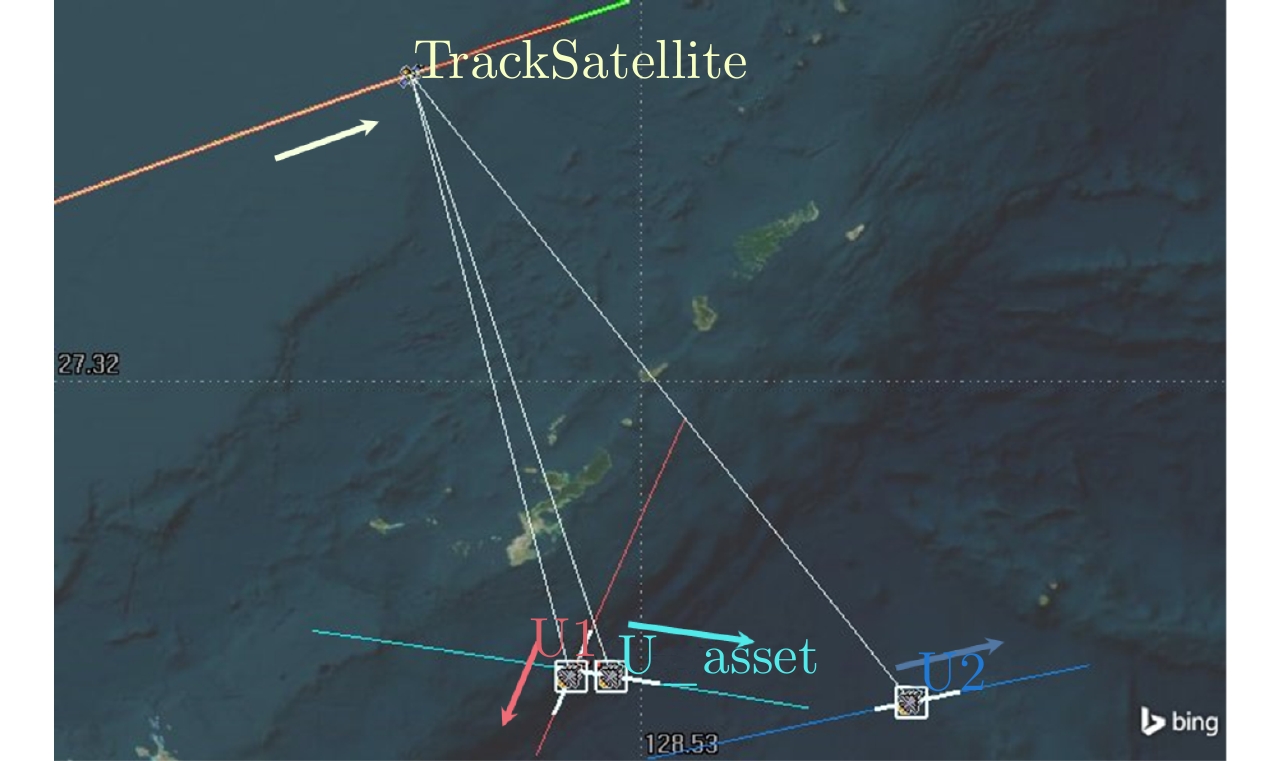
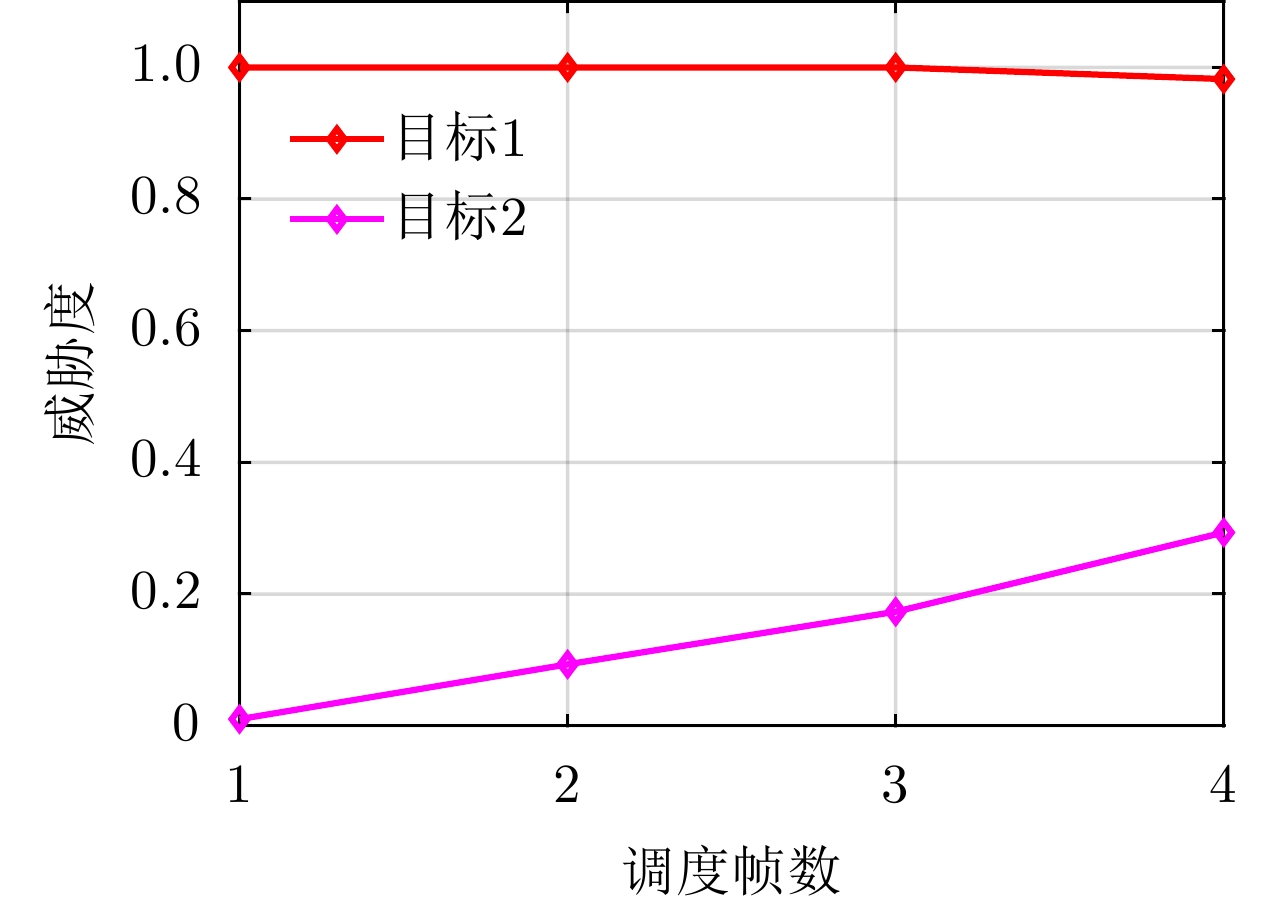
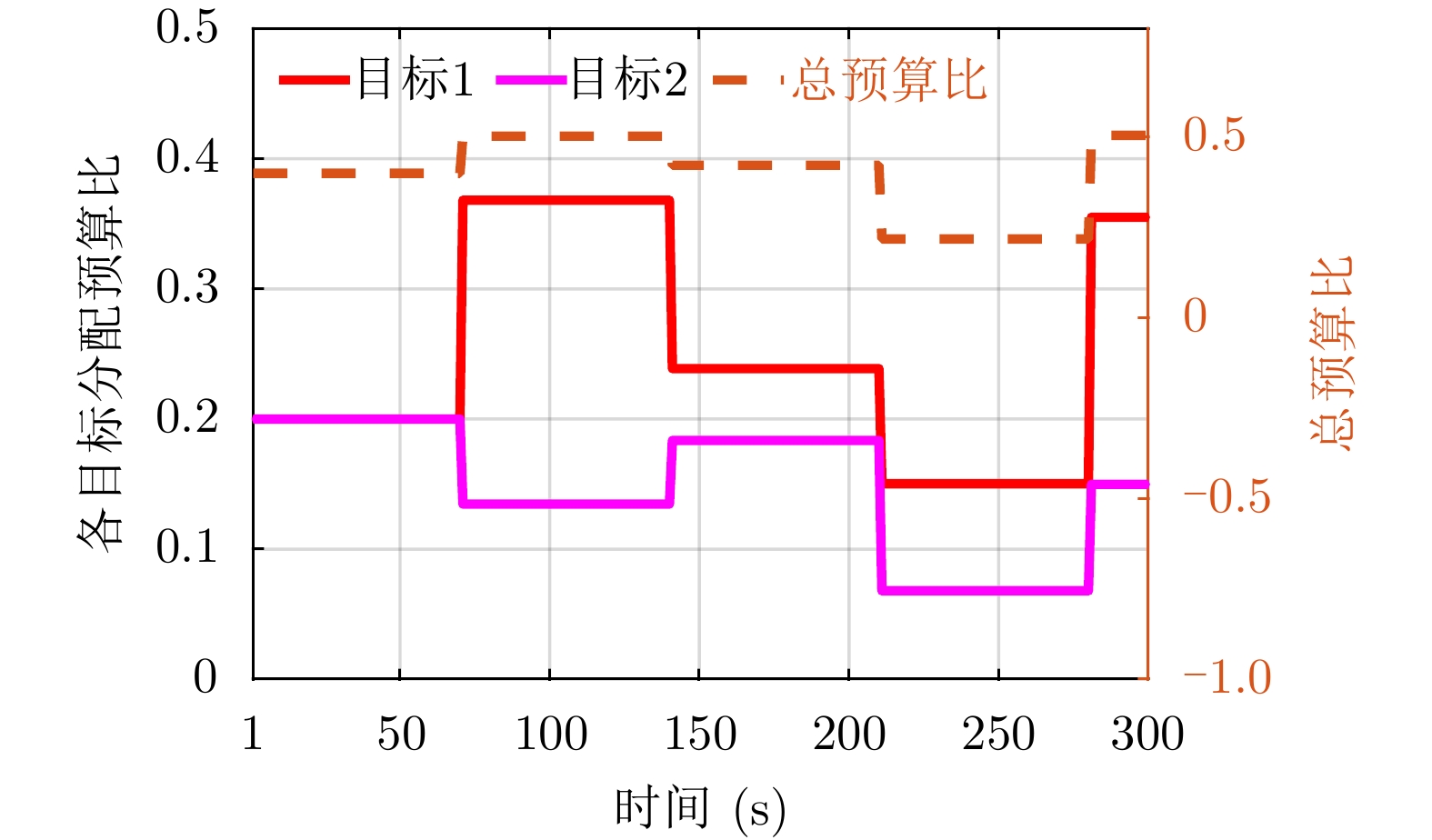
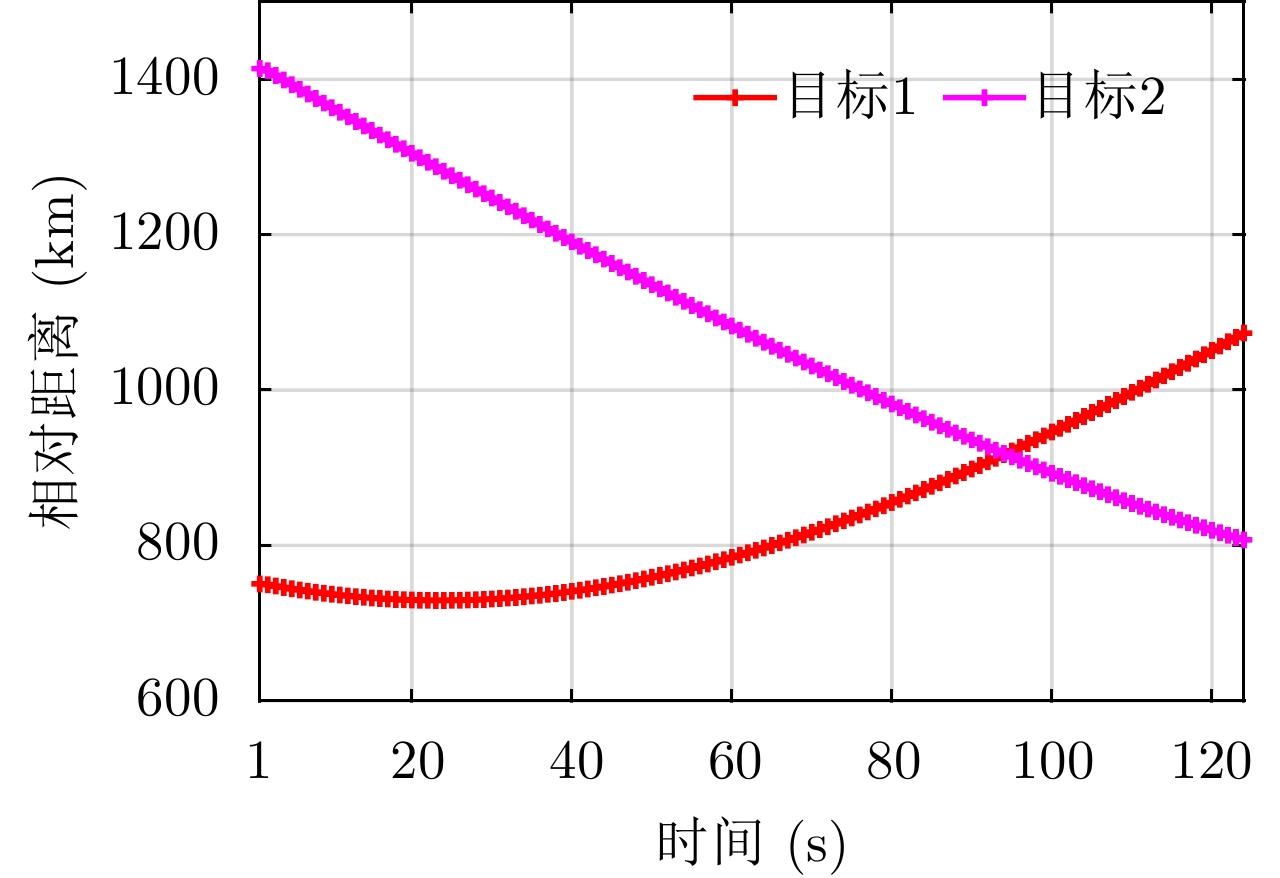
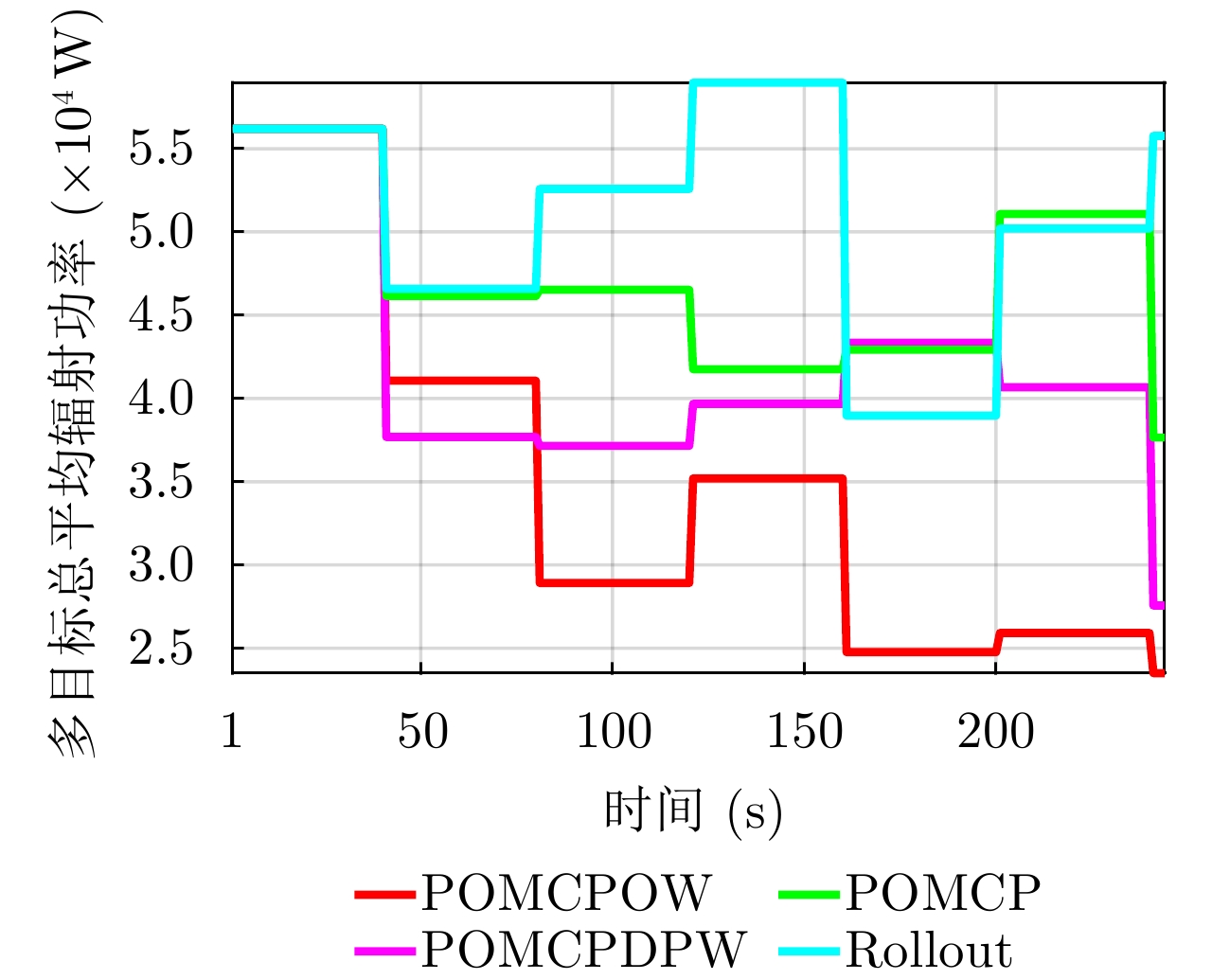
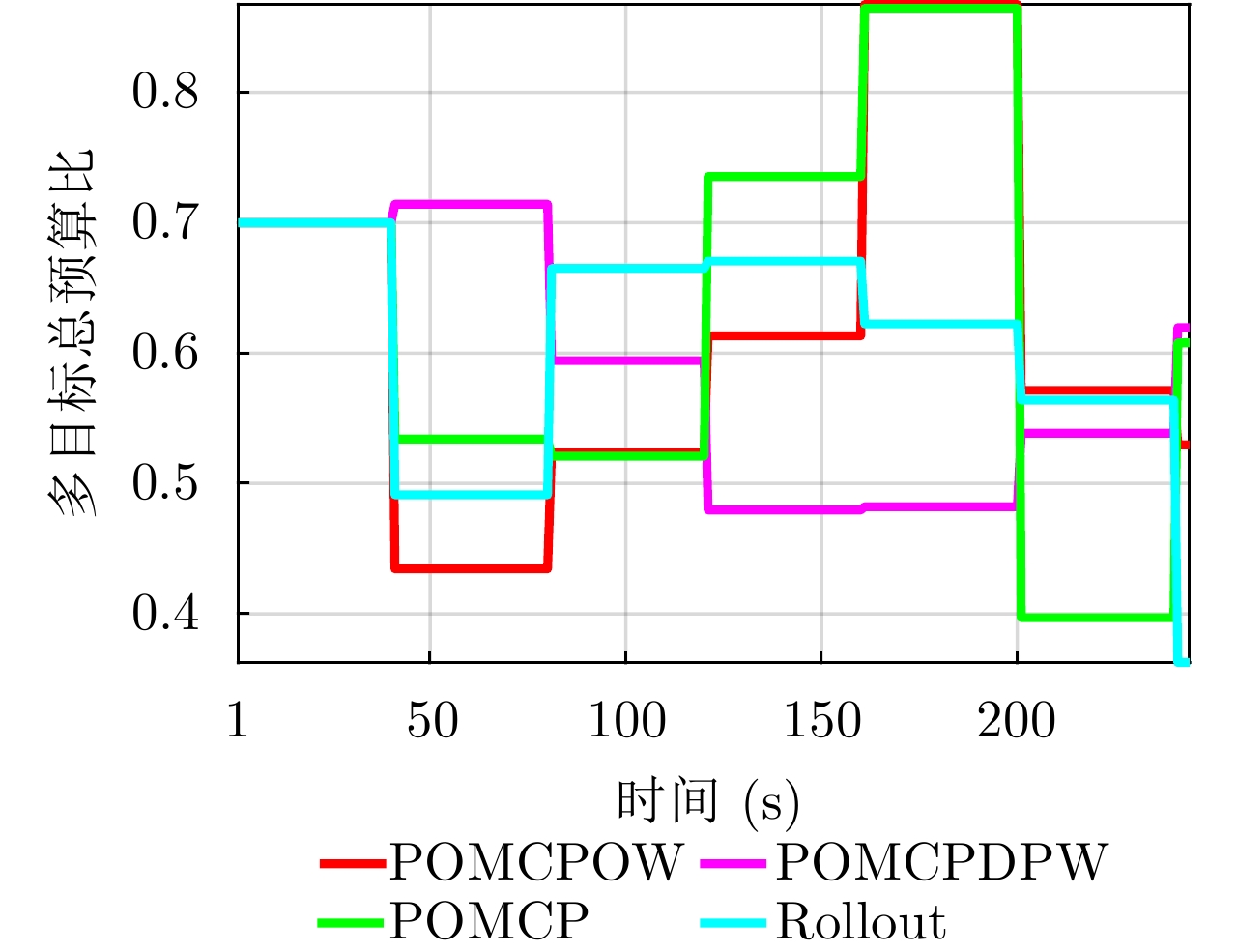
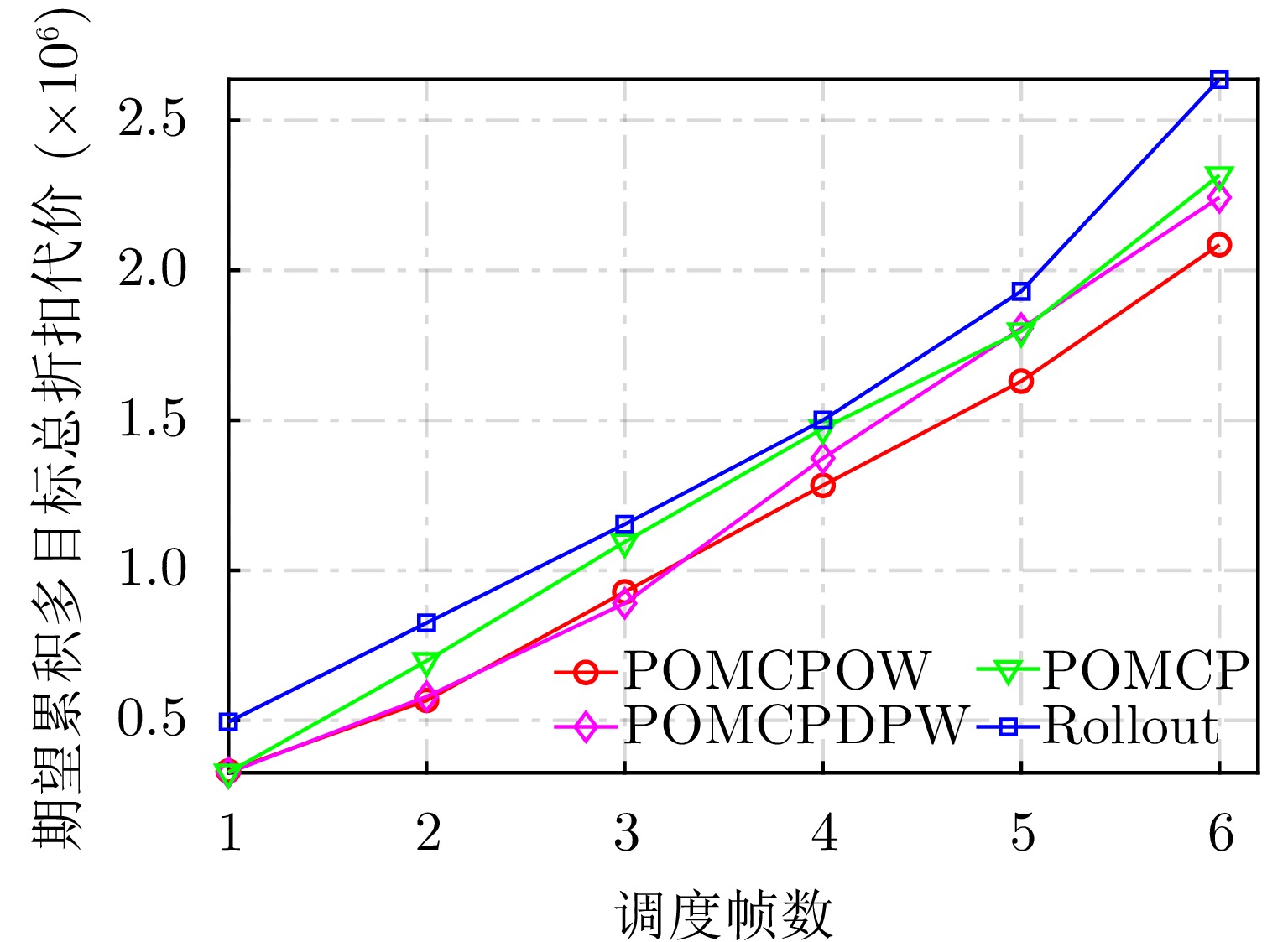
| [1] |
XIE Mingchi, YI Wei, KIRUBARAJAN T, et al. Joint node selection and power allocation strategy for multitarget tracking in decentralized radar networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(3): 729–743. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2777394 |
| [2] |
DAI Jinhui, YAN Junkun, WANG Penghui, et al. Optimal resource allocation for multiple target tracking in phased array radar network[C]. 2019 International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences (ICCAIS), Chengdu, China, 2019: 1–4.
|
| [3] |
SUN Jun, LU Xiujuan, YUAN Ye, et al. Resource allocation for multi-target tracking in multi-static radar systems with imperfect detection performance[C]. 2020 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf20), Florence, Italy, 2020: 1–6.
|
| [4] |
ZHANG Haowei, LIU Weijian, ZONG Binfeng, et al. An efficient power allocation strategy for maneuvering target tracking in cognitive MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1591–1602. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2020.3047227 |
| [5] |
LU Xiujuan, YI Wei, and KONG Lingjiang. Joint online route planning and resource optimization for multitarget tracking in airborne radar systems[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16(3): 4198–4209. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2021.3116020 |
| [6] |
SHI Chenguang, ZHOU Jianjiang, and WANG Fei. Adaptive resource management algorithm for target tracking in radar network based on low probability of intercept[J]. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 29(4): 1203–1226. doi: 10.1007/s11045-017-0494-8 |
| [7] |
SHI Chenguang, WANG Yijie, SALOUS S, et al. Joint transmit resource management and waveform selection strategy for target tracking in distributed phased array radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(4): 2762–2778. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3138869 |
| [8] |
CHHETRI A S, MORRELL D, and PAPANDREOU-SUPPAPPOLA A. Energy efficient target tracking in a sensor network using non-myopic sensor scheduling[C]. 2005 7th International Conference on Information Fusion, Philadelphia, USA, 2005: 558–565.
|
| [9] |
HERO A O and COCHRAN D. Sensor management: Past, present, and future[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2011, 11(12): 3064–3075. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2011.2167964 |
| [10] |
FERRI G, MUNAFÒ A, GOLDHAHN R, et al. A non-myopic, receding horizon control strategy for an AUV to track an underwater target in a bistatic sonar scenario[C]. 53rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Los Angeles, USA, 2014: 5352–5358.
|
| [11] |
JI Shihao, PARR R, and CARIN L. Nonmyopic multiaspect sensing with partially observable Markov decision processes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(6): 2720–2730. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.893747 |
| [12] |
KRISHNAMURTHY V and DJONIN D V. Optimal threshold policies for multivariate POMDPs in radar resource management[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(10): 3954–3969. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2022915 |
| [13] |
JIANG Xiaofeng, ZHOU Feng, JIAN Yang, et al. An optimal POMDP-based anti-jamming policy for cognitive radar[C]. 2017 13th IEEE Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Xi’an, China, 2017: 938–943.
|
| [14] |
SHAN Ganlin, XU Gongguo, and QIAO Chenglin. A non-myopic scheduling method of radar sensors for maneuvering target tracking and radiation control[J]. Defence Technology, 2020, 16(1): 242–250. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2019.10.001 |
| [15] |
SCHÖPE M I, DRIESSEN H, and YAROVOY A. A constrained POMDP formulation and algorithmic solution for radar resource management in multi-target tracking[J]. ISIF Journal of Advances in Information Fusion, 2021, 16(1): 31–47.
|
| [16] |
HAWKINS J T. A Langrangian decomposition approach to weakly coupled dynamic optimization problems and its applications[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2003.
|
| [17] |
CASTANON D A. Approximate dynamic programming for sensor management[C]. The 36th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, San Diego, USA, 1997: 1202–1207.
|
| [18] |
LI Yuan, ZHU Huayong, and SHEN Lincheng. The Lagrangian relaxation based resources allocation methods for air-to-ground operations under uncertainty circumstances[C]. 2009 Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Guilin, China, 2009: 5609–5614.
|
| [19] |
KURNIAWATI H, HSU D, and LEE W S. SARSOP: Efficient Point-based POMDP Planning by Approximating Optimally Reachable Belief Spaces[M]. BROCK O, TRINKLE J, and RAMOS F. Robotics: Science and Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2009: 1–8.
|
| [20] |
PINEAU J, GORDON G, and THRUN S. Point-based value iteration: An anytime algorithm for POMDPs[C]. The 18th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Acapulco, Mexico, 2003: 1025–1030.
|
| [21] |
SPAAN M T J and VLASSIS N. Perseus: Randomized point-based value iteration for POMDPs[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2005, 24: 195–220. doi: 10.1613/jair.1659 |
| [22] |
SMITH T and SIMMONS R. Heuristic search value iteration for POMDPs[C]. The 20th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Banff, Canada, 2004: 520–527.
|
| [23] |
ROSS S, PINEAU J, PAQUET S, et al. Online planning algorithms for POMDPs[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2008, 32: 663–704. doi: 10.1613/jair.2567 |
| [24] |
SILVER D and VENESS J. Monte-Carlo planning in large POMDPs[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, British, 2010: 2164–2172.
|
| [25] |
YE Nan, SOMANI A, HSU D, et al. DESPOT: Online POMDP planning with regularization[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2017, 58: 231–266. doi: 10.1613/jair.5328 |
| [26] |
KURNIAWATI H and YADAV V. An online POMDP Solver for Uncertainty Planning in Dynamic Environment[M]. INABA M and CORKE P. Robotics Research: The 16th International Symposium ISRR. Cham, Switzerland: Springer, 2016: 611–629.
|
| [27] |
SUNBERG Z and KOCHENDERFER M. Online algorithms for POMDPs with continuous state, action, and observation spaces[C]. The Thirty-Third International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling, Delft, The Netherlands, 2018: 259–263.
|
| [28] |
KERSHAW D J and EVANS R J. Optimal waveform selection for tracking systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1994, 40(5): 1536–1550. doi: 10.1109/18.333866 |
| [29] |
SIRA S P, PAPANDREOU-SUPPAPPOLA A, and MORRELL D. Dynamic configuration of time-varying waveforms for agile sensing and tracking in clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2007, 55(7): 3207–3217. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.894418 |
| [30] |
LI Xi, CHENG Ting, SU Yang, et al. Joint time-space resource allocation and waveform selection for the collocated MIMO radar in multiple targets tracking[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 176: 107650. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107650 |
| [31] |
KOCH W. Adaptive parameter control for phased-array tracking[C]. SPIE 3809, Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 1999, Denver, USA, 1999: 444–455.
|
| [32] |
KATSILIERIS F, DRIESSEN H, and YAROVOY A. Threat-based sensor management for target tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(4): 2772–2785. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140052 |
| [33] |
HU Yumei, WANG Xuezhi, LAN Hua, et al. An iterative nonlinear filter using variational Bayesian optimization[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(12): 4222. doi: 10.3390/s18124222 |
| [34] |
何子述, 程子扬, 李军, 等. 集中式MIMO雷达研究综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(5): 805–829. doi: 10.12000/JR22128HE Zishu, CHENG Ziyang, LI Jun, et al. A survey of collocated MIMO radar[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(5): 805–829. doi: 10.12000/JR22128 |
| [35] |
LIM M H, TOMLIN C J, and SUNBERG Z N. Sparse tree search optimality guarantees in POMDPs with continuous observation spaces[C]. Twenty-Ninth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Yokohama, Japan, 2020: 1–16.
|
| [36] |
JI Shihao, PARR R, LI Hui, et al. Point-based policy iteration[C]. The Twenty-Second National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, British, 2007: 1243–1249.
|
| [37] |
SCHÖPE M I, DRIESSEN H, and YAROVOY A. Multi-task sensor resource balancing using Lagrangian relaxation and policy rollout[C]. 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Rustenburg, South Africa, 2020: 1–8.
|




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: