| [1] |
刘天亮, 谯庆伟, 万俊伟, 等. 融合空间-时间双网络流和视觉注意的人体行为识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(10): 2395–2401. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171116LIU Tianliang, QIAO Qingwei, WAN Junwei, et al. Human action recognition via spatio-temporal dual network flow and visual attention fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2018, 40(10): 2395–2401. doi: 10.11999/JEIT171116 |
| [2] |
吴培良, 杨霄, 毛秉毅, 等. 一种视角无关的时空关联深度视频行为识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(4): 904–910. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180477WU Peiliang, YANG Xiao, MAO Bingyi, et al. A perspective-independent method for behavior recognition in depth video via temporal-spatial correlating[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2019, 41(4): 904–910. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180477 |
| [3] |
JIN Tian, HE Yuan, LI Xinyu, et al. Advances in human activity sensing using ultra-wide band radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1147–1155. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211044 |
| [4] |
LV Wen, XU Guili, CHENG Yuehua, et al. Soft Classification in action recognition based on local spatio-temporal features[J]. Computer and Modernization, 2014(3): 94–98, 103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2475.2014.03.023 |
| [5] |
DING Yipeng and SHE Yanlong. Research status and prospect of human movement recognition technique using through-wall radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1156–1175. doi: 10.11999/JEIT211051 |
| [6] |
金添, 宋勇平, 崔国龙, 等. 低频电磁波建筑物内部结构透视技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119JIN Tian, SONG Yongping, CUI Guolong, et al. Advances on penetrating imaging of building layout technique using low frequency radio waves[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119 |
| [7] |
JIN Tian and SONG Yongping. Sparse imaging of building layouts in ultra-wideband radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(3): 275–284. doi: 10.12000/JR18031 |
| [8] |
夏正欢, 张群英, 叶盛波, 等. 一种便携式伪随机编码超宽带人体感知雷达设计[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(5): 527–537. doi: 10.12000/JR15027XIA Zhenghuan, ZHANG Qunying, YE Shengbo, et al. Design of a handheld pseudo random coded UWB radar for human sensing[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(5): 527–537. doi: 10.12000/JR15027 |
| [9] |
FALCONER D G, FICKLIN R W, and KONOLIGE K G. Robot-mounted through-wall radar for detecting, locating, and identifying building occupants[C]. Millennium Conference. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, USA, 2000: 1868–1875.
|
| [10] |
FALCONER D G, FICKLIN R W, and KONOLIGE K G. Detection, location, and identification of building occupants using a robot-mounted through-wall radar[C]. SPIE 4037, Digitization of the Battlespace V and Battlefield Biomedical Technologies II, Orlando, USA, 2000: 72–81.
|
| [11] |
LAI C P, RUAN Qing, and NARAYANAN R M. Hilbert-Huang Transform (HHT) processing of through-wall noise radar data for human activity characterization[C]. 2007 IEEE Workshop on Signal Processing Applications for Public Security and Forensics, Washington, USA, 2007: 1–6.
|
| [12] |
LI Jing, ZENG Zhaofa, SUN Jiguang, et al. Through-wall detection of human Being’s movement by UWB radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(6): 1079–1083. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2012.2190707 |
| [13] |
QI Fugui, LIANG Fulai, LV Hao, et al. Detection and classification of finer-grained human activities based on stepped-frequency continuous-wave through-wall radar[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(6): 885. doi: 10.3390/s16060885 |
| [14] |
QI Fugui, LV Hao, LIANG Fulai, et al. MHHT-based method for analysis of micro-doppler signatures for human finer-grained activity using through-wall SFCW Radar[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(3): 260. doi: 10.3390/rs9030260 |
| [15] |
PENG Yansong and GUO Shisheng. Detailed feature representation and analysis of low frequency UWB Radar range profile for improving through-wall human activity recognition[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–6.
|
| [16] |
QI Fugui, LI Zhao, MA Yangyang, et al. Generalization of channel micro-Doppler capacity evaluation for improved finer-grained human activity classification using MIMO UWB radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2021, 69(11): 4748–4761. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2021.3076055 |
| [17] |
WANG Xiang, CHEN Pengyun, XIE Hangchen, et al. Through-wall human activity classification using complex-valued convolutional neural network[C]. 2021 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf21), Atlanta, USA, 2021: 1–4.
|
| [18] |
ARBABI E, BOULIC R, and THALMANN D. A fast method for finding range of motion in the Human joints[C]. The 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Lyon, France, 2007: 5079–5082.
|
| [19] |
MAAREF N, MILLOT P, PICHOT C, et al. A study of UWB FM-CW radar for the detection of human beings in motion inside a building[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(5): 1297–1300. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2010709 |
| [20] |
JIN Tian and YAROVOY A. A through-the-wall radar imaging method based on a realistic model[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2015, 2015: 539510. doi: 10.1155/2015/539510 |
| [21] |
MA Ruowen, LIU Weiguo, MIAO Chen, et al. The simulation of human walking micro-Doppler echo and comparison of time-frequency analysis method[C]. The First International Conference on Electronics Instrumentation & Information Systems (EIIS), Harbin, China, 2017: 1–6.
|
| [22] |
JOHANSSON T, RAHM J, GUSTAVSSON J, et al. Through-the-wall detection of human activity[C]. SPIE 8021, Radar Sensor Technology XV, Orlando, USA, 2011: 446–454.
|
| [23] |
FAIRCHILD D P and NARAYANAN R M. Classification of human motions using empirical mode decomposition of human micro-Doppler signatures[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2014, 8(5): 425–434. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0165 |
| [24] |
OH B S, GUO Xin, and LIN Zhiping. A UAV classification system based on FMCW radar micro-Doppler signature analysis[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 132: 239–255. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.05.007 |
| [25] |
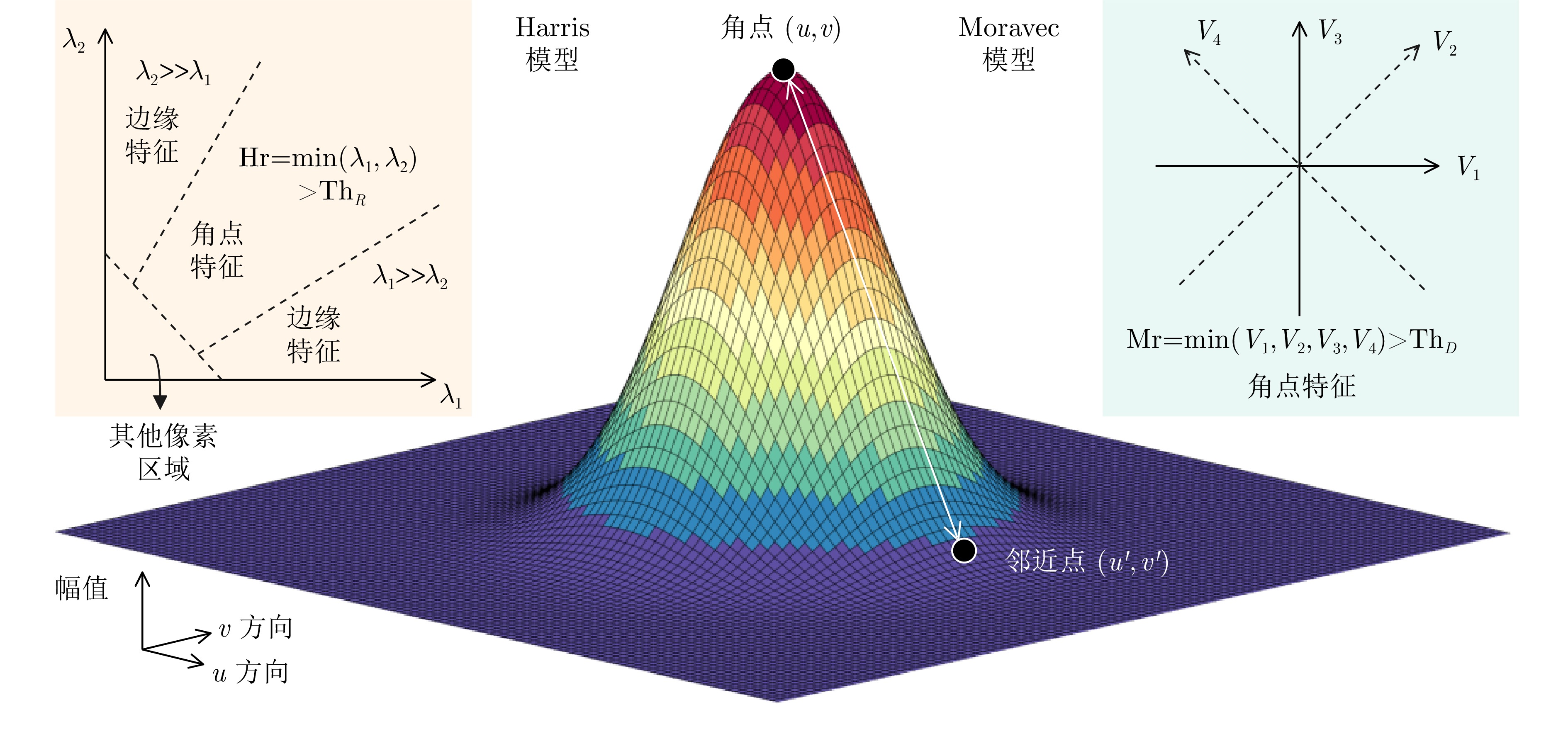
SAFY M, SHI Guangming, and AMEIN A S. Semi-automatic image registration using Harris corner detection and RANdom SAmple Consensus (RANSAC)[C]. IET International Radar Conference 2013, Xi’an, China, 2013: 1–4.
|
| [26] |
KUMARI M S and SHEKAR B H. On the use of Moravec operator for text detection in document images and video frames[C]. 2011 International Conference on Recent Trends in Information Technology (ICRTIT), Chennai, India: 2011: 910–914.
|
| [27] |
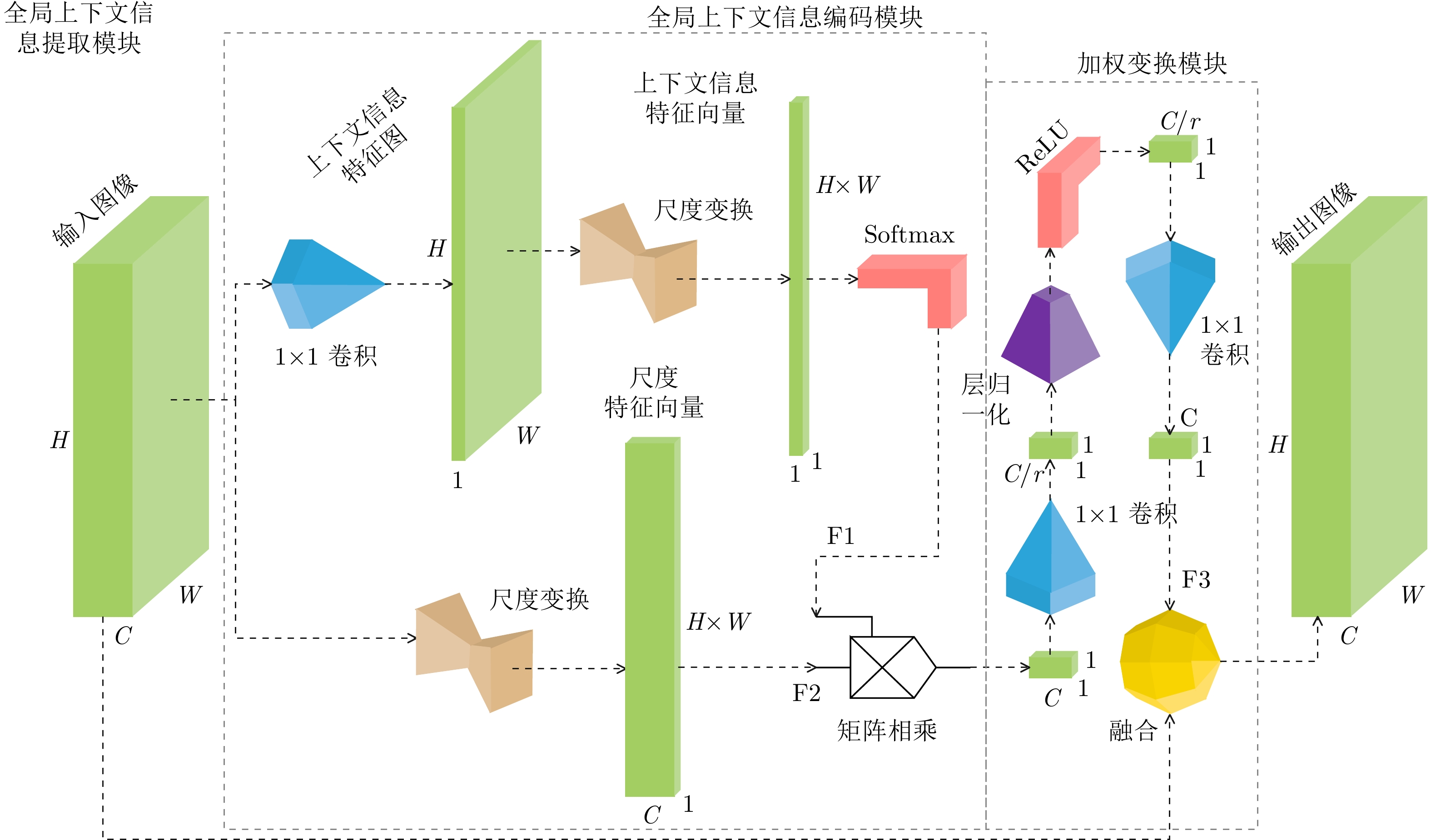
CAO Yue, XU Jiarui, LIN S, et al. GCNet: Non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, Korea (South), 2020: 1971–1980.
|
| [28] |
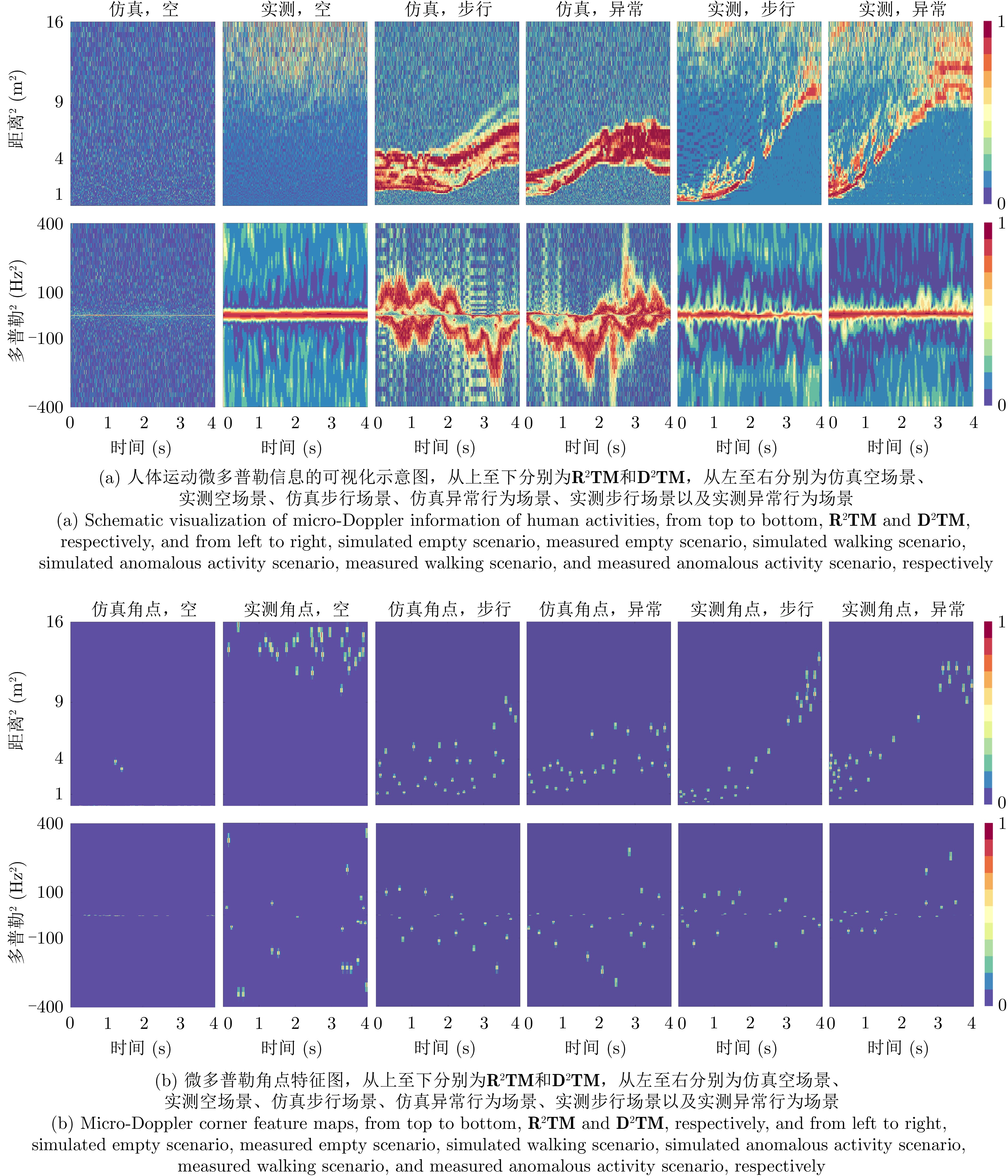
VISHWAKARMA S, LI Wenda, TANG Chong, et al. SimHumalator: An open-source end-to-end radar simulator for human activity recognition[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2022, 37(3): 6–22. doi: 10.1109/MAES.2021.3138948 |
| [29] |
BHAT S A, DAR M A, SZCZUKO P, et al. Sensing direction of human motion using Single-Input-Single-Output (SISO) channel model and neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 56823–56844. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3177273 |
| [30] |
CHENG Can, LING Fei, GUO Shisheng, et al. A real-time human activity recognition method for through-the-wall radar[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–5.
|
| [31] |
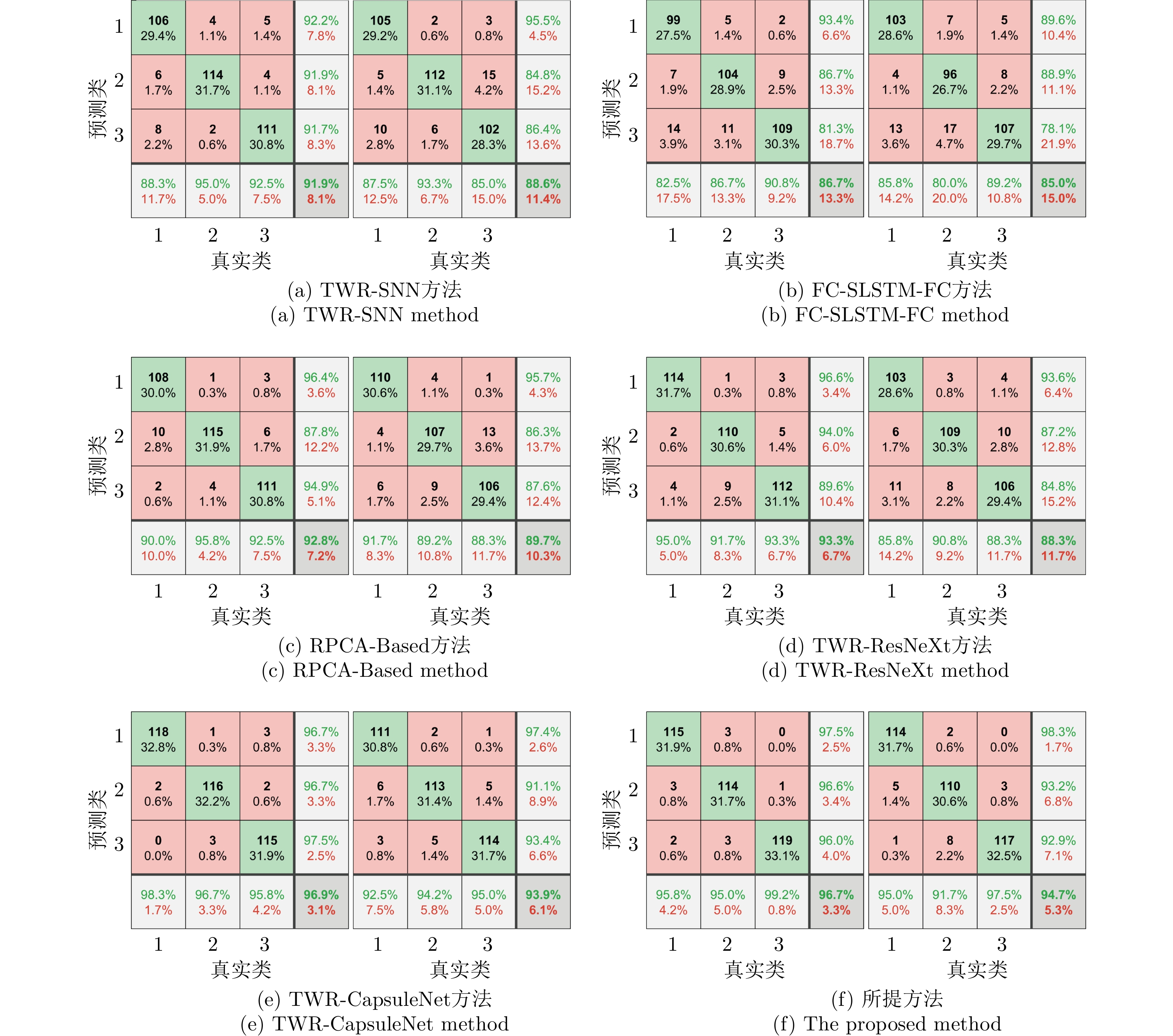
AN Qiang, WANG Shuoguang, YAO Lei, et al. RPCA-based high resolution through-the-wall human motion feature extraction and classification[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(17): 19058–19068. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3088122 |
| [32] |
CHEN Pengyun, GUO Shisheng, LI Huquan, et al. Through-wall human motion recognition based on transfer learning and ensemble learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 3505305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3070374 |
| [33] |
WANG Xiang, WANG Yumiao, GUO Shisheng, et al. Capsule network with multiscale feature fusion for hidden human activity classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 2504712. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2023.3238749 |
| [34] |
SAVAGE R, PALAFOX L F, MORRISON C T, et al. A Bayesian approach to subkilometer crater shape analysis using individual HiRISE images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(10): 5802–5812. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2825608 |
| [35] |
WINKELMANN S, SCHAEFFTER T, EGGERS H, et al. SNR enhancement in radial SSFP imaging using partial k-space averaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2005, 24(2): 254–262. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2004.840845 |
| [36] |
KRIG S. Computer Vision Metrics: Survey, Taxonomy, and Analysis[M]. Berkeley: Apress, 2014: 85.
|
| [37] |
VISHWAKARMA S, LI Wenda, ADVE R, et al. Learning salient features in radar micro-Doppler signatures using Attention Enhanced Alexnet[C]. International Conference on Radar Systems (RADAR 2022), Hybrid Conference, UK, 2022: 190–195.
|
| [38] |
LI Jiefang, CHEN Xiaolong, YU Gang, et al. High-precision human activity classification via radar micro-Doppler signatures based on deep neural network[C]. IET International Radar Conference (IET IRC 2020), 2020: 1124–1129.
|
| [39] |
JIA Yong, GUO Yong, SONG Ruiyuan, et al. ResNet-based counting algorithm for moving targets in through-the-wall radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(6): 1034–1038. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2990742 |
| [40] |
CHUMA E L and IANO Y. Human movement recognition system using CW Doppler radar sensor with FFT and convolutional neural network[C]. 2020 IEEE MTT-S Latin America Microwave Conference (LAMC 2020), Cali, Colombia, 2021: 1–4.
|
| [41] |
ZHAO Wenwei, WANG Runze, QI Yunliang, et al. BASCNet: Bilateral adaptive spatial and channel attention network for breast density classification in the mammogram[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 70: 103073. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103073 |
| [42] |
RAJAMANI K T, SIEBERT H, and HEINRICH M P. Dynamic deformable attention network (DDANet) for COVID-19 lesions semantic segmentation[J]. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2021, 119: 103816. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2021.103816 |
| [43] |
CHI Lu, YUAN Zehuan, MU Yadong, et al. Non-local neural networks with grouped bilinear attentional transforms[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 11801–11810.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: