- Home
- Articles & Issues
-
Data
- Dataset of Radar Detecting Sea
- SAR Dataset
- SARGroundObjectsTypes
- SARMV3D
- AIRSAT Constellation SAR Land Cover Classification Dataset
- 3DRIED
- UWB-HA4D
- LLS-LFMCWR
- FAIR-CSAR
- MSAR
- SDD-SAR
- FUSAR
- SpaceborneSAR3Dimaging
- Sea-land Segmentation
- SAR Multi-domain Ship Detection Dataset
- SAR-Airport
- Hilly and mountainous farmland time-series SAR and ground quadrat dataset
- SAR images for interference detection and suppression
- HP-SAR Evaluation & Analytical Dataset
- GDHuiYan-ATRNet
- Multi-System Maritime Low Observable Target Dataset
- DatasetinthePaper
- DatasetintheCompetition
- Report
- Course
- About
- Publish
- Editorial Board
- Chinese
| Citation: | Lei Wentai, Liang Qiong, Tan Qianying. A New Ground Penetrating Radar Signal Denoising Algorithm Based on Automatic Reversed-phase Correction and Kurtosis Value Comparison[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(3): 294-302. doi: 10.12000/JR17113 |
A New Ground Penetrating Radar Signal Denoising Algorithm Based on Automatic Reversed-phase Correction and Kurtosis Value Comparison
DOI: 10.12000/JR17113 CSTR: 32380.14.JR17113
-
Abstract
When using Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) on the occasion of complex underground medium detection, radar echo can be easily affected by various noise. In order to improve GPR detection resolution and data interpretation quality, this paper proposed a new GPR denoising algorithm based on automatic reversed-phase correction and kurtosis value comparison. GPR echo signal and random noise with the same length were fitted and two signals can be obtained. By using Independent Component Analysis (ICA) algorithm, these two signals can be decomposed into two other signals, one with high kurtosis named S1 and one with low kurtosis named S2. S1 signal’s phase was determined and automatic phase correction was carried out. By using Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (CEEMD) algorithm, S1 after automatic phase correction was decomposed, several Intrinsic Mode Function (IMF) can be obtained and kurtosis value of each IMF can be calculated. S2 signal’s kurtosis value was set as a threshold. The IMFs whose kurtosis values are lower than this threshold are classified as noise components, while the other IMFs whose kurtosis values are higher than this threshold are classified as signal components. By summing the IMFs of signal components, GPR echo signal can be reconstructed and denoising. This new GPR denoising algorithm solves the problems of phase uncertainty in ICA and manual IMF components classification in CEEMD and thus improves GPR denoising effects with higher computation efficiency. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is verified by simulation and real data processing experiments. -

-
References
[1] Harry M J, 雷文太, 童孝忠, 周旸, 等译. 探地雷达理论与应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2011: 2–24.Harry M J. Lei Wen-tai, Tong Xiao-zhong, Zhou Yang, et al.. Ground Penetrating Radar: Theory and Application[M]. Beijing: Publishing House Of Electronics Industry, 2011: 2–24.[2] 冯晅, 曾昭发, 刘四新, 等. 探地雷达信号处理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014: 3–15.Feng Xuan, Zeng Zhao-fa, Liu Si-xin, et al.. Ground Penetrating Radar Signal Processing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014: 3–15.[3] 杨峰, 彭苏萍. 地质雷达探测原理与方法研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 5–30.Yang Feng and Peng Su-ping. Study on the Principle and Method of GPR Detection[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010: 5–30.[4] 石国杰, 王晋国, 侯兆阳, 等. 地质雷达数据处理新方法研究[J]. 洛阳理工学院学报(自然科学版), 2017, 27(1): 42–44. DOI: 10.3969/i.issn.1674-5403.2017.01.012Shi Guo-jie, Wang Jin-guo, Hou Zhao-yang, et al. Study on new methods of ground penetrating radar data analysis[J]. Journal of Luoyang Institute of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 27(1): 42–44. DOI: 10.3969/i.issn.1674-5403.2017.01.012 [5] 王超, 沈斐敏. 小波变换在探地雷达弱信号去噪中的研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(2): 421–424. DOI: 10.11720/wtyht.2015.2.35Wang Chao and Shen Fei-min. Study of wavelet transform in ground penetration radar weak signal denoising[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(2): 421–424. DOI: 10.11720/wtyht.2015.2.35[6] 许军才, 刘立桥, 任青文, 等. 探地雷达信号的EEMD时域分析方法[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 38(5): 639–642. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2015.05.014Xu Jun-cai, Liu Li-qiao, Ren Qing-wen, et al. EEMD analysis of GPR signal in time domain[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2015, 38(5): 639–642. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2015.05.014 [7] Abujarad F and Omar A. Comparison of Independent Component Analysis (ICA) algorithms for GPR detection of non-metallic land mines[C]. Proceedings of SPIE Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XII, Stockholm, Sweden, 2006: 1–12.[8] 段炜. 基于小波变换的探地雷达信号去噪方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中南大学, 2008.Duan Wei. Research on denoising method of ground penetrating radar signal based on wavelet transform[D]. [Master dissertation], Central South University, 2008.[9] 张春城, 周正欧. 基于ICA的步进频率探地雷达目标信息提取研究[J]. 安徽理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 29(2): 1–4. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1098.2009.02.001Zhang Chun-cheng and Zhou Zheng-ou. Research on target information extraction in step frequency ground penetrating radar data based on independent component analysis[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Science and Technology(Natural Science), 2009, 29(2): 1–4. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1098.2009.02.001 [10] 陈玲娜. 基于CEEMD和PCA的探地雷达数据处理研究与应用[D]. [硕士论文], 吉林大学, 2016.Chen Ling-na. The study and application of GPR data processing based on CEEMD and PCA[D]. [Master dissertation], Jilin University, 2016.[11] Li J, Liu C, Zeng Z F, et al. GPR signal denoising and target extraction with the CEEMD method[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(8): 1615–1619. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2415736[12] 明锋, 杨元喜, 曾安敏. 共模误差PCA与ICA提取方法的比较[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2017, 37(4): 385–389. DOI: 10.14075/j.jgg.2017.04.012Ming Feng, Yang Yuan-xi, and Zeng An-min. Analysis and comparison of common mode error extraction using principal component analysis and independent component analysis[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2017, 37(4): 385–389. DOI: 10.14075/j.jgg.2017.04.012[13] Wu Z H and Huang N E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1–41. DOI: 10.1142/S1793536909000047[14] Yen J R, Shieh J S, and Huang N E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2010, 2(2): 135–156. DOI: 10.1142/S1793536910000422[15] Torres M E, Colominas M A, Schlotthauer G, et al.. A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise[C]. Proceedings of 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Prague, Czech Republic, 2011: 4144–4147. DOI: 10.1109/ICASSP.2011.5947265.[16] 王姣, 李振春, 王德营. 基于CEEMD的地震数据小波阈值去噪方法研究[J]. 石油物探, 2014, 53(2): 164–172. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2014.02.006Wang Jiao, Li Zhen-chun, and Wang De-ying. A method for wavelet threshold denoising of seismic data based on CEEMD[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2014, 53(2): 164–172. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2014.02.006[17] Colominas M A, Schlotthauer G, and Torres M E. Improved complete ensemble EMD: A suitable tool for biomedical signal processing[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2014, 14: 19–29. DOI: 10.1016/j.bspc.2014.06.009[18] Warren C, Giannopoulos A, and Giannakis I. gprMax: Open source software to simulate electromagnetic wave propagation for ground penetrating radar[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2016, 209: 163–167. DOI: 10.1016/j.cpc.2016.08.020 -
Proportional views

- Figure 1. The flow diagram of ICA
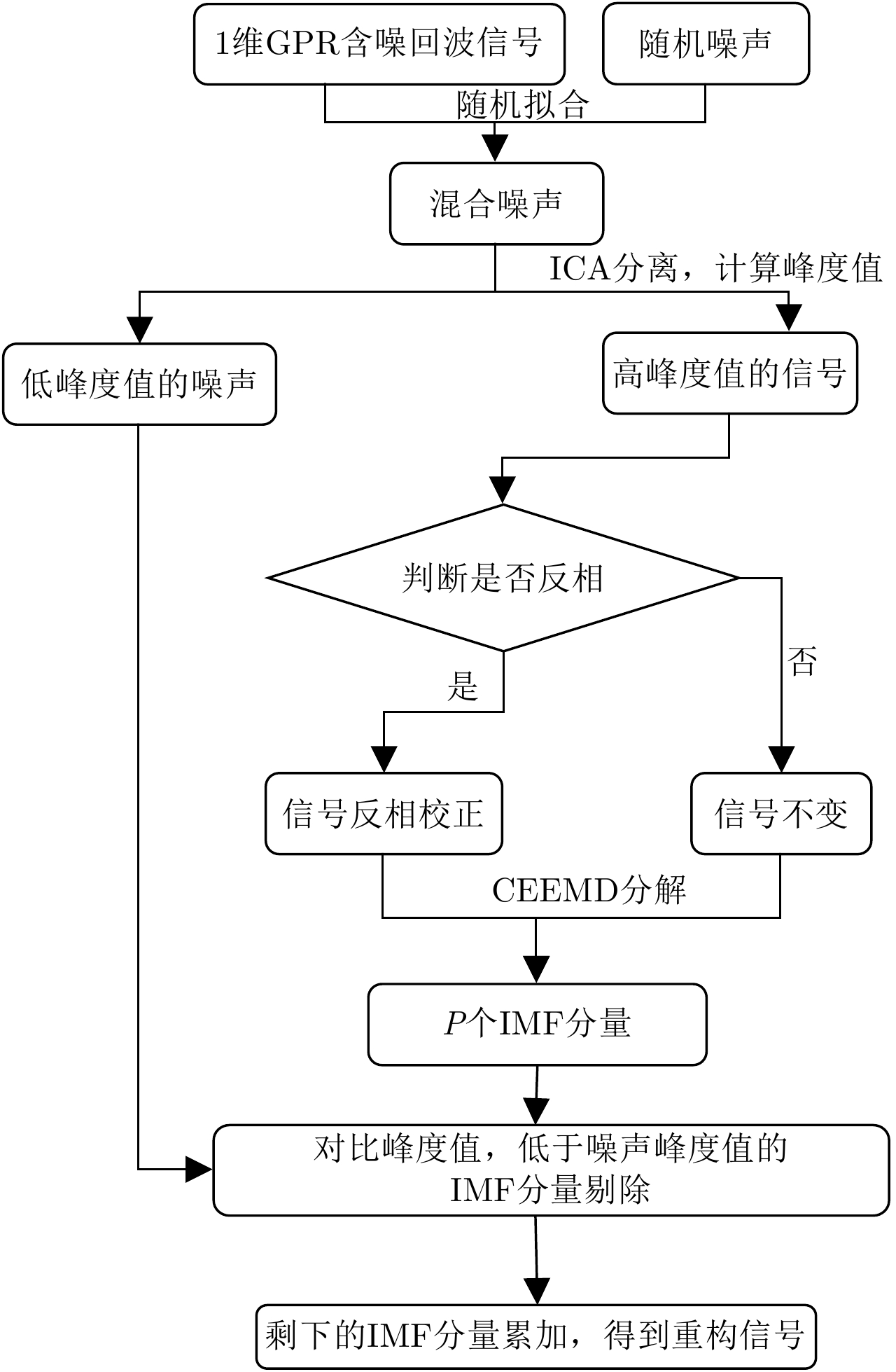
- Figure 2. The flow diagram of the algorithm
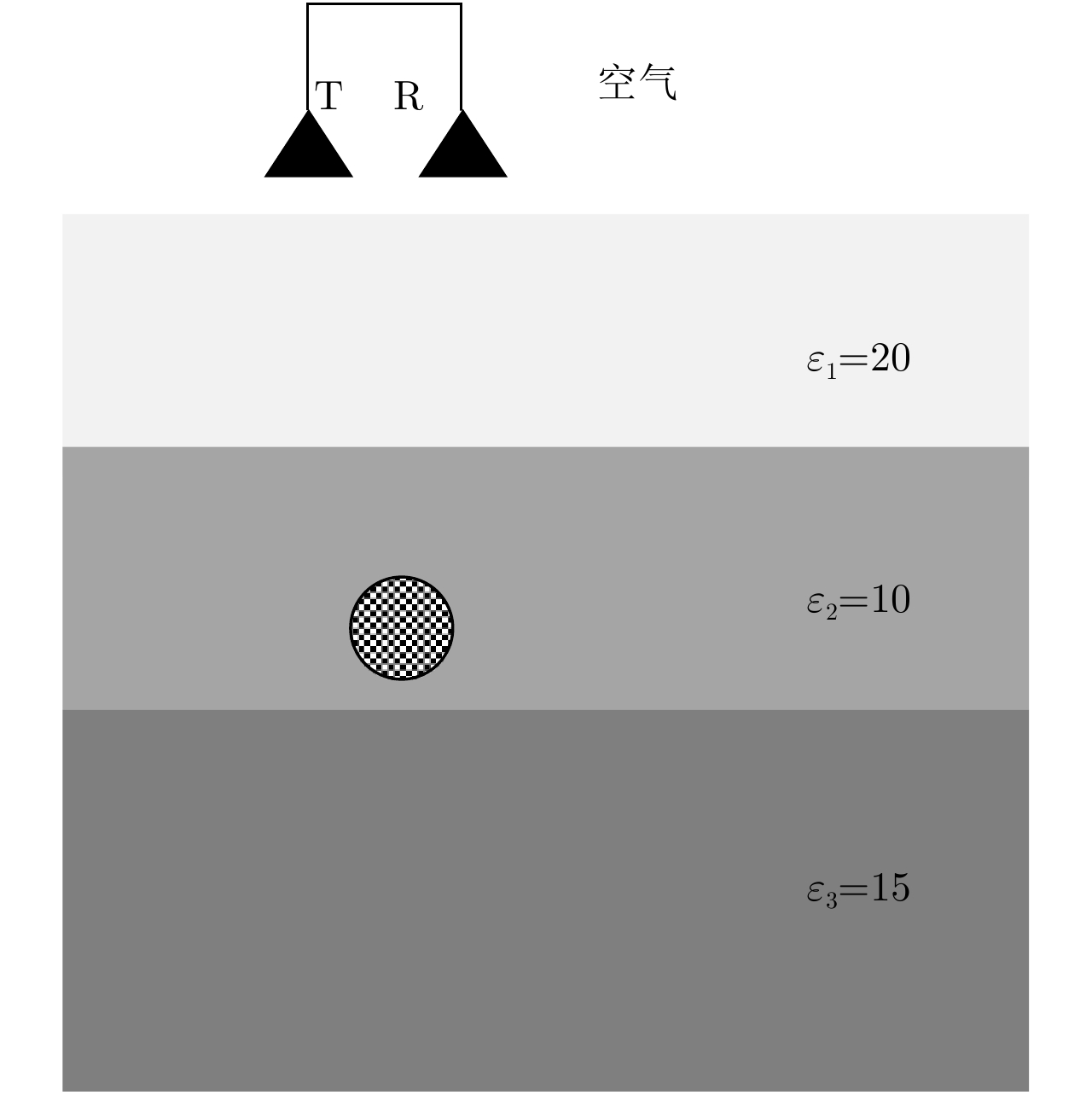
- Figure 3. The forward model diagram of GPR
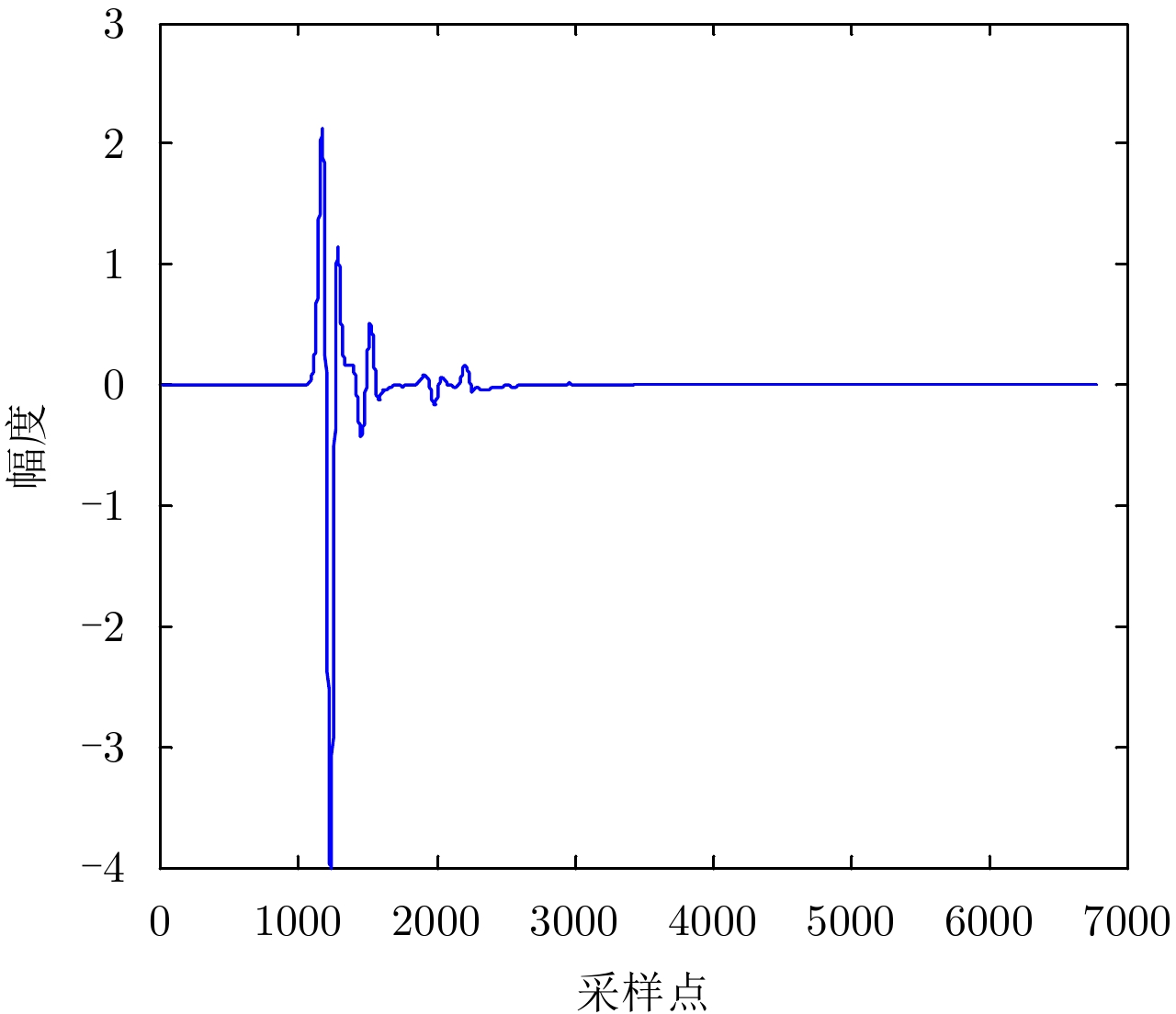
- Figure 4. The GPR no-noise echo signal by forward modeling
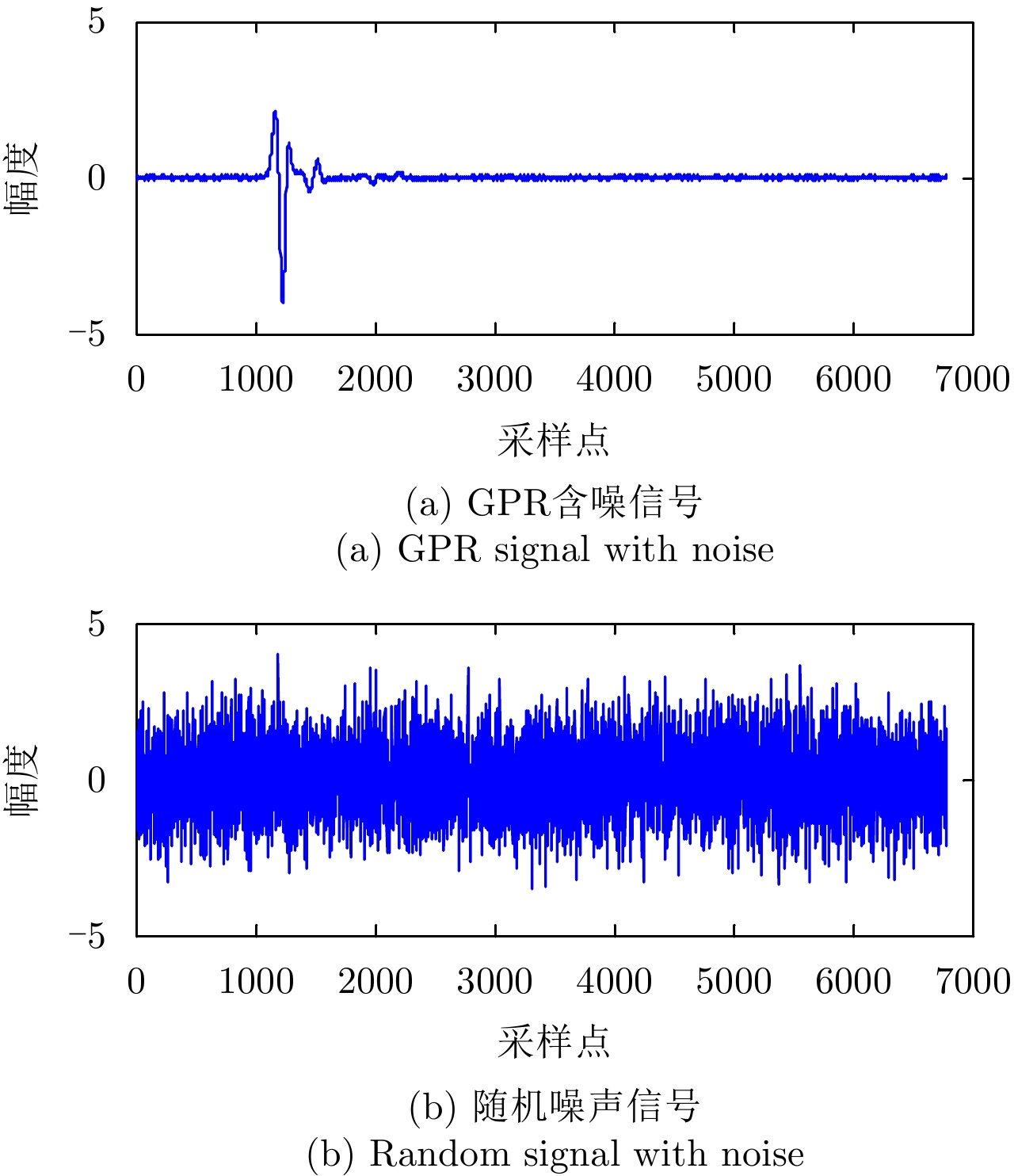
- Figure 5. The GPR noise signal and the generated equal length random noise signal obtained by adding noise
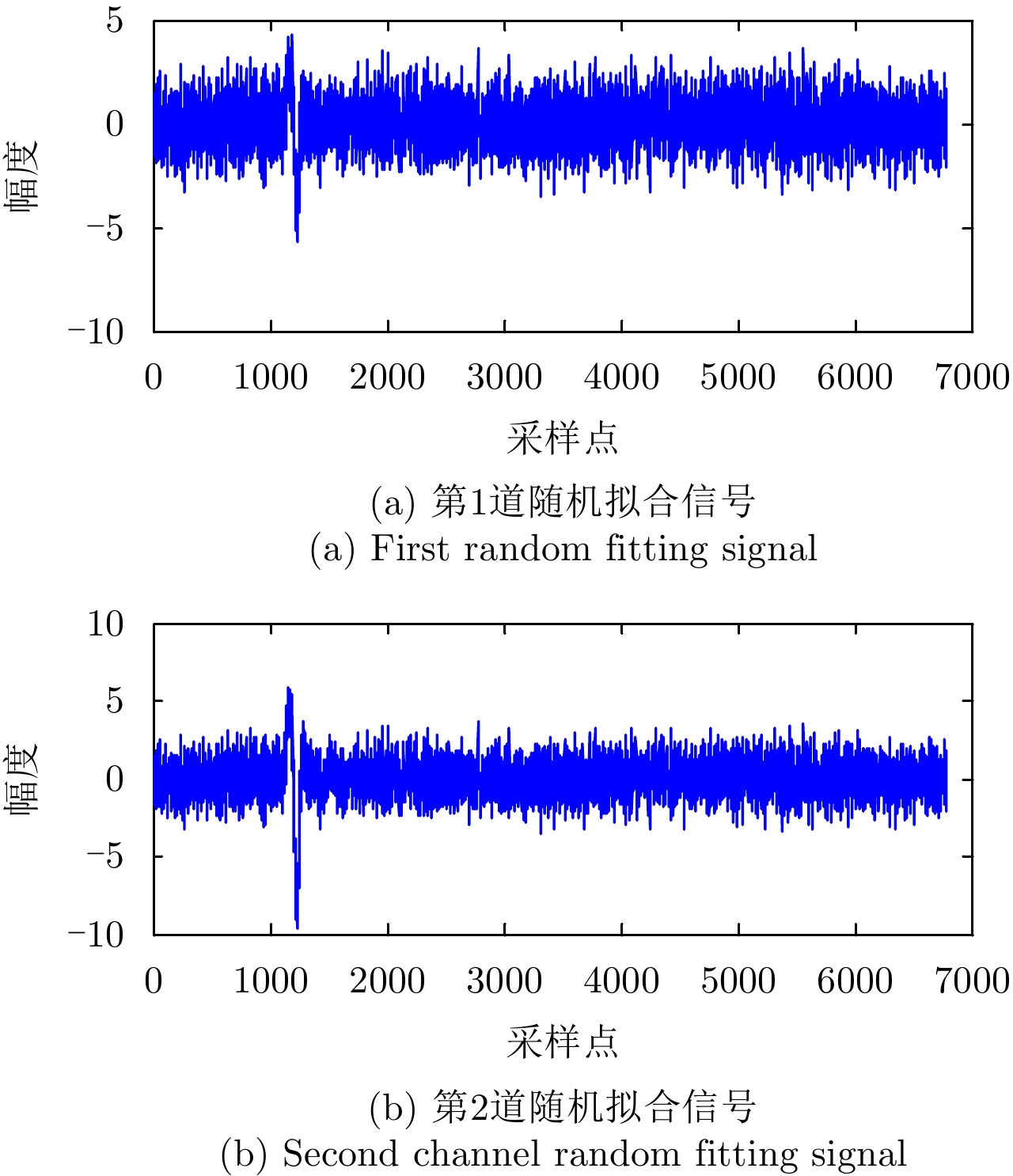
- Figure 6. Two channel signals obtained after random fitting
- Figure 7. Two channel signals separated by ICA algorithm
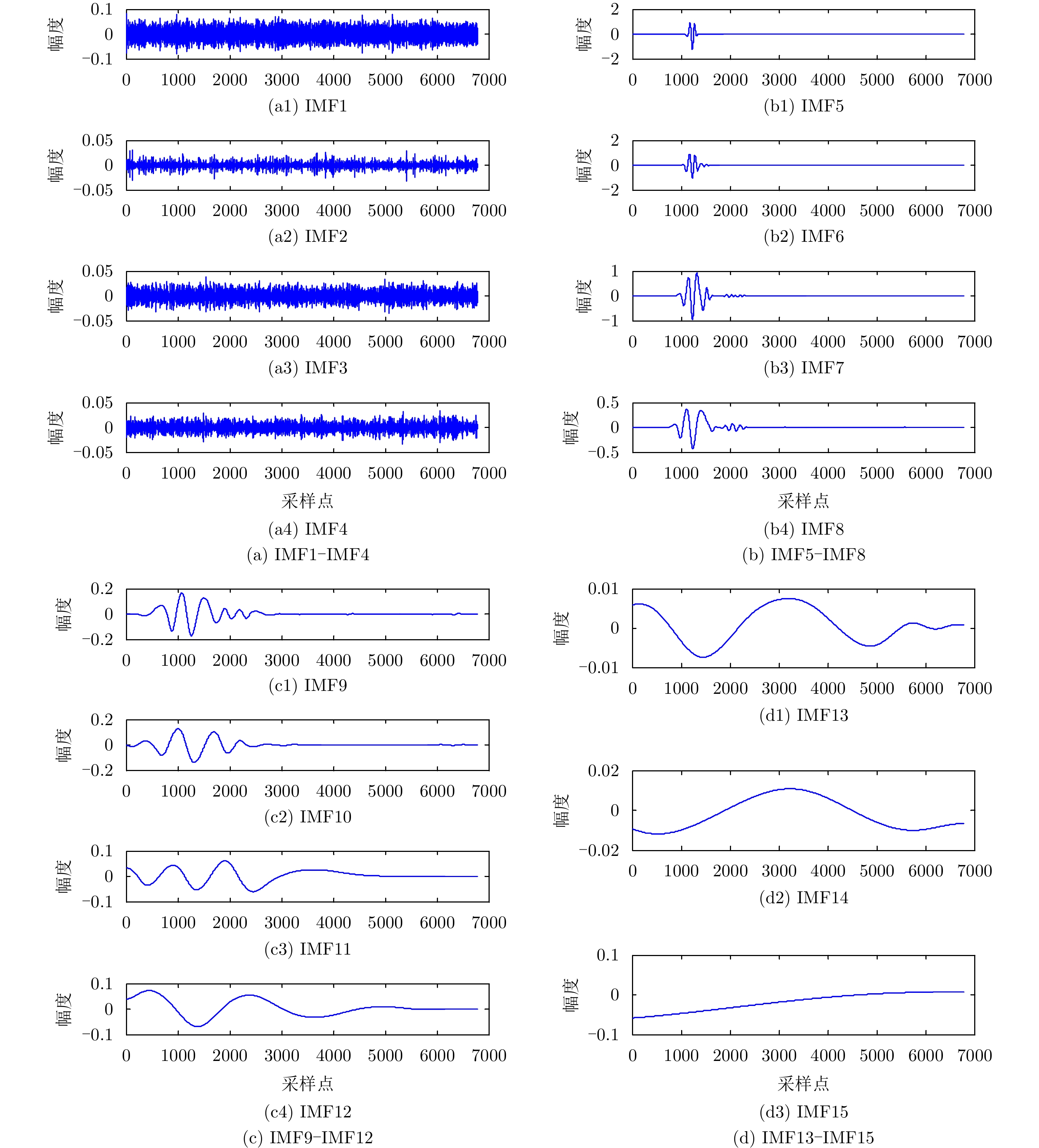
- Figure 8. The IMF component waveform diagram after CEEMD decomposition
- Figure 9. The signal of cumulative reconfiguration after the IMF components classified by kurtosis threshold value
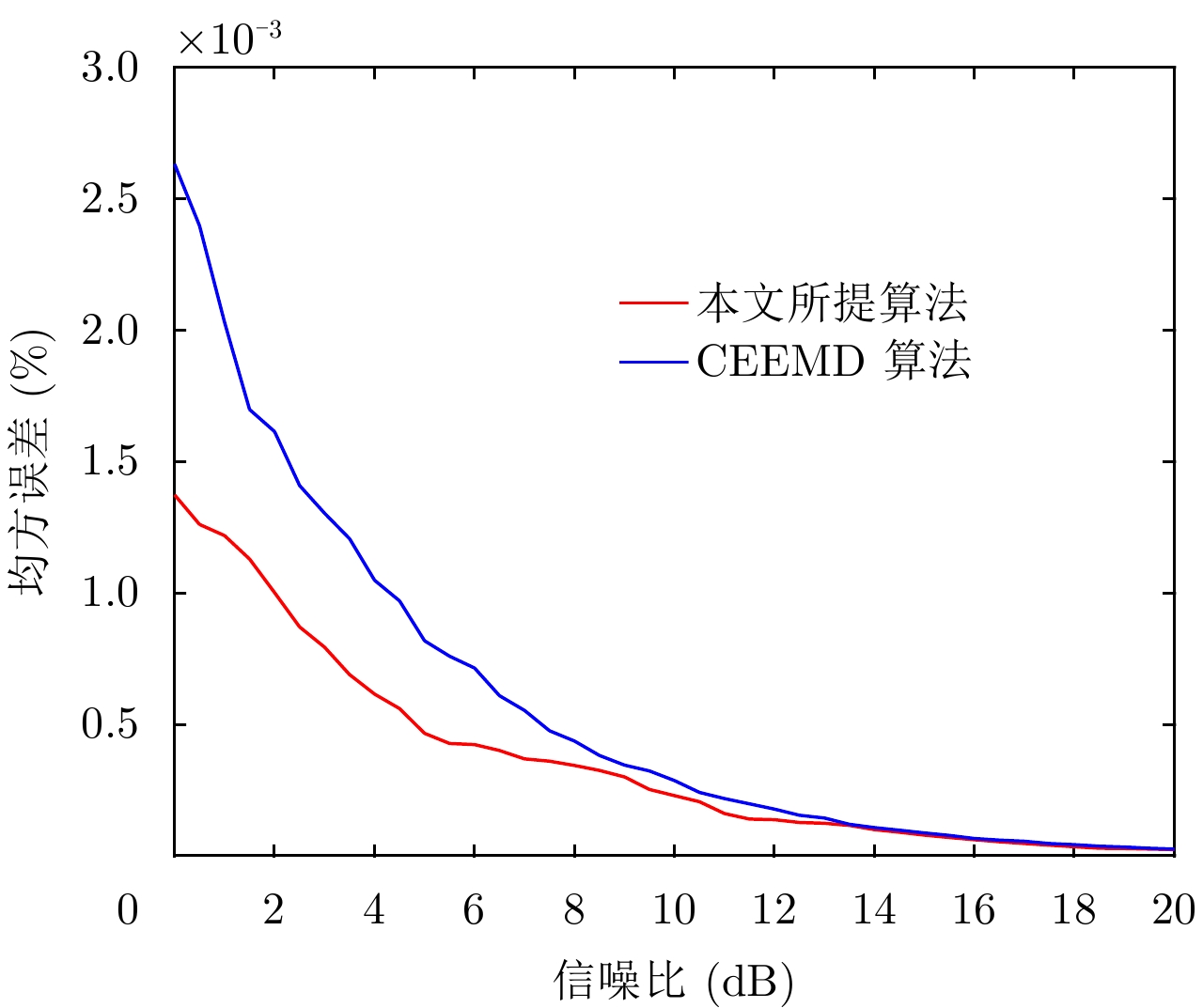
- Figure 10. The contrast diagram of the variation curve of denoising error and signa-to-noise ratio of the algorithm and the conventional algorithm
- Figure 11. The original GPR B-Scan
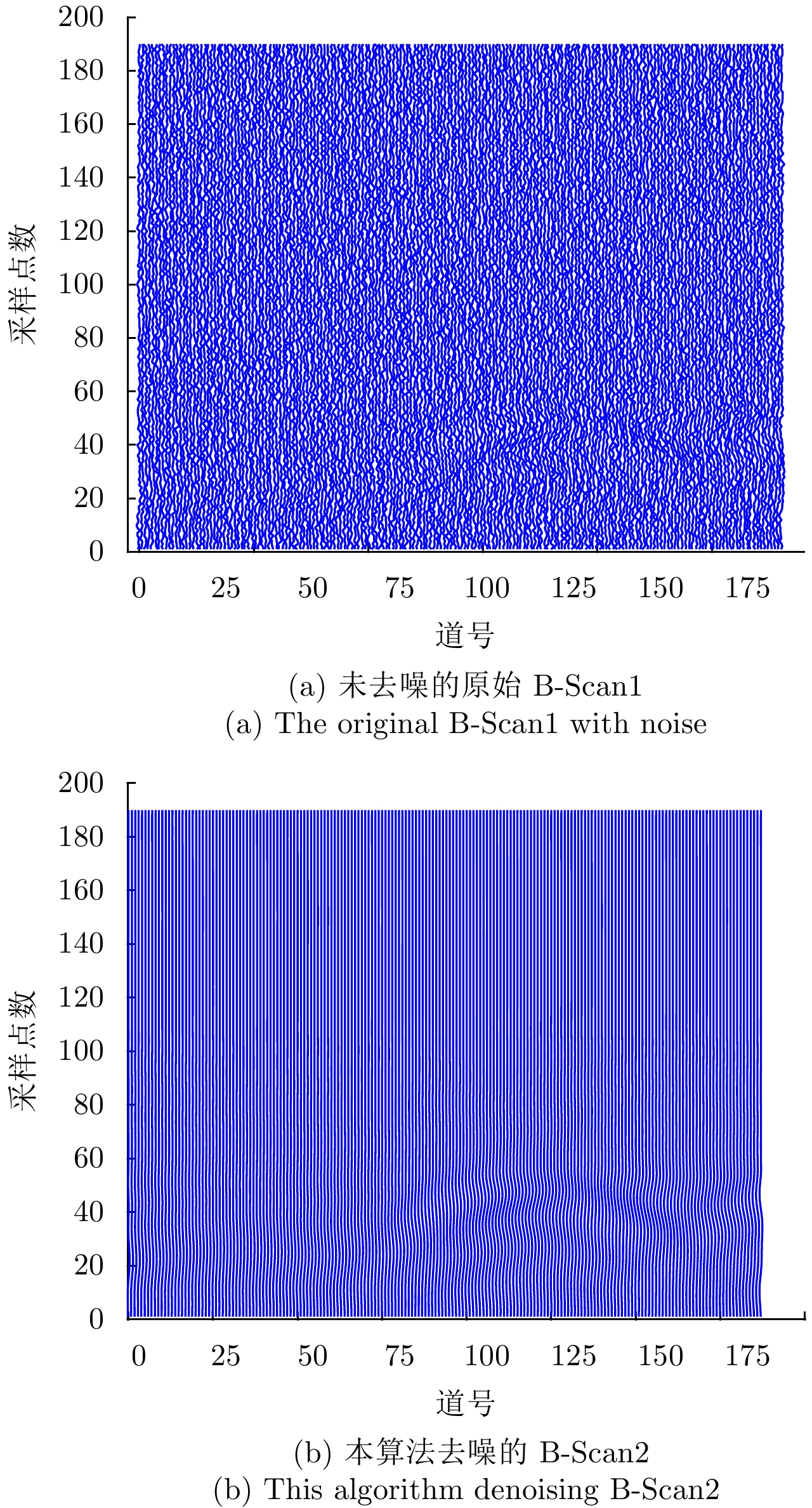
- Figure 12. The contrast diagram of the original B-Scan1 with noise and the denoising result of B-Scan2 in the present algorithm
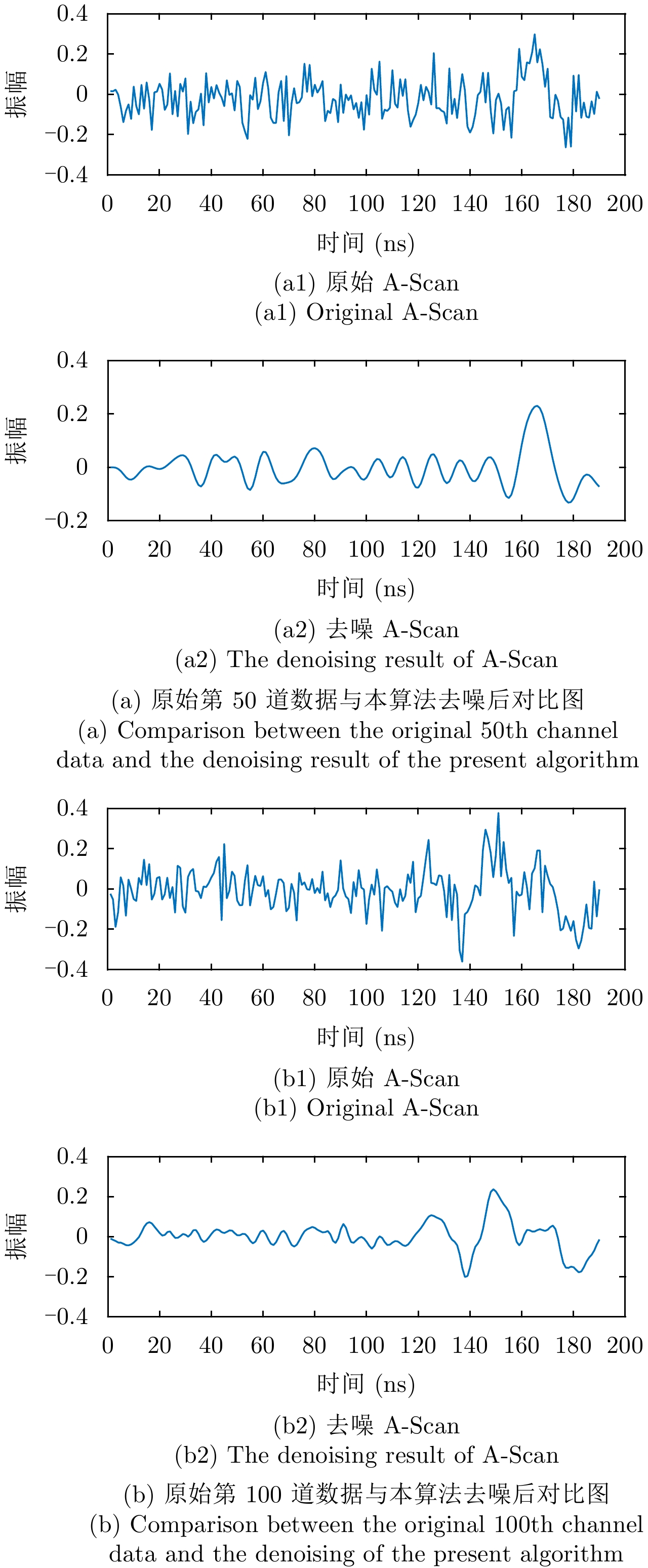
- Figure 13. The contrast diagram of the original A-Scan with noise and the denoising result of A-Scan in the present algorithm


 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: