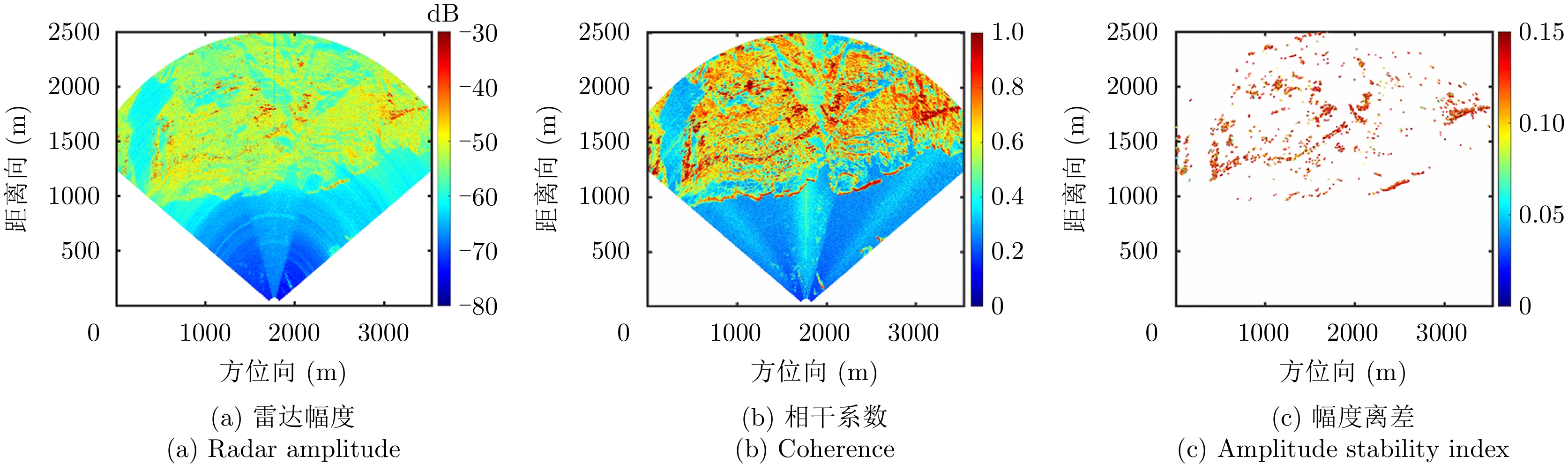
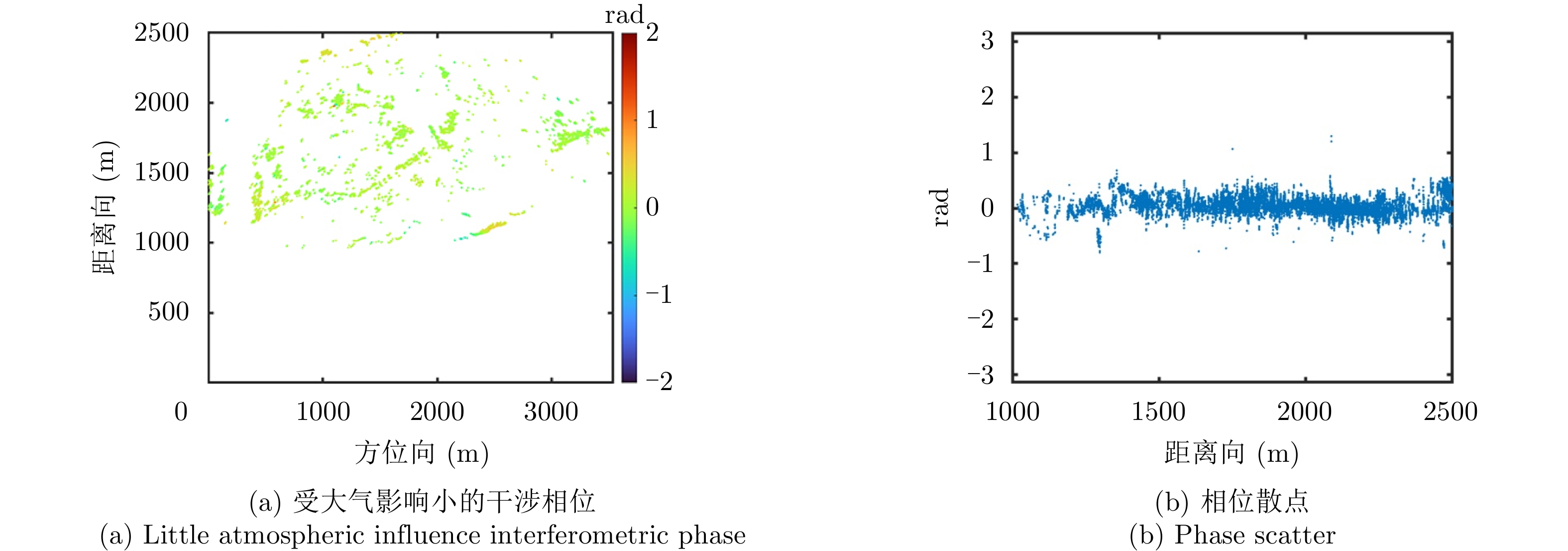
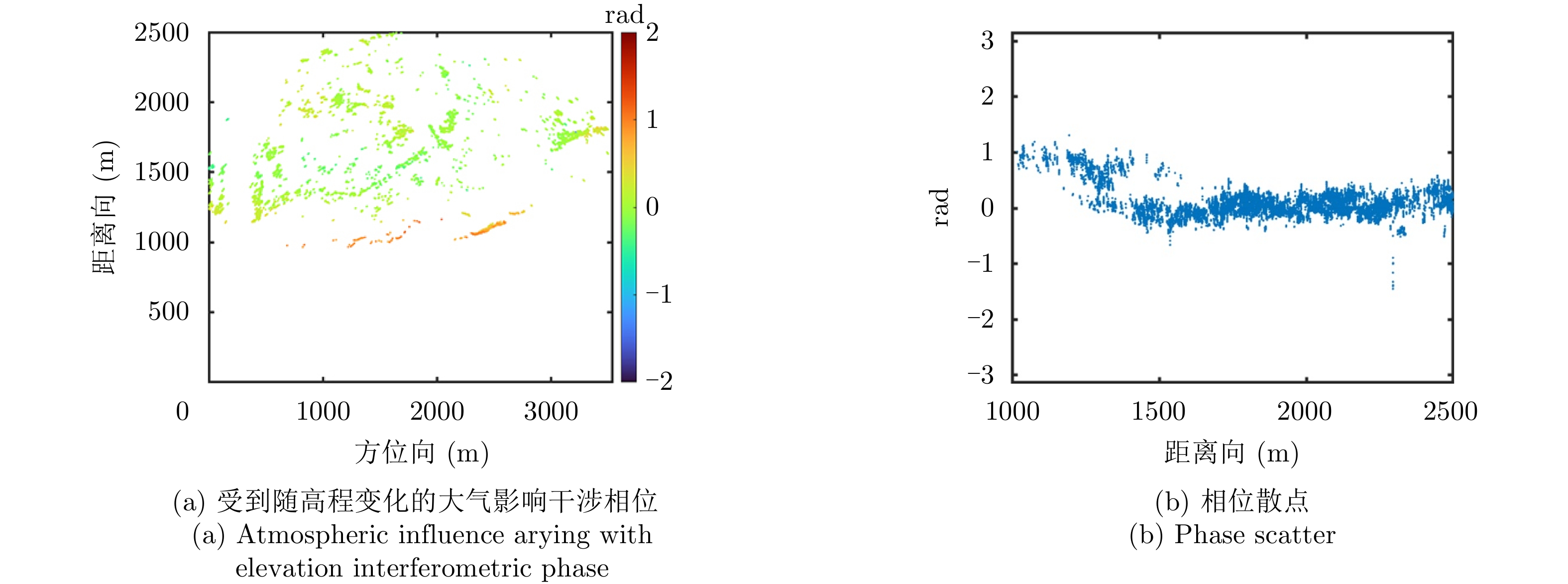
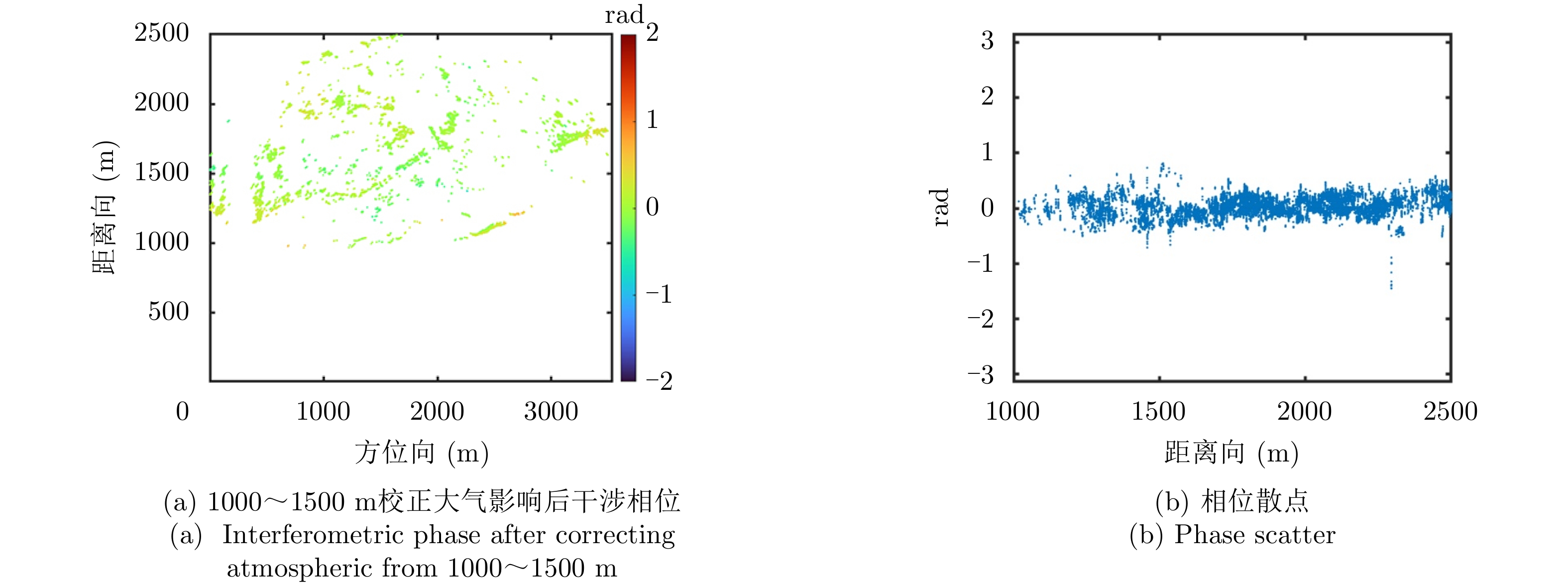
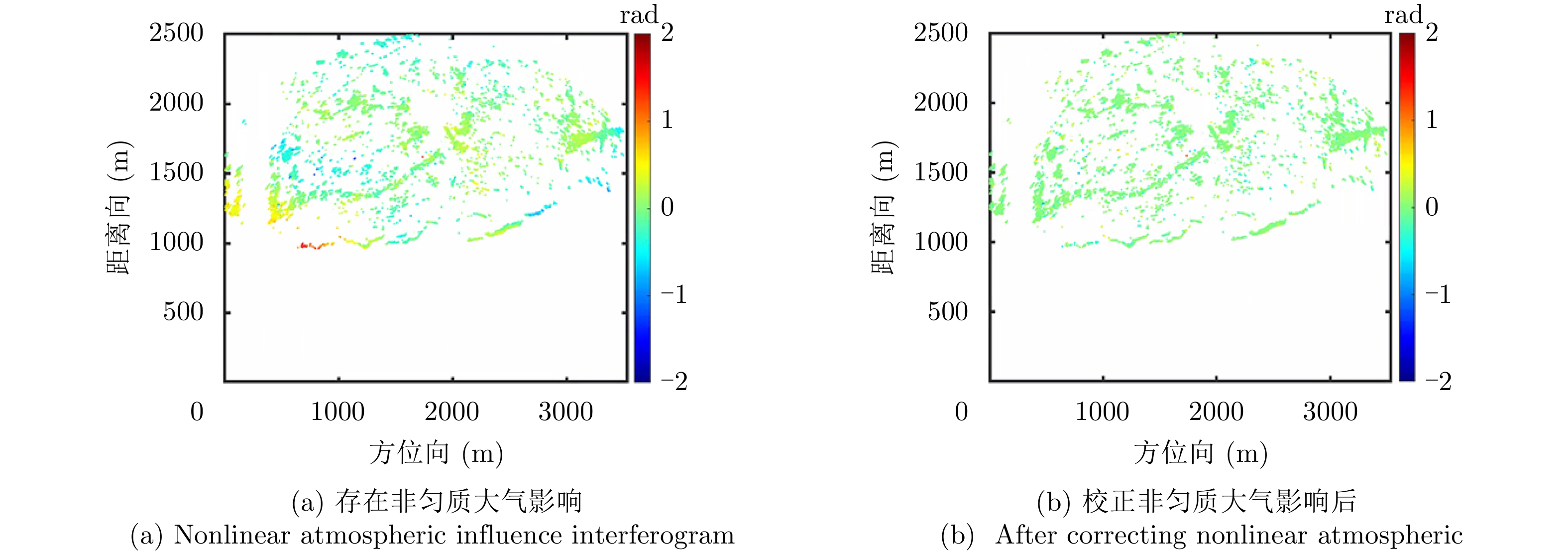
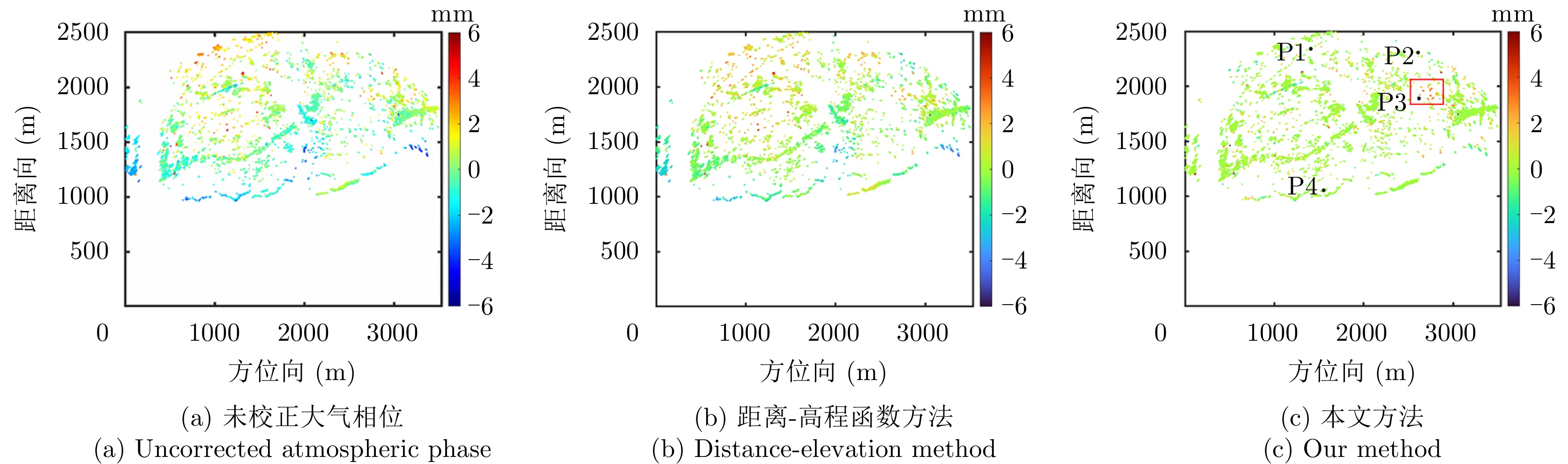
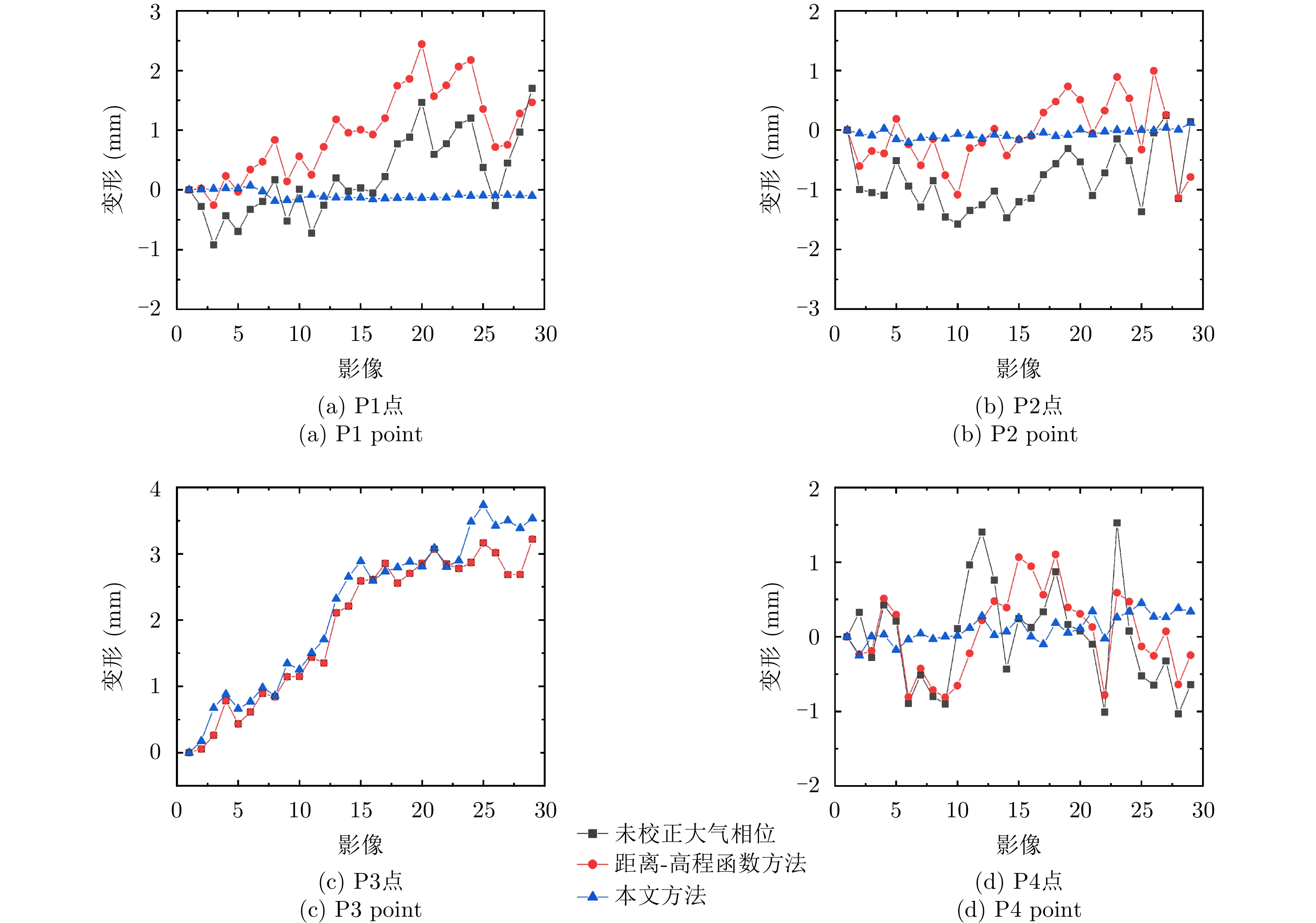
| [1] |
WANG Yanping, HONG Wen, ZHANG Yuan, et al. Ground-based differential interferometry SAR: A review[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2020, 8(1): 43–70. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2019.2963169 |
| [2] |
LIU Bin, GE Daqing, LI Man, et al. Ground-based interferometric synthetic aperture radar and its applications[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2017, 29(1): 1–6. doi: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2017.01.01 |
| [3] |
BAI Zechao, WANG Yanping, and BALZ T. Beijing land subsidence revealed using PS-InSAR with long time series TerraSAR-X SAR data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(11): 2529. doi: 10.3390/rs14112529 |
| [4] |
HU Jun, LIU Jihong, LI Zhiwei, et al. Estimating three-dimensional coseismic deformations with the SM-VCE method based on heterogeneous SAR observations: Selection of homogeneous points and analysis of observation combinations[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2021, 255: 112298. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112298 |
| [5] |
RODELSPERGER S. Real-Time Processing of Ground Based Synthetic Aperture Radar (GB-SAR) Measurements[M]. Darmstadt: Technische Universität Darmstadt, 2011.
|
| [6] |
IGLESIAS R, AGUASCA A, FABREGAS X, et al. Ground-based polarimetric SAR interferometry for the monitoring of terrain displacement phenomena–Part I: Theoretical description[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(3): 980–993. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2360040 |
| [7] |
PIERACCINI M and MICCINESI L. Ground-based radar interferometry: A bibliographic review[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(9): 1029. doi: 10.3390/rs11091029 |
| [8] |
LUZI G, PIERACCINI M, MECATTI D, et al. Ground-based radar interferometry for landslides monitoring: Atmospheric and instrumental decorrelation sources on experimental data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(11): 2454–2466. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.836792 |
| [9] |
NOFERINI L, PIERACCINI M, MECATTI D, et al. Permanent scatterers analysis for atmospheric correction in ground-based SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2005, 43(7): 1459–1471. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.848707 |
| [10] |
PIPIA L, FABREGAS X, AGUASCA A, et al. Atmospheric artifact compensation in ground-based DInSAR applications[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2008, 5(1): 88–92. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2007.908364 |
| [11] |
XU Yaming, ZHOU Xiao, WANG Peng, et al. A method of constructing permanent scatterers network to correct the meteorological disturbance by GB-SAR[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2016, 41(8): 1007–1012, 1020. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20140507 |
| [12] |
HUANG Qihuan and YUE Jianping. GBSAR atmospheric turbulence calibration based on weighted stable points[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(1): 202–208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2017.01.028 |
| [13] |
IANNINI L and GUARNIERI A M. Atmospheric phase screen in ground-based radar: Statistics and compensation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(3): 537–541. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2090647 |
| [14] |
IGLESIAS R, FABREGAS X, AGUASCA A, et al. Atmospheric phase screen compensation in ground-based SAR with a multiple-regression model over mountainous regions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(5): 2436–2449. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2261077 |
| [15] |
KARUNATHILAKE A and SATO M. Atmospheric phase compensation in extreme weather conditions for ground-based SAR[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 3806–3815. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3004341 |
| [16] |
LIU Jie, YANG Honglei, XU Linlin, et al. Novel model-based approaches for non-homogenous atmospheric compensation of GB-InSAR in the azimuth and horizontal directions[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(11): 2153. doi: 10.3390/rs13112153 |
| [17] |
HU Cheng, DENG Yunkai, TIAN Weiming, et al. A compensation method for a time-space variant atmospheric phase applied to time-series GB-SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(20): 2350. doi: 10.3390/rs11202350 |
| [18] |
DENG Yunkai, HU Cheng, TIAN Weiming, et al. A grid partition method for atmospheric phase compensation in GB-SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5206713. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3074161 |
| [19] |
DENG Yunkai, HU Cheng, TIAN Weiming, et al. 3-D deformation measurement based on three GB-MIMO radar systems: Experimental verification and accuracy analysis[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(12): 2092–2096. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3014342 |
| [20] |
胡程, 邓云开, 田卫明, 等. 地基干涉合成孔径雷达图像非线性大气相位补偿方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 831–840. doi: 10.12000/JR19073HU Cheng, DENG Yunkai, TIAN Weiming, et al. A compensation method of nonlinear atmospheric phase applied for GB-InSAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 831–840. doi: 10.12000/JR19073 |
| [21] |
IZUMI Y, ZOU Lilong, KIKUTA K, et al. Iterative atmospheric phase screen compensation for near-real-time ground-based InSAR measurements over a mountainous slope[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(8): 5955–5968. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2973533 |
| [22] |
FERRETTI A, PRATI C, and ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 8–20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661 |
| [23] |
ROSEN P A, HENSLEY S, ZEBKER H A, et al. Surface deformation and coherence measurements of Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii, from SIR-C radar interferometry[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 1996, 101(E10): 23109–23125. doi: 10.1029/96JE01459 |
| [24] |
肖捷夫. 库水涨落和降雨条件下藕塘滑坡变形演化机制及其预测模型研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国地质大学, 2021.
XIAO Jiefu. Deformation evolution mechanism and displacement prediction model of Outang landslide under water level fluctuation and rainfall[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], China University of Geosciences, 2021.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: