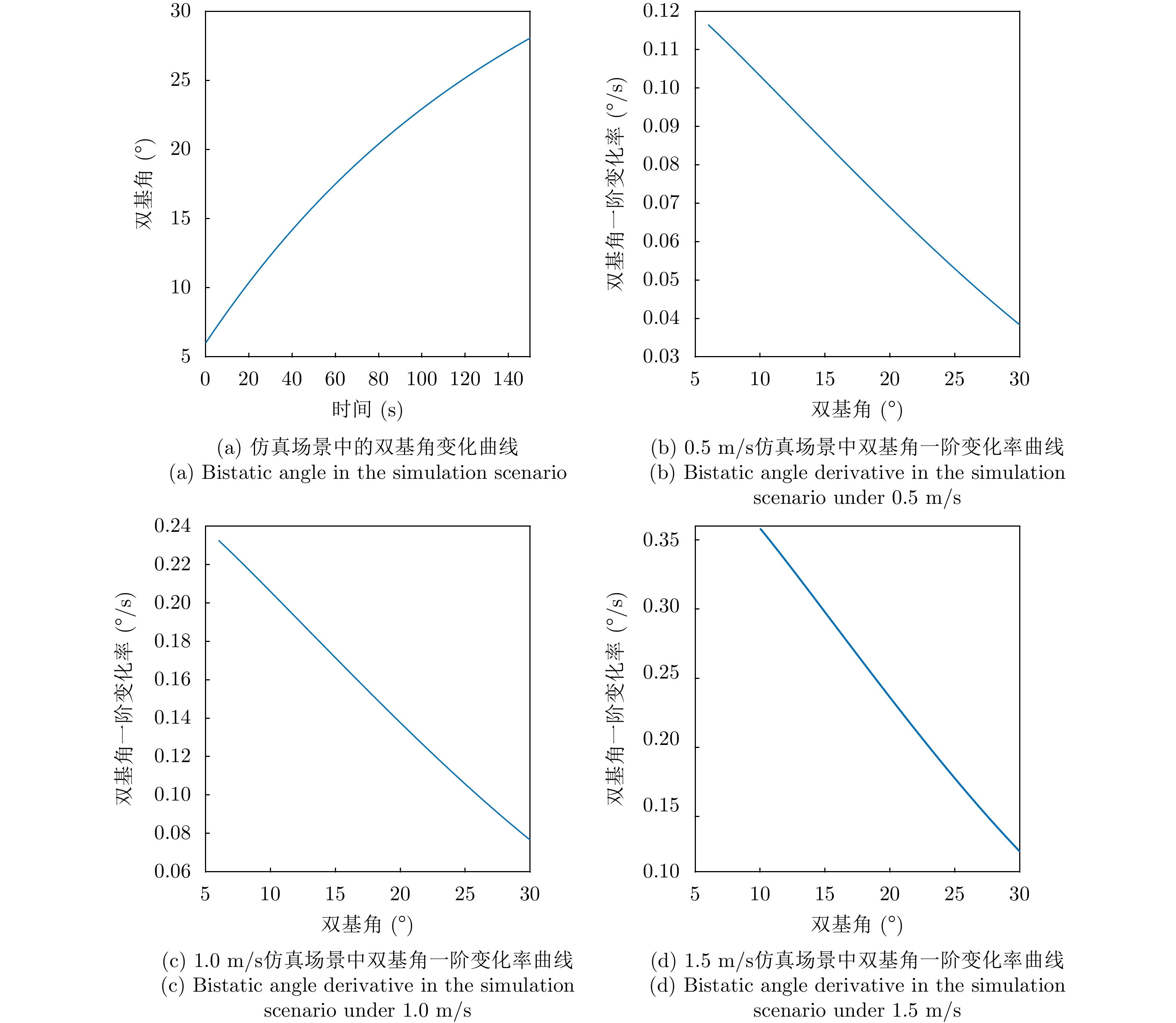
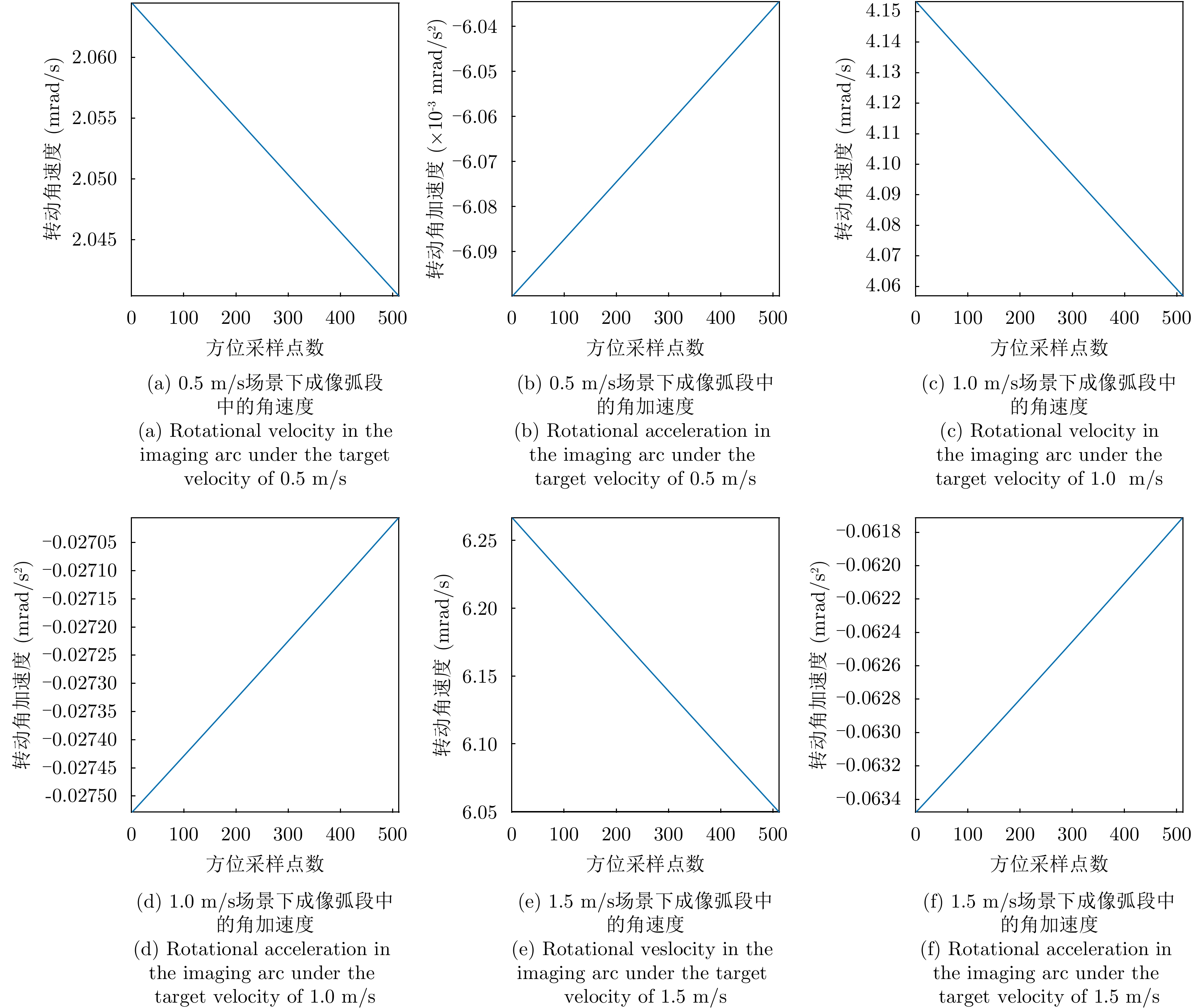
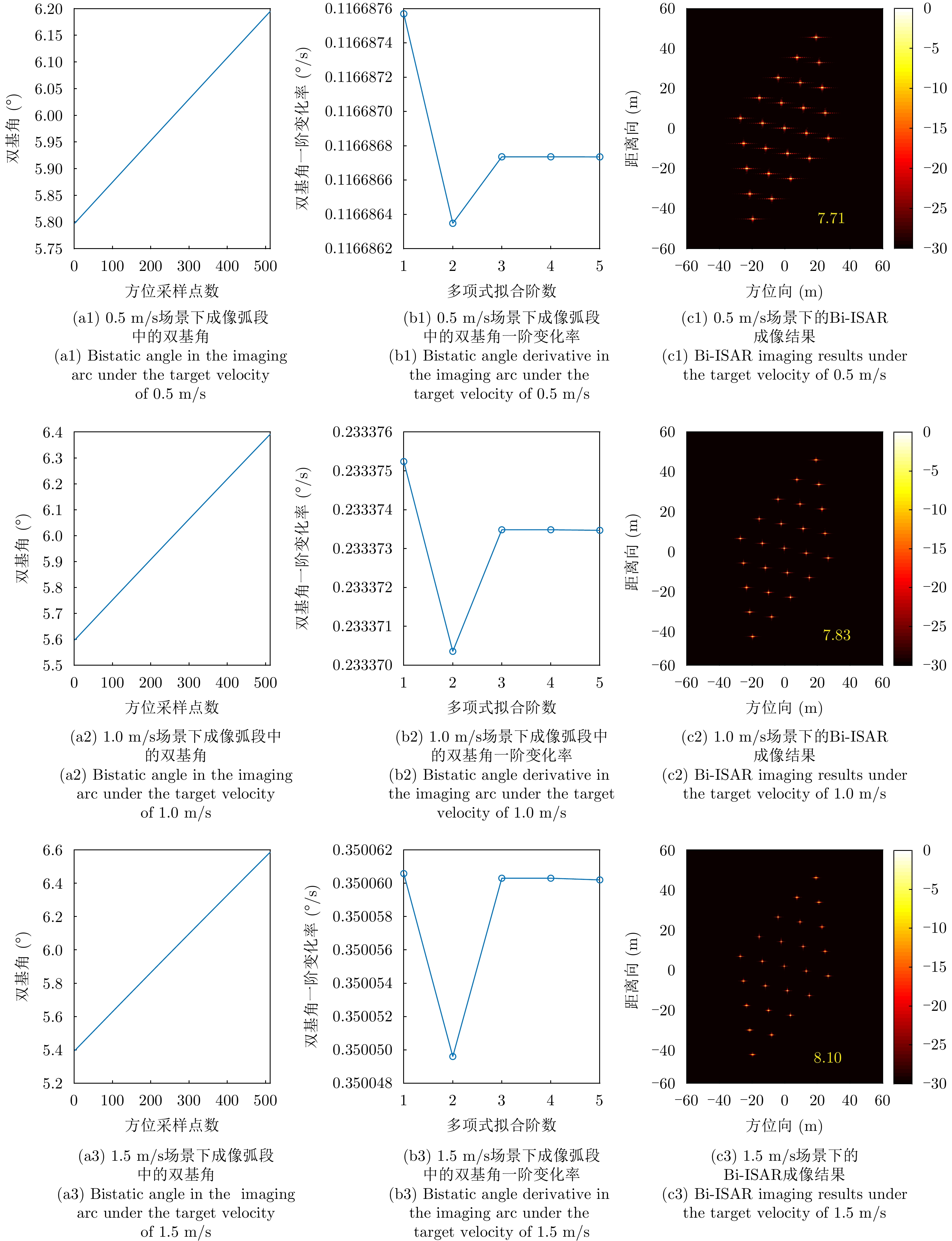
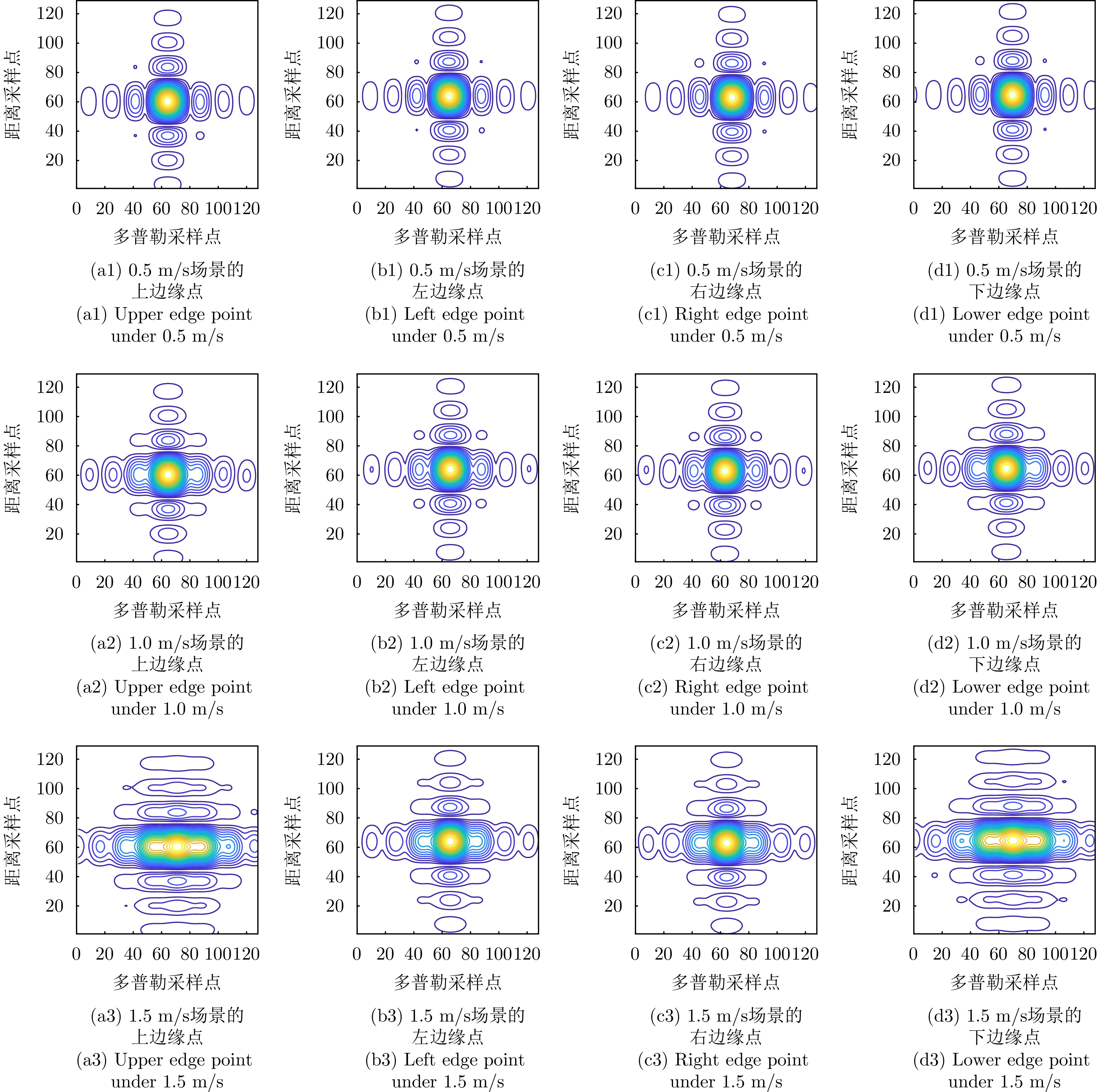
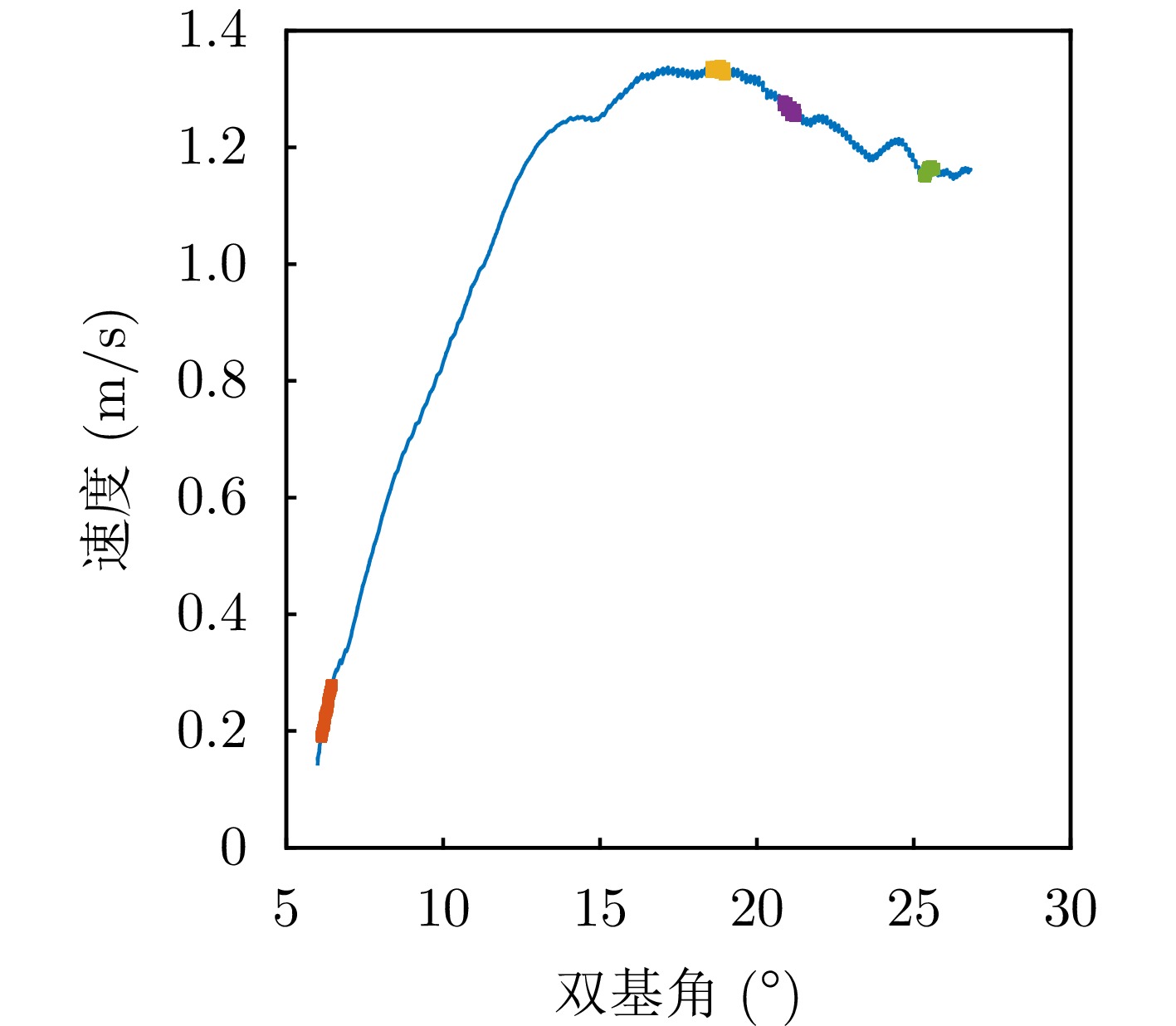
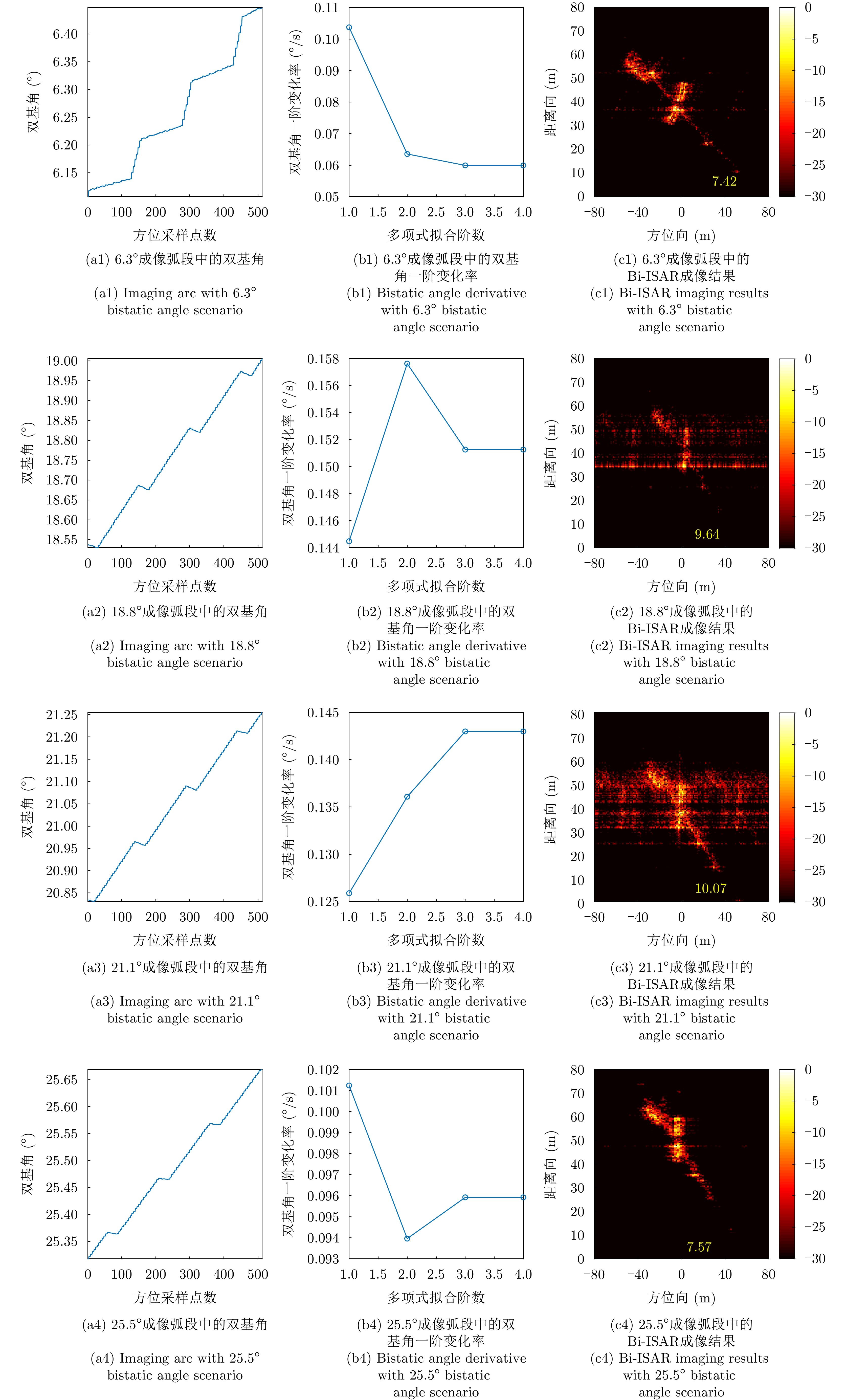
| [1] |
SKOLNIK M I. Radar Handbook[M]. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2008: 23.1–23.36.
|
| [2] |
RICHARDS M A. Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2005: 1–38.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
CUOMO K M, COUTTS S D, MCHARG J C, et al. Wideband aperture coherence processing for next generation radar (NexGen)[R]. MIT Lincoln Laboratory Report NG-3, 2004.
|
| [5] |
鲁耀兵, 高红卫. 分布孔径雷达[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 216–217.
LU Yaobing and GAO Hongwei. Distributed Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 216–217.
|
| [6] |
LIU Quanhua, ZHANG Kaixiang, LIANG Zhennan, et al. Research overview of ground-based distributed coherent aperture radar[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(12): 2443–2459. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.12.001. |
| [7] |
王元昊, 王宏强, 杨琪. 动平台分布孔径雷达相参合成探测方法与试验验证[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(6): 1279–1297. doi: 10.12000/JR24141. WANG Yuanhao, WANG Hongqiang, and YANG Qi. Coherent detection method for moving platform based distributed aperture radar and experimental verification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(6): 1279–1297. doi: 10.12000/JR24141. |
| [8] |
保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 2–11.
BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Technique[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 2–11.
|
| [9] |
杨建宇. 双基合成孔径雷达[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 4–20.
YANG Jianyu. Bistatic Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 4–20.
|
| [10] |
ZENG Tao. Bistatic SAR: State of the art and development trend[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(4): 329–341. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2012.20093. |
| [11] |
邢孟道, 林浩, 陈溅来, 等. 多平台合成孔径雷达成像算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102. XING Mengdao, LIN Hao, CHEN Jianlai, et al. A review of imaging algorithms in multi-platform-borne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102. |
| [12] |
ZENG Tao, WANG Rui, LI Feng, et al. A modified nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for spaceborne/stationary bistatic SAR based on series reversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(5): 3108–3118. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2219057. |
| [13] |
WANG R, WANG Wei, SHAO Yunfeng, et al. First bistatic demonstration of digital beamforming in elevation with TerraSAR-X as an illuminator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(2): 842–849. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2467176. |
| [14] |
SHI Tianyue, MAO Xinhua, JAKOBSSON A, et al. Efficient BiSAR PFA wavefront curvature compensation for arbitrary radar flight trajectories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5221514. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3332759. |
| [15] |
WU Junjie, LI Zhongyu, HUANG Yulin, et al. Focusing bistatic forward-looking SAR with stationary transmitter based on Keystone transform and nonlinear chirp scaling[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(1): 148–152. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2250904. |
| [16] |
PU Wei, WU Junjie, HUANG Yulin, et al. Fast factorized backprojection imaging algorithm integrated with motion trajectory estimation for bistatic forward-looking SAR[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(10): 3949–3965. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2945118. |
| [17] |
LI Yachao, ZHANG Tinghao, MEI Haiwen, et al. Focusing translational-variant bistatic forward-looking SAR data using the modified omega-K algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5203916. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3063780. |
| [18] |
武俊杰, 孙稚超, 吕争, 等. 星源照射双/多基地SAR成像[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(1): 13–35. doi: 10.12000/JR22213. WU Junjie, SUN Zhichao, LV Zheng, et al. Bi/multi-static synthetic aperture radar using spaceborne illuminator[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(1): 13–35. doi: 10.12000/JR22213. |
| [19] |
LI Wenchao, WANG Lei, LIU Dan, et al. Raw data simulation under undulating terrain for bistatic SAR with arbitrary configuration[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 12878–12892. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3427704. |
| [20] |
SUN Zhichao, SUN Huarui, AN Hongyang, et al. Trajectory optimization for maneuvering platform bistatic SAR with geosynchronous illuminator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5203715. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3358303. |
| [21] |
RODRIGUES-SILVA E, RODRIGUEZ-CASSOLA M, KRIEGER G, et al. GNSS-based phase synchronization for bistatic and multistatic synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5213614. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3406797. |
| [22] |
TANG Tao, WANG Pengbo, ZENG Hongcheng, et al. An efficient coarse-to-fine doppler parameter search method for moving target detection using GNSS-based passive bistatic radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3509105. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3450209. |
| [23] |
FAN Lei, WANG Hongqiang, YANG Qi, et al. High-quality airborne terahertz video SAR imaging based on echo-driven robust motion compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 2001817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3357697. |
| [24] |
ZHANG Tinghao, LI Yachao, YUAN Mingze, et al. Focusing highly squinted FMCW-SAR data using the modified wavenumber-domain algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 1999–2011. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3266886. |
| [25] |
FAN Lei, WANG Hongqiang, YANG Qi, et al. THz-ViSAR-oriented fast indication and imaging of rotating targets based on nonparametric method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5217515. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3427653. |
| [26] |
ZHANG Lei, DUAN Jia, QIAO Zhijun, et al. Phase adjustment and ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets with sparse apertures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(3): 1955–1973. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.130115. |
| [27] |
田彪, 刘洋, 呼鹏江, 等. 宽带逆合成孔径雷达高分辨成像技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 765–802. doi: 10.12000/JR20060. TIAN Biao, LIU Yang, HU Pengjiang, et al. Review of high-resolution imaging techniques of wideband inverse synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 765–802. doi: 10.12000/JR20060. |
| [28] |
FU Jixiang, XING Mengdao, and AMIN M G. ISAR imaging motion compensation in low SNR environments using phase gradient and filtering techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(6): 4296–4312. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3098129. |
| [29] |
MAI Yanbo, ZHANG Shuanghui, JIANG Weidong, et al. ISAR imaging of targets exhibiting micro-motion under the joint constraints of low SNR and sparse rate[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(5): 6233–6249. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3273203. |
| [30] |
CHEN V C, DES ROSIERS A, and LIPPS R. Bi-static ISAR range-Doppler imaging and resolution analysis[C]. 2009 IEEE Radar Conference, Pasadena, USA, 2009: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2009.4977060. |
| [31] |
MARTORELLA M. Analysis of the robustness of bistatic inverse synthetic aperture radar in the presence of phase synchronisation errors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(4): 2673–2689. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2011.6034658. |
| [32] |
MARTORELLA M, CATALDO D, and BRISKEN S. Bistatically equivalent monostatic approximation for bistatic ISAR[C]. 2013 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarCon13), Ottawa, Canada, 2013: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2013.6586074. |
| [33] |
KANG B S, BAE J H, KANG M S, et al. Bistatic-ISAR cross-range scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(4): 1962–1973. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2677798. |
| [34] |
DING Jiabao, LI Yachao, WANG Jiadong, et al. Joint motion compensation and distortion correction for maneuvering target bistatic ISAR imaging based on parametric minimum entropy optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5118919. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3213579. |
| [35] |
SHI Hongyin, YANG Zixin, YANG Ting, et al. Bistatic ISAR imaging for maneuvering target with complex motion based on phase retrieval-assisted ICBA[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2025, 25(10): 17434–17446. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2025.3549833. |
| [36] |
DING Jiabao, LI Yachao, WANG Jiadong, et al. Integration of high-order motion compensation and 2-D scaling for maneuvering target bistatic ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 60: 5205120. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2025.3533881. |
| [37] |
ZHU Hanshen, HU Wenhua, GUO Baofeng, et al. Bistatic ISAR sparse aperture maneuvering target MTRC compensation imaging algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(7): 2022–2030. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.07.12. |
| [38] |
ZHANG Shuanghui, LIU Yongxiang, and LI Xiang. Bayesian bistatic ISAR imaging for targets with complex motion under low SNR condition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(5): 2447–2460. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2803300. |
| [39] |
符吉祥, 张超, 邢文洁, 等. 基于修正牛顿法的双基ISAR空变补偿快速成像与几何校正图像定标方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(5): 1253–1275. doi: 10.12000/JR25052. FU Jixiang, ZHANG Chao, XING Wenjie, et al. Fast space-variant phase error compensation and geometric correction for bistatic ISAR imaging using a modified newton’s method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(5): 1253–1275. doi: 10.12000/JR25052. |
| [40] |
LI Zhongyu, ZHANG Xiaodong, YANG Qing, et al. Hybrid SAR-ISAR image formation via joint FrFT-WVD processing for BFSAR ship target high-resolution imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5215713. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3117280. |
| [41] |
QIAN Guangzhao and WANG Yong. Monostatic-equivalent algorithm via Taylor expansion for BiSAR ship target imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5200919. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3233384. |
| [42] |
CHEN Hongmeng, LI Jun, ZHOU Rui, et al. Optimal Bi-ISAR imaging arc selection method with bistatic angle derivative constraint[C]. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Zhuhai, China, 2024: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICSIDP62679.2024.10869106. |
| [43] |
CHEN V C and QIAN Shi’e. Joint time-frequency transform for radar range-Doppler imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1998, 34(2): 486–499. doi: 10.1109/7.670330. |
| [44] |
WANG Ling, ZHU Zhaoda, and ZHU Daiyin. Interval selections for side-view or top-view imaging of ship targets with airborne ISAR[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2008, 30(12): 2835–2839. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2007.00919. |
| [45] |
LI Ning, SHEN Qingyuan, WANG Ling, et al. Optimal time selection for ISAR imaging of ship targets based on time-frequency analysis of multiple scatterers[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4017505. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3103915. |
| [46] |
CAO Rui, WANG Yong, ZHANG Yun, et al. Optimal time selection for ISAR imaging of ship target via novel approach of centerline extraction with RANSAC algorithm[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 9987–10005. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3220496. |
| [47] |
SHAO Shuai, ZHANG Lei, and LIU Hongwei. An optimal imaging time interval selection technique for marine targets ISAR imaging based on sea dynamic prior information[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(13): 4940–4953. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2903399. |
| [48] |
王雅慧, 杨青, 李中余, 等. 双基SAR舰船目标成像时段寻优成像处理方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2025, 14(5): 1230–1252. doi: 10.12000/JR24193. WANG Yahui, YANG Qing, LI Zhongyu, et al. Imaging time optimization method for ship targets of bistatic SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2025, 14(5): 1230–1252. doi: 10.12000/JR24193. |
| [49] |
JIANG Yicheng, WEI Jin, and LIU Zitao. Bistatic ISAR imaging and scaling algorithm based on the estimation of bistatic factor and effective rotation velocity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(6): 8522–8538. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3432109. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

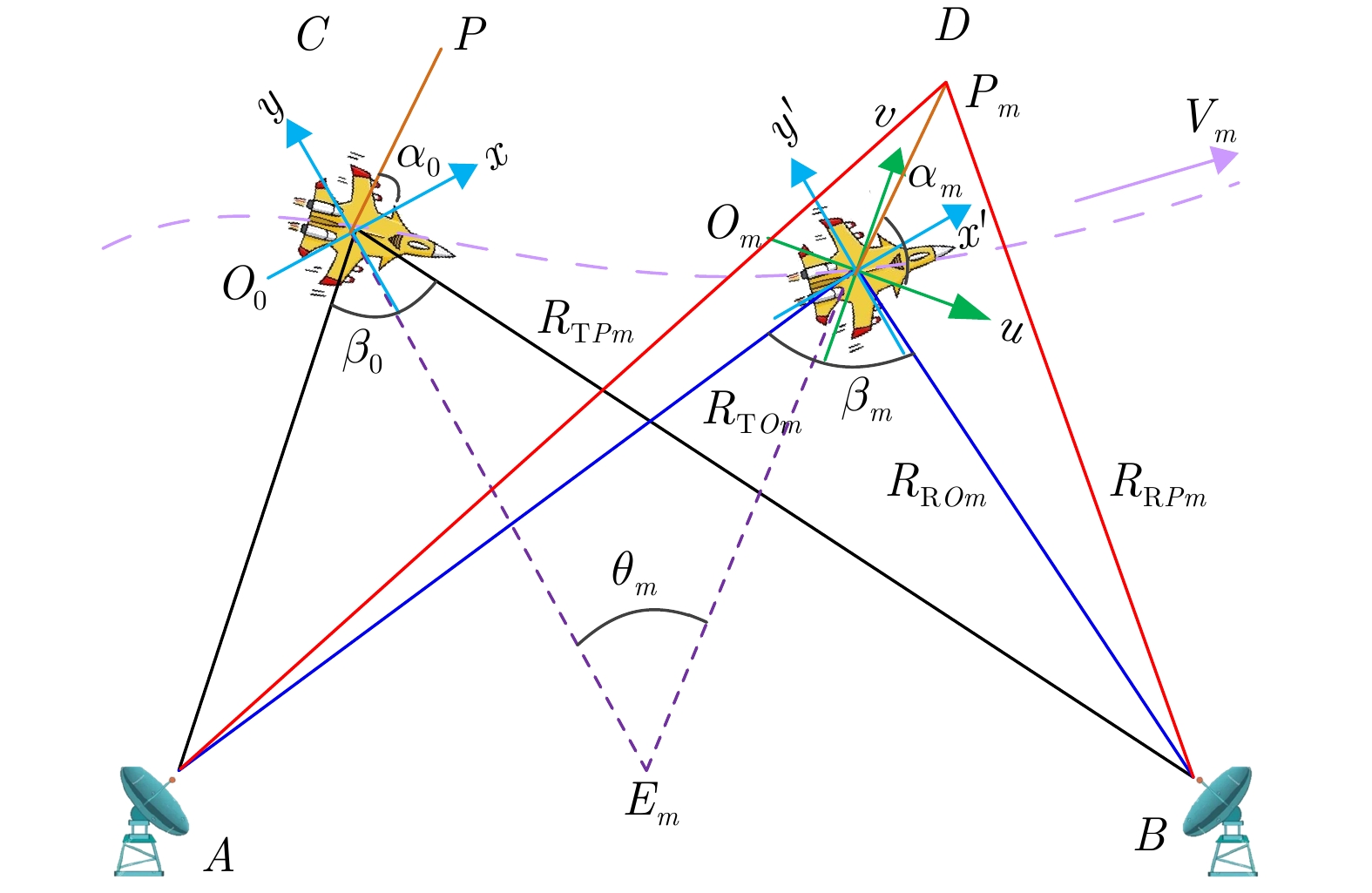



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: