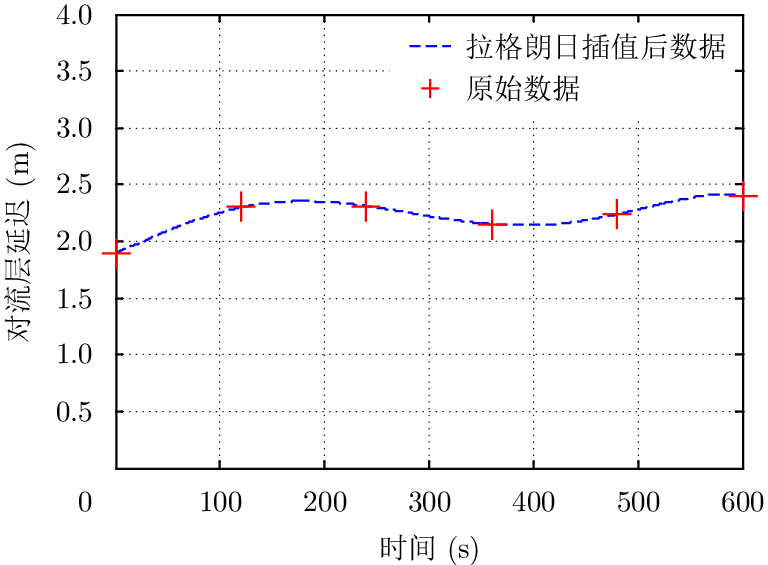
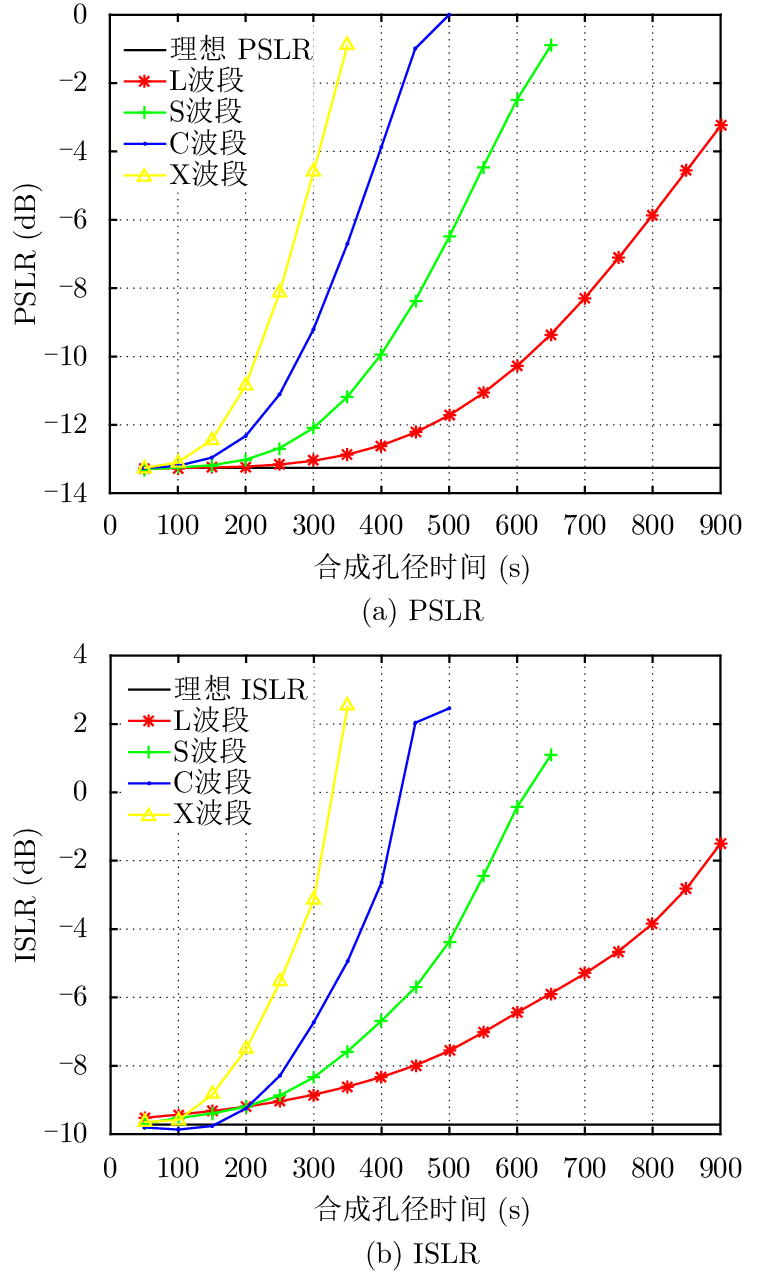
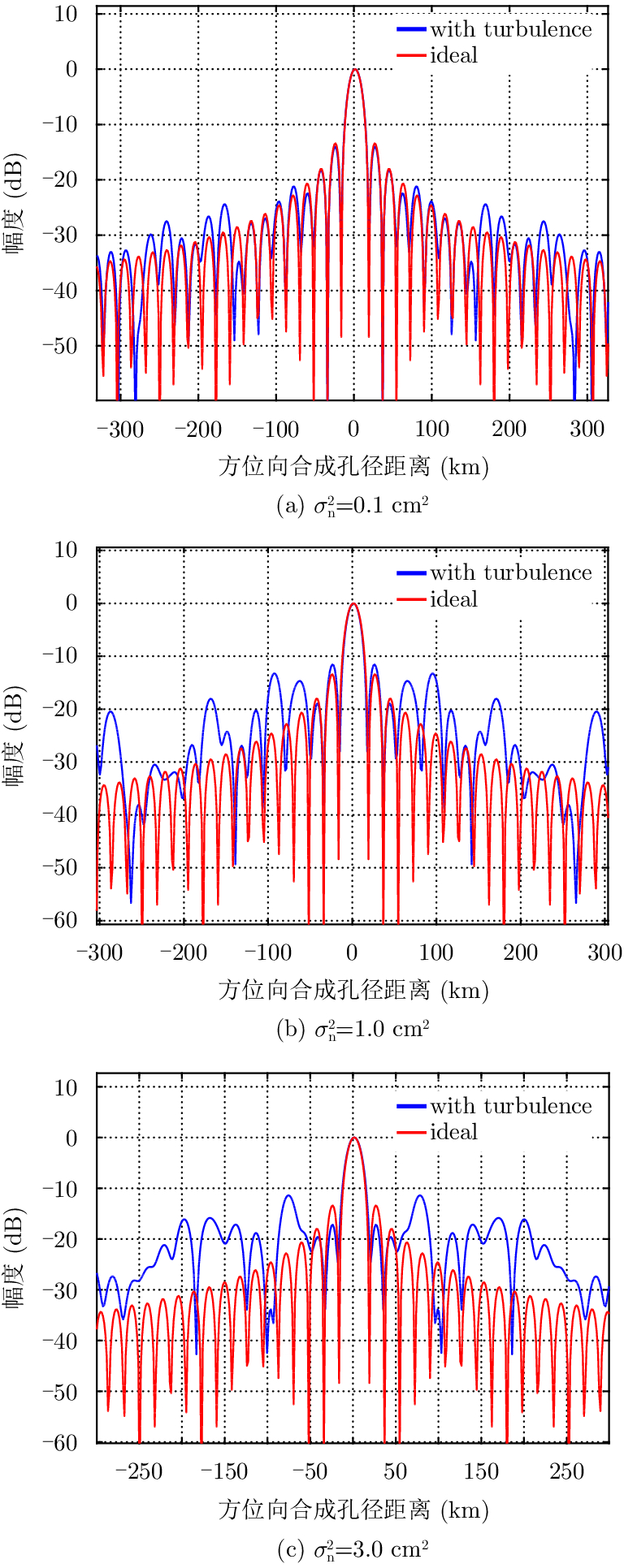
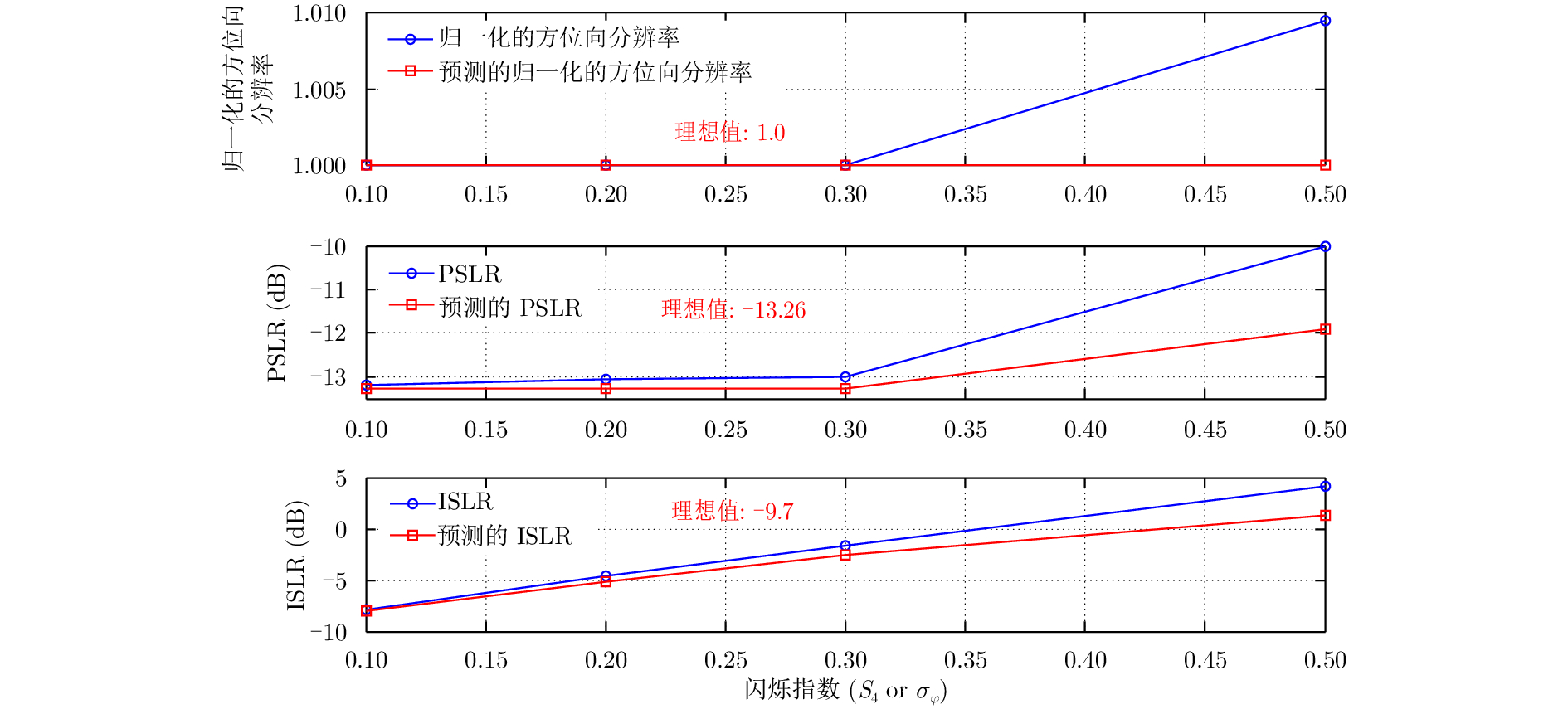
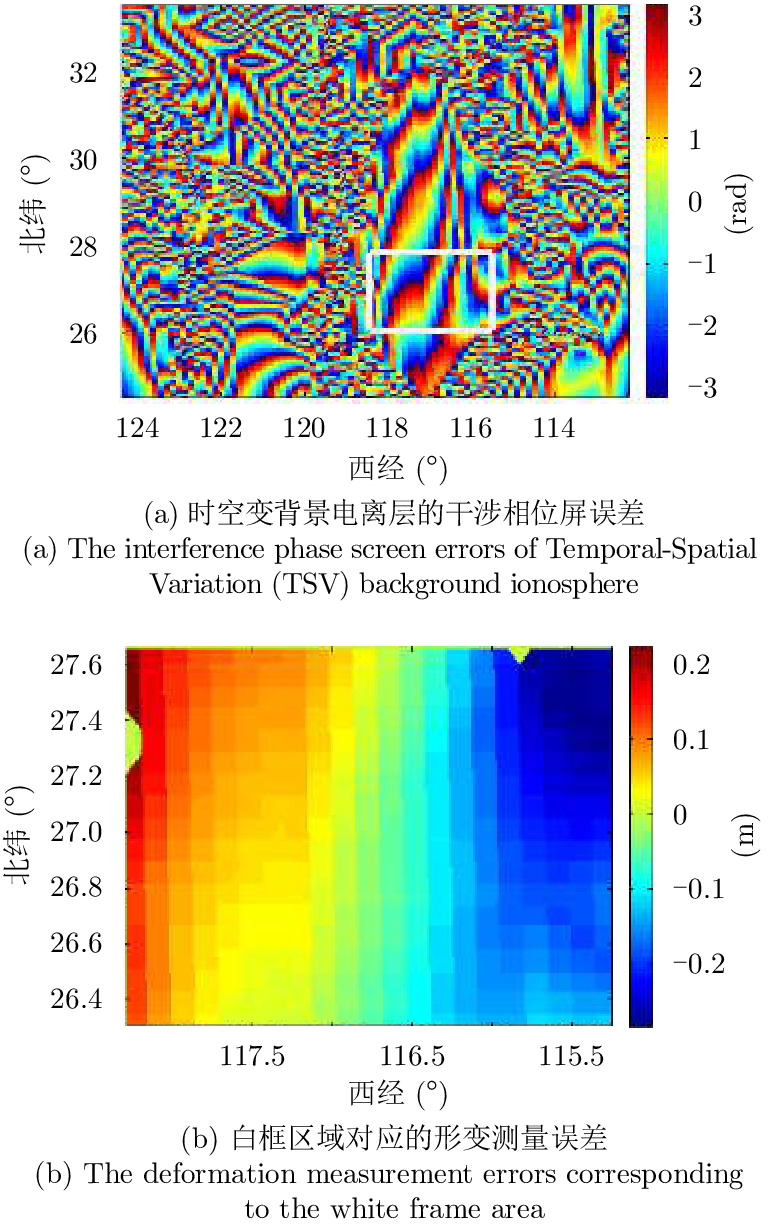
| [1] |
Tomiyasu K. Synthetic aperture radar in geosynchronous orbit[C]. Proceedings of 1978 Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 1978: 42–45
|
| [2] |
Tomiyasu K and Pacelli J L. Synthetic aperture radar imaging from an inclined geosynchronous orbit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1983, 21(3): 324–329. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.1983.350561 |
| [3] |
NASA and JPL. Global earthquake satellite system: A 20-year plan to enable earthquake prediction[EB/OL]. http://solidearth.jpl.nasa.gov/GESS/3123_GESS_Rep_2003.pdf, 2015, 9
|
| [4] |
Edelstein W N, Madsen S N, Moussessian A, et al.. Concepts and technologies for synthetic aperture radar from MEO and geosynchronous orbits[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 5659, Enabling Sensor and Platform Technologies for Spaceborne Remote Sensing, Honolulu, Hawaii, 2005: 195–203
|
| [5] |
Laurence Gray A, Mattar K E, and Sofko G. Influence of ionospheric electron density fluctuations on satellite radar interferometry[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2000, 27(10): 1451–1454. DOI: 10.1029/2000GL000016 |
| [6] |
Meyer F, Bamler R, Jakowski N, et al. The potential of low-frequency SAR systems for mapping ionospheric TEC distributions[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2006, 3(4): 560–564. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2006.882148 |
| [7] |
Meyer F J and Nicoll J. The impact of the ionosphere on interferometric SAR processing[C]. Proceedings of 2008 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 2008: II-391–II-394
|
| [8] |
Meyer F J. Performance requirements for ionospheric correction of low-frequency SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3694–3702. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2146786 |
| [9] |
Sun J P, Bi Y K, Wang Y P, et al.. High resolution SAR performance limitation by the change of tropospheric refractivity[C]. Proceedings of 2011 IEEE CIE International Conference on Radar, Chengdu, China, 2011
|
| [10] |
Zhang F, Li G J, Li W, et al. Multiband microwave imaging analysis of ionosphere and troposphere refraction for spaceborne SAR[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 2014: 913056.
|
| [11] |
Hanssen R F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis[M]. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2001
|
| [12] |
Danklmayer A, Doring B J, Schwerdt M, et al. Assessment of atmospheric propagation effects in SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(10): 3507–3518. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2022271 |
| [13] |
Hobbs S, Mitchell C, Forte B, et al. System design for geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar missions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(12): 7750–7763. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2318171 |
| [14] |
Bruno D and Hobbs S E. Radar imaging from geosynchronous orbit: Temporal decorrelation aspects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(7): 2924–2929. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2042062 |
| [15] |
Bruno D, Hobbs S E, and Ottavianelli G. Geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar: Concept design, properties and possible applications[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2006, 59(1–5): 149–156. DOI: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2006.02.005 |
| [16] |
Ruiz Rodon J, Broquetas A, Guarnieri A M, et al. Geosynchronous SAR focusing with atmospheric phase screen retrieval and compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(8): 4397–4404. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2242202 |
| [17] |
Ruiz-Rodon J, Broquetas A, Makhoul E, et al. Nearly zero inclination geosynchronous SAR mission analysis with long integration time for earth observation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(10): 6379–6391. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2296357 |
| [18] |
Guarnieri A M, Rocca F, and Ibars A B. Impact of atmospheric water vapor on the design of a Ku band geosynchronous SAR system[C]. Proceedings of 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 2009
|
| [19] |
Guarnieri A M, Tebaldini S, Rocca F, et al.. GEMINI: Geosynchronous SAR for earth monitoring by interferometry and imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012
|
| [20] |
Monti Guarnieri A, Broquetas A, Recchia A, et al. Advanced radar geosynchronous observation system: ARGOS[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(7): 1406–1410. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2404214 |
| [21] |
Monti Guarnieri A, Leanza A, Recchia A, et al. Atmospheric phase screen in GEO-SAR: Estimation and compensation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(3): 1668–1679. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2766084 |
| [22] |
Hu C, Long T, Zeng T, et al. The accurate focusing and resolution analysis method in geosynchronous SAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(10): 3548–3563. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2160402 |
| [23] |
Hu C, Tian Y, Yang X P, et al. Background ionosphere effects on geosynchronous SAR focusing: Theoretical analysis and verification based on the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS)[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(3): 1143–1162. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2475283 |
| [24] |
Dong X C, Hu C, Tian Y, et al. Experimental study of ionospheric impacts on geosynchronous SAR using GPS signals[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(6): 2171–2183. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2537401 |
| [25] |
Tian Y, Hu C, Dong X C, et al.. Analysis of effects of time variant troposphere on geosynchronous SAR imaging[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 5051–5054
|
| [26] |
Tian Ye, Dong Xi-chao, and Hu Cheng. Analysis of troposphere impacts on geosynchronous SAR imaging[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2015, 31(12): 1562–1567. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2015.12.003 |
| [27] |
Tian Y, Hu C, Dong X C, et al. Theoretical analysis and verification of time variation of background ionosphere on geosynchronous SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(4): 721–725. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2360235 |
| [28] |
Wang R, et al. Joint amplitude-phase compensation for ionospheric scintillation in GEO SAR imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(6): 3454–3465.
|
| [29] |
Hu C, Li Y H, Dong X C, et al. Performance analysis of L-band geosynchronous SAR imaging in the presence of ionospheric scintillation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 3454–3465. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2602939 |
| [30] |
Li Y H, Hu C, Dong X C, et al. Impacts of ionospheric scintillation on geosynchronous SAR focusing: Preliminary experiments and analysis[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2015, 58(10): 1–3.
|
| [31] |
Hu C, Li Y H, Dong X C, et al. Impacts of temporal-spatial variant background ionosphere on repeat-track GEO D-InSAR system[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(11): 916. DOI: 10.3390/rs8110916 |
| [32] |
Kou L L, Wang X Q, Xiang M S, et al. Effect of orbital errors on the geosynchronous circular synthetic aperture radar imaging and interferometric processing[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science C, 2011, 12(5): 404–416. DOI: 10.1631/jzus.C1000170 |
| [33] |
Kou L L, Xiang M S, Wang X Q, et al. Tropospheric effects on L-band geosynchronous circular SAR imaging[J]. IET Radar,Sonar&Navigation, 2013, 7(6): 693–701.
|
| [34] |
Ji Y F, Zhang Q L, Zhang Y S, et al. L-band geosynchronous SAR imaging degradations imposed by ionospheric irregularities[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2017, 60(6): 060308. DOI: 10.1007/s11432-016-9064-1 |
| [35] |
Li D X, Rodriguez-Cassola M, Prats-Iraola P, et al. Modelling of tropospheric delays in geosynchronous synthetic aperture radar[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2017, 60(6): 060307. DOI: 10.1007/s11432-016-9065-1 |
| [36] |
Tofsted D H. Turbulence simulation: Outer scale effects on the refractive index spectrum[R]. Technical Report ARL-TR-548. US Army Research Lab. NM, 2000
|
| [37] |
Von Kármán T. Progress in the statistical theory of turbulence[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1948, 34(11): 530–539. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.34.11.530 |
| [38] |
Tunick A D. The Refractive Index Structure Parameter/Atmospheric Optical Turbulence Model: CN2[M]. U.S. Adelphi: A.R. Laboratory, 1998
|
| [39] |
Liu Z P, Hu C, Zeng T, et al. Improved secondary range compression focusing method in GEO SAR[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 2011: 1373–1376
|
| [40] |
Long T, Hu C, Ding Z, et al.. Geosynchronous SAR: System and Signal Processing[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2018
|
| [41] |
Zhang D D, Chen Z Y, Dong X C, et al.. Simulating the impacts of ionospheric scintillation on geosynchronous SAR[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Radar Symposium (IRS), Prague, Czech Republic, 2017
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

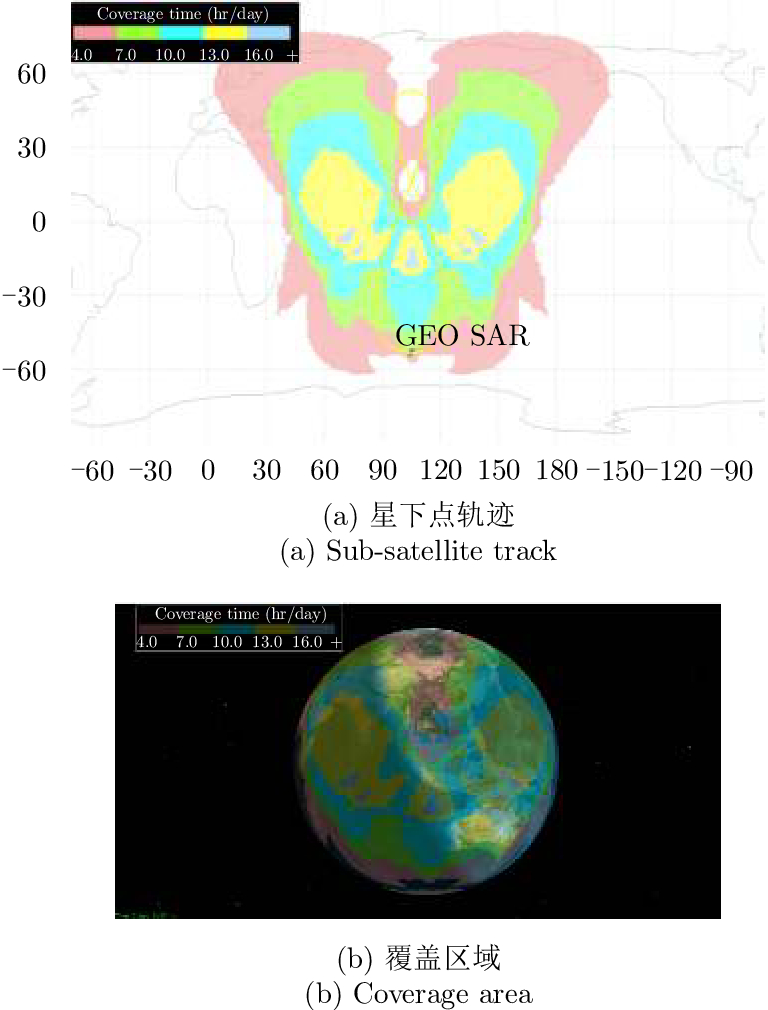



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: