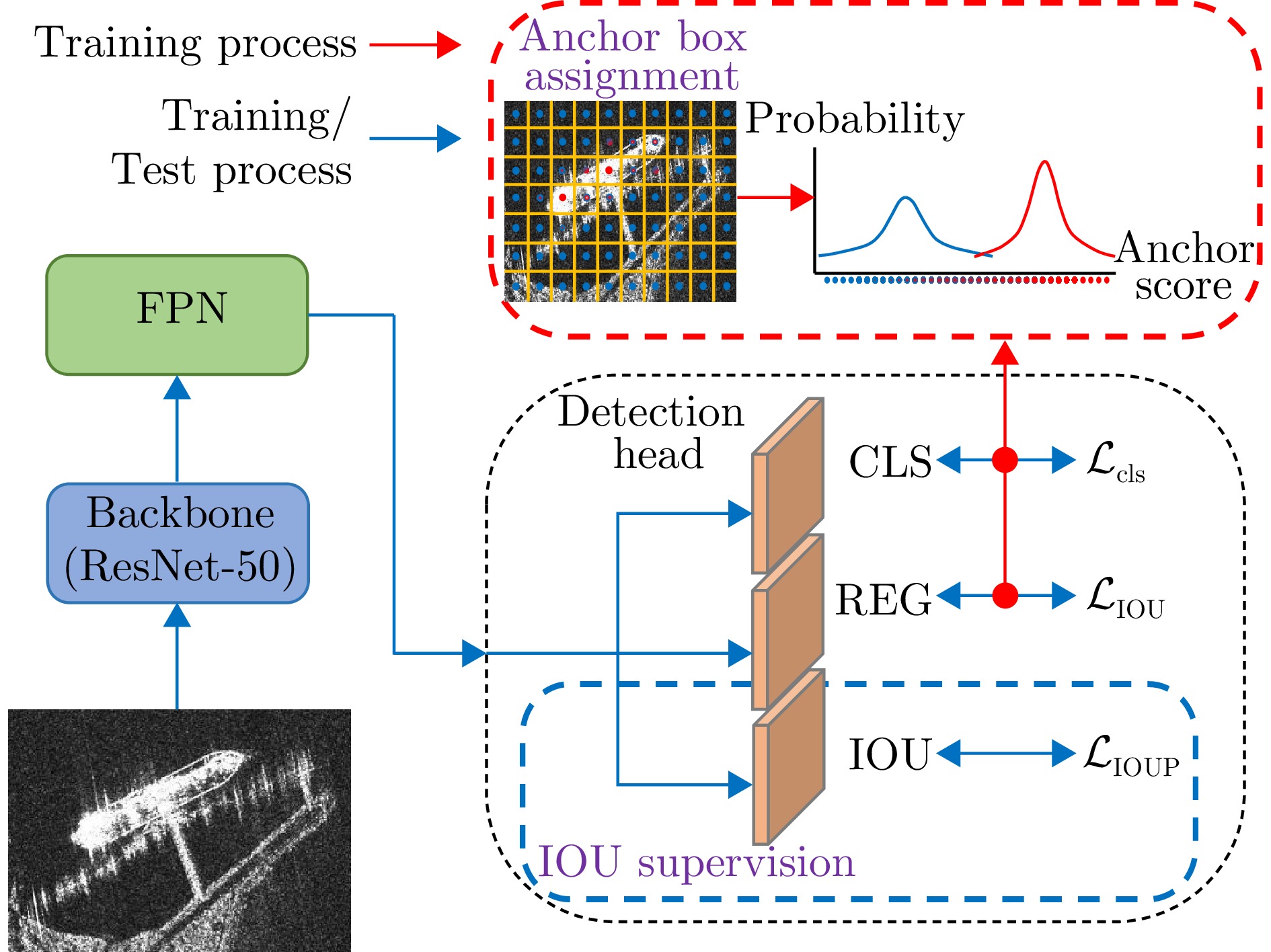
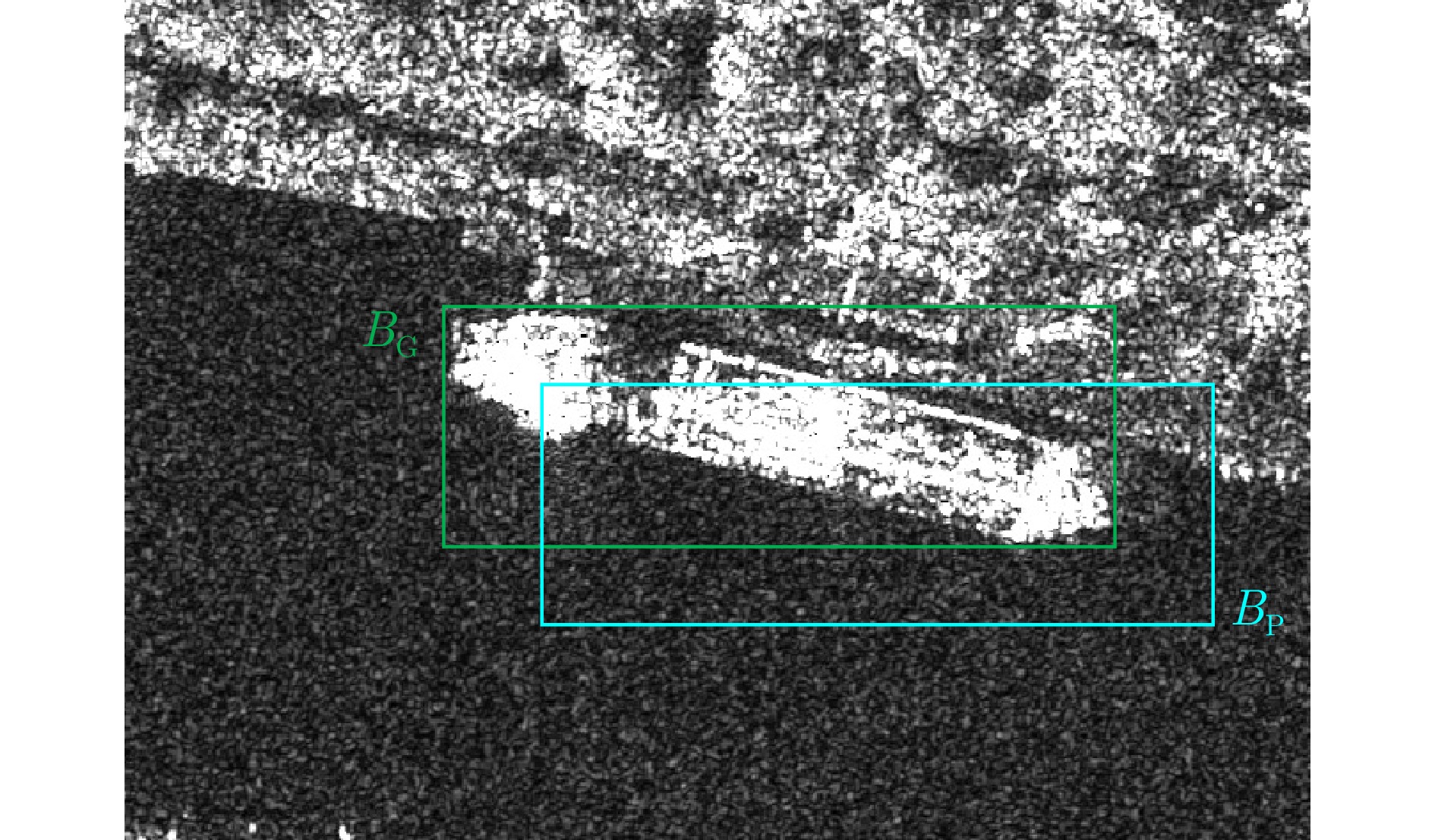
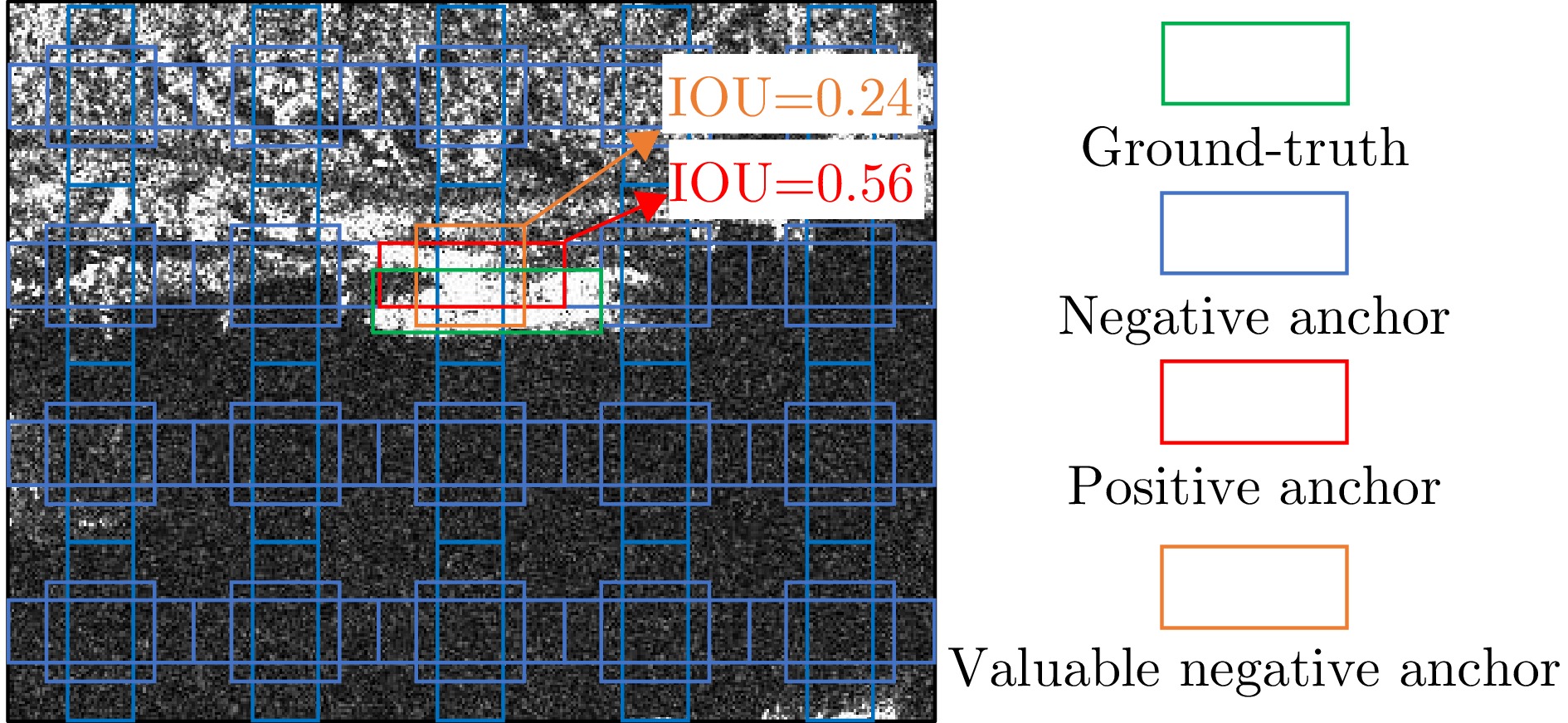
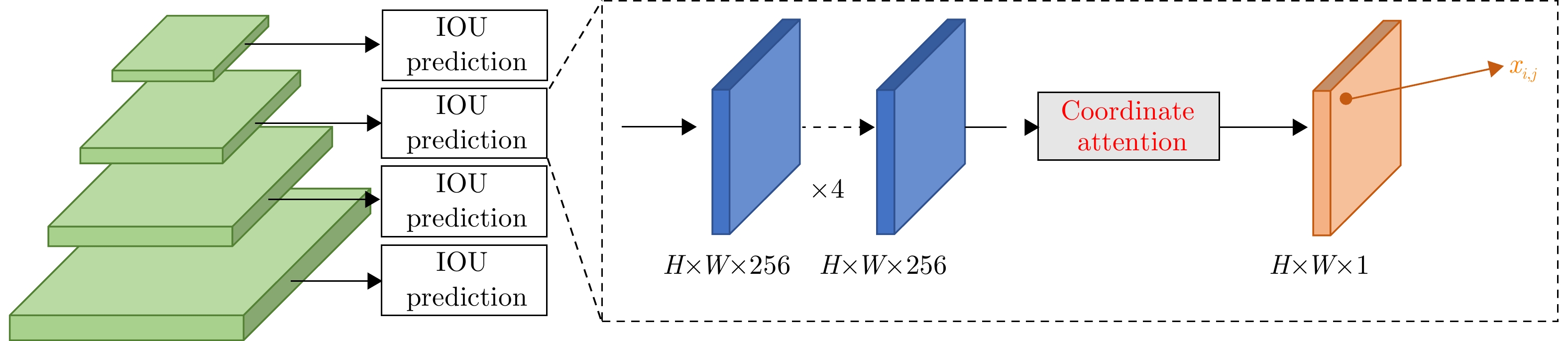
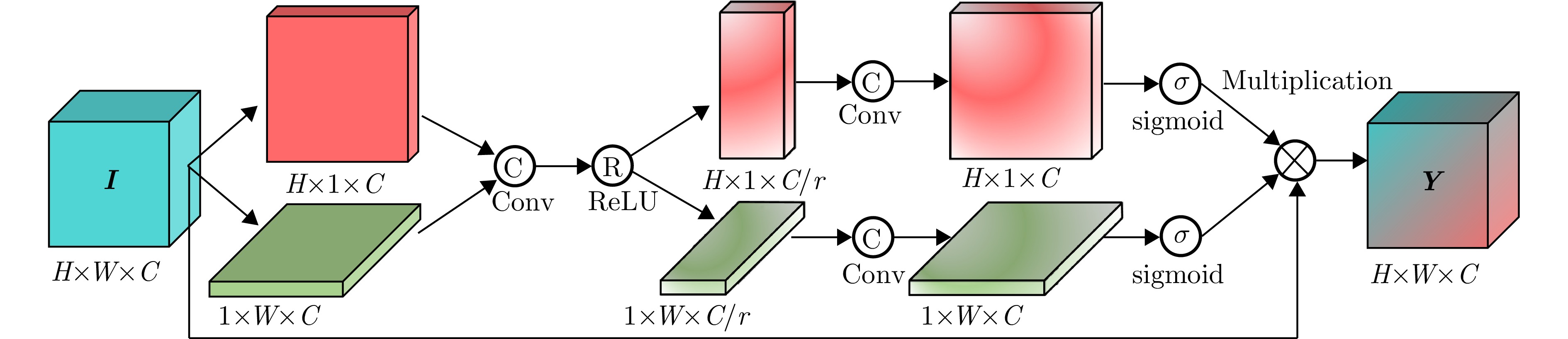
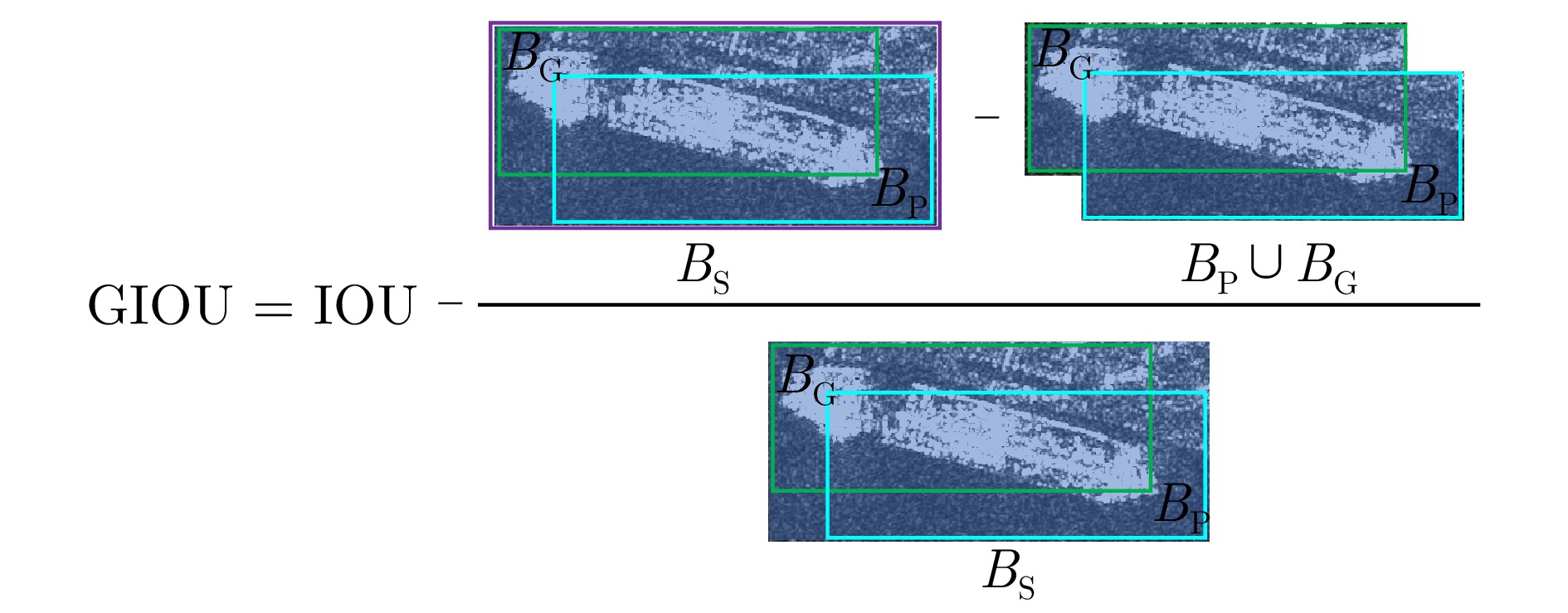
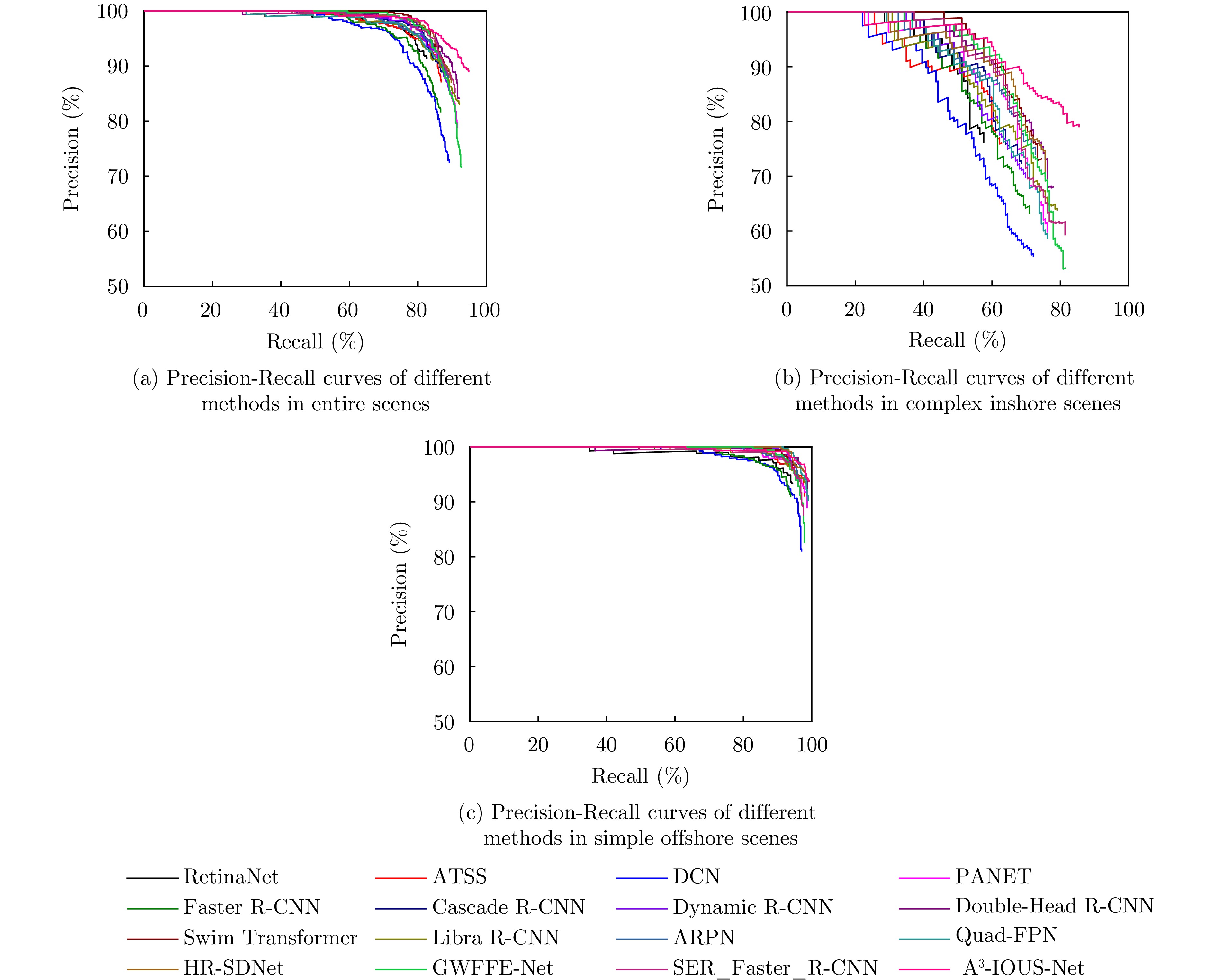
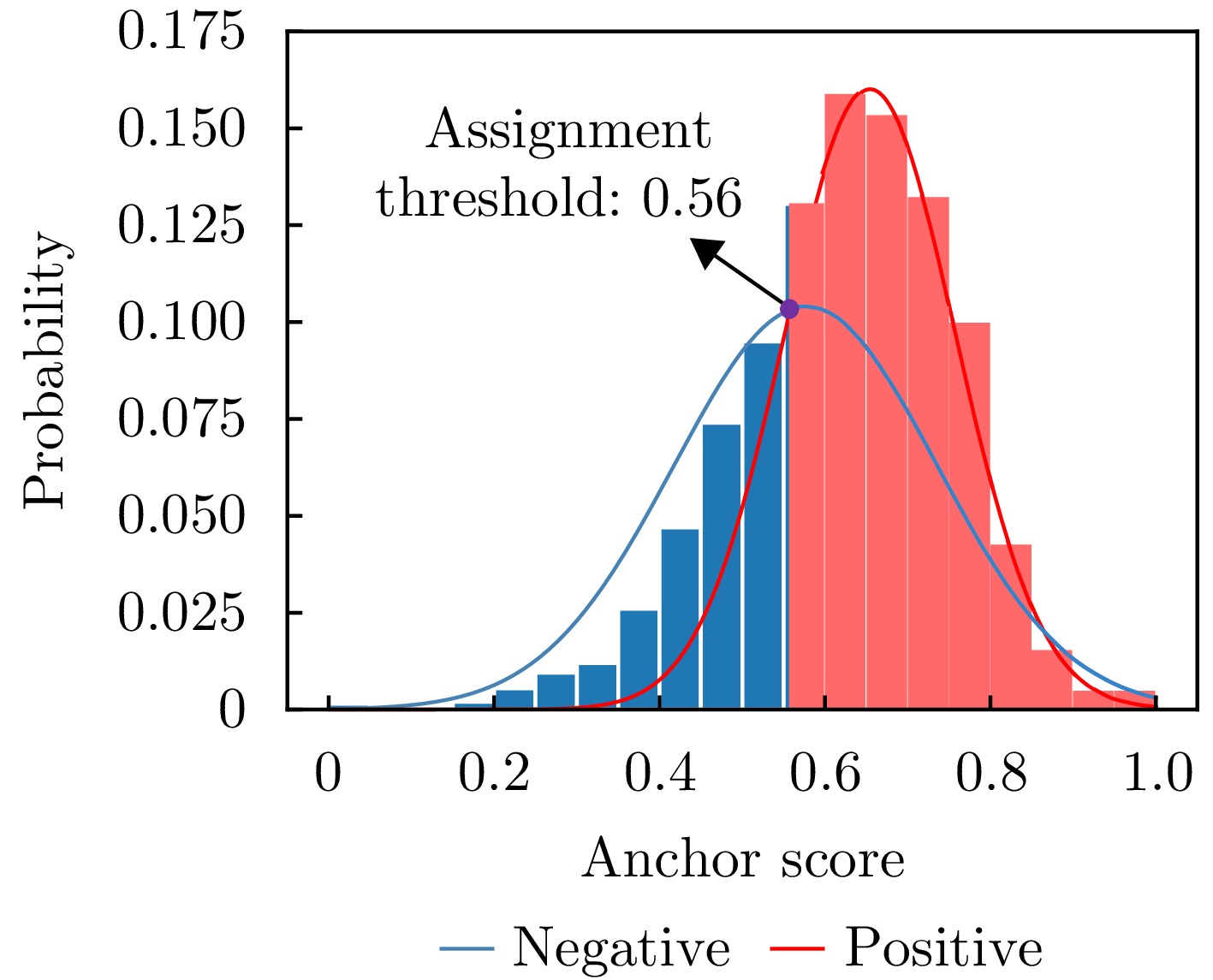
| [1] |
刘方坚, 李媛. 基于视觉显著性的SAR遥感图像NanoDet舰船检测方法[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(6): 885–894. doi: 10.12000/JR21105. LIU Fangjian and LI Yuan. SAR remote sensing image ship detection method NanoDet based on visual saliency[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(6): 885–894. doi: 10.12000/JR21105. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, KE Xiao, et al. HOG-ShipCLSNet: A novel deep learning network with hog feature fusion for SAR ship classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5210322. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3082759. |
| [3] |
ZHANG Tianwen and ZHANG Xiaoling. Injection of traditional hand-crafted features into modern CNN-based models for SAR ship classification: What, why, where, and how[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(11): 2091. doi: 10.3390/rs13112091. |
| [4] |
XU Xiaowo, ZHANG Xiaoling, ZHANG Tianwen, et al. Shadow-background-noise 3D spatial decomposition using sparse low-rank Gaussian properties for video-SAR moving target shadow enhancement[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4516105. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3223514. |
| [5] |
ZHANG Tianwen and ZHANG Xiaoling. High-speed ship detection in SAR images based on a grid convolutional neural network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(10): 1206. doi: 10.3390/rs11101206. |
| [6] |
ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, SHI Jun, et al. Balance scene learning mechanism for offshore and inshore ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4004905. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.3033988. |
| [7] |
徐从安, 苏航, 李健伟, 等. RSDD-SAR: SAR舰船斜框检测数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2022, 11(4): 581–599. doi: 10.12000/JR22007. XU Cong’an, SU Hang, LI Jianwei, et al. RSDD-SAR: Rotated ship detection dataset in SAR images[J]. Journal of Radars, 2022, 11(4): 581–599. doi: 10.12000/JR22007. |
| [8] |
ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, SHI Jun, et al. Depthwise separable convolution neural network for high-speed SAR ship detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(21): 2483. doi: 10.3390/rs11212483. |
| [9] |
TANG Gang, ZHUGE Yichao, CLARAMUNT C, et al. N-YOLO: A SAR ship detection using noise-classifying and complete-target extraction[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(5): 871. doi: 10.3390/rs13050871. |
| [10] |
ZHANG Tianwen and ZHANG Xiaoling. HTC+ for SAR ship instance segmentation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(10): 2395. doi: 10.3390/rs14102395. |
| [11] |
HE Bokun, ZHANG Qingyi, TONG Ming, et al. Oriented ship detector for remote sensing imagery based on pairwise branch detection head and SAR feature enhancement[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(9): 2177. doi: 10.3390/rs14092177. |
| [12] |
XU Xiaowo, ZHANG Xiaoling, and ZHANG Tianwen. Lite-YOLOv5: A lightweight deep learning detector for on-board ship detection in large-scene sentinel-1 SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(4): 1018. doi: 10.3390/rs14041018. |
| [13] |
ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, SHI Jun, et al. HyperLi-Net: A hyper-light deep learning network for high-accurate and high-speed ship detection from synthetic aperture radar imagery[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 167: 123–153. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.05.016. |
| [14] |
ZHANG Tianwen and ZHANG Xiaoling. A mask attention interaction and scale enhancement network for SAR ship instance segmentation[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4511005. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2022.3189961. |
| [15] |
XU Xiaowo, ZHANG Xiaoling, SHAO Zikang, et al. A group-wise feature enhancement-and-fusion network with dual-polarization feature enrichment for SAR ship detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(20): 5276. doi: 10.3390/rs14205276. |
| [16] |
LI Jianwei, XU Cong’an, SU Hang, et al. Deep learning for SAR ship detection: Past, present and future[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(11): 2712. doi: 10.3390/rs14112712. |
| [17] |
LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318–327. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826. |
| [18] |
ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, KE Xiao, et al. LS-SSDD-v1.0: A deep learning dataset dedicated to small ship detection from large-scale Sentinel-1 SAR images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(18): 2997. doi: 10.3390/rs12182997. |
| [19] |
KIM K and LEE H S. Probabilistic anchor assignment with IoU prediction for object detection[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 355–371.
|
| [20] |
REYNOLDS D. Gaussian Mixture Models[M]. LI S Z and JAIN A. Encyclopedia of Biometrics. Boston, USA: Springer, 2009: 659–663.
|
| [21] |
DEMPSTER A P, LAIRD N M, and RUBIN D B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B ( Methodological), 1977, 39(1): 1–22. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1977.tb01600.x. |
| [22] |
ZHANG Caiguang, XIONG Boli, LI Xiao, et al. TCD: Task-collaborated detector for oriented objects in remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2023, 61: 4700714. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3244953. |
| [23] |
ZHANG Tianwen and ZHANG Xiaoling. Squeeze-and-excitation Laplacian pyramid network with dual-polarization feature fusion for ship classification in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4019905. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3119875. |
| [24] |
HOU Qibin, ZHOU Daquan, and FENG Jiashi. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 13708–13717.
|
| [25] |
ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, LI Jianwei, et al. SAR ship detection dataset (SSDD): Official release and comprehensive data analysis[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(18): 3690. doi: 10.3390/rs13183690. |
| [26] |
KETKAR N. Introduction to PyTorch[M]. KETKAR N. Deep Learning with Python: A Hands-on Introduction. Berkeley, USA: Apress, 2017: 195–208.
|
| [27] |
CHEN Kai, WANG Jiaqi, PANG Jiangmiao, et al. MMDetection: Open MMLab detection toolbox and benchmark[J]. arXiv: 1906.07155, 2019.
|
| [28] |
ZHANG Shifeng, CHI Cheng, YAO Yongqiang, et al. Bridging the gap between anchor-based and anchor-free detection via adaptive training sample selection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 9756–9765.
|
| [29] |
ZHU Xizhou, HU Han, LIN S, et al. Deformable ConvNets V2: More deformable, better results[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 9300–9308.
|
| [30] |
LIU Shu, QI Lu, QIN Haifeng, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[J]. arXiv: 1803.01534, 2018.
|
| [31] |
REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031. |
| [32] |
CAI Zhaowei and VASCONCELOS N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into high quality object detection[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6154–6162.
|
| [33] |
ZHANG Hongkai, CHANG Hong, MA Bingpeng, et al. Dynamic R-CNN: Towards high quality object detection via dynamic training[C]. 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 260–275.
|
| [34] |
WU Yue, CHEN Yinpeng, YUAN Lu, et al. Rethinking classification and localization for object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10183–10192.
|
| [35] |
LIU Ze, LIN Yutong, CAO Yue, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 9992–10002.
|
| [36] |
PANG Jiangmiao, CHEN Kai, SHI Jianping, et al. Libra R-CNN: Towards balanced learning for object detection[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 821–830.
|
| [37] |
ZHAO Yan, ZHAO Lingjun, XIONG Boli, et al. Attention receptive pyramid network for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 2738–2756. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2997081. |
| [38] |
ZHANG Tianwen, ZHANG Xiaoling, and KE Xiao. Quad-FPN: A novel quad feature pyramid network for SAR ship detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(14): 2771. doi: 10.3390/rs13142771. |
| [39] |
WEI Shunjun, SU Hao, MING Jing, et al. Precise and robust ship detection for high-resolution SAR imagery based on HR-SDNet[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(1): 167. doi: 10.3390/rs12010167. |
| [40] |
LIN Zhao, JI Kefeng, LENG Kiangguang, et al. Squeeze and excitation rank faster R-CNN for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(5): 751–755. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2882551. |
| [41] |
VO X T and JO K H. A review on anchor assignment and sampling heuristics in deep learning-based object detection[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 506: 96–116. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.07.003. |
| [42] |
孙显, 王智睿, 孙元睿, 等. AIR-SARShip-1.0: 高分辨率SAR舰船检测数据集[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097. SUN Xian, WANG Zhirui, and SUN Yuanrui, et al. AIR-SARShip-1.0: High-resolution SAR ship detection dataset[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(6): 852–862. doi: 10.12000/JR19097. |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: