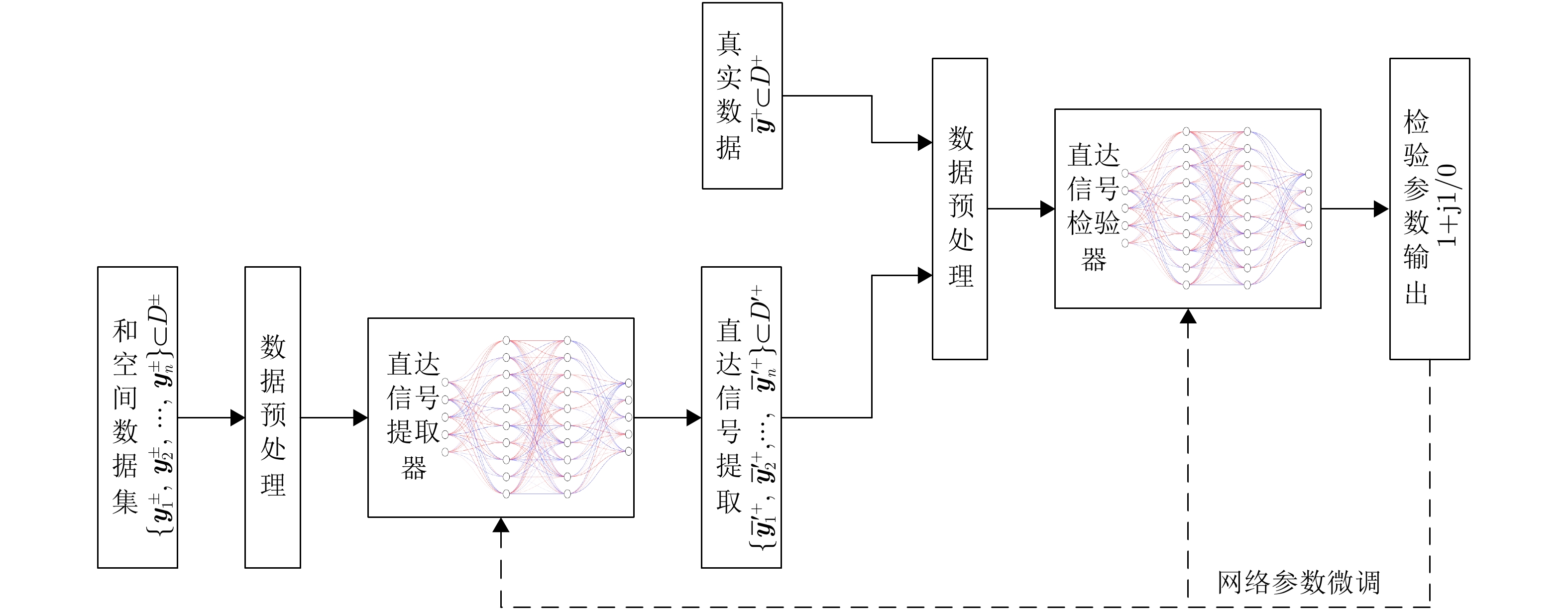
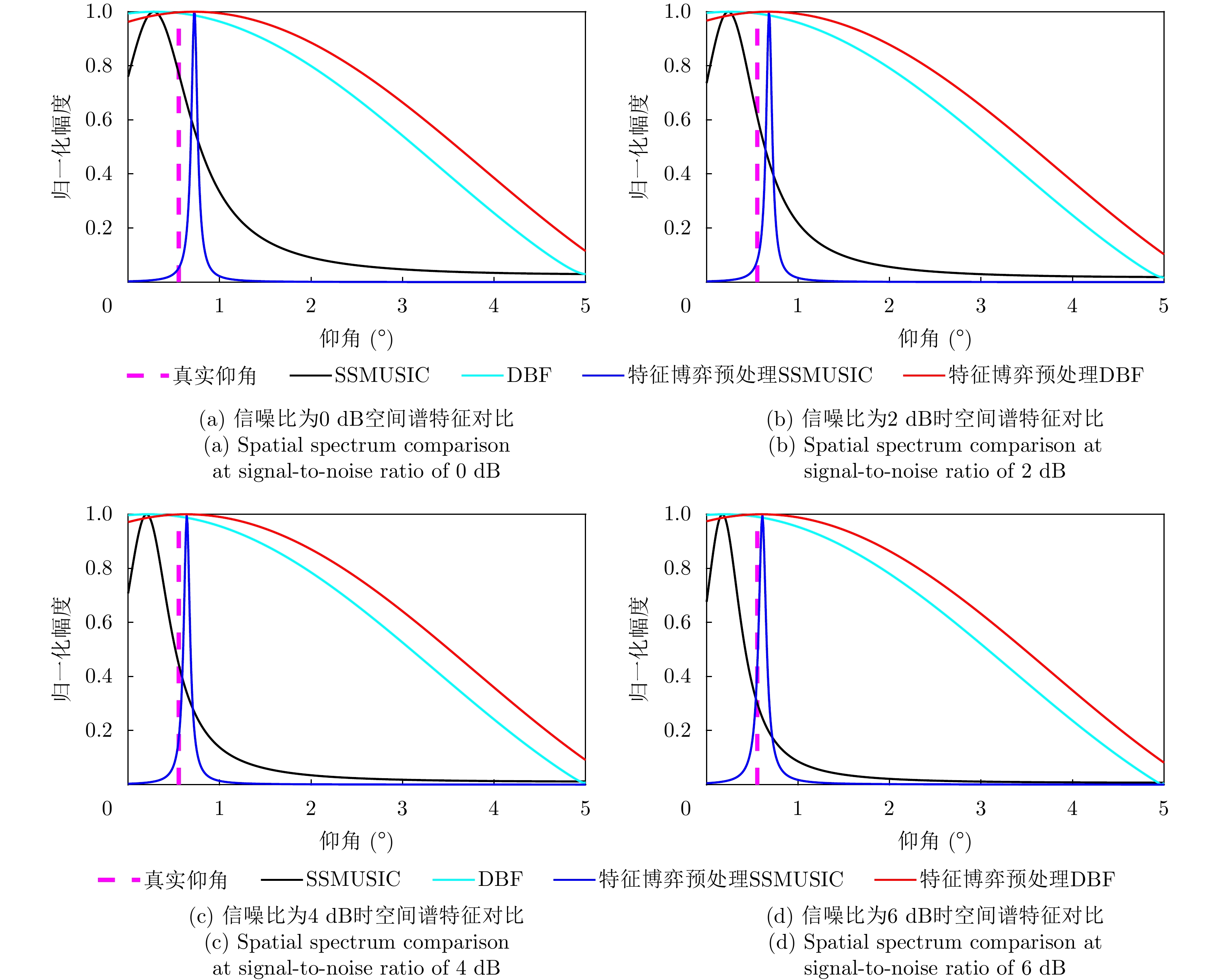
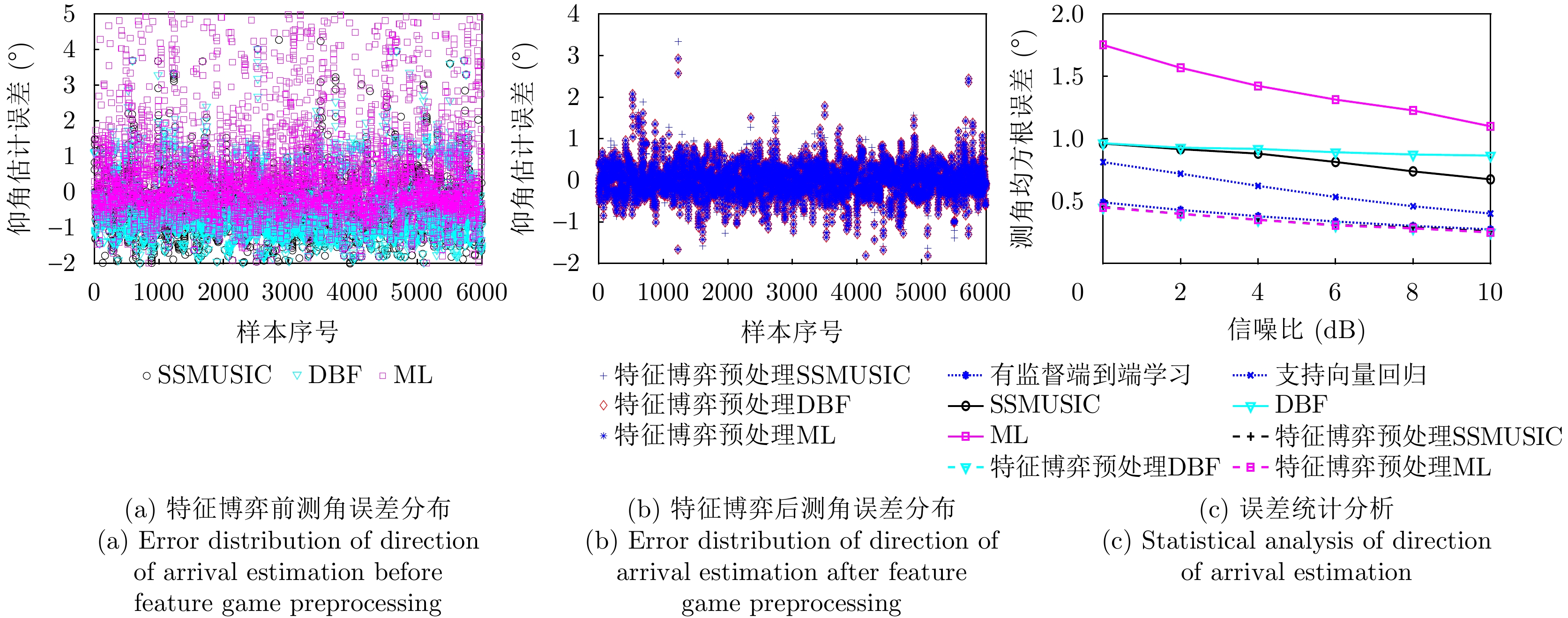
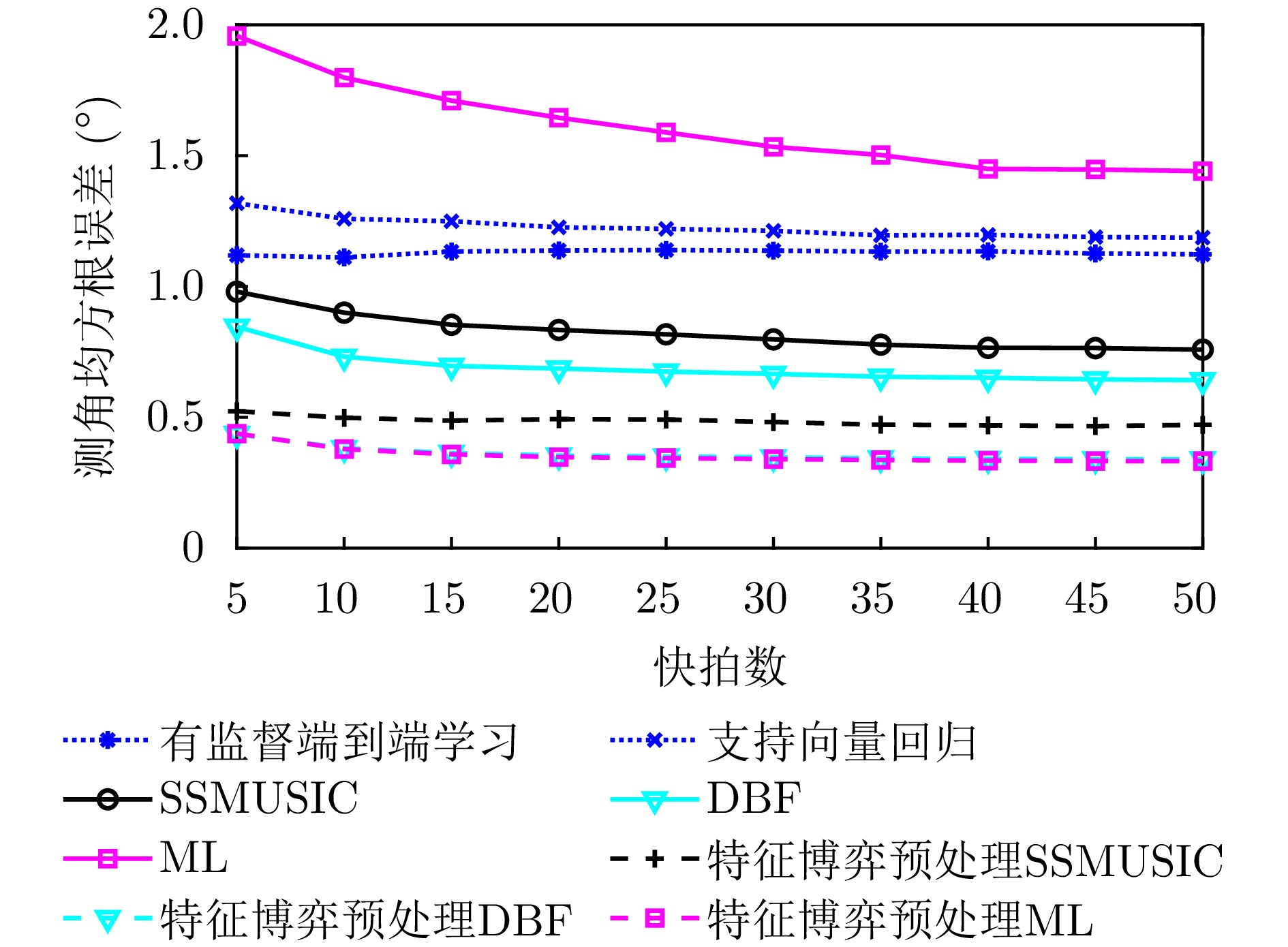
| [1] |
吴剑旗. 先进米波雷达[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2015: 294.
WU Jianqi. Advanced Metric Wave Radar[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2015: 294.
|
| [2] |
WU Jianqi, ZHU Wei, and CHEN Baixiao. Compressed sensing techniques for altitude estimation in multipath conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(3): 1891–1900. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.130841. |
| [3] |
WANG Hongzhen, ZHENG Guimei, CHEN Chen, et al. Analysis and prospect of low elevation estimation technology for meter wave radar[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2023, 48(11): 6–16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2023.11.002. |
| [4] |
ZHENG Yisong and CHEN Baixiao. Multipath model and inversion method for low-angle target in very high frequency radar[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38(6): 1468–1474. doi: 10.11999/JEIT151013. |
| [5] |
SCHMIDT R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(3): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143830. |
| [6] |
ROY R and KAILATH T. ESPRIT-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1989, 37(7): 984–995. doi: 10.1109/29.32276. |
| [7] |
ZISKIND I and WAX M. Maximum likelihood localization of diversely polarized sources by simulated annealing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1990, 38(7): 1111–1114. doi: 10.1109/8.55625. |
| [8] |
LE JEUNE D, JARRY P, SALAUN A, et al. Performance evaluation of Marple modified FBLP and MINNORM methods for angle of arrival estimation using real multipath active sonar data[C]. The Fifth ASSP Workshop on Spectrum Estimation and Modeling, Rochester, USA, 1990: 352–356. doi: 10.1109/SPECT.1990.205606. |
| [9] |
PAN Jingjing, SUN Meng, WANG Yide, et al. Simplified spatial smoothing for DOA estimation of coherent signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2023, 70(2): 841–845. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2022.3214321. |
| [10] |
ZISKIND I and WAX M. Maximum likelihood localization of multiple sources by alternating projection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1988, 36(10): 1553–1560. doi: 10.1109/29.7543. |
| [11] |
XIANG Houhong. Study on super-resolution DOA estimation methods based on deep learning for VHF radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2021. doi: 10.27389/d.cnki.gxadu.2021.000059. |
| [12] |
李存勖. 米波雷达低仰角测高相关问题研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2018.
LI Cunxu. Study on some issues of altitude measurement of low-angle target for VHF array radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2018.
|
| [13] |
朱伟. 米波数字阵列雷达低仰角测高方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2013.
ZHU Wei. Study on low-angle altitude measurement in VHF radar[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2013.
|
| [14] |
李妙歌, 陈渤, 王东升, 等. 面向SAR图像目标分类的CNN模型可视化方法[J]. 雷达学报(中英文), 2024, 13(2): 359–373. doi: 10.12000/JR23107. LI Miaoge, CHEN Bo, WANG Dongsheng, et al. CNN model visualization method for SAR image target classification[J]. Journal of Radars, 2024, 13(2): 359–373. doi: 10.12000/JR23107. |
| [15] |
张群, 胡健, 罗迎, 等. 微动目标雷达特征提取、成像与识别研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049. ZHANG Qun, HU Jian, LUO Ying, et al. Research progresses in radar feature extraction, imaging, and recognition of target with micro-motions[J]. Journal of Radars, 2018, 7(5): 531–547. doi: 10.12000/JR18049. |
| [16] |
牟效乾, 陈小龙, 关键, 等. 基于INet的雷达图像杂波抑制和目标检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 640–653. doi: 10.12000/JR20090. MOU Xiaoqian, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Clutter suppression and marine target detection for radar images based on INet[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 640–653. doi: 10.12000/JR20090. |
| [17] |
XU Xiaoxuan and HUANG Qinghua. MD-DOA: A model-based deep learning DOA estimation architecture[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(12): 20240–20253. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3396337. |
| [18] |
LABBAF N, DALILI OSKOUEI H R, and ABEDI M R. Robust DOA estimation in a uniform circular array antenna with errors and unknown parameters using deep learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2023, 7(4): 2143–2152. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2023.3294448. |
| [19] |
YU Jiarun and WANG Yafeng. Deep learning-based multipath DoAs estimation method for mmWave massive MIMO systems in low SNR[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 72(6): 7480–7490. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3239402. |
| [20] |
LIU Zhangmeng, ZHANG Chenwei, and YU P S. Direction-of-arrival estimation based on deep neural networks with robustness to array imperfections[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2018, 66(12): 7315–7327. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2874430. |
| [21] |
WU Liuli and HUANG Zhitao. Coherent SVR learning for wideband direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(4): 642–646. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2901641. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: