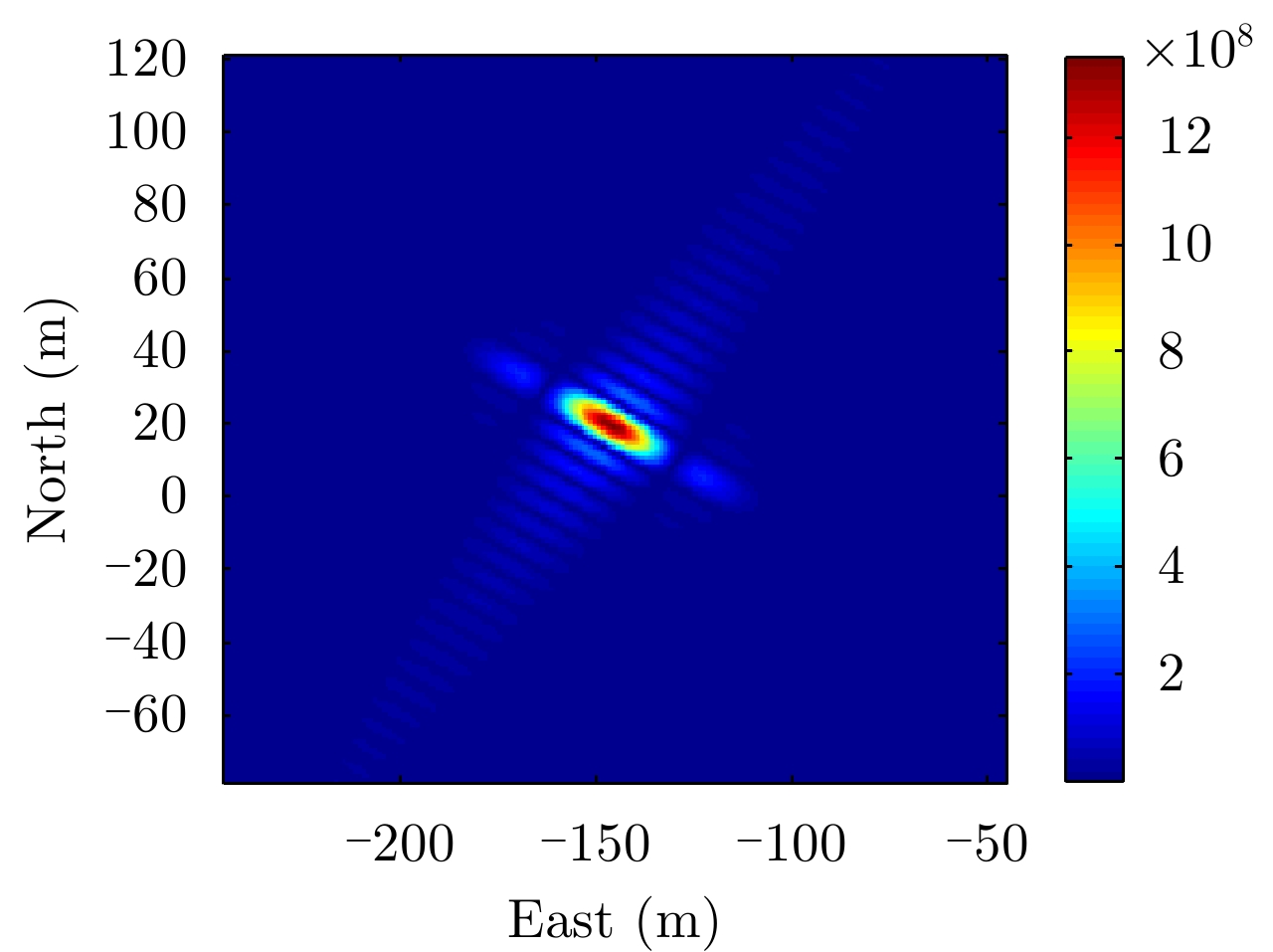
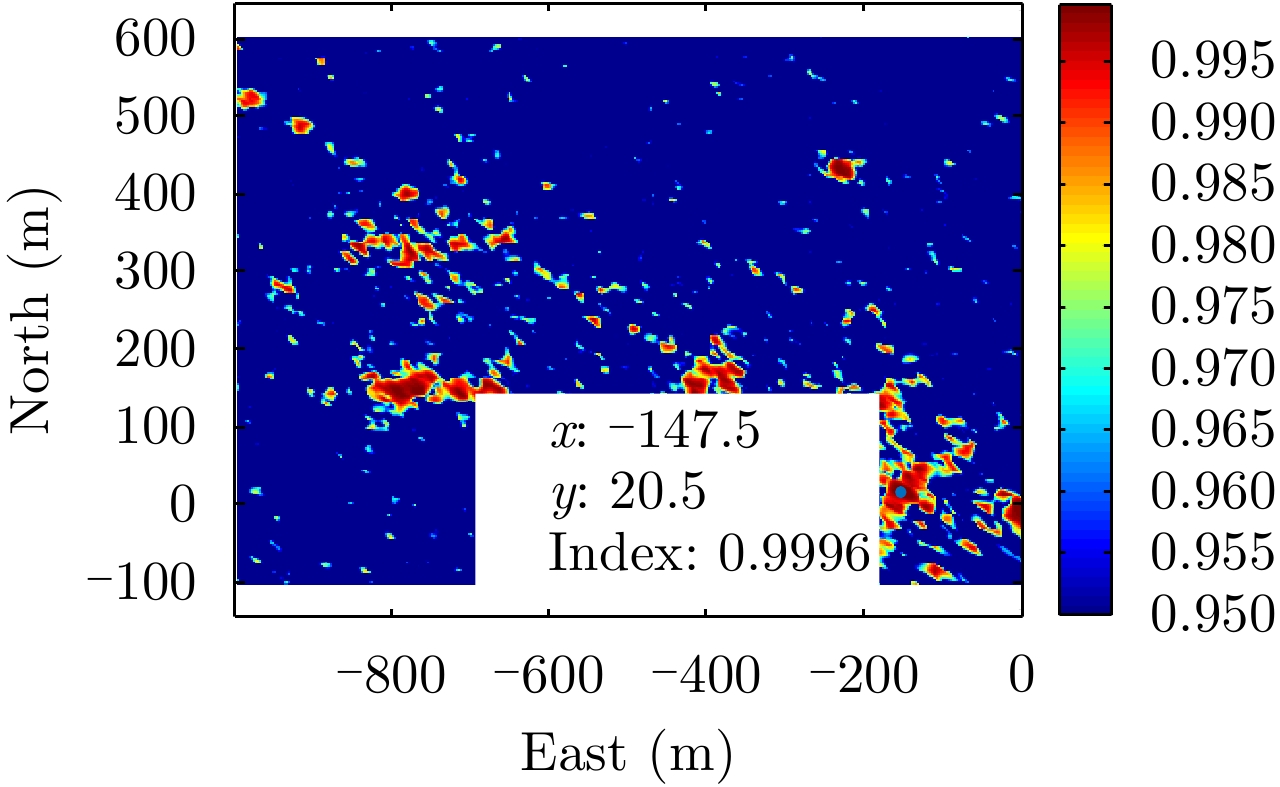
| [1] |
CHERNIAKOV M. Space-surface bistatic synthetic aperture radar—prospective and problems[C]. Proceedings of RADAR 2002, Edinburgh, UK, 2002.
|
| [2] |
ANTONIOU M and CHERNIAKOV M. Experimental demonstration of passive GNSS-based SAR imaging modes[C]. Proceedings of IET International Radar Conference 2013, Xi’an, China, 2013.
|
| [3] |
ZENG Tao, ZHANG Tian, TIAN Weiming, et al. A novel subsidence monitoring technique based on space-surface bistatic differential interferometry using GNSS as transmitters[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(6): 1–16.
|
| [4] |
ZENG Tao, ZHANG Tian, TIAN Weiming, et al. Bistatic SAR imaging processing and experiment results using BeiDou-2/Compass-2 as illuminator of opportunity and a fixed receiver[C]. Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Singapore, Singapore, 2015.
|
| [5] |
FAN Xuezhen, LIU Feifeng, ZHANG Tian, et al. Passive SAR with GNSS transmitters: Latest results and research progress[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, USA, 2017.
|
| [6] |
ANTONIOU M, CHERNIAKOV M, and MA Hui. Space-surface bistatic synthetic aperture radar with navigation satellite transmissions: A review[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(6): 1–20.
|
| [7] |
LIU Feifeng, ANTONIOU M, ZENG Zhangfan, et al. Point spread function analysis for BSAR with GNSS transmitters and long dwell times: Theory and experimental confirmation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(4): 781–785. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2223655 |
| [8] |
MA Hui, ANTONIOU M, and CHERNIAKOV M. Passive GNSS-based SAR resolution improvement using joint Galileo E5 signals[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(8): 1640–1644. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2417594 |
| [9] |
ZENG Tao, ZHANG Tian, TIAN Weiming, et al. Space-surface bistatic SAR image enhancement based on repeat-pass coherent fusion with Beidou-2/Compass-2 as illuminators[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(12): 1832–1836. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2614337 |
| [10] |
ANTONIOU M, LIU F, ZENG Z, et al. Coherent change detection using GNSS-based passive SAR: First experimental results[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IET International Conference on Radar Systems, Glasgow, UK, 2012.
|
| [11] |
TZAGKAS D, ANTONIOU M, and CHERNIAKOV M. Coherent change detection experiments with GNSS-based passive SAR[C]. Proceedings of 2016 European Radar Conference, London, UK, 2016.
|
| [12] |
LIU Feifeng, FAN Xuezhen, ZHANG Tian, et al. GNSS-based SAR interferometry for 3-D deformation retrieval: Algorithms and feasibility study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 5736–5748.
|
| [13] |
DONG Xichao, HU Cheng, TIAN Weiming, et al. Feasibility study of inclined geosynchronous SAR focusing using Beidou IGSO signals[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2016, 59(12): 129302. doi: 10.1007/s11432-016-5524-x |
| [14] |
LIU Feifeng, FAN Xuezhen, ZHANG Lingzhi, et al. GNSS-based SAR for urban area imaging: Topology optimization and experimental confirmation[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 40(12): 4668–4682. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2019.1569790 |
| [15] |
ZHANG Qilei, ANTONIOU M, CHANG Wenge, et al. Spatial decorrelation in GNSS-based SAR coherent change detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(1): 219–228. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2321145 |
| [16] |
ZEBKER H A and VILLASENOR J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1992, 30(5): 950–959. doi: 10.1109/36.175330 |
| [17] |
FERRETTI A, PRATI C, and ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 8–20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661 |
| [18] |
ZENG Tao, CHERNIAKOV M, and LONG Teng. Generalized approach to resolution analysis in BSAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(2): 461–474. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2005.1468741 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

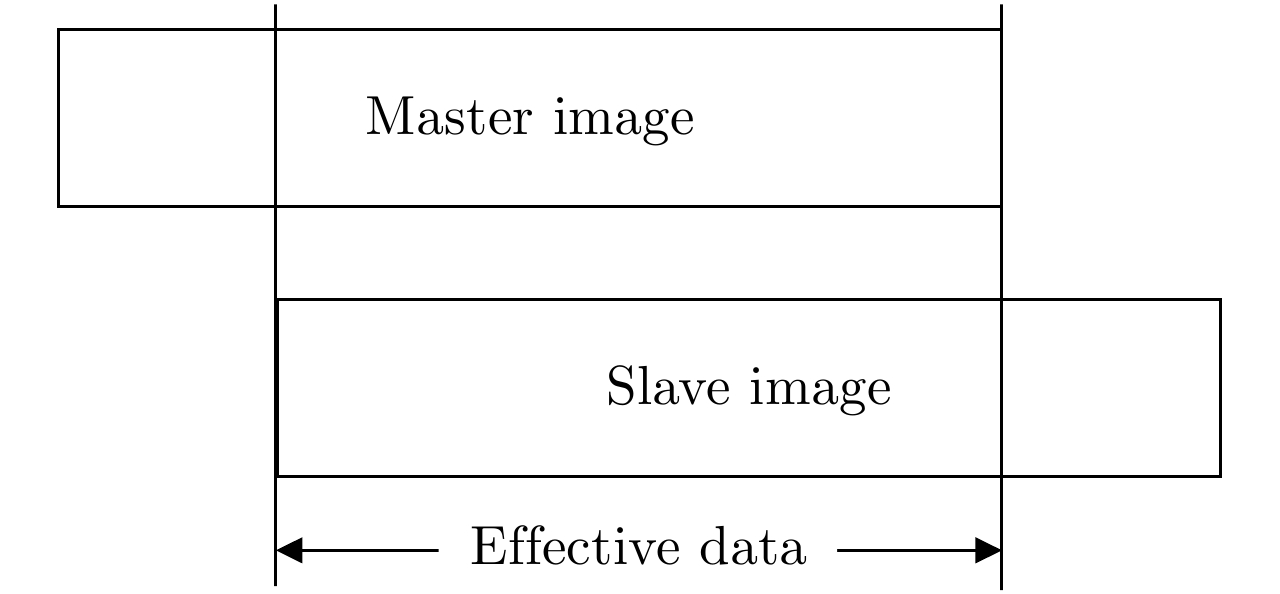



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: