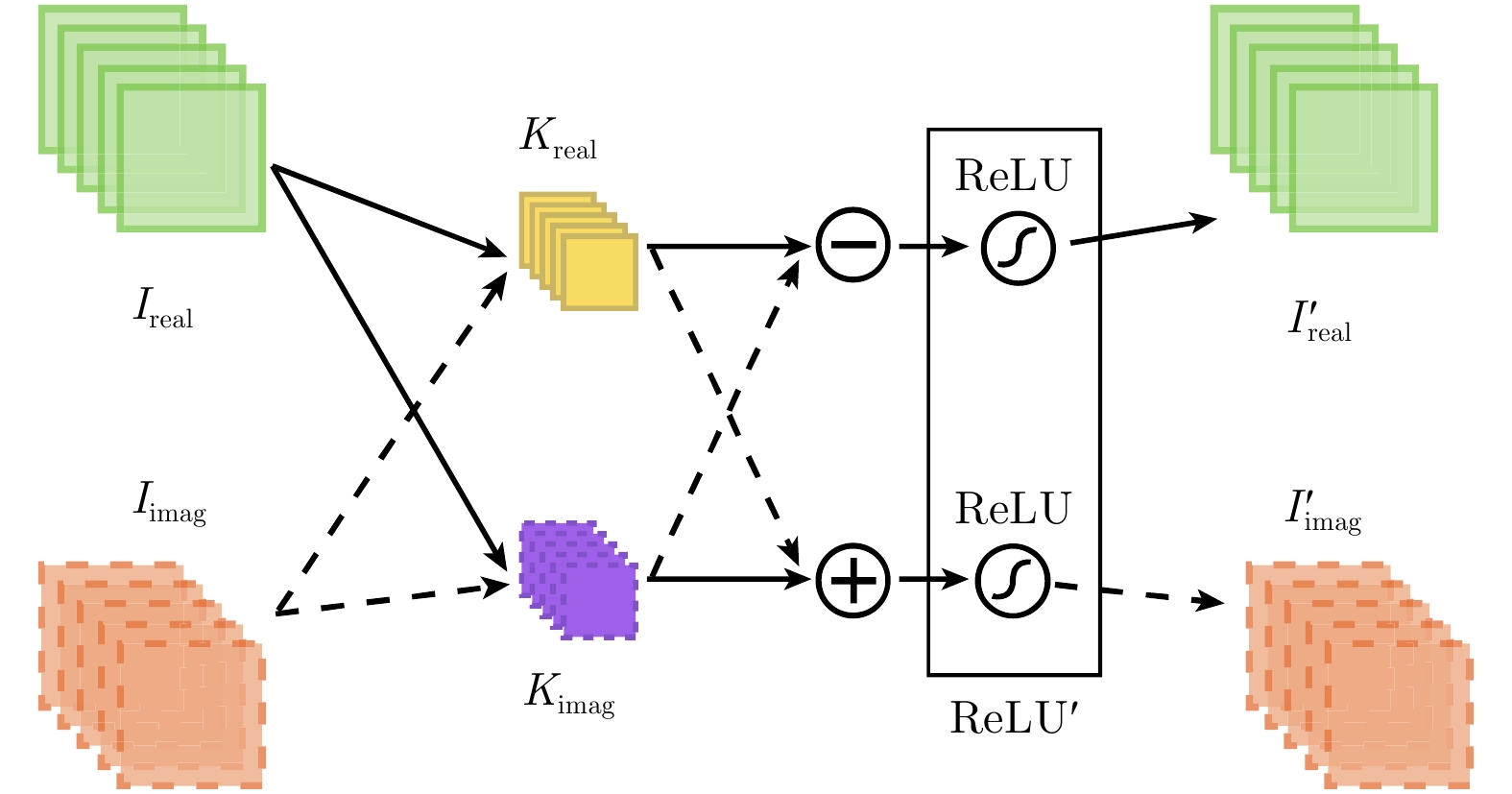
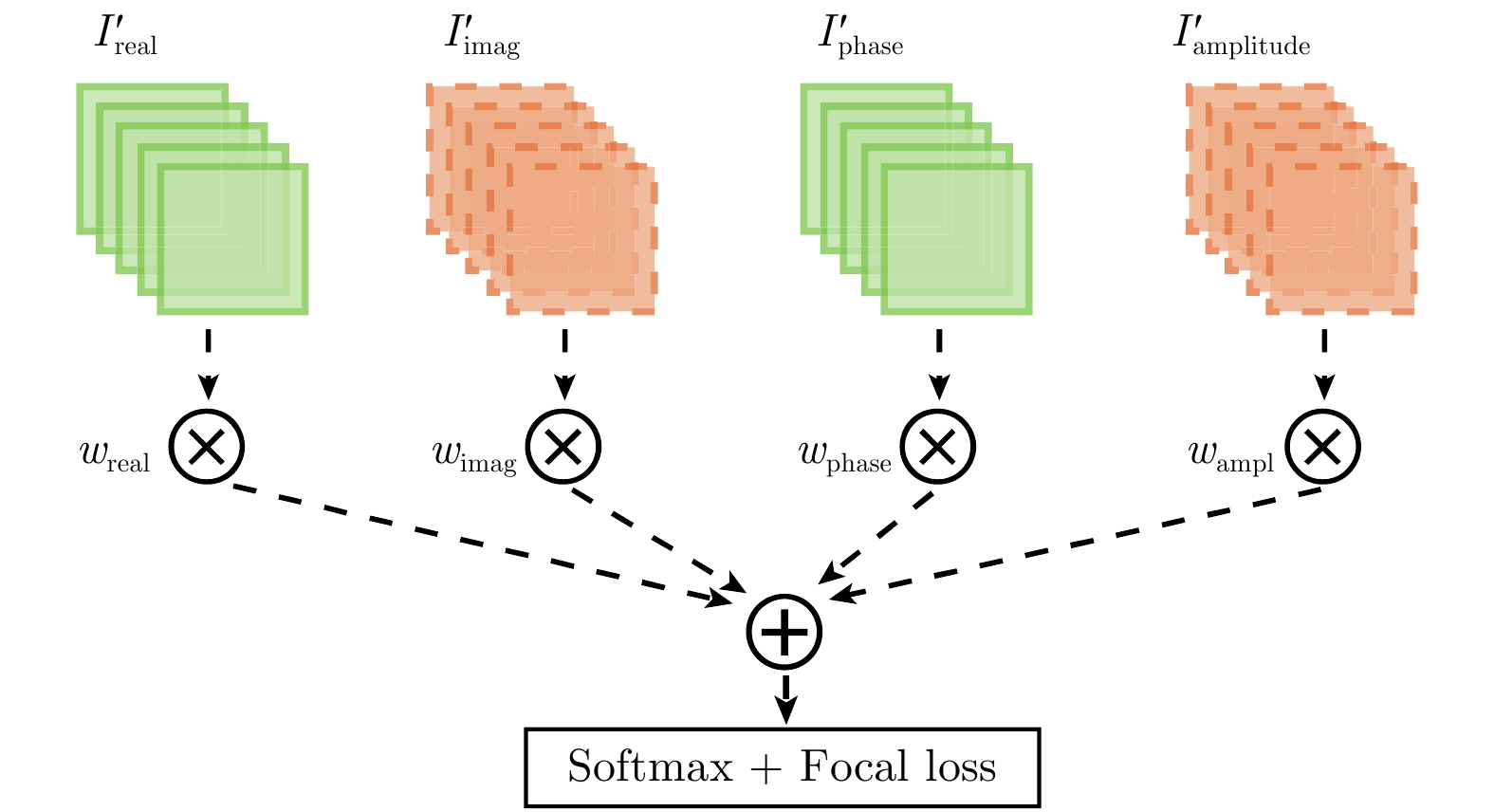
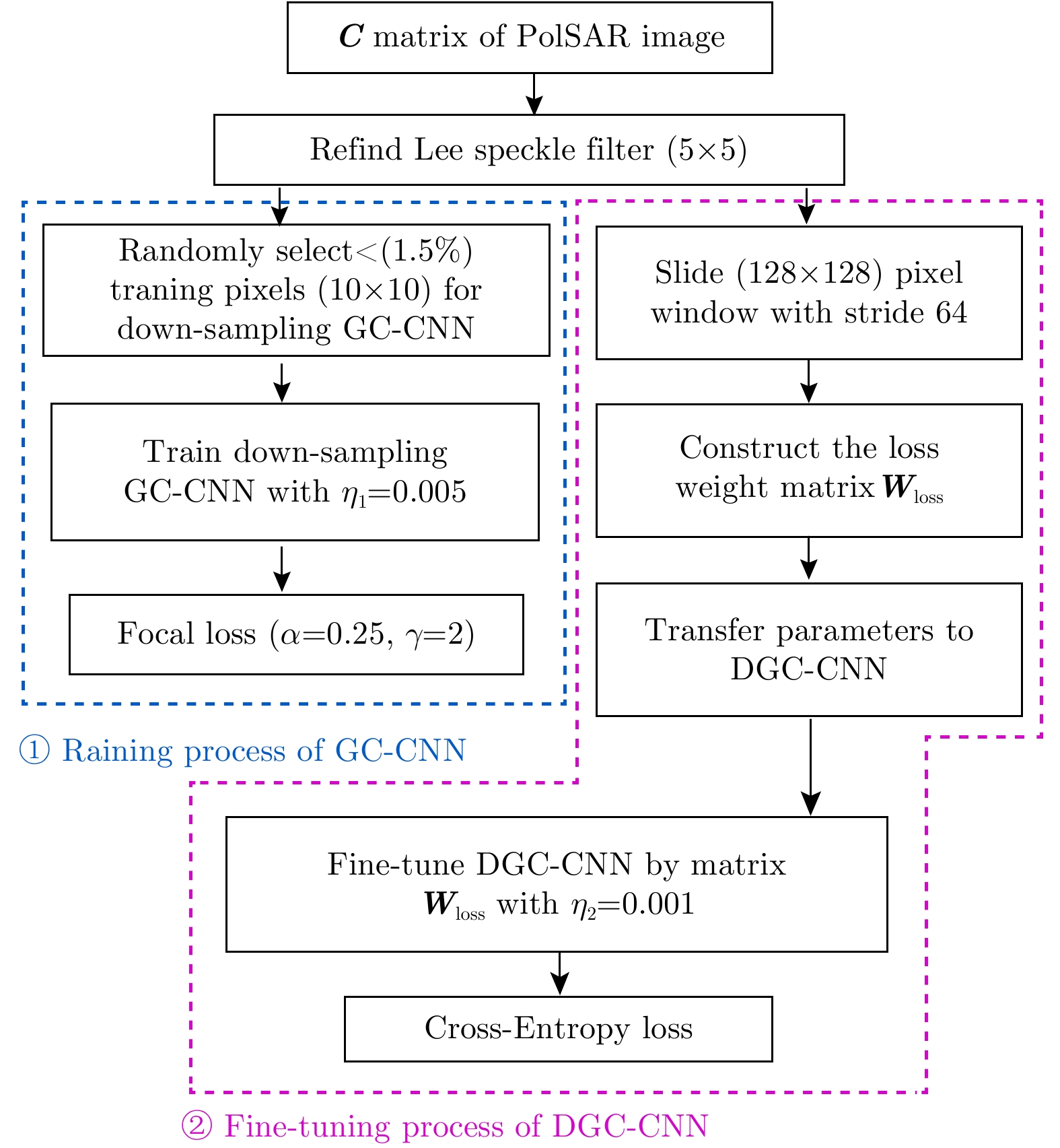
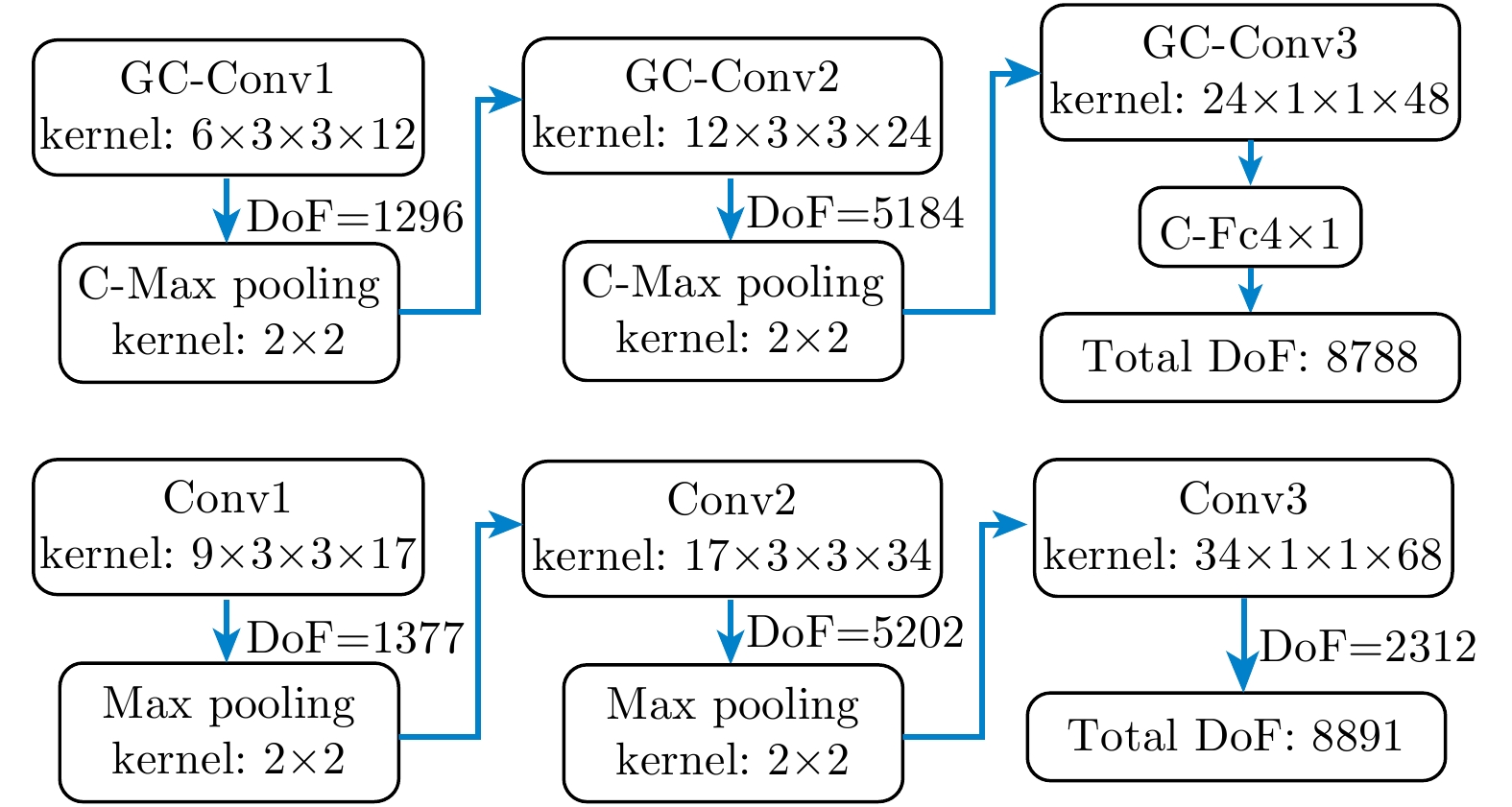
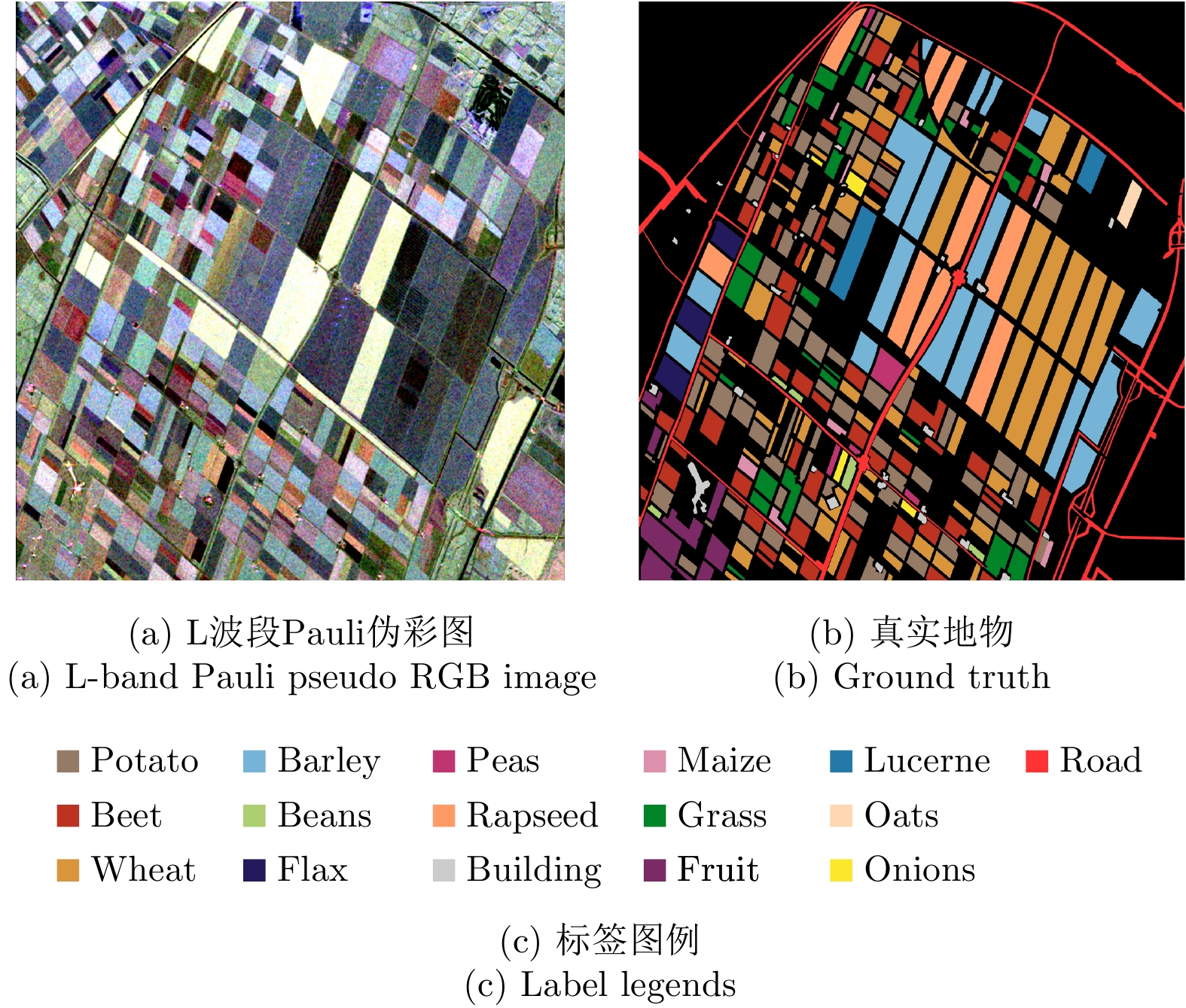
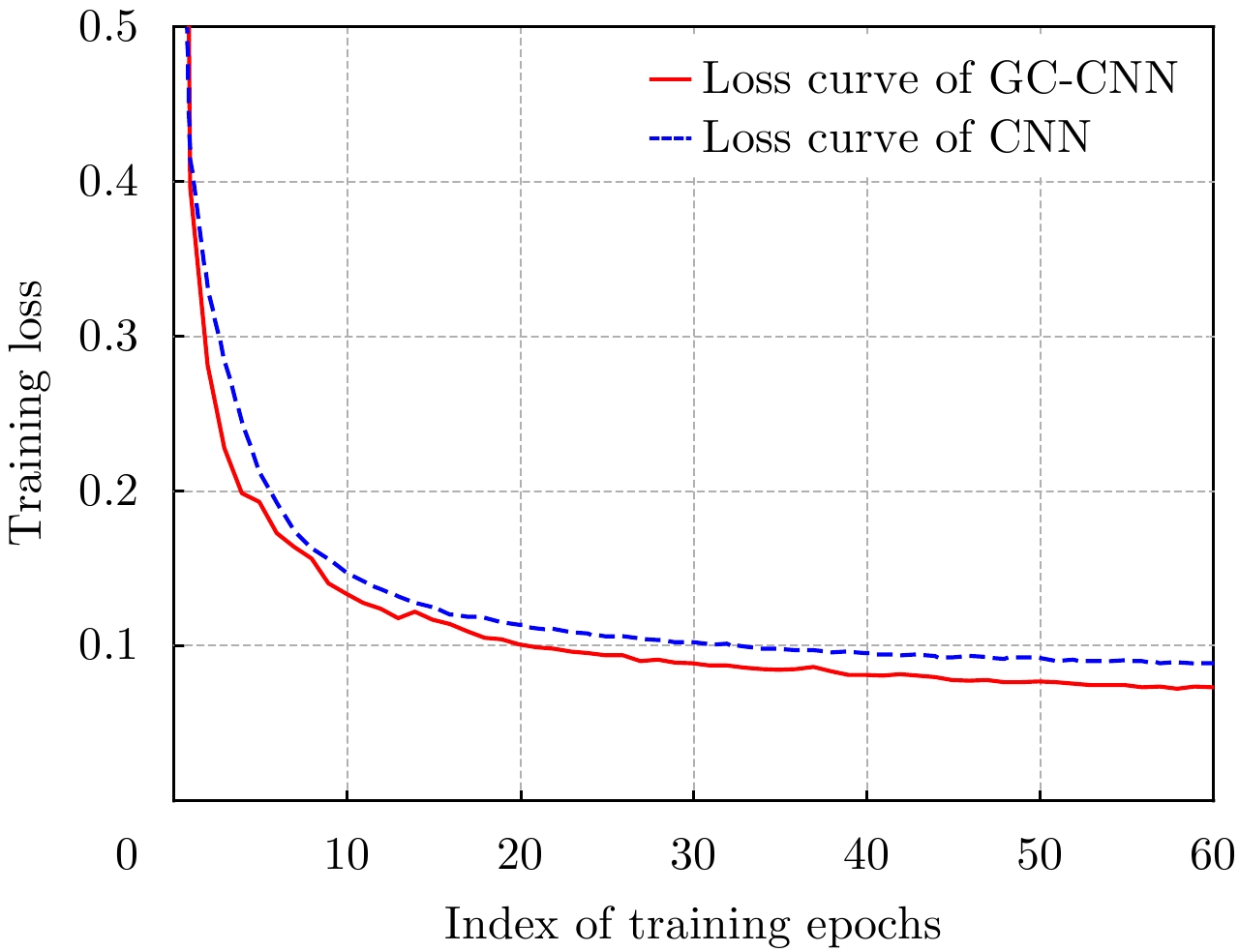
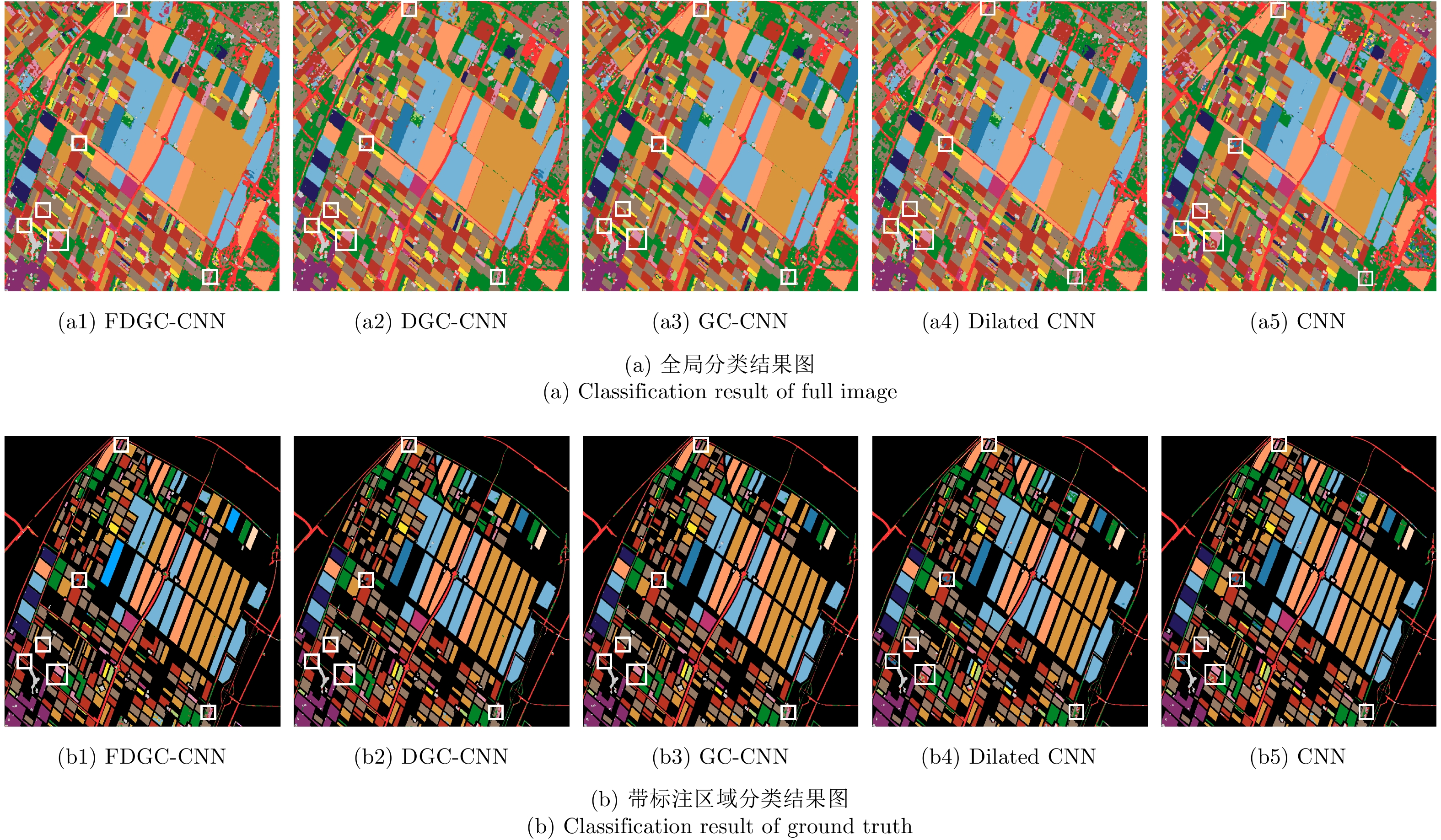
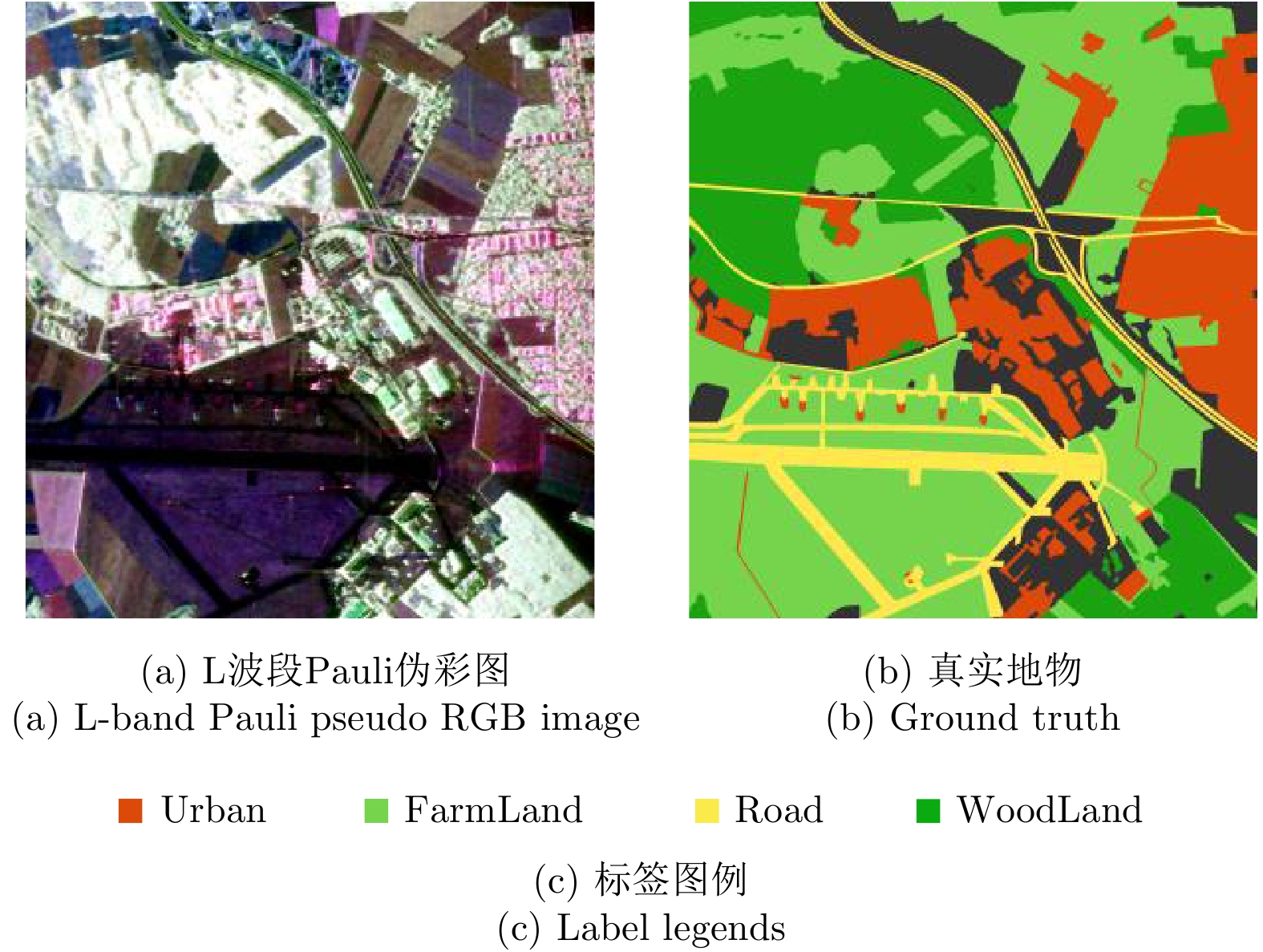
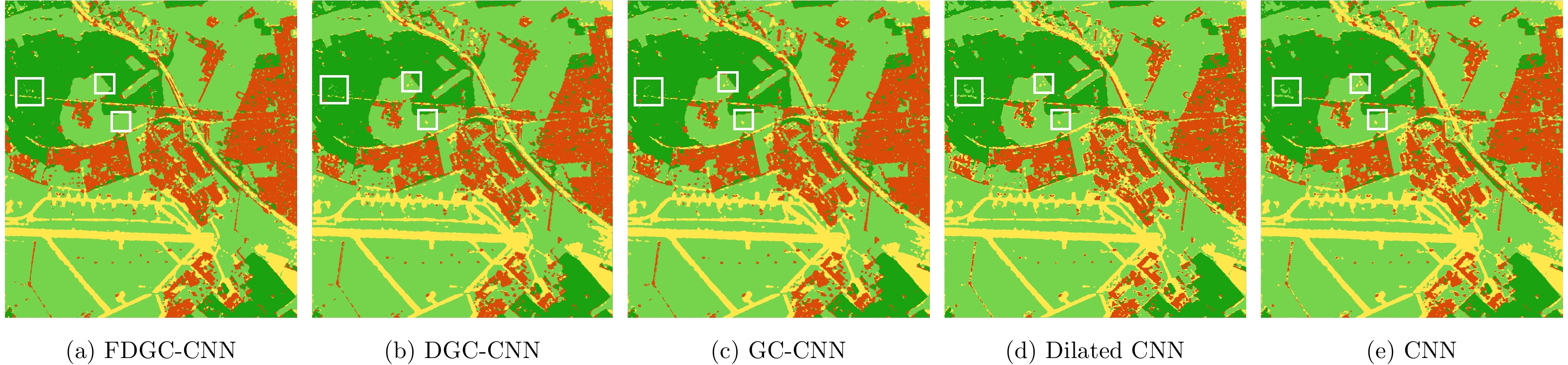
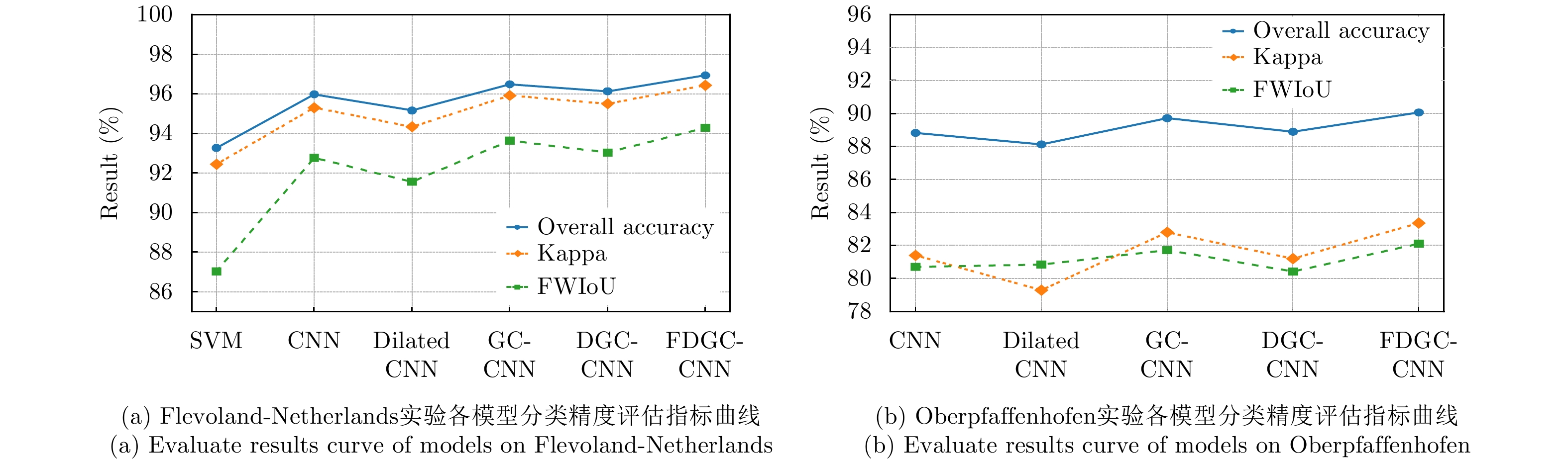
| [1] |
YANG Wen, ZHONG Neng, YANG Xiangli, et al. Rie-mannian sparse coding for classification of PolSAR images[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 2016: 5698–5701. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7730488. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Xiang, DENG Kazhong, FAN Hongdong, et al. PolSAR SVM supervised classification method combining with polarimetric target decomposition[J]. Application Re-search of Computers, 2013, 30(1): 295–298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2013.01.076 |
| [3] |
ZHANG Hongsheng, ZHANG Yuanzhi, and LIN Hui. Urban land cover mapping using random forest combined with optical and SAR data[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Munich, Germany, 2012: 6809–6812. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6352600. |
| [4] |
ZHANG Guangyun and JIA Xiuping. Simplified conditional random fields with class boundary constraint for spec-tral-spatial based remote sensing image classification[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(5): 856–860. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2186279 |
| [5] |
ZHANG Zhimian, WANG Haipeng, XU Feng, et al. Complex-valued convolutional neural network and its application in polarimetric SAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 7177–7188. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2743222 |
| [6] |
徐真, 王宇, 李宁, 等. 一种基于CNN的SAR图像变化检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 483–491. doi: 10.12000/JR17075XU Zhen, WANG R, LI Ning, et al. A novel approach to change detection in SAR images with CNN classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 483–491. doi: 10.12000/JR17075 |
| [7] |
BI Haixia, SUN Jian, and XU Zongben. A graph-based semisupervised deep learning model for PolSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(4): 2116–2132. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2871504 |
| [8] |
CHEN Siwei and TAO Chensong. PolSAR image classification using polarimetric-feature-driven deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(4): 627–631. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2799877 |
| [9] |
CHEN Siwei, TAO Chensong, WANG Xuesong, et al. PolSAR target classification using polarimetric-feature-driven deep convolutional neural network[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Valencia, Spain, 2018. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2018.8518529. |
| [10] |
KONG J A, SWARTZ A A, YUEH H A, et al. Identification of terrain cover using the optimum polarimetric classifier[J]. Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 1988, 2(2): 171–194.
|
| [11] |
LEE J S, GRUNES M R, and KWOK R. Classification of multi-look polarimetric SAR imagery based on complex Wishart distribution[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 1994, 15(11): 2299–2311. doi: 10.1080/01431169408954244 |
| [12] |
KOUSKOULAS Y, ULABY F T, and PIERCE L E. The Bayesian Hierarchical Classifier (BHC) and its application to short vegetation using multifrequency polarimetric SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(2): 469–477. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.821066 |
| [13] |
邹焕新, 罗天成, 张月, 等. 基于组合条件随机场的极化SAR图像监督地物分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(5): 541–553. doi: 10.12000/JR16109ZOU Huanxin, LUO Tiancheng, ZHANG Yue, et al. Combined conditional random fields model for supervised PolSAR images classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(5): 541–553. doi: 10.12000/JR16109 |
| [14] |
YU F and KOLTUN V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1511.07122, 2015.
|
| [15] |
LONG J, SHELHAMER E, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 2015: 3431–3440. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298965. |
| [16] |
BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, and CIPOLLA R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. arXiv preprint ar-Xiv: 1511.00561, 2015.
|
| [17] |
RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmenta-tion[C]. Proceedings of 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Inter-vention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241.
|
| [18] |
BENGIO Y, LECUN Y, NOHL C, et al. LeRec: A NN/HMM hybrid for on-line handwriting recognition[J]. Neural Computation, 1995, 7(6): 1289–1303. doi: 10.1162/neco.1995.7.6.1289 |
| [19] |
NAIR V and HINTON G E. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines[C]. Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), Haifa, Israel, 2010: 807–814.
|
| [20] |
SHANG W, SOHN K, ALMEIDA D, et al. Understanding and improving convolutional neural networks via concatenated rectified linear units[C]. International Conference on Machine Learning, 2016: 2217–2225.
|
| [21] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level per-formance on imagenet classification[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1026–1034. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.123. |
| [22] |
SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolu-tional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014.
|
| [23] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al.. Identity mappings in deep residual networks[C]. Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 630–645.
|
| [24] |
HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. |
| [25] |
HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 2261–2269. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.243 |
| [26] |
LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2999–3007. doi: 10.1109.ICCV.2017.324. |
| [27] |
HOEKMAN D H and VISSERS M A M. A new polarimetric classification approach evaluated for agricultural crops[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(12): 2881–2889. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.817795 |
| [28] |
HOU Biao, KOU Hongda, and JIAO Licheng. Classification of polarimetric SAR images using multilayer autoencoders and superpixels[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(7): 3072–3081. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2553104 |
| [29] |
GUO Yanhe, WANG Shuang, GAO Chenqiong, et al. Wishart RBM based DBN for polarimetric synthetic radar data classification[C]. 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 2015: 1841–1844. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2015.7326150. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

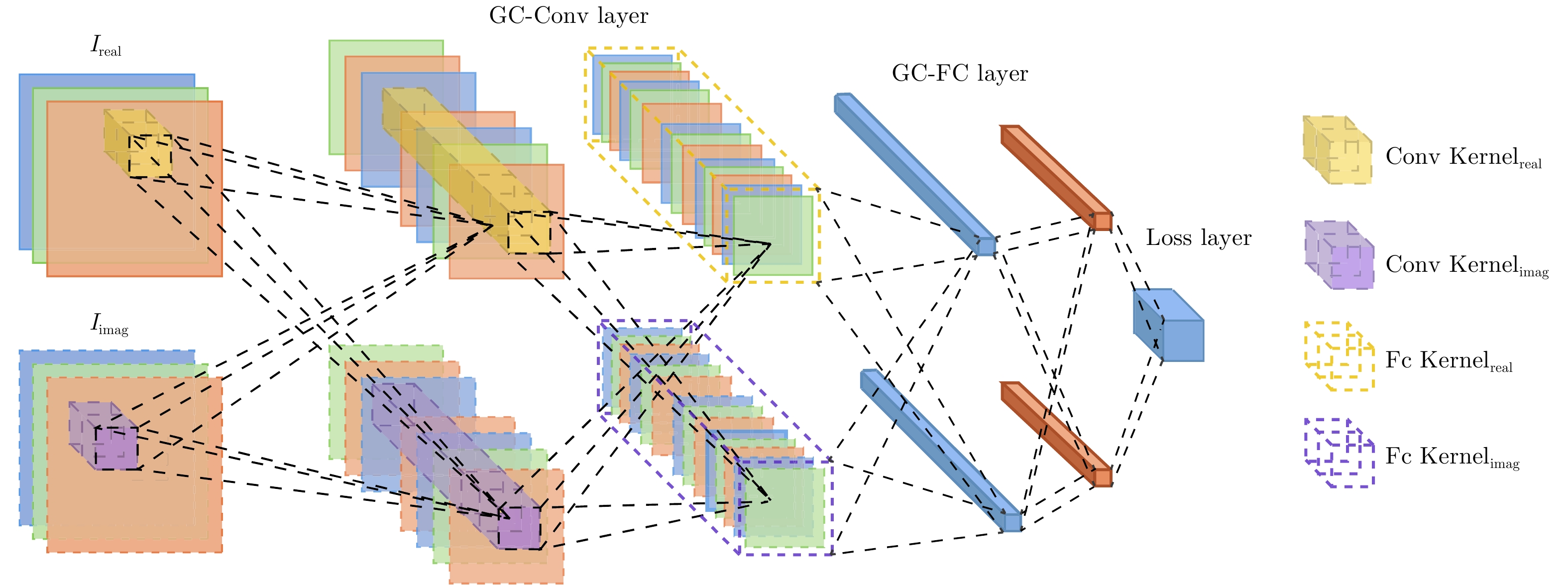



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: