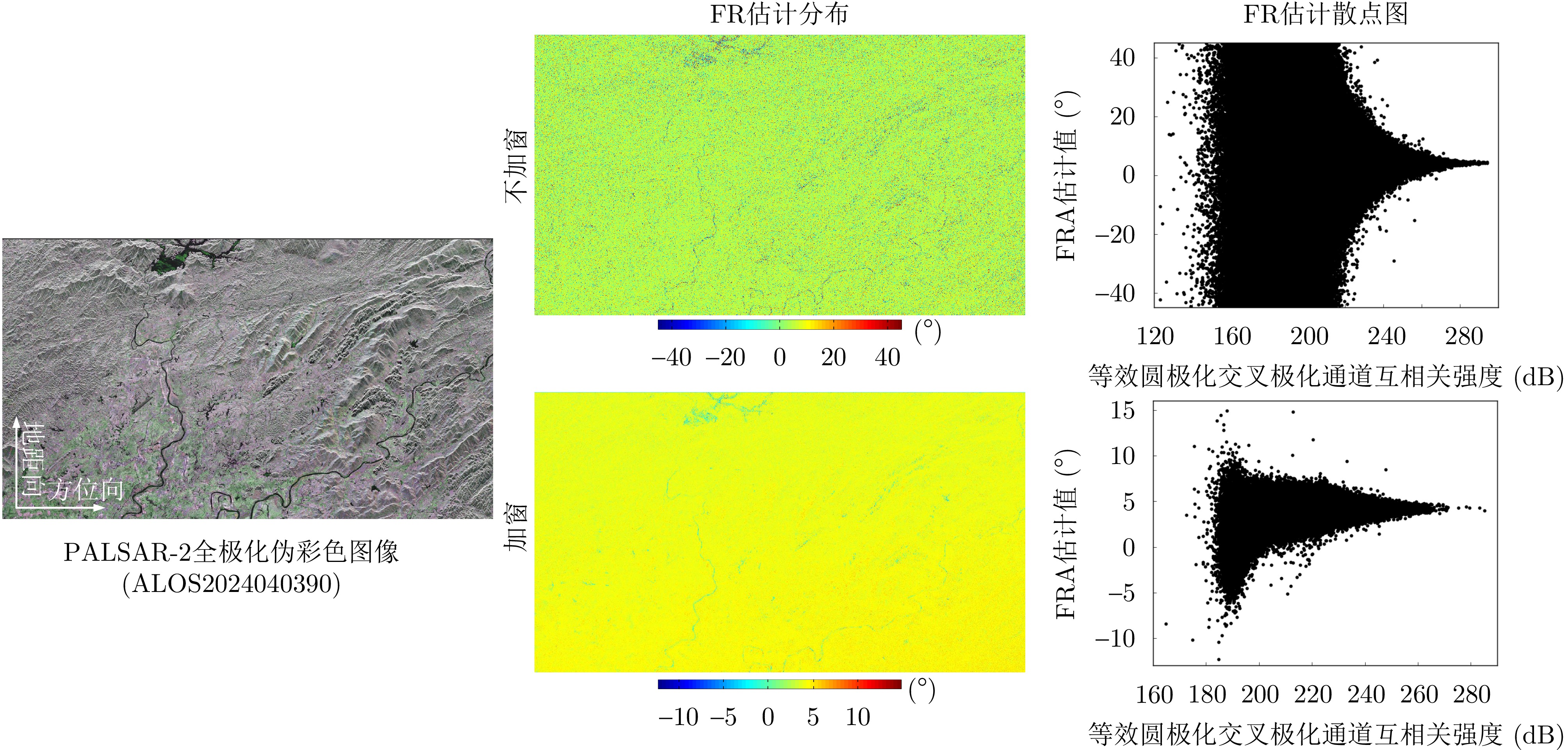
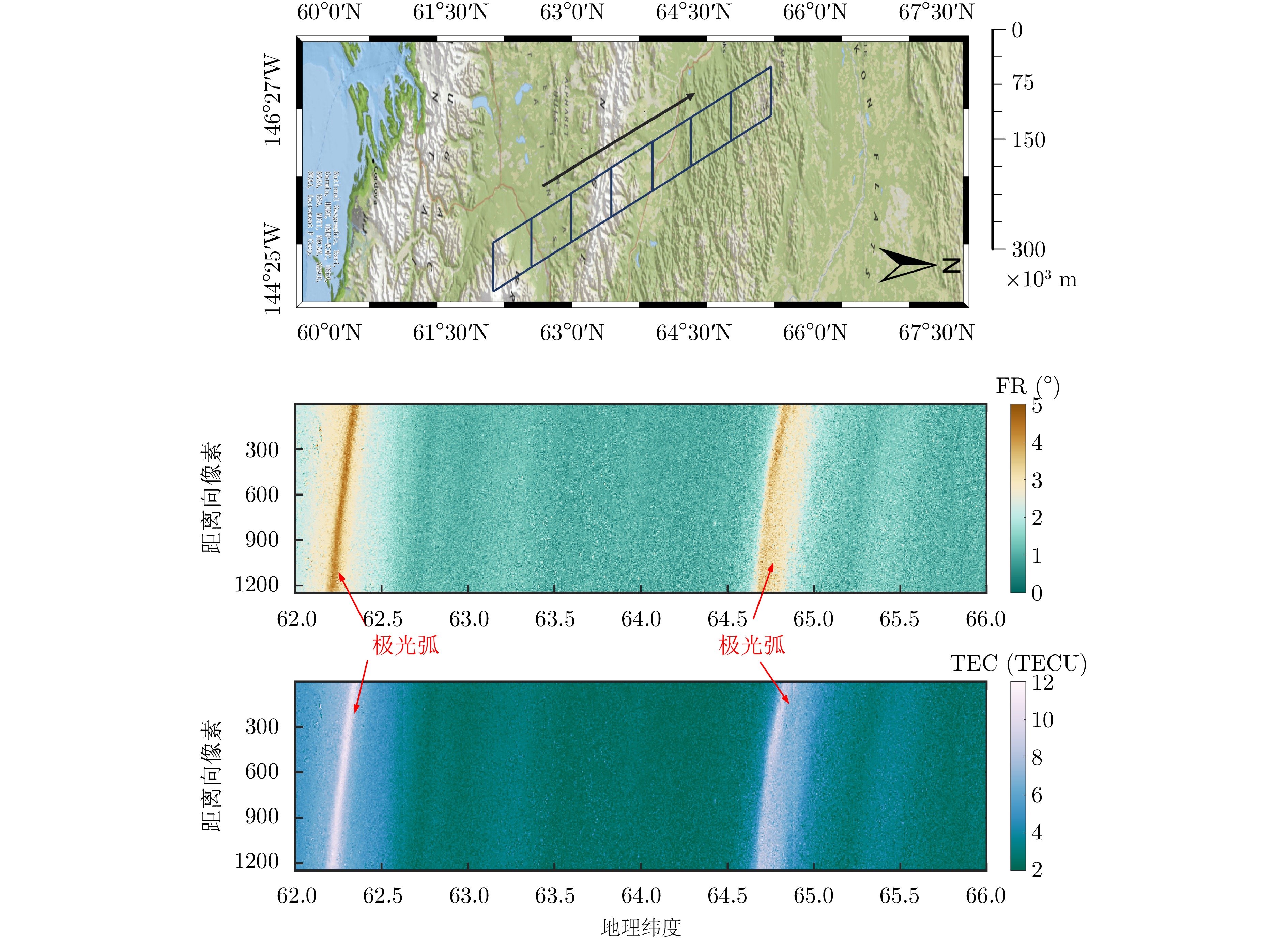
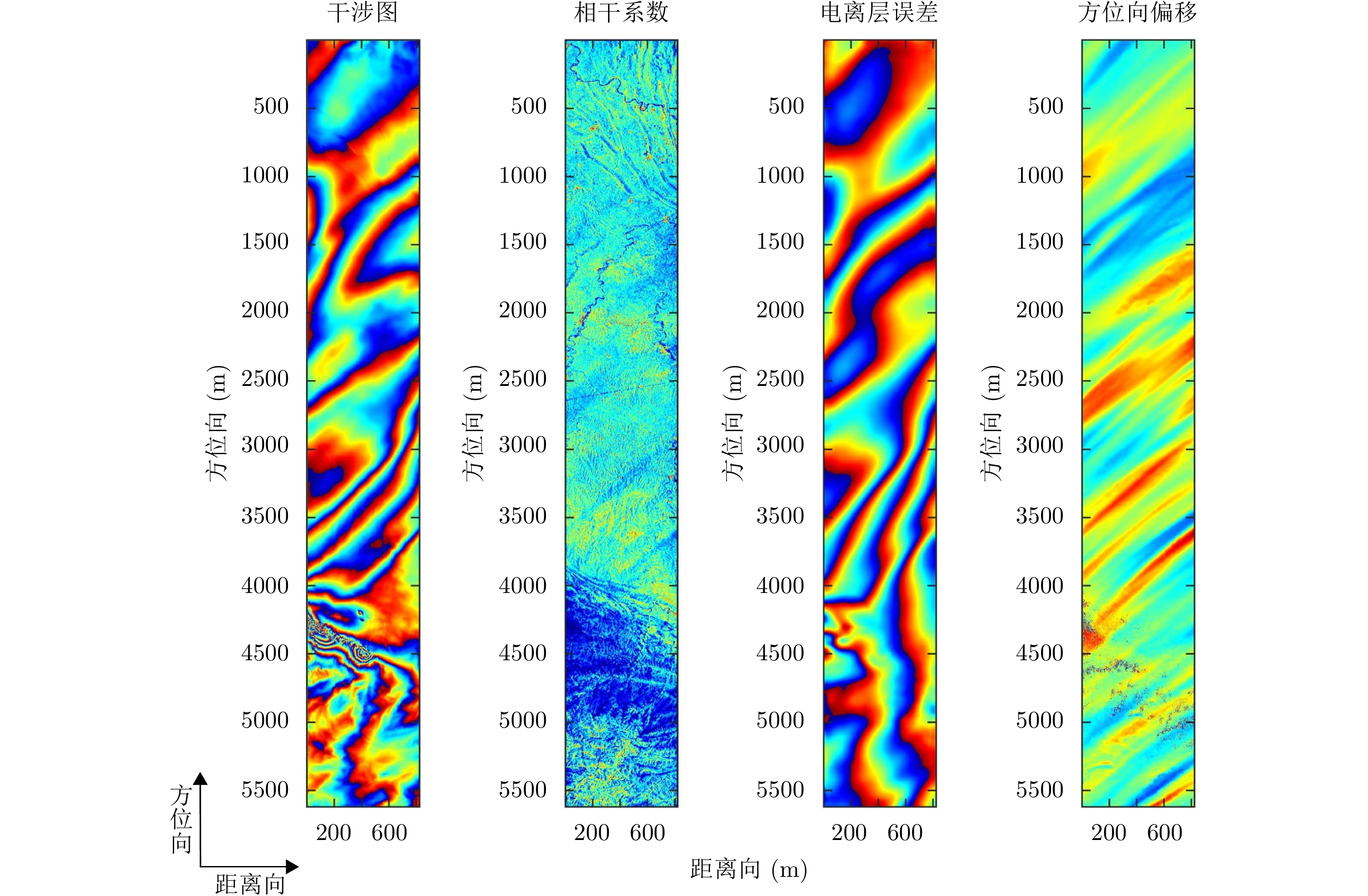
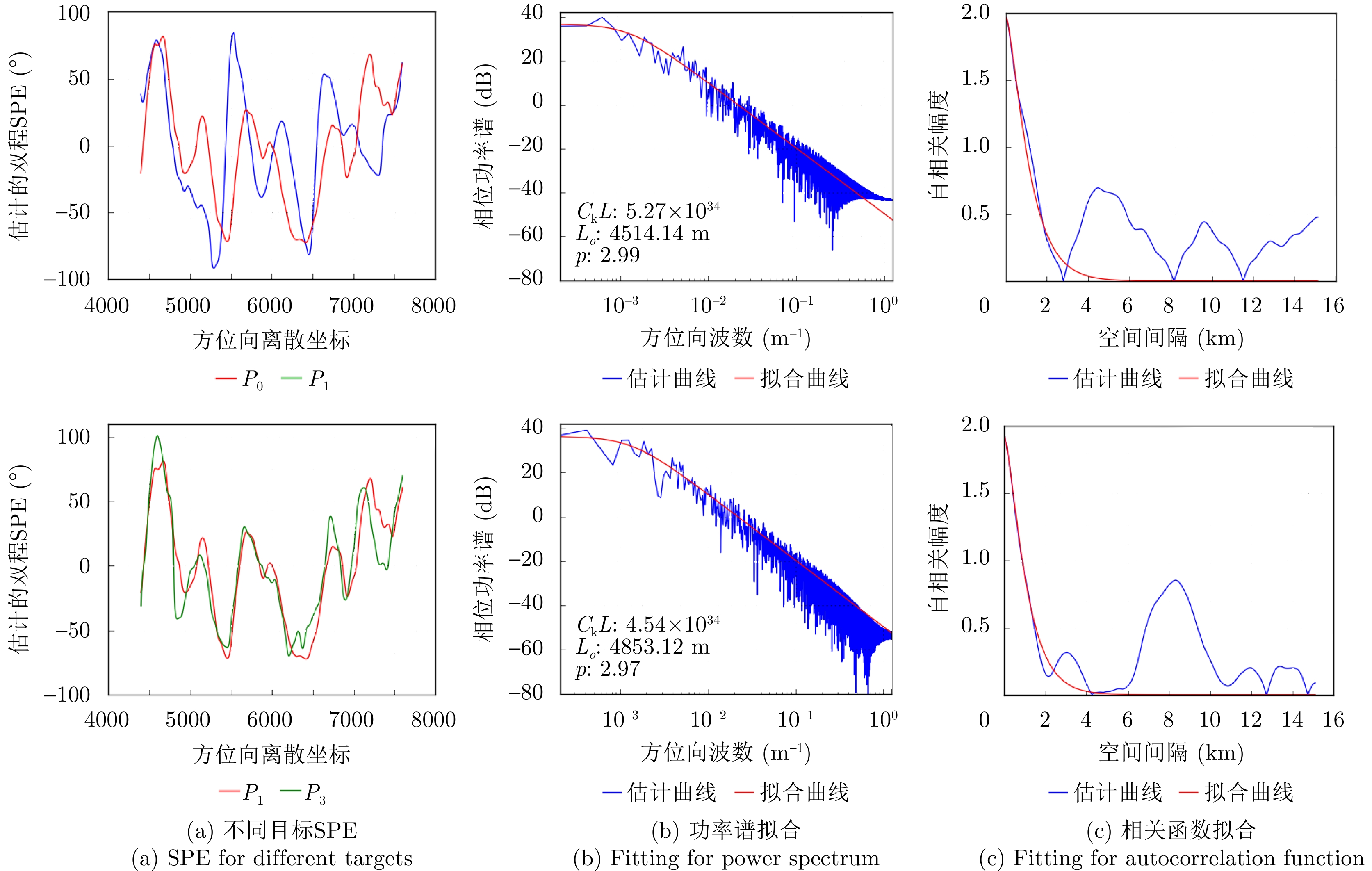
| [1] |
SHIMADA M, ITOH T, MOTOOKA T, et al. New global forest/non-forest maps from ALOS PALSAR data (2007–2010)[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 155: 13–31. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.04.014. |
| [2] |
BANDA F, MANCON S, ALESSANDRO M M, et al. Biomass interferometric calibration processor design[C]. 2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2023: 7785–7788. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS52108.2023.10283343. |
| [3] |
YANG Lin, ZHAO Ning, YAO Baidong, et al. Parameter design of a high resolution space-borne P-band SAR system[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2017, 15(1): 19–28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2017.01.004. |
| [4] |
HU Cheng, CHEN Zhiyang, LI Yuanhao, et al. Research progress on geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar[J]. Fundamental Research, 2021, 1(3): 346–363. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2021.04.008. |
| [5] |
ISHIMARU A, KUGA Y, LIU Jun, et al. Ionospheric effects on synthetic aperture radar at 100 MHz to 2 GHz[J]. Radio Science, 1999, 34(1): 257–268. doi: 10.1029/1998RS900021. |
| [6] |
XU Zhengwen, WU Jian, and WU Zhensen. A survey of ionosphere effects on space-based radar[J]. Waves in Random Media, 2004, 14(2): S189–S273. doi: 10.1088/0959-7174/14/2/008. |
| [7] |
MEYER F. A review of ionospheric effects in low-frequency SAR—signals, correction methods, and performance requirements[C]. 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, USA, 2010: 29–32. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2010.5654258. |
| [8] |
MEYER F J. Performance requirements for ionospheric correction of low-frequency SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3694–3702. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2146786. |
| [9] |
JI Yifei. Research on influential analysis and correction approaches of ionospheric effects on spaceborne synthetic aperture radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2020. doi: 10.27052/d.cnki.gzjgu.2020.000296. |
| [10] |
HU Cheng, TIAN Ye, YANG Xiaopeng, et al. Background ionosphere effects on geosynchronous SAR focusing: Theoretical analysis and verification based on the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS)[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1143–1162. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2475283. |
| [11] |
李亮, 洪峻, 明峰. 电离层对中高轨SAR影响机理研究[J]. 雷达学报, 2017, 6(6): 619–629. doi: 10.12000/JR17016. LI Liang, HONG Jun, and MING Feng. Mechanism study of ionospheric effects on medium-earth-orbit SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2017, 6(6): 619–629. doi: 10.12000/JR17016. |
| [12] |
LI Liang, HONG Jun, LIU Guikun, et al. Study about the effects on range imaging for MEOSAR induced by ionospheric irregularity[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(10): 1610–1615. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2020.0167. |
| [13] |
JI Yifei, ZHANG Qilei, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. L-band geosynchronous SAR imaging degradations imposed by ionospheric irregularities[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2017, 60(6): 060308. doi: 10.1007/s11432-016-9064-1. |
| [14] |
JI Yifei, ZHANG Yongsheng, DONG Zhen, et al. Impacts of ionospheric irregularities on L-band geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(6): 3941–3954. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2959702. |
| [15] |
张永胜, 计一飞, 董臻. 时-空变化的背景电离层对星载合成孔径雷达方位向成像的影响分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(10): 2781–2789. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200777. ZHANG Yongsheng, JI Yifei, and DONG Zhen. Research on background ionospheric impacts imposed by spatio-temporal variations on spaceborne synthetic aperture radar azimuth imaging[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43(10): 2781–2789. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200777. |
| [16] |
CHEN A C and ZEBKER H A. Reducing ionospheric effects in InSAR data using accurate coregistration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(1): 60–70. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2236098. |
| [17] |
MEYER F J, PAPATHANASSIOU K, KIM J S, et al. IonoSAR–collaborative research towards understanding and mitigating ionospheric effects in SAR[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 6039–6042. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6352230. |
| [18] |
PI Xiaoqing. Ionospheric effects on spaceborne synthetic aperture radar and a new capability of imaging the ionosphere from space[J]. Space Weather, 2015, 13(11): 737–741. doi: 10.1002/2015SW001281. |
| [19] |
MEYER F J, BAMLER R, JAKOWSKI N, et al. The potential of low-frequency SAR systems for mapping ionospheric TEC distributionse[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2006, 3(4): 560–564. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.882148. |
| [20] |
MEYER F J, CHOTOO K, CHOTOO S D, et al. The influence of equatorial scintillation on L-band SAR image quality and phase[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(2): 869–880. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2468573. |
| [21] |
JI Yifei, ZHANG Yongsheng, ZHANG Qilei, et al. Comments on “The influence of equatorial scintillation on L-Band SAR image quality and phase”[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 7300–7301. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2912450. |
| [22] |
JEHLE M, FREY O, SMALL D, et al. Measurement of ionospheric TEC in spaceborne SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(6): 2460–2468. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2040621. |
| [23] |
LI Liang, HONG Jun, MING Feng, et al. An approach for ionospheric effects correction on spaceborne SAR calibration based on active radar calibrator[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2012, 34(5): 1096–1101. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2011.00978. |
| [24] |
李亮, 洪峻, 明峰. 一种基于星载SAR编码有源定标器的电离层TEC测量方法[J]. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2014, 44(4): 511–526. doi: 10.1360/N112013-00056. LI Liang, HONG Jun, and MING Feng. An approach for measuring ionospheric TEC based on coded active radar calibrator of spaceborne SAR[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2014, 44(4): 511–526. doi: 10.1360/N112013-00056. |
| [25] |
BELCHER D P. Theoretical limits on SAR imposed by the ionosphere[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2008, 2(6): 435–448. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn:20070188. |
| [26] |
ZHAO Ning, TAN Lulu, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. A double frequency measurement and correction method for ionospheric effects in space-borne P-band SAR[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2013, 11(3): 255–261. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2013.03.006. |
| [27] |
YANG Lin, XING Mengdao, and SUN Guangcai. Ionosphere correction algorithm for spaceborne SAR imaging[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 27(5): 993–1000. doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2016.05.07. |
| [28] |
WANG Cheng, ZHANG Min, XU Zhengwen, et al. TEC retrieval from spaceborne SAR data and its applications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2014, 119(10): 8648–8659. doi: 10.1002/2014JA020078. |
| [29] |
LI Zhuo and ZAN Yinkai. Performance analysis of autofocus algorithms for compensating ionospheric dispersion effect on spaceborne low-frequency SAR focusing[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(2): 331–335. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2970720. |
| [30] |
HIRANO H, ISOGUCHI O, MOTOHKA T, et al. Estimation of ionospheric TEC from ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 split-band data[C]. 2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, USA, 2023: 1861–1864. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS52108.2023.10282622. |
| [31] |
LIN Haoyu, DENG Yunkai, ZHANG Heng, et al. Estimating and removing ionospheric effects for L-band spaceborne bistatic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5219816. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3137860. |
| [32] |
SMITH E M and TSYNKOV S V. Dual carrier probing for spaceborne SAR imaging[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2011, 4(2): 501–542. doi: 10.1137/10078325X. |
| [33] |
GILMAN M, SMITH E, and TSYNKOV S. Reduction of ionospheric distortions for spaceborne synthetic aperture radar with the help of image registration[J]. Inverse Problems, 2013, 29(5): 054005. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/29/5/054005. |
| [34] |
BICKEL S H and BATES R H T. Effects of magneto-ionic propagation on the polarization scattering matrix[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1965, 53(8): 1089–1091. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1965.4097. |
| [35] |
FREEMAN A. Calibration of linearly polarized polarimetric SAR data subject to Faraday rotation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2004, 42(8): 1617–1624. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.830161. |
| [36] |
QI Renyuan and JIN Yaqiu. Analysis of the effects of Faraday rotation on spaceborne polarimetric SAR observations at P-band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(5): 1115–1122. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.892583. |
| [37] |
CHEN Jie and QUEGAN S. Improved estimators of Faraday rotation in spaceborne polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2010, 7(4): 846–850. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2047002. |
| [38] |
LI Li, ZHANG Yongsheng, DONG Zhen, et al. New Faraday rotation estimators based on polarimetric covariance matrix[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2014, 11(1): 133–137. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2013.2250478. |
| [39] |
WANG Cheng, LIU Lu, CHEN Liang, et al. Improved TEC retrieval based on spaceborne PolSAR data[J]. Radio Science, 2017, 52(3): 288–304. doi: 10.1002/2016RS006116. |
| [40] |
JEHLE M, RUEGG M, ZUBERBUHLER L, et al. Measurement of ionospheric Faraday rotation in simulated and real spaceborne SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(5): 1512–1523. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2004710. |
| [41] |
MEYER F J and NICOLL J B. Prediction, detection, and correction of Faraday rotation in full-polarimetric L-band SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(10): 3076–3086. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2003002. |
| [42] |
ROGERS N C and QUEGAN S. The accuracy of Faraday rotation estimation in satellite synthetic aperture radar images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(8): 4799–4807. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2284635. |
| [43] |
QUEGAN S and LOMAS M R. The impact of system effects on estimates of Faraday rotation from synthetic aperture radar measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(8): 4284–4298. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2395076. |
| [44] |
JI Yifei, ZHANG Yongsheng, ZHANG Qilei, et al. Retrieval of ionospheric Faraday rotation angle in low-frequency polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7(1): 3181–3193. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2888928. |
| [45] |
WANG Xun, ZHANG Yunhua, and LI Dong. Estimation of ionospheric Faraday rotation over ocean areas using L-band spaceborne PolSAR data[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2024, 45(9): 3054–3074. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2024.2339206. |
| [46] |
LI Jinhui, JI Yifei, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. A novel strategy of ambiguity correction for the improved Faraday rotation estimator in linearly full-polarimetric SAR data[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(4): 1158. doi: 10.3390/s18041158. |
| [47] |
张永胜, 于春锐, 计一飞, 等. 一种基于频域解模糊的星载P波段全极化SAR法拉第旋转效应校正方法[J]. 电子学报, 2023, 51(3): 585–592. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210698. ZHANG Yongsheng, YU Chunrui, JI Yifei, et al. A correction method of the Faraday rotation effect based on the frequency-domain ambiguity-resolving in spaceborne P-band full-polarimetric SAR[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2023, 51(3): 585–592. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210698. |
| [48] |
MEYER F J, NICOLL J, and BRISTOW B. Mapping aurora activity with SAR––a case study[C]. 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009: IV-1–IV-4. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2009.5417610. |
| [49] |
PI Xiaoqing, FREEMAN A, CHAPMAN B, et al. Imaging ionospheric inhomogeneities using spaceborne synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2011, 116(A4): A04303. doi: 10.1029/2010JA016267. |
| [50] |
KIM J S and PAPATHANASSIOU K P. TEC and ionospheric height estimation by means of azimuth subaperture analysis in quad-polarimetric spaceborne SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 6279–6290. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3085130. |
| [51] |
WEGMULLER U, WERNER C, STROZZI T, et al. Ionospheric electron concentration effects on SAR and INSAR[C]. 2006 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Denver, USA, 2006: 3731–3734. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2006.956. |
| [52] |
GRAY A L, MATTAR K E, and SOFKO G. Influence of ionospheric electron density fluctuations on satellite radar interferometry[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2000, 27(10): 1451–1454. doi: 10.1029/2000GL000016. |
| [53] |
CHEN Jingyi and ZEBKER H A. Ionospheric artifacts in simultaneous L-band InSAR and GPS observations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(4): 1227–1239. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2164805. |
| [54] |
RAUCOULES D and DE MICHELE M. Assessing ionospheric influence on L-band SAR data: Implications on coseismic displacement measurements of the 2008 Sichuan earthquake[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2010, 7(2): 286–290. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2009.2033317. |
| [55] |
WEGMULLER U, STROZZI T, and WERNER C. Ionospheric path delay estimation using split-beam interferometry[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 3631–3634. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6350630. |
| [56] |
HU Jun, LI Zhiwei, ZHANG Lei, et al. Correcting ionospheric effects and monitoring two-dimensional displacement fields with multiple-aperture InSAR technology with application to the Yushu earthquake[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2012, 55(12): 1961–1971. doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4509-x. |
| [57] |
LIU Zhen, JUNG H S, and LU Zhong. Joint correction of ionosphere noise and orbital error in L-band SAR interferometry of interseismic deformation in southern California[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(6): 3421–3427. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2272791. |
| [58] |
JUNG H S, LEE D T, LU Zhong, et al. Ionospheric correction of SAR interferograms by multiple-aperture interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(5): 3191–3199. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2218660. |
| [59] |
JUNG H S and LEE W J. An improvement of ionospheric phase correction by multiple-aperture interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(9): 4952–4960. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2413948. |
| [60] |
ZHANG Bochen, DING Xiaoli, ZHU Wu, et al. Mitigating ionospheric artifacts in coseismic interferogram based on offset field derived from ALOS-PALSAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(7): 3050–3059. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2533441. |
| [61] |
MAO Wenfei, WANG Xiaowen, LIU Guoxiang, et al. Ionospheric phase delay correction for time series multiple-aperture InSAR constrained by polynomial deformation model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 4006605. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3281343. |
| [62] |
ROSEN P A, HENSLEY S, and CHEN C. Measurement and mitigation of the ionosphere in L-band Interferometric SAR data[C]. 2010 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2010: 1459–1463. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2010.5494385. |
| [63] |
BRCIC R, PARIZZI A, EINEDER M, et al. Estimation and compensation of ionospheric delay for SAR interferometry[C]. 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, USA, 2010: 2908–2911. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2010.5652231. |
| [64] |
BRCIC R, PARIZZI A, EINEDER M, et al. Ionospheric effects in SAR interferometry: An analysis and comparison of methods for their estimation[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 1497–1500. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2011.6049351. |
| [65] |
GOMBA G, PARIZZI A, DE ZAN F, et al. Toward operational compensation of ionospheric effects in SAR interferograms: The split-spectrum method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(3): 1446–1461. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2481079. |
| [66] |
ZHANG Bochen, WANG Chisheng, DING Xiaoli, et al. Correction of ionospheric artifacts in SAR data: Application to fault slip inversion of 2009 southern Sumatra earthquake[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(9): 1327–1331. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2844686. |
| [67] |
ZHANG Bochen, DING Xiaoli, AMELUNG F, et al. Impact of ionosphere on InSAR observation and coseismic slip inversion: Improved slip model for the 2010 Maule, Chile, earthquake[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2021, 267: 112733. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112733. |
| [68] |
ROSEN P, LAVALLE M, PI Xiaoqing, et al. Techniques and tools for estimating ionospheric effects in interferometric and polarimetric SAR data[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 1501–1504. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2011.6049352. |
| [69] |
LIANG Cunren, LIU Zhen, FIELDING E J, et al. InSAR time series analysis of L-band wide-swath SAR data acquired by ALOS-2[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(8): 4492–4506. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2821150. |
| [70] |
GOMBA G, GONZALEZ F R, and DE ZAN F D. Ionospheric phase screen compensation for the Sentinel-1 TOPS and ALOS-2 ScanSAR modes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 223–235. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2604461. |
| [71] |
KUSK A, ANDERSEN J K, and BONCORI J P M. Burst overlap coregistration for Sentinel-1 TOPS DInSAR ice velocity measurements[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4010905. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3062905. |
| [72] |
LIAO Heming, MEYER F J, SCHEUCHL B, et al. Ionospheric correction of InSAR data for accurate ice velocity measurement at polar regions[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2018, 209: 166–180. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2018.02.048. |
| [73] |
MAO Wenfei, WANG Xiaowen, LIU Guoxiang, et al. Time series InSAR ionospheric delay estimation, correction, and ground deformation monitoring with reformulating range split-spectrum interferometry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5213118. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3298919. |
| [74] |
ZHANG Bochen, DING Xiaoli, ZHU Wu, et al. An asymmetric split-spectrum method for estimating the ionospheric artifacts in InSAR data[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 517–520. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2018.8518936. |
| [75] |
ZHU Wu, DING Xiaoli, JUNG H S, et al. Mitigation of ionospheric phase delay error for SAR interferometry: An application of FR-based and azimuth offset methods[J]. Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 8(1): 58–67. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2016.1235808. |
| [76] |
ZHU W, JUNG H S, and CHEN Jingyuan. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry (InSAR) ionospheric correction based on Faraday rotation: Two case studies[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(18): 3871. doi: 10.3390/app9183871. |
| [77] |
GOMBA G and DE ZAN F D. Bayesian data combination for the estimation of ionospheric effects in SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(11): 6582–6593. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2730438. |
| [78] |
MAO Wenfei, LIU Guoxiang, WANG Xiaowen, et al. An InSAR ionospheric correction method based on variance component estimation with integration of MAI and RSS measurements[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 1423–1433. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.3045267. |
| [79] |
MAO Wenfei, WANG Xiaowen, LIU Guoxiang, et al. Estimation and compensation of ionospheric phase delay for multi-aperture InSAR: An azimuth split-spectrum interferometry approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5209414. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3095272. |
| [80] |
KIM J S. Development of ionosphere estimation techniques for the correction of SAR data[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], ETH Zurich, 2013.
|
| [81] |
ZHANG Bochen, ZHU Wu, DING Xiaoli, et al. A review of methods for mitigating ionospheric artifacts in differential SAR interferometry[J]. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2022, 13(2): 160–169. doi: 10.1016/j.geog.2021.12.001. |
| [82] |
MAO Wenfei, MA Peifeng, and TANG Jun. Mapping high spatial resolution ionospheric total electron content by integrating time series InSAR with international reference ionosphere model[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2024, 214: 153–166. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2024.06.003. |
| [83] |
KIM J S, SATO H, and PAPATHANASSIOU K. Validation of ionospheric mapping by means of SAR through ground based radar measurements[C]. 11th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Hamburg, Germany, 2016: 1–6.
|
| [84] |
KIM J S and PAPATHANASSIOU K. Polar ionosphere irregularity structure and dynamics by means of X-band space-borne synthetic aperture radar[C]. 13th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, online, 2021: 1–4.
|
| [85] |
KIM J S and PAPATHANASSIOU K. SAR observation of ionosphere using range/azimuth sub-bands[C]. 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Berlin, German, 2014: 1–4.
|
| [86] |
WANG Cheng, GUO Wulong, ZHAO Haisheng, et al. Improving the topside profile of ionosonde with TEC retrieved from spaceborne polarimetric SAR[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(3): 516. doi: 10.3390/s19030516. |
| [87] |
GUO Wulong, WANG Cheng, ZHAO Haisheng, et al. Ionospheric sounding based on spaceborne PolSAR in P-band[J]. Atmosphere, 2022, 13(4): 524. doi: 10.3390/atmos13040524. |
| [88] |
ZHU Wu, CHEN Jingyuan, ZHANG Qin, et al. Mapping of high-spatial-resolution three-dimensional electron density by combing of full-polarimetric SAR and IRI model[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2020, 8: 181. doi: 10.3389/feart.2020.00181. |
| [89] |
ZHU Wu, CHEN Jingyuan, SUN Quan, et al. Reconstructing of high-spatial-resolution three-dimensional electron density by ingesting SAR-derived VTEC into IRI model[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4508305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3178242. |
| [90] |
GANGULY S, WICKWAR V, and GOODMAN J M. New generation topside sounder[J]. Radio Science, 2001, 36(5): 1167–1179. doi: 10.1029/1999RS002415. |
| [91] |
LI Zhuo, CHEN Jie, and LI Chunsheng. Spaceborne SIMO-SAR for three-dimensional ionospheric irregularity sounding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(4): 2830–2846. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120214. |
| [92] |
LI Lianlin and LI Fang. Ionosphere tomography based on spaceborne SAR[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2008, 42(7): 1187–1193. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2007.11.022. |
| [93] |
HU Cheng, TIAN Ye, DONG Xichao, et al. Computerized ionospheric tomography based on geosynchronous SAR[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics, 2017, 122(2): 2686–2705. doi: 10.1002/2016JA023542. |
| [94] |
WANG Cheng, CHEN Liang, LIU Lu, et al. Robust computerized ionospheric tomography based on spaceborne polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(9): 4022–4031. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2703098. |
| [95] |
WANG Cheng, CHEN Liang, ZHAO Haisheng, et al. Ionospheric reconstructions using Faraday rotation in spaceborne polarimetric SAR data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(11): 1169. doi: 10.3390/rs9111169. |
| [96] |
WANG Cheng, GUO Wulong, ZHANG Qinghe, et al. 3-D computerized ionospheric tomography with GPS, SAR, and ionosonde[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5210109. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3285744. |
| [97] |
WANG Cheng, ZHAO Haisheng, WANG Liming, et al. GPS-based ionospheric tomography from the combination of PolSAR and E-CHAIM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5205714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3367420. |
| [98] |
WANG Cheng, WANG Liming, ZHAO Haisheng, et al. Ionospheric electron density reconstruction based on space-borne SAR in Alaska regions[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 4011805. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2024.3412799. |
| [99] |
BELCHER D P and CANNON P S. Amplitude scintillation effects on SAR[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2014, 8(6): 658–666. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0168. |
| [100] |
JI Yifei, ZHANG Qilei, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. Spaceborne P-band SAR imaging degradation by anisotropic ionospheric irregularities: A comprehensive numerical study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(8): 5516–5526. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2966710. |
| [101] |
TANG Feixiang, JI Yifei, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. Drifting ionospheric scintillation simulation for L-band geosynchronous SAR[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 842–854. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3330752. |
| [102] |
EICHEL P H, GHIGLIA D C, and JAKOWATZ C V. Speckle processing method for synthetic-aperture-radar phase correction[J]. Optics Letters, 1989, 14(1): 1–3. doi: 10.1364/OL.14.000001. |
| [103] |
QUEGAN S, GREEN J, ZANDONA-SCHNEIDER R, et al. Quantifying and correcting ionospheric effects on P-band SAR images[C]. 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, USA, 2008: II-541–II-544. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2008.4779048. |
| [104] |
LI Zhuo, QUEGAN S, CHEN Jie, et al. Performance analysis of phase gradient autofocus for compensating ionospheric phase scintillation in BIOMASS P-band SAR data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(6): 1367–1371. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2402833. |
| [105] |
ZENG Hongcheng, YANG Wei, WANG Pengbo, et al. A modified PGA for spaceborne SAR scintillation compensation based on the weighted maximum likelihood estimator and data division[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 3938–3947. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3175263. |
| [106] |
WANG Rui, HU Cheng, LI Yuanhao, et al. Joint amplitude-phase compensation for ionospheric scintillation in GEO SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(6): 3454–3465. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2672078. |
| [107] |
YU Lei, ZHANG Yongsheng, ZHANG Qilei, et al. Minimum-entropy autofocusing based on Re-PSO for ionospheric scintillation mitigation in P-band SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 84580–84590. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2924802. |
| [108] |
JI Yifei, DONG Zhen, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. Extended scintillation phase gradient autofocus in future spaceborne P-band SAR mission[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2021, 64(11): 212303. doi: 10.1007/s11432-019-2797-4. |
| [109] |
JI Yifei, YU Chunrui, ZHANG Qilei, et al. An ionospheric phase screen projection method of phase gradient autofocus in spaceborne SAR[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4504205. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3147036. |
| [110] |
JI Yifei, DONG Zhen, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. An autofocus approach with applications to ionospheric scintillation compensation for spaceborne SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(2): 989–1004. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3108117. |
| [111] |
JI Yifei, DONG Zhen, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. Measuring ionospheric scintillation parameters from SAR images using phase gradient autofocus: A case study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5200212. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3044657. |
| [112] |
KIM J S, PAPATHANASSIOU K P, QUEGAN S, et al. Estimation and correction of scintillation effects on spaceborne P-band SAR images[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 5101–5104. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6352463. |
| [113] |
KIM J S, PAPATHANASSIOU K P, SCHEIBER R, et al. Correcting distortion of polarimetric SAR data induced by ionospheric scintillation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(12): 6319–6335. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2431856. |
| [114] |
TANG Feixiang, JI Yifei, DONG Yongsheng, et al. Ionospheric phase scintillation correction based on multi-aperture Faraday rotation estimation in spaceborne P-band full-polarimetric SAR data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(22): 5659. doi: 10.3390/rs14225659. |
| [115] |
GRACHEVA V, KIM J S, PRATS-IRAOLA P, et al. Combined estimation of ionospheric effects in SAR images exploiting Faraday rotation and autofocus[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 8018705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3102597. |
| [116] |
BELCHER D P. Sidelobe prediction in transionospheric SAR imaging radar from the ionospheric turbulence strength CkL[C]. 2008 International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, Australia, 2008: 54–59. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2008.4653891. |
| [117] |
BELCHER D P, MANNIX C R, and CANNON P S. Measurement of the ionospheric scintillation parameter CkL from SAR images of clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(10): 5937–5943. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2717081. |
| [118] |
MANNIX C R, BELCHER D P, and CANNON P S. Measurement of ionospheric scintillation parameters from SAR images using corner reflectors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 6695–6702. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2727319. |
| [119] |
ROTH A P, HUXTABLE B D, CHOTOO K, et al. Detection and mitigation of ionospheric stripes in PALSAR data[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 1621–1624. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2012.6351218. |
| [120] |
GAMA F F, WIEDERKEHR N C, and DA CONCEIÇÃO BISPO P. Removal of ionospheric effects from sigma naught images of the ALOS/PALSAR-2 satellite[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(4): 962. doi: 10.3390/rs14040962. |
| [121] |
MOHANTY S, KHATI U, SINGH G, et al. Correction of amplitude scintillation effect in fully polarimetric SAR coherency matrix data[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 164: 184–199. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.04.005. |
| [122] |
GAN Nan, JI Yifei, TANG Feixiang, et al. Correcting and measuring ionospheric scintillation amplitude stripes in L-band SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4515505. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3220232. |
| [123] |
JI Yifei, DONG Zhen, ZHANG Yongsheng, et al. Equatorial ionospheric scintillation measurement in advanced land observing satellite (ALOS) phased array-type L-band synthetic aperture radar (PALSAR) observations[J]. Engineering, 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2024.01.027. |
| [124] |
KIM J S, PAPATHANASSIOU K P, SATO H, et al. Detection and estimation of equatorial spread F scintillations using synthetic aperture radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(12): 6713–6725. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2731943. |
| [125] |
KIM J S, SATO H, and PAPATHANASSIOU K. Estimation of drift of equatorial ionosphere of post sunset-sector by means of low frequency space-borne SAR[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 6946–6949. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2016.7730812. |
| [126] |
MOHANTY S, SINGH G, CARRANO C S, et al. Ionospheric scintillation observation using space-borne synthetic aperture radar data[J]. Radio Science, 2018, 53(10): 1187–1202. doi: 10.1029/2017RS006424. |
| [127] |
MOHANTY S, CARRANO C S, and SINGH G. Effect of anisotropy on ionospheric scintillations observed by SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6888–6899. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2909078. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: