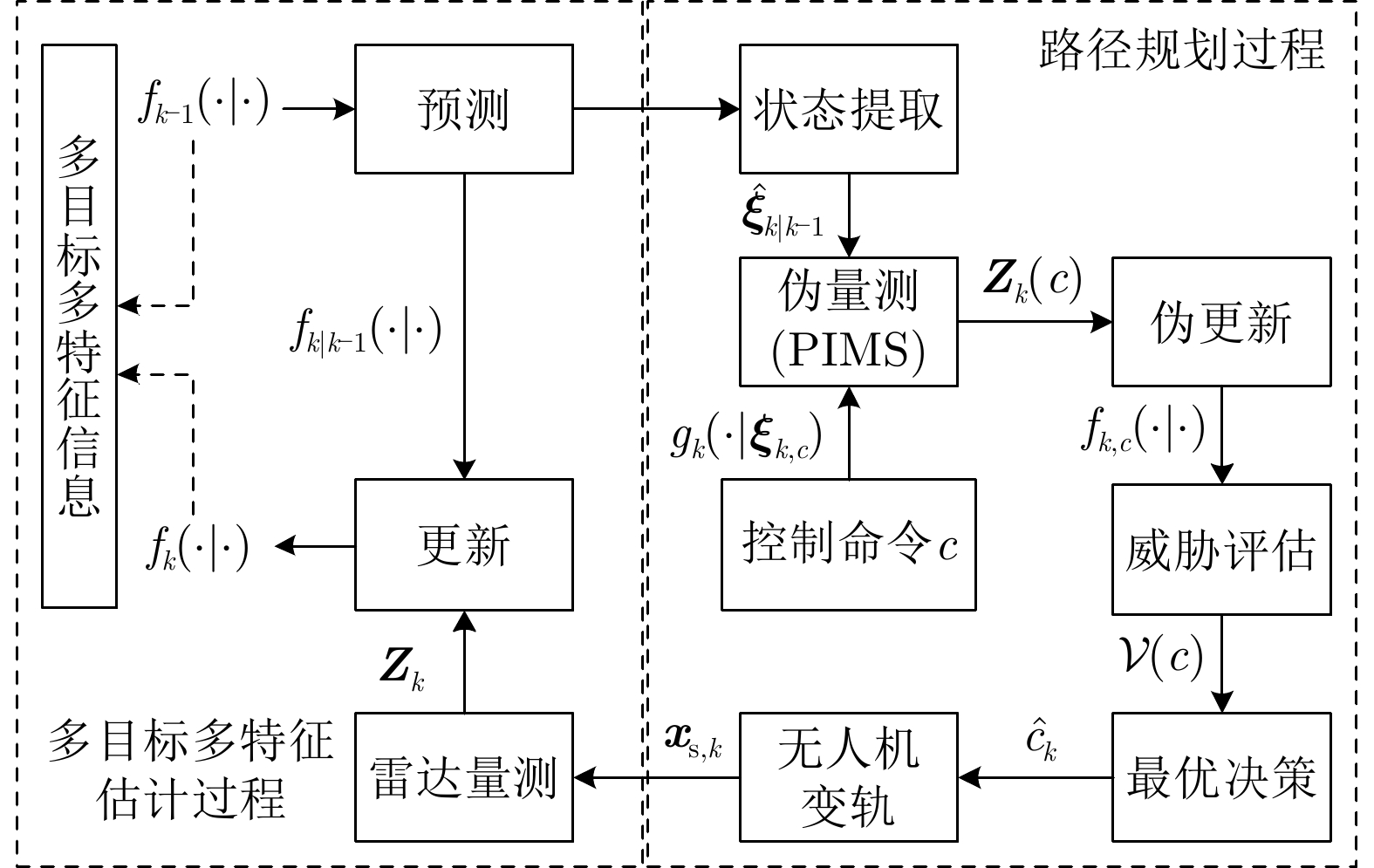
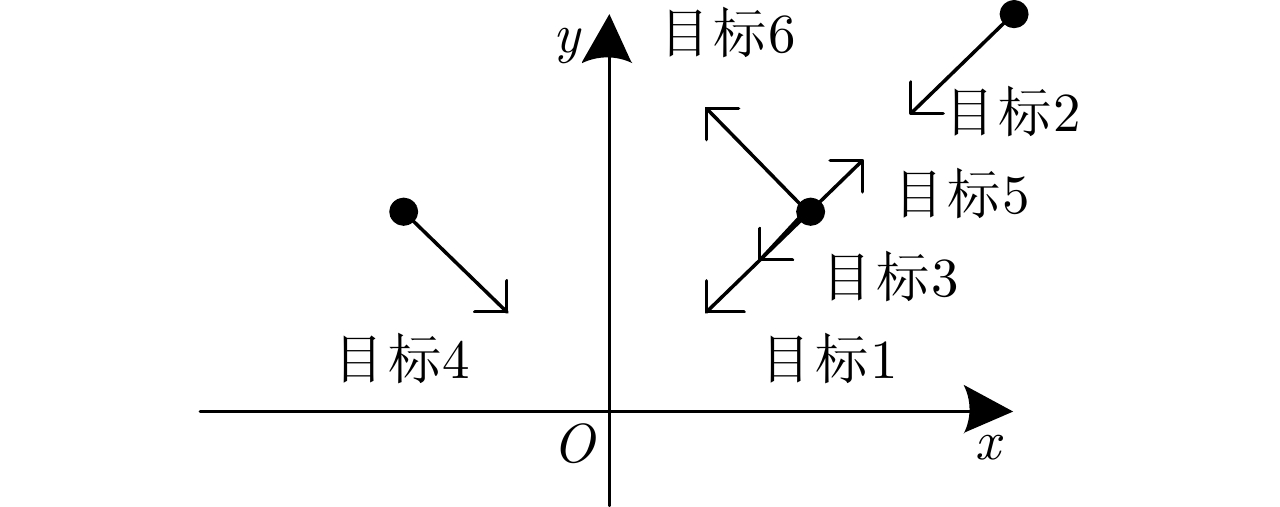
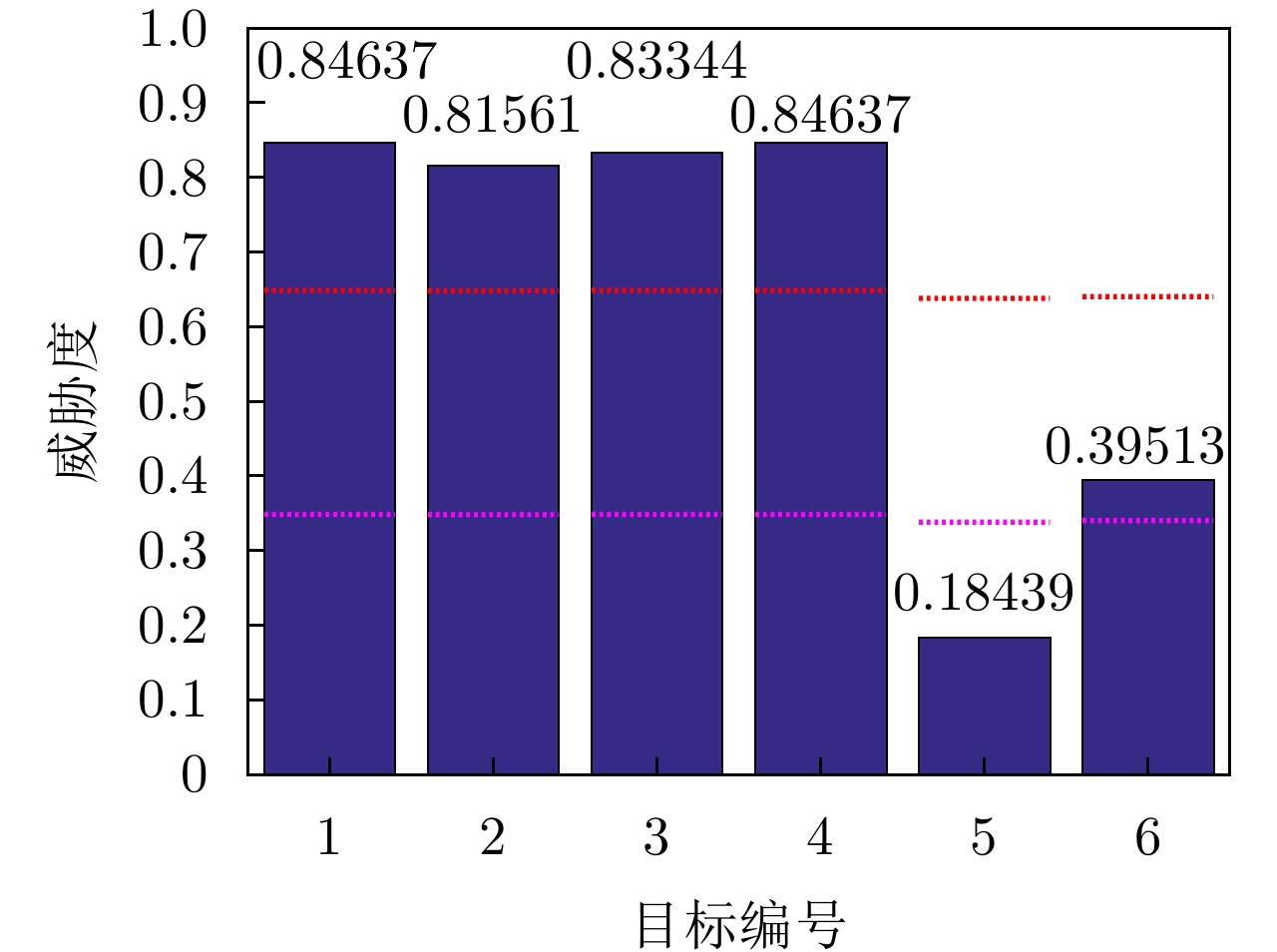
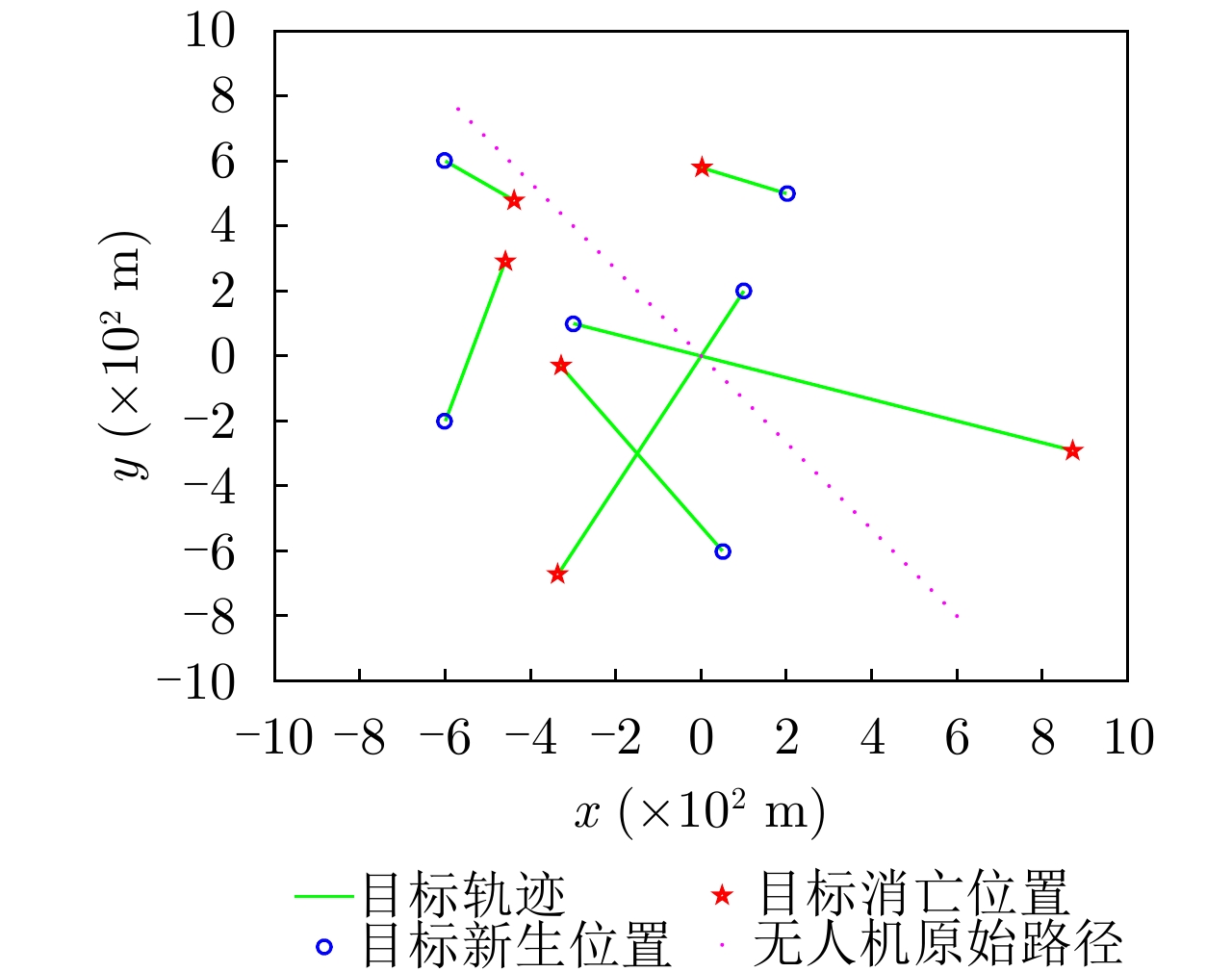
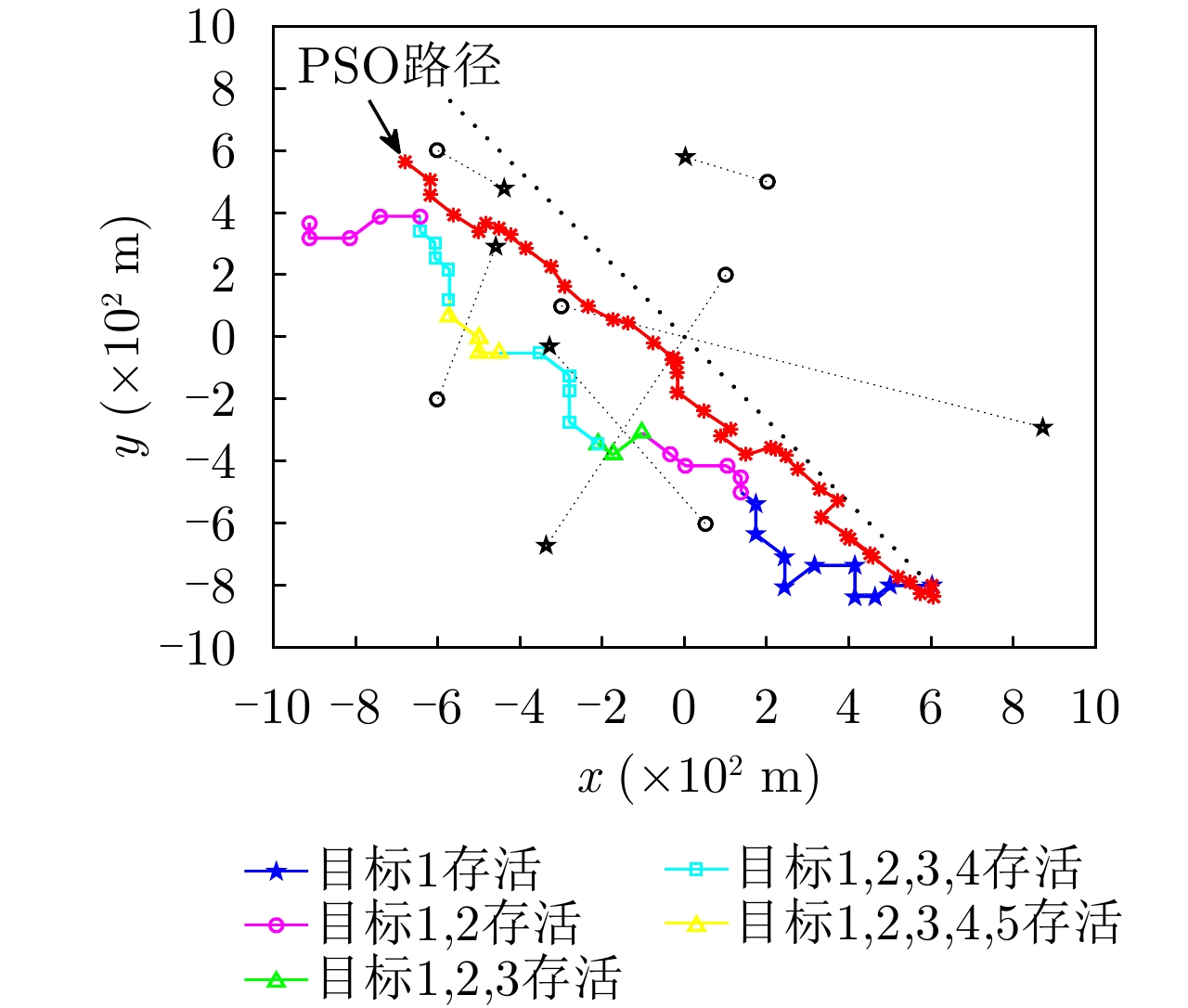
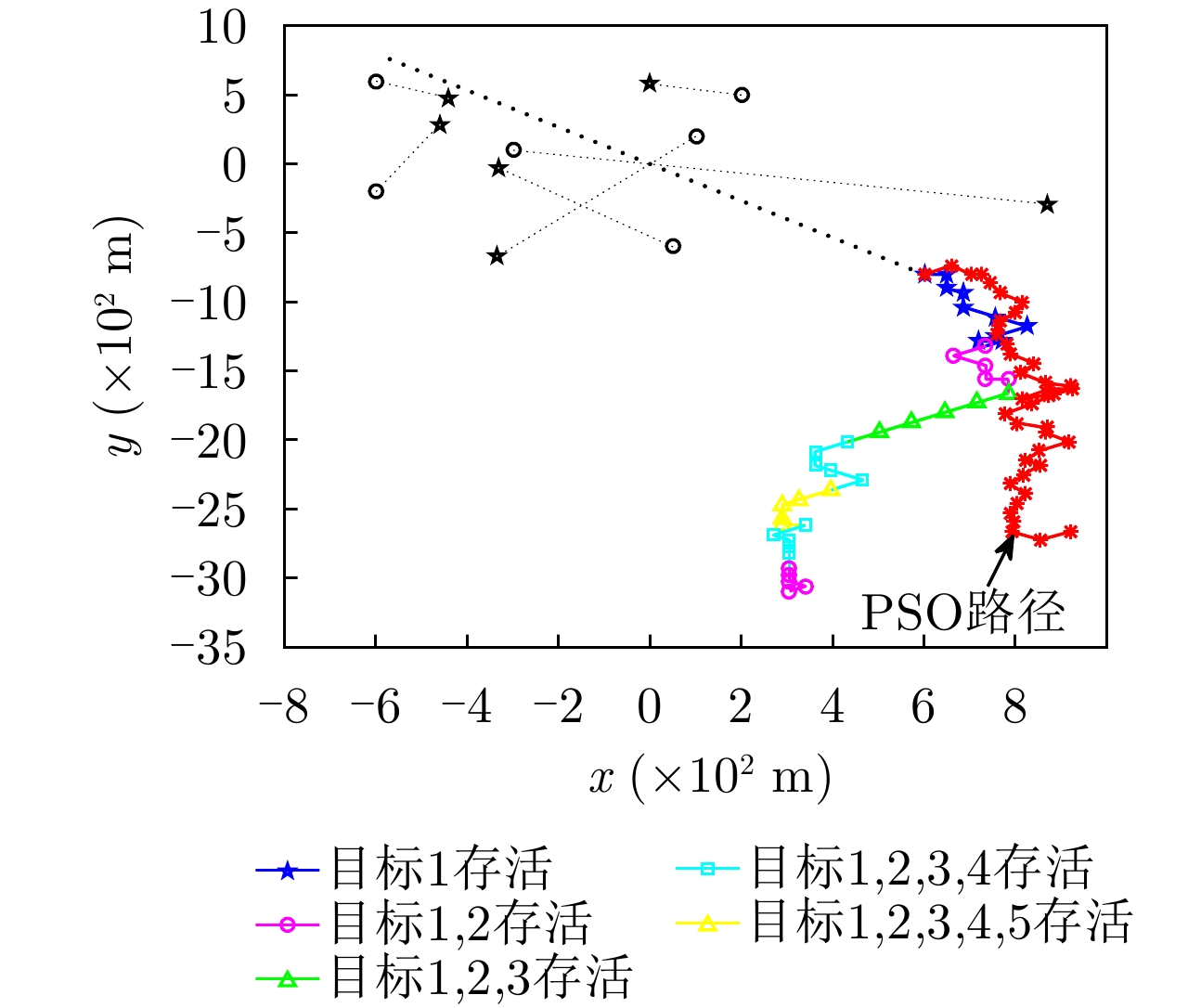
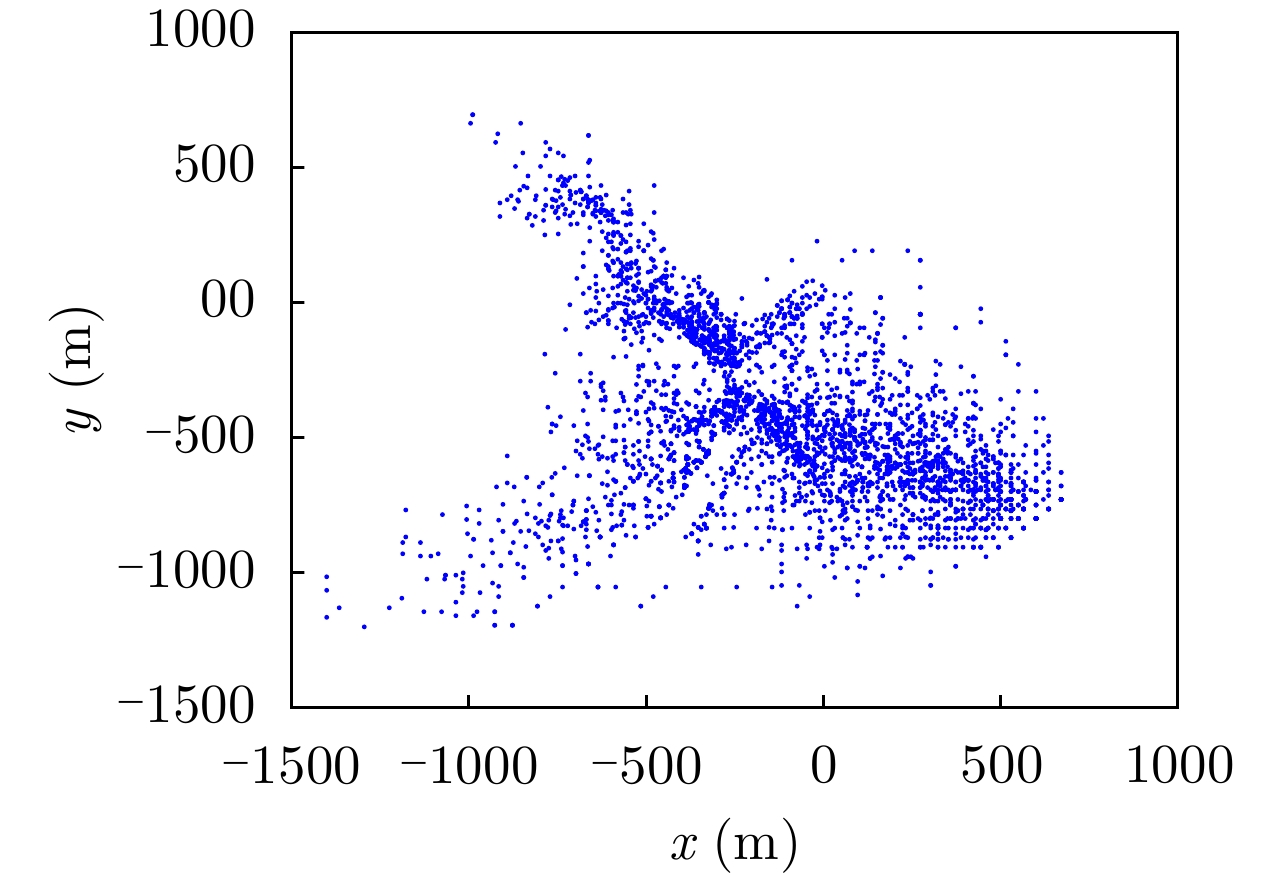
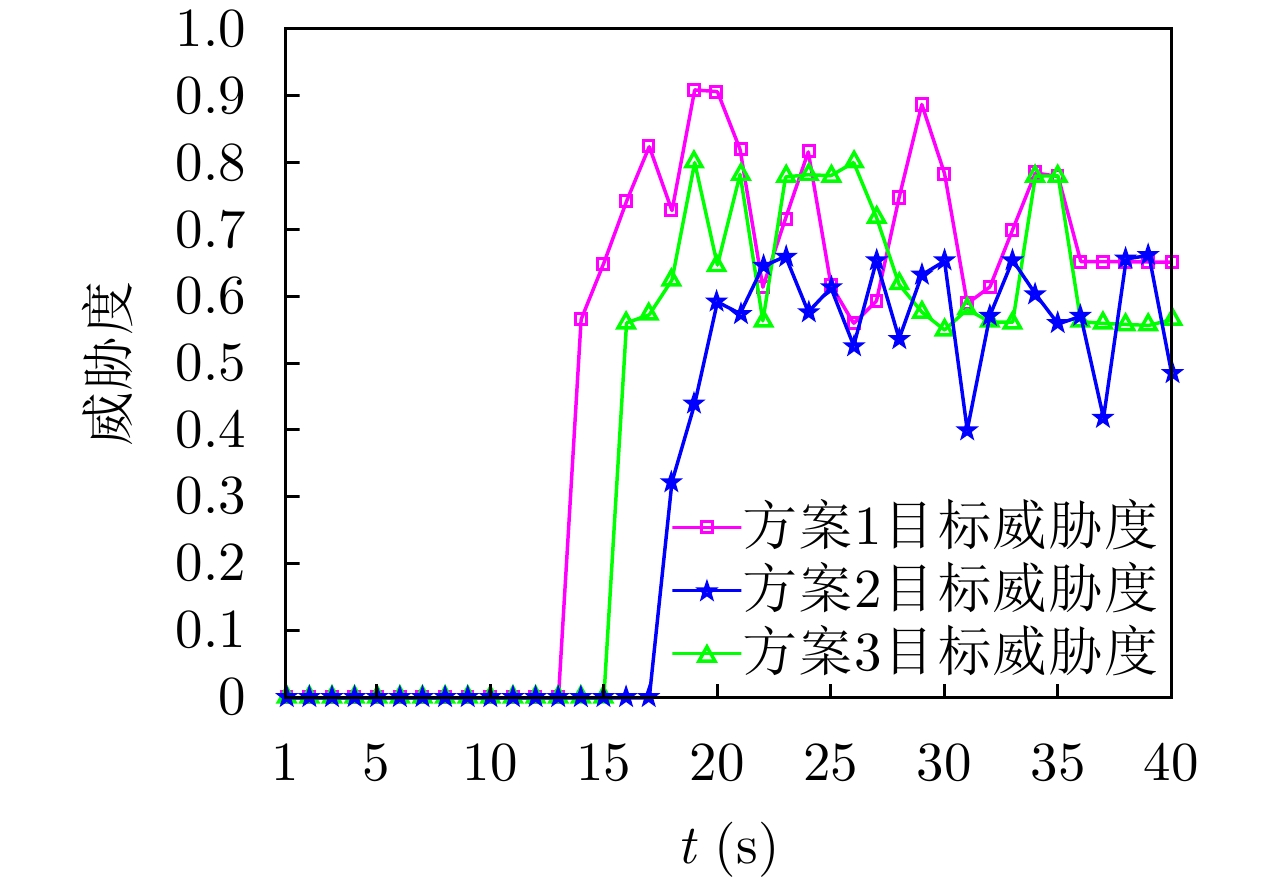
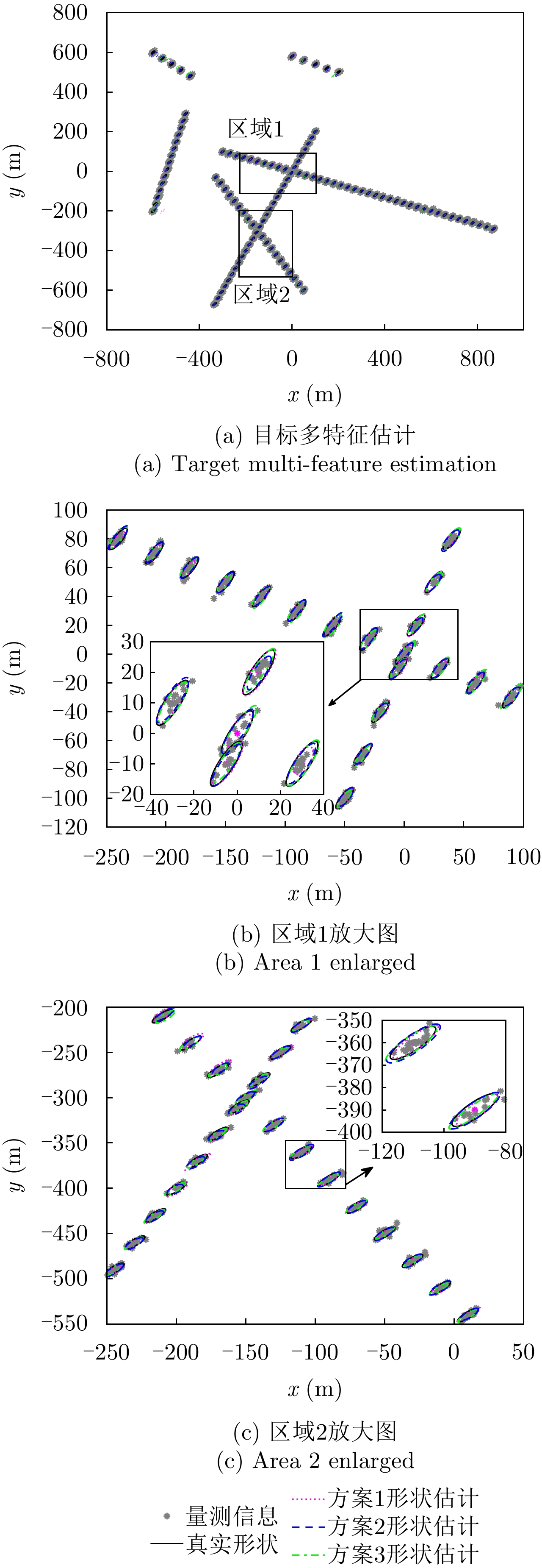
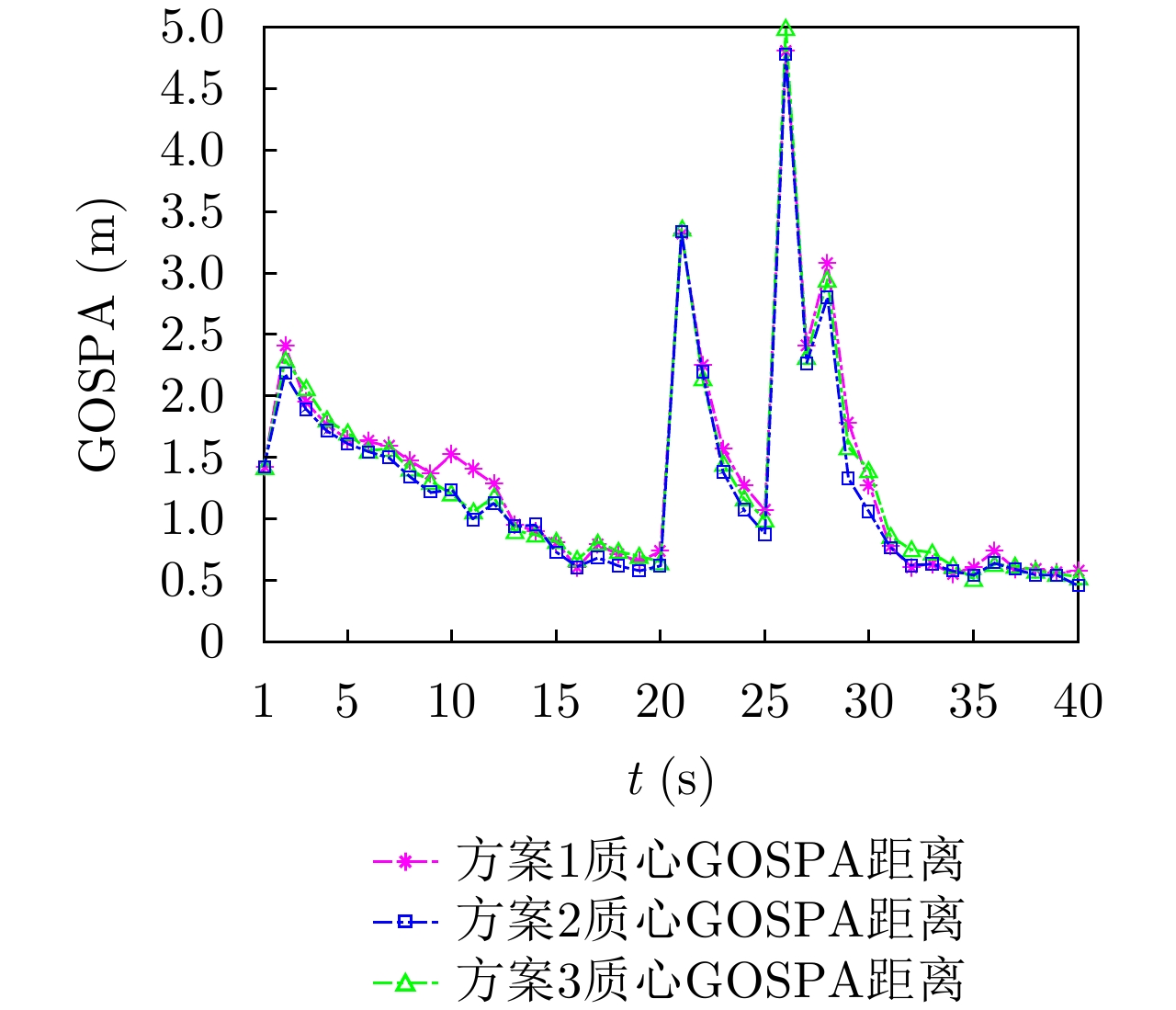
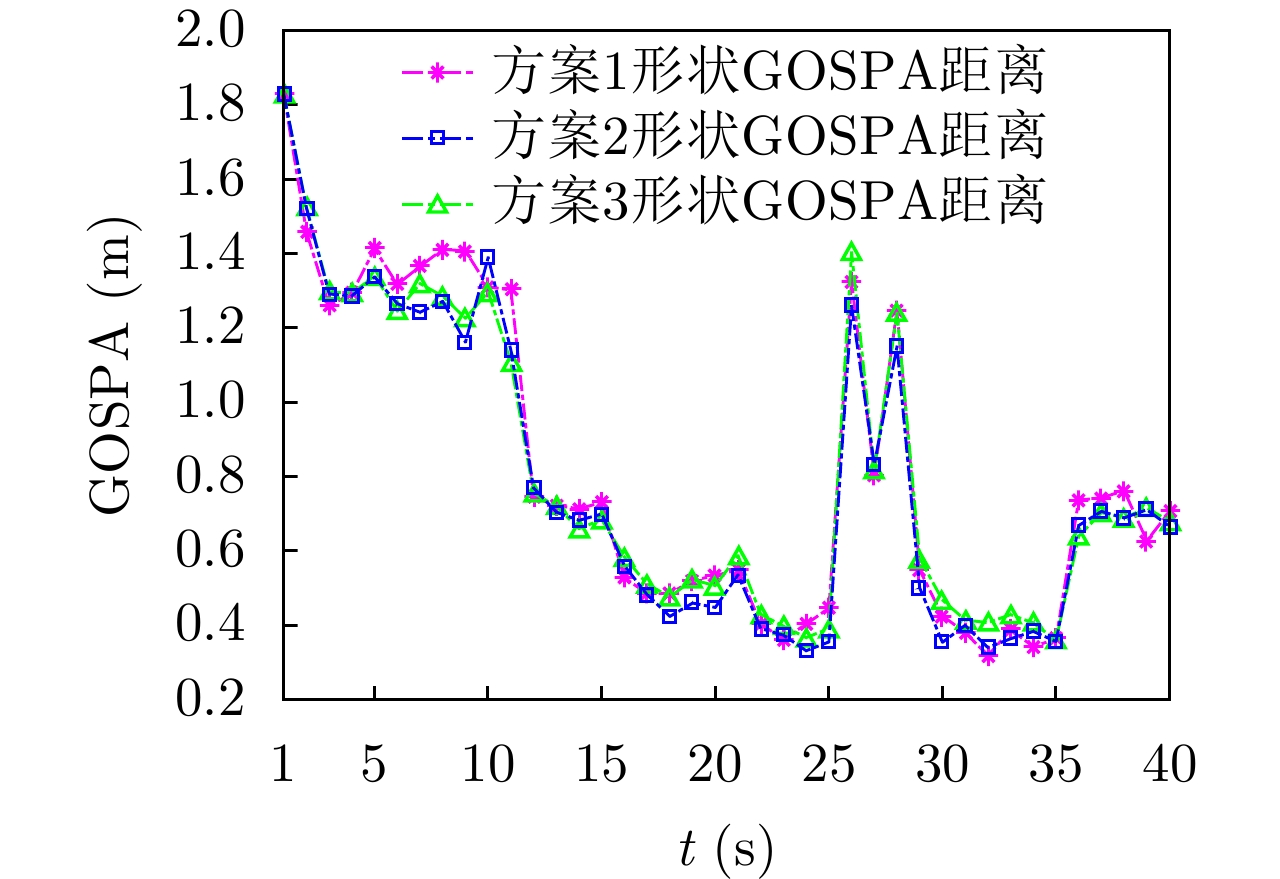
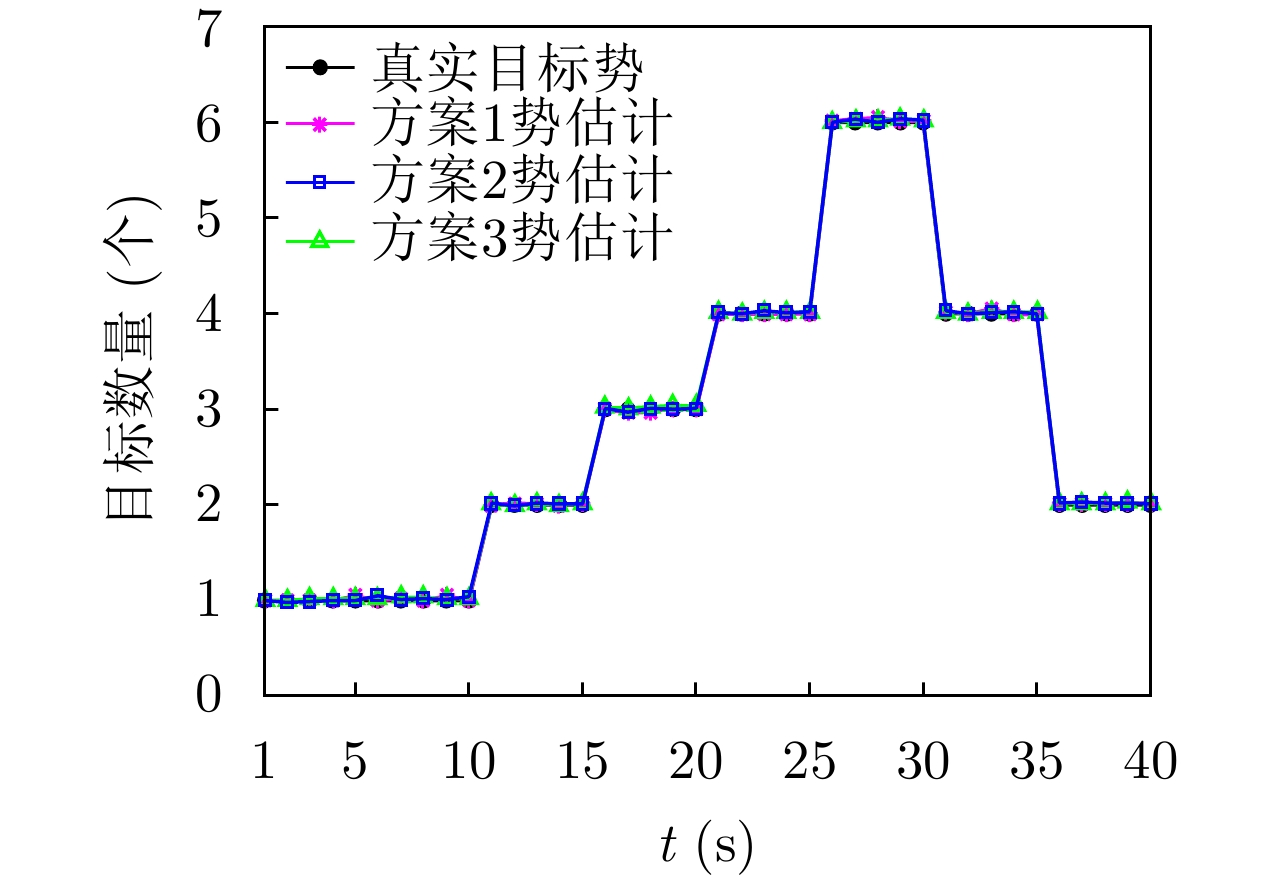
| [1] |
AGGARWAL S and KUMAR N. Path planning techniques for unmanned aerial vehicles: A review, solutions, and challenges[J]. Computer Communications, 2020, 149: 270–299. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2019.10.014 |
| [2] |
BAYERLEIN H, THEILE M, CACCAMO M, et al. Multi-UAV path planning for wireless data harvesting with deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2021, 2: 1171–1187. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2021.3081996 |
| [3] |
BOLOURIAN N and HAMMAD A. LiDAR-equipped UAV path planning considering potential locations of defects for bridge inspection[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 117: 103250. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103250 |
| [4] |
BASIRI A, MARIANI V, SILANO G, et al. A survey on the application of path-planning algorithms for multi-rotor UAVs in precision agriculture[J]. Journal of Navigation, 2022, 75(2): 364–383. doi: 10.1017/S0373463321000825 |
| [5] |
KARUR K, SHARMA N, DHARMATTI C, et al. A survey of path planning algorithms for mobile robots[J]. Vehicles, 2021, 3(3): 448–468. doi: 10.3390/vehicles3030027 |
| [6] |
REN Tianzhu, ZHOU Rui, XIA Jie, et al. Three-dimensional path planning of UAV based on an improved A algorithm[C]. 2016 IEEE Chinese Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference (CGNCC), Nanjing, China, 2016: 140–145.
|
| [7] |
SARANYA C, UNNIKRISHNAN M, ALI S A, et al. Terrain based D* algorithm for path planning[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2016, 49(1): 178–182. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2016.03.049 |
| [8] |
MAUROVIĆ I, SEDER M, LENAC K, et al. Path planning for active SLAM based on the D* algorithm with negative edge weights[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2017, 48(8): 1321–1331. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2668603 |
| [9] |
RUZ J J, AREVALO O, DE LA CRUZ J M, et al. Using MILP for UAVs trajectory optimization under radar detection risk[C]. 2006 IEEE Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation, Prague, Czech Republic, 2006: 957–960.
|
| [10] |
PEHLIVANOGLU Y V. A new vibrational genetic algorithm enhanced with a Voronoi diagram for path planning of autonomous UAV[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2012, 16(1): 47–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2011.02.006 |
| [11] |
PHUNG M D and HA Q P. Safety-enhanced UAV path planning with spherical vector-based particle swarm optimization[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 107: 107376. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107376 |
| [12] |
KONATOWSKI S. Application of the ACO algorithm for UAV path planning[J]. Przeglad Elektrotechniczny, 2019, 1(7): 117–121. doi: 10.15199/48.2019.07.24 |
| [13] |
ZHOU Bin, GUO Yan, LI Ning, et al. Path planning of UAV using guided enhancement Q-learning algorithm[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(9): 325109. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2021.25109 |
| [14] |
XU Liang and NIU Ruixin. Tracking visual object as an extended target[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Anchorage, USA, 2021: 664–668.
|
| [15] |
CHEN Hui, DU Jinrui, and HAN Chongzhao. A multiple extended target multi-bernouli filter based on star-convex random hypersurface model[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(5): 909–922. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180130 |
| [16] |
KHALKHALI M B, VAHEDIAN A, and YAZDI H S. Multi-target state estimation using interactive Kalman filter for multi-vehicle tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(3): 1131–1144. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2902664 |
| [17] |
KIM D Y, VO B N, VO B T, et al. A labeled random finite set online multi-object tracker for video data[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 90: 377–389. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.02.004 |
| [18] |
MAHLER R P S. Advances in Statistical Multisource-Multitarget Information Fusion[M]. Boston, USA: Artech House, 2014: 825–860.
|
| [19] |
MAHLER R P S. Statistical Multisource-Multitarget Information Fusion[M]. Boston, USA: Artech House, 2007: 655–667.
|
| [20] |
YANG Wei, FU Yaowen, LONG Jianqian, et al. The FISST-based target tracking techniques: A survey[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2012, 40(7): 1440–1448. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.07.025 |
| [21] |
MAHLER R P S. Multitarget Bayes filtering via first-order multitarget moments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic systems, 2003, 39(4): 1152–1178. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2003.1261119 |
| [22] |
VO B N, SINGH S, and DOUCET A. Sequential Monte Carlo methods for multitarget filtering with random finite sets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(4): 1224–1245. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2005.1561884 |
| [23] |
VO B N and MA W K. The Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4091–4104. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.881190 |
| [24] |
VO B T, VO B N, and CANTONI A. The cardinality balanced multi-target multi-Bernoulli filter and its implementations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(2): 409–423. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2007924 |
| [25] |
VO B T and VO B N. Labeled random finite sets and multi-object conjugate priors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(13): 3460–3475. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2259822 |
| [26] |
VO B N, VO B T, and PHUNG D. Labeled random finite sets and the Bayes multi-target tracking filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(24): 6554–6567. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2364014 |
| [27] |
REUTER S, VO B T, VO B N, et al. The labeled multi-Bernoulli filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(12): 3246–3260. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2323064 |
| [28] |
BAUM M and HANEBECK U D. Random hypersurface models for extended object tracking[C]. 2009 IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology (ISSPIT), Ajman, United Arab Emirates, 2009: 178–183.
|
| [29] |
THORMANN K, BAUM M, and HONER J. Extended target tracking using Gaussian processes with high-resolution automotive radar[C]. 2018 21st International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Cambridge, United Kingdom, 2018: 1764–1770.
|
| [30] |
KOCH J W. Bayesian approach to extended object and cluster tracking using random matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44(3): 1042–1059. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4655362 |
| [31] |
FELDMANN M, FRÄNKEN D, and KOCH W. Tracking of extended objects and group targets using random matrices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(4): 1409–1420. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2101064 |
| [32] |
ZHANG Yinyan and LI Bicheng. Method of target threat assessment based on cloudy MIN-MAX center of gravity reasoning[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2014, 26(2): 411–418. doi: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2014.02.041 |
| [33] |
LI Te, FENG Qi, and ZHANG Kun. Threat assessment based on entropy weight grey incidence and D-S theory of evidence[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2013, 30(2): 380–382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2013.02.016 |
| [34] |
GAO Xiaoguang, LI Qingyuan, and DI Ruohai. MPC three-dimensional dynamic path planning for UAV based on DBN threat assessment[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(11): 2199–2205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.11.14 |
| [35] |
ZHANG Kun, WANG Xue, ZHANG Caikun, et al. Evaluating and sequencing of air target threat based on IFE and dynamic intuitionistic fuzzy sets[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(4): 697–701. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2014.04.15 |
| [36] |
GAO Yang, LI Dongsheng, and ZHONG Hua. A novel target threat assessment method based on three-way decisions under intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute decision making environment[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 87: 103276. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2019.103276 |
| [37] |
WANG Yi, LIU Sanyang, NIU Wei, et al. Threat assessment method based on intuitionistic fuzzy similarity measurement reasoning with orientation[J]. China Communications, 2014, 11(6): 119–128. doi: 10.1109/CC.2014.6879010 |
| [38] |
WANG Xiaoyi, LIU Zaiwen, HOU Chaozhen, et al. Method of object threat assessment based on fuzzy MADM[J]. Control and Decision, 2007, 22(8): 859–863. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0920.2007.08.004 |
| [39] |
GRANSTRÖM K, FATEMI M, and SVENSSON L. Gamma Gaussian inverse-Wishart Poisson multi-Bernoulli filter for extended target tracking[C]. 2016 19th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Heidelberg, Germany, 2016: 893–900.
|
| [40] |
LIAN Feng, MA Dongdong, YUAN Xianghui, et al. CBMeMBer filter for extended targets and its Gaussian mixture implementations[J]. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(4): 611–616. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2014.0286 |
| [41] |
GOSTAR A K, HOSEINNEZHAD R, BAB-HADIASHAR A, et al. Sensor-management for multitarget filters via minimization of posterior dispersion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(6): 2877–2884. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2718280 |
| [42] |
RAHMATHULLAH A S, GARCÍA-FERNÁNDEZ Á F, and SVENSSON L. Generalized optimal sub-pattern assignment metric[C]. 2017 20th International Conference on Information Fusion (Fusion), Xi’an, China, 2017: 1–8.
|
| [43] |
LUNDQUIST C, GRANSTRÖM K, and ORGUNER U. An extended target CPHD filter and a gamma Gaussian inverse Wishart implementation[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2013, 7(3): 472–483. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2245632 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: