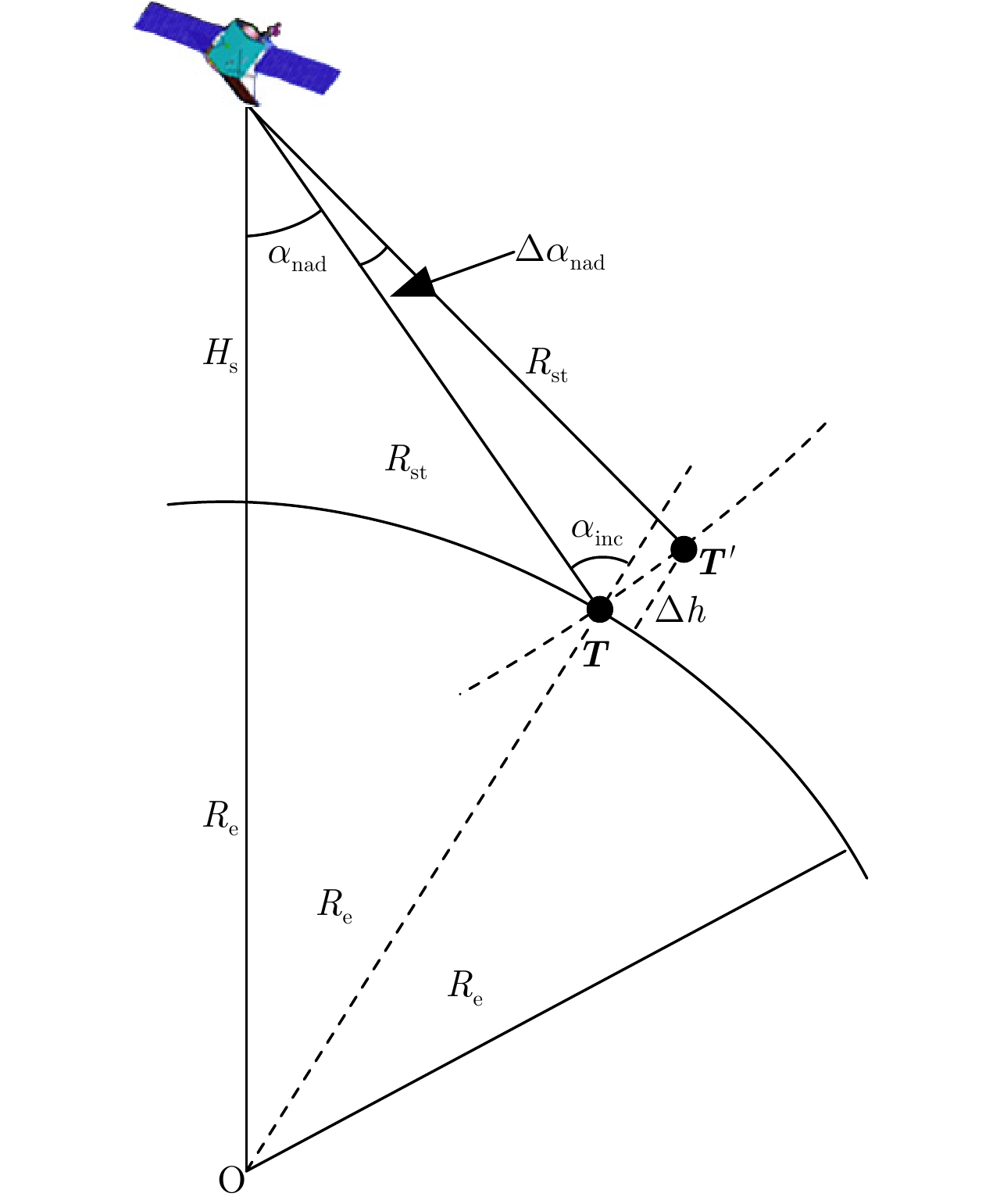
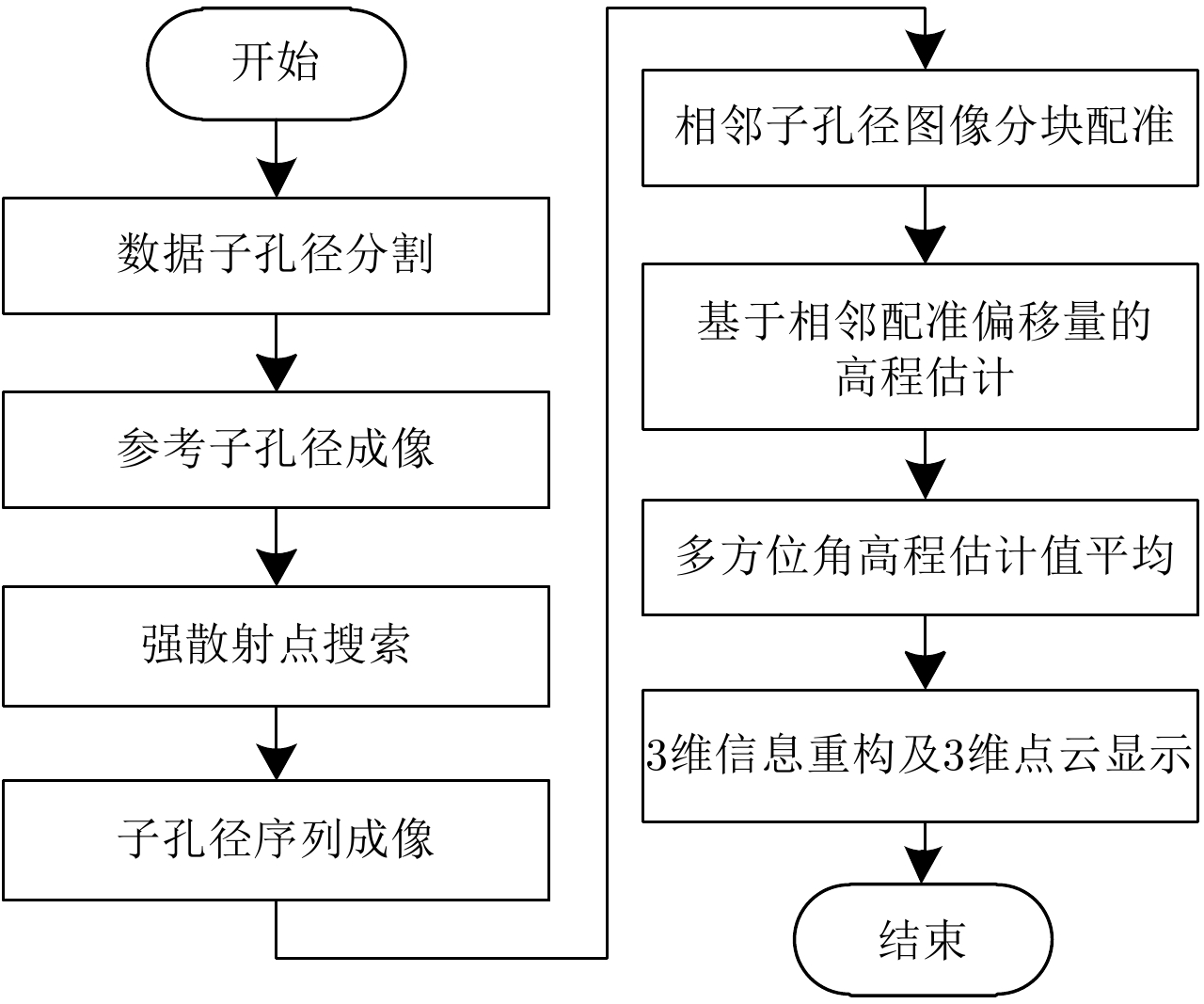
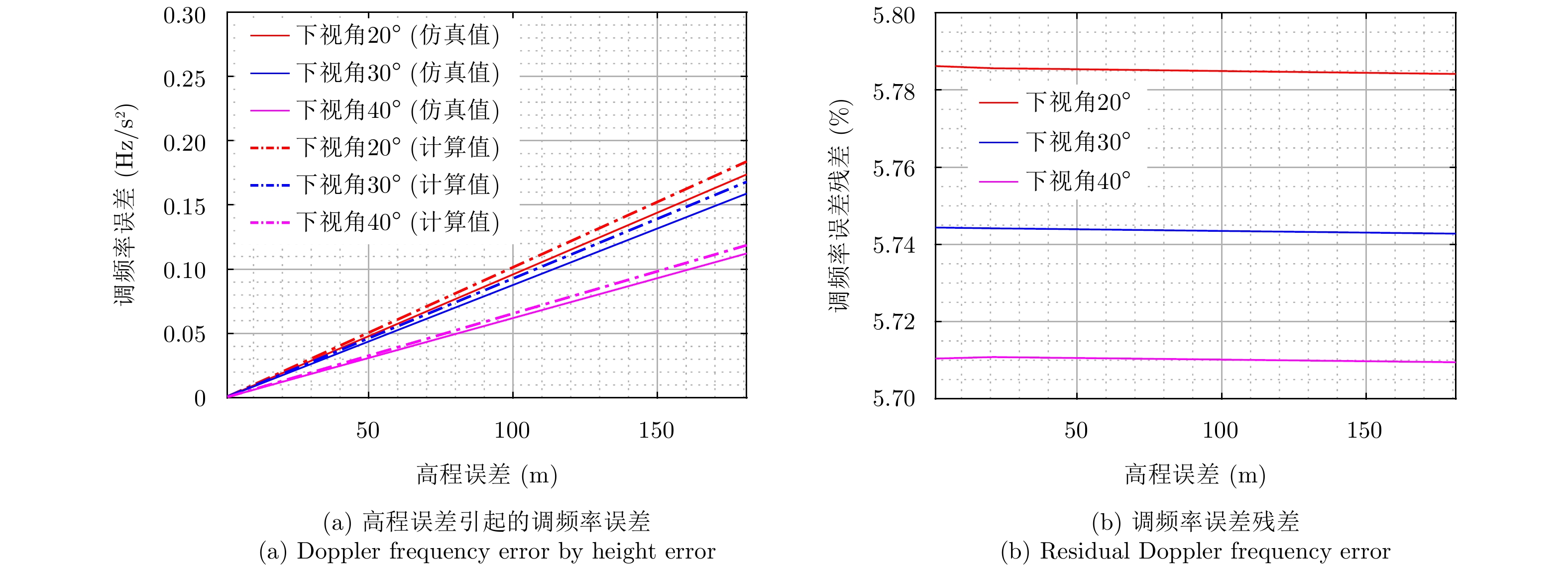
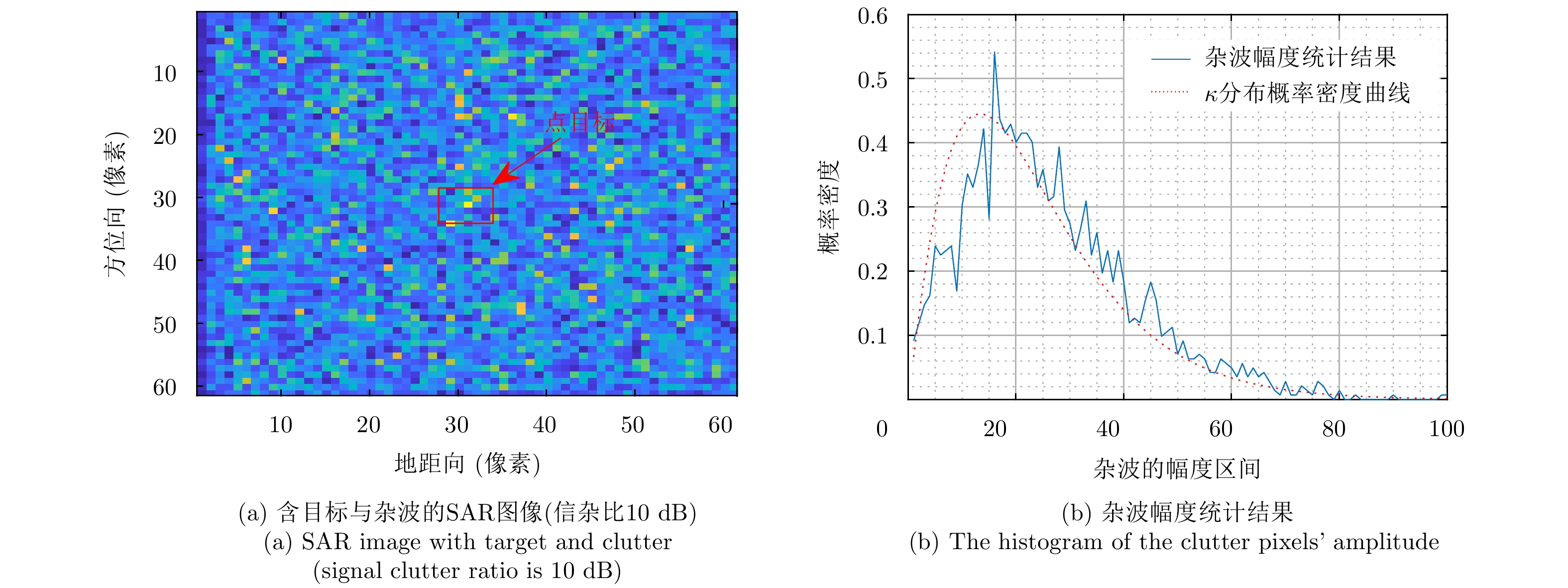
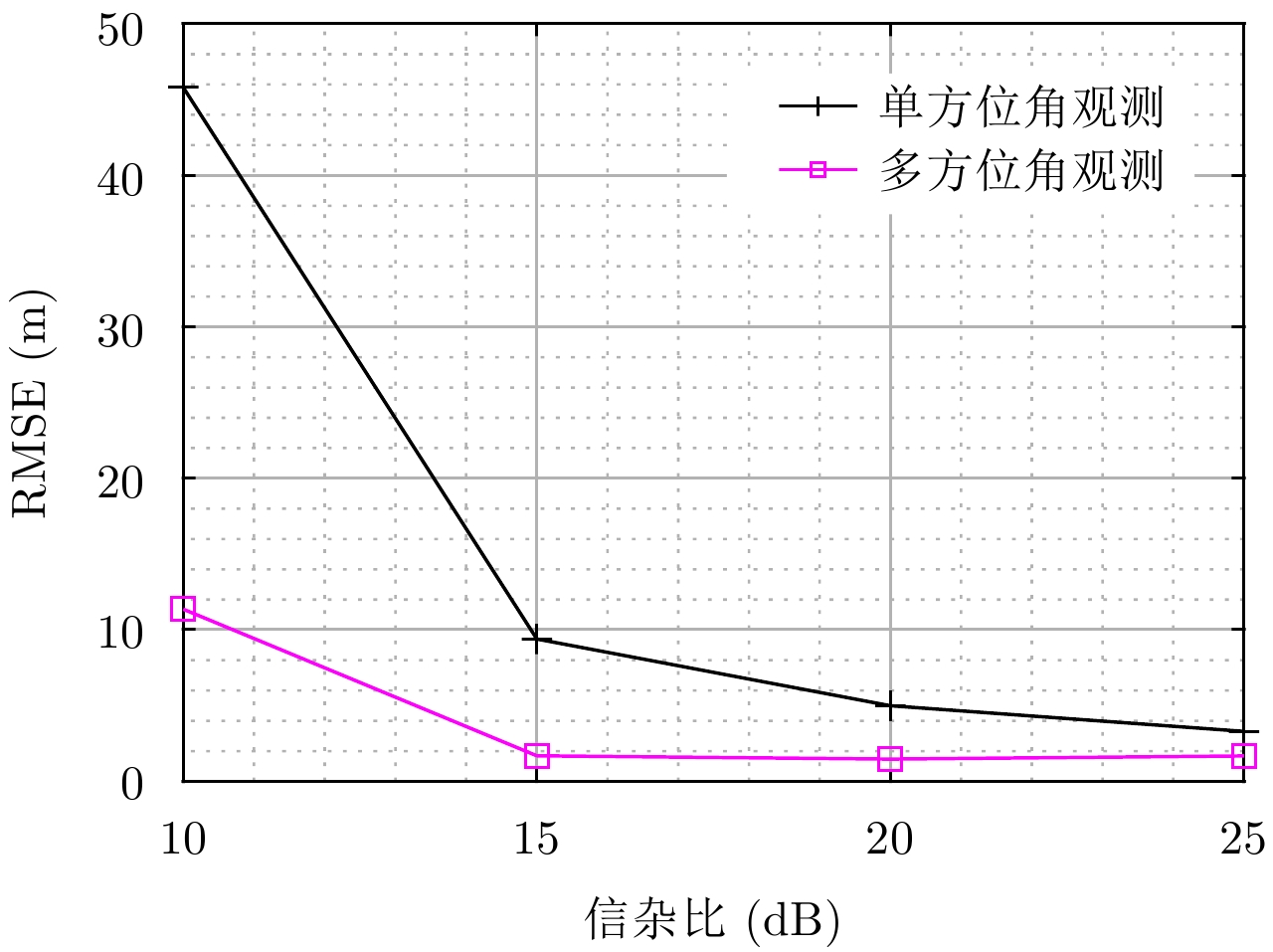
| [1] |
杨汝良, 李海英, 李世强, 等. 高分辨率微波成像[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013: VII–IX.
Yang Ru-liang, Li Hai-ying, Li Shi-qiang, et al.. High Resolution Microwave Imaging[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2013: VII–IX.
|
| [2] |
Hou Jian-guo, Zhang Qin, and Yang Cheng-sheng. Introduction to InSAR and its applications in geohazards[J]. Geomatics& Spatial Information Technology, 2007, 30(6): 28–30, 35. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2007.06.008 |
| [3] |
Krieger G, Hajnsek I, Younis M, et al. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (SAR) missions employing formation flying[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(5): 816–843. DOI: 10.1109/JPROC.2009.2038948 |
| [4] |
Reigber A and Moreira A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. DOI: 10.1109/36.868873 |
| [5] |
Poncos V. On the use of TerraSAR-X and Radarsat-2 spotlight data for persistent scatterers and tomographic analysis[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012.
|
| [6] |
Zhou Han-fei, Li Yu, and Su Yi. Three-dimensional imaging with multi-aspect SAR data[J]. Journal of Electronics& Information Technology, 2013, 35(10): 2467–2474. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01534 |
| [7] |
Zhou Han-fei, Li Yu, and Su Yi. Multi-aspect SAR feature extraction based on compressive sensing[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2013, 41(3): 543–548. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2013.03.021 |
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
Ertin E, Austin C D, Sharma S, et al.. GOTCHA experience report: Three-dimensional SAR imaging with complete circular apertures[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 6568, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XIV, Orlando, United States, 2007: 656802. DOI: 10.1117/12.723245. |
| [10] |
Knaell K. Three-dimensional SAR from curvilinear apertures[C]. Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE National Radar Conference, Ann Arbor, USA, 1996: 220–225. DOI: 10.1109/NRC.1996.510684. |
| [11] |
何峰, 杨阳, 董臻, 等. 曲线合成孔径雷达三维成像研究进展与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 130–135. DOI: 10.12000/JR14119He Feng, Yang Yang, Dong Zhen, et al. Progress and prospects of curvilinear SAR 3-D imaging[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 130–135. DOI: 10.12000/JR14119 |
| [12] |
Ferrara M, Jackson J A, and Austin C. Enhancement of multi-pass 3D circular SAR images using sparse reconstruction techniques[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 7337, Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XVI, Orlando, Florida, United States, 2009: 733702. DOI: 10.1117/12.820256. |
| [13] |
Zhang J Q, Suo Z Y, Li Z F, et al. DEM Generation using circular SAR data based on low-rank and sparse matrix decomposition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(5): 724–728. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2809905 |
| [14] |
Chen L P, An D X, Huang X T, et al. A 3D reconstruction strategy of vehicle outline based on single-pass single-polarization CSAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(11): 5545–5554. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2738566 |
| [15] |
Dungan K E and Potter L C. 3-D imaging of vehicles using wide aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2011, 47(1): 187–200. DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2011.5705669 |
| [16] |
Duque S, Breit H, Balss U, et al. Absolute height estimation using a single TerraSAR-X staring spotlight acquisition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(8): 1735–1739. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2422893 |
| [17] |
Curlander J C. Location of spaceborne SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1982, GE-20(3): 359–364. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.1982.350455 |
| [18] |
Ferretti A, Monti-Guarnieri A, Prati C, et al.. InSAR Principles - Guidelines for SAR Interferometry Processing and Interpretation[M]. The Netherlands: ESA Publications, 2007.
|
| [19] |
Cumming I G, Wong F H, 洪文, 胡东辉. 合成孔径雷达成像: 算法与实现[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2012: 385–389.
Cumming I G, Wong F H, Hong Wen, Hu Dong-hui. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2012: 385–389.
|
| [20] |
Menon K R, Balakrishnan N, Janakiraman M, et al. Characterization of fluctuation statistics of radar clutter for Indian terrain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1995, 33(2): 317–324. DOI: 10.1109/36.377931 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

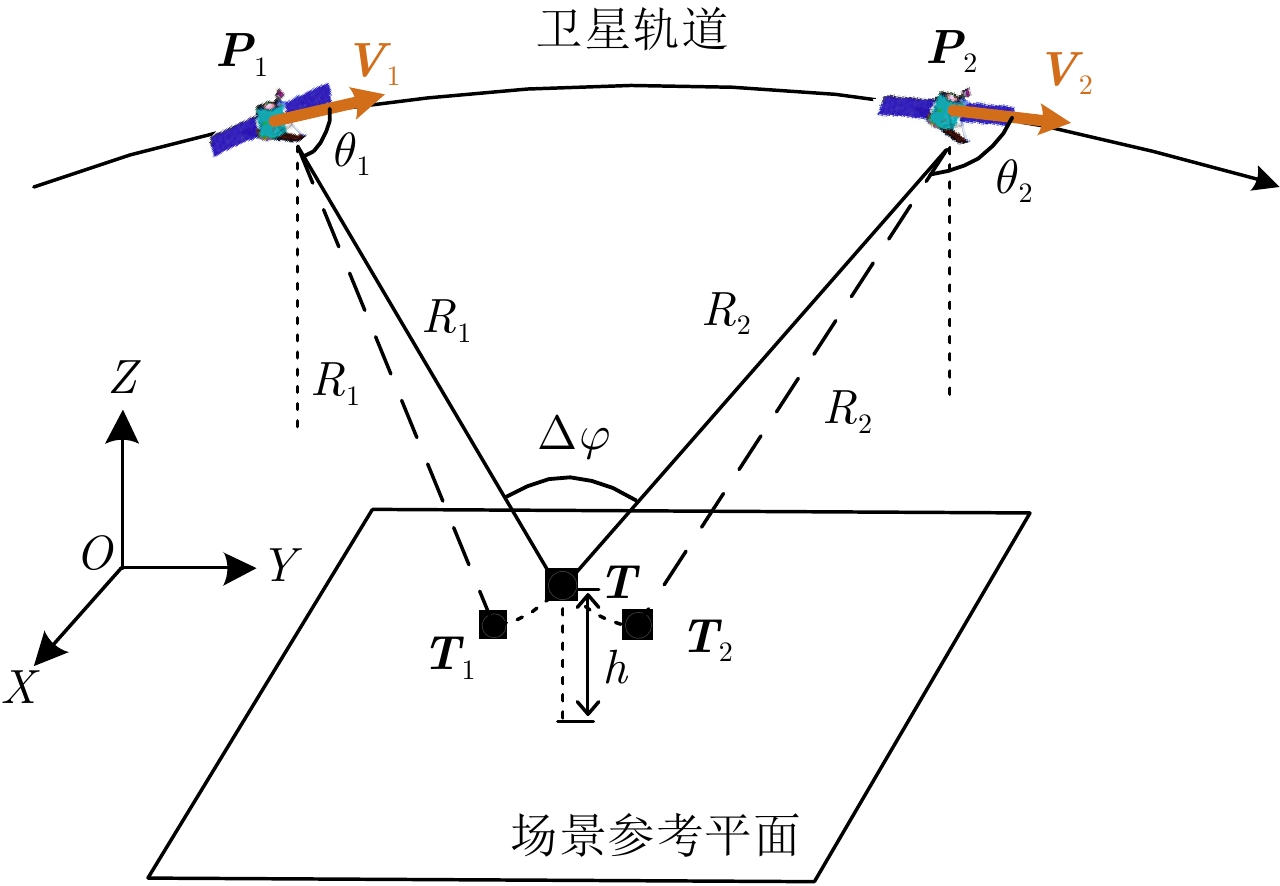



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: