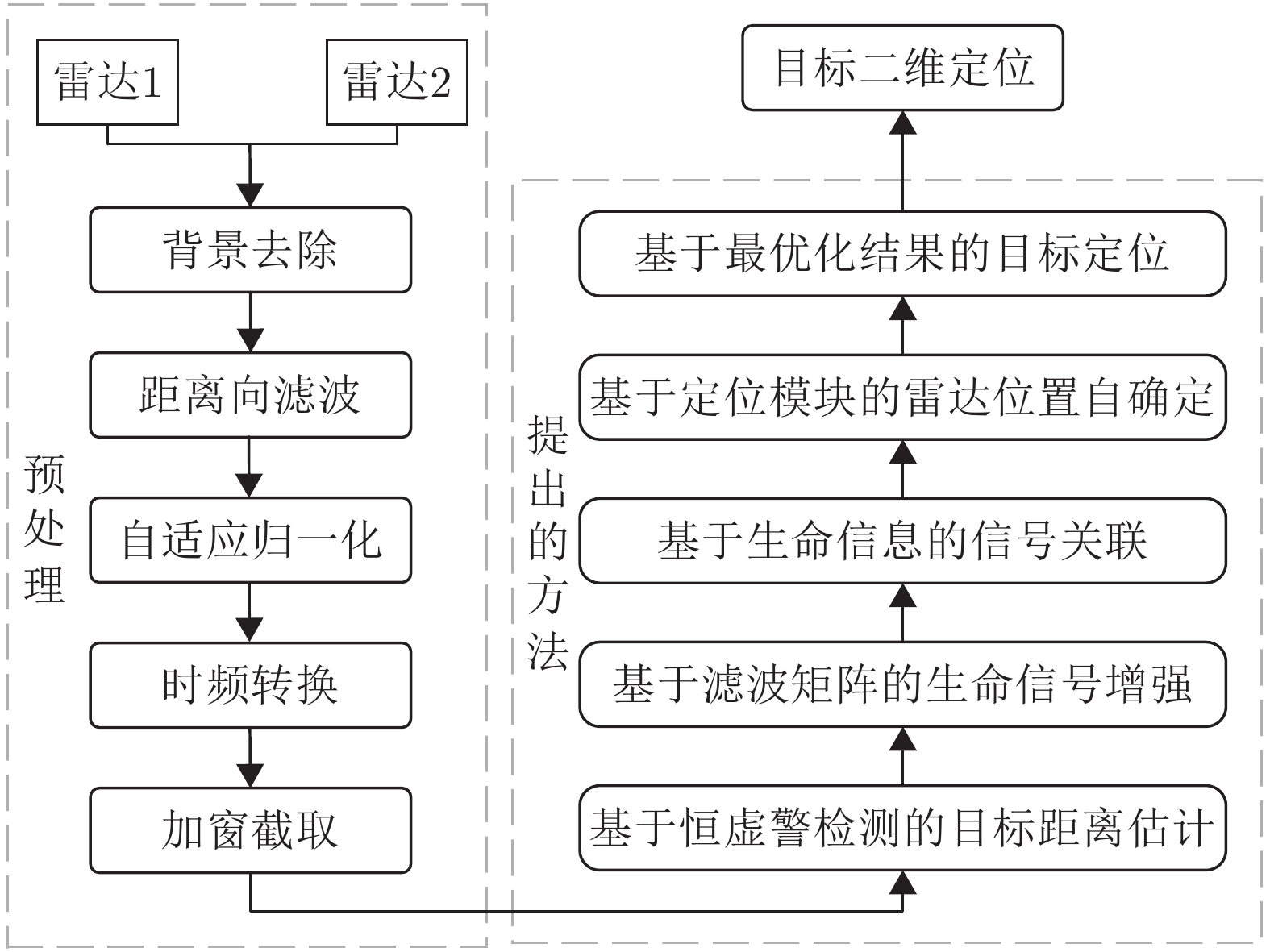
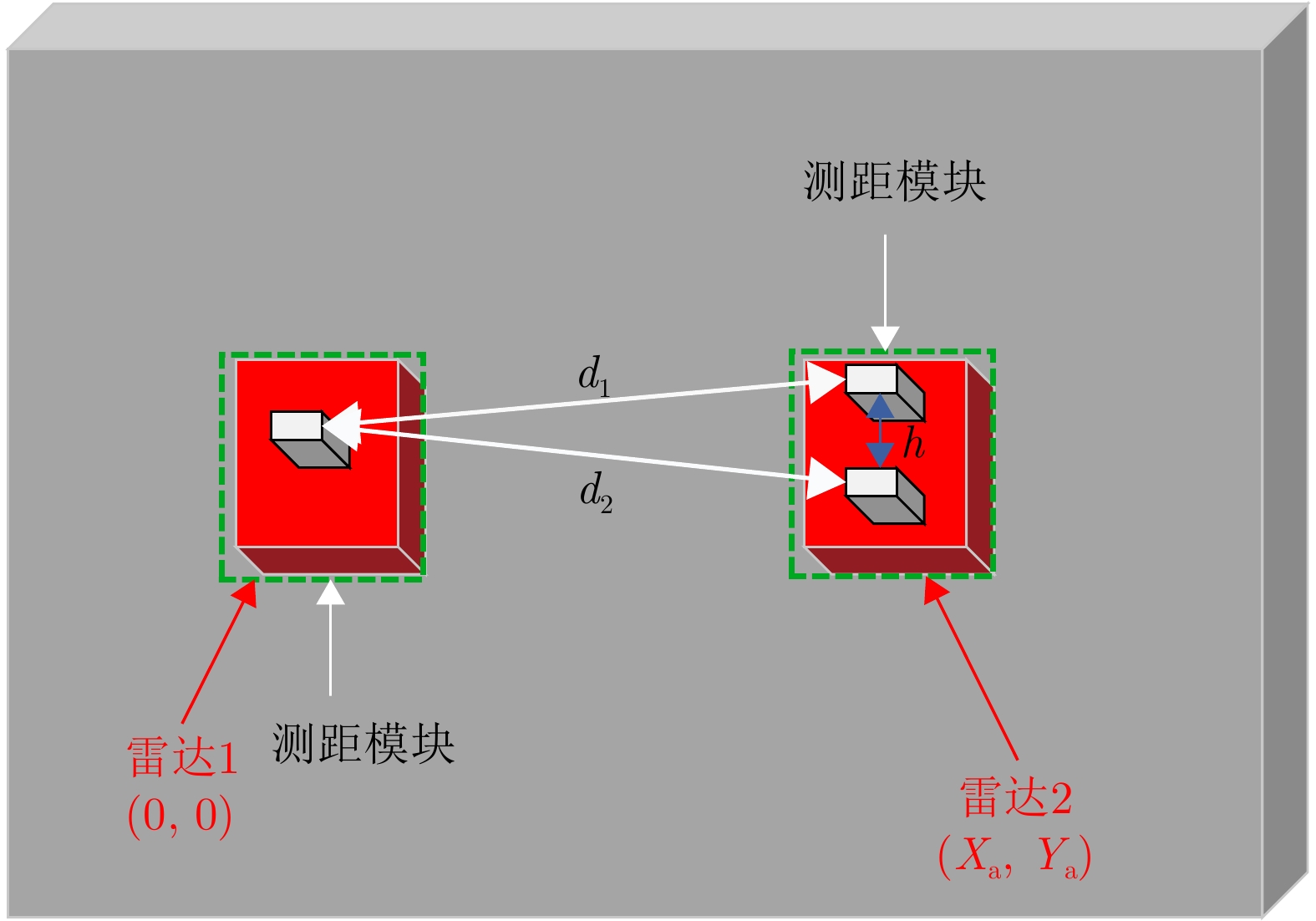
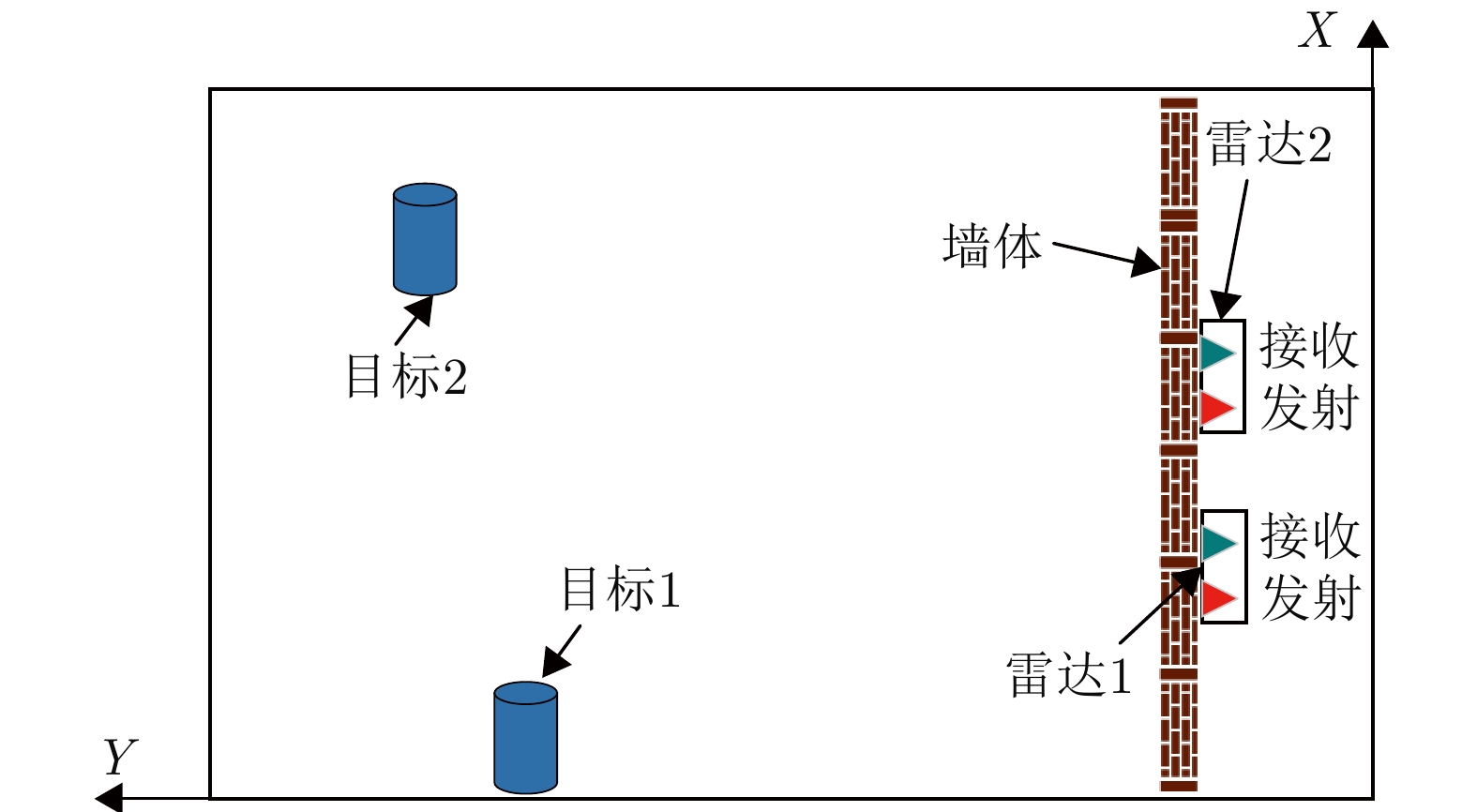
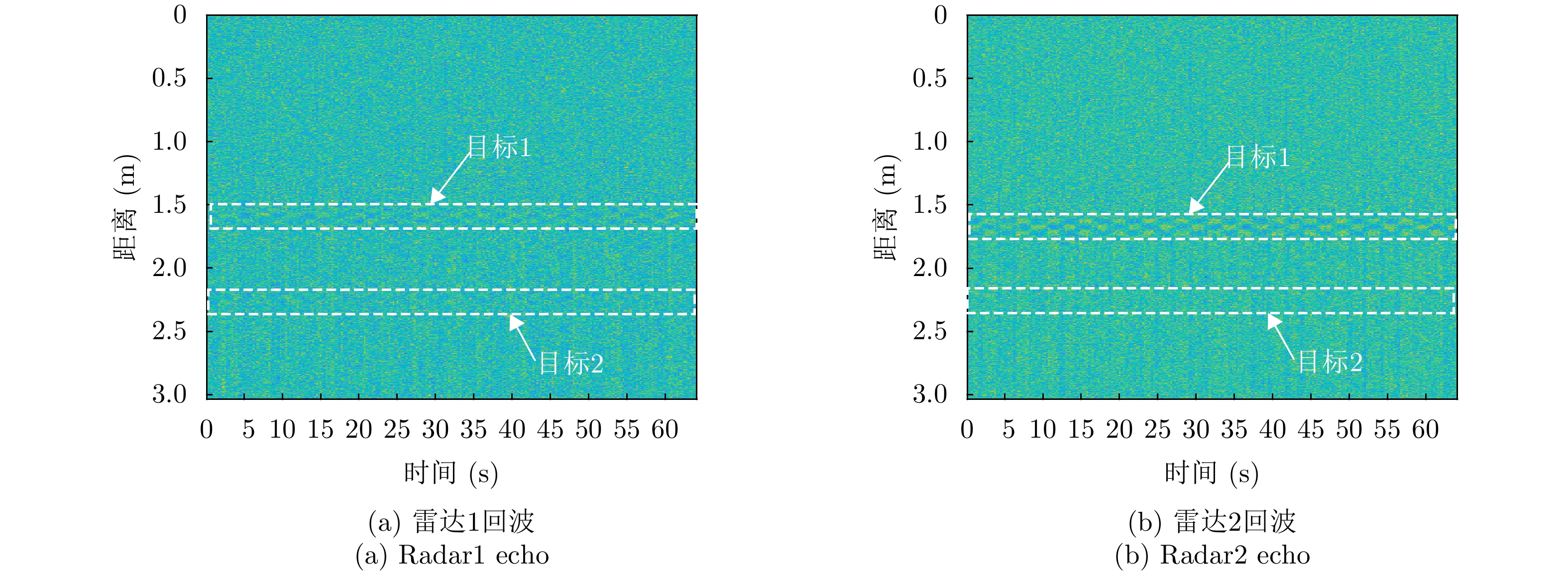
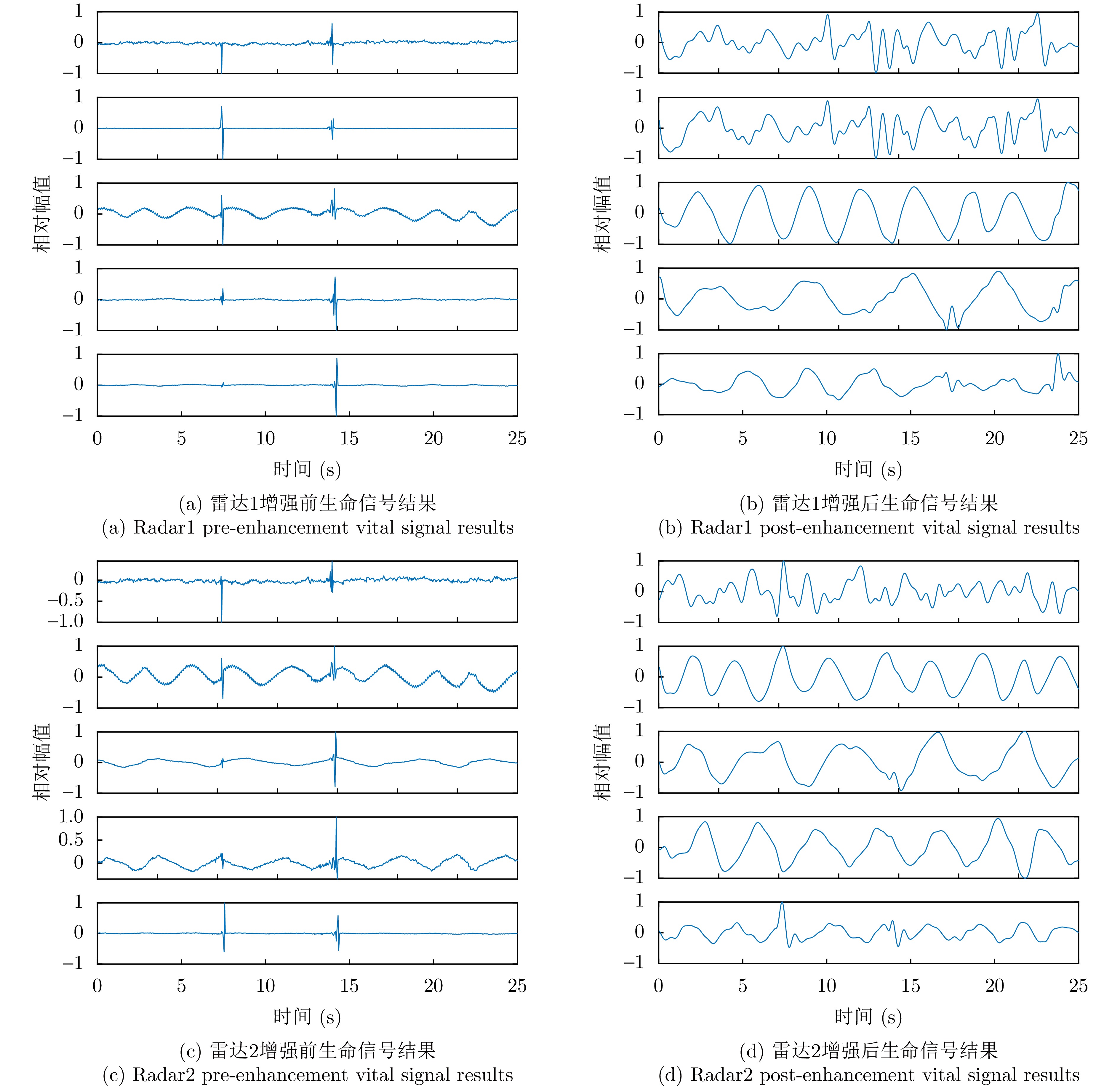
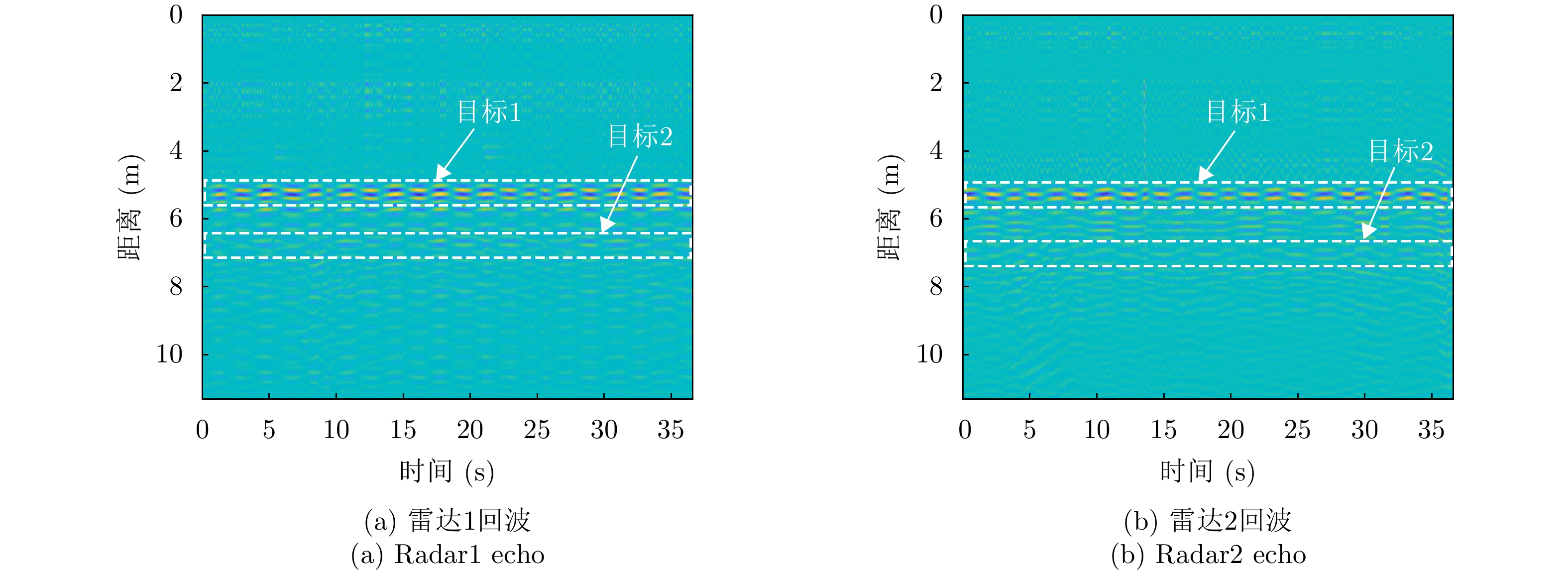
| [1] |
杨望笑, 窦银科, 稂时楠, 等. 基于改进剥层法的南极冰盖密度反演算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1311–1317. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210410. YANG Wangxiao, DOU Yinke, LANG Shinan, et al. Antarctic ice sheet density inversion algorithm based on improved layer stripping method[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1311–1317. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210410. |
| [2] |
JIN Tian and SONG Yongping. Review on human target detection using through-wall radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2020, 35(4): 486–495. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020040804. |
| [3] |
刘新, 阎焜, 杨光耀, 等. UWB-MIMO穿墙雷达三维成像与运动补偿算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2253–2260. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190356. LIU Xin, YAN Kun, YANG Guangyao, et al. Study on 3D imaging and motion compensation algorithm for UWB-MIMO through-wall radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2253–2260. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190356. |
| [4] |
YAN Kun, WU Shiyou, and FANG Guangyou. Detection of quasi-static trapped human being using mono-static UWB life-detection radar[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(7): 3129. doi: 10.3390/app11073129. |
| [5] |
LIANG Xiao, PAN Jun, ZHENG Zhijie, et al. Enhancement of vital signals for UWB through-wall radar using nonconvex regularization[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 14(4): 392–401. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2023.2204197. |
| [6] |
HARIKESH, CHAUHAN S S, BASU A, et al. Through the wall human subject localization and respiration rate detection using multichannel Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(2): 1510–1518. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3016755. |
| [7] |
PAN Jun, YE Shengbo, NI Zhikang, et al. Enhancement of vital signals based on low-rank, sparse representation for UWB through-wall radar[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 13(1): 98–106. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2021.1995069. |
| [8] |
ROHMAN B P A, ANDRA M B, and NISHIMOTO M. Through-the-wall human respiration detection using UWB impulse radar on hovering drone[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 6572–6584. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3087668. |
| [9] |
XU Yanyun, DAI Shun, WU Shiyou, et al. Vital sign detection method based on multiple higher order cumulant for Ultrawideband radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(4): 1254–1265. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2164928. |
| [10] |
刘新, 朱海滨, 刘宗强, 等. 分布式无线组网超宽带穿墙雷达系统设计与联合定位[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(4): 747–760. doi: 10.12000/JR23239. LIU Xin, ZHU Haibin, LIU Zongqiang, et al. The design and joint positioning method of an ultra-wideband through-wall radar system for distributed wireless networking[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(4): 747–760. doi: 10.12000/JR23239. |
| [11] |
史城, 叶盛波, 潘俊, 等. 一种基于分布式穿墙雷达的复杂条件下人体目标检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1193–1202. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211203. SHI Cheng, YE Shengbo, PAN Jun, et al. A human target detection method under complex conditions by distributed through-wall radar system[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1193–1202. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211203. |
| [12] |
ZHANG Yang, CHEN Fuming, XUE Huijun, et al. Detection and identification of multiple stationary human targets via bio-radar based on the cross-correlation method[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(11): 1793. doi: 10.3390/s16111793. |
| [13] |
KOCUR D, ŠVECOVÁ M, and ROVŇÁKOVÁ J. Through-the-wall localization of a moving target by two independent ultra wideband (UWB) radar systems[J]. Sensors, 2013, 13(9): 11969–11997. doi: 10.3390/s130911969. |
| [14] |
JIA Yong, GUO Yong, YAN Chao, et al. Detection and localization for multiple stationary human targets based on cross-correlation of dual-station SFCW radars[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(12): 1428. doi: 10.3390/rs11121428. |
| [15] |
NAHAR S, PHAN T, QUAIYUM F, et al. An electromagnetic model of human vital signs detection and its experimental validation[J]. IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, 2018, 8(2): 338–349. doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2018.2811339. |
| [16] |
ZETIK R, CRABBE S, KRAJNAK J, et al. Detection and localization of persons behind obstacles using M-sequence through-the-wall radar[C]. Conference on Sensors, and Command, Control, Communications, and Intelligence, Orlando (Kissimmee), USA, 2006: 62010I. doi: 10.1117/12.667989. |
| [17] |
XU Yanyun, WU Shiyou, CHEN Chao, et al. A novel method for automatic detection of trapped victims by ultrawideband radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(8): 3132–3142. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2178248. |
| [18] |
XIAO Qiang, ZENG Qingning, WANG Yao, et al. Speech enhancement of microphone array based on MGSC and improved Wiener filter[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2017, 36(6): 567–573. doi: 10.16300/j.cnki.1000-3630.2017.06.012. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

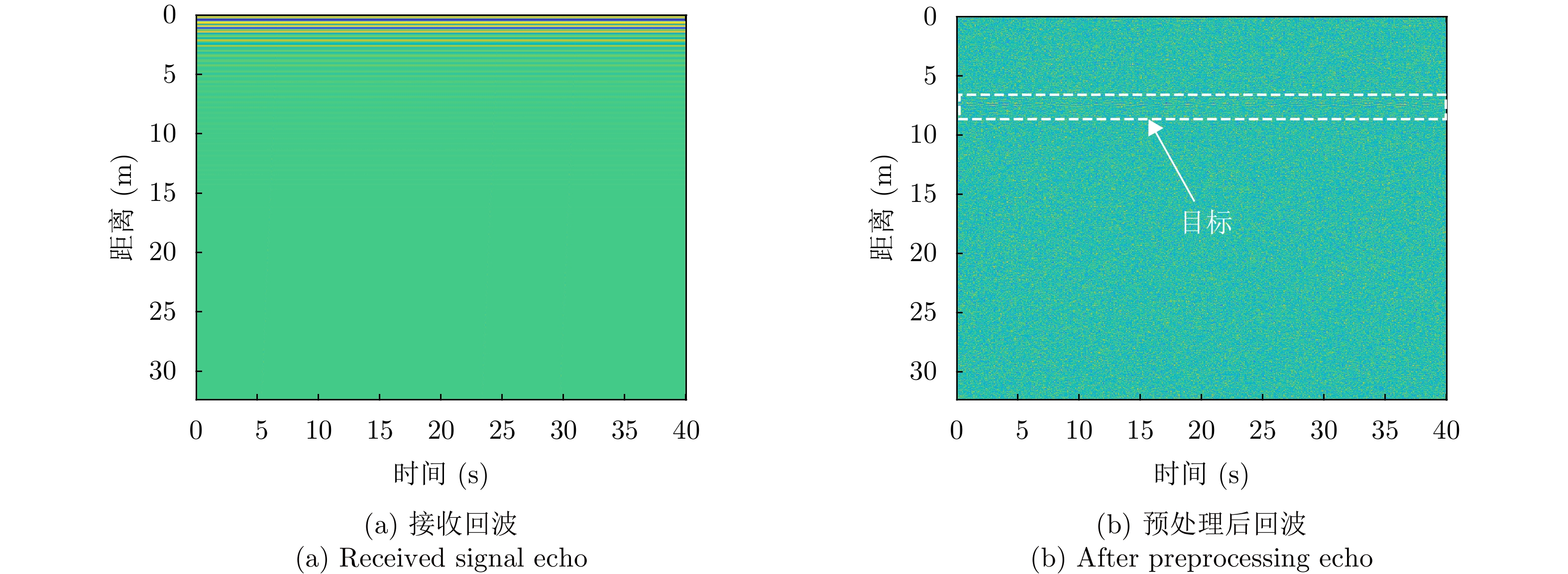



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: