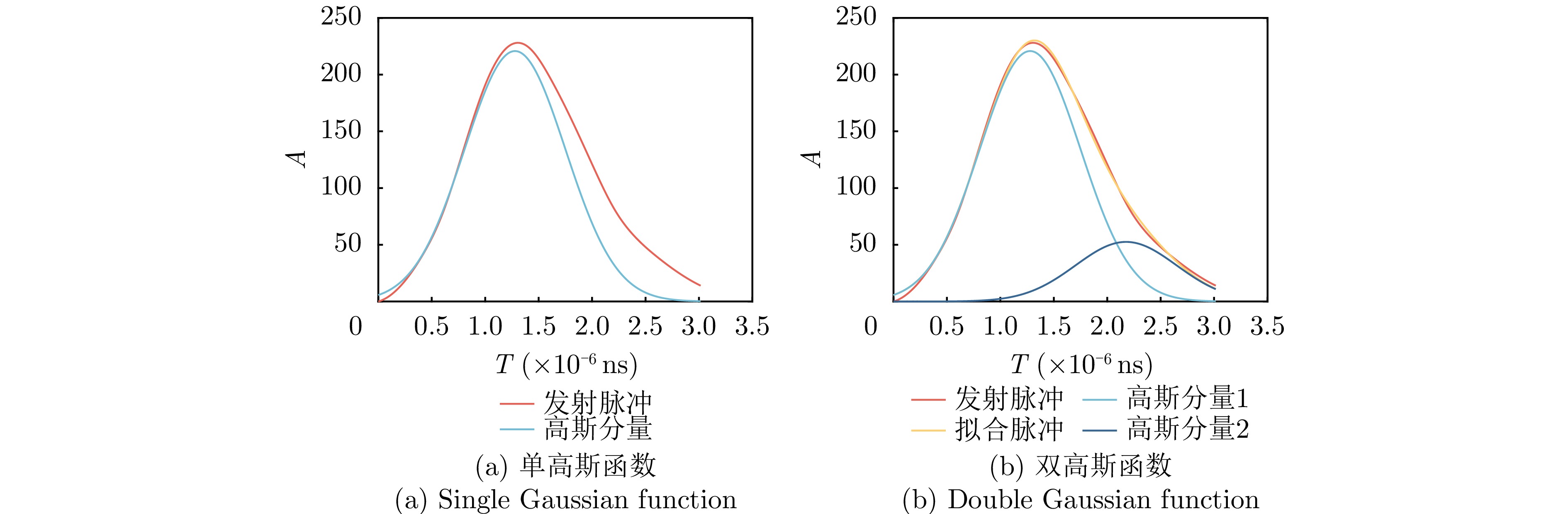
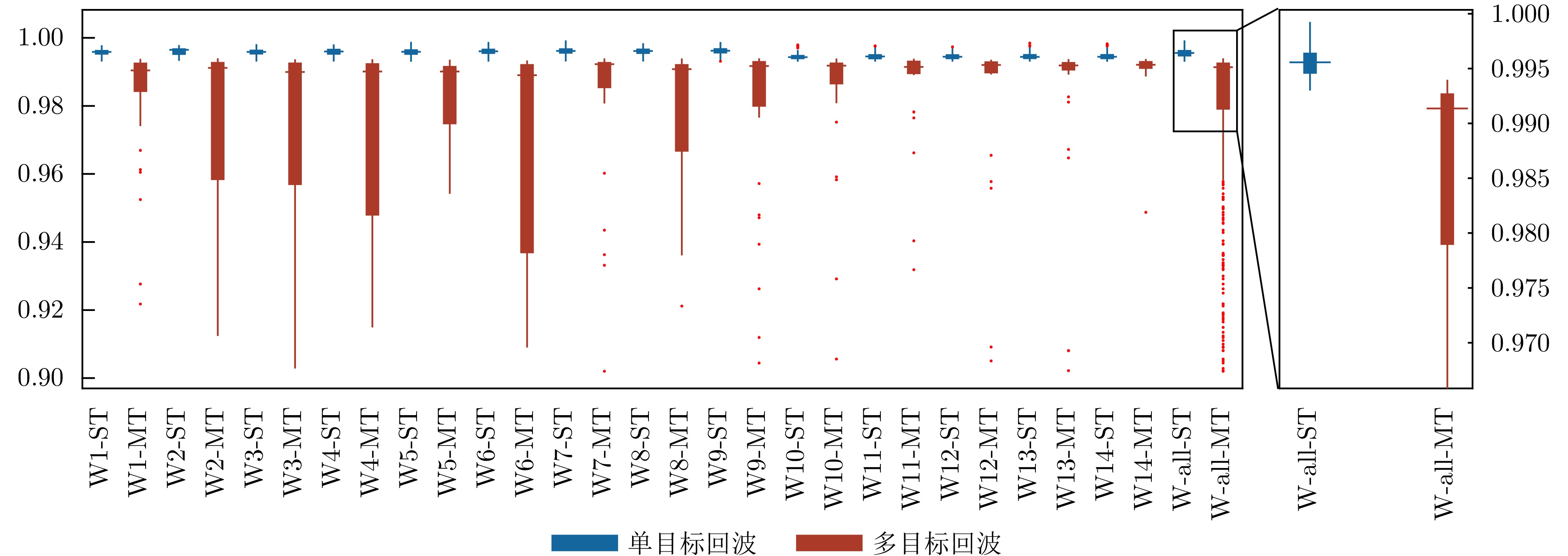
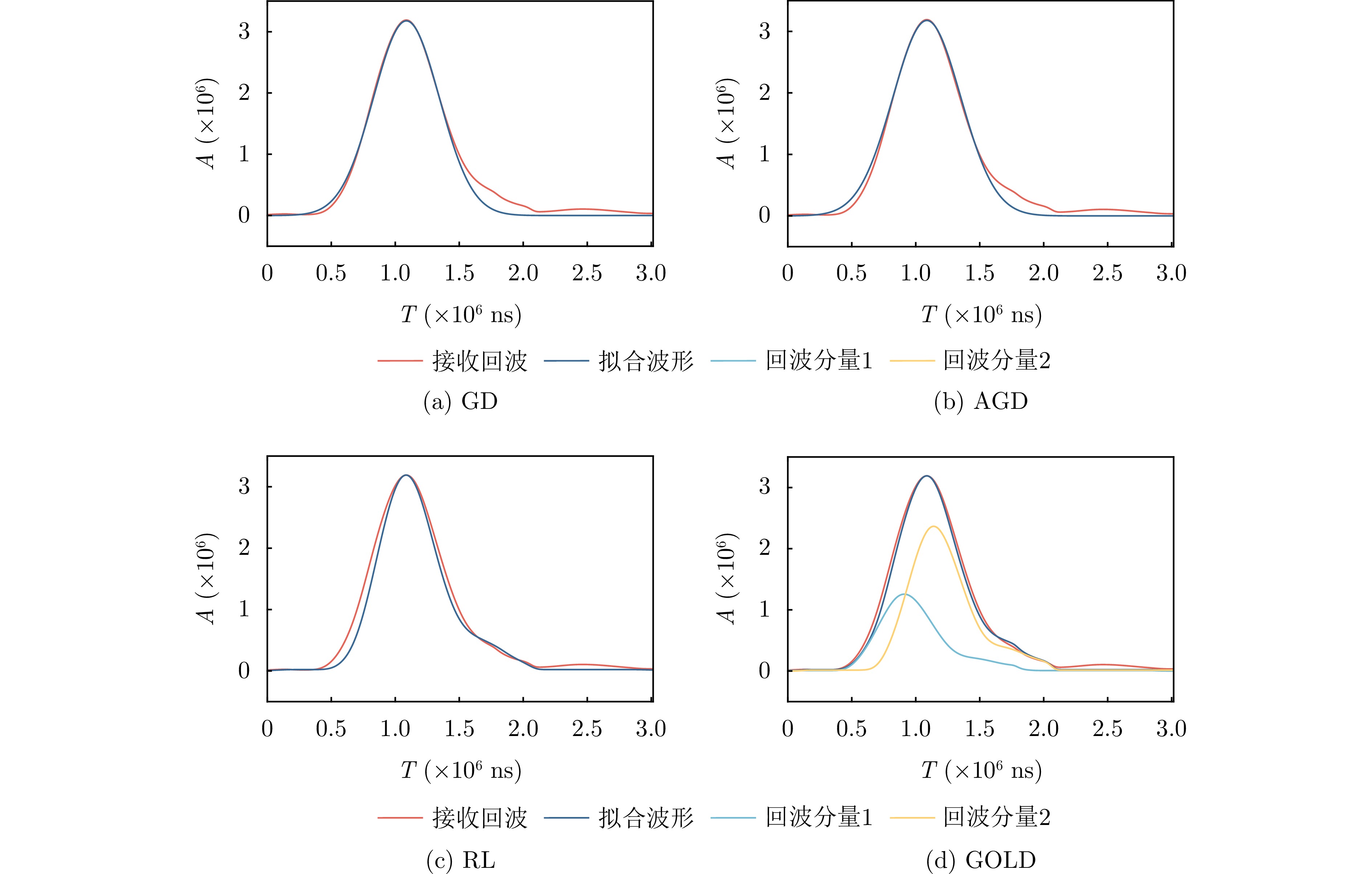
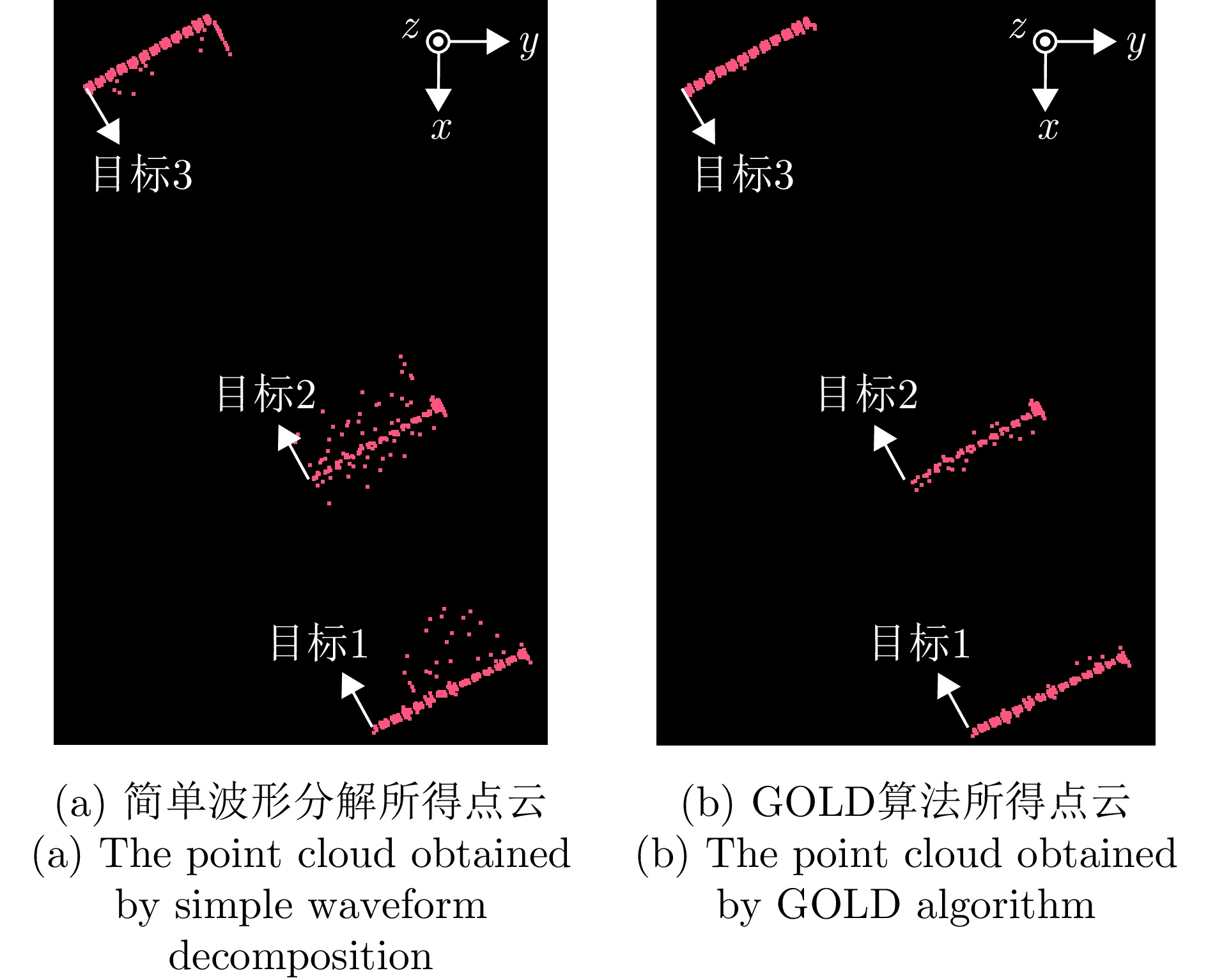
| [1] |
GOETZ A F H. Imaging spectrometry for remote sensing: Vision to reality in 15 years[C]. The SPIE 2480, Imaging Spectrometry, Orlando, FL, United States, 1995: 2–13. doi: 10.1117/12.210867. |
| [2] |
WEHR A and LOHR U. Airborne laser scanning—an introduction and overview[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 1999, 54(2): 68–82. doi: 10.1016/S0924-2716(99)00011-8. |
| [3] |
YOU R J and LIN B C. A quality prediction method for building model reconstruction using LiDAR data and topographic maps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(9): 3471–3480. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2128326. |
| [4] |
GONZALEZ-AGUILERA D, CRESPO-MATELLAN E, HERNANDEZ-LOPEZ D, et al. Automated urban analysis based on LiDAR-derived building models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 51(3): 1844–1851. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2205931. |
| [5] |
GUAN Hongcan, SU Yanjun, HU Tianyu, et al. A novel framework to automatically fuse multiplatform LiDAR data in forest environments based on tree locations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(3): 2165–2177. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2953654. |
| [6] |
JI Xue, YANG Bisheng, WANG Yuan, et al. Full-waveform classification and segmentation-based signal detection of single-wavelength bathymetric LiDAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1–14. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3198168. |
| [7] |
GROLLIUS S, LIGGES M, RUSKOWSKI J, et al. Concept of an automotive LiDAR target simulator for direct time-of-flight LiDAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2023, 8(1): 825–835. doi: 10.1109/TIV.2021.3128808. |
| [8] |
MALLET C and BRETAR F. Full-waveform topographic LiDAR: State-of-the-art[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2009, 64(1): 1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2008.09.007. |
| [9] |
SHEN Jun, SHANG Jianhua, and HE Yan . Research process of data processing technology of full-waveform airborne laser radars[J]. Laser Technology, 2018, 42(3): 295–299. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2018.03.002. |
| [10] |
ZHANG Zhengnan, CAO Lin, LIU Hao, et al. Assessing the 3-D structure of bamboo forests using an advanced pseudo-vertical waveform approach based on airborne full-waveform LiDAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(12): 10647–10670. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3042790. |
| [11] |
GAO Shuai, NIU Zheng, SUN Gang, et al. Height extraction of maize using airborne full-waveform LIDAR data and a deconvolution algorithm[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(9): 1978–1982. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2441655. |
| [12] |
YANG Fanlin, CHAO Qi, SU Dianpeng, et al. An airborne LiDAR bathymetric waveform decomposition method in very shallow water: A case study around Yuanzhi Island in the South China Sea[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2022, 109: 102788. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2022.102788. |
| [13] |
RiUNITE[OL]. http://www.riegl.com/products/software-packages/riunite/.
|
| [14] |
WANG Zining, XU Lijun, LI Duan, et al. Online multi-target laser ranging using waveform decomposition on FPGA[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(9): 10879–10889. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3060158. |
| [15] |
LIU Gangping and KE Jun. End-to-end full-waveform echo decomposition based on self-attention classification and U-Net decomposition[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 7978–7987. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3203130. |
| [16] |
WANG Cheng, YANG Xuebo, XI Xiaohuan, et al. Introduction to LiDAR Remote Sensing[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2024: 26–29. doi: 10.1201/9781032671512. |
| [17] |
MOUNTRAKIS G and LI Yuguang. A linearly approximated iterative Gaussian decomposition method for waveform LiDAR processing[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2017, 129: 200–211. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.05.009. |
| [18] |
ZHOU Guoqing, LONG Shuhua, XU Jiasheng, et al. Comparison analysis of five waveform decomposition algorithms for the airborne LiDAR echo signal[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 7869–7880. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3096197. |
| [19] |
ZHOU Guoqing, DENG Ronghua, ZHOU Xiang, et al. Gaussian inflection point selection for LiDAR hidden echo signal decomposition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3107438. |
| [20] |
ZHOU Tan, POPESCU S C, KRAUSE K, et al. Gold—A novel deconvolution algorithm with optimization for waveform LiDAR processing[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2017, 129: 131–150. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.04.021. |
| [21] |
LIU Chang, XU Lijun, SI Lin, et al. A robust deconvolution method of airborne LiDAR waveforms for dense point clouds generation in forest[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1–14. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3061166. |
| [22] |
XIAO Zhen, GU Yanfeng, LI Xian, et al. Application of landweber with optimization for small footprint waveform lidar decomposition[C]. IGARSS 2024 - 2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 2024: 6408–6411. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS53475.2024.10640890. |
| [23] |
WANG Binhui, SONG Shalei, SHI Shuo, et al. Multichannel interconnection decomposition for hyperspectral LiDAR waveforms detected from over 500 m[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5515714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3108160. |
| [24] |
SONG Shalei, WANG Binhui, GONG Wei, et al. A new waveform decomposition method for multispectral LiDAR[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2019, 149: 40–49. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.01.014. |
| [25] |
BAI Jie, NIU Zheng, BI Kaiyi, et al. Toward an advanced method for full-waveform hyperspectral LiDAR data processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5702516. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3382481. |
| [26] |
BAI Jie, NIU Zheng, HUANG Yanru, et al. Full-waveform hyperspectral LiDAR data decomposition via ranking central locations of natural target echoes (Rclonte) at different wavelengths[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2024, 310: 114227. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2024.114227. |
| [27] |
XIA Yuhao, XU Shilong, SHAO Hui, et al. Range resolution enhanced method with spectral properties for hyperspectral LiDAR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5703517. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3301896. |
| [28] |
XU Fan, LI Fenfang, and WANG Yuanqing. Modified levenberg-marquardt-based optimization method for LiDAR waveform decomposition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(4): 530–534. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2522387. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: