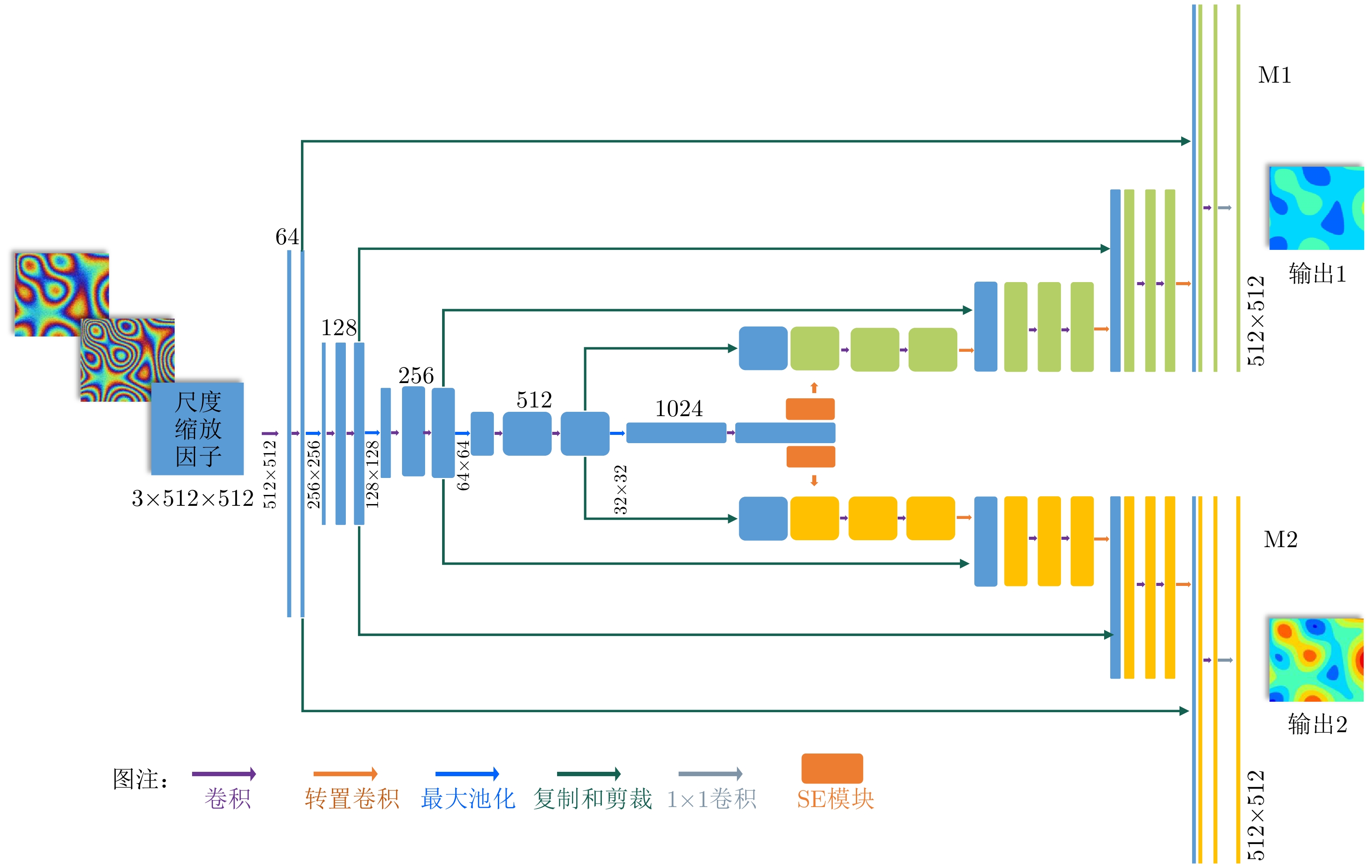
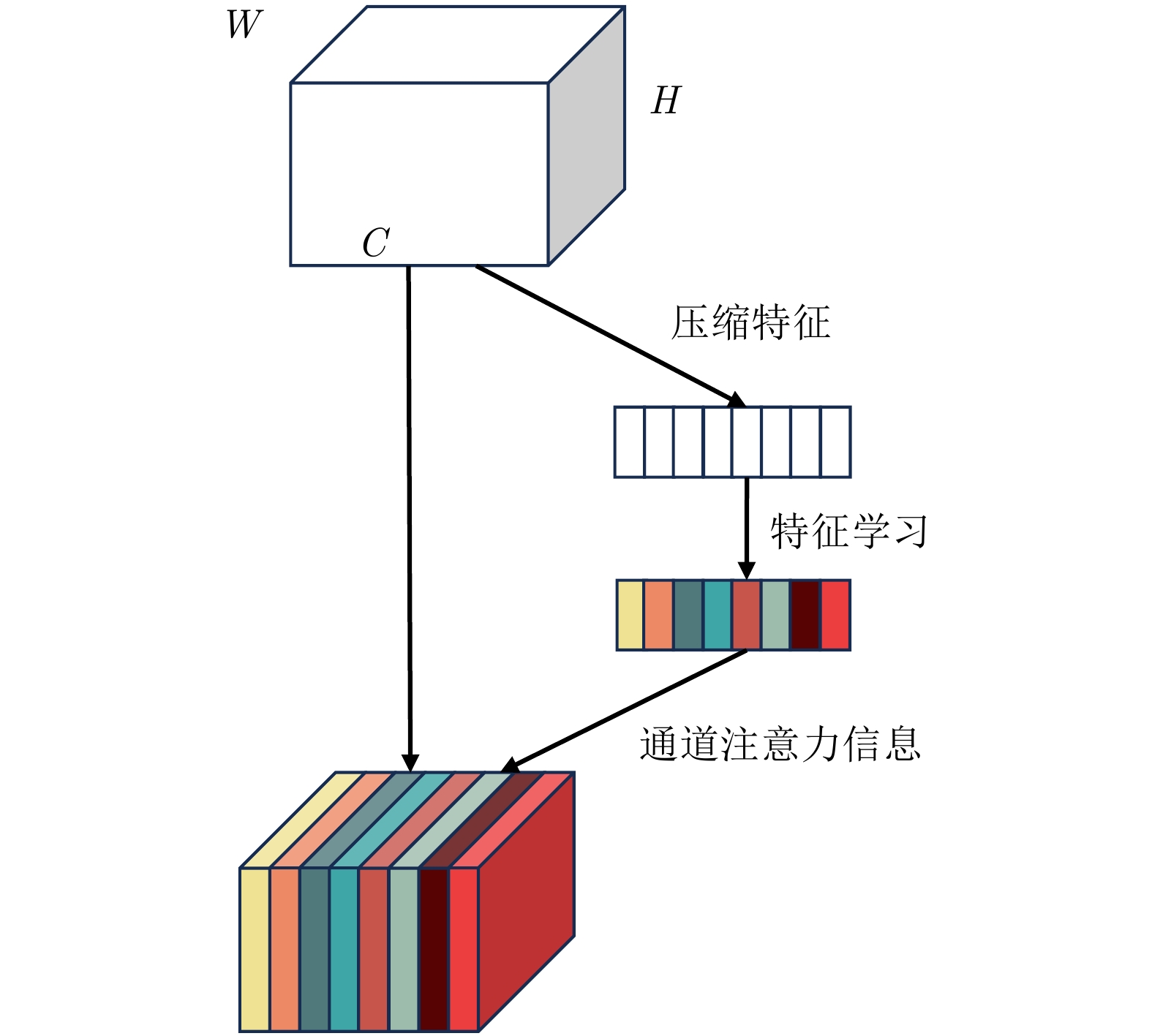
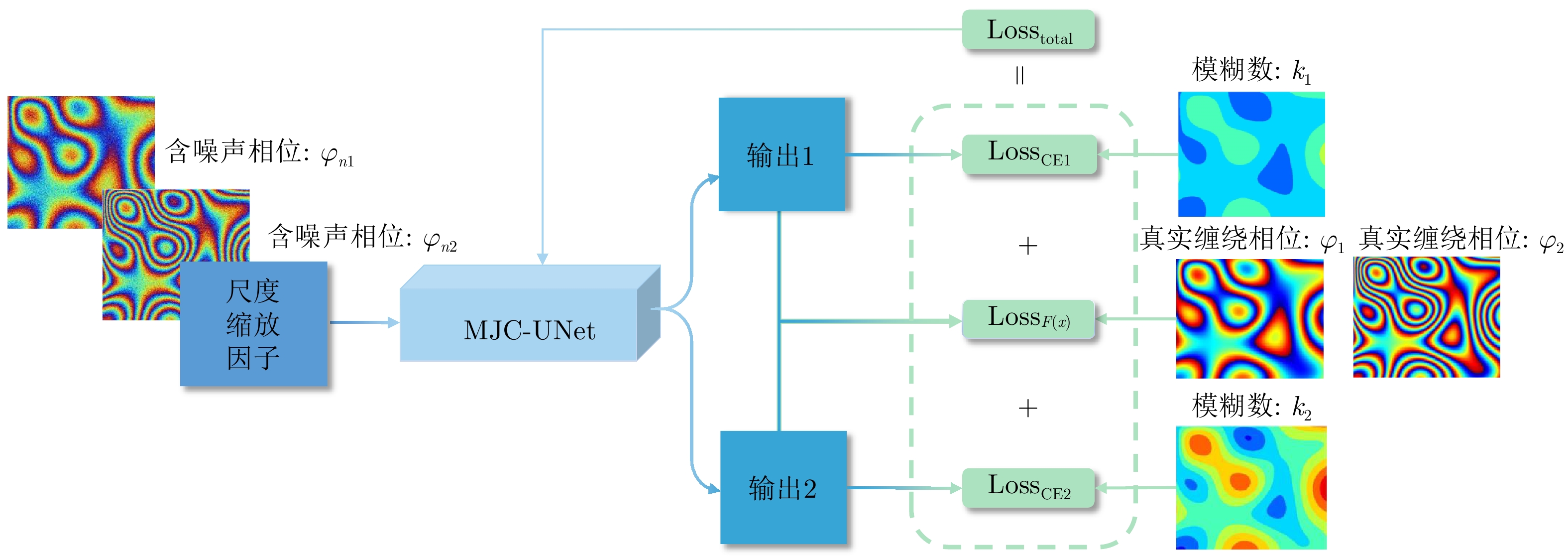
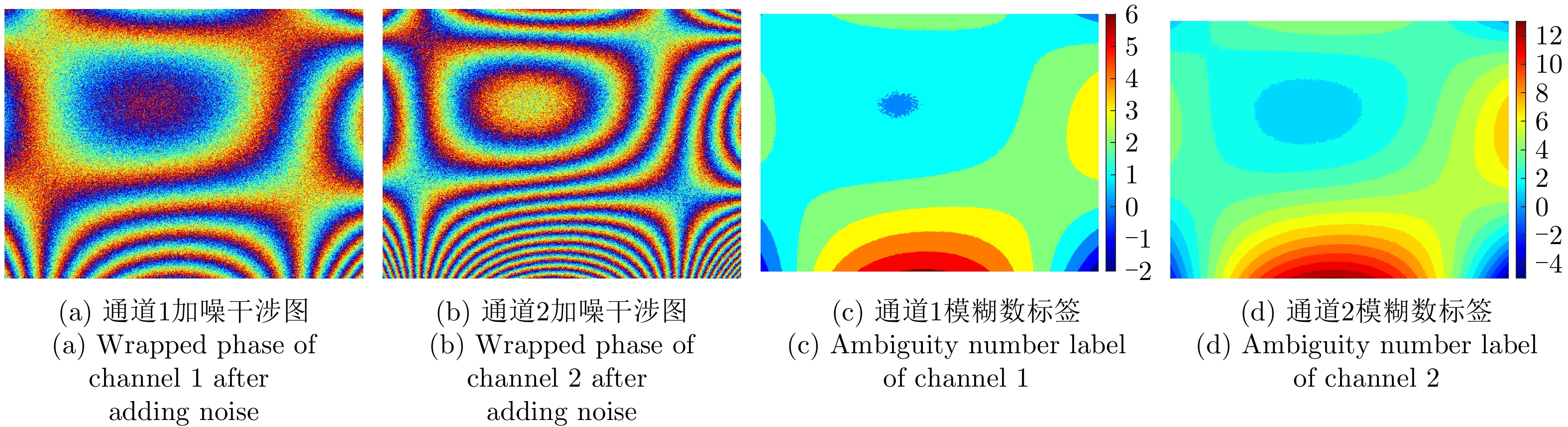
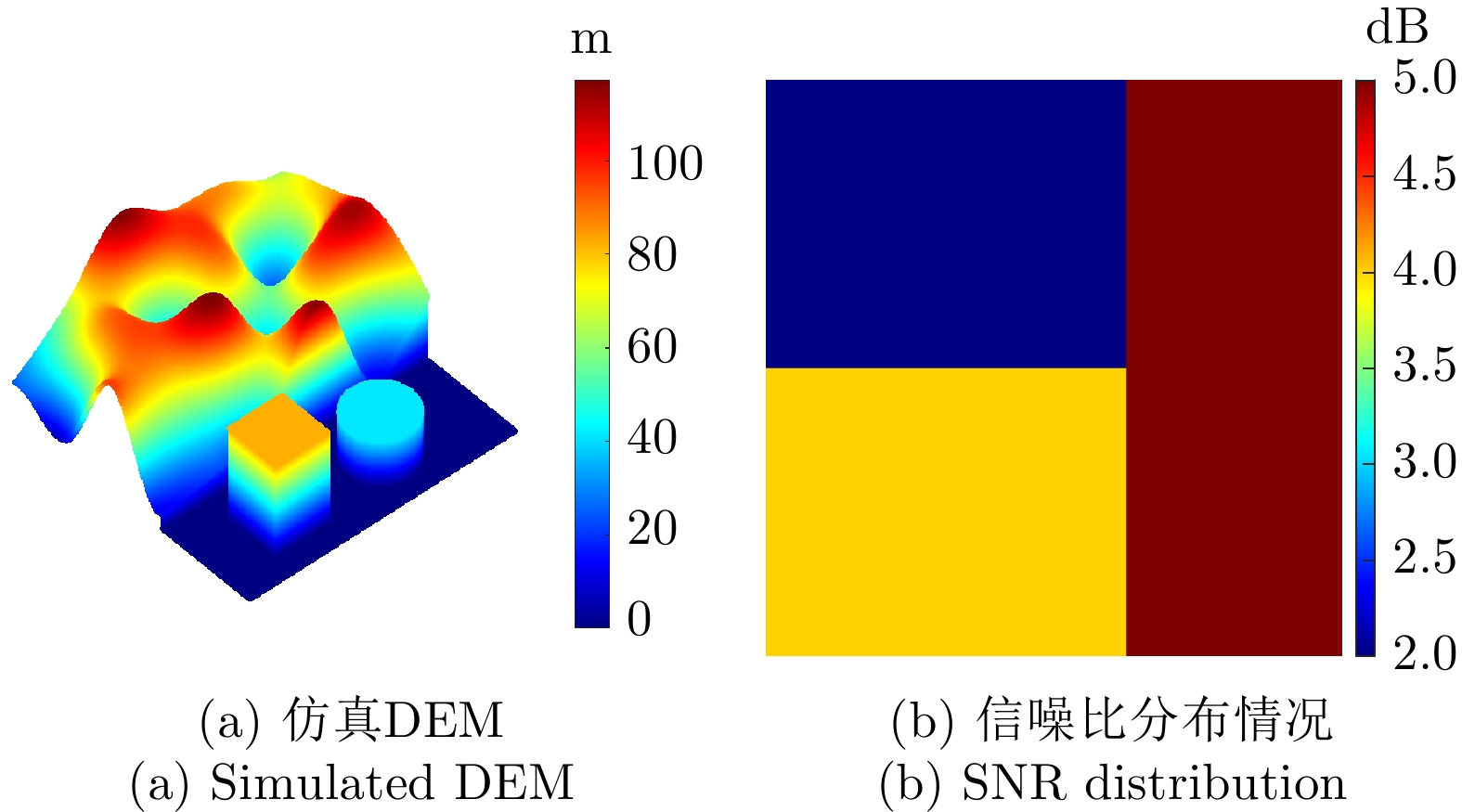
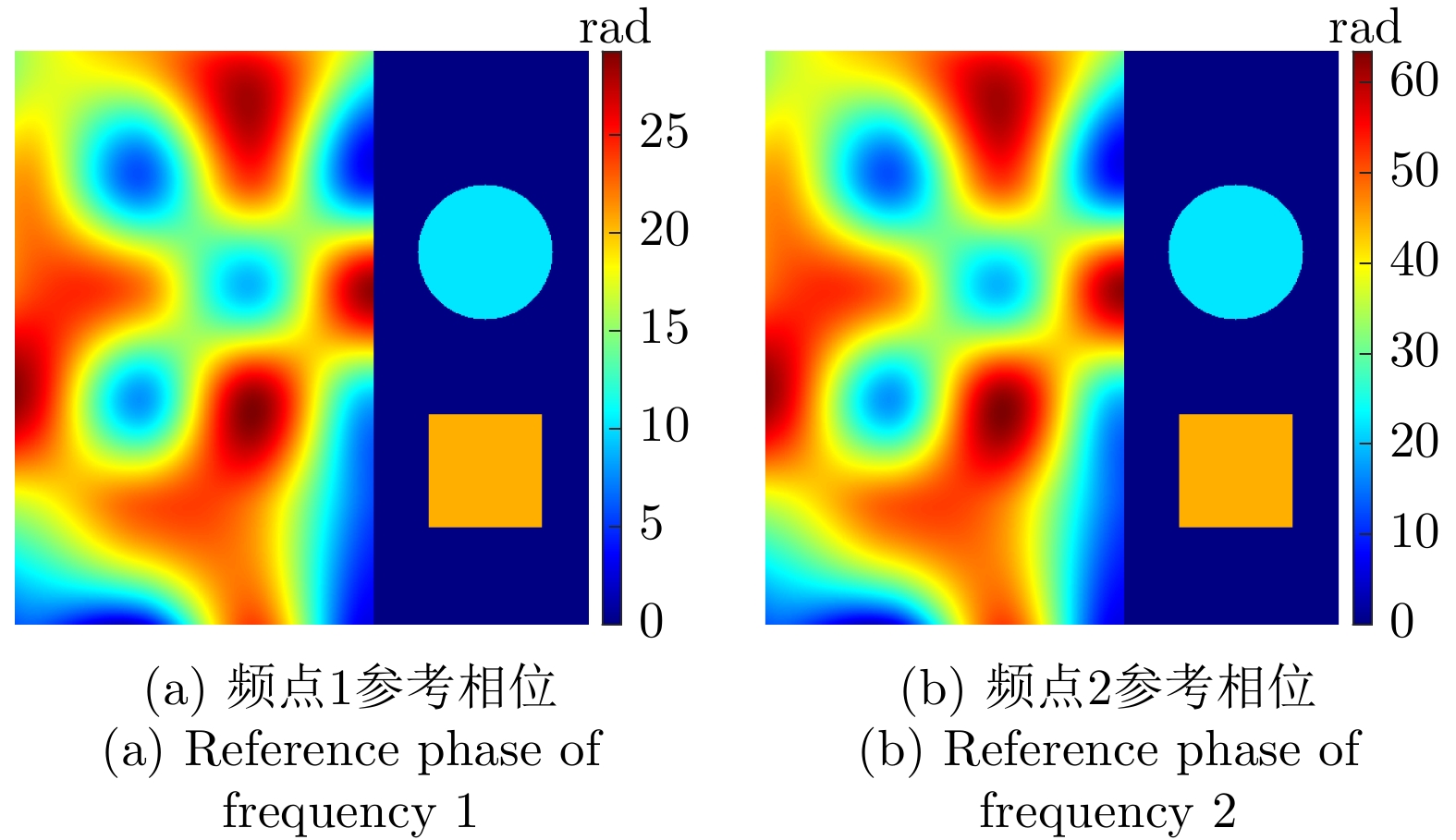
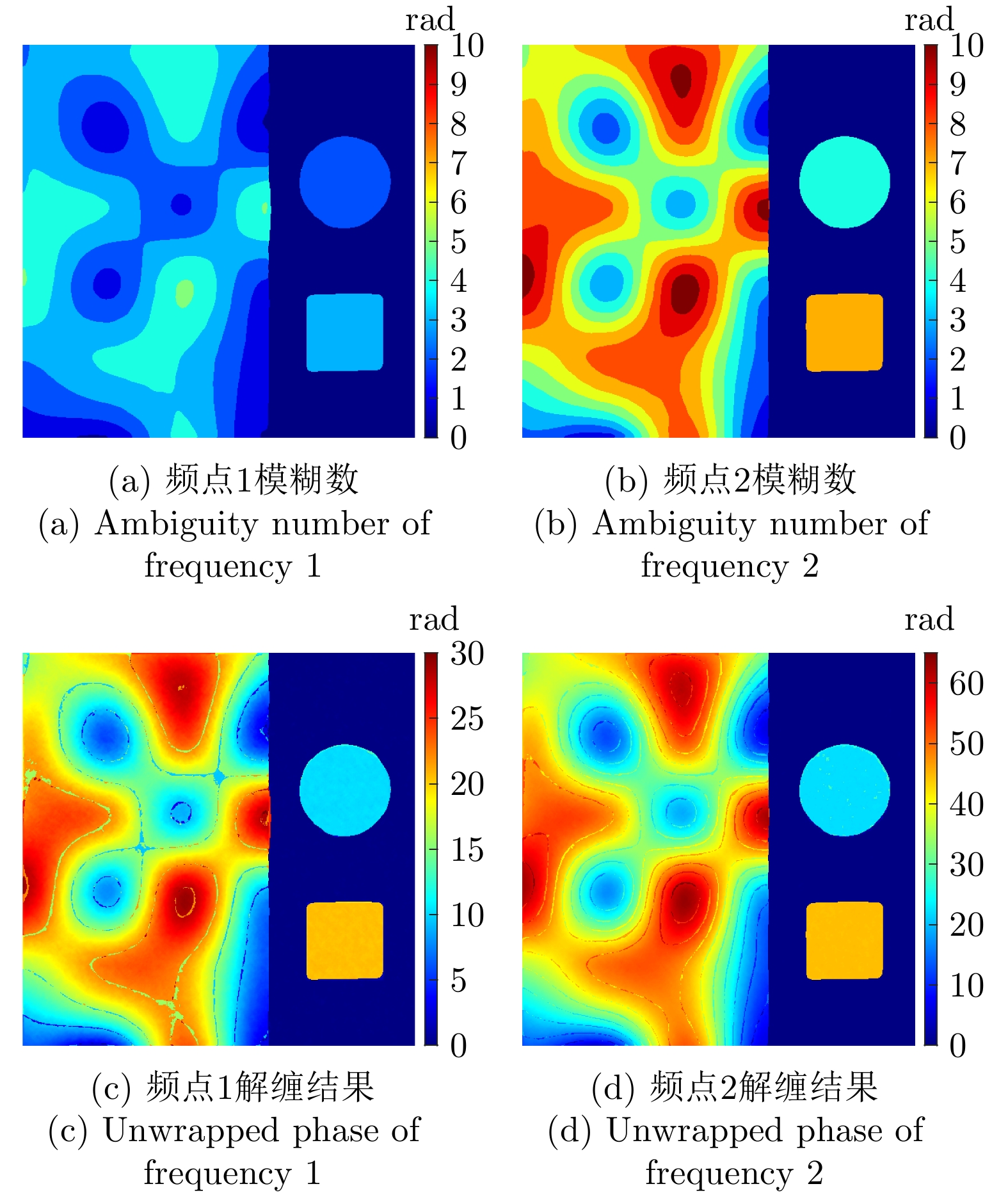
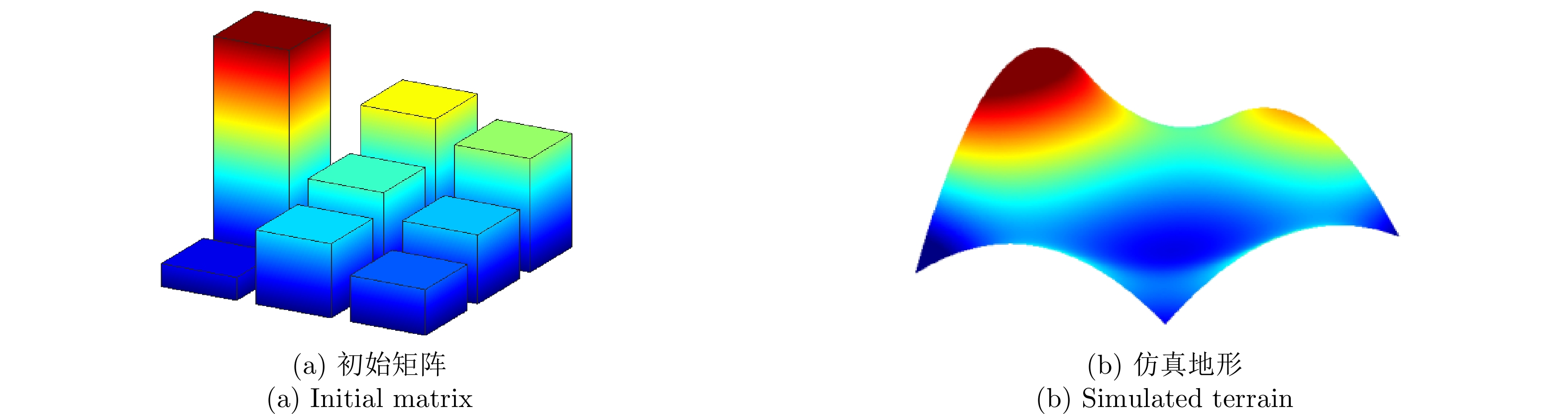| [1] |
BAMLER R and HARTL P. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry[J]. Inverse Problems, 1998, 14(4): R1–R54. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/14/4/001 |
| [2] |
BÜRGMANN R, ROSEN P A, and FIELDING E J. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry to measure earth’s surface topography and its deformation[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28: 169–209. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.169 |
| [3] |
ITOH K. Analysis of the phase unwrapping algorithm[J]. Applied Optics, 1982, 21(14): 2470. doi: 10.1364/AO.21.002470 |
| [4] |
EINEDER M and KRIEGER G. Interferometric digital elevation model reconstruction-experiences from SRTM and multi channel approaches for future missions[C]. 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, Korea (South), 2005: 2664–2667.
|
| [5] |
JORDAN R L, HUNEYCUTT B L, and WERNER M. The SIR-C/X-SAR synthetic aperture radar system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1995, 33(4): 829–839.
|
| [6] |
LIN Sheng, WANG Zhen, DING Zegang, et al. Local fringe frequencies estimation method based on multi-frequency InSAR[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2017, 33(3): 314–318. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2017.03.009 |
| [7] |
GINI F and LOMBARDINI F. Multibaseline cross-track SAR interferometry: A signal processing perspective[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2005, 20(8): 71–93. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2005.1499278 |
| [8] |
ZHU Xiaoxiang, WANG Yuanyuan, MONTAZERI S, et al. A review of ten-year advances of multi-baseline SAR interferometry using TerraSAR-X data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(9): 1374. doi: 10.3390/rs10091374 |
| [9] |
DING Zegang, WANG Zhen, WANG Yan, et al. Refined multifrequency interferometric SAR phase unwrapping for extremely steep terrain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5221320. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3142996 |
| [10] |
DING Zegang, WANG Zhen, LIN Sheng, et al. Local fringe frequency estimation based on multifrequency InSAR for phase-noise reduction in highly sloped terrain[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(9): 1527–1531. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2720695 |
| [11] |
PASCAZIO V and SCHIRINZI G. Multifrequency InSAR height reconstruction through maximum likelihood estimation of local planes parameters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2002, 11(12): 1478–1489. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2002.804274 |
| [12] |
FERRAIOLI G, SHABOU A, TUPIN F, et al. Multichannel phase unwrapping with graph cuts[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(3): 562–566. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2021165 |
| [13] |
XU Wei, CHANG E C, KWOH L K, et al. Phase-unwrapping of SAR interferogram with multi-frequency or multi-baseline[C]. 1994 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2007: 730–732.
|
| [14] |
YU Hanwen, LI Zhenfang, and BAO Zheng. A cluster-analysis-based efficient multibaseline phase-unwrapping algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(1): 478–487. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2055569 |
| [15] |
FORNARO G, PAUCIULLO A, and SANSOSTI E. Phase difference-based multichannel phase unwrapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2005, 14(7): 960–972. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2005.849302 |
| [16] |
ZENG Tao, LIU Tiandong, DING Zegang, et al. Phase unwrapping method based on multi-frequency InSAR in highly sloped terrain[J]. Electronics Letters, 2016, 52(12): 1058–1059. doi: 10.1049/el.2015.3795 |
| [17] |
葛仕奇, 陈亮, 丁泽刚, 等. 利用梯度重建的稳健多频InSAR相位解缠方法[J]. 测绘学报, 2013, 42(3): 367–373, 396.
GE Shiqi, CHEN Liang, DING Zegang, et al. A robust multi-frequency phase unwrapping[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographiea Siniea, 2013, 42(3): 367–373, 396.
|
| [18] |
YU Hanwen and LAN Yang. Robust two-dimensional phase unwrapping for multibaseline SAR interferograms: A two-stage programming approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(9): 5217–5225. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2016.2558541 |
| [19] |
ZHOU Lifan, YU Hanwen, LAN Yang, et al. Deep learning-based branch-cut method for InSAR two-dimensional phase unwrapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5209615. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3099997 |
| [20] |
ZHOU Lifan, YU Hanwen, and LAN Yang. Deep convolutional neural network-based robust phase gradient estimation for two-dimensional phase unwrapping using SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(7): 4653–4665. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2965918 |
| [21] |
WANG Kaiqiang, LI Ying, KEMAO Q, et al. One-step robust deep learning phase unwrapping[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(10): 15100–15115. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.015100 |
| [22] |
ZHOU Lifan, YU Hanwen, LAN Yang, et al. CANet: An unsupervised deep convolutional neural network for efficient cluster-analysis-based multibaseline InSAR phase unwrapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5212315. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3110518 |
| [23] |
RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241.
|
| [24] |
HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141.
|
| [25] |
HUANG Guoman. An airborne interferometric SAR mapping system with multi-band and multi-polarization—CASMSAR[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2014, 39(8): 111–115. doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2014.08.011 |
| [26] |
周良将, 汪丙南, 王亚超, 等. 机载多维度SAR航空观测系统实验初步进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(4): 1243–1253. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220250ZHOU Liangjiang, WANG Bingnan, WANG Yachao, et al. Preliminary process of airborne multidimensional space joint-observation SAR system[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2023, 45(4): 1243–1253. doi: 10.11999/JEIT220250 |
| [27] |
丁赤飚, 仇晓兰, 徐丰, 等. 合成孔径雷达三维成像—从层析、阵列到微波视觉[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090DING Chibiao, QIU Xiaolan, XU Feng, et al. Synthetic aperture radar three-dimensional imaging—from TomoSAR and array InSAR to microwave vision[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 693–709. doi: 10.12000/JR19090 |
| [28] |
仇晓兰, 焦泽坤, 杨振礼, 等. 微波视觉三维SAR关键技术及实验系统初步进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027QIU Xiaolan, JIAO Zekun, YANG Zhenli, et al. Key technology and preliminary progress of microwave vision 3D SAR experimental system[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR22027 |
| [29] |
WANG Wenjie and XIA Xianggen. A closed-form robust Chinese remainder theorem and its performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(11): 5655–5666. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2066974 |
| [30] |
SHELHAMER E, LONG J, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640–651. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 |
| [31] |
YANG Zhenzhen, SUN Xue, SHAO Jing, et al. Medical image segmentation based on multiscale even convolution attention U-Net[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(9): 1912–1921. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2022.09.014 |
| [32] |
LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 |
| [33] |
LIANG Feng, XIE Xianming, XU Youmiao, et al. An improved U-Net phase unwrapping method[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2021, 36(5): 134–141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2021.05.018 |
| [34] |
KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1412.6980.
|
| [35] |
LOSHCHILOV I and HUTTER F. SGDR: Stochastic gradient descent with warm restarts[EB/OL]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1608.03983.
|
| [36] |
GOLDSTEIN R M and WERNER C L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1998, 25(21): 4035–4038. doi: 10.1029/1998GL900033 |
| [37] |
ASF data search vertex[EB/OL]. https://search.asf.alaska.edu/, 2023.
|
| [38] |
GESCH D B, OIMOEN M J, and EVANS G A. Accuracy assessment of the U.S. Geological Survey national elevation dataset, and comparison with other large-area elevation datasets: SRTM and ASTER[R]. Open-File Report 2014-1008, 2014.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: