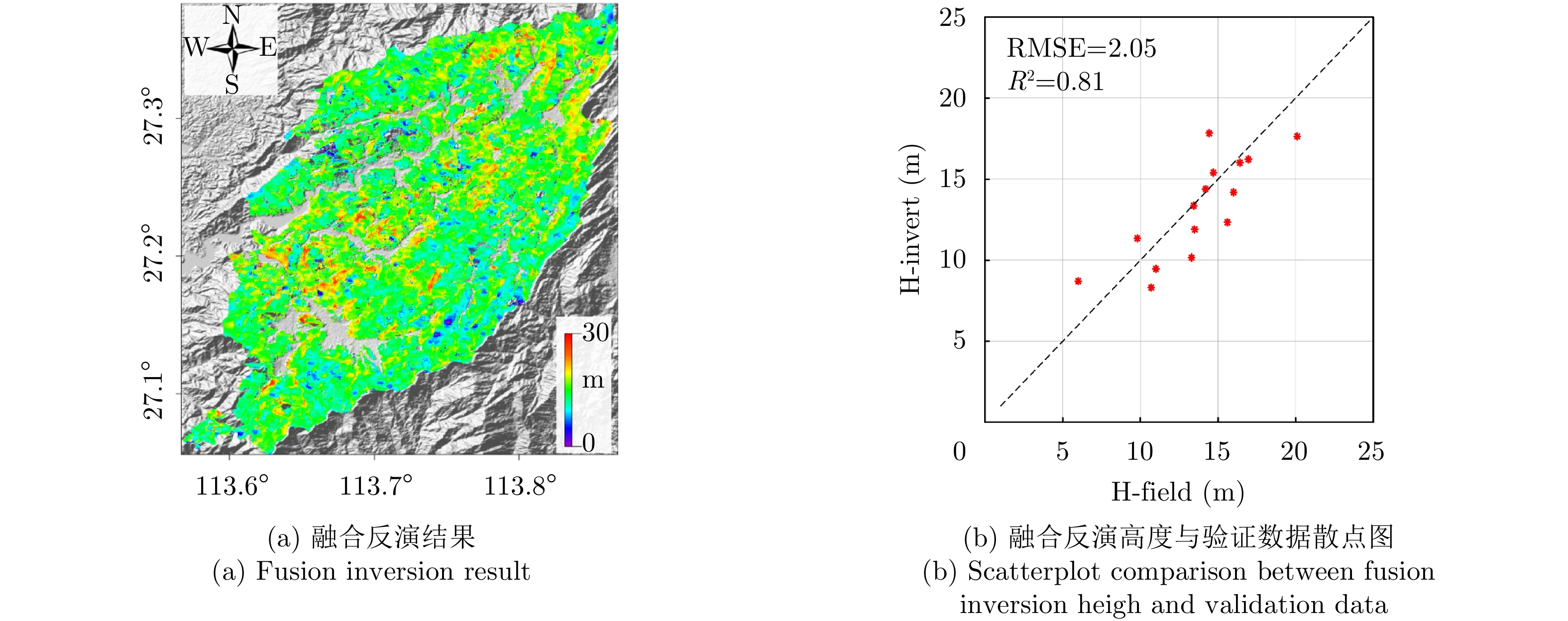
| [1] |
郭华东. 雷达对地观测理论与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000: 126–131.
GUO Huadong. Radar for Earth Observation[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000: 126–131.
|
| [2] |
TREUHAFT R N, MADSEN S N, MOGHADDAM M, et al. Vegetation characteristics and underlying topography from interferometric radar[J]. Radio Science, 1996, 31(6): 1449–1485. doi: 10.1029/96rs01763 |
| [3] |
PAPATHANASSIOU K P and CLOUDE S R. Single-baseline polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(11): 2352–2363. doi: 10.1109/36.964971 |
| [4] |
CLOUDE S R and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. Three-stage inversion process for polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2003, 150(3): 125–134. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:20030449 |
| [5] |
PRAKS J, KUGLER F, PAPATHANASSIOU K P, et al. Height estimation of boreal forest: Interferometric model-based inversion at L- and X-band versus HUTSCAT profiling scatterometer[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2007, 4(3): 466–470. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2007.898083 |
| [6] |
HAJNSEK I, KUGLER F, LEE S K, et al. Tropical-forest-parameter estimation by means of Pol-InSAR: The INDREX-II campaign[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(2): 481–493. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2009437 |
| [7] |
FU Haiqiang, WANG Changcheng, ZHU Jianjun, et al. Inversion of vegetation height from PolInSAR using complex least squares adjustment method[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2015, 58(6): 1018–1031. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5070-1 |
| [8] |
LEI Yang and SIQUEIRA P. Estimation of forest height using spaceborne repeat-pass L-band InSAR correlation magnitude over the US state of maine[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(11): 10252–10285. doi: 10.3390/rs61110252 |
| [9] |
LAVALLE M and HENSLEY S. Extraction of structural and dynamic properties of forests from polarimetric-interferometric SAR data affected by temporal decorrelation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(9): 4752–4767. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2409066 |
| [10] |
PAPATHANASSIOU K P and CLOUDE S R. The effect of temporal decorrelation on the inversion of forest parameters from Pol-InSAR data[C]. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2003.1294134. |
| [11] |
LEI Yang, SIQUEIRA P, TORBICK N, et al. Generation of large-scale moderate-resolution forest height mosaic with spaceborne repeat-pass SAR interferometry and lidar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(2): 770–787. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2860590 |
| [12] |
CLOUDE S R and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. Polarimetric SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(5): 1551–1565. doi: 10.1109/36.718859 |
| [13] |
NEUMANN M, FERRO-FAMIL L, and REIGBER A. Pol-InSAR coherence set theory and application[C]. The 6th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Dresden, Germany, 2006.
|
| [14] |
XU Liying, LI Shiqiang, DENG Yunkai, et al. Improved three-stage algorithm of forest height retrieval with PolInSAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2014, 3(1): 28–34. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1300.2014.13089 |
| [15] |
BAI Lu, CAO Fang, and HONG Wen. Fast approach to estimate the longest axis in coherence region and its applications[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2010, 32(3): 548–553. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.00211 |
| [16] |
BAMLER R and HARTL P. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Inverse Problems, 1998, 14(4): R1–R54. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/14/4/001 |
| [17] |
MOON T K and STIRLING W C. Mathematical Methods and Algorithms for Signal Processing[M]. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 2000.
|
| [18] |
LAVALLE M, SOLIMINI D, POTTIER E, et al. Forest parameters inversion using polarimetric and interferometric SAR data[C]. 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Cape Town, South Africa, 2009. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2009.5417355. |
| [19] |
DENBINA M, SIMARD M, and HAWKINS B. Forest height estimation using multibaseline PolInSAR and sparse lidar data fusion[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(10): 3415–5433. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2841388 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: