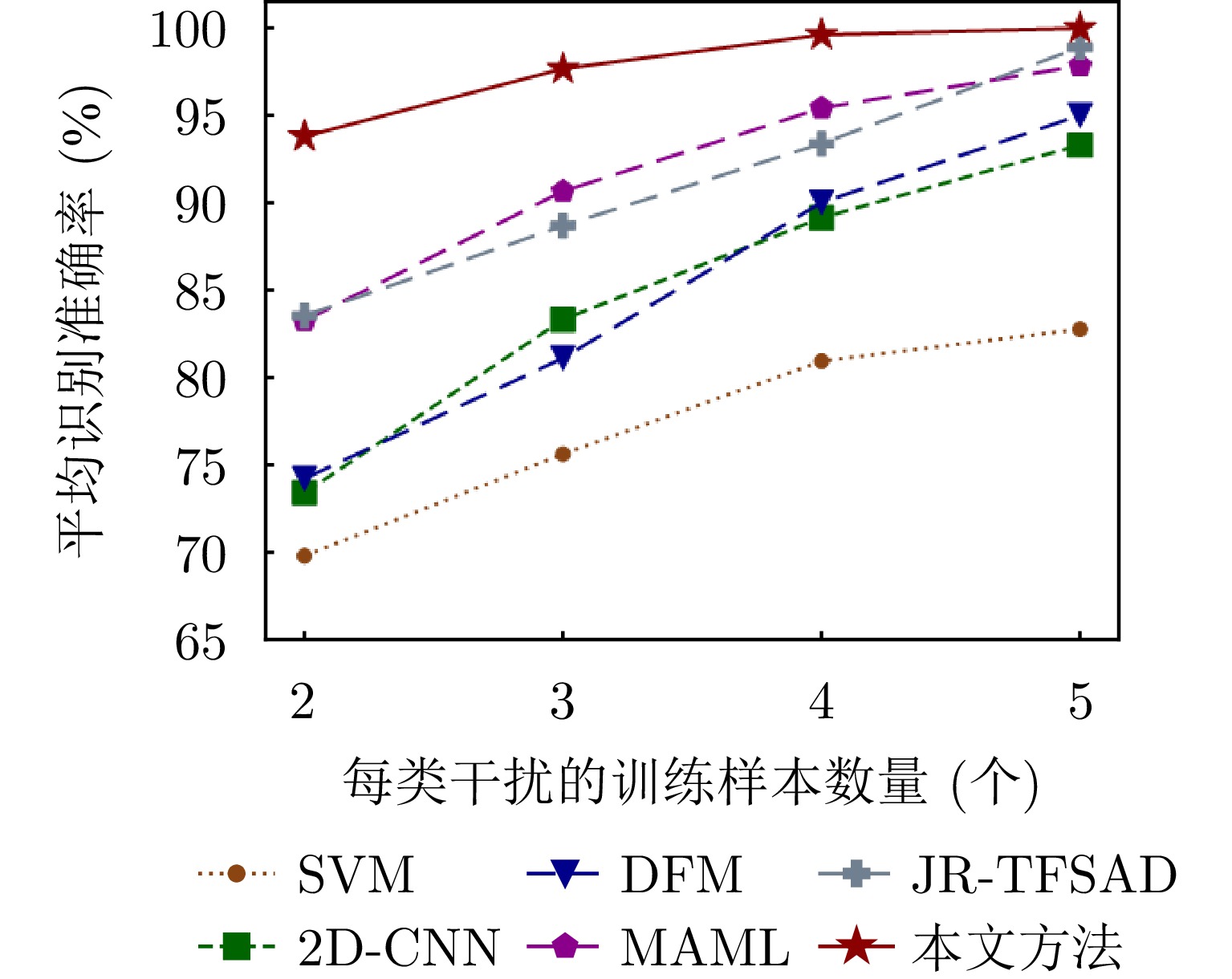
| [1] |
崔国龙, 余显祥, 魏文强, 等. 认知智能雷达抗干扰技术综述与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191. CUI Guolong, YU Xianxiang, WEI Wenqiang, et al. An overview of antijamming methods and future works on cognitive intelligent radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(6): 974–1002. doi: 10.12000/JR22191. |
| [2] |
解烽, 刘环宇, 胡锡坤, 等. 基于复数域深度强化学习的多干扰场景雷达抗干扰方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(6): 1290–1304. doi: 10.12000/JR23139. XIE Feng, LIU Huanyu, HU Xikun, et al. A radar anti-jamming method under multi-jamming scenarios based on deep reinforcement learning in complex domains[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(6): 1290–1304. doi: 10.12000/JR23139. |
| [3] |
ZHOU Hongping, WANG Ziwei, and GUO Zhongyi. Overview on recognition algorithms of radar active jamming[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2022, 37(1): 1–20. doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2022.01.001. |
| [4] |
LV Qinzhe, FAN Hanxin, LIU Junliang, et al. Multilabel deep learning-based lightweight radar compound jamming recognition method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 2521115. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2024.3400337. |
| [5] |
CAO Ru, CAO Jiuwen, MEI Jianping, et al. Radar emitter identification with bispectrum and hierarchical extreme learning machine[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2019, 78(20): 28953–28970. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-6134-y. |
| [6] |
QU Qizhe, WANG Yongliang, LIU Weijian, et al. IRNet: Interference recognition networks for automotive radars via autocorrelation features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2022, 70(5): 2762–2774. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2022.3151635. |
| [7] |
WU Zhenhua, QIAN Jun, ZHANG Man, et al. High-confidence sample augmentation based on label-guided denoising diffusion probabilistic model for active deception jamming recognition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 3508305. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2023.3316282. |
| [8] |
ZOU Wenxu, XIE Kai, and LIN Jinjian. Light-weight deep learning method for active jamming recognition based on improved MobileViT[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2023, 17(8): 1299–1311. doi: 10.1049/rsn2.12420. |
| [9] |
LV Qinzhe, QUAN Yinghui, FENG Wei, et al. Radar deception jamming recognition based on weighted ensemble CNN with transfer learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5107511. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3129645. |
| [10] |
LUO Zhenyu, CAO Yunhe, YEO T S, et al. Few-shot radar jamming recognition network via time-frequency self-attention and global knowledge distillation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 5105612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3280322. |
| [11] |
KONG Yukai, XIA Senlin, DONG Luxin, et al. Compound jamming recognition via contrastive learning for distributed MIMO radars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(6): 7892–7907. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3358996. |
| [12] |
KONG Yukai, WANG Xiang, WU Changxin, et al. Active deception jamming recognition in the presence of extended target[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4024905. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3184997. |
| [13] |
ZHOU Hongping, WANG Lei, and GUO Zhongyi. Recognition of radar compound jamming based on convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(6): 7380–7394. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3288080. |
| [14] |
PENG Ruihui, WEI Wenbin, SUN Dianxing, et al. Dense false target jamming recognition based on fast-slow time domain joint frequency response features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(6): 9142–9159. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3316125. |
| [15] |
WEI Gengli, LI Lianghai, YAN Haipeng, et al. Radar jamming signal identification based on multimode feature fusion[J]. Journal of Telemetry, Tracking and Command, 2023, 44(4): 80–87. doi: 10.12347/j.ycyk.20230328001. |
| [16] |
张顺生, 陈爽, 陈晓莹, 等. 面向小样本的多模态雷达有源欺骗干扰识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(4): 882–891. doi: 10.12000/JR23104. ZHANG Shunsheng, CHEN Shuang, CHEN Xiaoying, et al. Active deception jamming recognition method in multimodal radar based on small samples[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(4): 882–891. doi: 10.12000/JR23104. |
| [17] |
SHAO Guangqing, CHEN Yushi, and WEI Yinsheng. Deep fusion for radar jamming signal classification based on CNN[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 117236–117244. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3004188. |
| [18] |
ZHANG Yipeng, LU Dongdong, QIU Xiaolan, et al. Scattering-point topology for few-shot ship classification in SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2023, 16: 10326–10343. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2023.3328066. |
| [19] |
GENG Jie, ZHANG Yuhang, and JIANG Wen. Polarimetric SAR image classification based on hierarchical scattering-spatial interaction transformer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5205014. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3362360. |
| [20] |
郭帅, 陈婷, 王鹏辉, 等. 基于角度引导Transformer融合网络的多站协同目标识别方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12(3): 516–528. doi: 10.12000/JR23014. GUO Shuai, CHEN Ting, WANG Penghui, et al. Multistation cooperative radar target recognition based on an angle-guided Transformer fusion network[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12(3): 516–528. doi: 10.12000/JR23014. |
| [21] |
CHEN Xiaolong, SU Ningyuan, HUANG Yong, et al. False-alarm-controllable radar detection for marine target based on multi features fusion via CNNs[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(7): 9099–9111. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3054744. |
| [22] |
RADFORD A, KIM J W, HALLACY C, et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision[C]. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2021: 8748–8763.
|
| [23] |
LI Hong, ZHENG Guangyong, GUO Lei, et al. Jamming analysis of radar coherent suppressing[J]. Electronic Information Warfare Technology, 2013, 28(3): 36–40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2230.2013.03.009. |
| [24] |
WEI Shaopeng, ZHANG Lei, LU Jingyue, et al. Modulated-ISRJ rejection using online dictionary learning for synthetic aperture radar imagery[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 35(2): 316–329. doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2023.000076. |
| [25] |
TAN Mingxing and LE Q V. EfficientNetV2: Smaller models and faster training[C]. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2021: 10096–10106.
|
| [26] |
GONG Heng, FENG Xiaocheng, QIN Bing, et al. Table-to-text generation with effective hierarchical encoder on three dimensions (row, column and time)[C]. The 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Hong Kong, China, 2019: 3143–3152. doi: 10.18653/v1/D19-1310. |
| [27] |
LI Liang, MA Can, YUE Yinliang, et al. Improving encoder by auxiliary supervision tasks for table-to-text generation[C]. The 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers), 2021: 5979–5989. doi: 10.18653/v1/2021.acl-long.466. |
| [28] |
RADFORD A, WU J, CHILD R, et al. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners[J]. OpenAI Blog, 2019, 1(8): 9.
|
| [29] |
KHOSLA P, TETERWAK P, WANG Chen, et al. Supervised contrastive learning[C]. The 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’20), Vancouver, Canada, 2020: 1567.
|
| [30] |
WANG Feng and LIU Huaping. Understanding the behaviour of contrastive loss[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 2495–2504. doi: 10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.00252. |
| [31] |
LIU Mingqian, LIU Zilong, LU Weidang, et al. Distributed few-shot learning for intelligent recognition of communication jamming[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2022, 16(3): 395–405. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3137028. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work

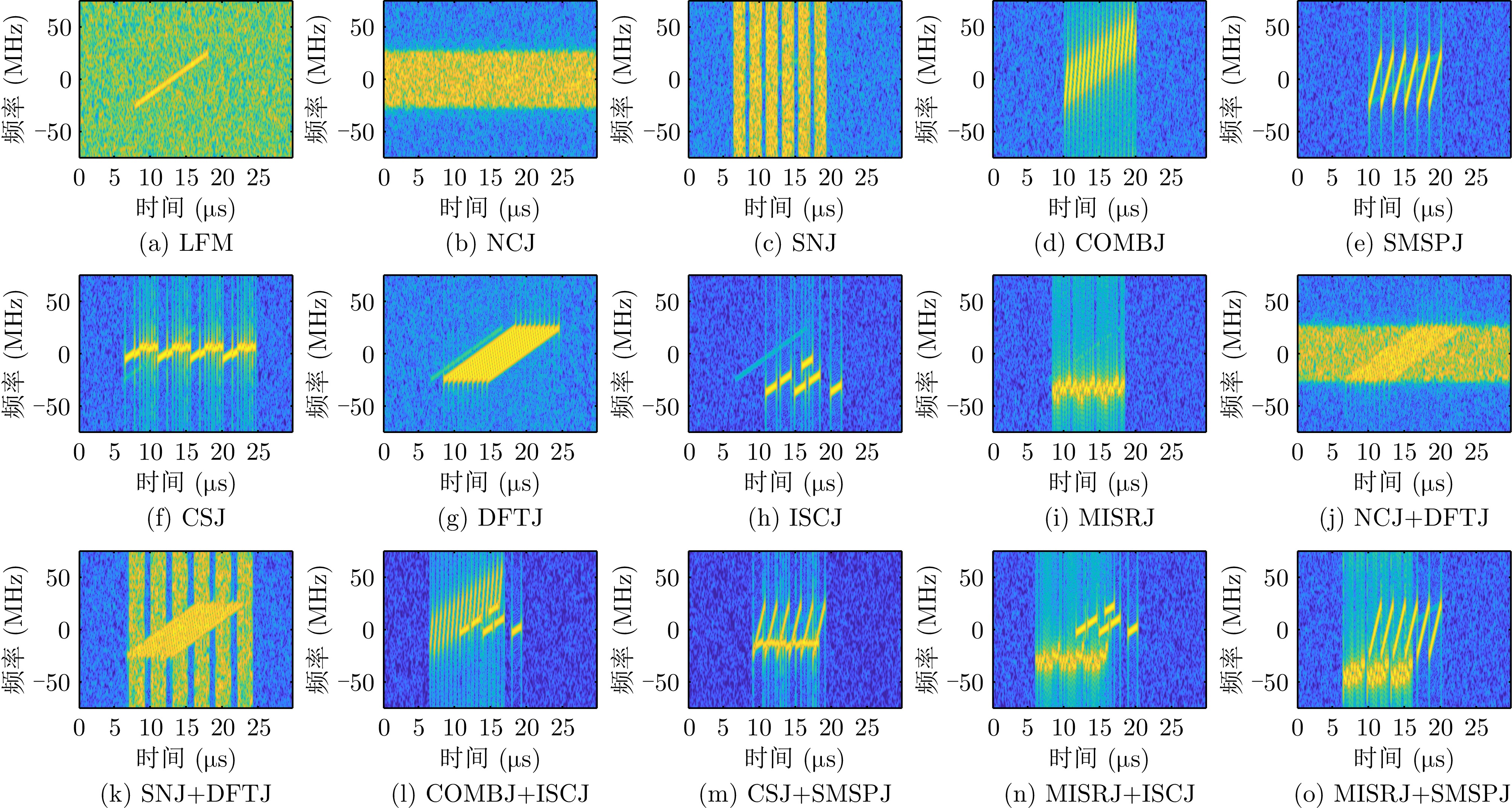



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: