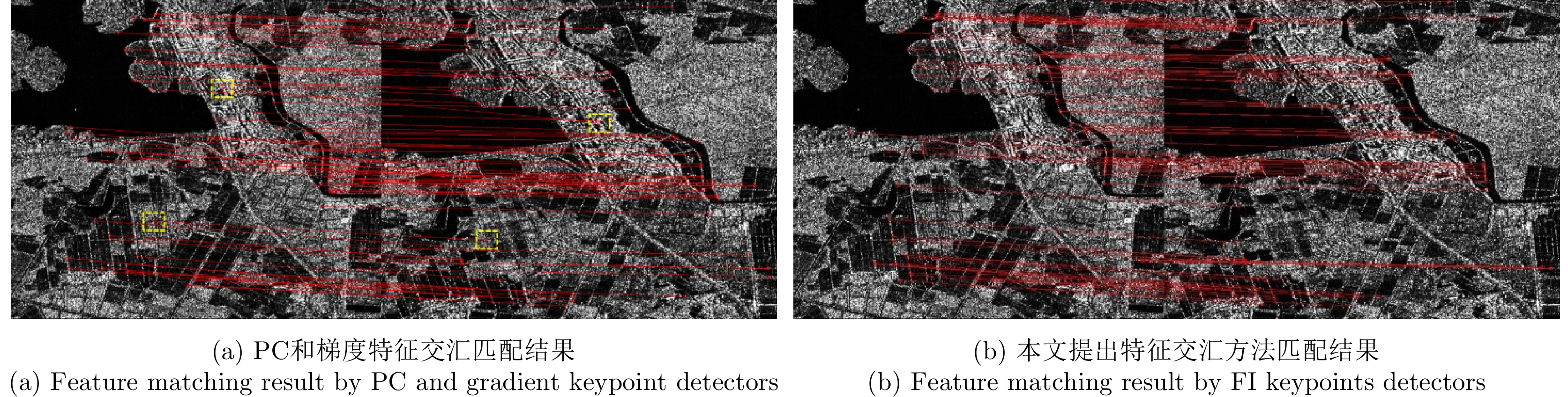
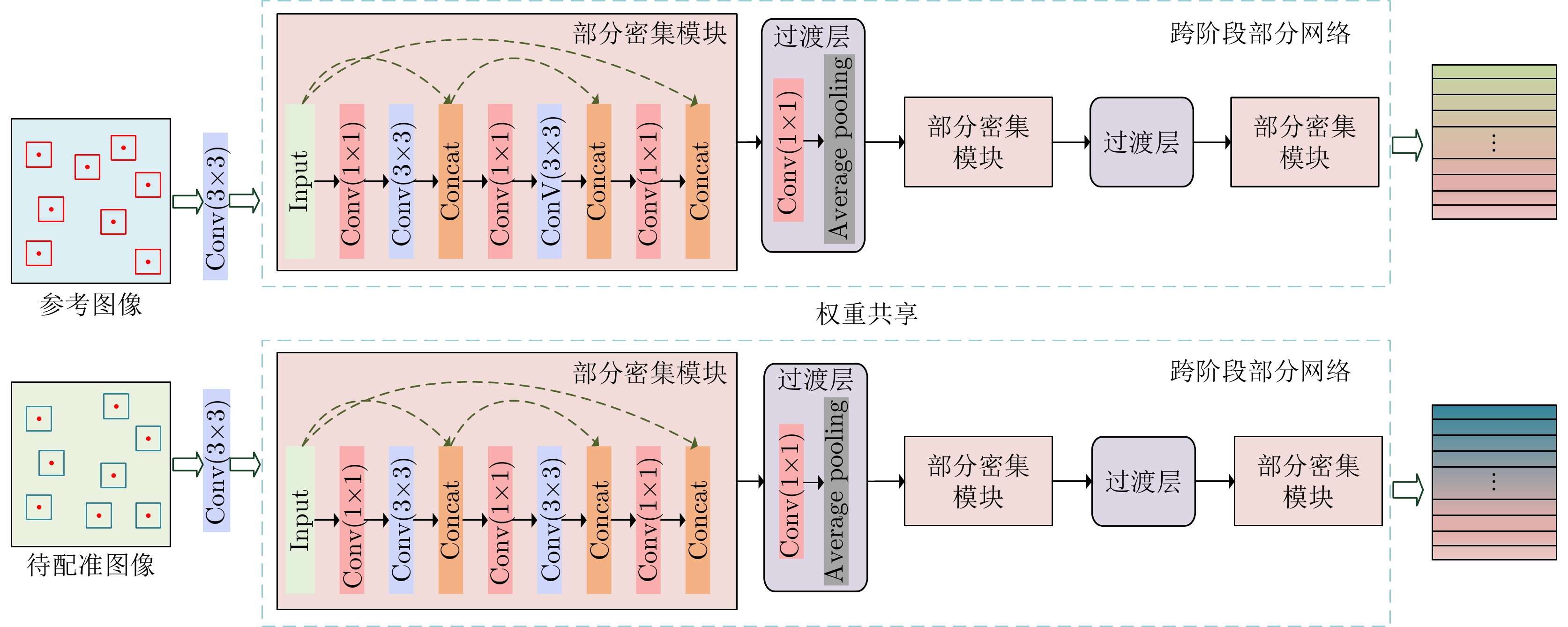
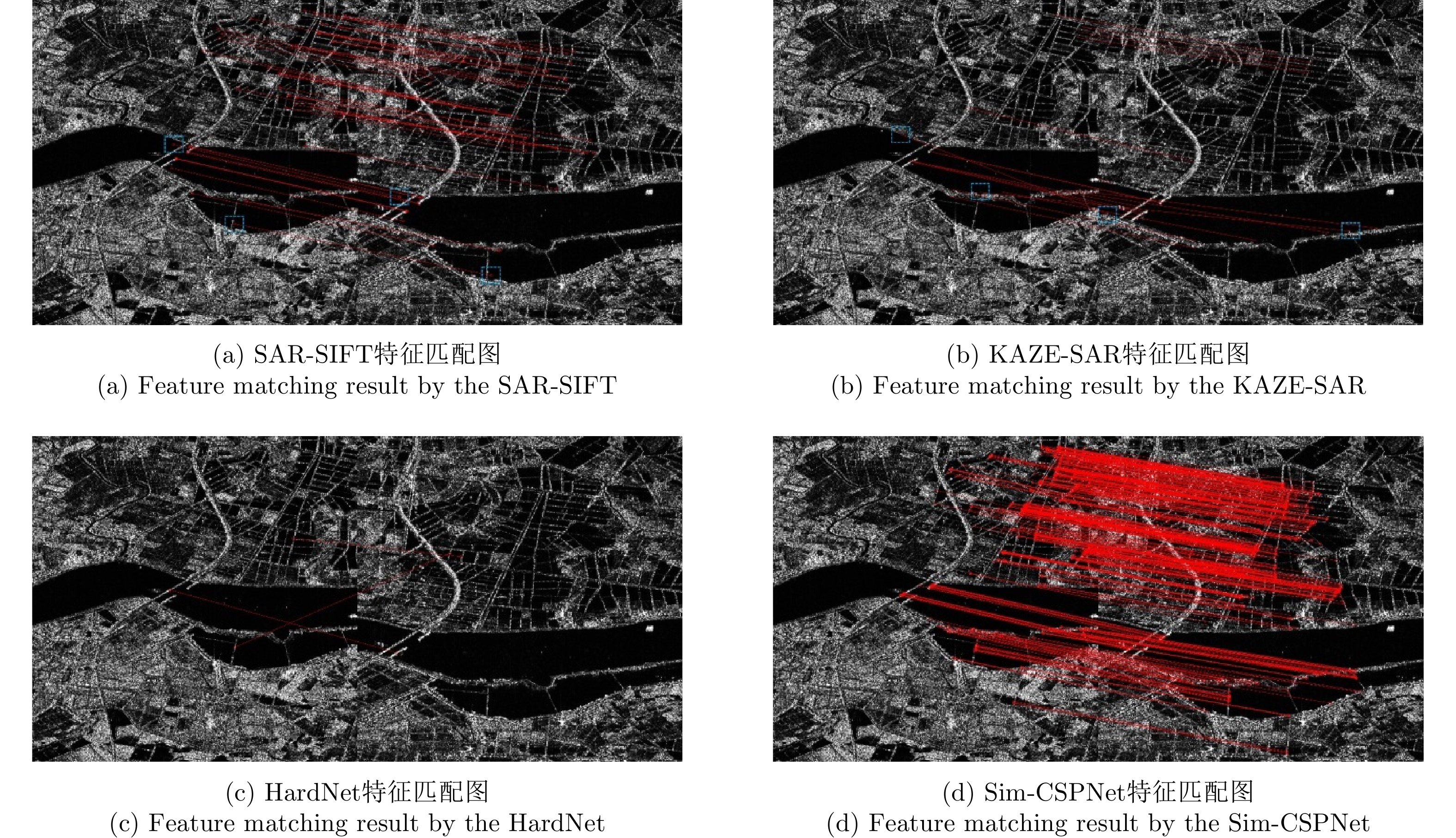
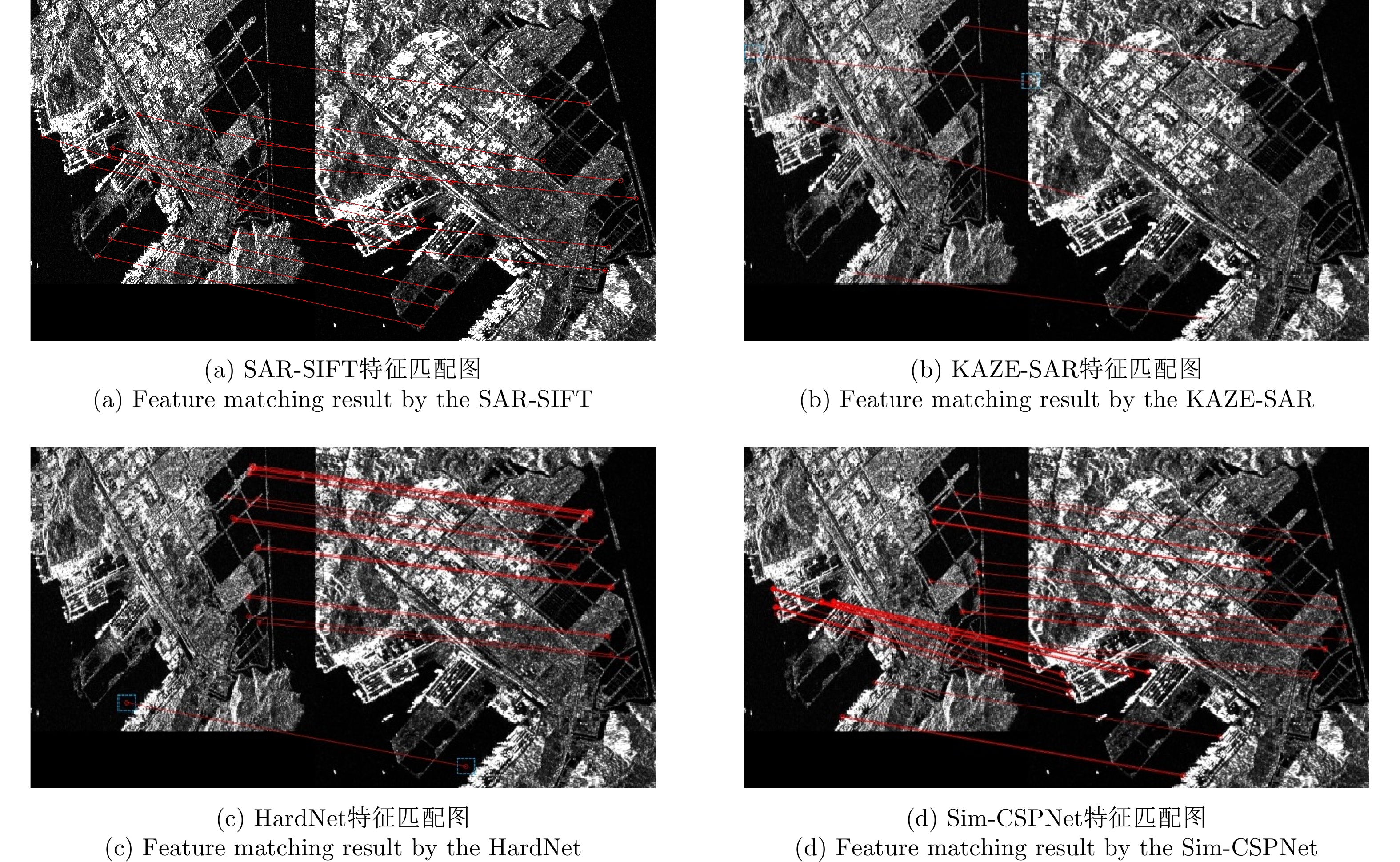
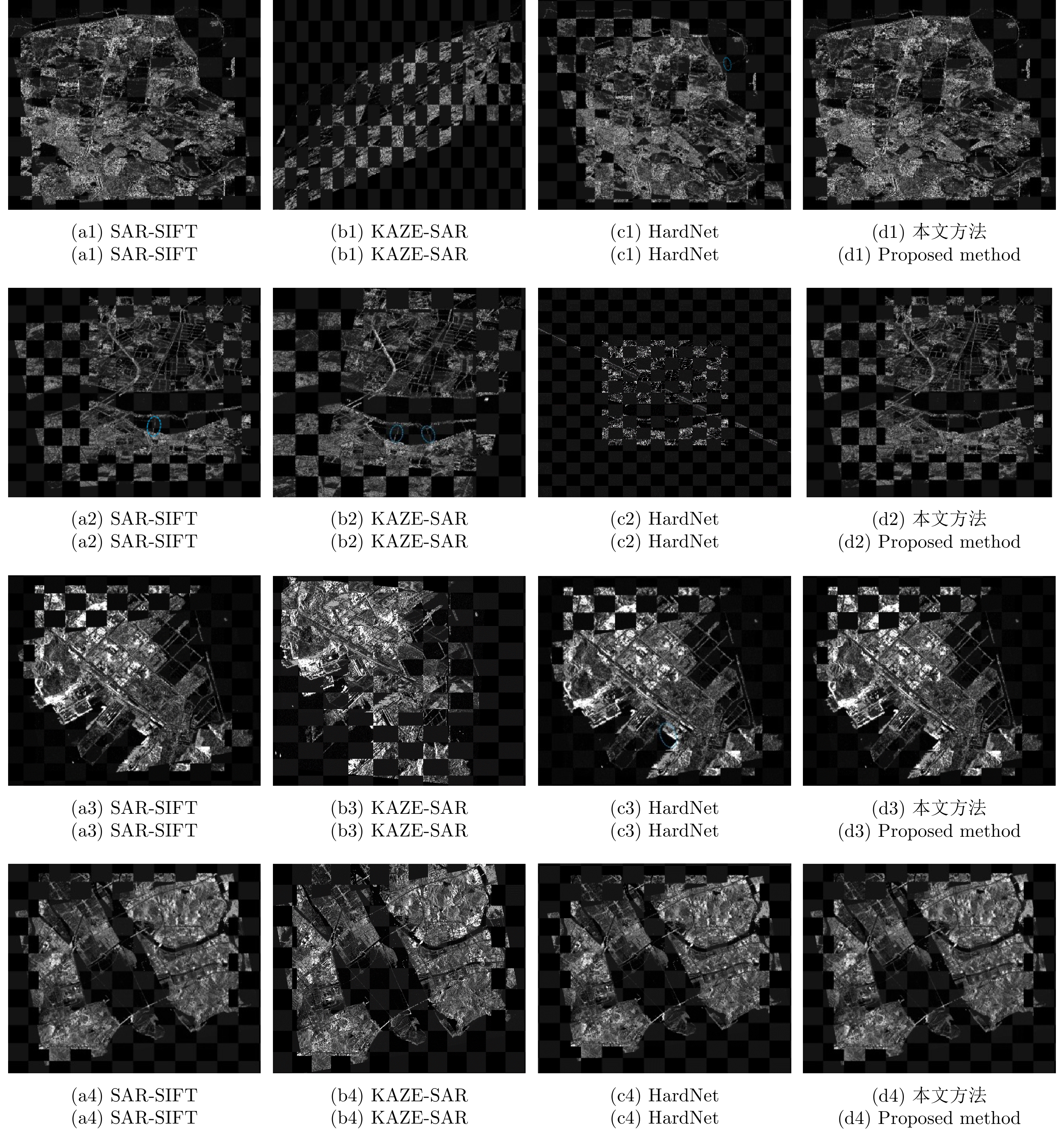
| [1] |
SUN Yili, LEI Lin, LI Xiao, et al. Structure consistency-based graph for unsupervised change detection with homogeneous and heterogeneous remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1–21. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3053571 |
| [2] |
苏娟, 李彬, 王延钊. 一种基于封闭均匀区域的SAR图像配准方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12): 3282–3288. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160141SU Juan, LI Bin, and WANG Yanzhao. SAR image registration algorithm based on closed uniform regions[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38(12): 3282–3288. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160141 |
| [3] |
张王菲, 陈尔学, 李增元, 等. 雷达遥感农业应用综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 444–461. doi: 10.12000/JR20051ZHANG Wangfei, CHEN Erxue, LI Zengyuan, et al. Review of applications of radar remote sensing in agriculture[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 444–461. doi: 10.12000/JR20051 |
| [4] |
周荣荣. 山地SAR影像配准方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 长安大学, 2019.
ZHOU Rongrong. Research on registration method of mountainous SAR images[D]. [Master dissertation], Chang’an University, 2019.
|
| [5] |
SURI S and REINARTZ P. Mutual-information-based registration of TerraSAR-X and Ikonos imagery in urban areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(2): 939–949. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2034842 |
| [6] |
YOO J C and HAN T H. Fast normalized cross-correlation[J]. Circuits, Systems and Signal Processing, 2009, 28(6): 819–843. doi: 10.1007/s00034-009-9130-7 |
| [7] |
SHI Wei, SU Fenzhen, WANG Ruirui, et al. A visual circle based image registration algorithm for optical and SAR imagery[C]. 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Munich, Germany, 2012: 2109–2112.
|
| [8] |
WANG Fei and VEMURI B C. Non-rigid multi-modal image registration using cross-cumulative residual entropy[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2007, 74(2): 201–215. doi: 10.1007/s11263-006-0011-2 |
| [9] |
PAUL S and PATI U C. SAR image registration using an improved SAR-SIFT algorithm and Delaunay-triangulation-based local matching[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(8): 2958–2966. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2918211 |
| [10] |
LOWE D G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features[C]. Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 1999: 1150–1157.
|
| [11] |
MIKOLAJCZYK K and SCHMID C. A performance evaluation of local descriptors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(10): 1615–1630. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.188 |
| [12] |
MA Wenping, WEN Zelian, WU Yue, et al. Remote sensing image registration with modified SIFT and enhanced feature matching[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(1): 3–7. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2600858 |
| [13] |
XIANG Yuming, WANG Feng, and YOU Hongjian. OS-SIFT: A robust SIFT-like algorithm for high-resolution optical-to-SAR image registration in suburban areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(6): 3078–3090. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2790483 |
| [14] |
SCHWIND P, SURI S, REINARTZ P, et al. Applicability of the SIFT operator to geometric SAR image registration[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2010, 31(8): 1959–1980. doi: 10.1080/01431160902927622 |
| [15] |
DELLINGER F, DELON J, GOUSSEAU Y, et al. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-like algorithm for SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(1): 453–466. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2323552 |
| [16] |
WANG Shanhu, YOU Hongjian, and FU Kun. BFSIFT: A novel method to find feature matches for SAR image registration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2012, 9(4): 649–653. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2177437 |
| [17] |
FAN Jianwei, WU Yan, WANG Fan, et al. SAR image registration using phase congruency and nonlinear diffusion-based SIFT[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(3): 562–566. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2351396 |
| [18] |
ELTANANY A S, AMEIN A S, and ELWAN M S. A modified corner detector for SAR images registration[J]. International Journal of Engineering Research in Africa, 2021, 53(106): 123–156. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/JERA.53.123 |
| [19] |
YE Yuanxin, WANG Mengmeng, HAO Siyuan, et al. A novel keypoint detector combining corners and blobs for remote sensing image registration[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 18(3): 451–455. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2020.2980620 |
| [20] |
ZHANG Han, NI Weiping, YAN Weidong, et al. Registration of multimodal remote sensing image based on deep fully convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2019, 12(8): 3028–3042. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2916560 |
| [21] |
GE Ynchen, XIONG Zhaolong, and LAI Zuomei. Image registration of SAR and optical based on salient image sub-patches[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 1961(1): 12–17. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1961/1/012017 |
| [22] |
ZHU Hao, JIAO Licheng, MA Wenping, et al. A novel neural network for remote sensing image matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 30(9): 2853–2865. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2888757 |
| [23] |
MISHCHUK A, MISHKIN D, RADENOVIC F, et al. Working hard to know your neighbor’s margins: Local descriptor learning loss[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 4829–4840.
|
| [24] |
DU Wenliang, ZHOU Yong, and ZHAO Jiaqi, et al. Exploring the potential of unsupervised image synthesis for SAR-optical image matching[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 71022–71033. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3079327 |
| [25] |
YE Famao, SU Yanfei, XIAO Hui, et al. Remote sensing image registration using convolutional neural network features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(2): 232–236. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2781741 |
| [26] |
WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M, WU Y H, et al. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, USA, 2020: 1571–1580.
|
| [27] |
WANG Lina, SUN Mingchao, LIU Jinghong, et al. A robust algorithm based on phase congruency for optical and SAR image registration in suburban areas[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(20): 3339. doi: 10.3390/rs12203339 |
| [28] |
XIANG Yuming, TAO Rongshu, WANG Feng, et al. Automatic registration of optical and SAR images VIA improved phase congruency[C]. IGARSS 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019: 931–934.
|
| [29] |
KOVESI P. Image features from phase congruency[J]. Videre: Journal of Computer Vision Research, 1999, 1(3): 1–26. doi: 10.1080/00268976.2015.1118568 |
| [30] |
XIE Hua, PIERCE L E, and ULABY F T. Statistical properties of logarithmically transformed speckle[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(3): 721–727. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.1000333 |
| [31] |
HARRIS C and STEPHENS M. A combined corner and edge detector[C]. Alvey Vision Conference, Manchester, UK, 1988.
|
| [32] |
HAN Xufeng, LEUNG T, JIA Yangqing, et al. MatchNet: Unifying feature and metric learning for patch-based matching[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 3279–3286.
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
MERKLE N, LUO Wenjie, AUER S, et al. Exploiting deep matching and SAR data for the geo-localization accuracy improvement of optical satellite images[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(6): 586. doi: 10.3390/rs9060586 |
| [35] |
BALNTAS V, RIBA E, PONSA D, et al. Learning local feature descriptors with triplets and shallow convolutional neural networks[C]. British Machine Vision Conference 2016, York, UK, 2016.
|
| [36] |
HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2016: 2261–2269.
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
POURFARD M, HOSSEINIAN T, SAEIDI R, et al. KAZE-SAR: SAR image registration using KAZE detector and modified SURF descriptor for tackling speckle noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 5207612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3084411 |
| [39] |
TIAN Yurun, FAN Bin, and WU Fuchao. L2-Net: Deep learning of discriminative patch descriptor in euclidean space[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honnolulu, USA, 2017: 6128–6136.
|
| [40] |
TIAN Yurun, YU Xin, FAN Bin, et al. SOSNet: Second order similarity regularization for local descriptor learning[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 11008–11017.
|
| [41] |
TOUZI R. A review of speckle filtering in the context of estimation theory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2002, 40(11): 2392–2404. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803727 |




 Submit Manuscript
Submit Manuscript Peer Review
Peer Review Editor Work
Editor Work




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: