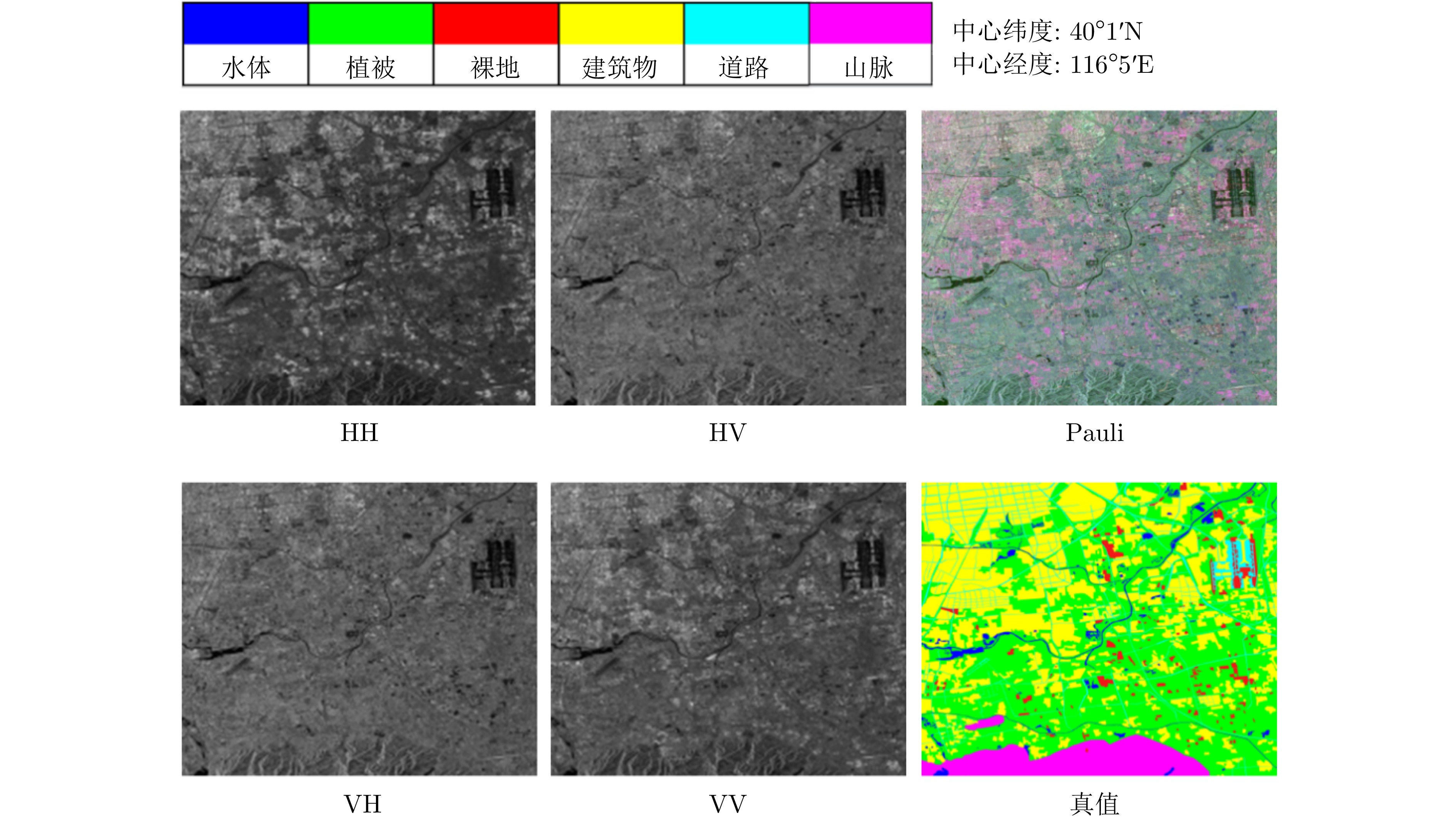
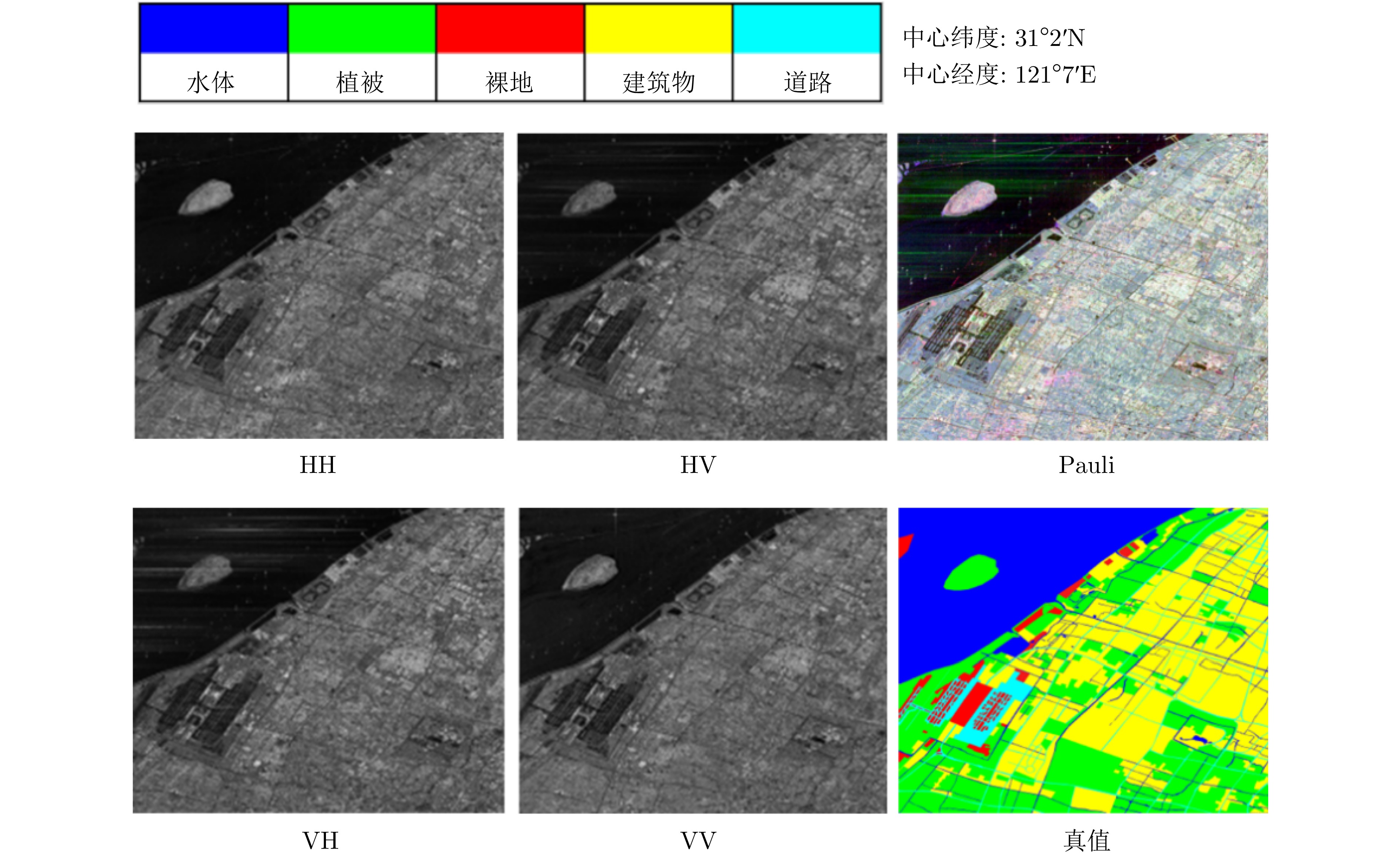
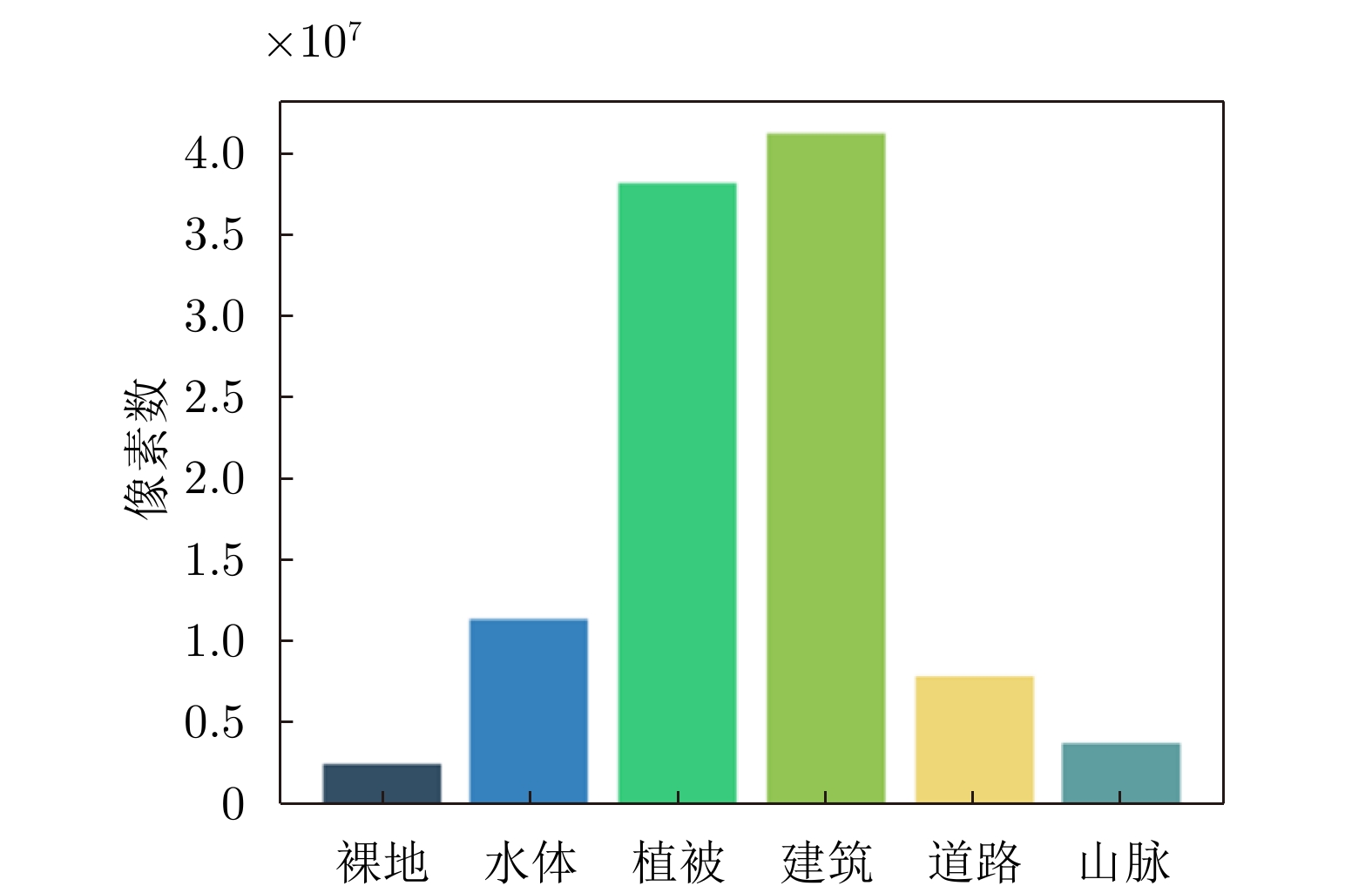
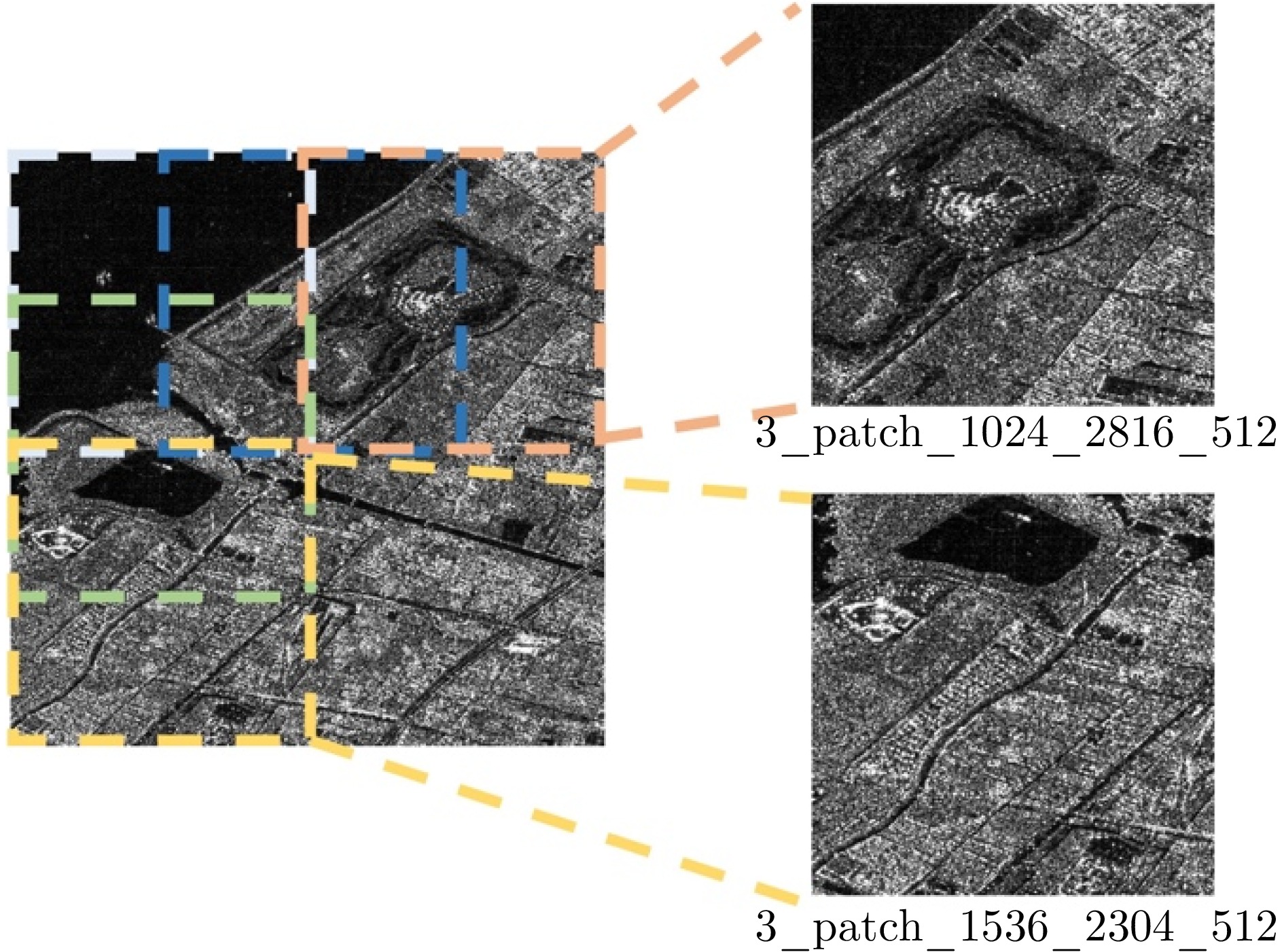
| [1] |
JACKSON C R and APEL J R. Synthetic Aperture Radar Marine User’s Manual[M]. Washington: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, 2004.
|
| [2] |
FU Kun, FU Jiamei, WANG Zhirui, et al. Scattering-keypoint-guided network for oriented ship detection in high-resolution and large-scale SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 11162–11178. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3109469. |
| [3] |
LEE J S and POTTIER E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2017: 1–10. doi: 10.1201/9781420054989. |
| [4] |
LIU Xu, JIAO Licheng, TANG Xu, et al. Polarimetric convolutional network for PolSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(5): 3040–3054. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2879984. |
| [5] |
PARIKH H, PATEL S, and PATEL V. Classification of SAR and PolSAR images using deep learning: A review[J]. International Journal of Image and Data Fusion, 2020, 11(1): 1–32. doi: 10.1080/19479832.2019.1655489. |
| [6] |
BI Haixia, SUN Jian, and XU Zongben. A graph-based semisupervised deep learning model for PolSAR image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(4): 2116–2132. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2871504. |
| [7] |
CHEN Siwei and TAO Chensong. PolSAR image classification using polarimetric-feature-driven deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(4): 627–631. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2799877. |
| [8] |
刘涛, 杨子渊, 蒋燕妮, 等. 极化SAR图像舰船目标检测研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR20155. LIU Tao, YANG Ziyuan, JIANG Yanni, et al. Review of ship detection in polarimetric synthetic aperture imagery[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 1–19. doi: 10.12000/JR20155. |
| [9] |
WU Wenjin, LI Hailei, LI Xinwu, et al. PolSAR image semantic segmentation based on deep transfer learning—realizing smooth classification with small training sets[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(6): 977–981. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2886559. |
| [10] |
XIAO Daifeng, WANG Zhirui, WU Youming, et al. Terrain segmentation in polarimetric SAR images using dual-attention fusion network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4006005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3038240. |
| [11] |
FREEMAN A and DURDEN S L. A three-component scattering model for polarimetric SAR data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1998, 36(3): 963–973. doi: 10.1109/36.673687. |
| [12] |
肖东凌, 刘畅. 基于精调的膨胀编组-交叉CNN的PolSAR地物分类[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(4): 479–489. doi: 10.12000/JR19039. XIAO Dongling and LIU Chang. PolSAR terrain classification based on fine-tuned dilated group-cross convolution neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(4): 479–489. doi: 10.12000/JR19039. |
| [13] |
秦先祥, 余旺盛, 王鹏, 等. 基于复值卷积神经网络样本精选的极化SAR图像弱监督分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 525–538. doi: 10.12000/JR20062. QIN Xianxiang, YU Wangsheng, WANG Peng, et al. Weakly supervised classification of PolSAR images based on sample refinement with complex-valued convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 525–538. doi: 10.12000/JR20062. |
| [14] |
邹焕新, 李美霖, 马倩, 等. 一种基于张量积扩散的非监督极化SAR图像地物分类方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(4): 436–447. doi: 10.12000/JR19057. ZOU Huanxin, LI Meilin, MA Qian, et al. An unsupervised PolSAR image classification algorithm based on tensor product graph diffusion[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(4): 436–447. doi: 10.12000/JR19057. |
| [15] |
FANG Zheng, ZHANG Gong, DAI Qijun, et al. Hybrid attention-based encoder-decoder fully convolutional network for PolSAR image classification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(2): 526. doi: 10.3390/rs15020526. |
| [16] |
ZHANG Mengxuan, SHI Jingyuan, LIU Long, et al. Evolutionary complex-valued CNN for PolSAR image classification[C]. 2024 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Yokohama, Japan, 2024: 1–8. doi: 10.1109/IJCNN60899.2024.10650936. |
| [17] |
SUN Xian, WANG Peijin, YAN Zhiyuan, et al. FAIR1M: A benchmark dataset for fine-grained object recognition in high-resolution remote sensing imagery[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2022, 184: 116–130. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2021.12.004. |
| [18] |
ZAMIR W S, ARORA A, GUPTA A, et al. iSAID: A large-scale dataset for instance segmentation in aerial images[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 28–37.
|
| [19] |
YANG Yi and NEWSAM S. Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification[C]. The 18th SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, San Jose, USA, 2010: 270–279. doi: 10.1145/1869790.1869829. |
| [20] |
ROTTENSTEINER F, SOHN G, GERKE M, et al. ISPRS semantic labeling contest[C]. Photogrammetric Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 5–7.
|
| [21] |
CHENG Gong, HAN Junwei, and LU Xiaoqiang. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2017, 105(10): 1865–1883. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2017.2675998. |
| [22] |
SHENG Guofeng, YANG Wen, XU Tao, et al. High-resolution satellite scene classification using a sparse coding based multiple feature combination[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2012, 33(8): 2395–2412. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2011.608740. |
| [23] |
LIU Xu, JIAO Licheng, LIU Fang, et al. PolSF: PolSAR image datasets on San Francisco[C]. The 5th IFIP TC 12 International Conference on Intelligence Science, Xi’an, China, 2022: 214–219. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-14903-0_23. |
| [24] |
WANG Zhirui, ZENG Xuan, YAN Zhiyuan, et al. AIR-PolSAR-Seg: A large-scale data set for terrain segmentation in complex-scene PolSAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2022, 15: 3830–3841. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3170326. |
| [25] |
HOCHSTUHL S, PFEFFER N, THIELE A, et al. Pol-InSAR-island—a benchmark dataset for multi-frequency pol-InSAR data land cover classification[J]. ISPRS Open Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2023, 10: 100047. doi: 10.1016/j.ophoto.2023.100047. |
| [26] |
WEST R D, HENRIKSEN A, STEINBACH E, et al. High-resolution fully-polarimetric synthetic aperture radar dataset[J]. Discover Geoscience, 2024, 2(1): 83. doi: 10.1007/s44288-024-00090-6. |
| [27] |
LONG J, SHELHAMER E, and DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3431–3440. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298965. |
| [28] |
ZHAO Hengshuang, SHI Jianping, QI Xiaojuan, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6230–6239. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.660. |
| [29] |
CHEN L C, ZHU Yukun, PAPANDREOU G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 833–851. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_49. |
| [30] |
KIRILLOV A, WU Yuxin, HE Kaiming, et al. PointRend: Image segmentation as rendering[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 9796–9805. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00982. |
| [31] |
FU Jun, LIU Jing, TIAN Haijie, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3141–3149. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00326. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: