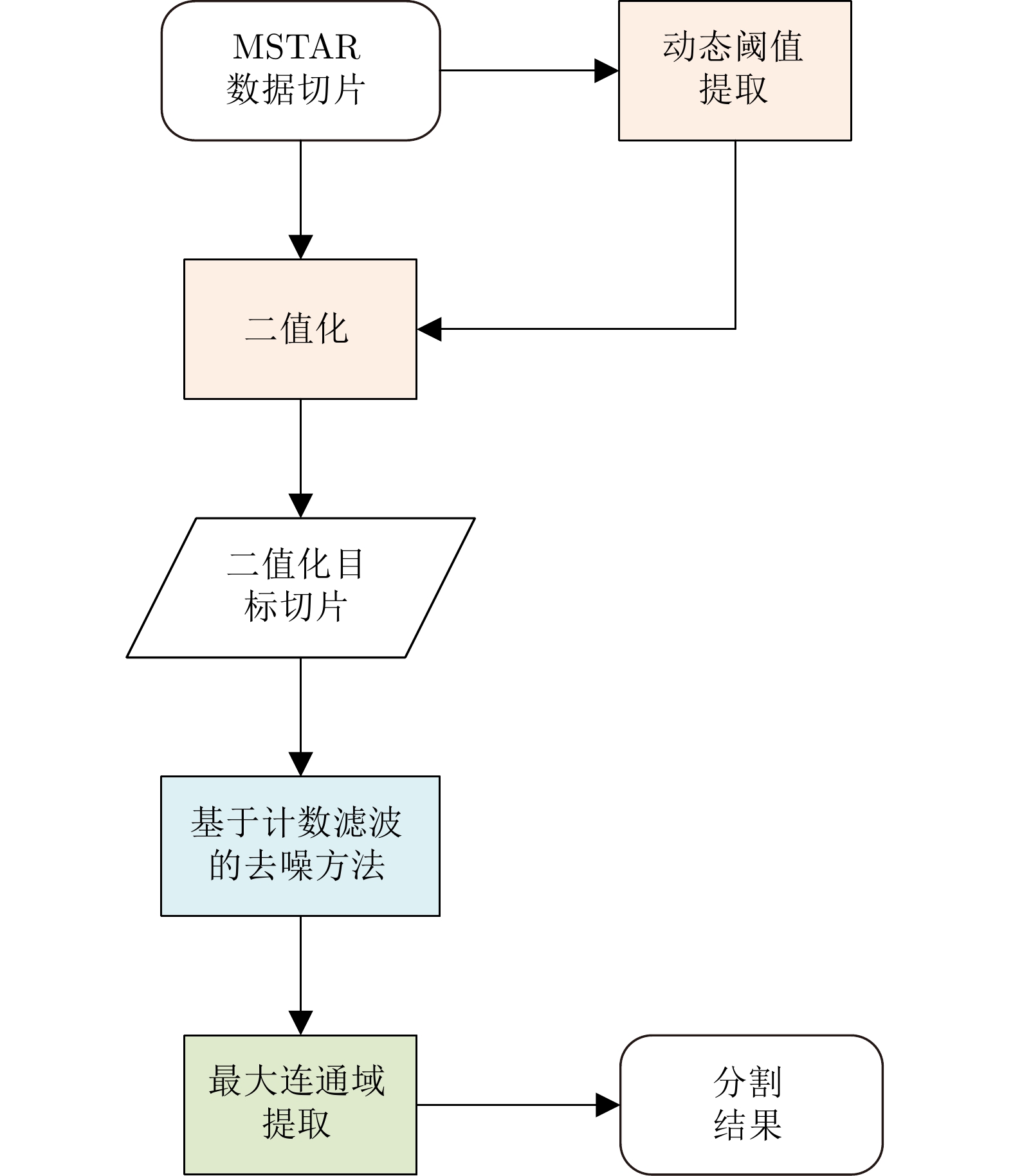
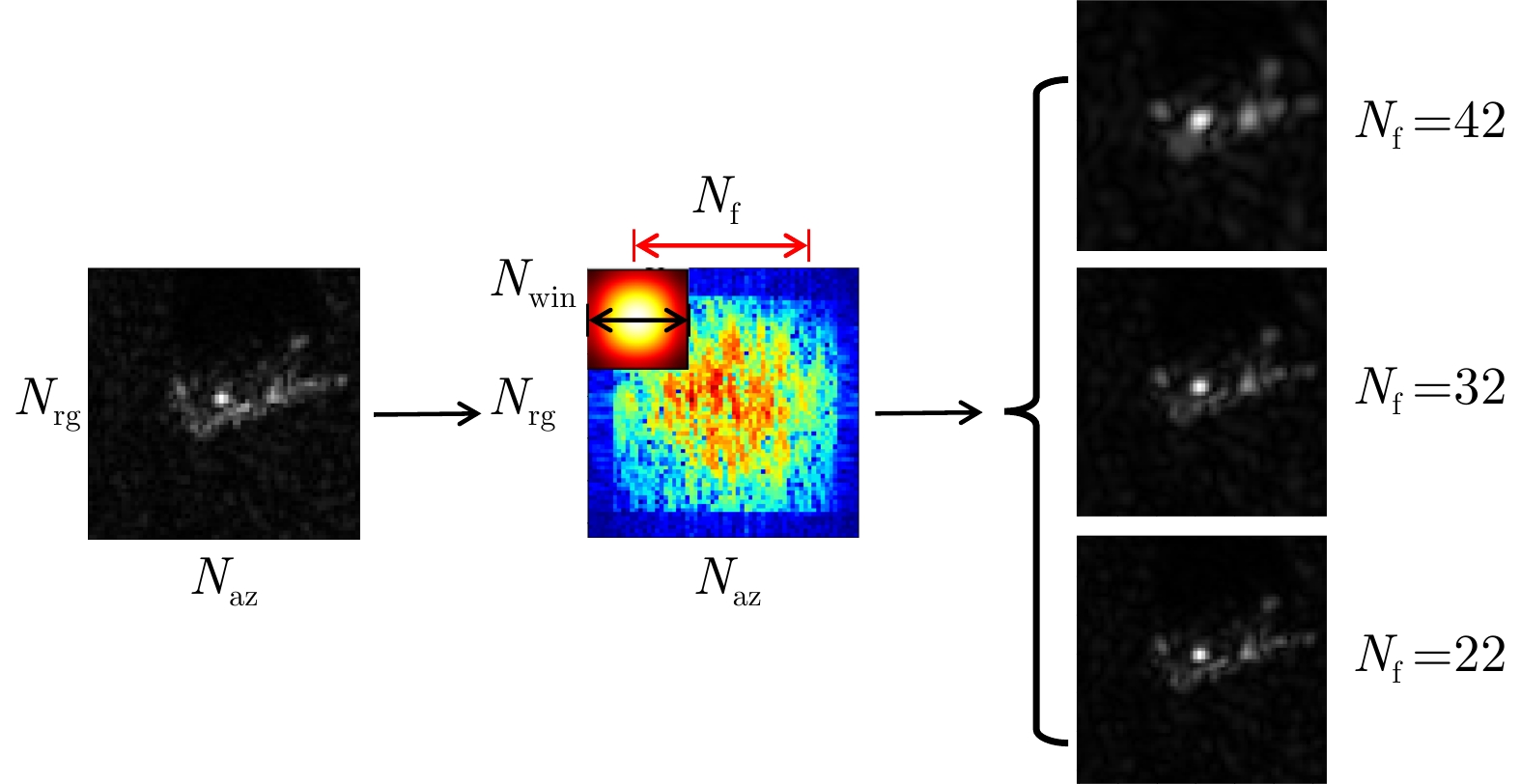
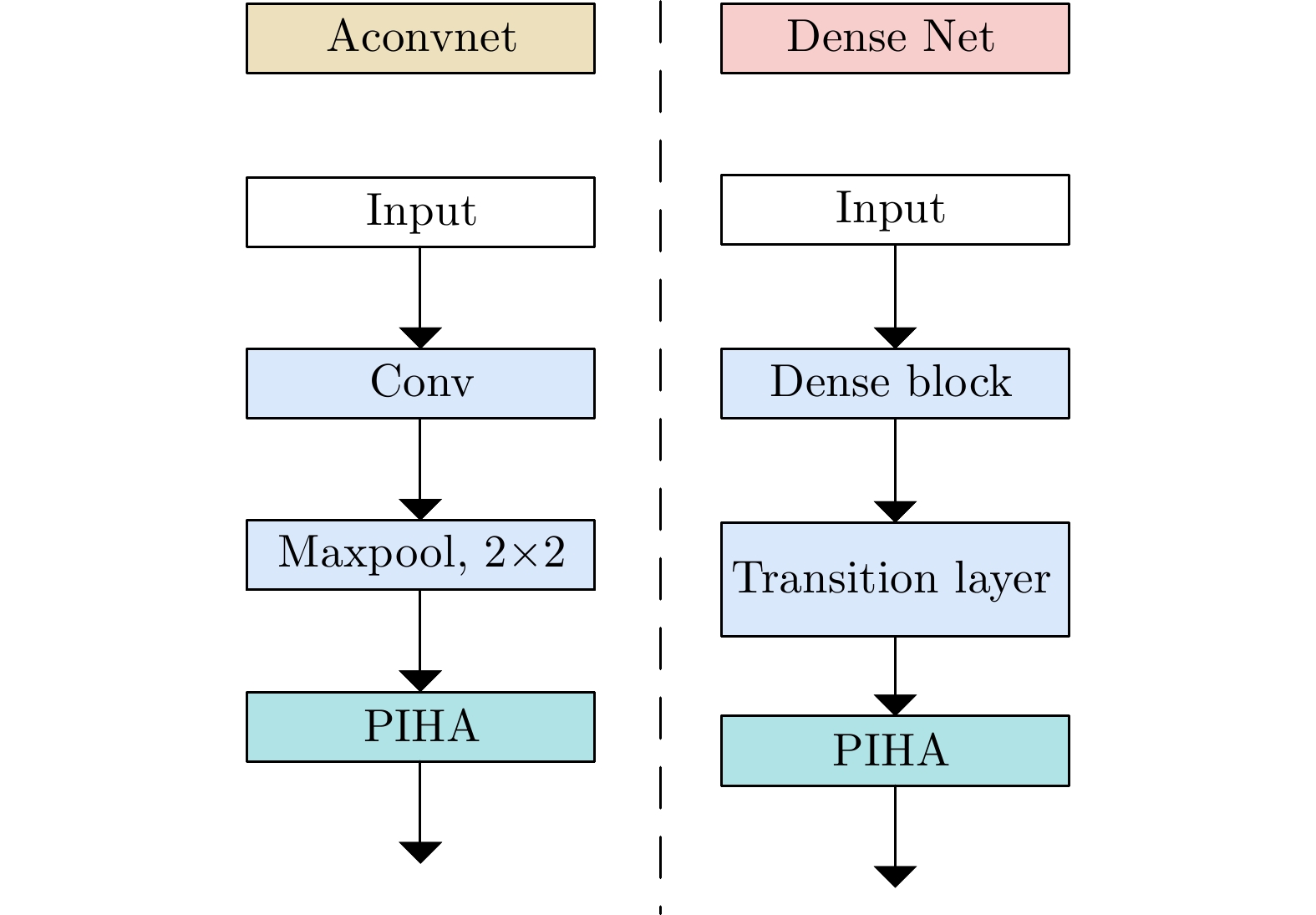
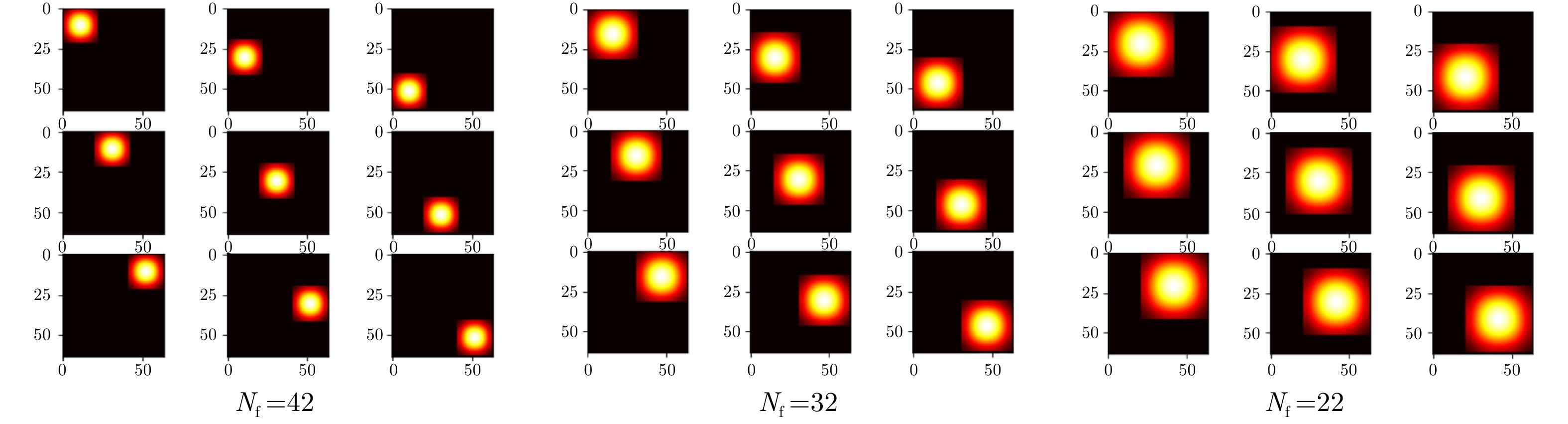
| [1] |
CHEN Keyang, PAN Zongxu, HUANG Zhongling, et al. Learning from reliable unlabeled samples for semi-supervised SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4512205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3197892. |
| [2] |
CHOI J H, LEE M J, JEONG N H, et al. Fusion of target and shadow regions for improved SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5226217. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3165849. |
| [3] |
ZENG Zhiqiang, SUN Jinping, HAN Zhu, et al. SAR automatic target recognition method based on multi-stream complex-valued networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5228618. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3177323. |
| [4] |
金亚秋. 多模式遥感智能信息与目标识别: 微波视觉的物理智能[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083. JIN Yaqiu. Multimode remote sensing intelligent information and target recognition: Physical intelligence of microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 710–716. doi: 10.12000/JR19083. |
| [5] |
DATCU M, HUANG Zhongling, ANGHEL A, et al. Explainable, physics-aware, trustworthy artificial intelligence: A paradigm shift for synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2023, 11(1): 8–25. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2023.3237465. |
| [6] |
黄钟泠, 姚西文, 韩军伟. 面向SAR图像解译的物理可解释深度学习技术进展与探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 107–125. doi: 10.12000/JR21165. HUANG Zhongling, YAO Xiwen, and HAN Junwei. Progress and perspective on physically explainable deep learning for synthetic aperture radar image interpretation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 107–125. doi: 10.12000/JR21165. |
| [7] |
文贡坚, 马聪慧, 丁柏圆, 等. 基于部件级三维参数化电磁模型的SAR目标物理可解释识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 608–621. doi: 10.12000/JR20099. WEN Gongjian, MA Conghui, DING Baiyuan, et al. SAR target physics interpretable recognition method based on three dimensional parametric electromagnetic part model[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 608–621. doi: 10.12000/JR20099. |
| [8] |
郭炜炜, 张增辉, 郁文贤, 等. SAR图像目标识别的可解释性问题探讨[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059. GUO Weiwei, ZHANG Zenghui, YU Wenxian, et al. Perspective on explainable SAR target recognition[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 462–476. doi: 10.12000/JR20059. |
| [9] |
KARPATNE A, ATLURI G, FAGHMOUS J H, et al. Theory-guided data science: A new paradigm for scientific discovery from data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2017, 29(10): 2318–2331. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2017.2720168. |
| [10] |
VON RUEDEN L, MAYER S, BECKH K, et al. Informed machine learning – A taxonomy and survey of integrating prior knowledge into learning systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2023, 35(1): 614–633. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2021.3079836. |
| [11] |
CHEN Sizhe, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(8): 4806–4817. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2551720. |
| [12] |
LI Yi, DU Lan, and WEI Di. Multiscale CNN based on component analysis for SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5211212. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3100137. |
| [13] |
INKAWHICH N, DAVIS E, MAJUMDER U, et al. Advanced techniques for robust SAR ATR: Mitigating noise and phase errors[C]. 2020 IEEE International Radar Conference, Washington, USA, 2020: 844–849. doi: 10.1109/RADAR42522.2020.9114784. |
| [14] |
PENG Bowen, PENG Bo, ZHOU Jie, et al. Scattering model guided adversarial examples for SAR target recognition: Attack and defense[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5236217. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3213305. |
| [15] |
FENG Sijia, JI Kefeng, WANG Fulai, et al. Electromagnetic scattering feature (ESF) module embedded network based on ASC model for robust and interpretable SAR ATR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5235415. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3208333. |
| [16] |
LIU Zhunga, WANG Longfei, WEN Zaidao, et al. Multilevel scattering center and deep feature fusion learning framework for SAR target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5227914. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3174703. |
| [17] |
邢孟道, 谢意远, 高悦欣, 等. 电磁散射特征提取与成像识别算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 921–942. doi: 10.12000/JR22232. XING Mengdao, XIE Yiyuan, GAO Yuexin, et al. Electromagnetic scattering characteristic extraction and imaging recognition algorithm: A review[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 921–942. doi: 10.12000/JR22232. |
| [18] |
BAI Xueru, ZHOU Xuening, ZHANG Feng, et al. Robust Pol-ISAR target recognition based on ST-MC-DCNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 9912–9927. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2930112. |
| [19] |
XUE Ruihang, BAI Xueru, and ZHOU Feng. SAISAR-Net: A robust sequential adjustment ISAR image classification network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5214715. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3113655. |
| [20] |
高悦欣, 李震宇, 盛佳恋, 等. 一种大转角SAR图像散射中心各向异性提取方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(8): 1956–1961. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151261. GAO Yuexin, LI Zhenyu, SHENG Jialian, et al. Extraction method for anisotropy characteristic of scattering center in wide-angle SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38(8): 1956–1961. doi: 10.11999/ JEIT151261.
|
| [21] |
KHAN S and GUIDA R. Feasibility of time-frequency urban area analysis on TerraSAR-X fully polarimetric dataset[C]. 2011 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event, Munich, Germany, 2011: 265–268. doi: 10.1109/JURSE.2011.5764770. |
| [22] |
ZHANG Lu, HUANG Yue, FERRO-FAMIL L, et al. Effect of polarimetric information on time-frequency analysis using spaceborne SAR image[C]. 13th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, 2021.
|
| [23] |
FERRO-FAMIL L and POTTIER E. Urban area remote sensing from L-band PolSAR data using time-frequency techniques[C]. 2007 Urban Remote Sensing Joint Event, Paris, France, 2007: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/URS.2007.371769. |
| [24] |
DUQUENOY M, OVARLEZ J P, FERRO-FAMIL L, et al. Study of dispersive and anisotropic scatterers behavior in radar imaging using time-frequency analysis and polarimetric coherent decomposition[C]. 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006: 180–185. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2006.1631794. |
| [25] |
FERRO-FAMIL L, REIGBER A, POTTIER E, et al. Scene characterization using subaperture polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(10): 2264–2276. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.817188. |
| [26] |
FERRO-FAMIL L, REIGBER A, and POTTIER E. Nonstationary natural media analysis from polarimetric SAR data using a two-dimensional time-frequency decomposition approach[J]. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing, 2005, 31(1): 21–29. doi: 10.5589/m04-062. |
| [27] |
HUANG Zhongling, DATCU M, PAN Zongxu, et al. HDEC-TFA: An unsupervised learning approach for discovering physical scattering properties of single-polarized SAR image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(4): 3054–3071. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3014335. |
| [28] |
SPIGAI M, TISON C, and SOUYRIS J C. Time-frequency analysis in high-resolution SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(7): 2699–2711. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2107914. |
| [29] |
HUANG Zhongling, WU Chong, YAO Xiwen, et al. Physics inspired hybrid attention for SAR target recognition[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2024, 207: 164–174. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2023.12.004. |
| [30] |
HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745. |
| [31] |
HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2261–2269. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.243. |
| [32] |
ZHANG Jinsong, XING Mengdao, and XIE Yiyuan. FEC: A feature fusion framework for SAR target recognition based on electromagnetic scattering features and deep CNN features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(3): 2174–2187. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3003264. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: