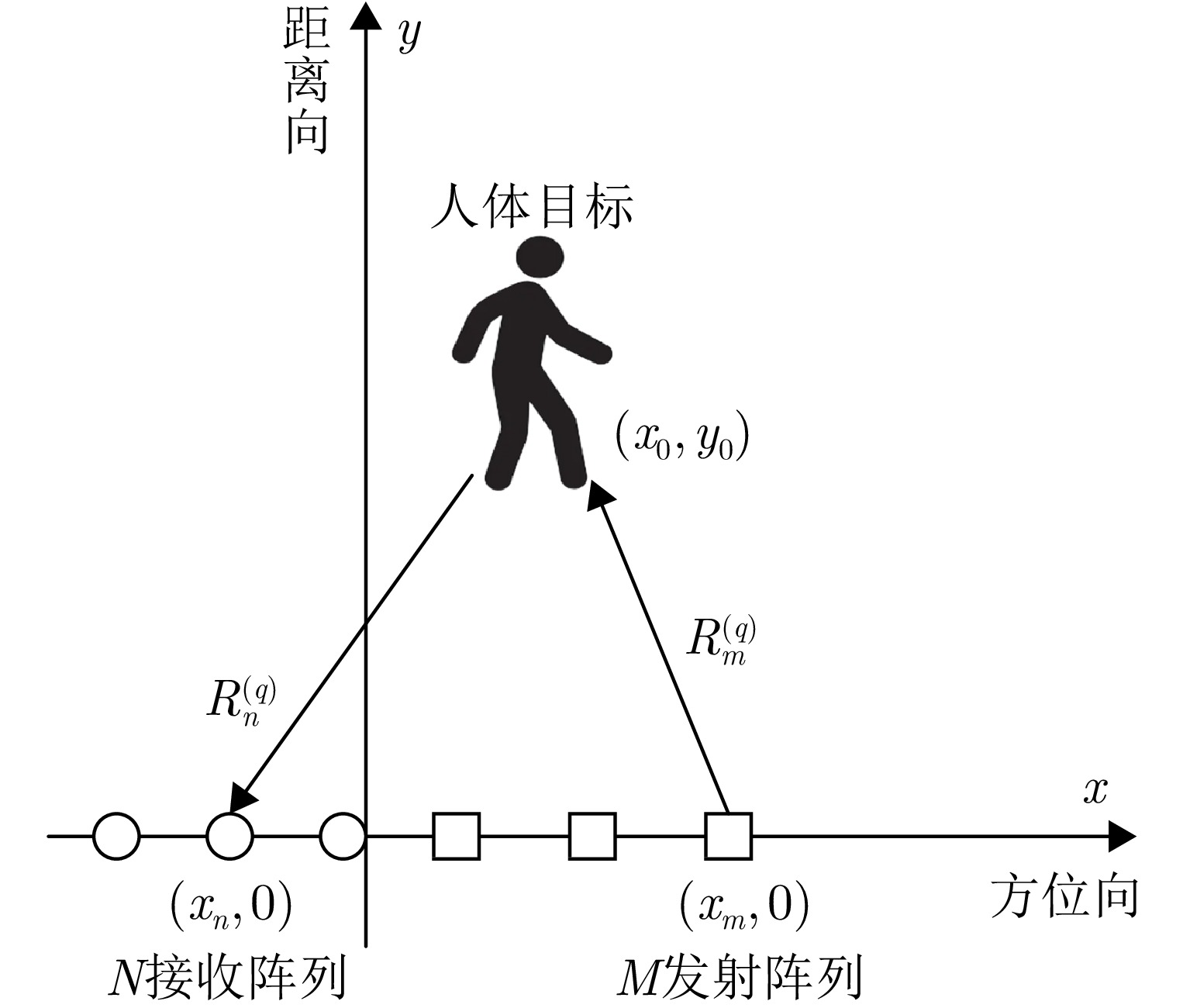
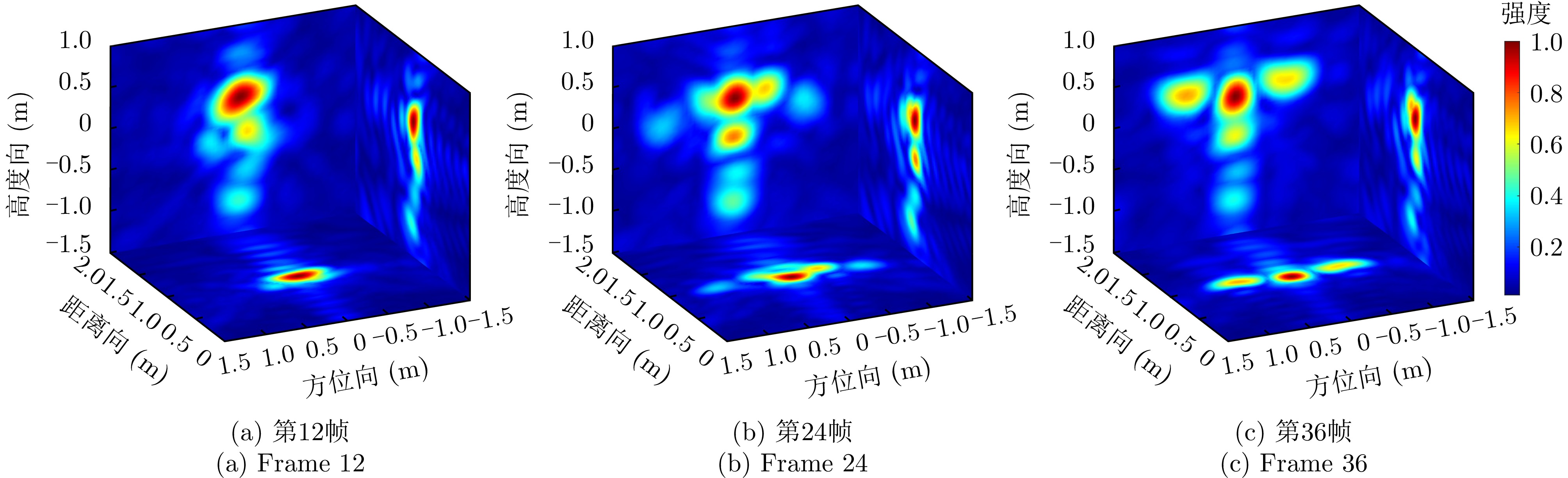
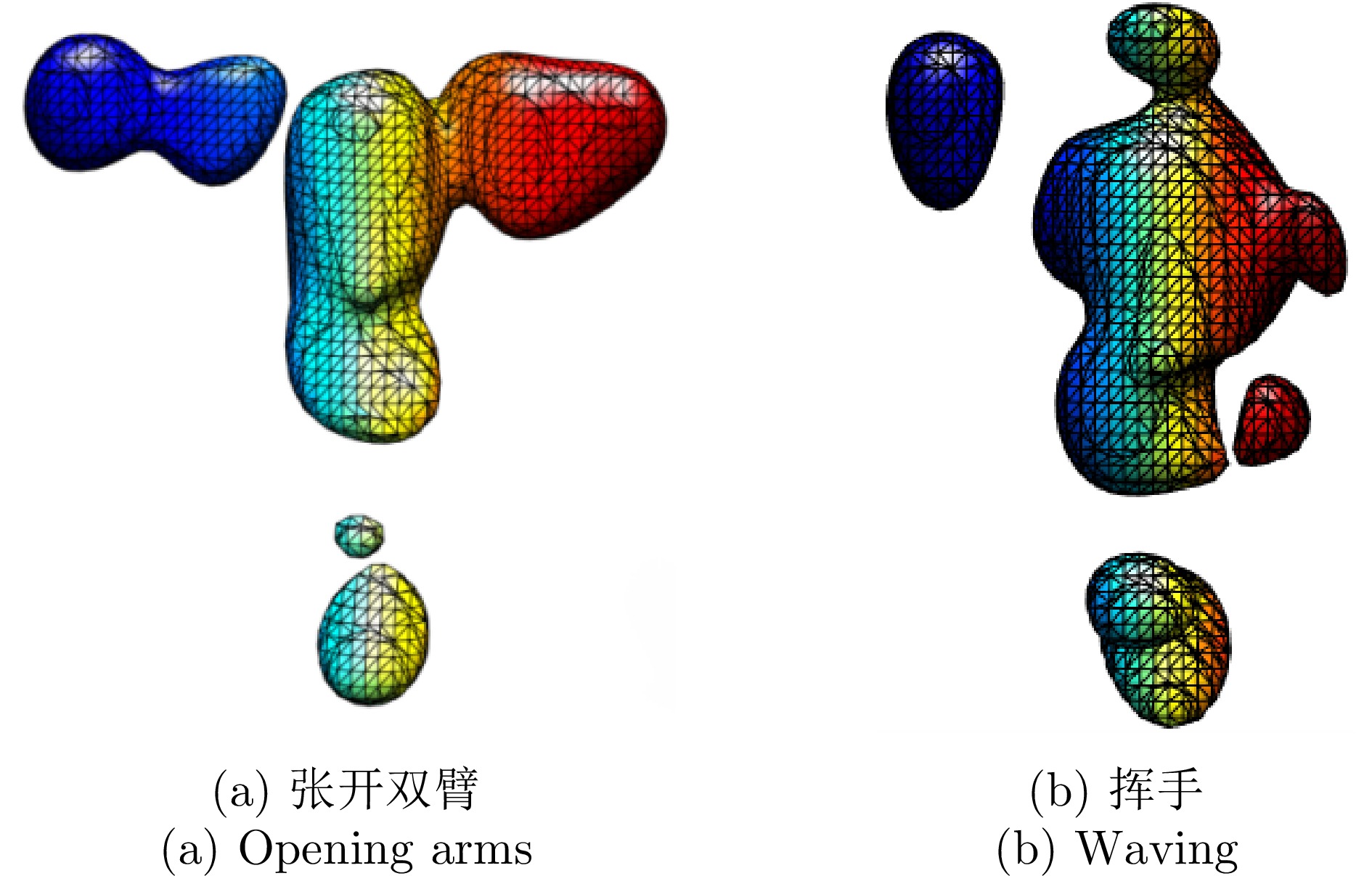
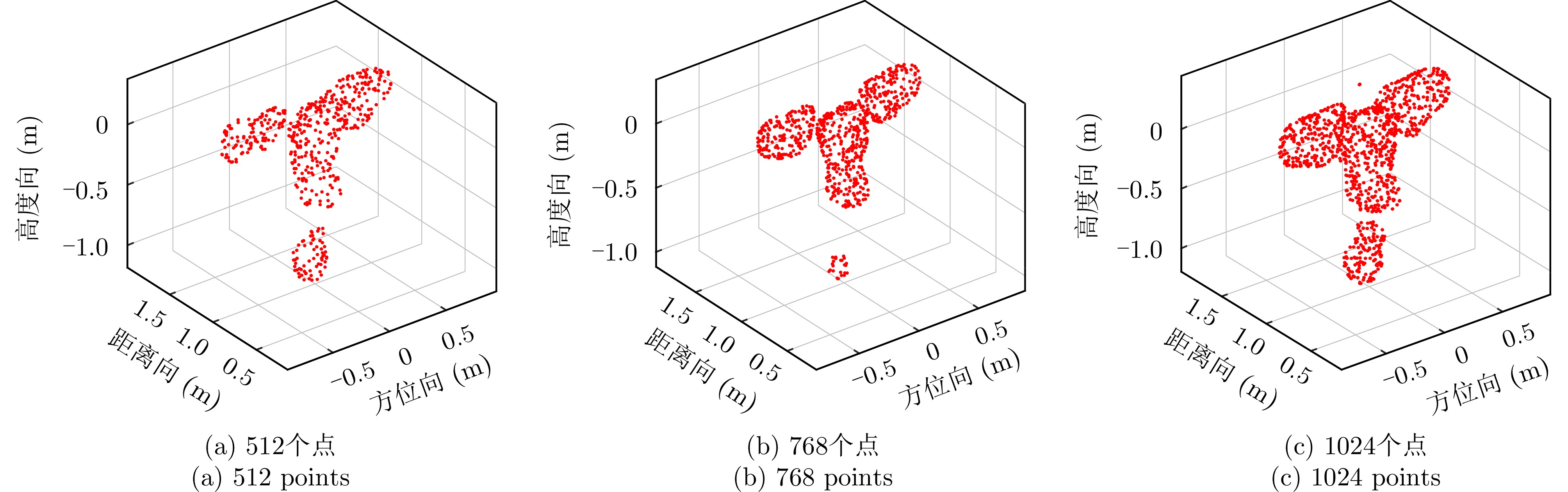
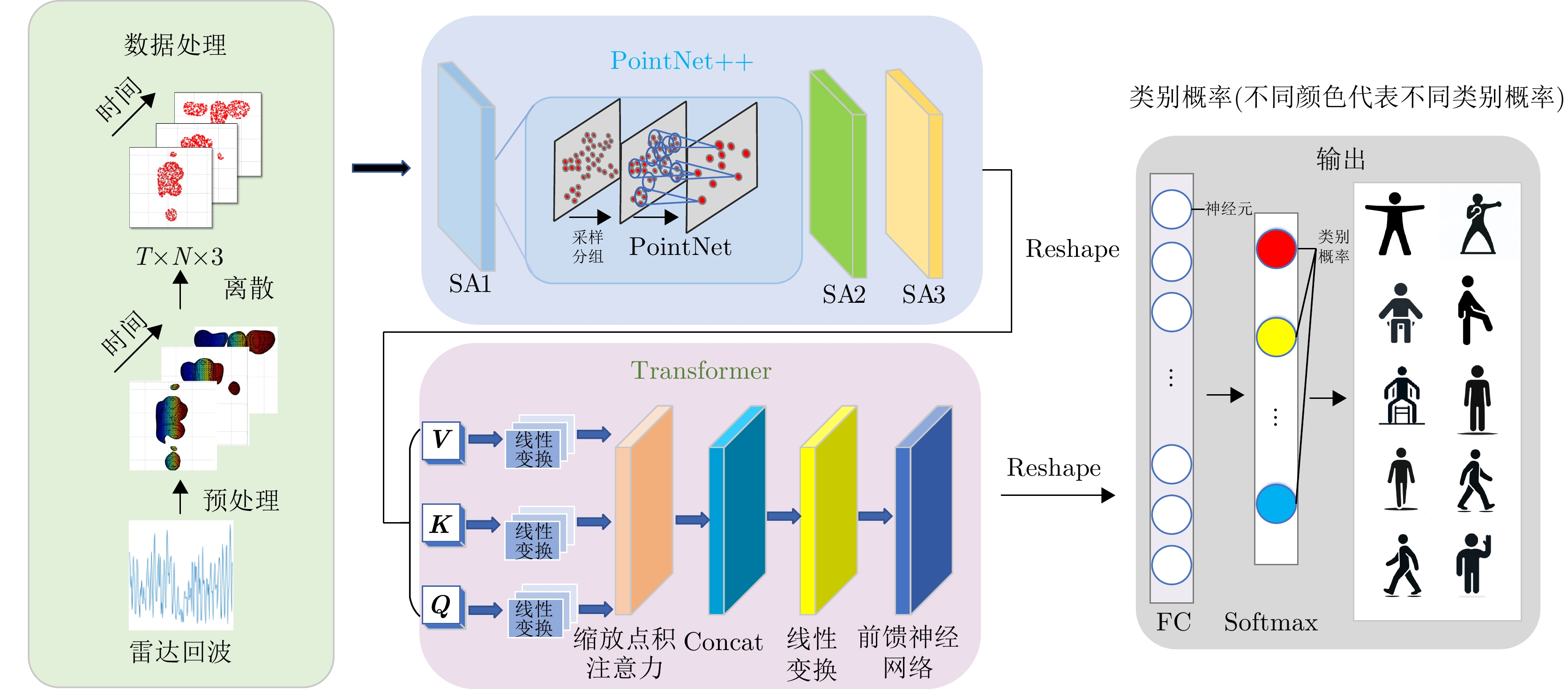
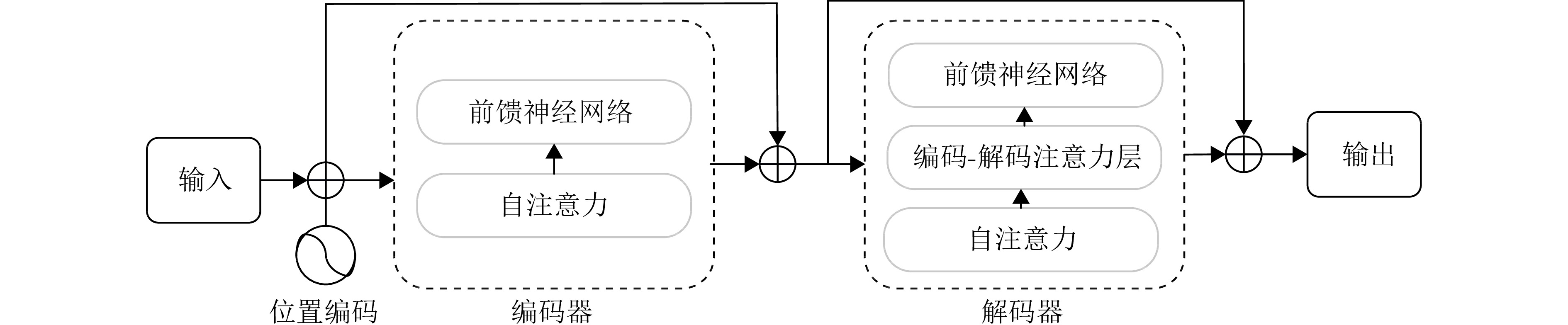
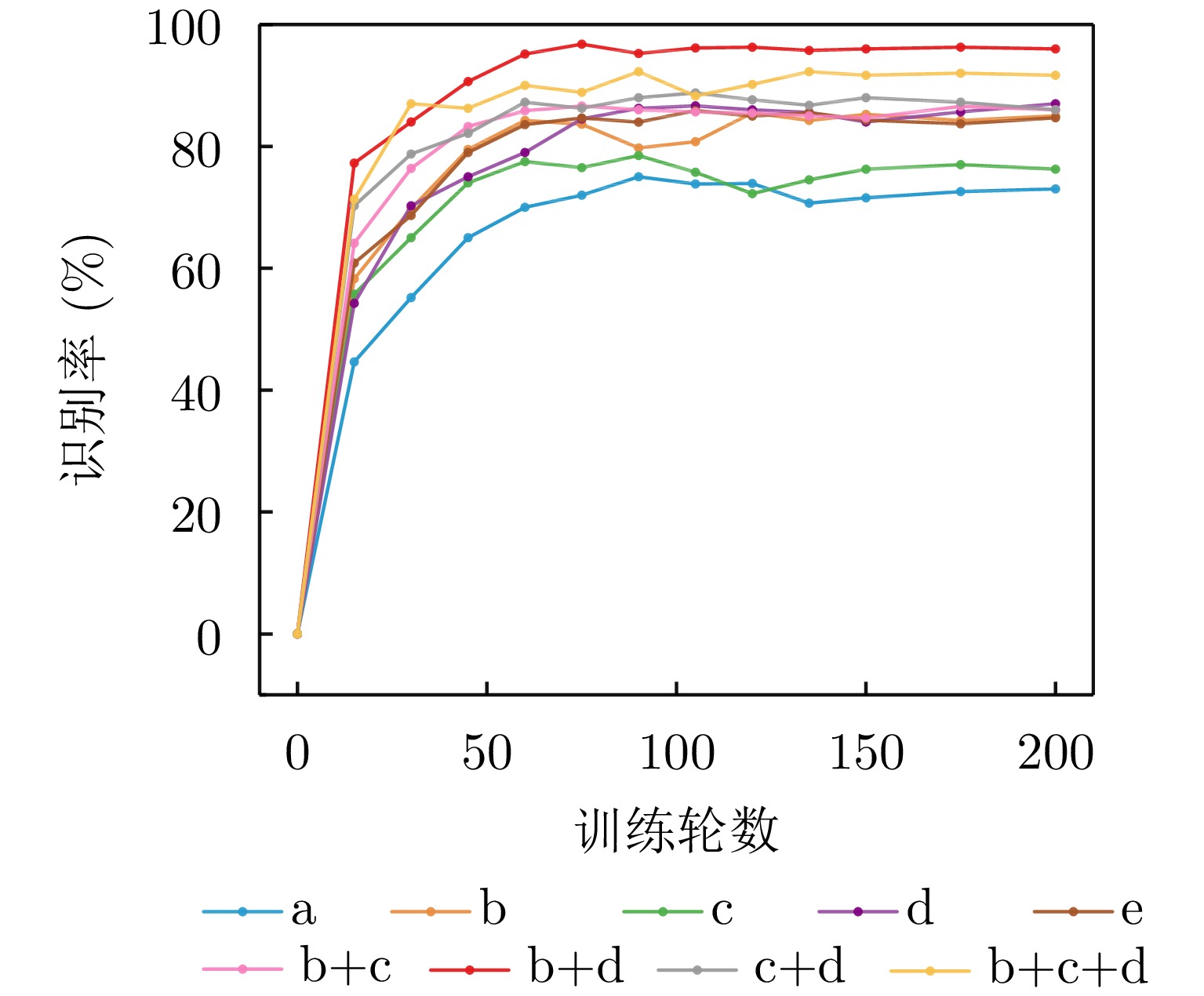
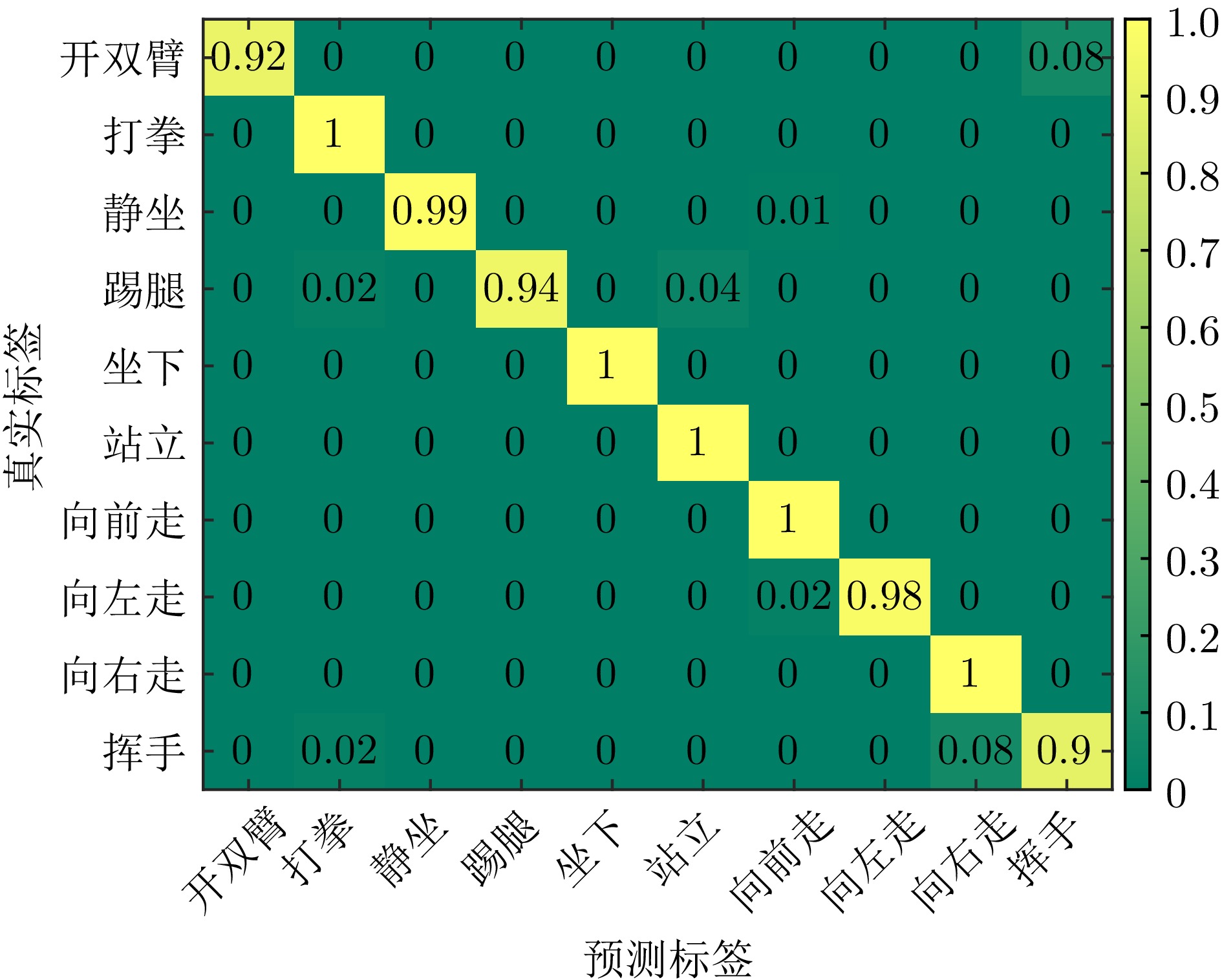
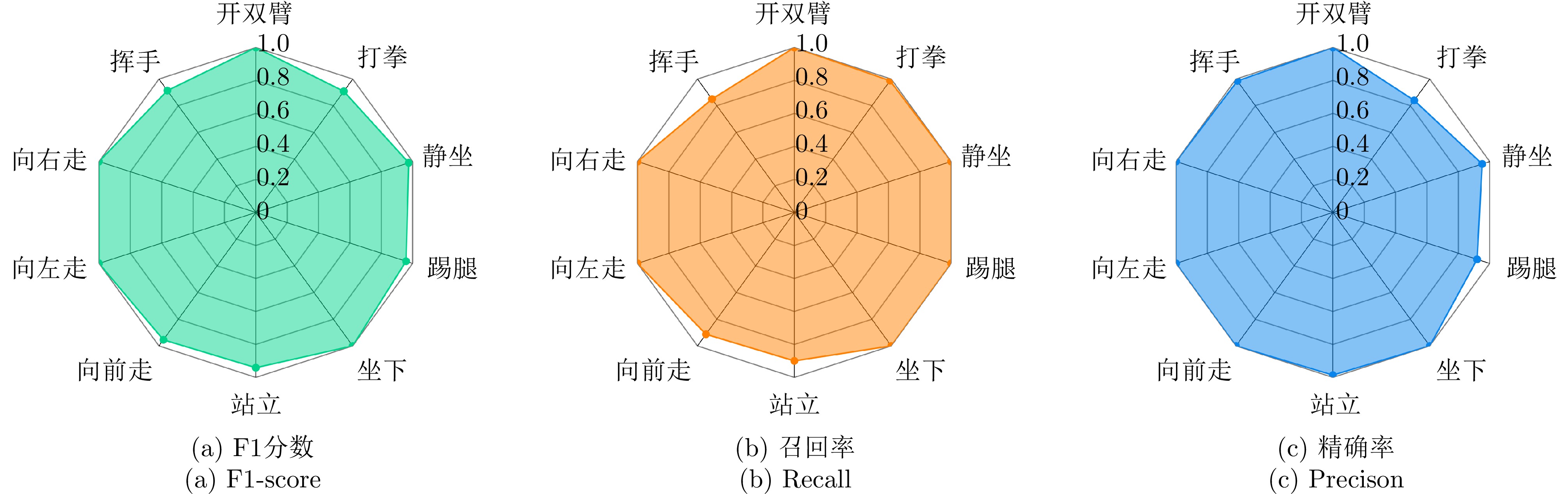
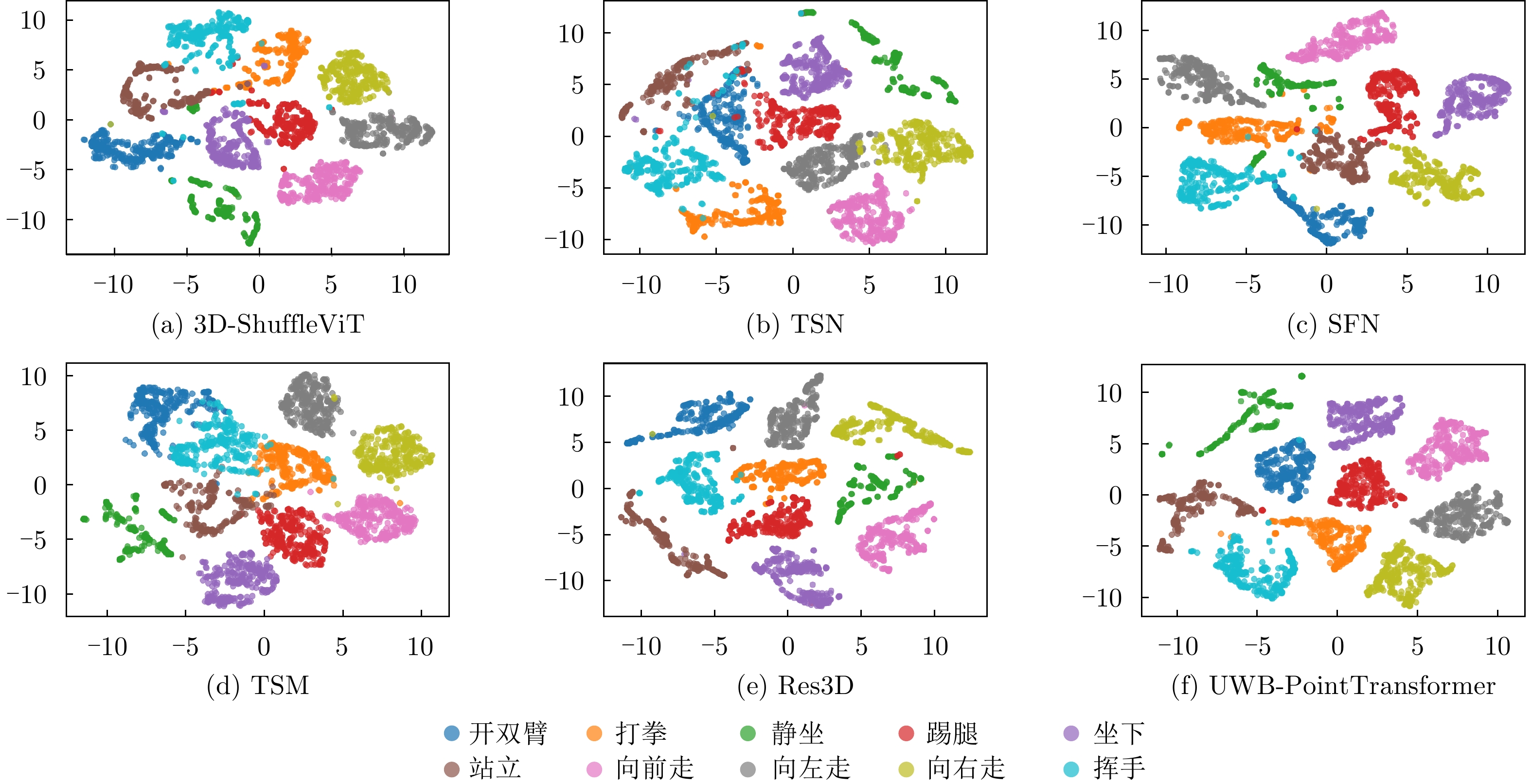
| [1] |
SUN Zehua, KE Qiuhong, RAHMANI H, et al. Human action recognition from various data modalities: A review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(3): 3200–3225. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3183112. |
| [2] |
PAREEK P and THAKKAR A. A survey on video-based human action recognition: Recent updates, datasets, challenges, and applications[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2021, 54(3): 2259–2322. doi: 10.1007/s10462-020-09904-8. |
| [3] |
元志安, 周笑宇, 刘心溥, 等. 基于RDSNet的毫米波雷达人体跌倒检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(4): 656–664. doi: 10.12000/JR21015. YUAN Zhian, ZHOU Xiaoyu, LIU Xinpu, et al. Human fall detection method using millimeter-wave radar based on RDSNet[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(4): 656–664. doi: 10.12000/JR21015. |
| [4] |
KONG Yu and FU Yun. Human action recognition and prediction: A survey[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2022, 130(5): 1366–1401. doi: 10.1007/s11263-022-01594-9. |
| [5] |
LI Maosen, CHEN Siheng, CHEN Xu, et al. Actional-structural graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3590–3598. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00371. |
| [6] |
杨小鹏, 高炜程, 渠晓东. 基于微多普勒角点特征与Non-Local机制的穿墙雷达人体步态异常终止行为辨识技术[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(1): 68–86. doi: 10.12000/JR23181. YANG Xiaopeng, GAO Weicheng, and QU Xiaodong. Human anomalous gait termination recognition via through-the-wall radar based on micro-Doppler corner features and Non-Local mechanism[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 68–86. doi: 10.12000/JR23181. |
| [7] |
SONG Yongkun, DAI Yongpeng, JIN Tian, et al. Dual-task human activity sensing for pose reconstruction and action recognition using 4-D imaging radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(19): 23927–23940. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3308788. |
| [8] |
DUAN Haodong, ZHAO Yue, CHEN Kai, et al. Revisiting skeleton-based action recognition[C]. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 2959–2968. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00298. |
| [9] |
JARAMILLO I E, JEONG J G, LOPEZ P R, et al. Real-time human activity recognition with IMU and encoder sensors in wearable exoskeleton robot via deep learning networks[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(24): 9690. doi: 10.3390/s22249690. |
| [10] |
PESENTI M, INVERNIZZI G, MAZZELLA J, et al. IMU-based human activity recognition and payload classification for low-back exoskeletons[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 1184. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28195-x. |
| [11] |
王秉路, 靳杨, 张磊, 等. 基于多传感器融合的协同感知方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(1): 87–96. doi: 10.12000/JR23184. WANG Binglu, JIN Yang, ZHANG Lei, et al. Collaborative perception method based on multisensor fusion[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(1): 87–96. doi: 10.12000/JR23184. |
| [12] |
DING Yipeng and SHE Yanlong. Research status and prospect of human movement recognition technique using through-wall radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1156–1175. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211051. |
| [13] |
NIU Kai, WANG Xuanzhi, ZHANG Fusang, et al. Rethinking Doppler effect for accurate velocity estimation with commodity WiFi devices[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2022, 40(7): 2164–2178. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2022.3155523. |
| [14] |
LECUN Y, BOSER B, DENKER J S, et al. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition[J]. Neural Computation, 1989, 1(4): 541–551. doi: 10.1162/neco.1989.1.4.541. |
| [15] |
SEYFIOGLU M S, EROL B, GURBUZ S Z, et al. DNN transfer learning from diversified micro-Doppler for motion classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(5): 2164–2180. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2883847. |
| [16] |
RANI S, CHOWDHURY A, CHAKRAVARTY T, et al. Exploiting unique state transitions to capture micro-Doppler signatures of human actions using CW radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(24): 27878–27886. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3126436. |
| [17] |
DING Chuanwei, ZHANG Li, CHEN Haoyu, et al. Sparsity-based human activity recognition with pointnet using a portable FMCW radar[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(11): 10024–10037. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2023.3235808. |
| [18] |
何密, 平钦文, 戴然. 深度学习融合超宽带雷达图谱的跌倒检测研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(2): 343–355. doi: 10.12000/JR22169. HE Mi, PING Qinwen, and DAI Ran. Fall detection based on deep learning fusing ultrawideband radar spectrograms[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(2): 343–355. doi: 10.12000/JR22169. |
| [19] |
WANG Zhengwei, SHE Qi, and SMOLIC A. Action-net: Multipath excitation for action recognition[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 13209–13218. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01301. |
| [20] |
MALIK N U R, ABU-BAKAR S A R, SHEIKH U U, et al. Cascading pose features with CNN-LSTM for multiview human action recognition[J]. Signals, 2023, 4(1): 40–55. doi: 10.3390/signals4010002. |
| [21] |
WANG Yinghui, ZHU Anlei, MA Haomiao, et al. 3D-ShuffleViT: An efficient video action recognition network with deep integration of self-attention and convolution[J]. Mathematics, 2023, 11(18): 3848. doi: 10.3390/math11183848. |
| [22] |
DONG Min, FANG Zhenglin, LI Yongfa, et al. AR3D: Attention residual 3D network for human action recognition[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(5): 1656. doi: 10.3390/s21051656. |
| [23] |
QI C R, SU Hao, KAICHUN M, et al. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 77–85. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.16. |
| [24] |
QI C R, YI Li, SU Hao, et al. PointNet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 5105–5114.
|
| [25] |
VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010.
|
| [26] |
郭帅, 陈婷, 王鹏辉, 等. 基于角度引导Transformer融合网络的多站协同目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 516–528. doi: 10.12000/JR23014. GUO Shuai, CHEN Ting, WANG Penghui, et al. Multistation cooperative radar target recognition based on an angle-guided Transformer fusion network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 516–528. doi: 10.12000/JR23014. |
| [27] |
石跃祥, 朱茂清. 基于骨架动作识别的协作卷积Transformer网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(4): 1485–1493. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220270. SHI Yuexiang and ZHU Maoqing. Collaborative convolutional transformer network based on skeleton action recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(4): 1485–1493. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220270. |
| [28] |
韩宗旺, 杨涵, 吴世青, 等. 时空自适应图卷积与Transformer结合的动作识别网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2024, 46(6): 2587–2595. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230551. HAN Zongwang, YANG Han, WU Shiqing, et al. Action recognition network combining spatio-temporal adaptive graph convolution and Transformer[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2024, 46(6): 2587–2595. doi: 10.11999/JEIT230551. |
| [29] |
XIAO Zhiqiang, YE Kuntao, and CUI Guolong. PointNet-transformer fusion network for in-cabin occupancy monitoring with mm-wave radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(4): 5370–5382. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3347893. |
| [30] |
金添, 宋永坤, 戴永鹏, 等. UWB-HA4D-1.0: 超宽带雷达人体动作四维成像数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 27–39. doi: 10.12000/JR22008. JIN Tian, SONG Yongkun, DAI Yongpeng, et al. UWB-HA4D-1.0: An ultra-wideband radar human activity 4D imaging dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 27–39. doi: 10.12000/JR22008. |
| [31] |
SONG Shaoqiu, DAI Yongpeng, SUN Shilong, et al. Efficient image reconstruction methods based on structured sparsity for short-range radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5212615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3404626. |
| [32] |
SOUMA R, KIDERA S, and KIRIMOTO T. Fast and accurate permittivity estimation algorithm for UWB internal imaging radar[C]. 2011 3rd International Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (APSAR), Seoul, Korea (South), 2011: 1–4.
|
| [33] |
ANDERSSON L E. On the determination of a function from spherical averages[J]. SIAM Journal on Mathematical Analysis, 1988, 19(1): 214–232. doi: 10.1137/0519016. |
| [34] |
CHEN Jiahui, LI Nian, GUO Shisheng, et al. Enhanced 3-D building layout tomographic imaging via tensor approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5105614. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3391282. |
| [35] |
ASH M, RITCHIE M, and CHETTY K. On the application of digital moving target indication techniques to short-range FMCW radar data[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(10): 4167–4175. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2823588. |
| [36] |
LORENSEN W E and CLINE H E. Marching cubes: A high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm[J]. ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics, 1987, 21(4): 163–169. doi: 10.1145/37402.37422. |
| [37] |
HOCHREITER S and SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735–1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735. |
| [38] |
CHUNG J, GÜLÇEHRE Ç, CHO K, et al. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.3555, 2014.
|
| [39] |
TRAN D, RAY J, SHOU Zheng, et al. ConvNet architecture search for spatiotemporal feature learning[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.05038, 2017.
|
| [40] |
FEICHTENHOFER C, FAN Haoqi, MALIK J, et al. SlowFast networks for video recognition[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 6202–6211. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00630. |
| [41] |
WANG Limin, XIONG Yuanjun, WANG Zhe, et al. Temporal segment networks: Towards good practices for deep action recognition[C]. 14th European Conference on European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 20–36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46484-8_2. |
| [42] |
LIN Ji, GAN Chuang, and HAN Song. TSM: Temporal shift module for efficient video understanding[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 7082–7092. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00718. |
| [43] |
VAN DER MAATEN L and HINTON G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9(86): 2579–2605.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

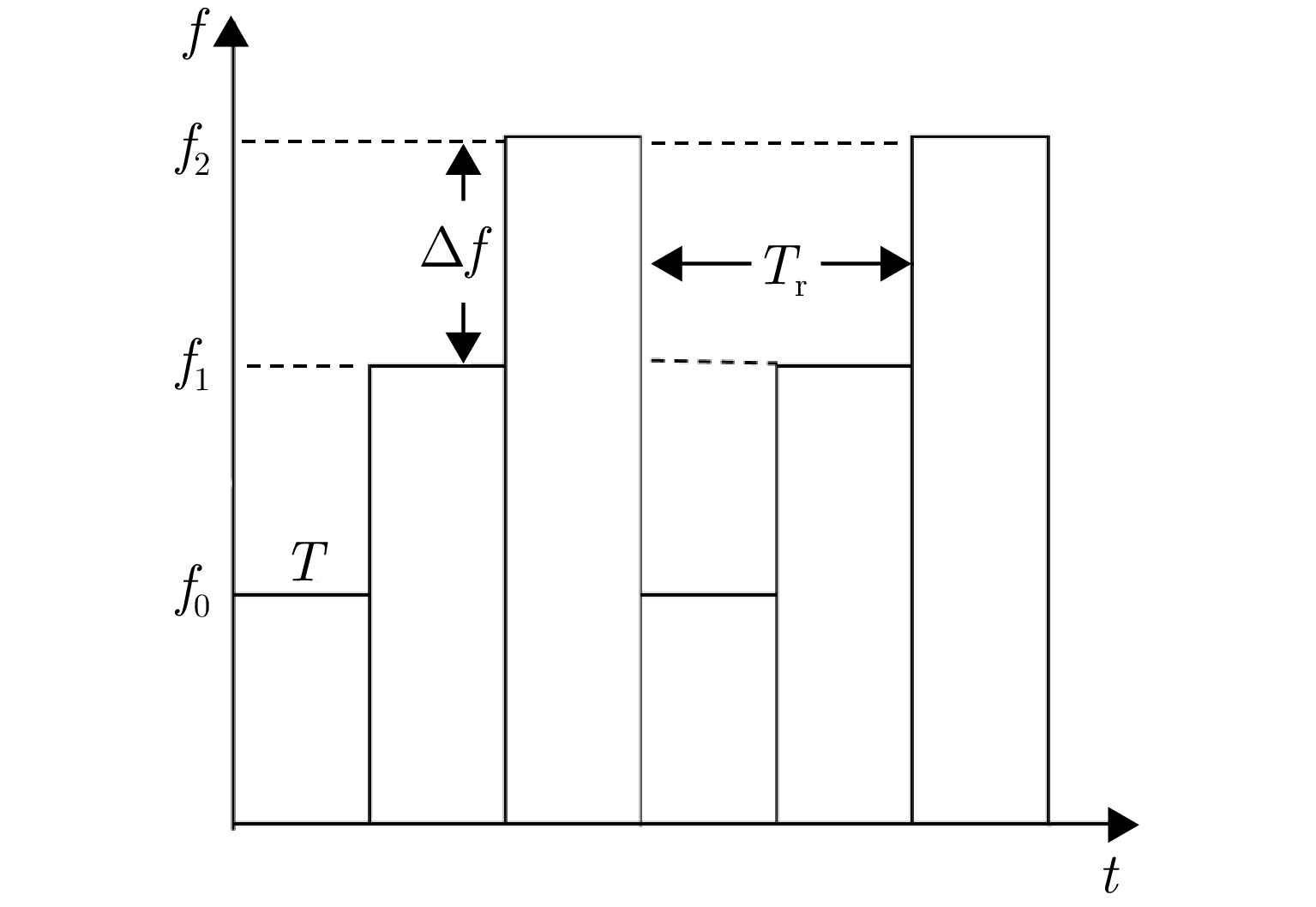



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: