| [1] |
SEEDS A J and WILLIAMS K J. Microwave photonics[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2006, 24(12): 4628–4641. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2006.885787. |
| [2] |
KIPPENBERG T J, HOLZWARTH R, and DIDDAMS S A. Microresonator-based optical frequency combs[J]. Science, 2011, 332(6029): 555–559. doi: 10.1126/science.1193968. |
| [3] |
PAN Shilong and ZHANG Yamei. Microwave photonic radars[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2020, 38(19): 5450–5484. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2020.2993166. |
| [4] |
ZHANG Fangzheng, GUO Qingshui, WANG Ziqian, et al. Photonics-based broadband radar for high-resolution and real-time inverse synthetic aperture imaging[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(14): 16274–16281. doi: 10.1364/oe.25.016274. |
| [5] |
MELO S, PINNA S, BOGONI A, et al. Dual-use system combining simultaneous active radar & communication, based on a single photonics-assisted transceiver[C]. 2016 17th International Radar Symposium, Krakow, Poland, 2016: 1–4. doi: 10.1109/IRS.2016.7497379. |
| [6] |
RASHIDINEJAD A and WEINER A M. Photonic radio-frequency Arbitrary waveform generation with maximal time-bandwidth product capability[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2014, 32(20): 3383–3393. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2014.2331491. |
| [7] |
SIMPSON T B, LIU J M, HUANG K F, et al. Nonlinear dynamics induced by external optical injection in semiconductor lasers[J]. Quantum and Semiclassical Optics: Journal of the European Optical Society Part B, 1997, 9(5): 765–784. doi: 10.1088/1355-5111/9/5/009. |
| [8] |
SERAFINO G, NOVIELLO C, MARESCA S, et al. Experimental dual-band coherent photonics-based radar network with ISAR imaging[C]. 2022 IEEE Radar Conference, New York City, USA, 2022: 1–6. doi: 10.1109/RadarConf2248738.2022.9763913. |
| [9] |
JIANG Wen, LIU Jianwei, YANG Jiyao, et al. A novel multiband fusion method based on a modified RELAX algorithm for high-resolution and anti-non-Gaussian colored clutter microwave imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5105312. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3109724. |
| [10] |
DEVGAN P S, URICK V J, DIEHL J F, et al. Improvement in the phase noise of a 10 GHz optoelectronic oscillator using all-photonic gain[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2009, 27(15): 3189–3193. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2008.2009472. |
| [11] |
YAO Jianping. Microwave photonics[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2009, 27(3): 314–335. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2008.2009551. |
| [12] |
LI Ruoming, LI Wangzhe, DONG Yongwei, et al. An ultrahigh-resolution continuous wave synthetic aperture radar with photonic-assisted signal generation and dechirp processing[C]. 2020 17th European Radar Conference, Utrecht, Netherlands, 2021: 13–16. doi: 10.1109/EuRAD48048.2021.00015. |
| [13] |
WANG Anle, WO Jianghai, LUO Xiong, et al. Ka-band microwave photonic ultra-wideband imaging radar for capturing quantitative target information[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(16): 20708–20717. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.020708. |
| [14] |
SERAFINO G, MARESCA S, DI MAURO L, et al. A photonics-assisted multi-band MIMO radar network for the port of the future[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 2021, 27(6): 6000413. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2021.3092880. |
| [15] |
MARESCA S, SERAFINO G, NOVIELLO C, et al. Field trial of a coherent, widely distributed, dual-band photonics-based MIMO radar with ISAR imaging capabilities[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2022, 40(20): 6626–6635. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2022.3182421. |
| [16] |
PAN Shilong and ZHU Dan. Broadband cognitive radio enabled by photonics[C]. 45th European Conference on Optical Communication, Dublin, Ireland, 2019: 1–3. doi: 10.1049/cp.2019.0776. |
| [17] |
PAN Shilong, YE Xingwei, ZHANG Yamei, et al. Microwave photonic array radars[J]. IEEE Journal of Microwaves, 2021, 1(1): 176–190. doi: 10.1109/JMW.2020.3034583. |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
CHANDRAKANTH R, SAIBABA J, VARADAN G, et al. Feasibility of high resolution SAR and multispectral data fusion[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 356–359. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2011.6048972. |
| [20] |
YOKOYA N, GROHNFELDT C, and CHANUSSOT J. Hyperspectral and multispectral data fusion: A comparative review of the recent literature[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 2017, 5(2): 29–56. doi: 10.1109/MGRS.2016.2637824. |
| [21] |
DENG Xu, XU Xin, and DONG Hao. Color feature coding and classification of single polarized synthetic aperture radar image[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2018, 38(7): 2056–2063. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2017112780. |
| [22] |
ZHANG Xinzheng, XIA Jili, TAN Xiaoheng, et al. PolSAR image classification via learned superpixels and QCNN integrating color features[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(15): 1831. doi: 10.3390/rs11151831. |
| [23] |
FRANCESCHETTI G, LANARI R, PASCAZIO V, et al. WASAR: A wide-angle SAR processor[J]. IEE Proceedings F (Radar and Signal Processing), 1992, 139(2): 107–114. doi: 10.1049/ip-f-2.1992.0014. |
| [24] |
INOUE Y, KUROSU T, MAENO H, et al. Season-long daily measurements of multifrequency (Ka, Ku, X, C, and L) and full-polarization backscatter signatures over paddy rice field and their relationship with biological variables[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2002, 81(2/3): 194–204. doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(01)00343-1. |
| [25] |
RANSON K J and SUN Guoqing. Mapping biomass of a northern forest using multifrequency SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(2): 388–396. doi: 10.1109/36.295053. |
| [26] |
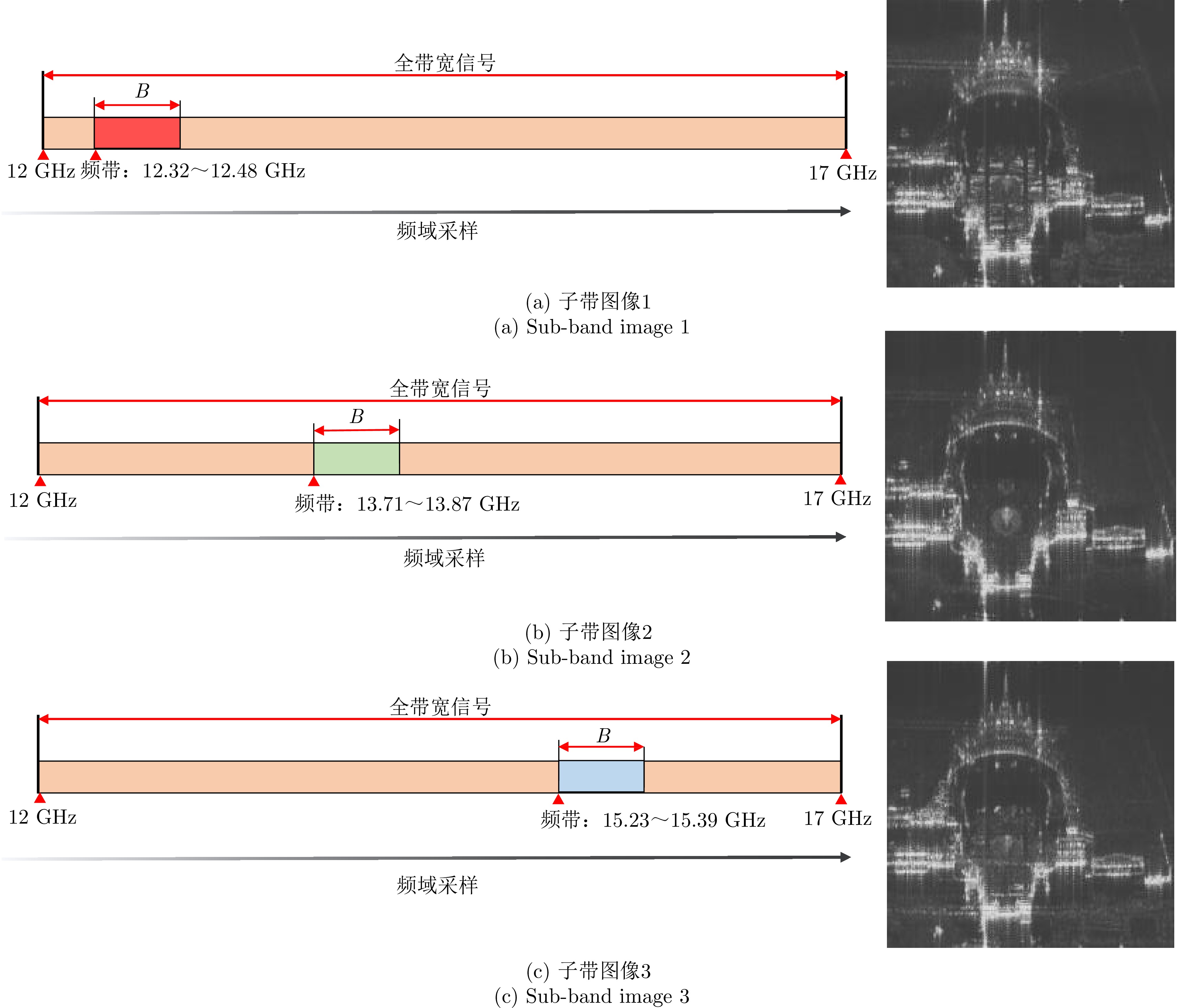
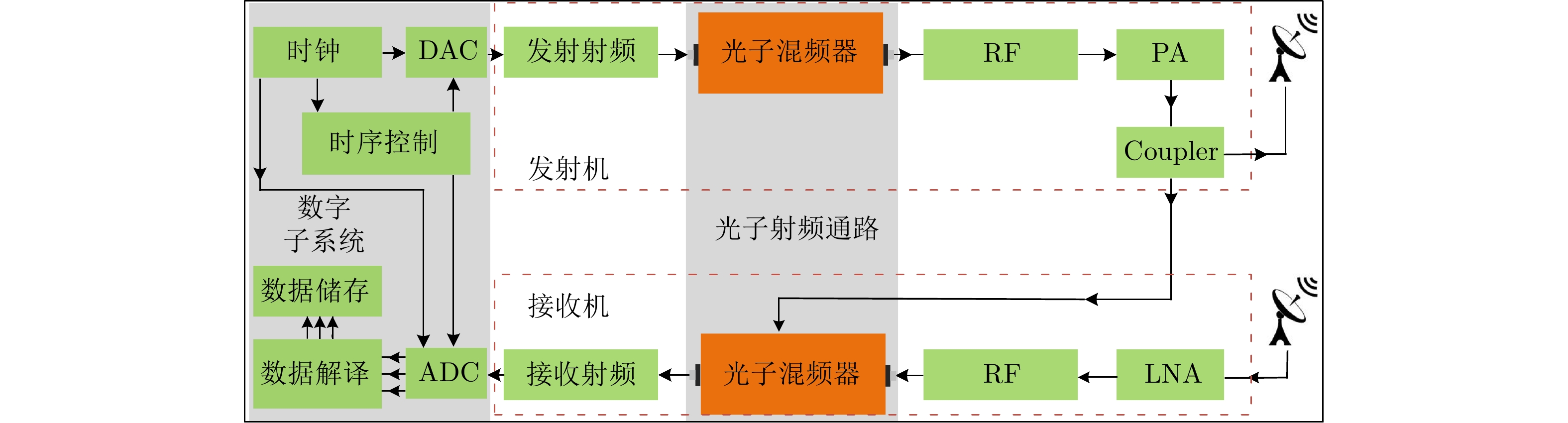
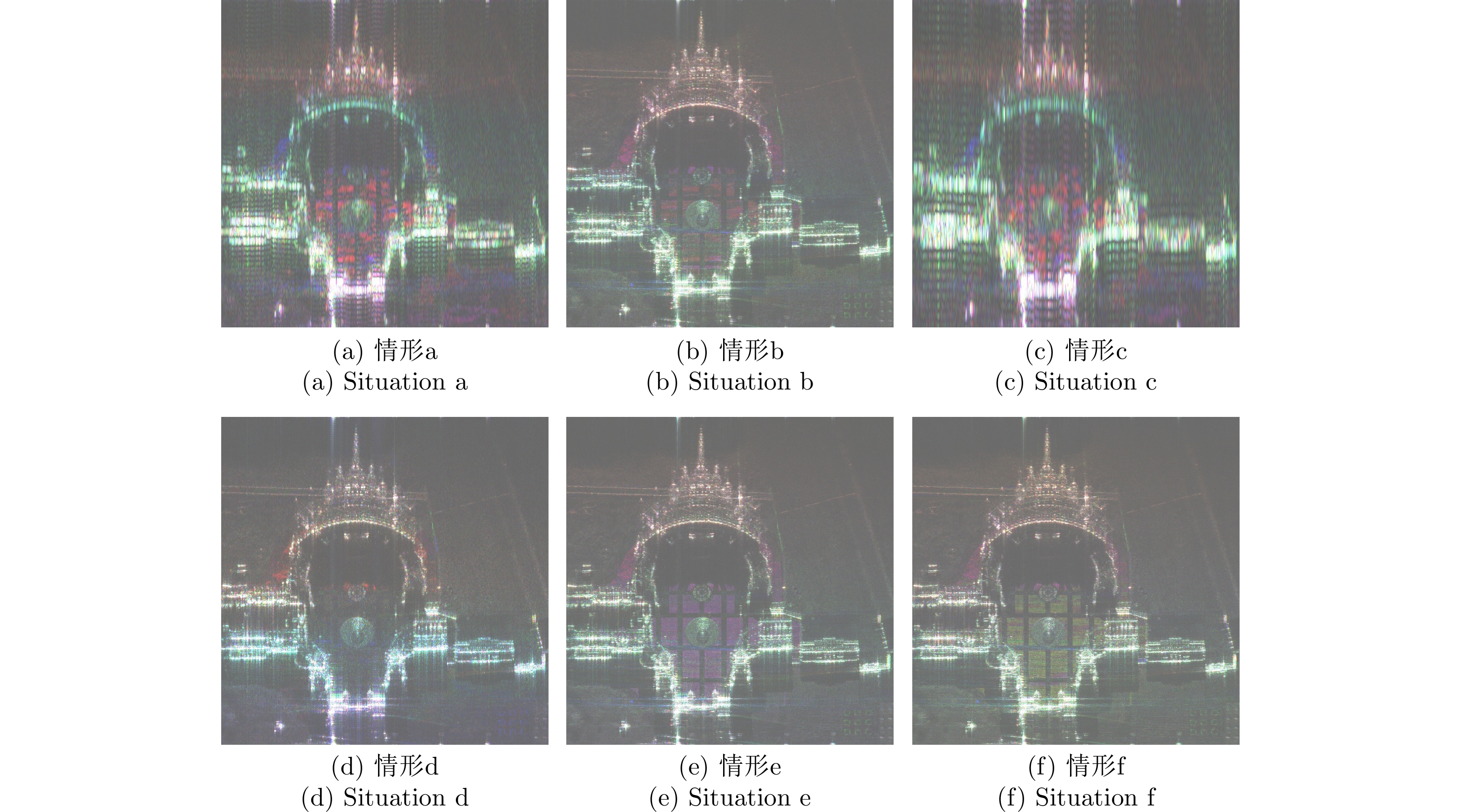
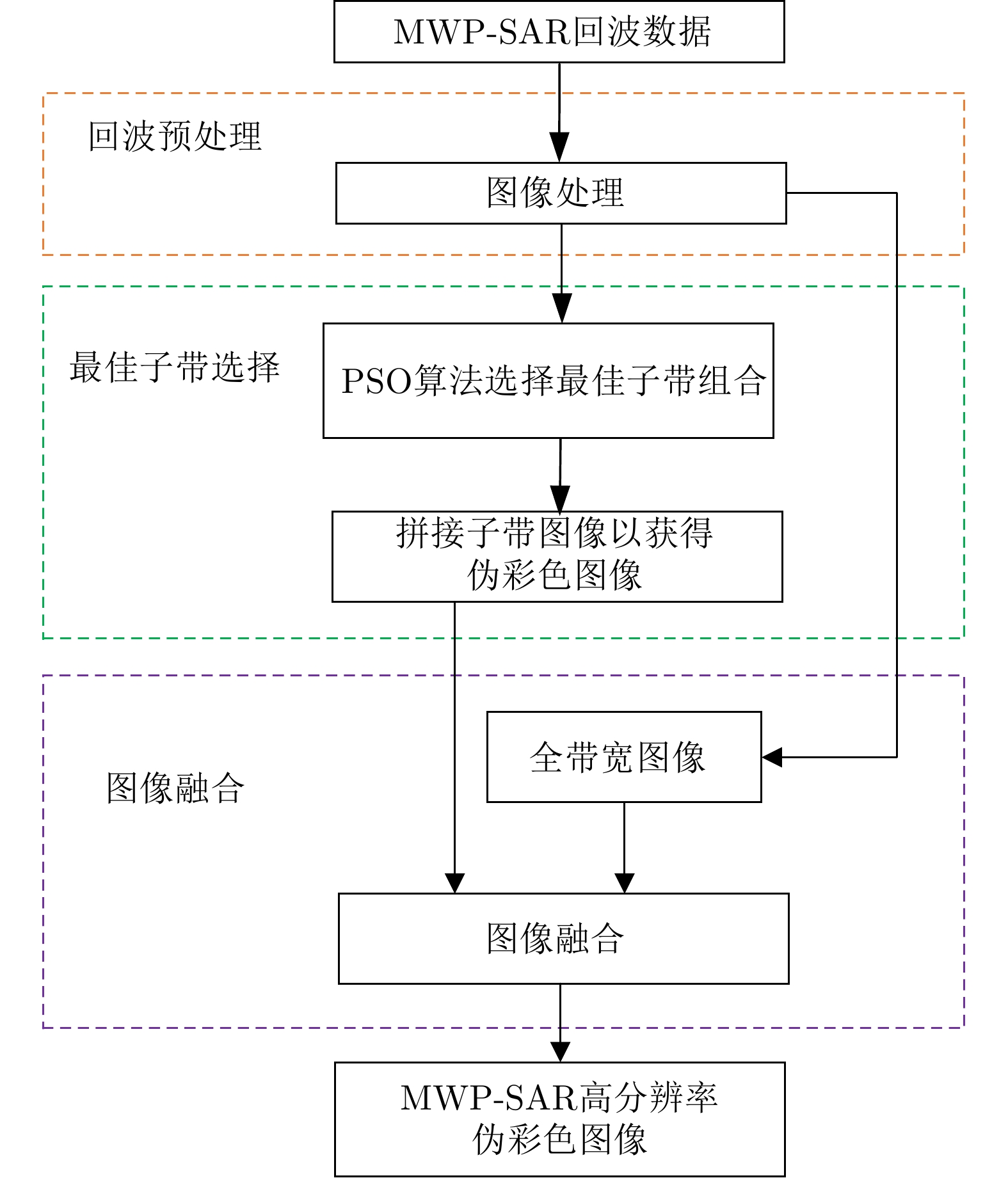
HAI Yu, LI zhongyu, WU Junjie, et al. Microwave photonic SAR high-precision imaging based on optimal subaperture division[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5232317. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3192583. |
| [27] |
XU Feng and JIN Yaqiu. From the emergence of intelligent science to the research of microwave vision[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2018, 36(10): 30–44. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2018.10.004. |
| [28] |
LI Ruoming, LI Wangzhe, DONG Yongwei, et al. FDIR—a wideband photonic-assisted SAR system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(4): 4333–4346. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3240111. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: