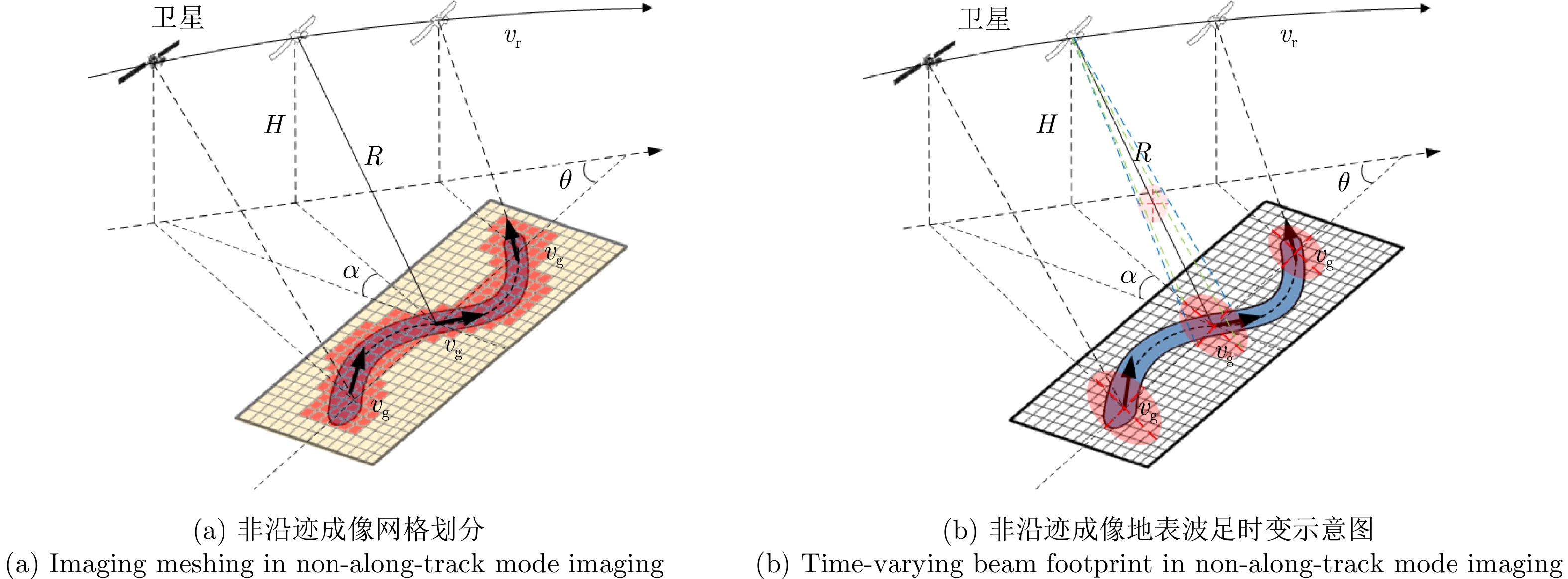
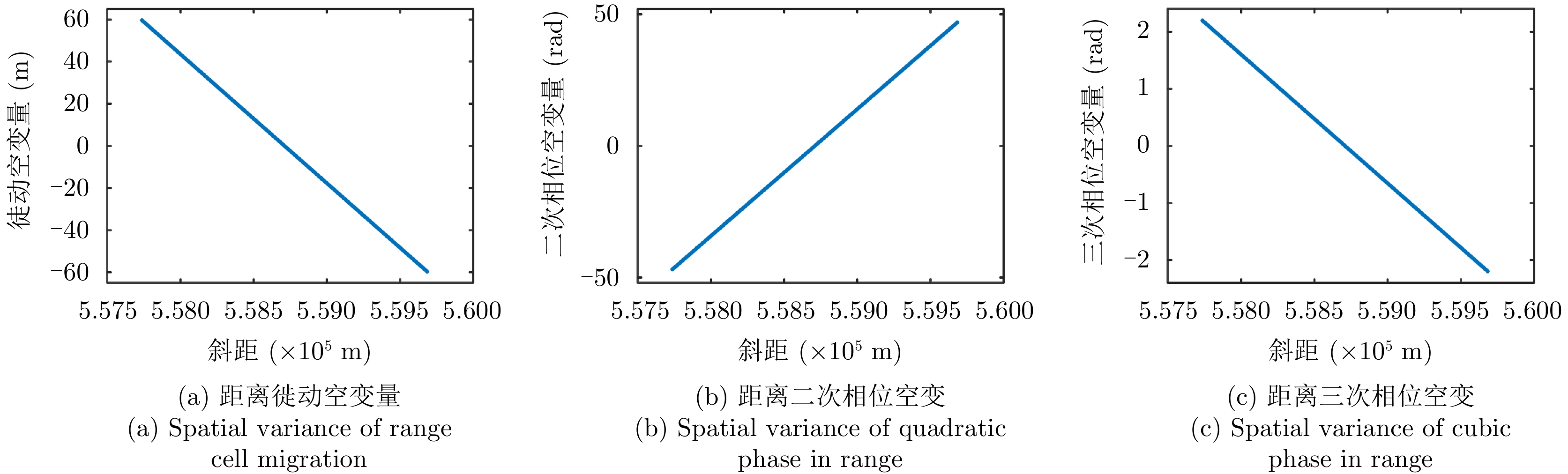
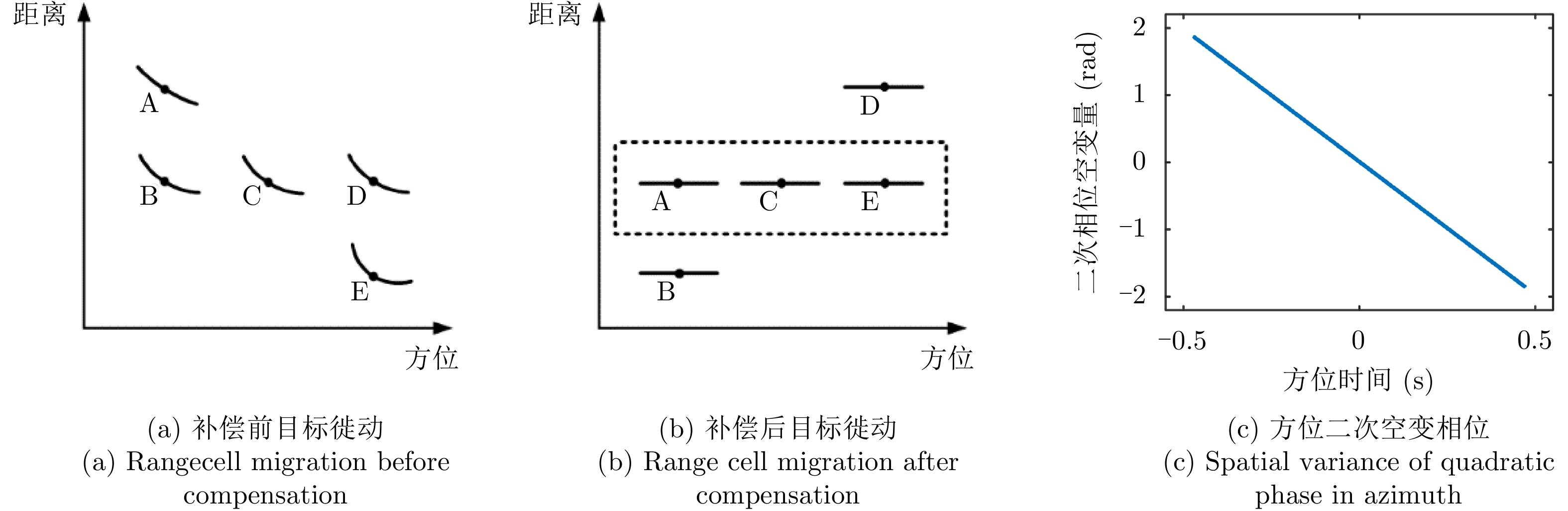
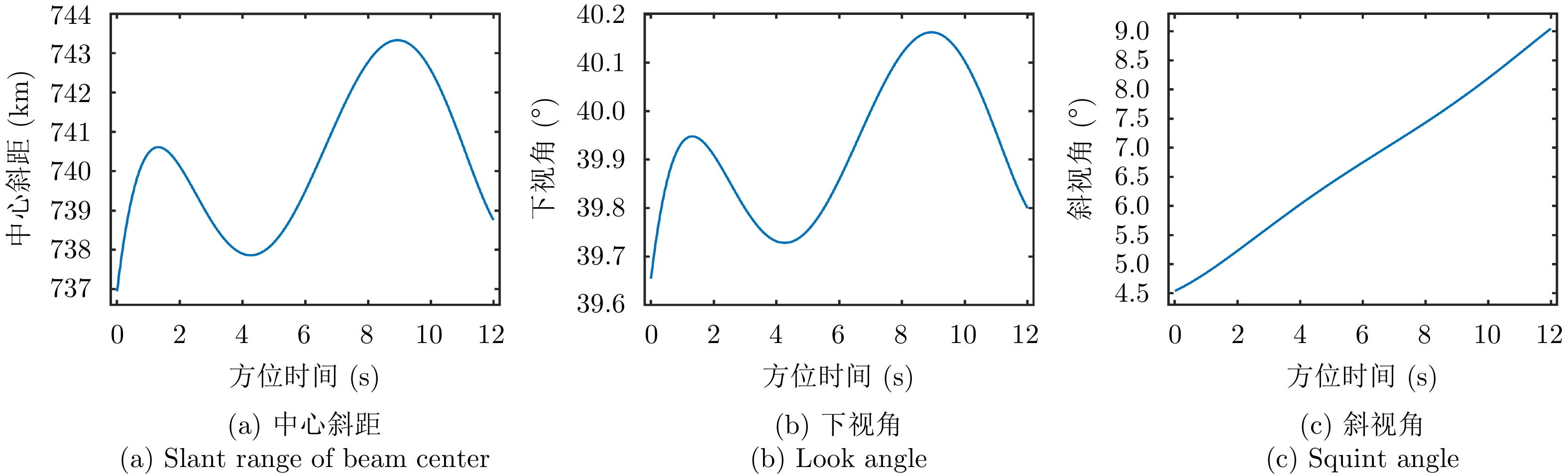
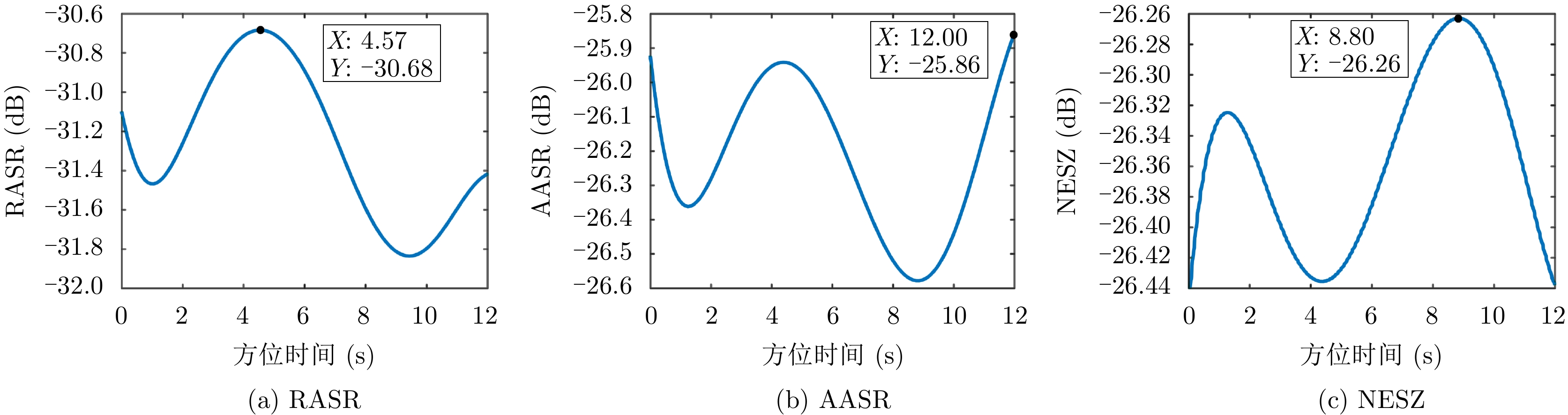
| [1] |
CURLANDER J C and MCDONOUGH R N. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing[M]. New York: Wiley, 1991: 4–8.
|
| [2] |
刘永坦. 雷达成像技术[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2014: 26–28.
LIU Yongtan. Radar Imaging Technology[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2014: 26–28.
|
| [3] |
魏钟铨. 合成孔径雷达卫星[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 67–68.
WEI Zhongquan. Synthetic Aperture Radar Satellite[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001: 67–68.
|
| [4] |
CUMMING I G and WONG F H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Boston: Artech House, 2004: 4–5.
|
| [5] |
保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 3–6.
BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Technology[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 3–6.
|
| [6] |
皮亦鸣, 杨建宇, 付毓生, 等. 合成孔径雷达成像原理[M]. 成都: 电子科技大学出版社, 2007: 51–52.
PI Yiming, YANG Jianyu, FU Yusheng, et al. Principle of Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging[M]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China Press, 2007: 51–52.
|
| [7] |
VILLANO M, PINHEIRO M, KRIEGER G, et al. Gapless imaging with the NASA-ISRO SAR (NISAR) mission: Challenges and opportunities of staggered SAR[C]. The 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 2018.
|
| [8] |
MOORE R K, CLAASSEN J P, and LIN Y H. Scanning spaceborne synthetic aperture radar with integrated radiometer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1981, AES-17(3): 410–421. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1981.309069 |
| [9] |
DE ZAN F and GUARNIERI A M. TOPSAR: Terrain observation by progressive scans[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2006, 44(9): 2352–2360. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.873853 |
| [10] |
ZHENG Ge, YAO Yiping, HE Dongsheng, et al. Optimization design of global low-orbit satellite constellation for multi-fold coverage[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Electronics and Communication Engineering, Xi’an, China, 2020.
|
| [11] |
EUGENIO F, MARCELLO J, and MARTIN J. High-resolution maps of bathymetry and benthic habitats in shallow-water environments using multispectral remote sensing imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(7): 3539–3549. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2377300 |
| [12] |
WU Xueling, LIU Chaoxian, and WU Guofeng. Spatial-temporal analysis and stability investigation of coastline changes: A case study in Shenzhen, China[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1): 45–56. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2755444 |
| [13] |
CHEN Ninghua, NI Nina, KAPP P, et al. Structural analysis of the hero range in the Qaidam Basin, Northwestern China, using integrated UAV, terrestrial LiDAR, Landsat 8, and 3-D seismic data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(9): 4581–4591. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2440171 |
| [14] |
WANG Xiaoqing, DOU Aixia, DING Xiang, et al. The development of rapid extraction and publishing system of earthquake damage based on remote sensing[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018.
|
| [15] |
QIN Xiaoqiong, LIAO Mingsheng, ZHANG Lu, et al. Structural health and stability assessment of high-speed railways via thermal dilation mapping with time-series InSAR analysis[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(6): 2999–3010. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2719025 |
| [16] |
BABU A and BAUMGARTNER S V. Road surface quality assessment using polarimetric airborne SAR[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference, Florence, Italy, 2020.
|
| [17] |
CARRARA W G, GOODMAN R S, and MAJEWSKI R M. Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar: Signal Processing Algorithms[M]. Boston: Artech House, 1995: 4−5.
|
| [18] |
MOREIRA A, PRATS-IRAOLA P, YOUNIS M, et al. A tutorial on synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2013, 1(1): 6–43. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2013.2248301 |
| [19] |
QUEGAN S. Spotlight synthetic aperture radar: Signal processing algorithms: Carrara W. G., Goodman R. S. and Majewski R. M., 1995, 554 pp. Artech House, Boston, London, £63, hb, ISBN 0-89006-728-7[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 1997, 59(5): 597–598. doi: 10.1016/S1364-6826(97)83336-6 |
| [20] |
FRANCESCHETTI G, GUIDA R, IODICE A, et al. Efficient simulation of hybrid stripmap/spotlight SAR raw signals from extended scenes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(11): 2385–2396. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.834763 |
| [21] |
BELCHER D P and BAKER C J. High resolution processing of hybrid strip-map/spotlight mode SAR[J]. IEE Proceedings-Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1996, 143(6): 366–374. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19960790 |
| [22] |
META A, MITTERMAYER J, PRATS P, et al. TOPS imaging with TerraSAR-X: Mode design and performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 759–769. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2026743 |
| [23] |
WANG Yan, LI Jingwen, YANG Jian, et al. Spaceborne stripmap range sweep SAR: Positive terrain tracking by continuous beam scanning in elevation[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 7(11): 1014–1022. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2016.1212416 |
| [24] |
WANG Yan, LI Zhe, DING Zegang, et al. Spaceborne large-squint terrain-matching synthetic aperture radar: Concept and technology[C]. The 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xiamen, China, 2019: 1–6.
|
| [25] |
WANG Yan, DING Zegang, XU Pei, et al. Strip layering diagram-based optimum continuously varying pulse interval sequence design for extremely high-resolution spaceborne sliding spotlight SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(8): 6751–6770. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3028973 |
| [26] |
WANG Yan, YANG Jian, and LI Jingwen. Data acquisition for a novel spaceborne azimuth-range sweep synthetic aperture radar[C]. 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, United States, 2017: 6004–6007.
|
| [27] |
WANG Yan, DING Zegang, JI Weiwei, et al. Time-varying nadir echo suppression for spaceborne stripmap range sweep synthetic aperture radar via waveform diversity[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(5): 826–830. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2989375 |
| [28] |
VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, and MOREIRA A. Ambiguities and image quality in staggered SAR[C]. The 5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Singapore, Singapore, 2015: 204–209.
|
| [29] |
VILLANO M, KRIEGER G, JÄGER M, et al. Staggered SAR: Performance analysis and experiments with real data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(11): 6617–6638. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2731047 |
| [30] |
SOUMEKH M. Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing with MATLAB Algorithms[M]. New York: John Wiley Sons, 1999: 486–539.
|
| [31] |
BAMLER R and EINEDER M. ScanSAR processing using standard high precision SAR algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1996, 34(1): 212–218. doi: 10.1109/36.481905 |
| [32] |
DAVIDSON G W and CUMMING I. Signal properties of spaceborne squint-mode SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1997, 35(3): 611–617. doi: 10.1109/36.581976 |
| [33] |
LUO Yunhua, ZHAO Bingji, HAN Xiaolei, et al. A novel high-order range model and imaging approach for high-resolution LEO SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(6): 3473–3485. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2273086 |
| [34] |
SUN Guangcai, JIANG Xiuwei, XING Mengdao, et al. Focus improvement of highly squinted data based on azimuth nonlinear scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(6): 2308–2322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2102040 |
| [35] |
WANG Yan, DING Zegang, ZENG Tao, et al. Interpolation free wide nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for spaceborne stripmap range sweep SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(4): 621–625. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2930537 |
| [36] |
WANG Yan, LI Jingwen, and YANG Jian. Wide nonlinear chirp scaling algorithm for spaceborne stripmap range sweep SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 6922–6936. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2737031 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

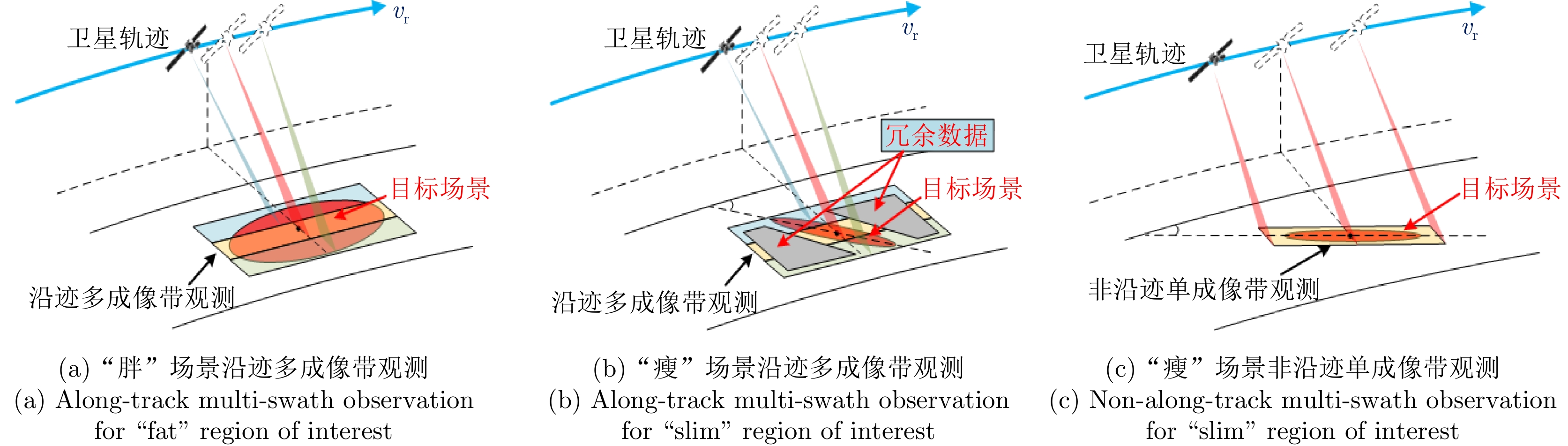



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: