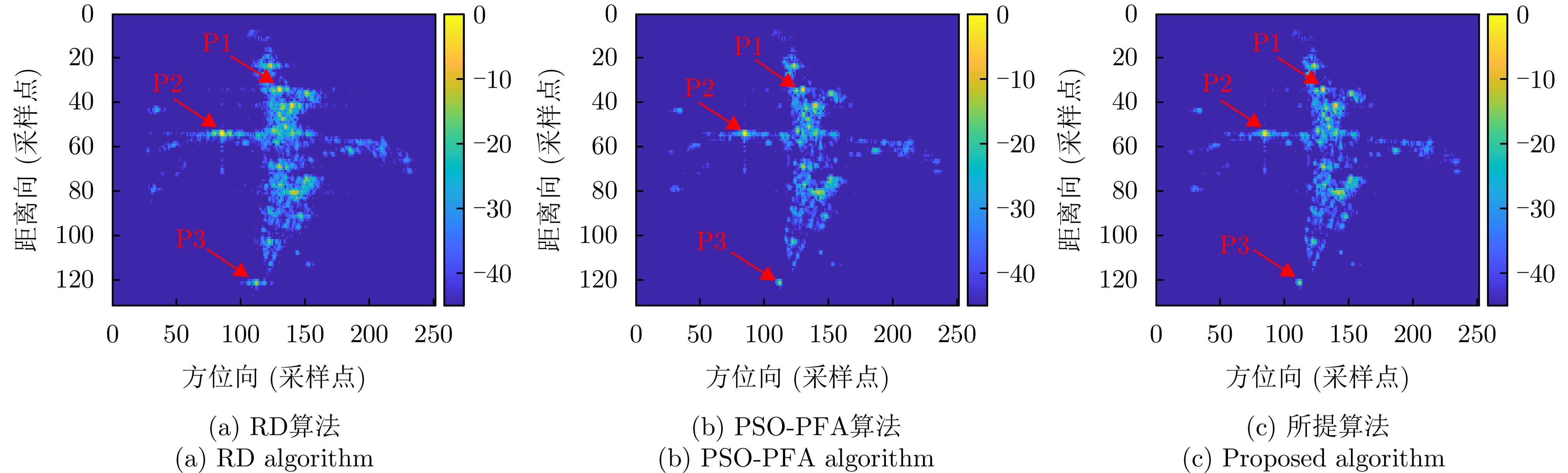
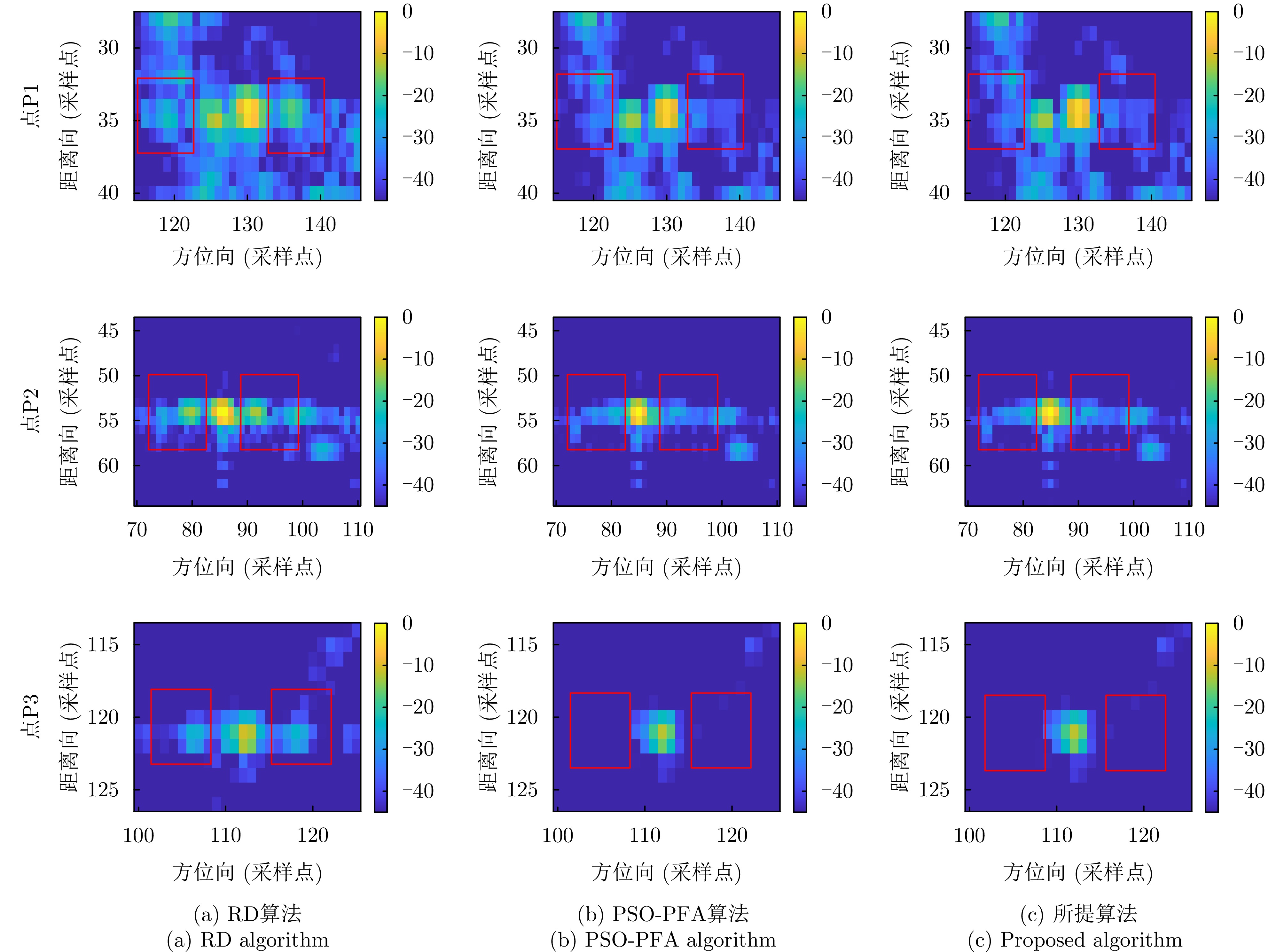
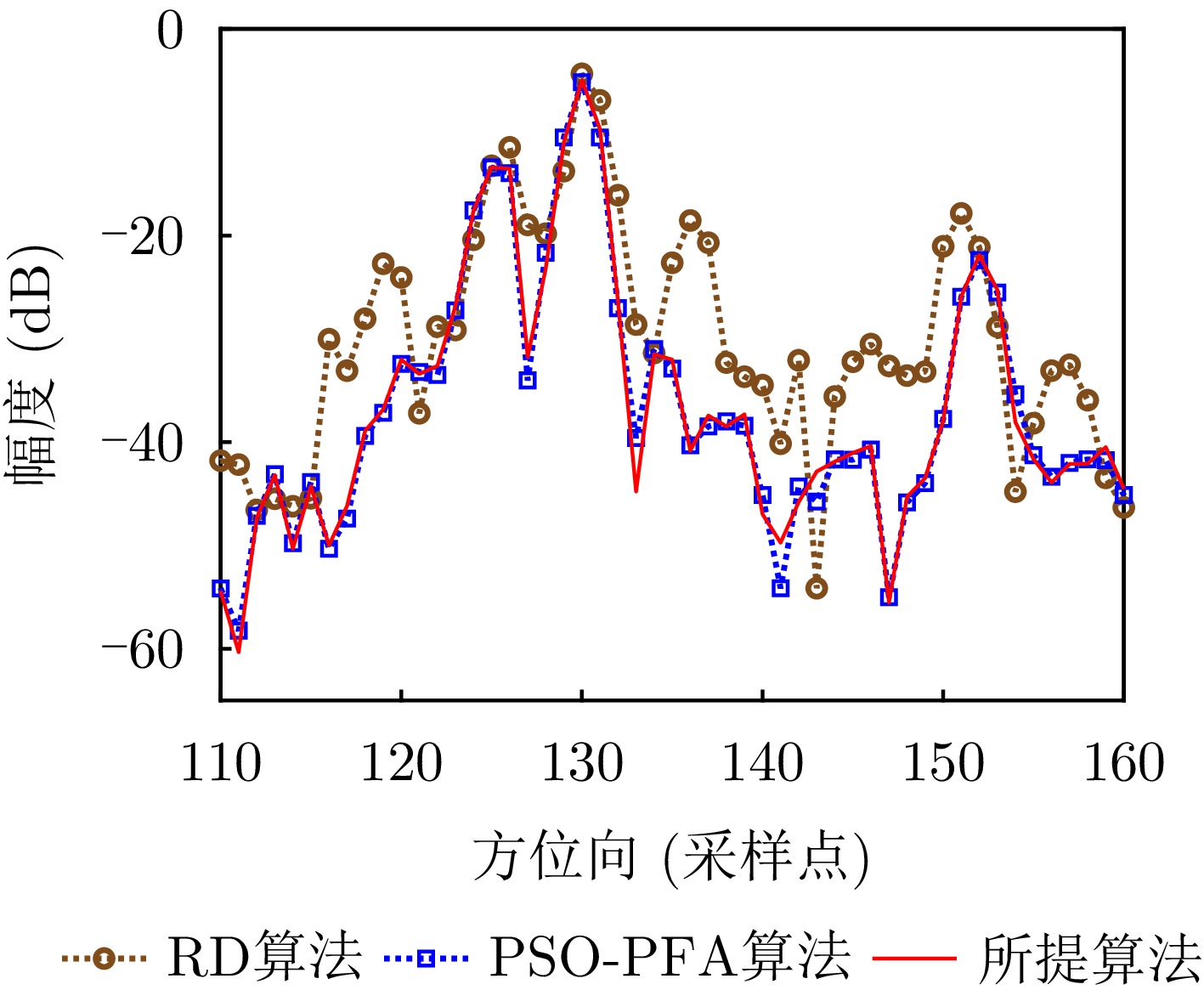
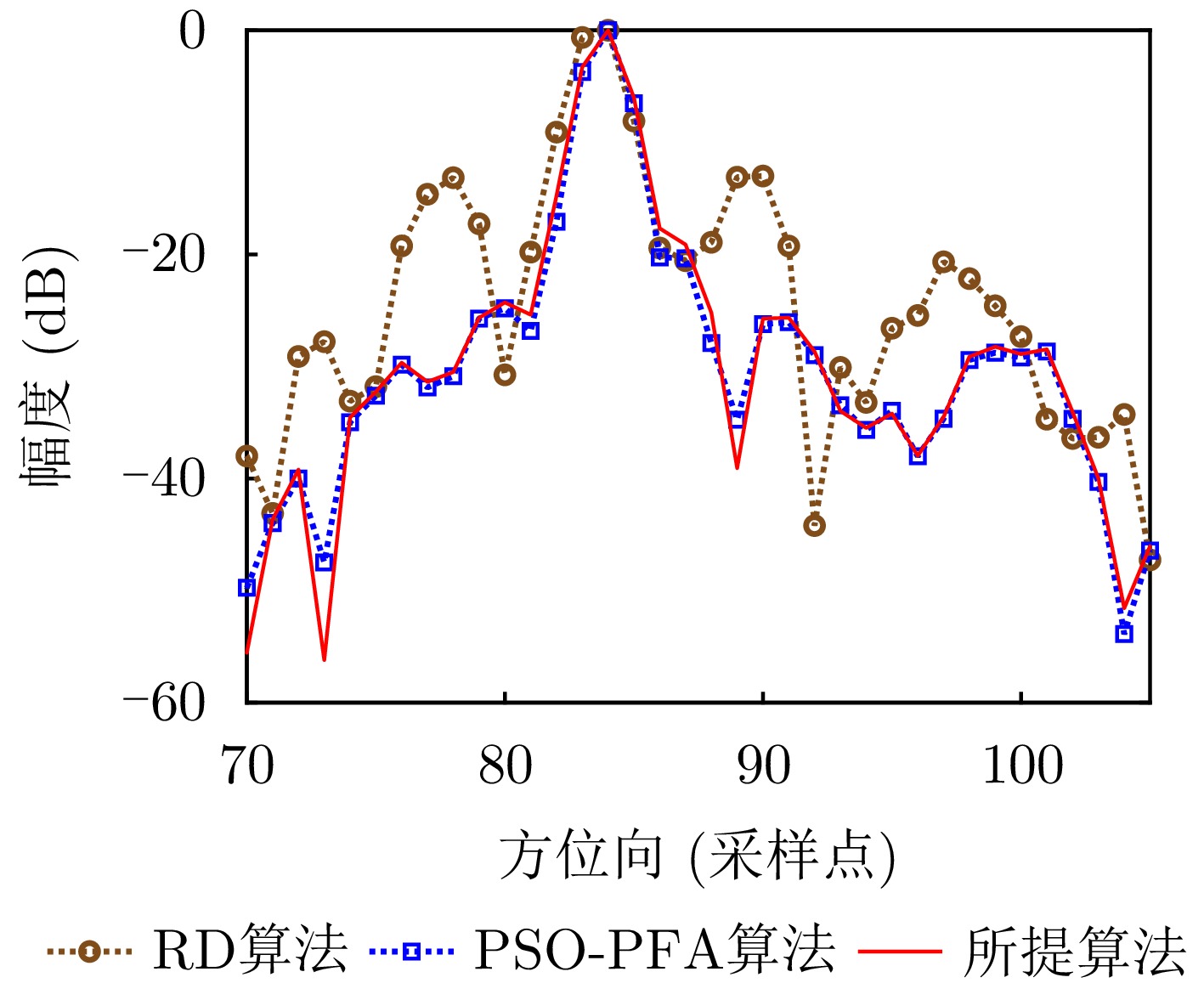
| [1] |
ANGER S, JIROUSEK M, DILL S, et al. High-resolution inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging of satellites in space[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2024, 18(4): 544–563. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12505. |
| [2] |
保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 6–70.
BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Techniques[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 6–70.
|
| [3] |
ANGER S, JIROUSEK M, Dill S, et al. Research on advanced space surveillance using the IoSiS radar system[C]. The 13th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Online, Germany, 2021: 1–4.
|
| [4] |
田彪, 刘洋, 呼鹏江, 等. 宽带逆合成孔径雷达高分辨成像技术综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(5): 765–802. doi: 10.12000/JR20060. TIAN Biao, LIU Yang, HU Pengjiang, et al. Review of high-resolution imaging techniques of wideband inverse synthetic aperture radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(5): 765–802. doi: 10.12000/JR20060. |
| [5] |
田彪, 刘洋, 呼鹏江, 等. 宽带逆合成孔径雷达高分辨成像技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022: 1–18.
TIAN Biao, LIU Yang, HU Pengjiang, et al. High-resolution Imaging Techniques of Wideband Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2022: 1–18.
|
| [6] |
夏靖远, 杨志雄, 周治兴, 等. 一种基于元学习的稀疏孔径ISAR成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 849–859. doi: 10.12000/JR23121. XIA Jingyuan, YANG Zhixiong, ZHOU Zhixing, et al. A metalearning-based sparse aperture ISAR imaging method[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 849–859. doi: 10.12000/JR23121. |
| [7] |
李中余, 桂亮, 海宇, 等. 基于变分模态分解与优选的超高分辨ISAR成像微多普勒抑制方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(4): 852–865. doi: 10.12000/JR24043. LI Zhongyu, GUI Liang, HAI Yu, et al. Ultrahigh-resolution ISAR micro-Doppler suppression methodology based on variational mode decomposition and mode optimization[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(4): 852–865. doi: 10.12000/JR24043. |
| [8] |
XING Mengdao, WU Renbiao, LAN Jinqiao, et al. Migration through resolution cell compensation in ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2004, 1(2): 141–144. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2004.824766. |
| [9] |
KARAMANAVIS V, DIRKS H, FUHRMANN L, et al. Characterization of deorbiting satellites and space debris with radar[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2023, 72(8): 3269–3281. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2023.07.033. |
| [10] |
PERRY R P, DIPIETRO R C, and FANTE R L. SAR imaging of moving targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(1): 188–200. doi: 10.1109/7.745691. |
| [11] |
LIPPS R and KERR D. Polar reformatting for ISAR imaging[C]. 1998 IEEE Radar Conference, RADARCON’98 Challenges in Radar Systems and Solutions, Dallas, USA, 1998: 275–280. doi: 10.1109/NRC.1998.678014. |
| [12] |
HUANG Penghui, LIAO Guisheng, YANG Zhiwei, et al. Ground maneuvering target imaging and high-order motion parameter estimation based on second-order keystone and generalized hough-HAF Transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 320–335. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2606436. |
| [13] |
LI Xiaolong, CUI Guolong, YI Wei, et al. Range migration correction for maneuvering target based on generalized keystone transform[C]. 2015 IEEE Radar Conference, Arlington, USA, 2015: 95–99. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2015.7130977. |
| [14] |
杨利超, 高悦欣, 邢孟道, 等. 基于广义keystone和频率变标的微波光子ISAR高分辨实时成像算法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(2): 215–223. doi: 10.12000/JR18120. YANG Lichao, GAO Yuexin, XING Mengdao, et al. High resolution microwave photonics radar real-time imaging based on generalized keystone and frequency scaling[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(2): 215–223. doi: 10.12000/JR18120. |
| [15] |
LU Guangyue and BAO Zheng. Analysis of the MTRC compensation algorithm in ISAR imaging[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 1999, 26(4): 487–492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.1999.04.022. |
| [16] |
GONG Rui, WANG Ling, and ZHU Daiyin. Three-dimensional high-resolution space-borne ISAR imaging with compact antenna configuration for large rotational angle[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 7422–7435. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3379584. |
| [17] |
WU Xipeng. Motion compensation for W-band radar’s high-resolution ISAR targets[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2021: 43–57. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.001254. |
| [18] |
DU Rongzhen. On-orbit state estimation methods of space targets utilizing multi-view ISAR images[D].[Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2022: 27–44. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2022.003472. |
| [19] |
LIU Yifei, YU Weidong, YANG Shenghui, et al. An effective space-borne ISAR high-resolution imaging approach for satellite on-orbit based on minimum entropy optimization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2024, 17: 4523–4537. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3359264. |
| [20] |
SHAO Shuai, LIU Hongwei, ZHANG Lei, et al. Ultrawideband ISAR imaging of maneuvering targets with joint high-order motion compensation and azimuth scaling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5214621. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3113007. |
| [21] |
WANG Jiadong, LI Yachao, SONG Ming, et al. Noise robust high-speed motion compensation for ISAR imaging based on parametric minimum entropy optimization[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(9): 2178. doi: 10.3390/rs14092178. |
| [22] |
ZHU Daiyin, WANG Ling, TAO Qingnian, et al. ISAR range alignment by minimizing the entropy of the average range profile[C]. 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, USA, 2006: 6. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2006.1631897. |
| [23] |
ZHU Daiyin, WANG Ling, YU Yusheng, et al. Robust ISAR range alignment via minimizing the entropy of the average range profile[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(2): 204–208. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2010562. |
| [24] |
WAHL D E, EICHEL P H, GHIGLIA D C, et al. Phase gradient autofocus-a robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1994, 30(3): 827–835. doi: 10.1109/7.303752. |
| [25] |
LI Xi, LIU Guosui, and NI Jinlin. Autofocusing of ISAR images based on entropy minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(4): 1240–1252. doi: 10.1109/7.805442. |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
LI Yuanyuan, FU Yaowen, and ZHANG Wenpeng. Distributed ISAR subimage fusion of nonuniform rotating target based on matching fourier transform[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(6): 1806. doi: 10.3390/s18061806. |
| [28] |
RONG Jiajia, WANG Yong, and HAN Tao. Iterative optimization-based ISAR imaging with sparse aperture and its application in interferometric ISAR imaging[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(19): 8681–8693. doi: 10.1109/jsen.2019.2923447. |
| [29] |
CHEN Chen, XU Zhiyong, and TIAN Sirui. An efficient sparse aperture ISAR imaging framework for maneuvering targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2024, 72(2): 1873–1886. doi: 10.1109/tap.2023.3344877. |
| [30] |
XU Gang, XING Mengdao, XIA Xianggen, et al. High-resolution inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging and scaling with sparse aperture[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(8): 4010–4027. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2015.2439266. |
| [31] |
刘浩洋, 户将, 李勇锋, 等. 最优化: 建模、算法与理论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2020: 254–262.
LIU Haoyang, HU Jiang, LI Yongfeng, et al. Optimization: Modeling, Algorithm and Theory[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2020: 254–262.
|
| [32] |
LI Ruoming, LI Wangzhe, DING Manlai, et al. Demonstration of a microwave photonic synthetic aperture radar based on photonic-assisted signal generation and stretch processing[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(13): 14334–14340. doi: 10.1364/oe.25.014334. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: