Article Navigation >
Journal of Radars
>
2024
> Online First
| Citation: | LI Kemeng, DAI Yongpeng, SONG Yongping, et al. Single-channel ultrawideband radar human pose-incremental estimation technology[J]. Journal of Radars, in press. doi: 10.12000/JR24109 |
Single-channel Ultrawideband Radar Human Pose-incremental Estimation Technology
DOI: 10.12000/JR24109
More Information-
Abstract
This study focuses on integrating optical and radar sensors for human pose estimation. Based on the physical correspondence between the continuous-time micromotion accumulation and pose increment, a single-channel ultrawideband radar human-pose incremental estimation scheme is proposed. Specifically, by constructing a spatiotemporal incremental estimation network, using spatiotemporal pseudo-3D convolutional and time-domain-dilated convolutional layers to extract spatiotemporal micromotion features step by step, mapping these features to human pose increments within a time period, and combining them with the initial pose values provided by optics, we can realize a 3D pose estimation of the human body. The measured data results show that fusion attitude estimation achieves an estimation error of 5.38 cm in the original action set and can achieve continuous attitude estimation for the period of walking actions. Comparison and ablation experiments with other radar attitude estimation methods demonstrate the advantages of the proposed method. -

-
References
[1] LI Ming, QIN Hao, HUANG M, et al. RGB-D image-based pose estimation with Monte Carlo localization[C]. 2017 3rd International Conference on Control, Automation and Robotics, Nagoya, Japan, 2017: 109–114. DOI: 10.1109/ICCAR.2017.7942670.[2] KHAN A, GUPTA S, and GUPTA S K. Multi-hazard disaster studies: Monitoring, detection, recovery, and management, based on emerging technologies and optimal techniques[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2020, 47: 101642. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.101642.[3] 鲁勇, 吕绍和, 王晓东, 等. 基于WiFi信号的人体行为感知技术研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2019, 42(2): 231–251. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2019.00231.LU Yong, LV Shaohe, WANG Xiaodong, et al. A survey on WiFi based human behavior analysis technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2019, 42(2): 231–251. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2019.00231.[4] VON MARCARD T, ROSENHAHN B, BLACK M J, et al. Sparse inertial poser: Automatic 3D human pose estimation from sparse IMUs[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2017, 36(2): 349–360. doi: 10.1111/cgf.13131.[5] DAI Yongpeng, JIN Tian, LI Haoran, et al. Imaging enhancement via CNN in MIMO virtual array-based radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(9): 7449–7458. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3035064.[6] 金添, 何元, 李新羽, 等. 超宽带雷达人体行为感知研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1147–1155. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211044.JIN Tian, HE Yuan, LI Xinyu, et al. Advances in human activity sensing using ultra-wide band radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1147–1155. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211044.[7] ADIB F, HSU C Y, MAO Hongzi, et al. Capturing the human figure through a wall[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2015, 34(6): 219. doi: 10.1145/2816795.2818072.[8] ZHAO Mingmin, LI Tianhong, ALSHEIKH M A, et al. Through-wall human pose estimation using radio signals[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7356–7365. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00768.[9] ZHAO Mingmin, TIAN Yonglong, ZHAO Hang, et al. RF-based 3D skeletons[C]. The 2018 Conference of the ACM Special Interest Group on Data Communication, Budapest, Hungary, 2018: 267–281. DOI: 10.1145/3230543.3230579.[10] SENGUPTA A, JIN Feng, ZHANG Renyuan, et al. mm-Pose: Real-time human skeletal posture estimation using mmWave radars and CNNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(17): 10032–10044. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2991741.[11] YU Cong, ZHANG Dongheng, WU Zhi, et al. RFPose-OT: RF-based 3D human pose estimation via optimal transport theory[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2023, 24(10): 1445–1457. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.2200550.[12] XIE Chunyang, ZHANG Dongheng, WU Zhi, et al. RPM: RF-based pose machines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2024, 26: 637–649. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2023.3268376.[13] XIE Chunyang, ZHANG Dongheng, WU Zhi, et al. RPM 2.0: RF-based pose machines for multi-person 3D pose estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2024, 34(1): 490–503. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2023.3287329.[14] SONG Yongkun, JIN Tian, DAI Yongpeng, et al. Through-wall human pose reconstruction via UWB MIMO radar and 3D CNN[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(2): 241. doi: 10.3390/rs13020241.[15] CHEN V C. The Micro-Doppler Effect in Radar[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2011.[16] ZHOU Xiaolong, JIN Tian, DAI Yongpeng, et al. MD-Pose: Human pose estimation for single-channel UWB radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biometrics, Behavior, and Identity Science, 2023, 5(4): 449–463. doi: 10.1109/TBIOM.2023.3265206.[17] DING Wen, CAO Zhongping, ZHANG Jianxiong, et al. Radar-based 3D human skeleton estimation by kinematic constrained learning[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(20): 23174–23184. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3107361.[18] CAO Zhongping, DING Wen, CHEN Rihui, et al. A joint global–local network for human pose estimation with millimeter wave radar[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2023, 10(1): 434–446. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3201005.[19] DU Hao, JIN Tian, SONG Yongping, et al. A three-dimensional deep learning framework for human behavior analysis using range-Doppler time points[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(4): 611–615. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2930636.[20] BOULIC R, THALMANN N M, and THALMANN D. A global human walking model with real-time kinematic personification[J]. The Visual Computer, 1990, 6(6): 344–358. doi: 10.1007/BF01901021.[21] ZHENG Ce, ZHU Sijie, MENDIETA M, et al. 3D human pose estimation with spatial and temporal transformers[C]. The 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 11636–11645. DOI: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.01145.[22] FANG Yuming, DING Guanqun, LI Jia, et al. Deep3DSaliency: Deep stereoscopic video saliency detection model by 3D convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(5): 2305–2318. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2885229.[23] QIU Zhaofan, YAO Ting, and MEI Tao. Learning spatio-temporal representation with pseudo-3d residual networks[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5534–5542. DOI: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.590.[24] PAVLLO D, FEICHTENHOFER C, GRANGIER D, et al. 3D human pose estimation in video with temporal convolutions and semi-supervised training[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2020: 7745–7754. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00794.[25] YU F, KOLTUN V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[J]. arXiv, 2016.[26] WANG Panqu, CHEN Pengfei, YUAN Ye, et al. Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation[C]. 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, USA, 2018: 1451–1460. DOI: 10.1109/WACV.2018.00163. -
Proportional views

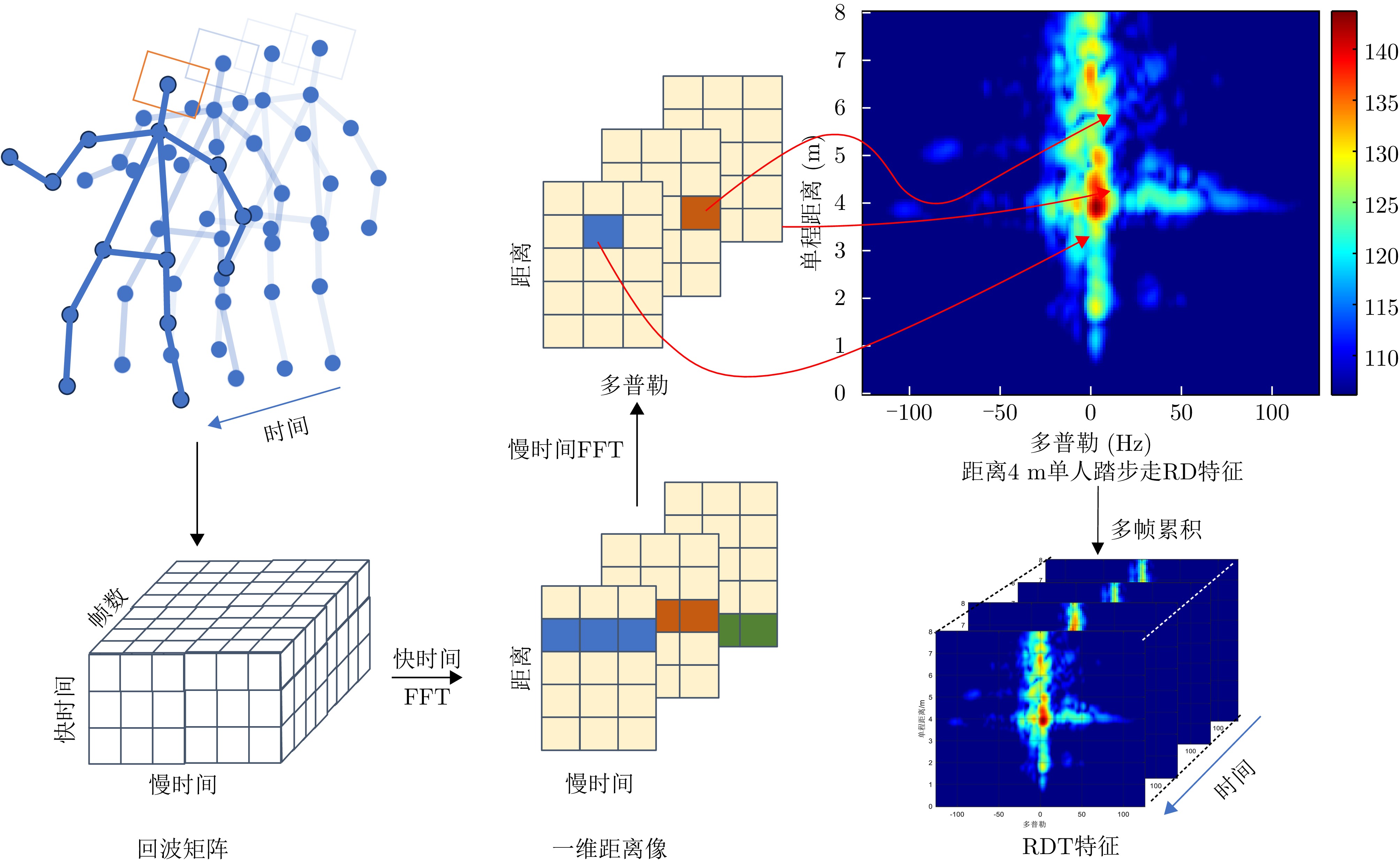
- Figure 1. Human body micro Doppler characteristics
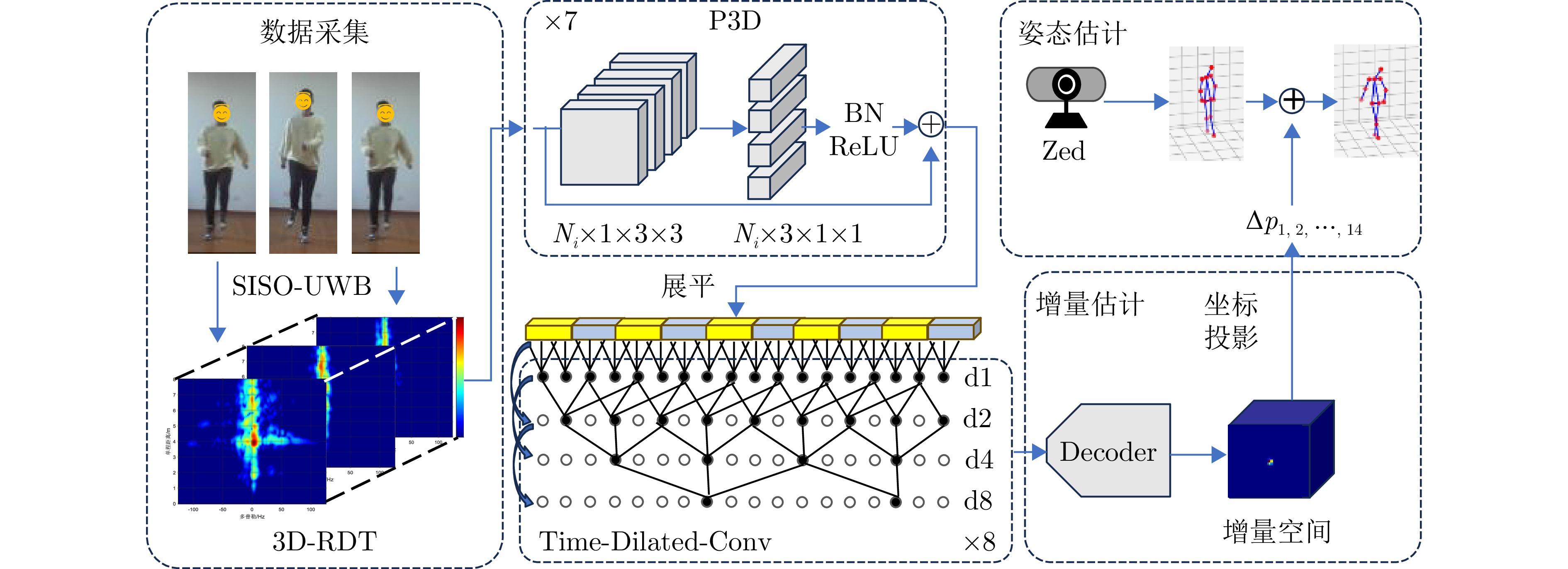
- Figure 2. Structure of pose increment estimation using spatiotemporal step-by-step
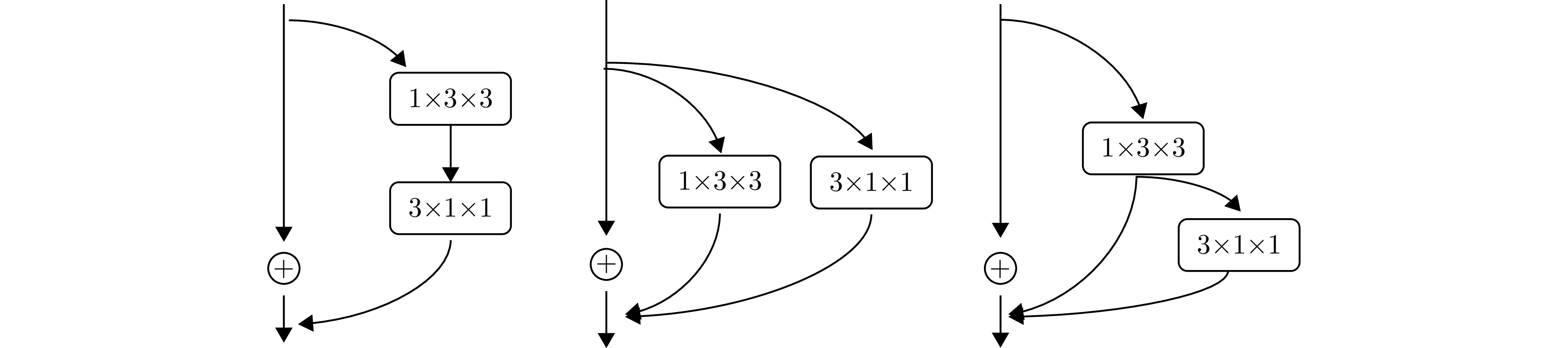
- Figure 3. Different organizational forms of P3D
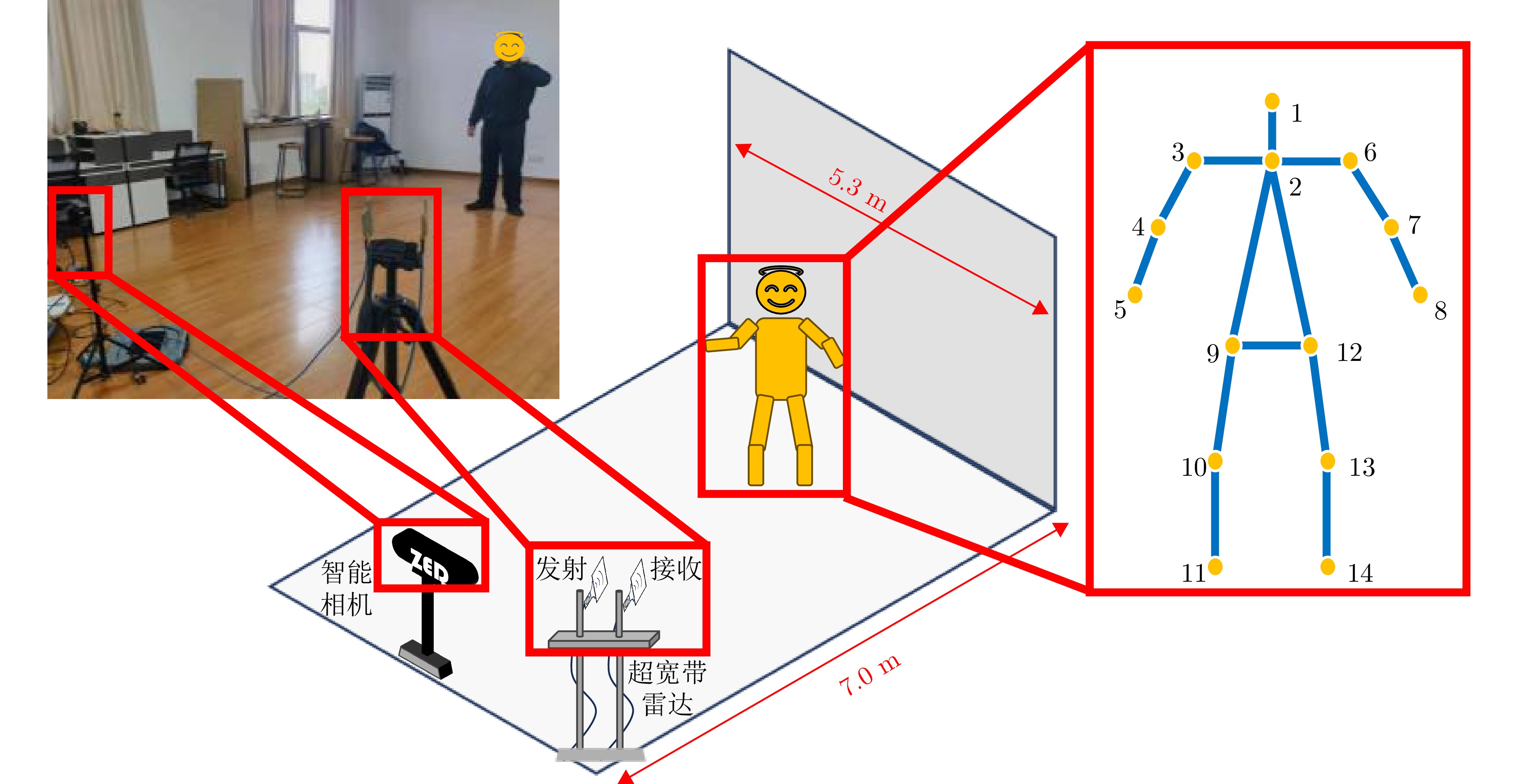
- Figure 4. Experimental scenario and joint definition
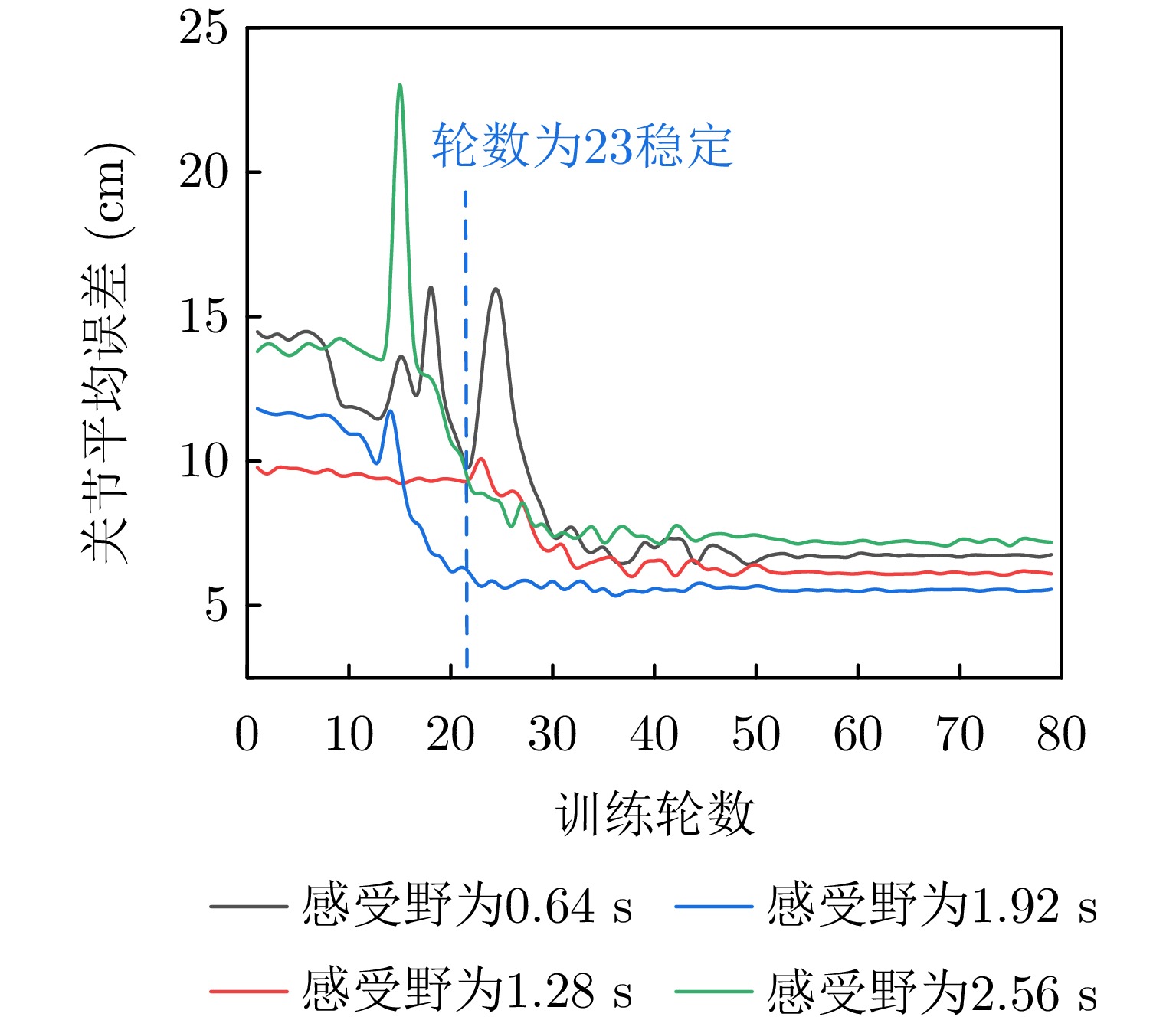
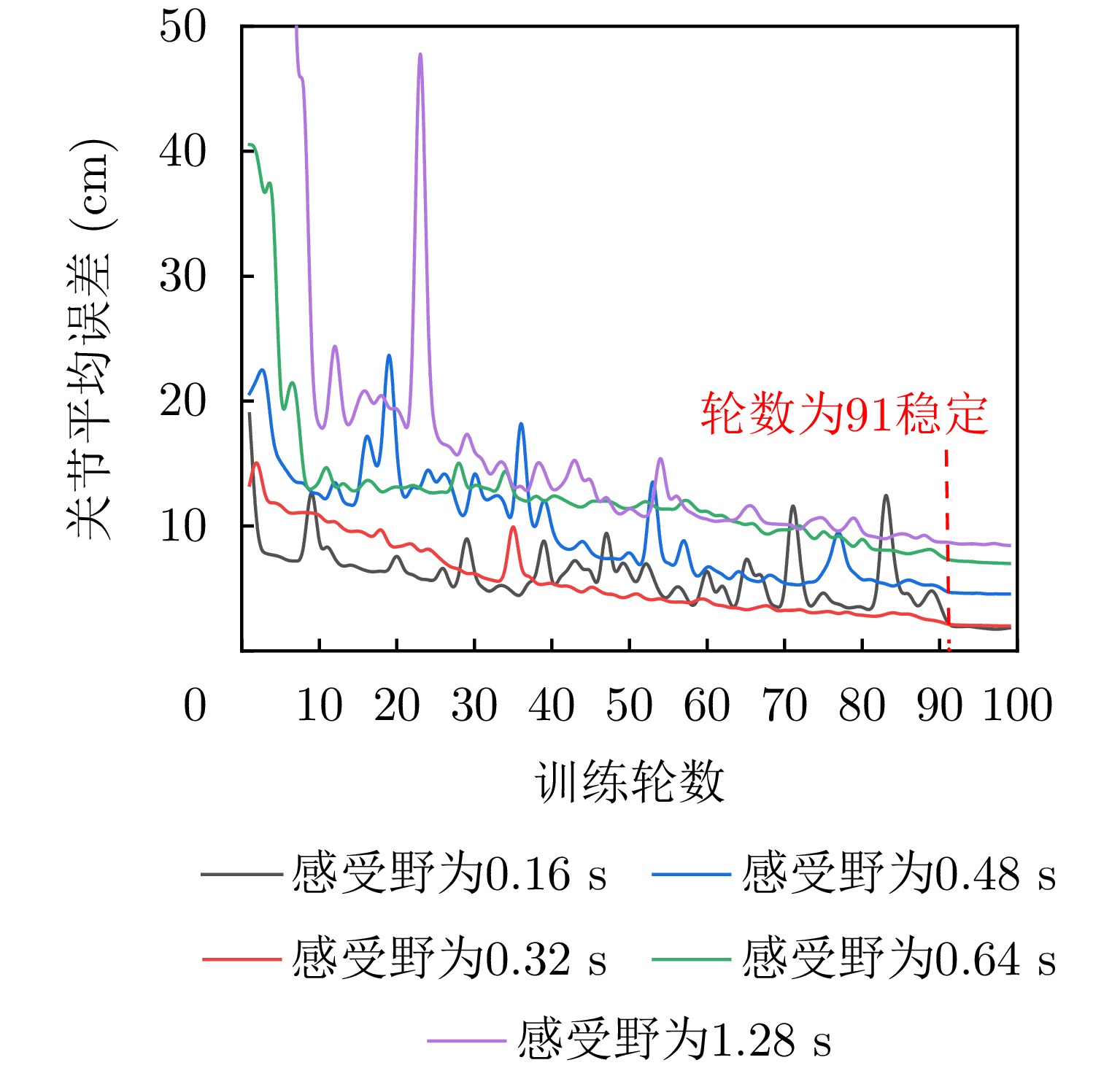
- Figure 5. Impact of time-domain receptive field on increment estimation in situ
- Figure 6. Impact of time-domain receptive field on increment estimation of walking
- Figure 7. Visualization results of attitude estimation
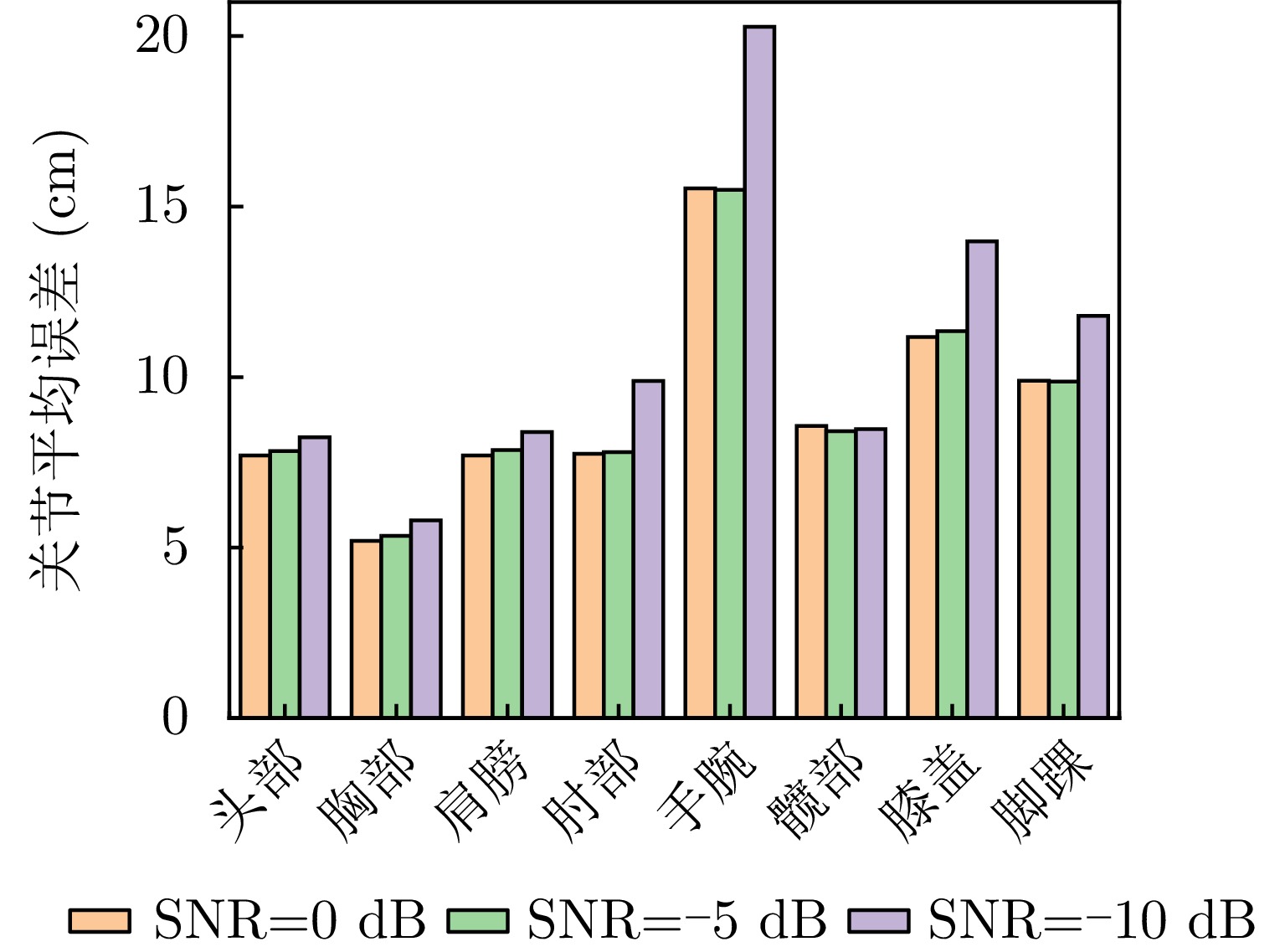
- Figure 8. The impact of noise on attitude estimation
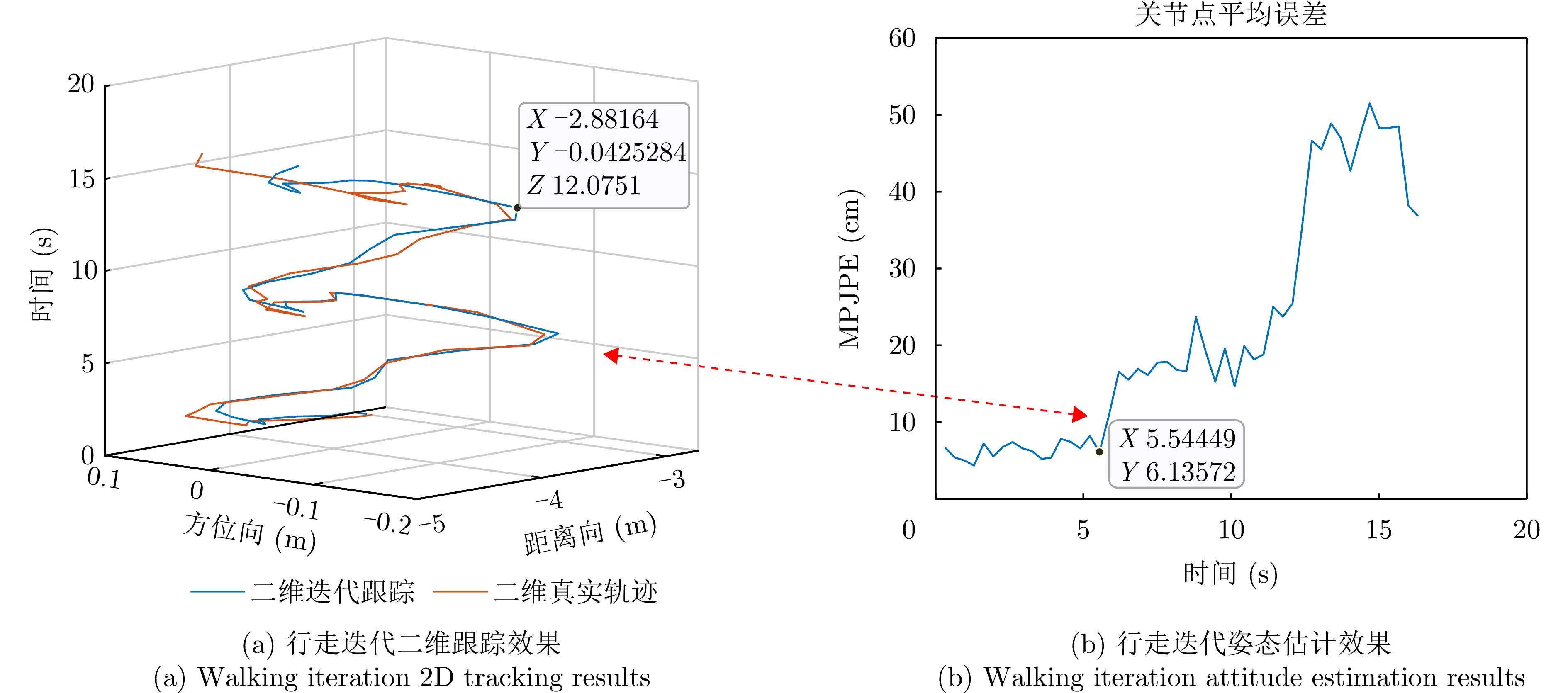
- Figure 9. Walking iteration estimation effect


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: