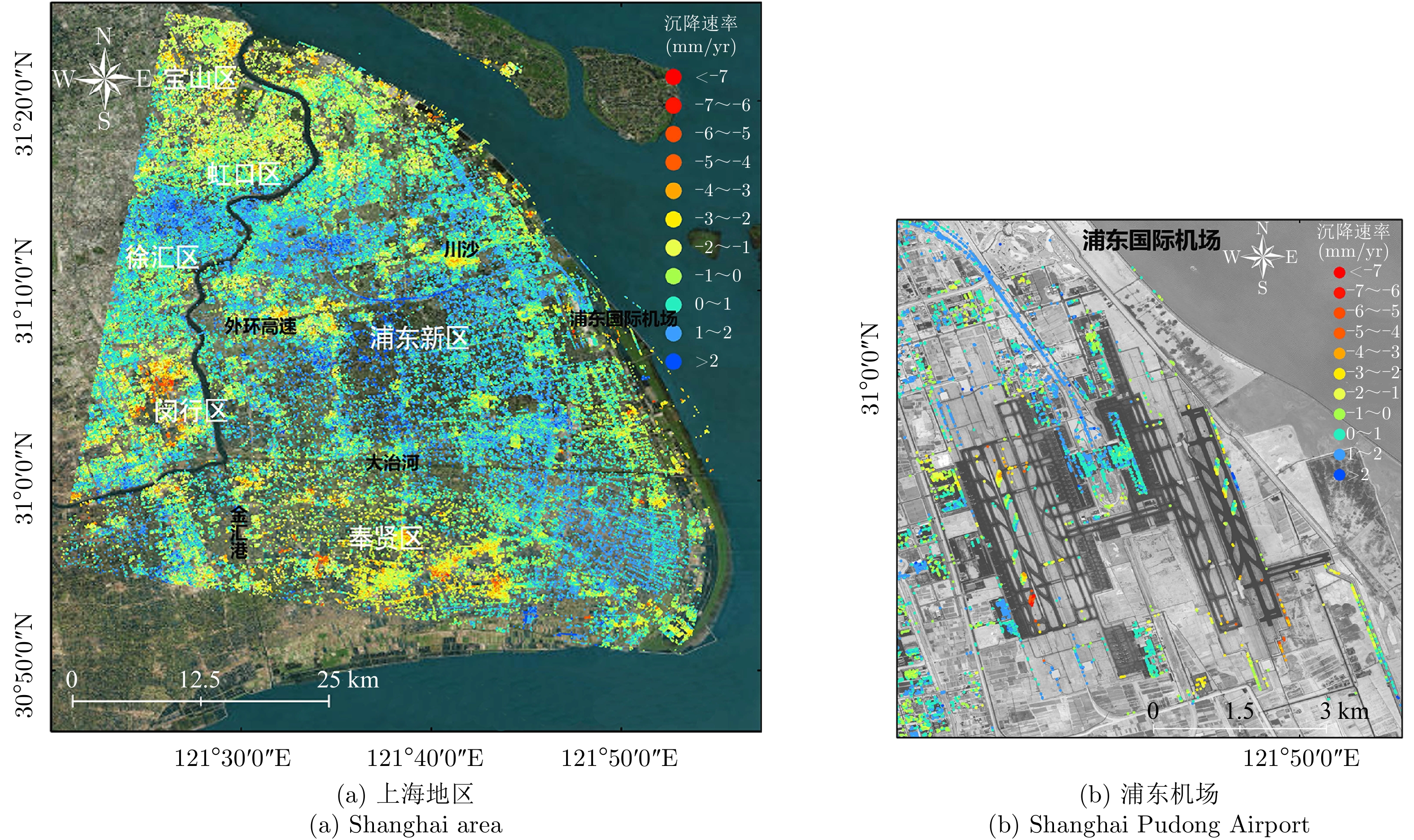
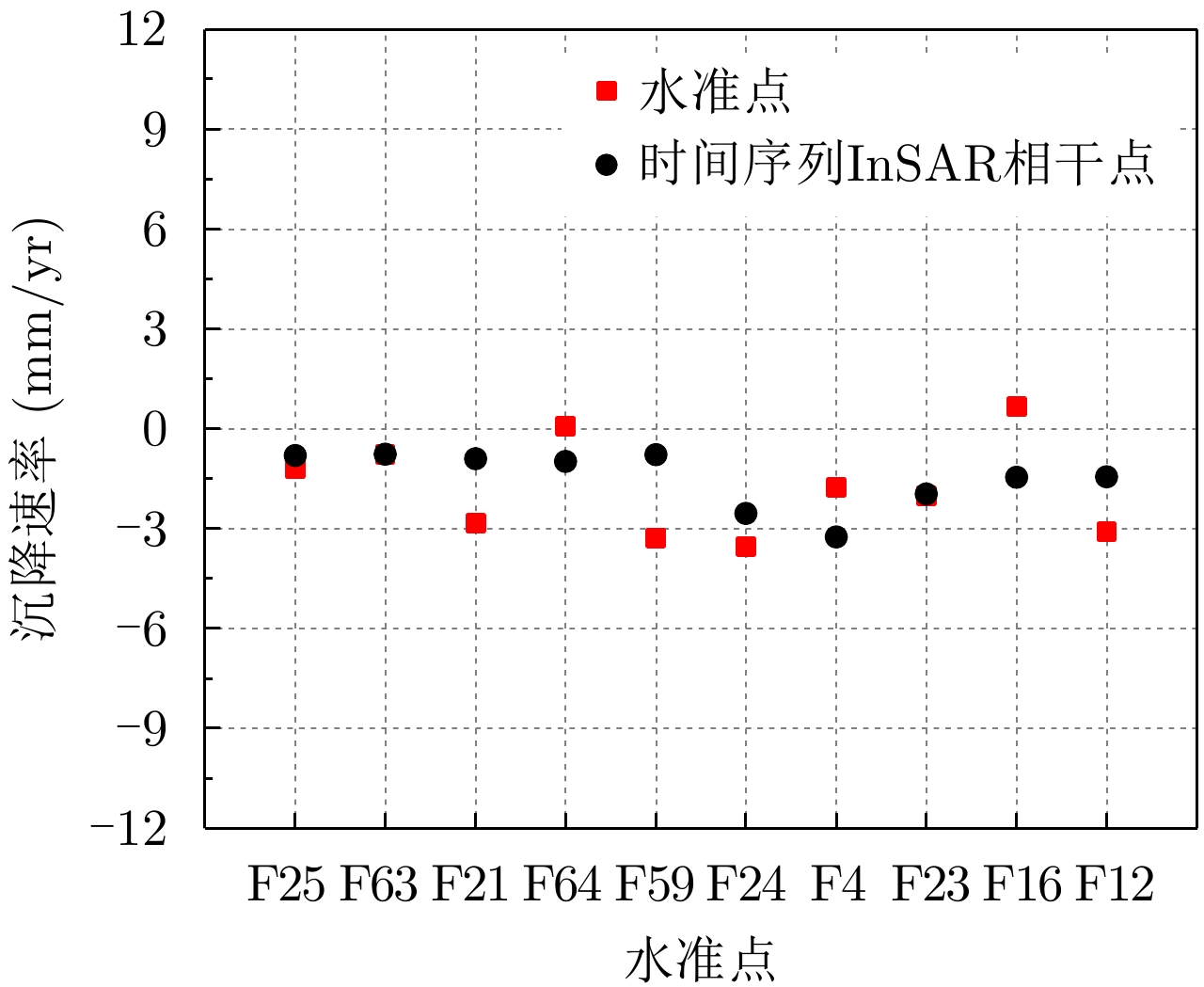
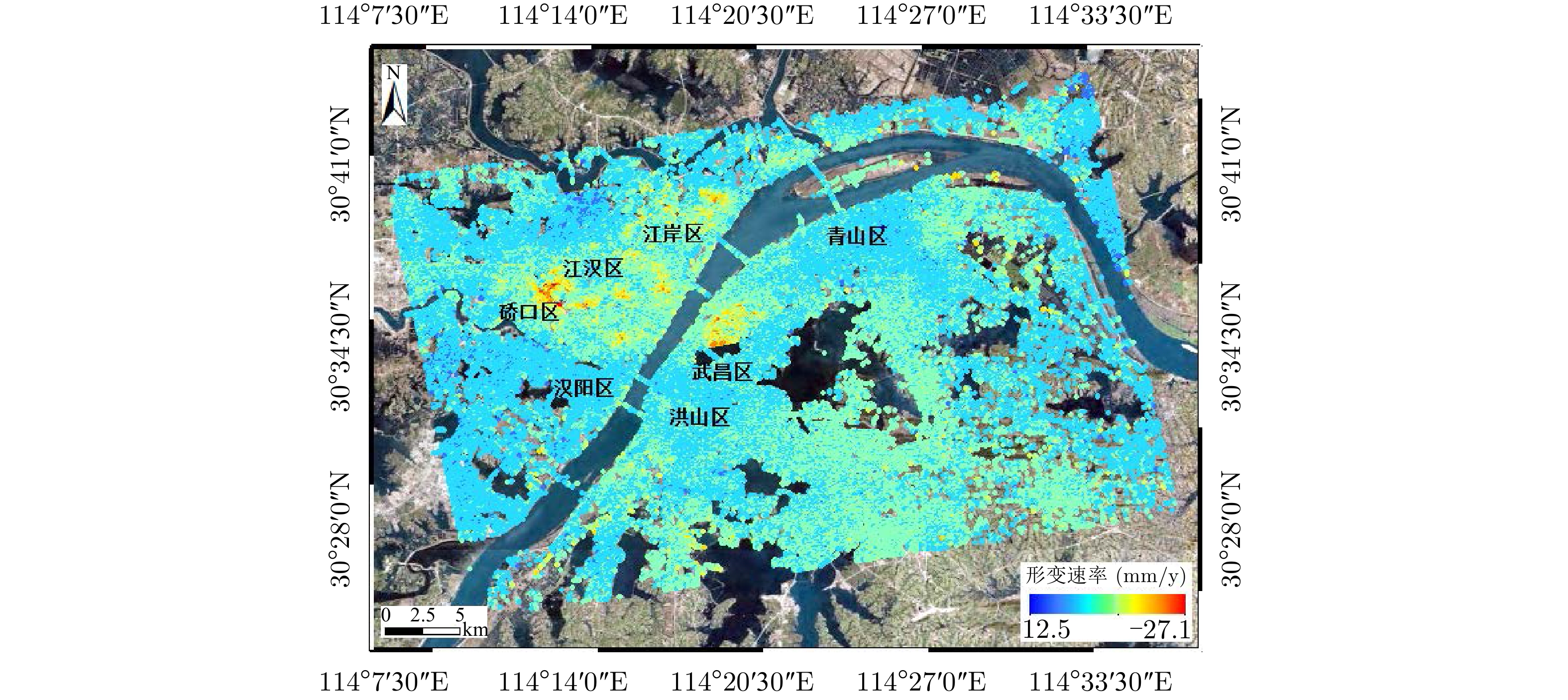
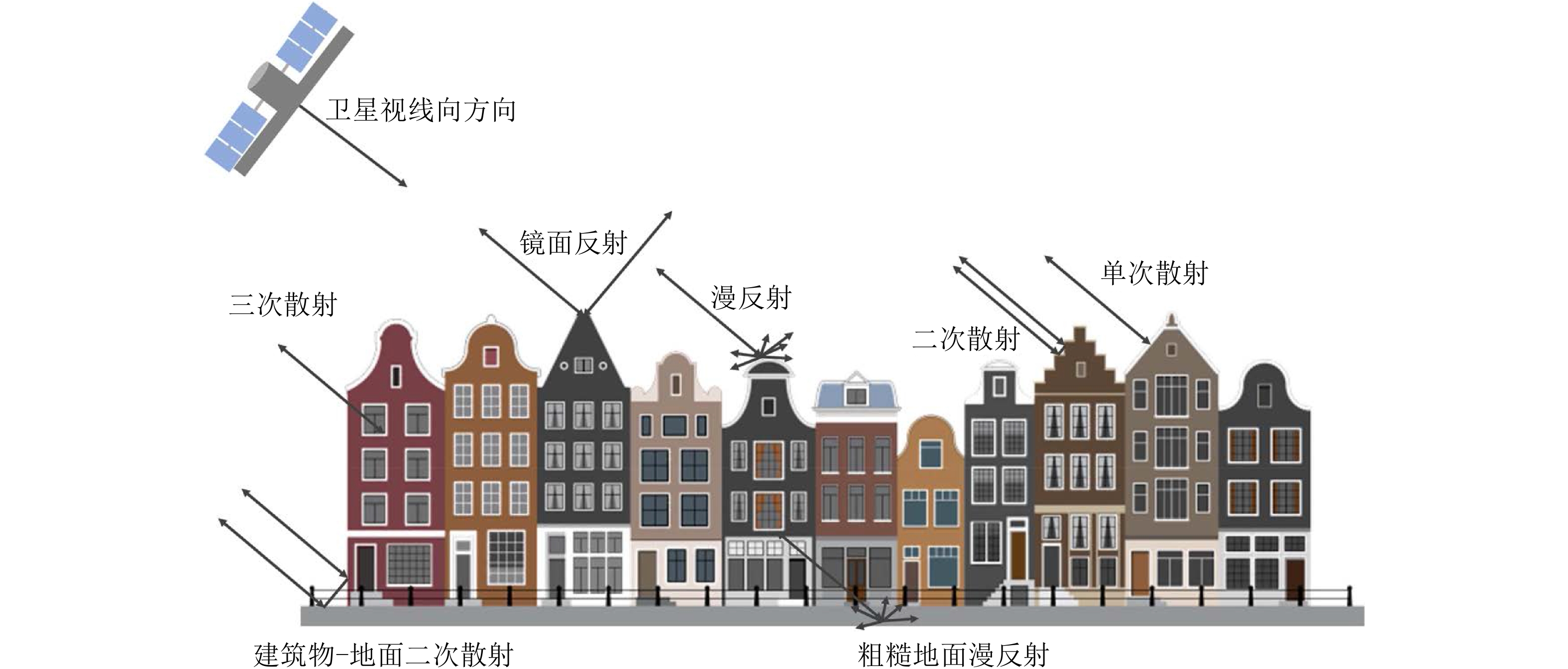
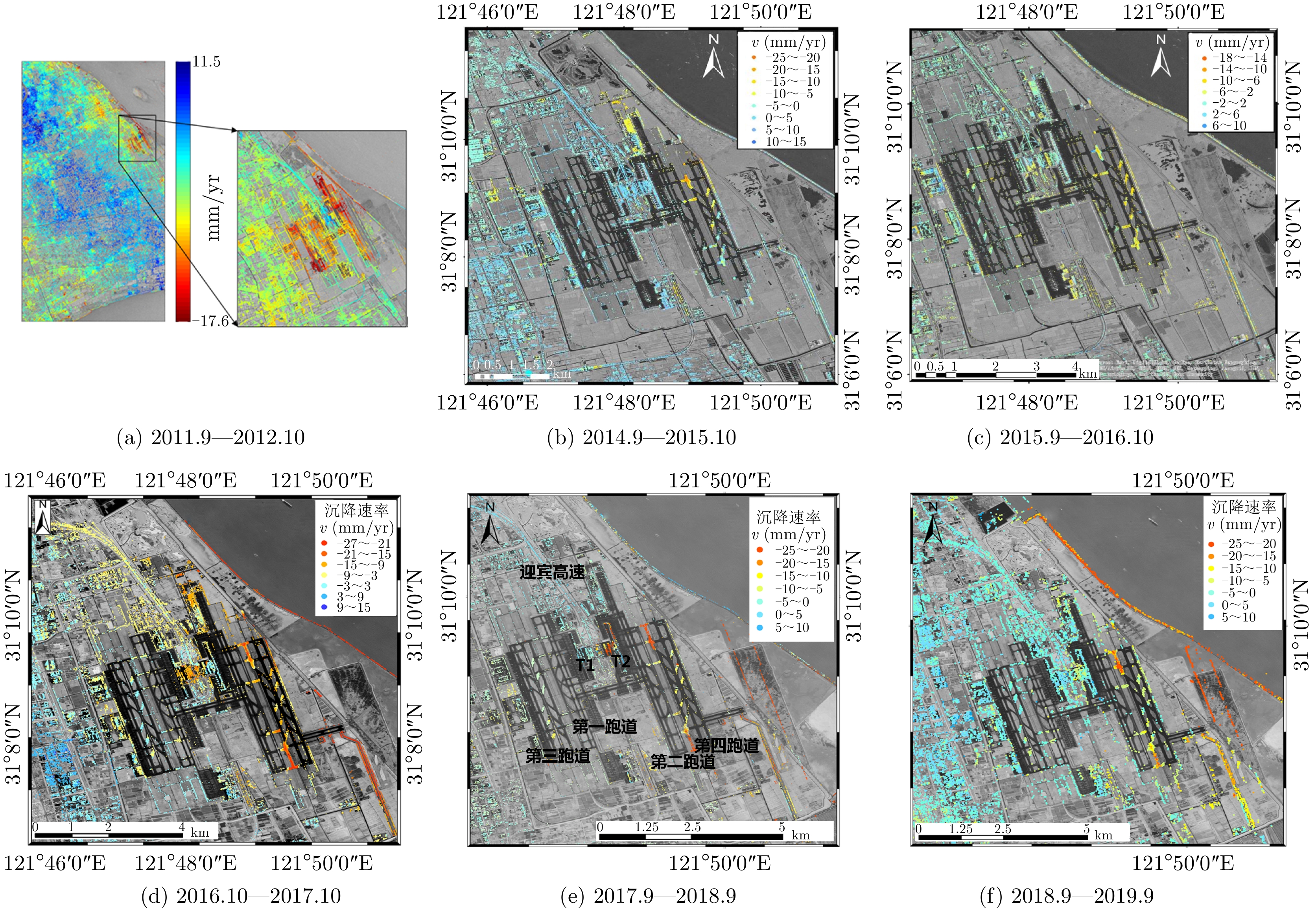
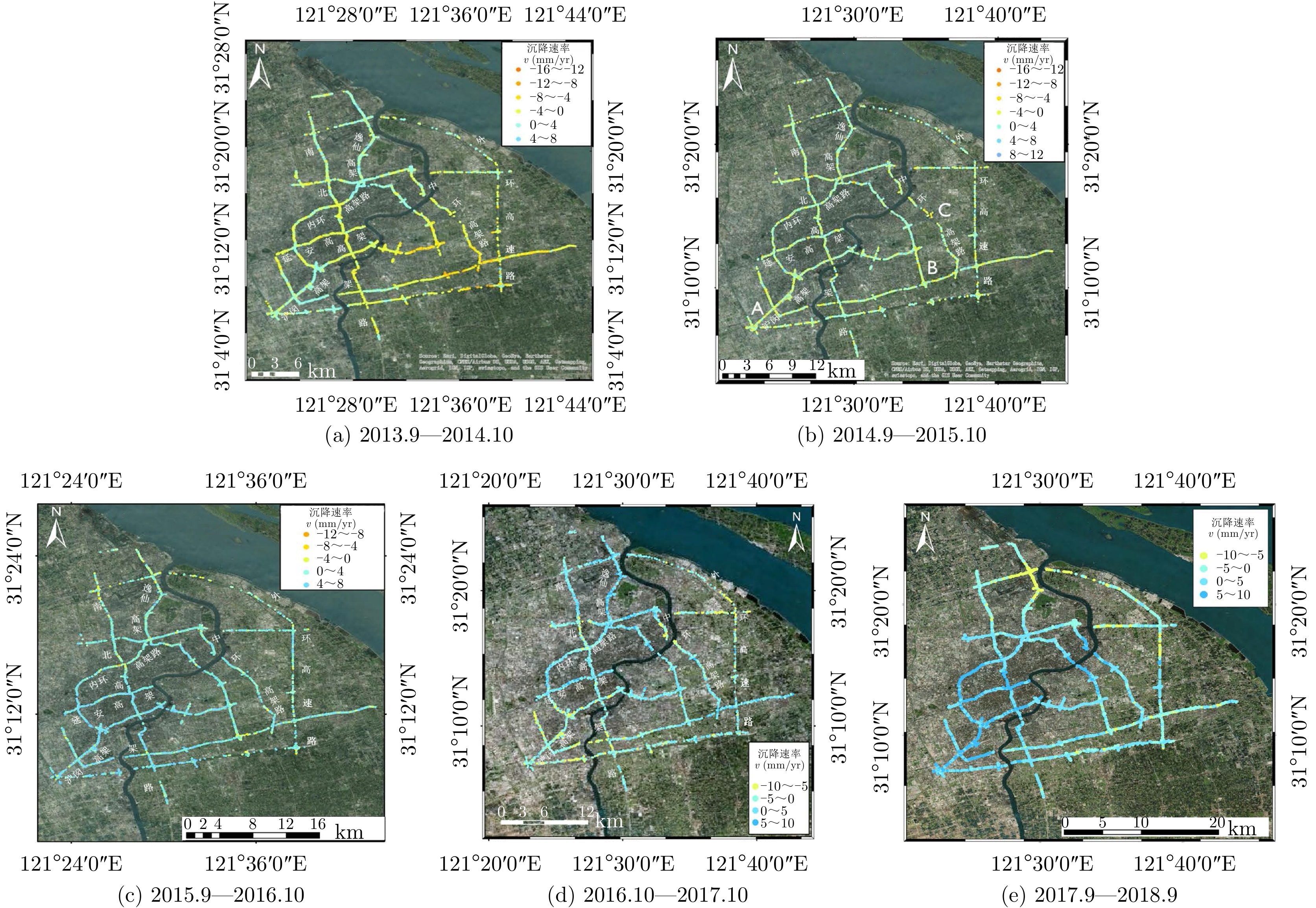
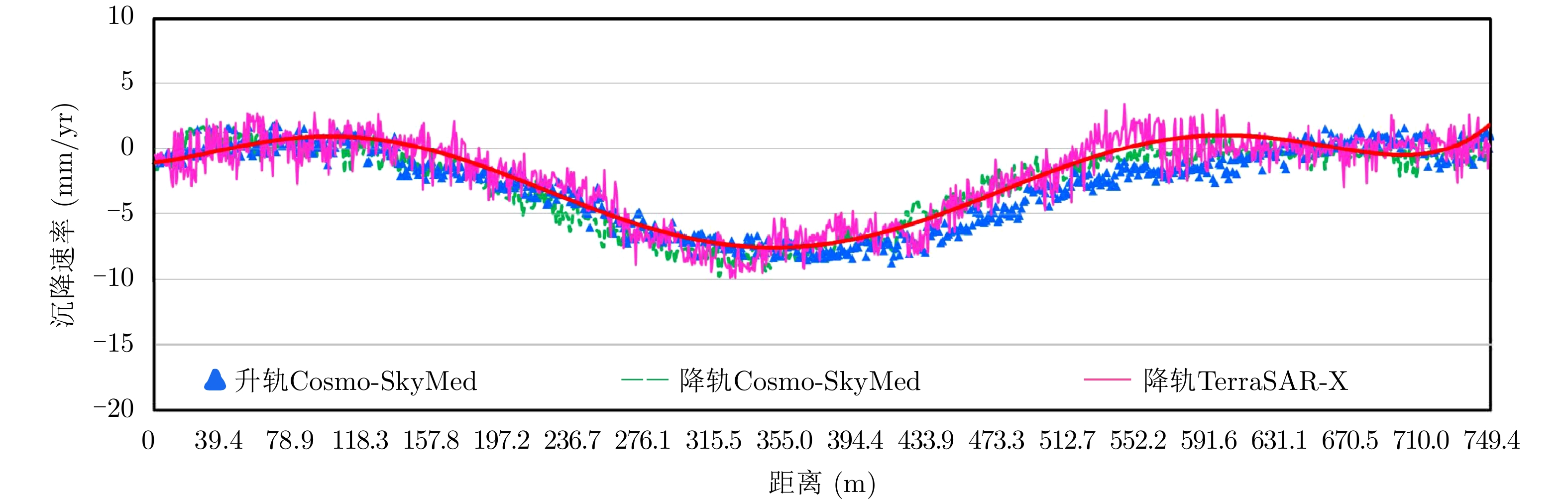
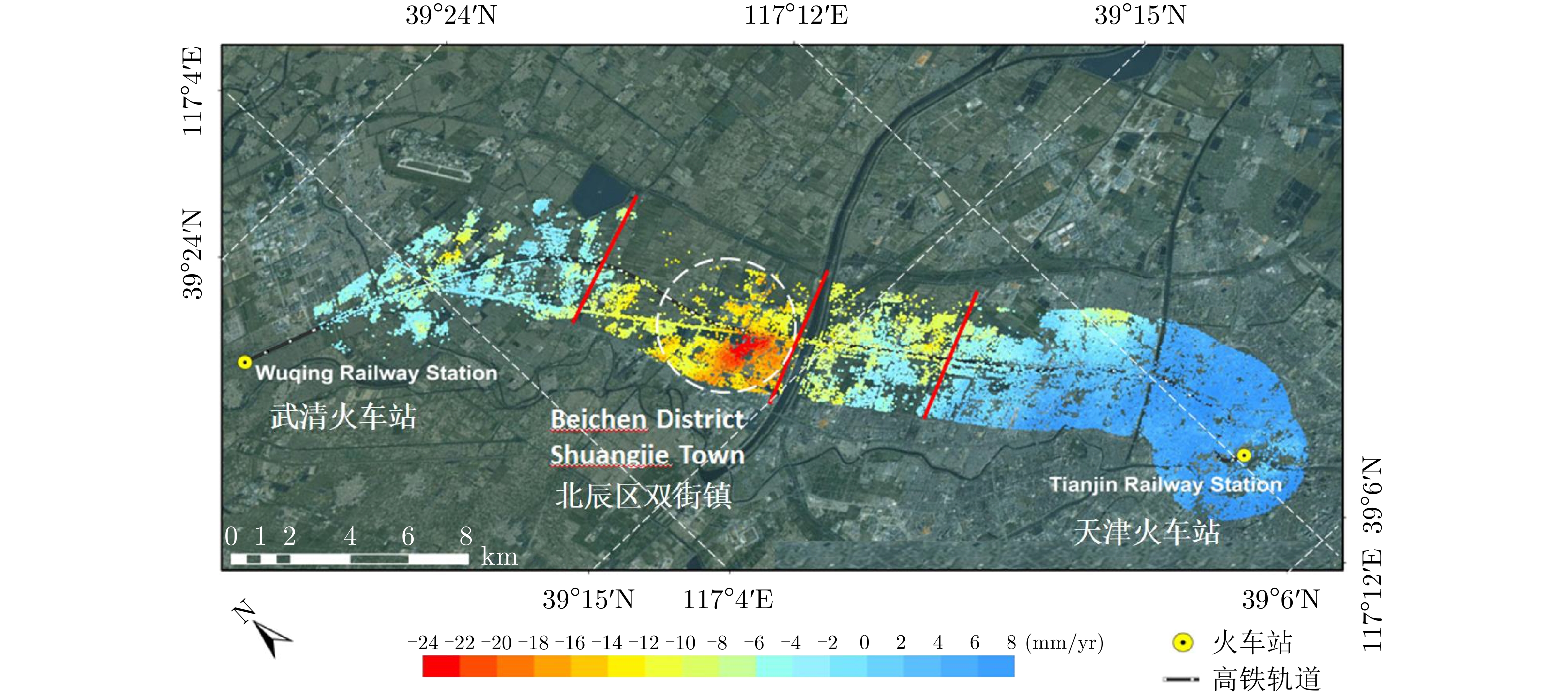
| [1] |
MONTGOMERY M R. The urban transformation of the developing world[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5864): 761–764. doi: 10.1126/science.1153012 |
| [2] |
HANSSEN R F. Satellite radar interferometry for deformation monitoring: a priori assessment of feasibility and accuracy[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2005, 6(3/4): 253–260. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2004.10.004 |
| [3] |
廖明生, 林珲. 雷达干涉测量: 原理与信号处理基础[M]. 北京: 测绘出版社, 2003: 1–12.
LIAO Mingsheng and LIN Hui. Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry: Principle and Singnal Processing[M]. Beijing: Surveying and Mapping Press, 2003: 1–12.
|
| [4] |
FERRETTI A, PRATI C, and ROCCA F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2001, 39(1): 8–20. doi: 10.1109/36.898661 |
| [5] |
BERARDINO P, FORNARO G, LANARI R, et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(11): 2375–2383. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2002.803792 |
| [6] |
FERRETTI A, SAVIO G, BARZAGHI R, et al. Submillimeter accuracy of InSAR time series: Experimental validation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(5): 1142–1153. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2007.894440 |
| [7] |
HOOPER A. A multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35(16): L16302. doi: 10.1029/2008gl034654 |
| [8] |
KAMPES B M. Radar Interferometry: Persistent Scatterer Technique[M]. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer, 2006: 21–60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-4723-7. |
| [9] |
云烨, 吕孝雷, 付希凯, 等. 星载InSAR技术在地质灾害监测领域的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 73–85. doi: 10.12000/JR20007YUN Ye, LÜ Xiaolei, FU Xikai, et al. Application of spaceborne Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar to geohazard monitoring[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 73–85. doi: 10.12000/JR20007 |
| [10] |
廖明生, 王腾. 时间序列InSAR技术与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014: 5–26.
LIAO Mingsheng and WANG Teng. Time Series InSAR Technology and Application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014: 5–26.
|
| [11] |
WU Lixin, GAO Junhai, GE Daqing, et al. Experimental study on surface subsidence monitoring with D-InSAR in mining area[J]. Journal of Northeastern University: Natural Science, 2005, 26(8): 778–782. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-3026.2005.08.018 |
| [12] |
TANG Yixian, ZHANG Hong, and WANG Chao. Research on Suzhou subsidence based on permanent scatterer radar interferometry[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2006, 16(8): 1015–1020. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008x.2006.08.015 |
| [13] |
WANG Yan, LIAO Mingsheng, LI Deren, et al. Subsidence velocity retrieval from long-term coherent targets in radar interferometric stacks[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2007, 50(2): 598–604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2007.02.034 |
| [14] |
罗小军, 黄丁发, 刘国祥. 基于永久散射体雷达差分干涉测量的城市地面沉降研究—以上海地面沉降监测为例[J]. 测绘通报, 2009, (4): 4–8.
LUO Xiaojun, HUANG Dingfa, and LIU Guoxiang. On urban ground subsidence detection based on PS-DInSAR—A case study for Shanghai[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2009(4): 4–8.
|
| [15] |
PERISSIN D and WANG Teng. Time-Series InSAR applications over urban areas in China[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2011, 4(1): 92–100. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2010.2046883 |
| [16] |
LIAO Mingsheng, PEI Yuanyuan, WANG Hanmei, et al. Subsidence monitoring in Shanghai using the PSInSAR technique[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources, 2012, 33(3): 5–10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1329.2012.03.006 |
| [17] |
裴媛媛, 廖明生, 王寒梅. 利用时序DInSAR监测填海造陆地区地表沉降[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2012, 37(9): 1092–1095.
PEI Yuanyuan, LIAO Mingsheng, and WANG Hanmei. Monitoring subsidence in reclamation area with time series DInSAR images[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2012, 37(9): 1092–1095.
|
| [18] |
YANG Mengshi, LIAO Mingsheng, SHI Xuguo, et al. Land subsidence monitoring by joint estimation of multi-platform time series InSAR observations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2017, 42(6): 797–802. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20140924 |
| [19] |
FAN Jinghui, LI Mei, GUO Xiaofang, et al. A preliminary study of the subsidence in Tianjin area using ASAR images based on PSInSAR technique[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2007, 19(4): 23–27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-070x.2007.04.005 |
| [20] |
LUO Qingli, PERISSIN D, ZHANG Yuanzhi, et al. L- and X-band multi-temporal InSAR analysis of tianjin subsidence[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014, 6(9): 7933–7951. doi: 10.3390/rs6097933 |
| [21] |
ZHANG Qin, ZHAO Chaoying, DING Xiaoli, et al. Research on recent characteristics of spatio-temporal evolution and mechanism of Xi’an land subsidence and ground fissure by using GPS and InSAR techniques[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(5): 1214–1222. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.05.010 |
| [22] |
CHEN Guohu, LIU Yunhua, and SHAN Xinjian. Application of PS-InSAR technique in the deformation monitoring in mining collapse areas in Beijing[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2010, 21(2): 59–63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.02.012 |
| [23] |
CHEN Mi, TOMÁS R, LI Zhenhong, et al. Imaging land subsidence induced by groundwater extraction in Beijing (China) using satellite radar interferometry[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(6): 468. doi: 10.3390/rs8060468 |
| [24] |
尹宏杰, 朱建军, 李志伟, 等. 基于SBAS的矿区形变监测研究[J]. 测绘学报, 2011, 40(1): 52–58.
YIN Hongjie, ZHU Jianjun, LI Zhiwei, et al. Ground subsidence monitoring in mining area using DInSAR SBAS algorithm[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2011, 40(1): 52–58.
|
| [25] |
HE Xiufeng, ZHONG Haibei, and HE Min. Ground subsidence detection of Nantong city based on PS-InSAR and GIS spatial analysis[J]. Journal of Tongji University: Natural Science, 2011, 39(1): 129–134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-374x.2011.01.025 |
| [26] |
李永生, 张景发, 罗毅, 等. 利用高分辨率聚束模式TerraSAR-X影像的PSInSAR监测地表变形[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2012, 37(12): 1452–1455.
LI Yongsheng, ZHANG Jingfa, LUO Yi, et al. Monitoring land deformation using PSInSAR with TerraSAR-X high resolution spotlight SAR images[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2012, 37(12): 1452–1455.
|
| [27] |
NG A H M, GE Linlin, LI Xiaojing, et al. Monitoring ground deformation in Beijing, China with persistent scatterer SAR interferometry[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2012, 86(6): 375–392. doi: 10.1007/s00190-011-0525-4 |
| [28] |
WANG Huiqiang, FENG Guangcai, XU Bing, et al. Deriving spatio-temporal development of ground subsidence due to subway construction and operation in delta regions with PS-InSAR data: A case study in Guangzhou, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(10): 1004. doi: 10.3390/rs9101004 |
| [29] |
WANG Ziyun, BALZ T, ZHANG Lu, et al. Using TSX/TDX pursuit monostatic SAR stacks for PS-InSAR analysis in urban areas[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(1): 26. doi: 10.3390/rs11010026 |
| [30] |
BAI Lin, JIANG Liming, WANG Hansheng, et al. Spatiotemporal characterization of land subsidence and uplift (2009–2010) over Wuhan in Central China revealed by TerraSAR-X InSAR analysis[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(4): 350. doi: 10.3390/rs8040350 |
| [31] |
TANG Wei and LIAO Mingsheng. Taiyuan city subsidence observed with Persistent Scatterer InSAR[J]. Wuhan University Journal of Natural Sciences, 2014, 19(6): 526–534. doi: 10.1007/s11859-014-1048-7 |
| [32] |
CHEN Fulong, WU Yuhua, ZHANG Yimeng, et al. Surface motion and structural instability monitoring of ming Dynasty City walls by two-step tomo-PSInSAR approach in Nanjing City, China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(4): 371. doi: 10.3390/rs9040371 |
| [33] |
林珲, 陈富龙, 江利明, 等. 多基线差分雷达干涉测量的大型人工线状地物形变监测[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2010, 12(5): 718–725.
LIN Hui, CHEN Fulong, JIANG Liming, et al. Preliminary research on large-scale man-made linear features deformation monitoring using multi-baseline Differential SAR Interferometry[J]. Geo-Information Science, 2010, 12(5): 718–725.
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
邢孟道, 林浩, 陈溅来, 等. 多平台合成孔径雷达成像算法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102XING Mengdao, LIN Hao, CHEN Jianlai, et al. A review of imaging algorithms in multi-platform-borne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 732–757. doi: 10.12000/JR19102 |
| [36] |
裴媛媛, 廖明生, 王寒梅. 时间序列SAR影像监测堤坝形变研究[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2013, 38(3): 266–269.
PEI Yuanyuan, LIAO Mingsheng, and WANG Hanmei. Monitoring levee deformation with repeat-track space-borne SAR images[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2013, 38(3): 266–269.
|
| [37] |
PERISSIN D, WANG Zhiying, and LIN Hui. Shanghai subway tunnels and highways monitoring through Cosmo-SkyMed Persistent Scatterers[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2012, 73: 58–67. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2012.07.002 |
| [38] |
QIN Xiaoqiong, YANG Mengshi, WANG Hanmei, et al. Application of high-resolution PS-InSAR in deformation characteristics probe of urban rail transit[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2016, 45(6): 713–721. doi: 10.11947/j.agcs.2016.20150440 |
| [39] |
QIN Xiaoqiong, LIAO Mingsheng, ZHANG Lu, et al. Structural health and stability assessment of high-speed railways via thermal dilation mapping with Time-Series InSAR analysis[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(6): 2999–3010. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2719025 |
| [40] |
QIN Xiaoqiong, YANG Mengshi, ZHANG Lu, et al. Health diagnosis of major transportation infrastructures in Shanghai metropolis using high-resolution Persistent Scatterer Interferometry[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(12): 2770. doi: 10.3390/s17122770 |
| [41] |
WANG Ru, YANG Tianliang, YANG Mengshi, et al. A safety analysis of elevated highways in Shanghai linked to dynamic load using long-term time-series of InSAR stacks[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 10(12): 1133–1142. doi: 10.1080/2150704x.2019.1648903 |
| [42] |
CHANG Ling, DOLLEVOET R P B J, and HANSSEN R F. Nationwide railway monitoring using satellite SAR Interferometry[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(2): 596–604. doi: 10.1109/jstars.2016.2584783 |
| [43] |
QIN Xiaoqiong, LIAO Mingsheng, YANG Mengshi, et al. Monitoring Shanghai relocation housing skew deformation using high resolution PS-InSAR technology[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2016(6): 18–21, 86. doi: 10.13474/j.cnki.11-2246.2016.0181 |
| [44] |
QIN Xiaoqiong, ZHANG Lu, DING Xiaoli, et al. Mapping and characterizing thermal dilation of civil infrastructures with multi-temporal X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(6): 941. doi: 10.3390/rs10060941 |
| [45] |
QIN Xiaoqiong, ZHANG Lu, YANG Mengshi, et al. Mapping surface deformation and thermal dilation of arch bridges by structure-driven multi-temporal DInSAR analysis[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2018, 216: 71–90. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2018.06.032 |
| [46] |
JIANG Yanan, LIAO Mingsheng, WANG Hanmei, et al. Deformation monitoring and analysis of the geological environment of Pudong International Airport with persistent scatterer SAR interferometry[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(12): 1021. doi: 10.3390/rs8121021 |
| [47] |
廖明生, 魏恋欢, 汪紫芸, 等. 压缩感知在城区高分辨率SAR层析成像中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031LIAO Mingsheng, WEI Lianhuan, WANG Ziyun, et al. Compressive sensing in high-resolution 3D SAR tomography of urban scenarios[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031 |
| [48] |
YANG Mengshi, LÓPEZ-DEKKER P, DHEENATHAYALAN P, et al. Linking persistent scatterers to the built environment using Ray tracing on urban models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 5764–5776. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2901904 |
| [49] |
YANG Mengshi, YANG Tianliang, ZHANG Lu, et al. Spatio-temporal characterization of a reclamation settlement in the Shanghai coastal area with time series analyses of X-, C-, and L-Band SAR datasets[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(2): 329. doi: 10.3390/rs10020329 |
| [50] |
WANG Fei, CHAI Bo, XU Guilai, et al. Evolution mechanism of karst sinkholes in Wuhan city[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(3): 824–832. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.03.030 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: