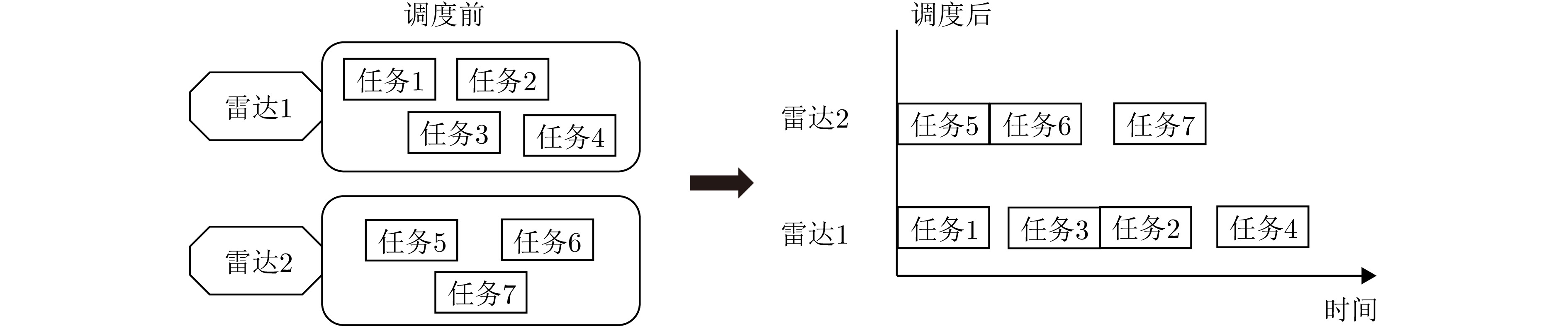
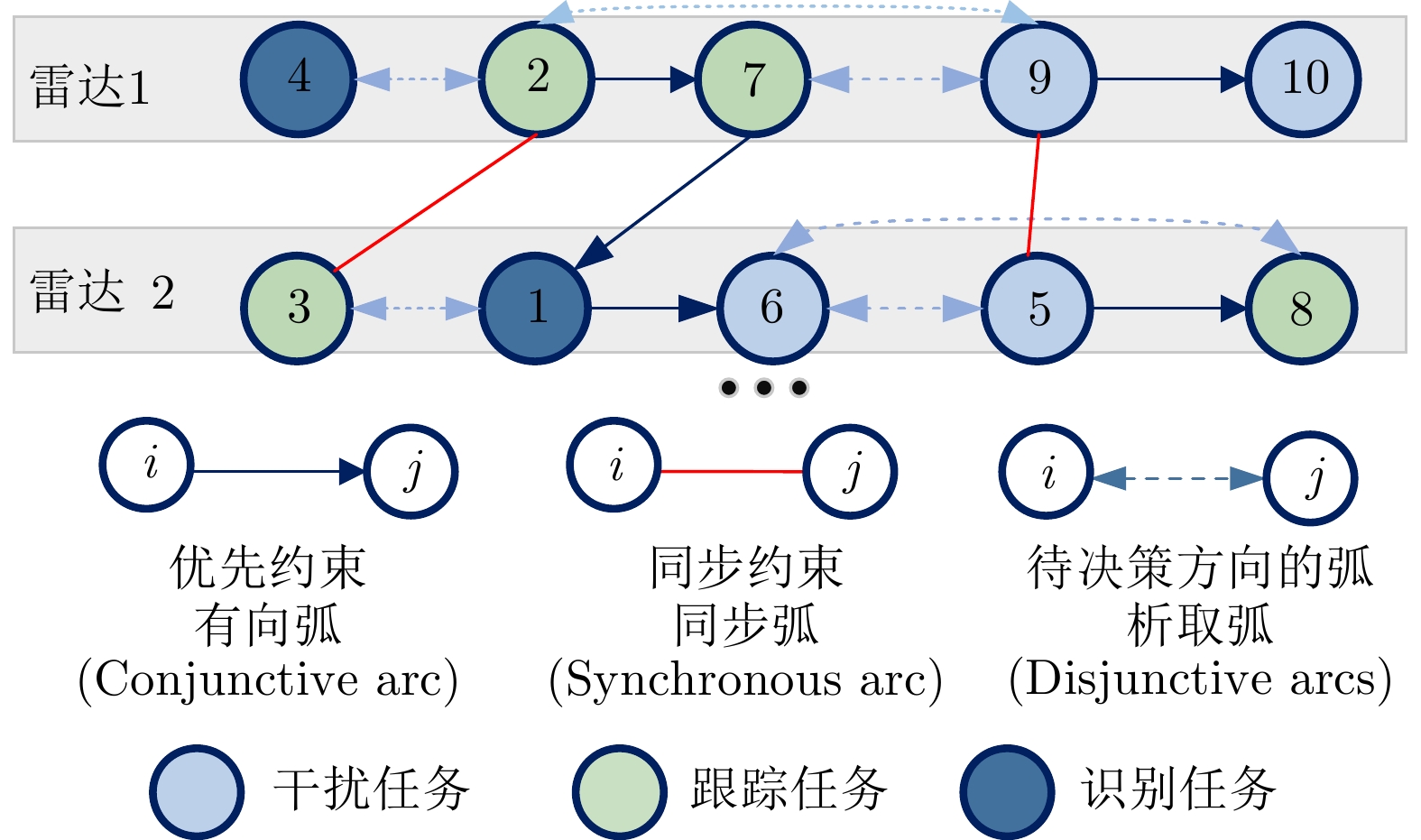
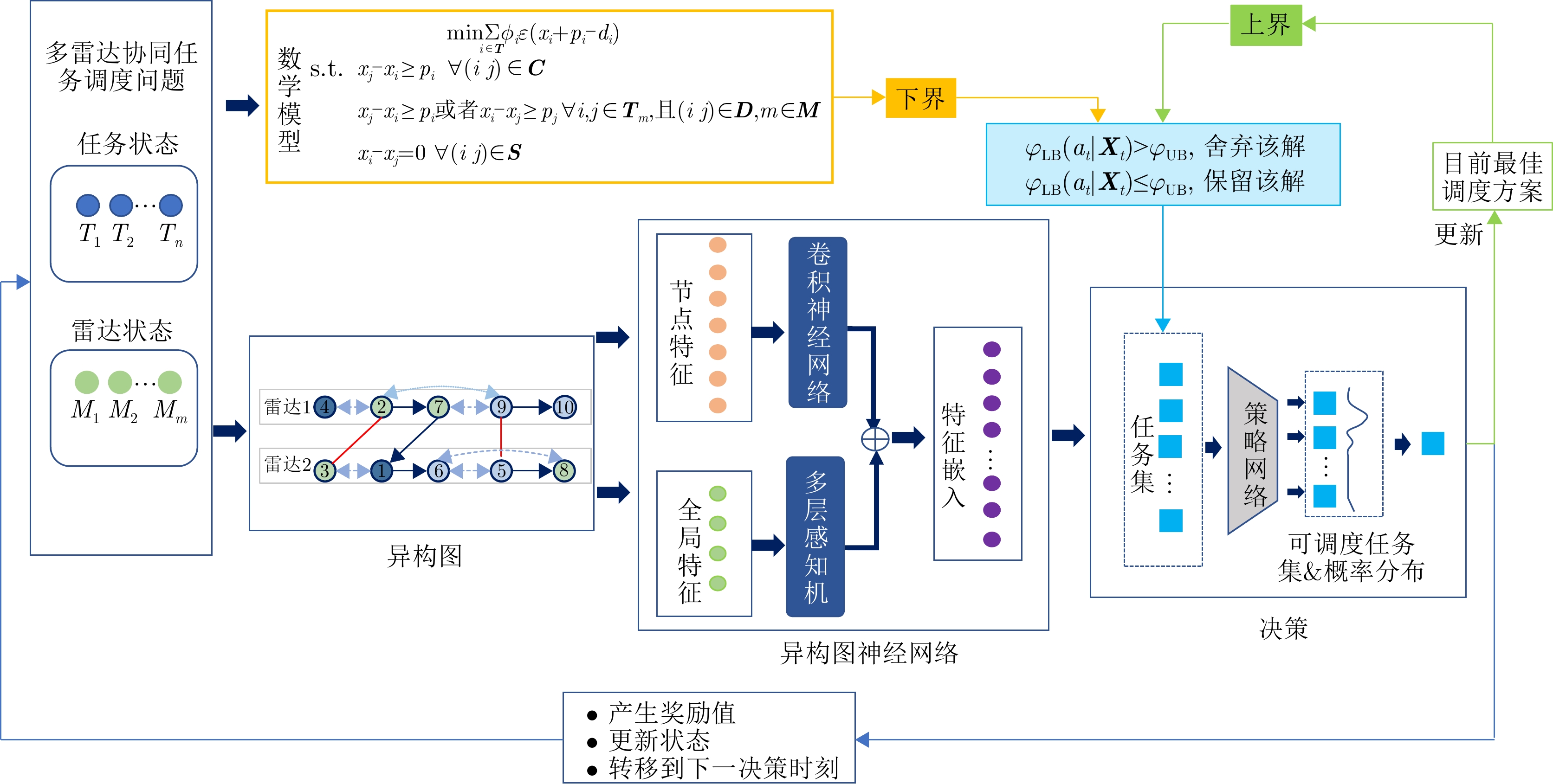
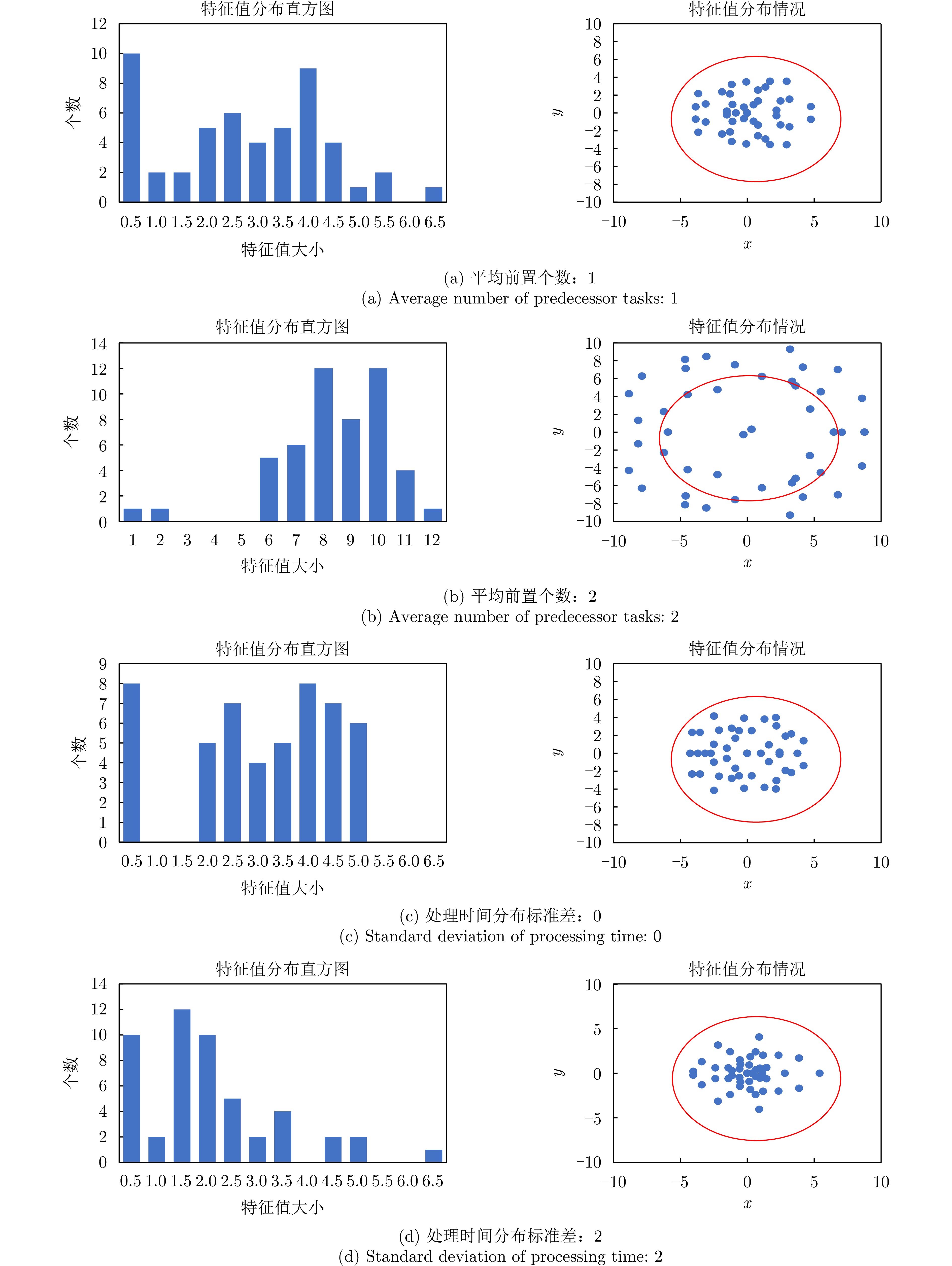
| [1] |
GU Long, TANG Jia, LUO Yun, et al. A multifunctional radar task scheduling algorithm based on multidimensional resource management[J]. Modern Radar, 2023, 45(10): 73–79. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2023.10.009. |
| [2] |
黄洁瑜, 谢军伟, 杨子晴, 等. 雷达资源管理技术发展研究综述[J/OL]. 现代雷达, 待出版. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/32.1353.tn.20231229.0910.002.
HUANG Jieyu, XIE Junwei, YANG Ziqing, et al. A review of radar resource management technology development research[J]. Modern Radar, in press. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/32.1353.tn.20231229.0910.002.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
ZHAO Jiayin and ZHAO Sifang. Design of shore based integrated electronic warfare system[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2021, 41(7): 9–11, 39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2021.07.002. |
| [5] |
LU Jianbin, HU Weidong, and YU Wenxian. Study on real-time task scheduling of multifunction phased array radars[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2006, 34(4): 732–736. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2006.04.032. |
| [6] |
DING Haiting, ZHOU Lin, and DIAO Weifeng. Knapsack problem-based algorithm for time resource management of multiple phased array radars for multiple targets tracking[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(5): 997–1003. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.05.012. |
| [7] |
易伟, 袁野, 刘光宏, 等. 多雷达协同探测技术研究进展: 认知跟踪与资源调度算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 471–499. doi: 10.12000/JR23036. YI Wei, YUAN Ye, LIU Guanghong, et al. Recent advances in multi-radar collaborative surveillance: Cognitive tracking and resource scheduling algorithms[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 471–499. doi: 10.12000/JR23036. |
| [8] |
LIU Hongwei, YAN Junkun, ZHANG Peng, et al. A multi-task oriented resource management method for phased array radar[J]. Modern Radar, 2023, 45(6): 8–16. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2023.06.002. |
| [9] |
JEFFAY K, STANAT D F, and MARTEL C U. On non-preemptive scheduling of period and sporadic tasks[C]. Proceedings Twelfth Real-Time Systems Symposium, San Antonio, TX, USA, 1991: 129–139. doi: 10.1109/REAL.1991.160366. |
| [10] |
WEI Gang, LIU Changyun, and GUO Xiangke. Algorithms of search mission planning in phased array radar based on multi-attribute decision[J]. Modern Radar, 2016, 38(10): 42–46. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2016.10.011. |
| [11] |
ZHU Xitong, YANG Ruijuan, LI Xiaobai, et al. A multifunctional sky-wave over-the-horizon radar task planning and scheduling method[J]. Ship Electronic Engineering, 2022, 42(2): 75–80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9730.2022.02.016. |
| [12] |
程婷, 恒思宇, 李中柱. 基于脉冲交错的分布式雷达组网系统波束驻留调度[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 616–628. doi: 10.12000/JR22211. CHENG Ting, HENG Siyu, and LI Zhongzhu. Real-time dwell scheduling algorithm for distributed phased array radar network based on pulse interleaving[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 616–628. doi: 10.12000/JR22211. |
| [13] |
DUAN Yi, TAN Xiansi, QU Zhiguo, et al. Phased array radar task scheduling algorithm based on branch and bound method[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(6): 1309–1315. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.06.018. |
| [14] |
袁野, 杨剑, 刘辛雨, 等. 基于任务效用最大化的多雷达协同任务规划算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 550–562. doi: 10.12000/JR23013. YUAN Ye, YANG Jian, LIU Xinyu, et al. Multiradar collaborative task planning based ontask utility maximization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 550–562. doi: 10.12000/JR23013. |
| [15] |
时晨光, 董璟, 周建江. 频谱共存下面向多目标跟踪的组网雷达功率时间联合优化算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 590–601. doi: 10.12000/JR22146. SHI Chenguang, DONG Jing, and ZHOU Jianjiang. Joint transmit power and dwell time allocation for multitarget tracking in radar networks under spectral coexistence[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 590–601. doi: 10.12000/JR22146. |
| [16] |
宋晓程, 李陟, 任海伟, 等. 目标动态威胁度驱动的分布式组网相控阵雷达资源优化分配算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 629–641. doi: 10.12000/JR22240. SONG Xiaocheng, LI Zhi, REN Haiwei, et al. Target-driven resource allocation algorithm for distributed netted phased array radars[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 629–641. doi: 10.12000/JR22240. |
| [17] |
ZHAO Yu, LI Jianxun, CAO Lanying, et al. Adaptive scheduling algorithm based on quadratic programming for multifunction phased array radars[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2012, 34(4): 698–703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2012.04.11. |
| [18] |
ZHANG Haowei, XIE Junwei, GE Jiaang, et al. Optimization model and online task interleaving scheduling algorithm for MIMO radar[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2018, 127: 865–874. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2018.11.024. |
| [19] |
ZHANG Haowei, XIE Junwei, HU Qiyong, et al. A hybrid DPSO with Levy flight for scheduling MIMO radar tasks[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 71: 242–254. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.06.028. |
| [20] |
ZHANG Haowei, XIE Junwei, HU Qiyong, et al. An entropy-based PSO for DAR task scheduling problem[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 73: 862–873. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.09.022. |
| [21] |
LI Jisan, JI Yanxing, CAO Ding, et al. Resource scheduling algorithm of rotating phased array radar based on generalized time window[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(5): 1050–1057. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210414. |
| [22] |
WANG Gaige, GAO Da, and PEDRYCZ W. Solving multiobjective fuzzy job-shop scheduling problem by a hybrid adaptive differential evolution algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(12): 8519–8528. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3165636. |
| [23] |
TIAN Tuanwei, ZHANG Tianxian, and KONG Lingjiang. Timeliness constrained task scheduling for multifunction radar network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(2): 525–534. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2878795. |
| [24] |
PARK Y and BASKIYAR S. Adaptive scheduling on heterogeneous systems using support vector machine[J]. Computing, 2017, 99(4): 405–425. doi: 10.1007/s00607-016-0513-x. |
| [25] |
GUPTA J N D, MAJUMDER A, and LAHA D. Flowshop scheduling with artificial neural networks[J]. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 2020, 71(10): 1619–1637. doi: 10.1080/01605682.2019.1621220. |
| [26] |
SHAGHAGHI M and ADVE R S. Machine learning based cognitive radar resource management[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference, Oklahoma City, 2018: 1433–1438. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2018.8378775. |
| [27] |
SONG Wen, CHEN Xinyang, LI Qiqiang, et al. Flexible job-shop scheduling via graph neural network and deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(2): 1600–1610. doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3189725. |
| [28] |
ANSOLA P G, HIGUERA A G, OTAMENDI F J, et al. Agent-based distributed control for improving complex resource scheduling: Application to airport ground handling operations[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2014, 8(4): 1145–1157. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2013.2272248. |
| [29] |
QU Zhen, DING Zhen, and MOO P. A machine learning task selection method for radar resource management (poster)[C]. 2019 22th International Conference on Information Fusion, Ottawa, Canada, 2019: 1–6. doi: 10.23919/FUSION43075.2019.9011342. |
| [30] |
ZHOU Longfei, ZHANG Lin, and HORN B K P. Deep reinforcement learning-based dynamic scheduling in smart manufacturing[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2020, 93: 383–388. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2020.05.163. |
| [31] |
王跃东, 顾以静, 梁彦, 等. 伴随压制干扰与组网雷达功率分配的深度博弈研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 642–656. doi: 10.12000/JR23023. WANG Yuedong, GU Yijing, LIANG Yan, et al. Deep game of escorting suppressive jamming and networked radar power allocation[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 642–656. doi: 10.12000/JR23023. |
| [32] |
KUO Teiwei, CHAO Yungsheng, KUO Chinfu, et al. Real-time dwell scheduling of component-oriented phased array radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2005, 54(1): 47–60. doi: 10.1109/TC.2005.10. |
| [33] |
MIR H S and GUITOUNI A. Variable dwell time task scheduling for multifunction radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2014, 11(2): 463–472. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2013.2285014. |
| [34] |
PINEDO M L. Scheduling: Theory, Algorithms, and Systems[M]. New York: Springer Publishing Company, 2008: 179–182.
|
| [35] |
BURAK C. Non-Hermitian random matrix theory for MIMO channels[D]. [Master dissertation], Norwegian University of Science and Technology, 2012: 18–20.
|
| [36] |
KRUZICK S and MOURA J M F. Optimal filter design for signal processing on random graphs: Accelerated consensus[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(5): 1258–1272. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2784359. |
| [37] |
SHI Xin and QIU R. Power system real-time operation situation assessment based on random matrix theory[C]. 2020 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting, Montreal, QC, 2020: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/PESGM41954.2020.9281475. |
| [38] |
PETERS T. Data-driven science and engineering: Machine learning, dynamical systems, and control[J]. Contemporary Physics, 2019, 60(4): 320. doi: 10.1080/00107514.2019.1665103. |
| [39] |
WANG Zekun, CHEN Hongjia, TENG Zhongming, et al. On perturbations for spectrum and singular value decompositions followed by deflation techniques[J]. Applied Mathematics Letters, 2025, 160: 109332. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2024.109332. |
| [40] |
ZHOU Jie, CUI Ganqu, HU Shengding, et al. Graph neural networks: A review of methods and applications[J]. AI Open, 2020, 1: 57–81. doi: 10.1016/j.aiopen.2021.01.001. |
| [41] |
SHORT M. Improved schedulability analysis of implicit deadline tasks under limited preemption EDF scheduling[C]. ETFA2011, Toulouse, France, 2011: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/ETFA.2011.6059008. |
| [42] |
LIU C L and LAYLAND J W. Scheduling algorithms for multiprogramming in a hard-real-time environment[J]. Journal of the ACM (JACM), 1973, 20(1): 46–61. doi: 10.1145/321738.321743. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: