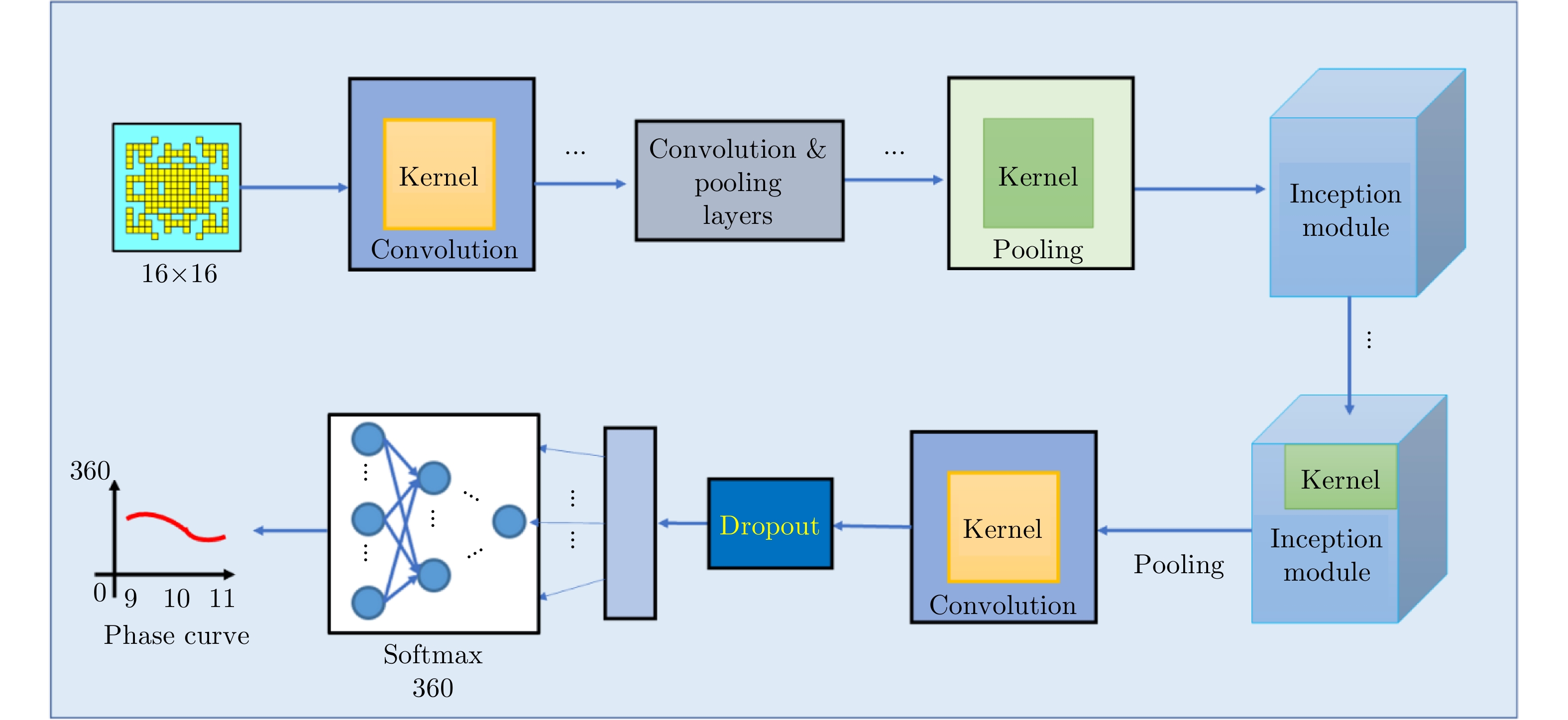
| [1] |
PENDRY J B. A chiral route to negative refraction[J]. Science, 2004, 306(5700): 1353–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.1104467 |
| [2] |
PENDRY J B, HOLDEN A J, STEWART W J, et al. Extremely low frequency plasmons in metallic mesostructures[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 76(25): 4773–4776. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.76.4773 |
| [3] |
PENDRY J B, HOLDEN A J, ROBBINS D J, et al. Magnetism from conductors and enhanced nonlinear phenomena[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1999, 47(11): 2075–2084. doi: 10.1109/22.798002 |
| [4] |
SMITH D R, PADILLA W J, VIER D C, et al. Composite medium with simultaneously negative permeability and permittivity[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2000, 84(18): 4184–4187. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.4184 |
| [5] |
CUI Tiejun, LIU Shuo, and LI Lianlin. Information entropy of coding metasurface[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2016, 5(11): e16172.
|
| [6] |
XIE Boyang, TANG Kun, CHENG Hua, et al. Coding acoustic metasurfaces[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(6): 1603507. doi: 10.1002/adma.201603507 |
| [7] |
史峰, 王辉, 郁磊, 等. MATLAB智能算法30个案例分析[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2011.
SHI Feng, WANG Hui, YU Lei, et al. Analysis of 30 Cases of MATLAB Intelligent Algorithm[M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics Press, 2011.
|
| [8] |
武飞周, 薛源. 智能算法综述[J]. 工程地质计算机应用, 2005, (2): 9–15.
WU Feizhou and XUE Yuan. Review of intelligent algorithms[J]. Engineering Geology Computer Application, 2005, (2): 9–15.
|
| [9] |
HU Han and LI Zhenyu. A survey of performance indicators for multi-objective evolutionary algorithms[J]. Software Guide, 2019, 18(9): 1–4. doi: 10.11907/rjdk.191024 |
| [10] |
MEI Zhiwei. Overview of multi objective evolutionary algorithm[J]. Software Guide, 2017, 16(6): 204–207. doi: 10.11907/rjdk.171169 |
| [11] |
CAI Haoyuan, SUN Yi, WANG Xiaoping, et al. Design of an ultra-broadband near-perfect bilayer grating metamaterial absorber based on genetic algorithm[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(10): 15347–15359. doi: 10.1364/OE.393423 |
| [12] |
HUANG Yixing, FAN Qunfu, CHEN Jin, et al. Optimization of flexible multilayered metastructure fabricated by dielectric-magnetic nano lossy composites with broadband microwave absorption[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2020, 191: 108066. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108066 |
| [13] |
QIU Tianshuo, SHI Xin, WANG Jiafu, et al. Deep learning: A rapid and efficient route to automatic metasurface design[J]. Advanced Science, 2019, 6(12): 1900128. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900128 |
| [14] |
TITTL A, LEITIS A, LIU Mingkai, et al. Imaging-based molecular barcoding with pixelated dielectric metasurfaces[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6393): 1105–1109. doi: 10.1126/science.aas9768 |
| [15] |
MA Wei, CHENG Feng, and LIU Yongmin. Deep-learning enabled on-demand design of chiral metamaterials[J]. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(6): 6326–6334. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b03569 |
| [16] |
LIU Che, YU Wenming, MA Qian, et al. Intelligent coding metasurface holograms by physics-assisted unsupervised generative adversarial network[J]. Photonics Research, 2021, 9(4): B159–B167. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.416287 |
| [17] |
PEURIFOY J, SHEN Yichen, YANG Yi, et al. Nanophotonic inverse design using artificial neural network[C]. Frontiers in Optics 2017, Washington, USA, 2017: FTh4A.4. doi: 10.1364/FIO.2017.FTh4A.4. |
| [18] |
VAI M M, WU Shuichi, LI Bin, et al. Reverse modeling of microwave circuits with bidirectional neural network models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 1998, 46(10): 1492–1494. doi: 10.1109/22.721152 |
| [19] |
KABIR H, WANG Ying, YU Ming, et al. Neural network inverse modeling and applications to microwave filter design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2008, 56(4): 867–879. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2008.919078 |
| [20] |
SELLERI S, MANETTI S, and PELOSI G. Neural network applications in microwave device design[J]. International Journal of RF and Microwave Computer-Aided Engineering, 2002, 12(1): 90–97. doi: 10.1002/mmce.7001 |
| [21] |
LIU Dianjing, TAN Yixuan, KHORAM E, et al. Training deep neural networks for the inverse design of nanophotonic structures[J]. ACS Photonics, 2018, 5(4): 1365–1369. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b01377 |
| [22] |
PEURIFOY J, SHEN Yichen, JING Li, et al. Nanophotonic particle simulation and inverse design using artificial neural networks[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(6): eaar4206. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aar4206 |
| [23] |
随赛. 新型人工电磁表面拓扑优化设计与应用研究[D]. [博士论文], 空军工程大学, 2019.
SUI Sai. Research on topology optimization design and application of new artificial electromagnetic surface[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Air Force Engineering University, 2019.
|
| [24] |
LANDY N I, SAJUYIGBE S, MOCK J J, et al. Perfect metamaterial absorber[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100(20): 207402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.207402 |
| [25] |
BAO Di, SHEN Xiaopeng, and CUI Tiejun. Progress of terahertz metamaterials[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(22): 228701. doi: 10.7498/aps.64.228701 |
| [26] |
SHEN Yang, ZHANG Jieqiu, PANG Yongqiang, et al. Transparent broadband metamaterial absorber enhanced by water-substrate incorporation[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(12): 15665–15674. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.015665 |
| [27] |
PANG Yongqiang, SHEN Yang, LI Yongfeng, et al. Water-based metamaterial absorbers for optical transparency and broadband microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 123(15): 155106. doi: 10.1063/1.5023778 |
| [28] |
PANG Yongqiang, LI Yongfeng, WANG Jiafu, et al. Electromagnetic reflection reduction of carbon composite materials mediated by collaborative mechanisms[J]. Carbon, 2019, 147: 112–119. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.03.004 |
| [29] |
SUI Sai, MA Hua, WANG Jiafu, et al. Absorptive coding metasurface for further radar cross section reduction[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2018, 51(6): 065603. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/aaa3be |
| [30] |
SUI Sai, MA Hua, WANG Jiafu, et al. Synthetic design for a microwave absorber and antireflection to achieve wideband scattering reduction[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2019, 52(3): 035103. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/aaeb12 |
| [31] |
CUI Yanxia, FUNG K H, XU Jun, et al. Ultrabroadband light absorption by a sawtooth anisotropic metamaterial slab[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(3): 1443–1447. doi: 10.1021/nl204118h |
| [32] |
FU Jiahui, WU Qun, ZHANG Shaoqing, et al. Design of multi-layers absorbers for low frequency applications[C]. 2010 Asia-Pacific International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Beijing, China, 2010. doi: 10.1109/APEMC.2010.5475478. |
| [33] |
SHEN Yang, ZHANG Jieqiu, WANG Jiafu, et al. Multistage dispersion engineering in a three-dimensional plasmonic structure for outstanding broadband absorption[J]. Optical Materials Express, 2019, 9(3): 1539–1550. doi: 10.1364/OME.9.001539 |
| [34] |
WU C, NEUNER III B, SHVETS G, et al. Large-area wide-angle spectrally selective plasmonic absorber[J]. Physical Review B, 2011, 84(7): 075102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.84.075102 |
| [35] |
CHENG Yongzhi, GONG Rongzhou, NIE Yan, et al. A wideband metamaterial absorber based on a magnetic resonator loaded with lumped resistors[J]. Chinese Physics B, 2012, 21(12): 127801. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/21/12/127801 |
| [36] |
SHEN Yang, ZHANG Jieqiu, WANG Wenjie, et al. Overcoming the pixel-density limit in plasmonic absorbing structure for broadband absorption enhancement[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2019, 18(4): 674–678. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2019.2900846 |
| [37] |
ZHU Ruichao, WANG Jiafu, SUI Sai, et al. Wideband absorbing plasmonic structures via profile optimization based on genetic algorithm[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2020, 8: 231. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2020.00231 |
| [38] |
NONG Jifu. Global exponential stability of delayed Hopfield neural networks[C]. 2012 International Conference on Computer Science and Information Processing, Xi’an, China, 2012. doi: 10.1109/CSIP.2012.6308827. |
| [39] |
AN Jinliang, GAO Jia, LEI Jinhui, et al. An improved algorithm for TSP problem solving with Hopfield neural networks[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2010, 143/144: 538–542. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.143-144.538 |
| [40] |
AIYER S V B, NIRANJAN M, and FALLSIDE F. A theoretical investigation into the performance of the Hopfield model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1990, 1(2): 204–215. doi: 10.1109/72.80232 |
| [41] |
ZHU Ruichao, QIU Tianshuo, WANG Jiafu, et al. Metasurface design by a hopfield network: Finding a customized phase response in a broadband[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2020, 53(41): 415001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/ab9785 |
| [42] |
VAN DEN DRIESSCHE P and ZOU Xingfu. Global attractivity in delayed hopfield neural network models[J]. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 1998, 58(6): 1878–1890. doi: 10.1137/S0036139997321219 |
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
SELL D, YANG Jianji, DOSHAY S, et al. Large-angle, multifunctional metagratings based on freeform multimode geometries[J]. Nano Letters, 2017, 17(6): 3752–3757. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b01082 |
| [45] |
FOROUZMAND A and MOSALLAEI H. Composite multilayer shared-aperture nanostructures: A functional multispectral control[J]. ACS Photonics, 2018, 5(4): 1427–1439. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b01441 |
| [46] |
TIPRAQSA P, CRASWELL E T, NOBLE A D, et al. Resource integration for multiple benefits: Multifunctionality of integrated farming systems in Northeast Thailand[J]. Agricultural Systems, 2007, 94(3): 694–703. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2007.02.009 |
| [47] |
LING Yonghong, HUANG Lirong, HONG Wei, et al. Polarization-switchable and wavelength-controllable multi-functional metasurface for focusing and surface-plasmon-polariton wave excitation[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(24): 29812–29821. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.029812 |
| [48] |
MAGUID E, YULEVICH I, YANNAI M, et al. Multifunctional interleaved geometric-phase dielectric metasurfaces[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2017, 6(8): e17027.
|
| [49] |
HUANG Cheng, ZHANG Changlei, YANG Jianing, et al. Reconfigurable metasurface for multifunctional control of electromagnetic waves[J]. Advanced Optical Materials, 2017, 5(22): 1700485. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700485 |
| [50] |
ZHU Ruichao, QIU Tianshuo, WANG Jiafu, et al. Multiplexing the aperture of a metasurface: Inverse design via deep-learning-forward genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2020, 53(45): 455002. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/aba64f |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

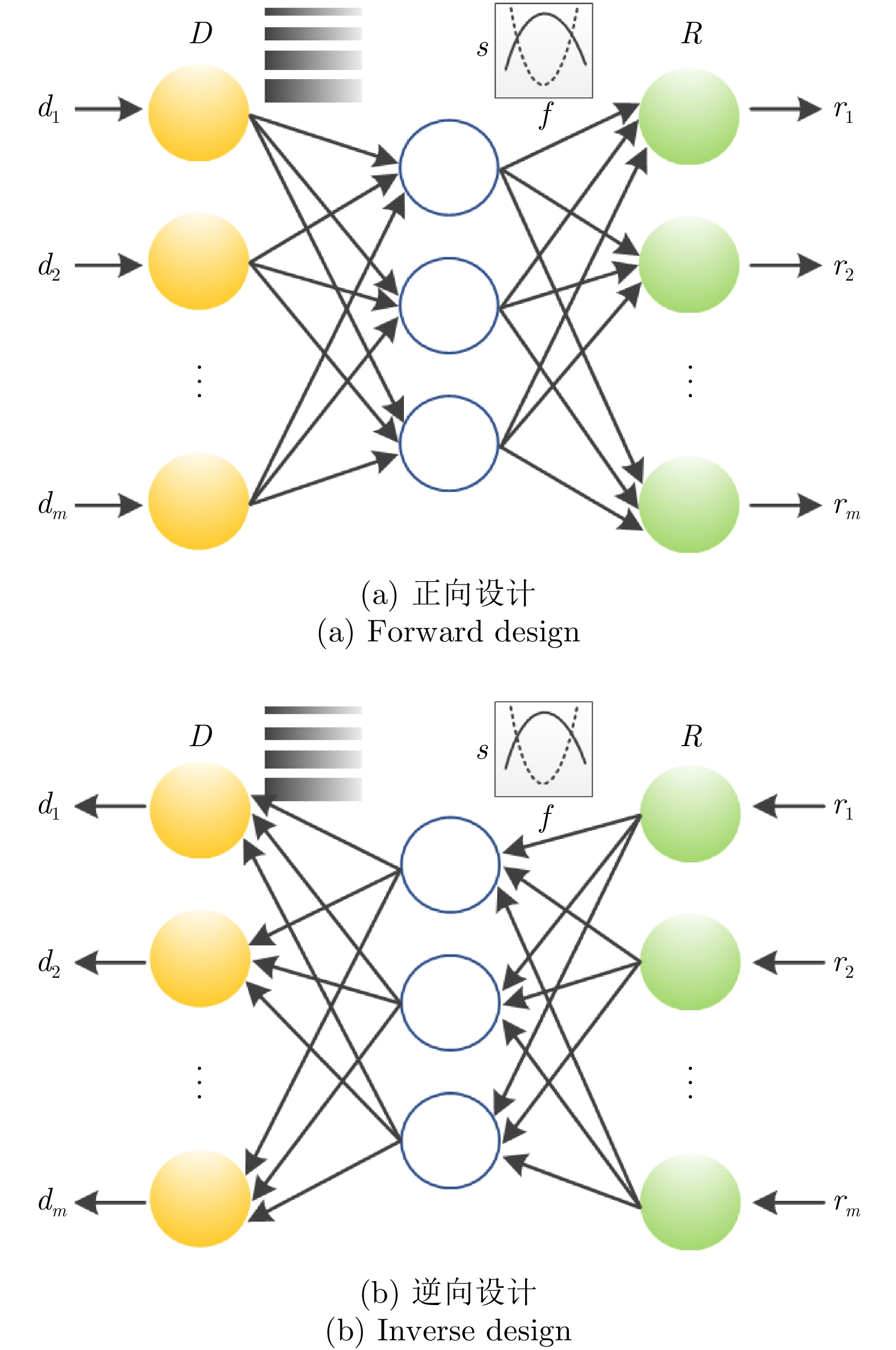



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: