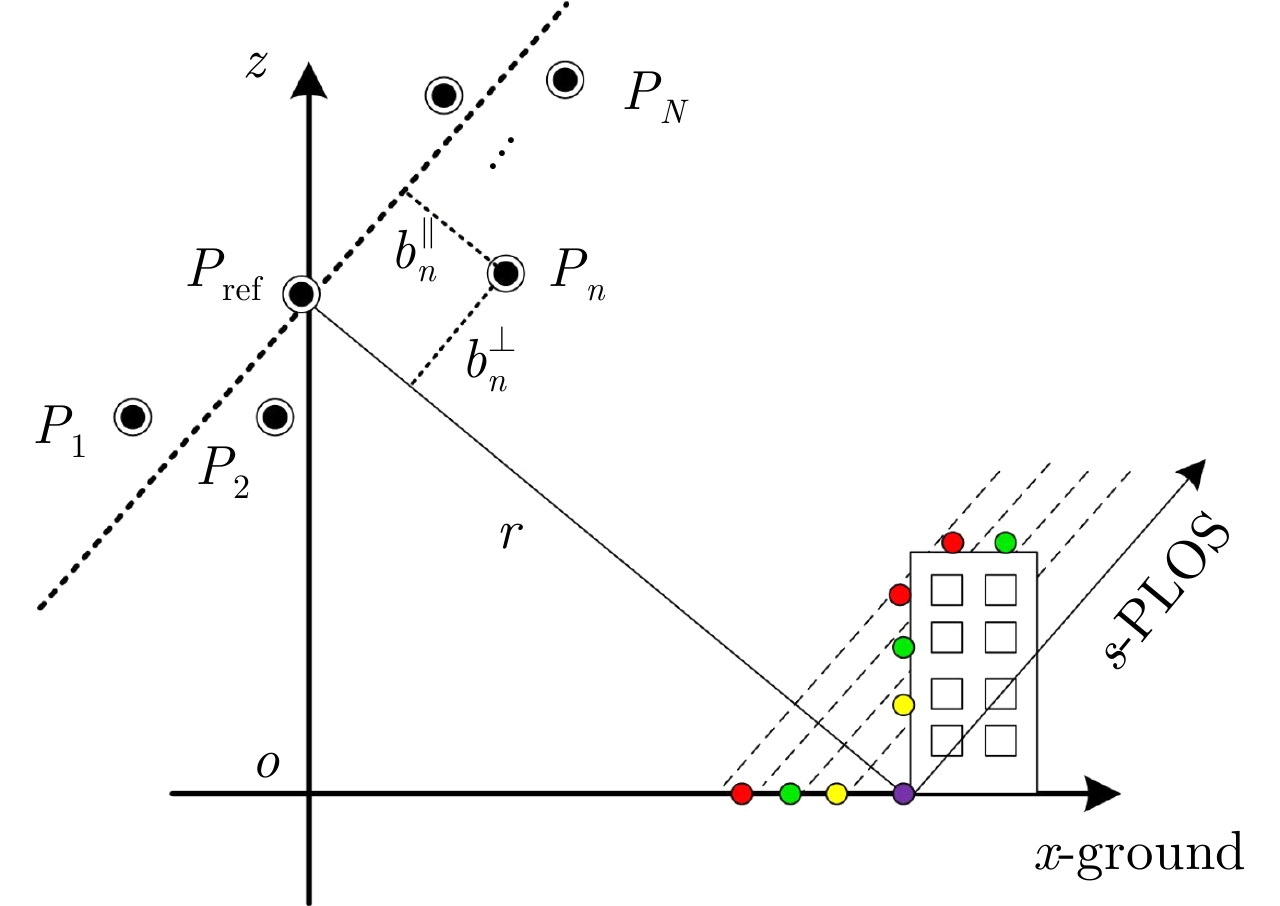
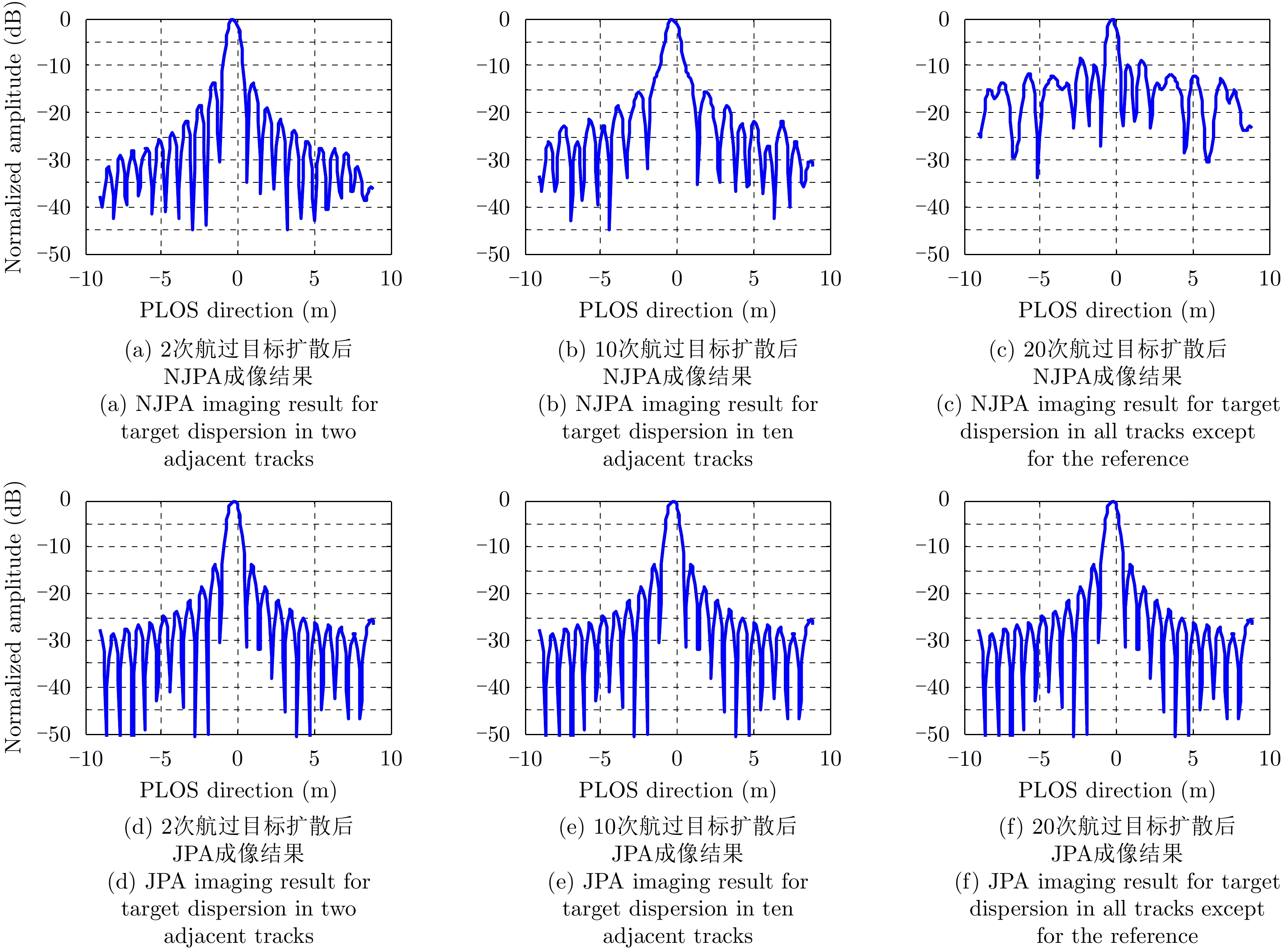
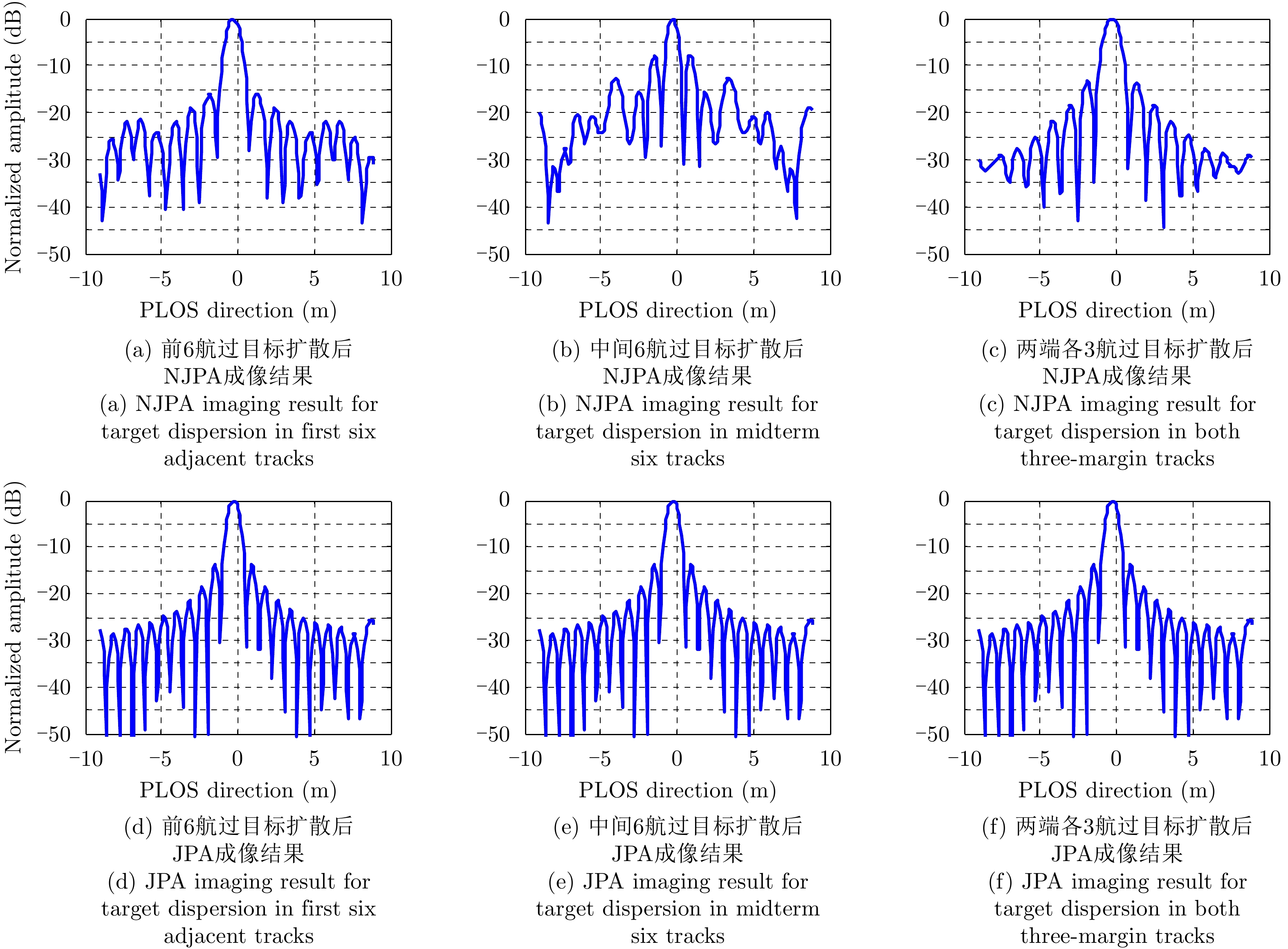
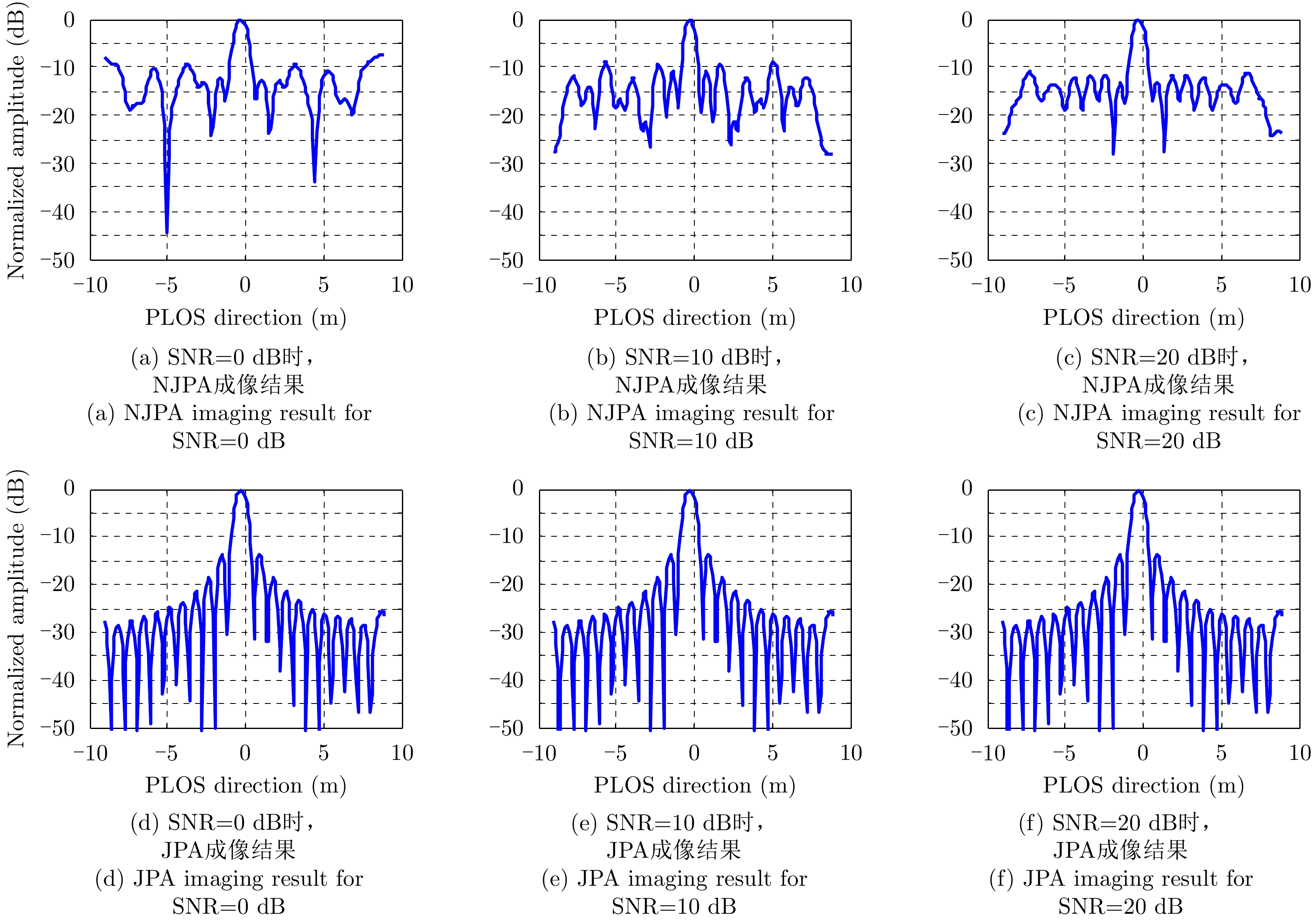
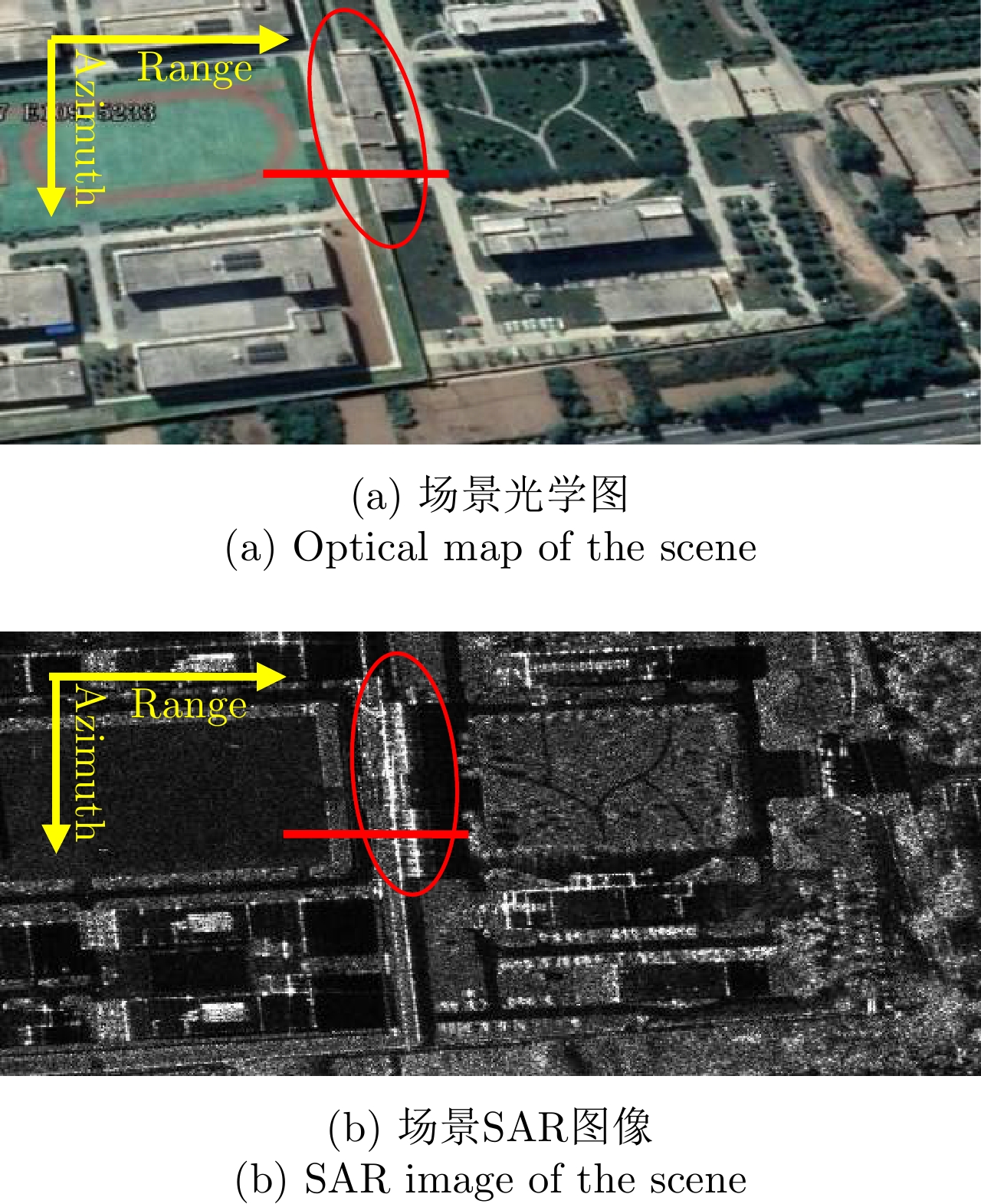
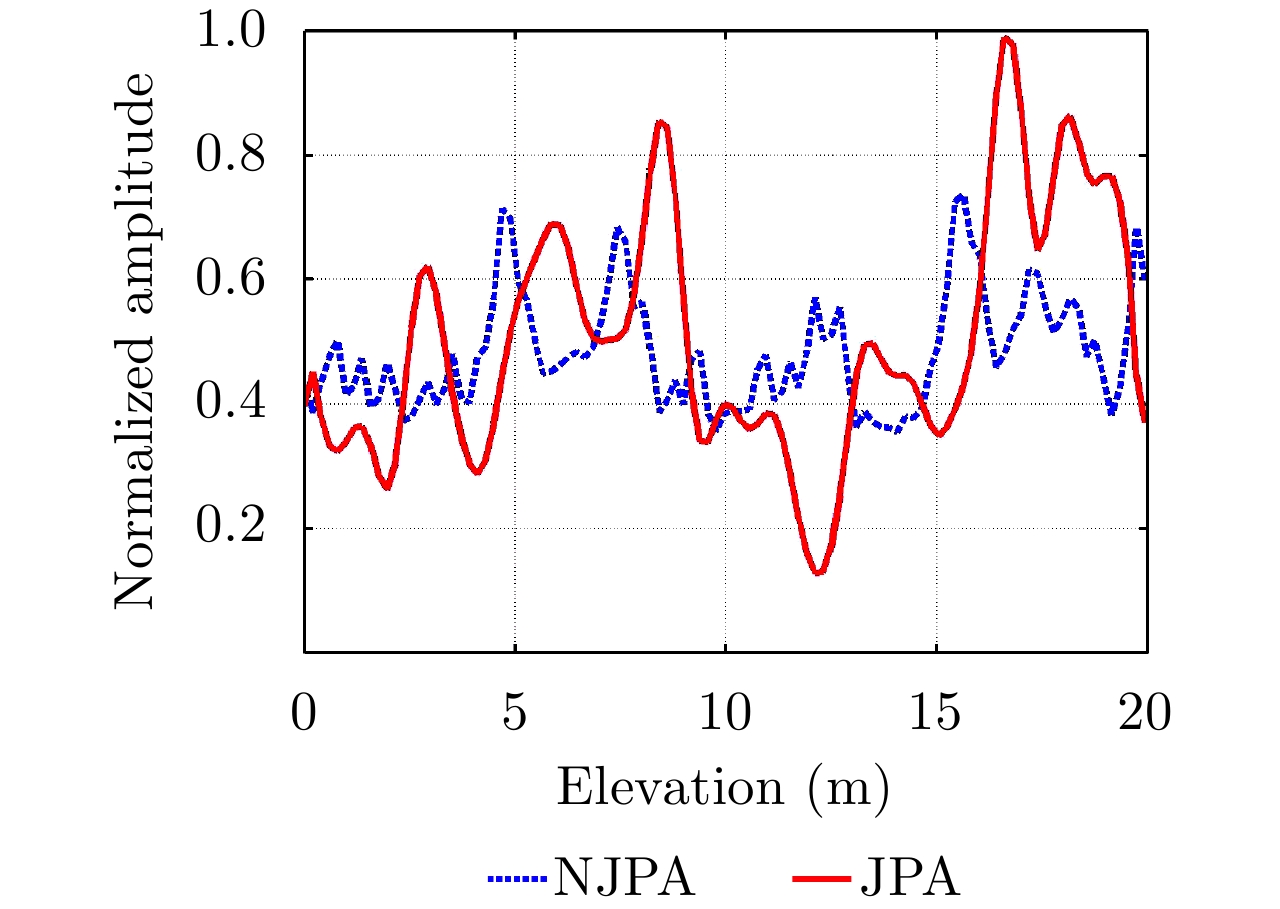
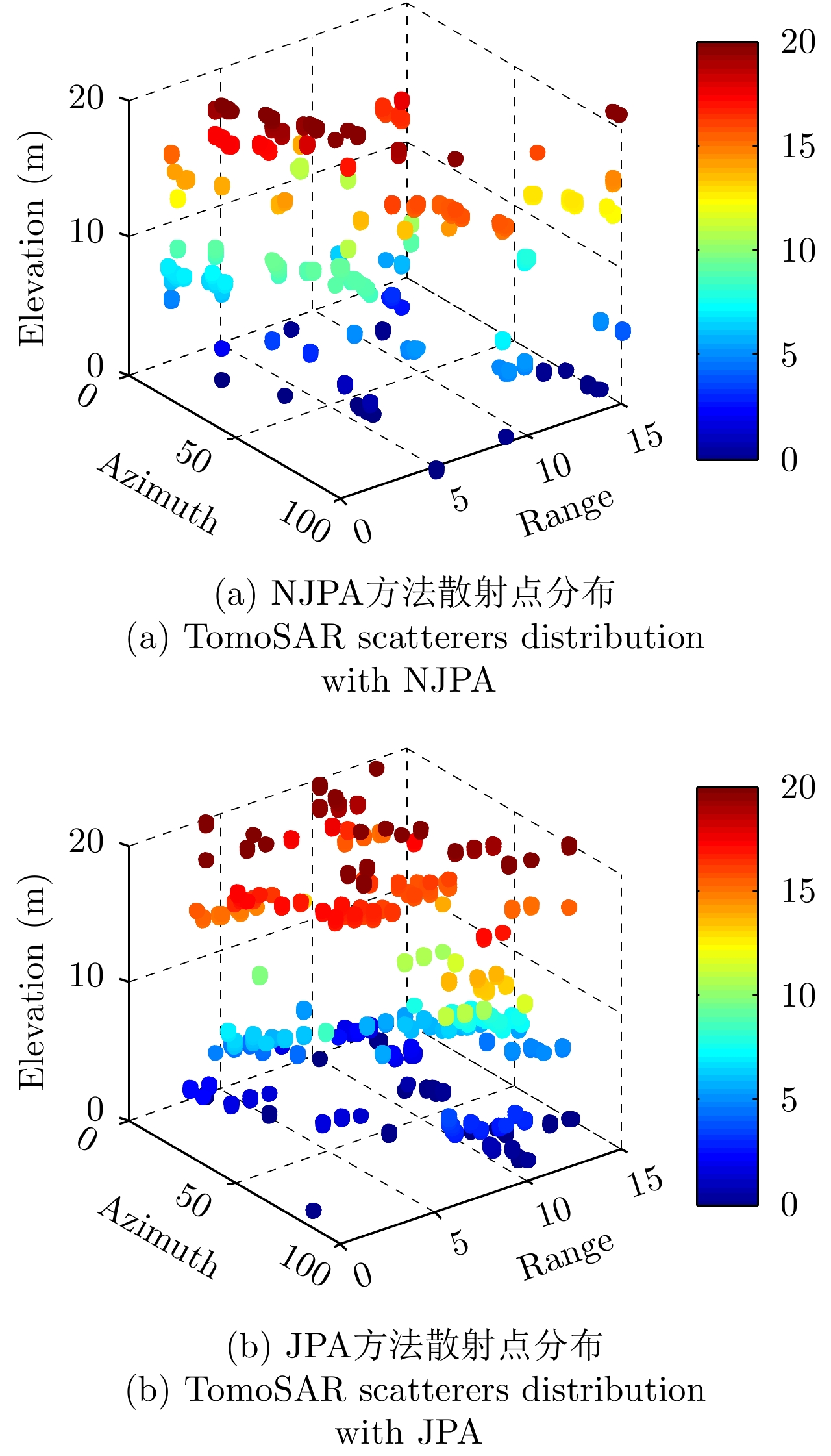
| [1] |
REIGBER A and MOREIRA A. First demonstration of airborne SAR tomography using multibaseline L-band data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2000, 38(5): 2142–2152. doi: 10.1109/36.868873 |
| [2] |
洪文, 王彦平, 林赟, 等. 新体制SAR三维成像技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109HONG Wen, WANG Yanping, LIN Yun, et al. Research progress on three-dimensional SAR imaging techniques[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(6): 633–654. doi: 10.12000/JR18109 |
| [3] |
廖明生, 魏恋欢, 汪紫芸, 等. 压缩感知在城区高分辨率SAR层析成像中的应用[J]. 雷达学报, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031LIAO Mingsheng, WEI Lianhuan, WANG Ziyun, et al. Compressive sensing in high-resolution 3D SAR tomography of urban scenarios[J]. Journal of Radars, 2015, 4(2): 123–129. doi: 10.12000/JR15031 |
| [4] |
ZHAO Kexiang, BI Hui, and ZHANG Bingchen. SAR tomography method based on fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(5): 1019–1023. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.05.11 |
| [5] |
LI Liechen and LI Daojing. Sparse array SAR 3D imaging for continuous scene based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2014, 36(9): 2166–2172. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01645 |
| [6] |
LI Liechen, LI Daojing, and ZHANG Qingjuan. Three-aperture millimeter-wave SAR side-looking three-dimensional imaging based on compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2013, 35(3): 552–558. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.01016 |
| [7] |
WEI Lianhuan, LIAO Mingsheng, BALZ T, et al. Layover building scatterers extraction via high-resolution spaceborne SAR tomography[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2014, 39(5): 536–540. doi: 10.13203/j.whugis20120460 |
| [8] |
BUDILLON A, JOHNSY A C, and SCHIRINZI G. A fast support detector for superresolution localization of multiple scatterers in SAR tomography[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(6): 2768–2779. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2657227 |
| [9] |
SAUER S, FERRO-FAMIL L, REIGBER A, et al. Three-dimensional imaging and scattering mechanism estimation over urban scenes using dual-baseline polarimetric InSAR observations at L-band[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(11): 4616–4629. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2147321 |
| [10] |
TEBALDINI S and GUARNIERI A M. On the role of phase stability in SAR multibaseline applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(7): 2953–2966. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2010.2043738 |
| [11] |
LOMBARDINI F and REIGBER A. Adaptive spectral estimation for multibaseline SAR tomography with airborne L-band data[C]. Proceedings of 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 2003: 2014–2016. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2003.1294324. |
| [12] |
GUILLASO S and REIGBER A. Polarimetric SAR tomography[C]. Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop POLINSAR 2005, Frascati, Italy, 2005.
|
| [13] |
GINI F and LOMBARDINI F. Multibaseline cross-track SAR interferometry: A signal processing perspective[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2005, 20(8): 71–93. doi: 10.1109/maes.2005.1499278 |
| [14] |
LOMBARDINI F, MONTANARI M, and GINI F. Reflectivity estimation for multibaseline interferometric radar imaging of layover extended sources[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2003, 51(6): 1508–1519. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2003.811239 |
| [15] |
FORNARO G, SERAFINO F, and SOLDOVIERI F. Three-dimensional focusing with multipass SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2003, 41(3): 507–517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2003.809934 |
| [16] |
MIN Rui, YANG Qianqian, PI Yiming, et al. SAR tomography imaging based on regularized orthogonal matching pursuit[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrument, 2012, 26(12): 1069–1073. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1187.2012.01069 |
| [17] |
ZHU Xiaoxiang and BAMLER R. Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(12): 4296–4308. doi: 10.1109/tgrs.2010.2050487 |
| [18] |
WEI Lianhuan, BALZ T, ZHANG Lu, et al. A novel fast approach for SAR tomography: Two-step iterative shrinkage/thresholding[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(6): 1377–1381. doi: 10.1109/lgrs.2015.2402124 |
| [19] |
BANDA F, DALL J, and TEBALDINI S. Single and multipolarimetric P-band SAR tomography of subsurface ice structure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(5): 2832–2845. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2015.2506399 |
| [20] |
XING Shiqi, LI Yongzhen, DAI Dahai, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of man-made objects using polarimetric tomographic SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(6): 3694–3705. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2220145 |
| [21] |
任笑真, 杨汝良. 一种基于幅度和相位迭代重建的四维合成孔径雷达成像方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2016, 5(1): 65–71. doi: 10.12000/JR15135REN Xiaozhen and YANG Ruliang. Four-dimensional SAR imaging algorithm based on iterative reconstruction of magnitude and phase[J]. Journal of Radars, 2016, 5(1): 65–71. doi: 10.12000/JR15135 |
| [22] |
SCHMITT M and STILLA U. Maximum-likelihood-based approach for single-pass synthetic aperture radar tomography over urban areas[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2014, 8(9): 1145–1153. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2013.0378 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
孙希龙. SAR层析与差分层析成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2012: 57–74.
SUN Xilong. Research on SAR tomography and differential SAR tomography imaging technology[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2012: 57–74.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

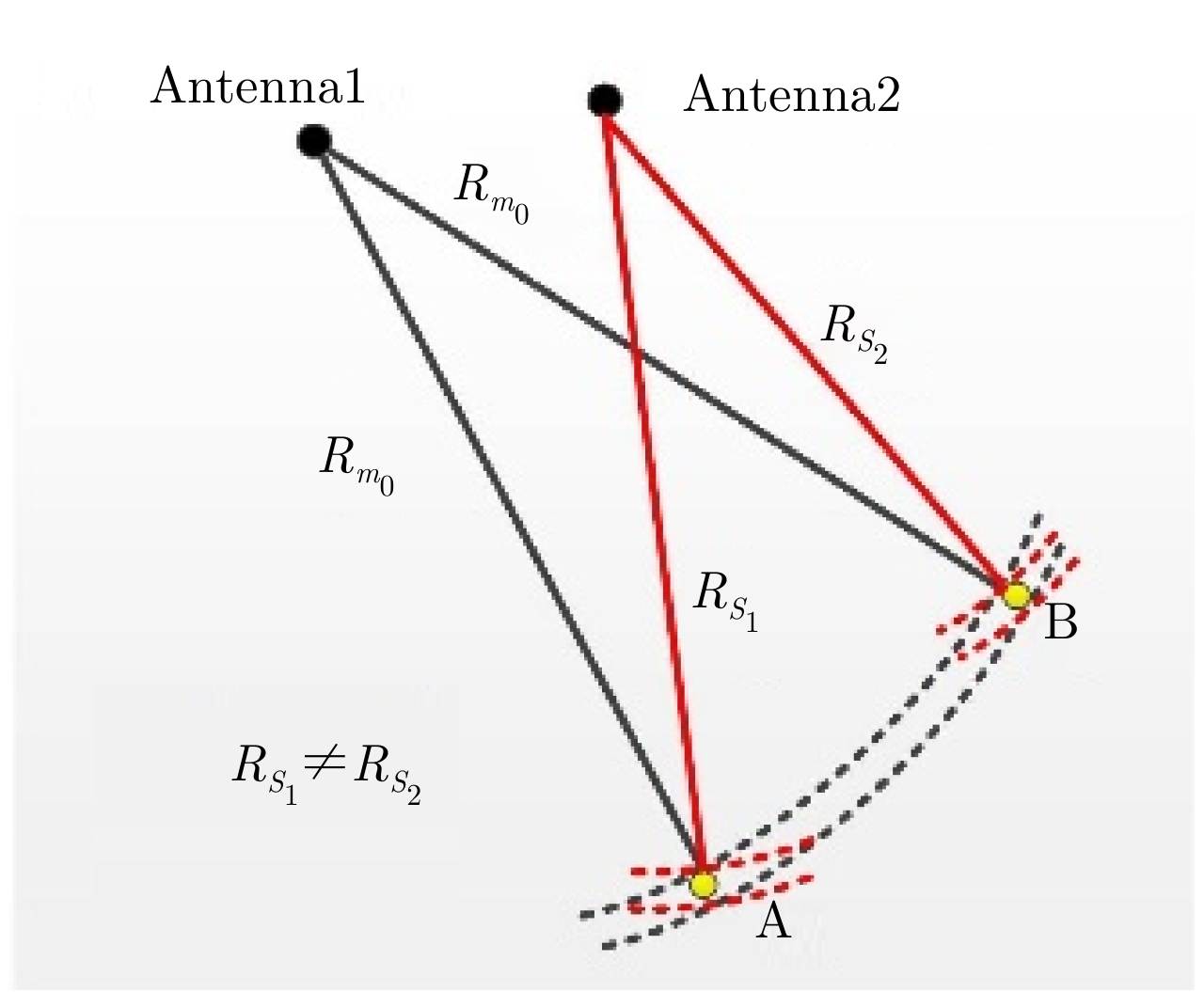



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: